Characterisation of Macrophage Inhibitory Factor-2 (MIF-2) in Haemonchus contortus and Teladorsagia circumcincta
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Parasites
2.2. RNA Isolation and Synthesis of cDNA
2.3. Protein Modelling and Structural Analysis of TcMIF-2 and HcMIF-2
2.4. Expression of Recombinant TcMIF-2 and HcMIF-2 in E. coli
2.5. Purification
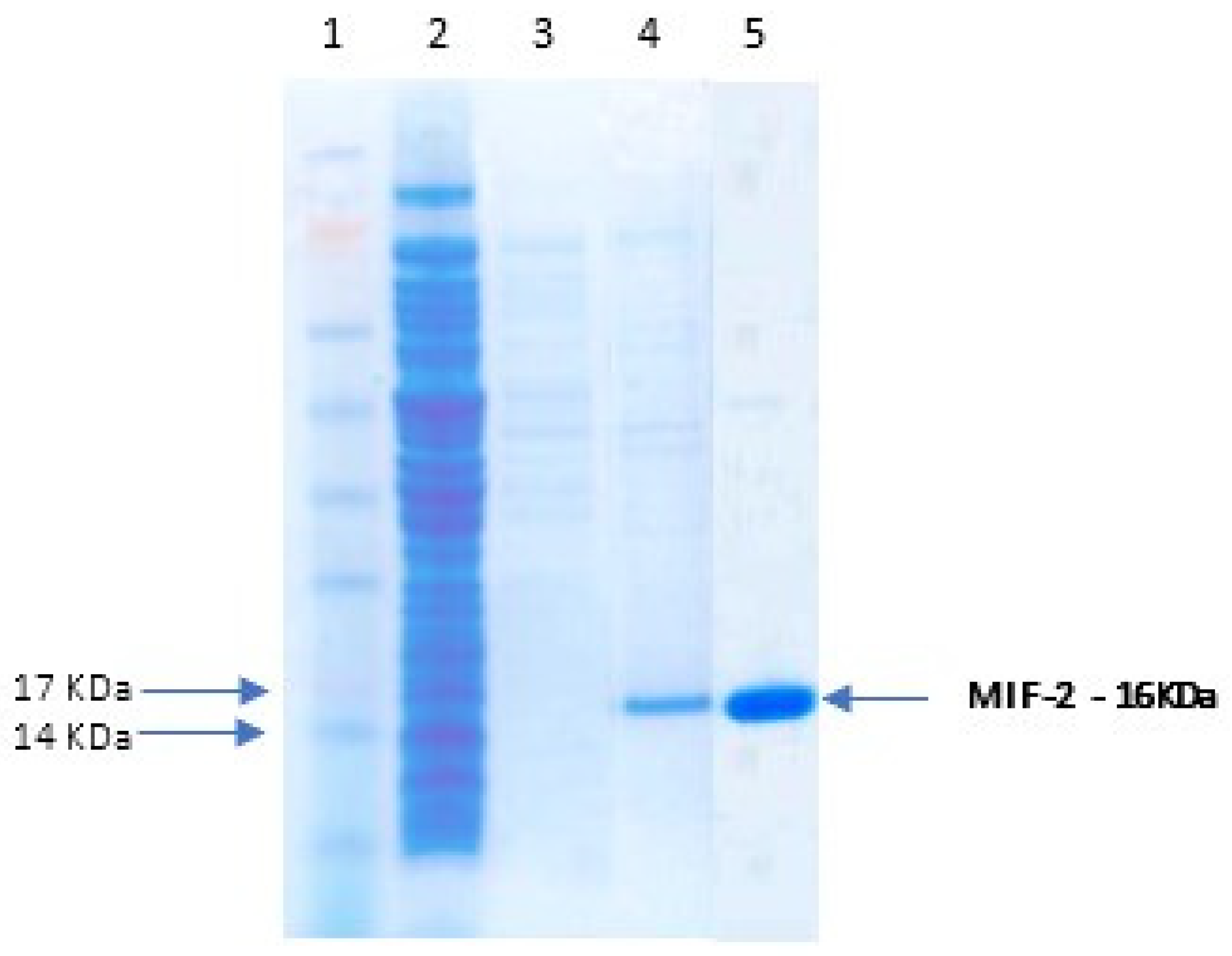
2.6. Gel Electrophoresis
2.7. HcMIF-2 and TcMIF-2 Assays
2.8. ELISA
3. Results
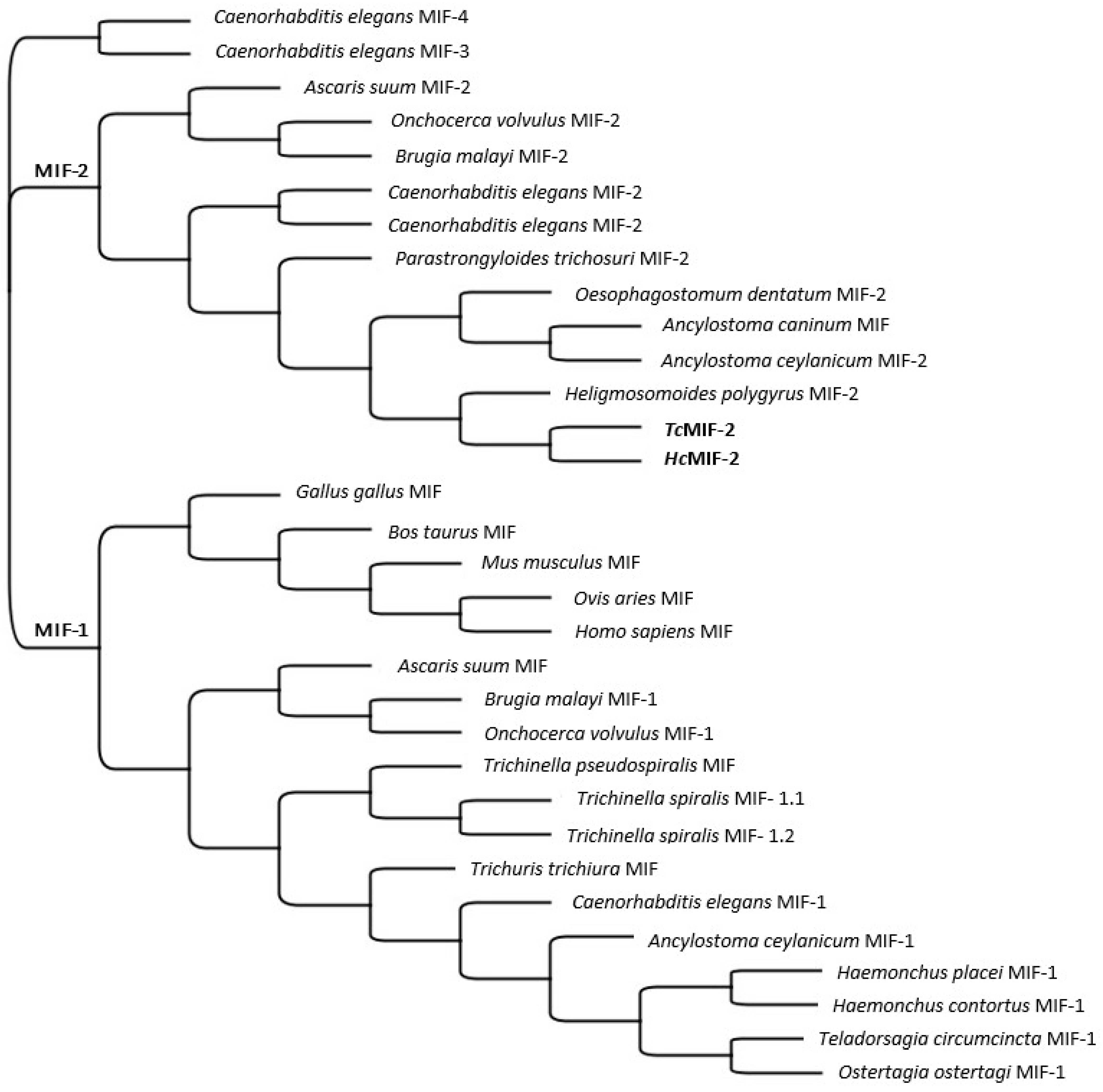
3.1. TcMIF-2 and HcMIF-2 Gene Sequences
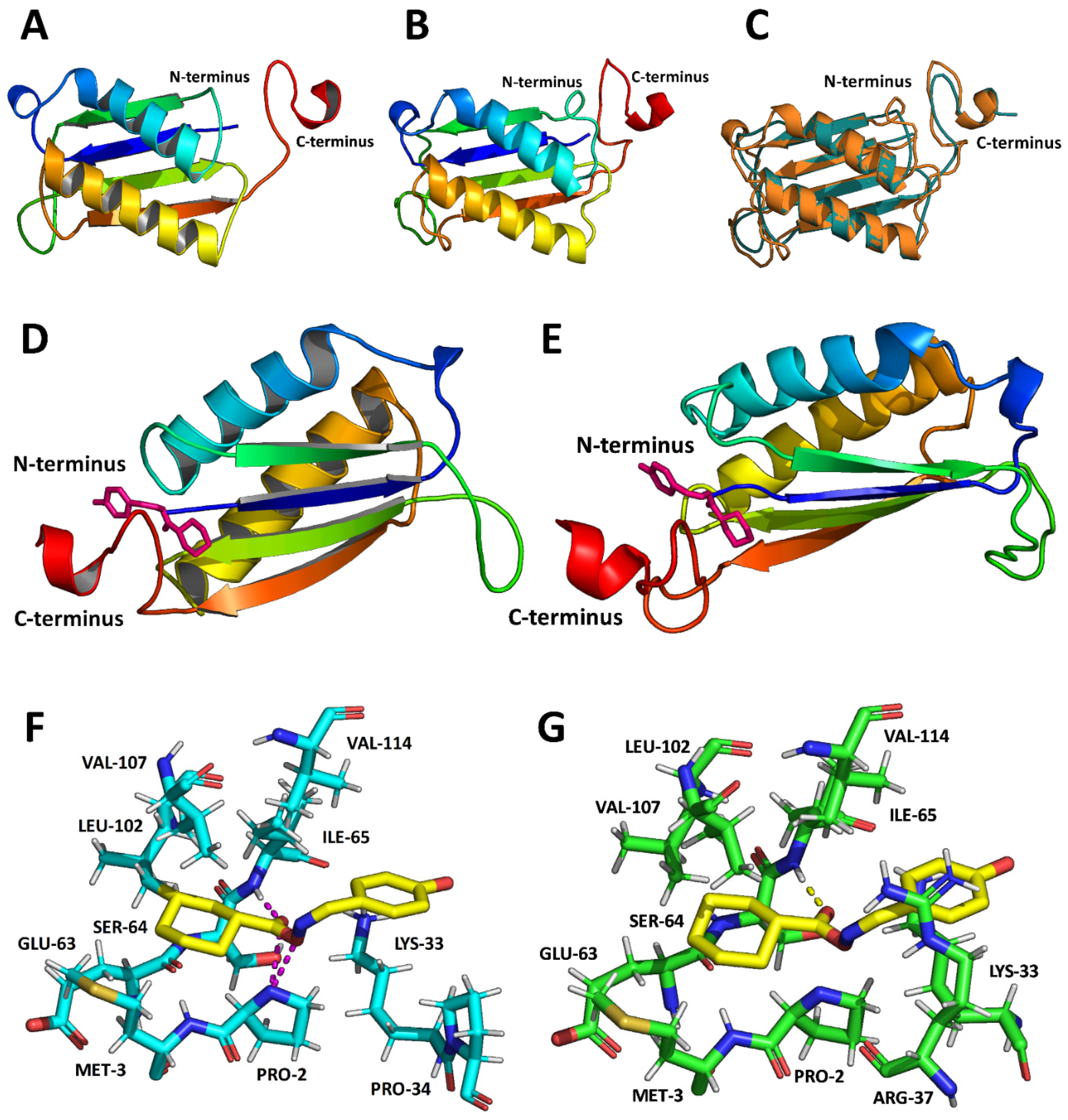
3.2. MIF-2 Structure
3.3. Recombinant Protein Expression
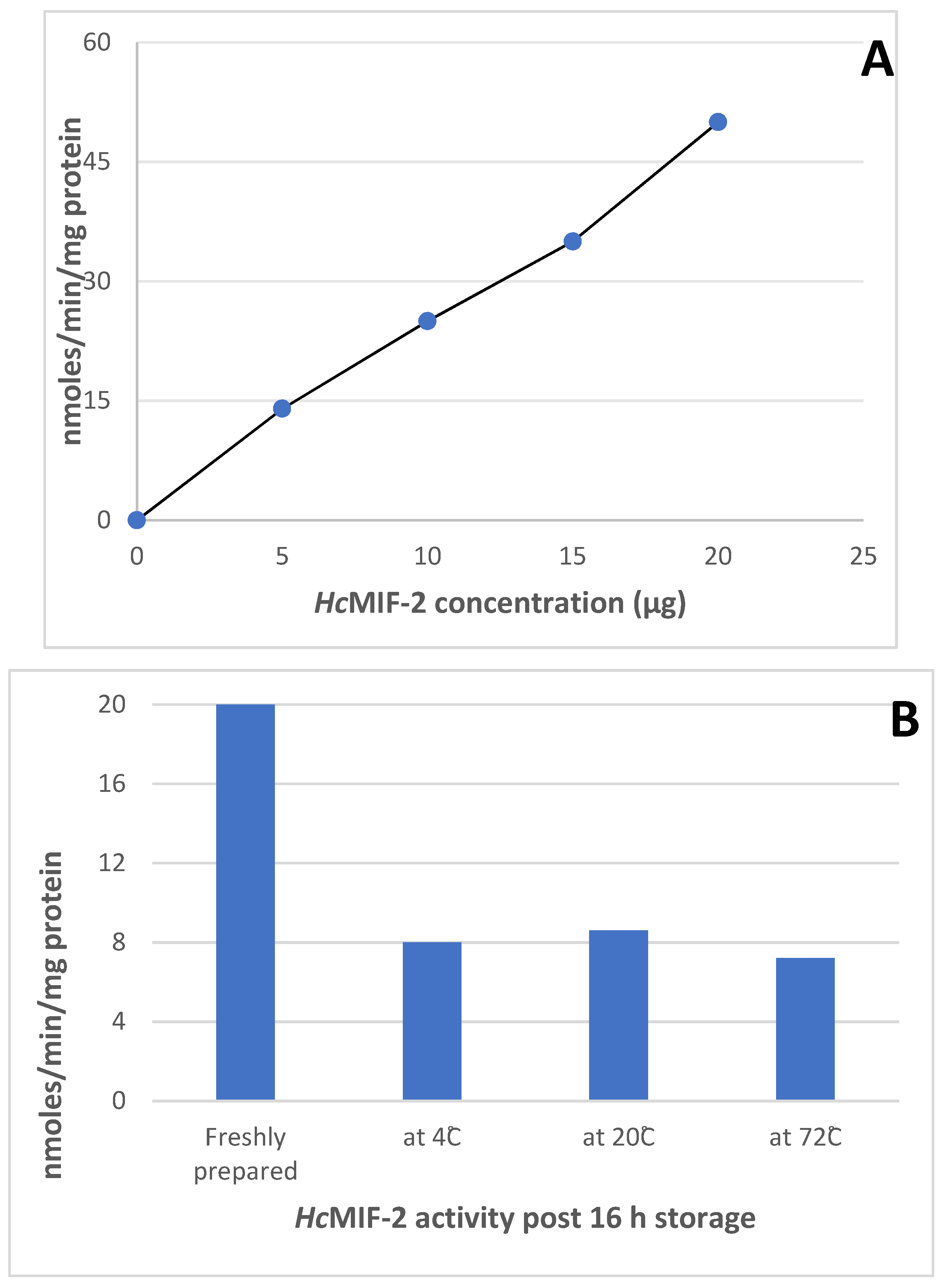
3.4. Enzyme Assays
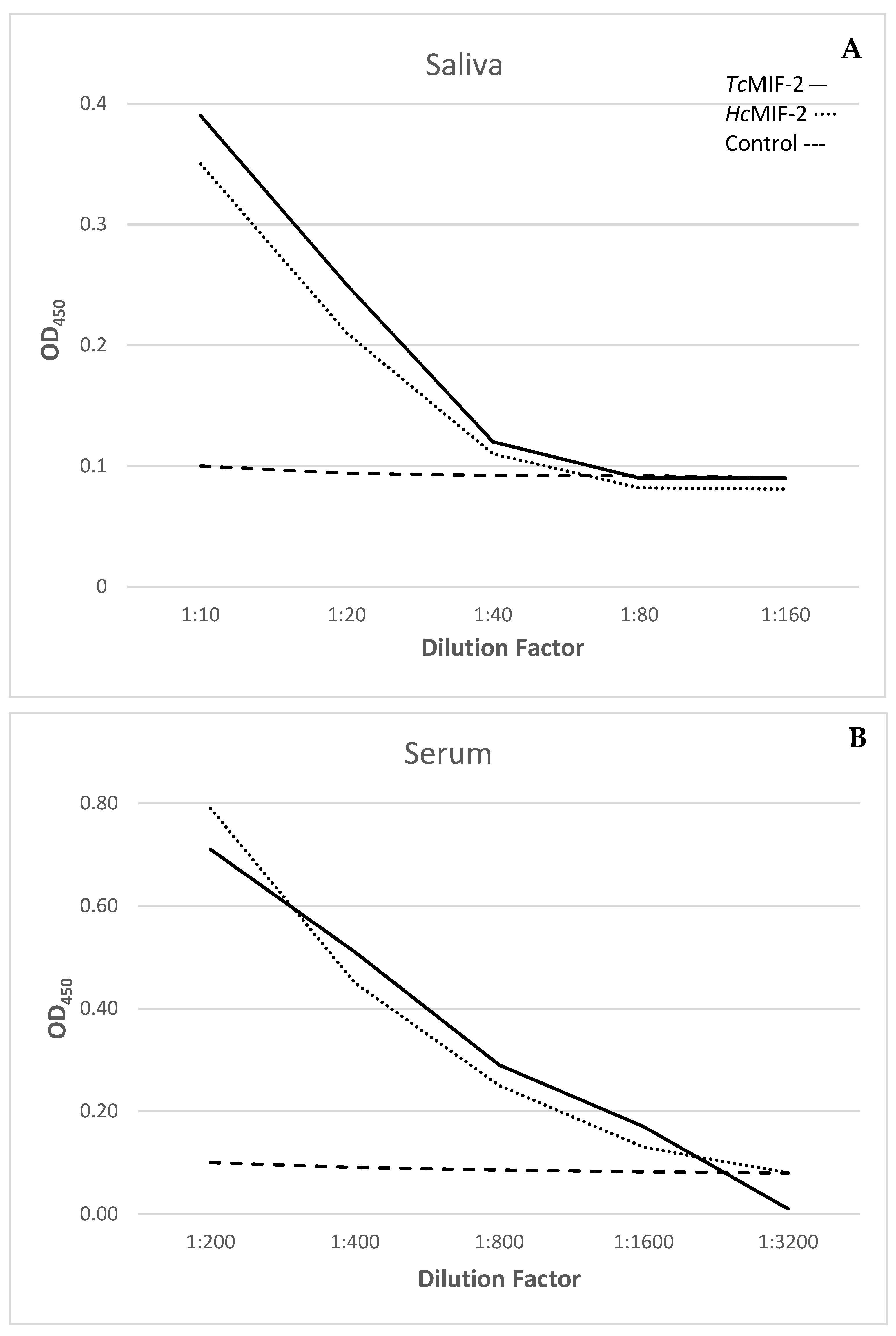
3.5. Host Recognition
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blocki, F.A.; Ellis, L.B.M.; Wackett, L.P. MIF protein are theta-class glutathione S-transferase homologs. Protein Sci. 1993, 2, 2095–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, L.; Metz, C.N.; Fang, Y.; Xu, J.; Donnelly, S.; Baugh, J.; Delohery, T.; Chen, Y.; Mitchell, R.A.; Bucala, R. MIF signal transduction initiated by binding to CD74. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 1467–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloom, B.R.; Bennett, B. Mechanism of a reaction in vitro associated with delayed-type hypersensitivity. Science 1966, 153, 80–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, J.R. Delayed hypersensitivity in vitro: Its mediation by cell-free substances formed by lymphoid cell-antigen interaction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1966, 56, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salminen, A.; Kaarniranta, K. Control of p53 and NF-κB signaling by WIP1 and MIF: Role in cellular senescence and organismal aging. Cell. Signal. 2011, 23, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauler, M.; Bucala, R.; Lee, P.J. Role of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in age-related lung disease. Amer. J. Physiol. 2015, 309, L1–L10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Pang, J.; Chen, Y.; Bucala, R.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, J. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) deficiency exacerbates aging-induced cardiac remodeling and dysfunction despite improved inflammation: Role of autophagy regulation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparkes, A.; De Baetselier, P.; Roelants, K.; De Trez, C.; Magez, S.; Van Ginderachter, J.A.; Raes, G.; Bucalaf, R.; Stijlemans, B. The non-mammalian MIF superfamily. Immunobiology 2017, 222, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastrana, D.V.; Raghavan, N.; Fitzgerald, P.; Eisinger, S.W.; Metz, C.; Bucala, R.; Schleimer, R.P.; Bickel, C.; Scott, A.L. Filarial nematode parasites secrete a homologue of the human cytokine macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Infect. Immunit. 1998, 66, 5955–5963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeire, J.J.; Cho, Y.; Lolis, E.; Bucala, R.; Cappello, M. Orthologs of macrophage migration inhibitory factor from parasitic nematodes. Trend. Parasitol. 2008, 24, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisbet, A.J.; Bell, N.E.; McNeilly, T.N.; Knox, D.P.; Maizels, R.M.; Meikle, L.I.; Wildblood, L.A.; Matthews, J.B. A macrophage migration inhibitory factor-like tautomerase from Teladorsagia circumcincta (Nematoda: Strongylida). Parasite Immunol. 2010, 32, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.; Jones, B.F.; Vermeire, J.J.; Leng, L.; DiFedele, L.; Harrison, L.M.; Xiong, H.; Kwong, Y.K.; Chen, Y.; Bucala, R.; et al. Structural and functional characterisation of a secreted hookworm Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF) that interacts with the human MIF receptor CD74. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 23447–23456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.; Hoti, S.L.; Meena, R.L.; Vasuki, V.; Sankari, T.; Kaliraj, P. Molecular and functional characterisation of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) homolog of human from lymphatic filarial parasite Wuchereria bancrofti. Parasitol. Res. 2012, 111, 2035–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younis, A.E.; Soblik, H.; Ajonina-Ekoti, I.; Erttmann, K.D.; Luersen, K.; Liebau, E.; Brattig, N.W. Characterisation of a secreted macrophage migration inhibitory factor homologue of the parasitic nematode Strongyloides acting at the parasite-host cell interface. Microbes Infect. 2012, 14, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajonina-Ekoti, I.; Kurosinski, M.A.; Younis, A.E.; Ndjonka, D.; Tanyi, M.K.; Achukwi, M.; Eisenbarth, A.; Ajonina, C.; Lüersen, K.; Breloer, M.; et al. Comparative analysis of macrophage migration inhibitory factors (MIFs) from the parasitic nematode Onchocerca volvulus and the free-living nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 11, 3335–3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, A.; Sharma, R.; Hoti, S.L. Identification and biochemical characterisation of macrophage migration inhibitory factor-2 (MIF-2) homologue of human lymphatic filarial parasite, Wuchereria bancrofti. Act. Tropica 2015, 142, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, X.; Taylor, P.; Wang, J.M.; Meyer, D.J.; Scott, A.L.; Walkinshaw, M.D.; Maizels, R.M. Homologues of Human Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor from a Parasitic Nematode. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 44261–44267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maizels, R.M.; Balic, A.; Gomez-Escobar, N.; Nair, M.; Taylor, M.D.; Allen, J.A. Helminth parasites—Masters of regulation. Immunol. Rev. 2004, 201, 89–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matoušová, P.; Vokrál, I.; Lamka, J.; Skálová, L. The role of xenobiotic metabolising enzymes in anthelmintic deactivation and resistance in helminths. Trend. Parasitol. 2016, 32, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, M.; Wang, S.; Ehsan, M.; Yan, R.; Song, X.; Xu, L.; Li, X. Characterisation of a secreted macrophage migration inhibitory factor homologue of the parasitic nematode Haemonchus contortus acting at the parasite-host cell interface. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 40052–40064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marson, A.L.; Tarr, E.K.; Scott, A.L. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (mif) transcription is significantly elevated in Caenorhabditis elegans dauer larvae. Gene 2001, 278, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umair, S.; Ria, C.; Knight, J.S.; Bland, R.J.; Simpson, H.V. Sarcosine metabolism in Haemonchus contortus and Teladorsagia circumcincta. Exp. Parasitol. 2013, 134, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, J.S.; Broadwell, A.H.; Grant, W.N.; Shoemaker, C.B. A strategy for shuffling numerous Bacillus thuringiensis crystal protein domains. J. Econ. Entomol. 2004, 9, 1805–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yan, R.; Roy, A.; Xu, D.; Poisson, J.; Zhang, Y. The I-TASSER Suite: Protein structure and function prediction. Nat. Method. 2015, 12, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskowski, R.A.; Rullmann, J.A.C.; MacArthur, M.W.; Kaptein, R.; Thornton, J.M. AQUA and PROCHECK-NMR: Programs for checking the quality of protein structures solved by NMR. J. Biomol. NMR 2004, 8, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiederstein, M.; Sippl, M.J. ProSA-web: Interactive web service for the recognition of errors in three-dimensional structures of proteins. Nucleic Acid. Res. 2007, 35, W407–W410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrodinger, L.L.C. The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System. Available online: https://pymol.org/2/ (accessed on 28 March 2022).
- Love, C.A.; Lilley, P.E.; Dixon, N.E. Stable high-copy-number bacteriophage lambda promoter vectors for overproduction of proteins in Escherichia coli. Gene 1996, 176, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swope, M.; Sun, H.-W.; Blake, P.R.; Lolis, E. Direct link between cytokine activity and a catalytic site for macrophage migration inhibitory factor. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 3534–3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palevich, N.; Maclean, P.H.; Baten, A.; Scott, R.W.; Leathwick, D.M. The Genome Sequence of the Anthelmintic-Susceptible New Zealand Haemonchus contortus. Genome Biol. Evol. 2019, 11, 1965–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palevich, N.; Britton, C.; Kamenetzky, L.; Mitreva, M.; de Moraes Mourão, M.; Slatko, B.E. Tackling hypotheticals in helminth genomes. Trends Parasitol. 2018, 34, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Umair, S.; Knight, J.S.; Bouchet, C.; Palevich, N.; Cleland, S.B.; Grant, W.; Simpson, H.V. Characterisation of Macrophage Inhibitory Factor-2 (MIF-2) in Haemonchus contortus and Teladorsagia circumcincta. Parasitologia 2022, 2, 338-349. https://doi.org/10.3390/parasitologia2040028
Umair S, Knight JS, Bouchet C, Palevich N, Cleland SB, Grant W, Simpson HV. Characterisation of Macrophage Inhibitory Factor-2 (MIF-2) in Haemonchus contortus and Teladorsagia circumcincta. Parasitologia. 2022; 2(4):338-349. https://doi.org/10.3390/parasitologia2040028
Chicago/Turabian StyleUmair, Saleh, Jacqueline S. Knight, Charlotte Bouchet, Nikola Palevich, Sheralee B. Cleland, Warwick Grant, and Heather V. Simpson. 2022. "Characterisation of Macrophage Inhibitory Factor-2 (MIF-2) in Haemonchus contortus and Teladorsagia circumcincta" Parasitologia 2, no. 4: 338-349. https://doi.org/10.3390/parasitologia2040028
APA StyleUmair, S., Knight, J. S., Bouchet, C., Palevich, N., Cleland, S. B., Grant, W., & Simpson, H. V. (2022). Characterisation of Macrophage Inhibitory Factor-2 (MIF-2) in Haemonchus contortus and Teladorsagia circumcincta. Parasitologia, 2(4), 338-349. https://doi.org/10.3390/parasitologia2040028






