Comparative Elemental Signatures of Full Metal Jacket (FMJ) and Lead Round Nose (LRN) Projectiles on Complex Biological Targets Using Micro-XRF and Portable XRF
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Elemental Transfer Mechanisms: FMJ vs. LRN
1.2. Rationalizing Micro-XRF and Portable XRF Methodologies
1.3. Research Gaps: Range and Taphonomic Persistence
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Firearms and Ammunition
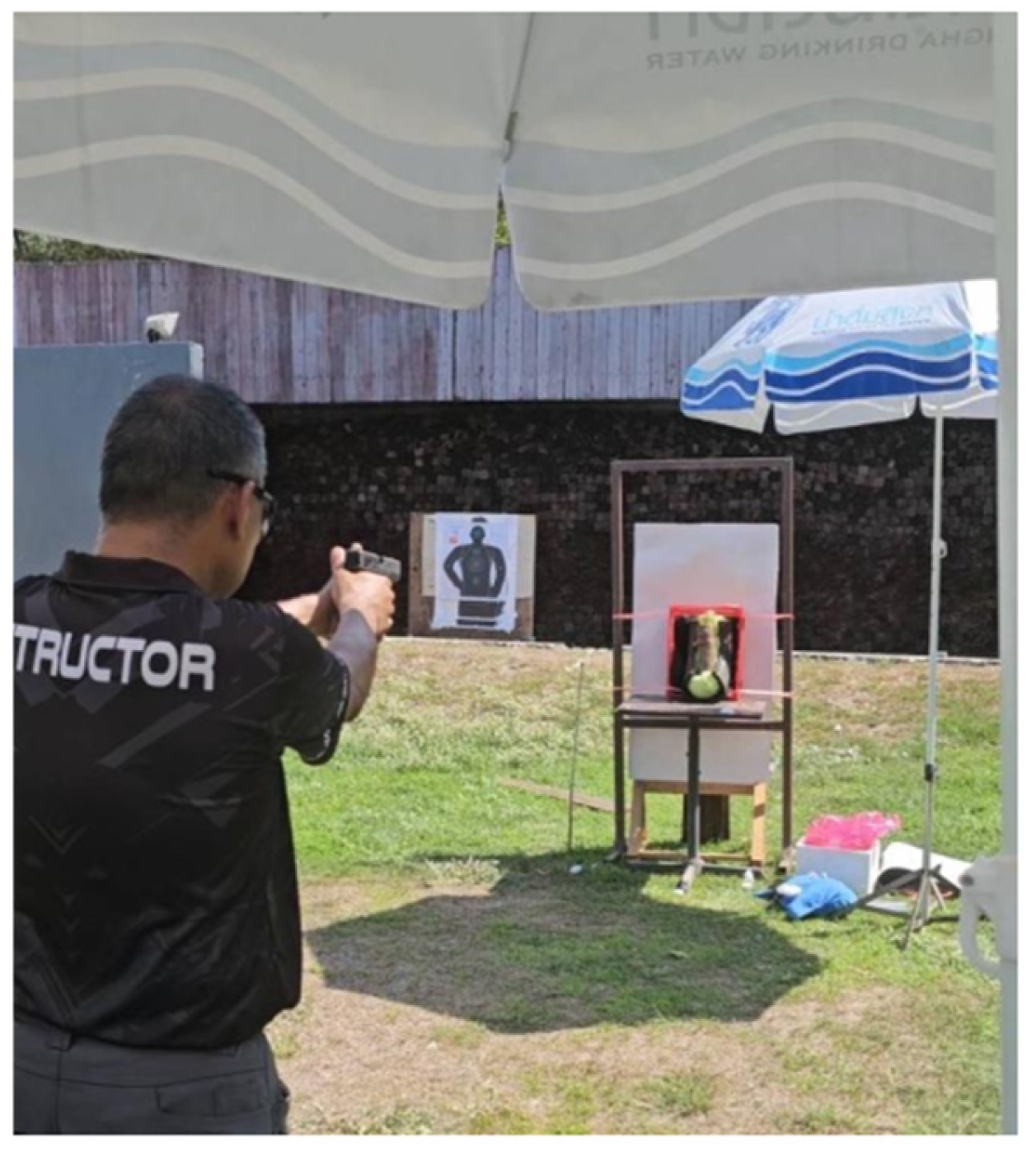
2.2. Experimental Setup and Firing Protocol
2.3. Non-Destructive Analysis and Taphonomy Simulation
3. Results
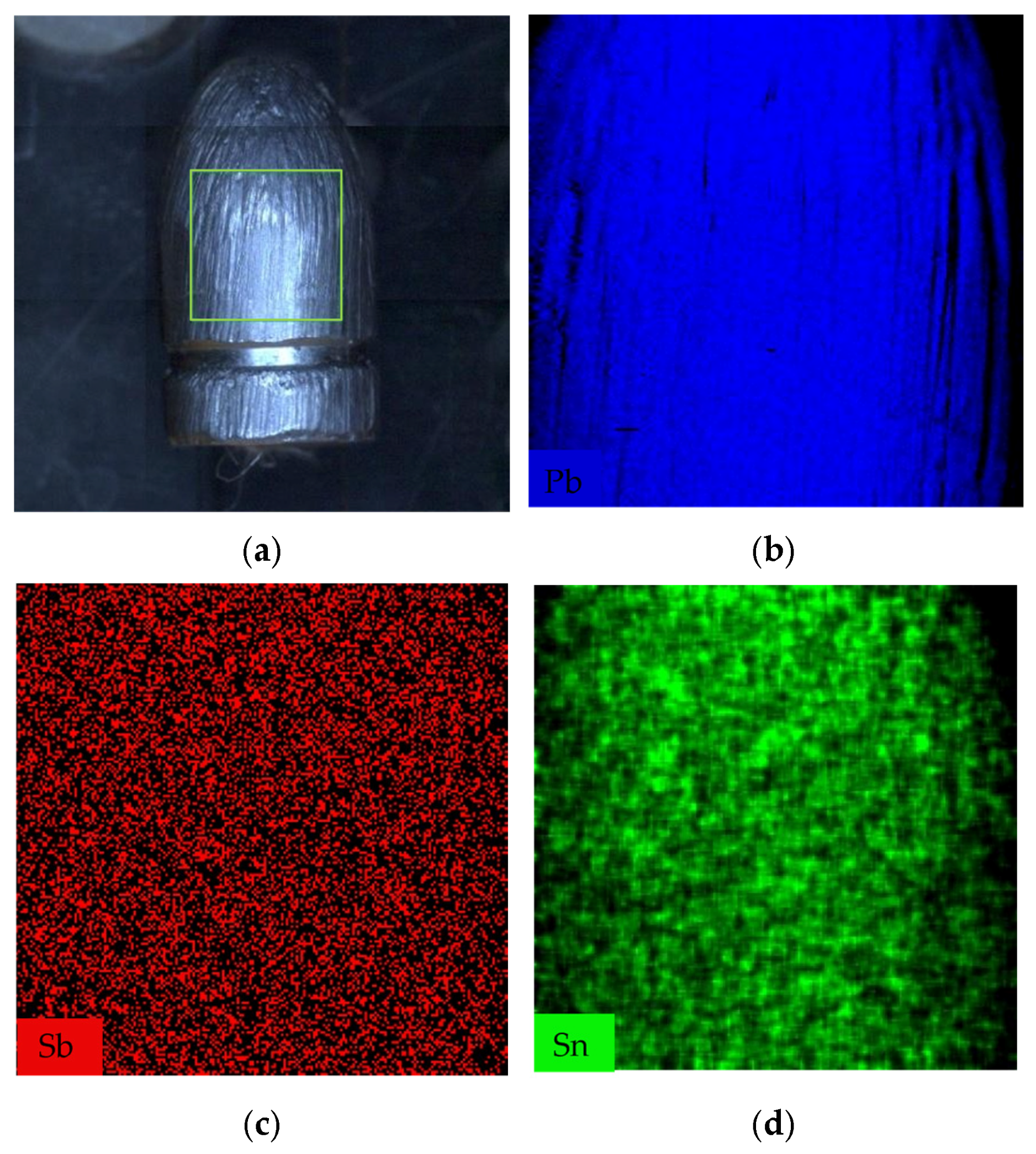
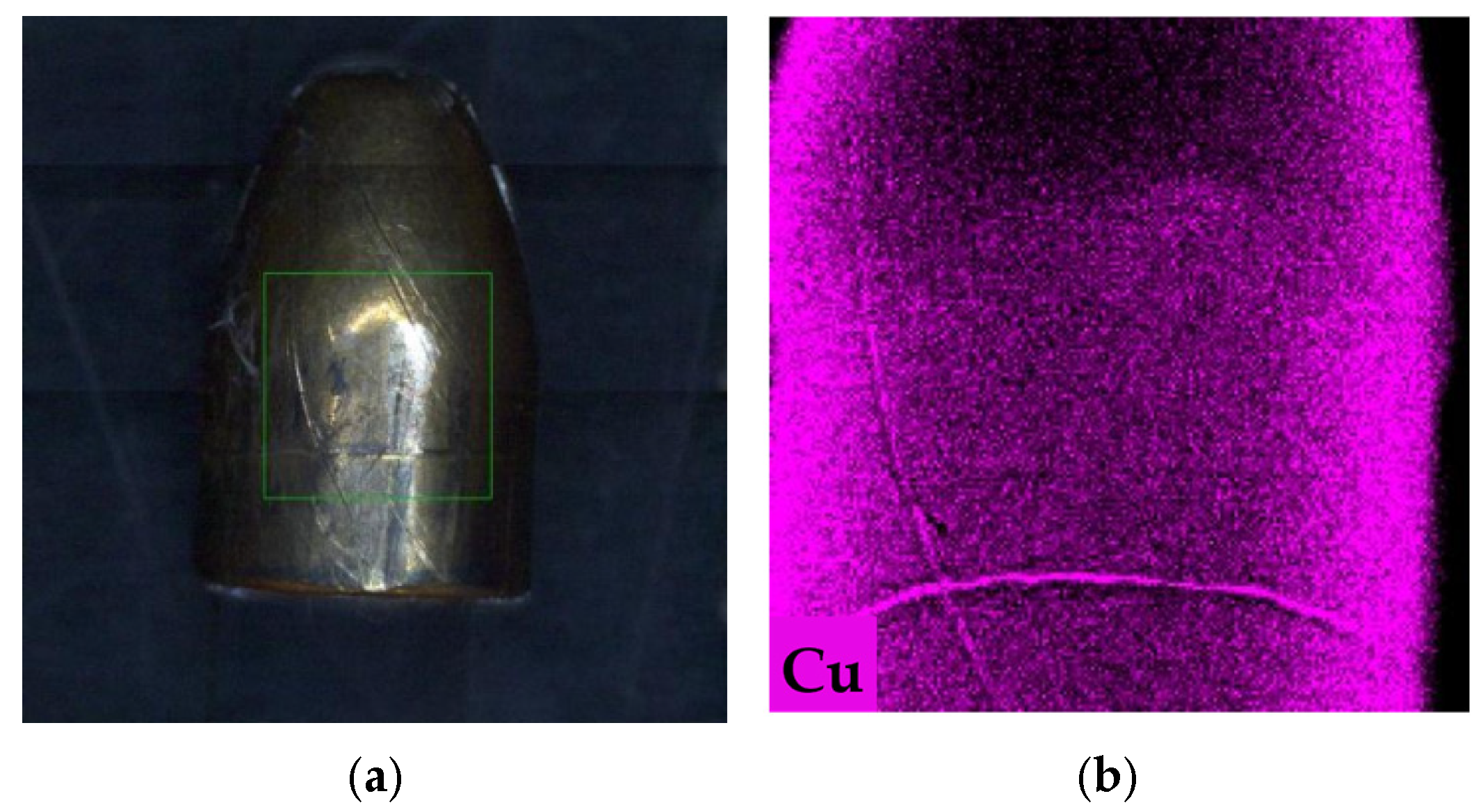
3.1. Basic Composition of Ammunition and Control Analysis
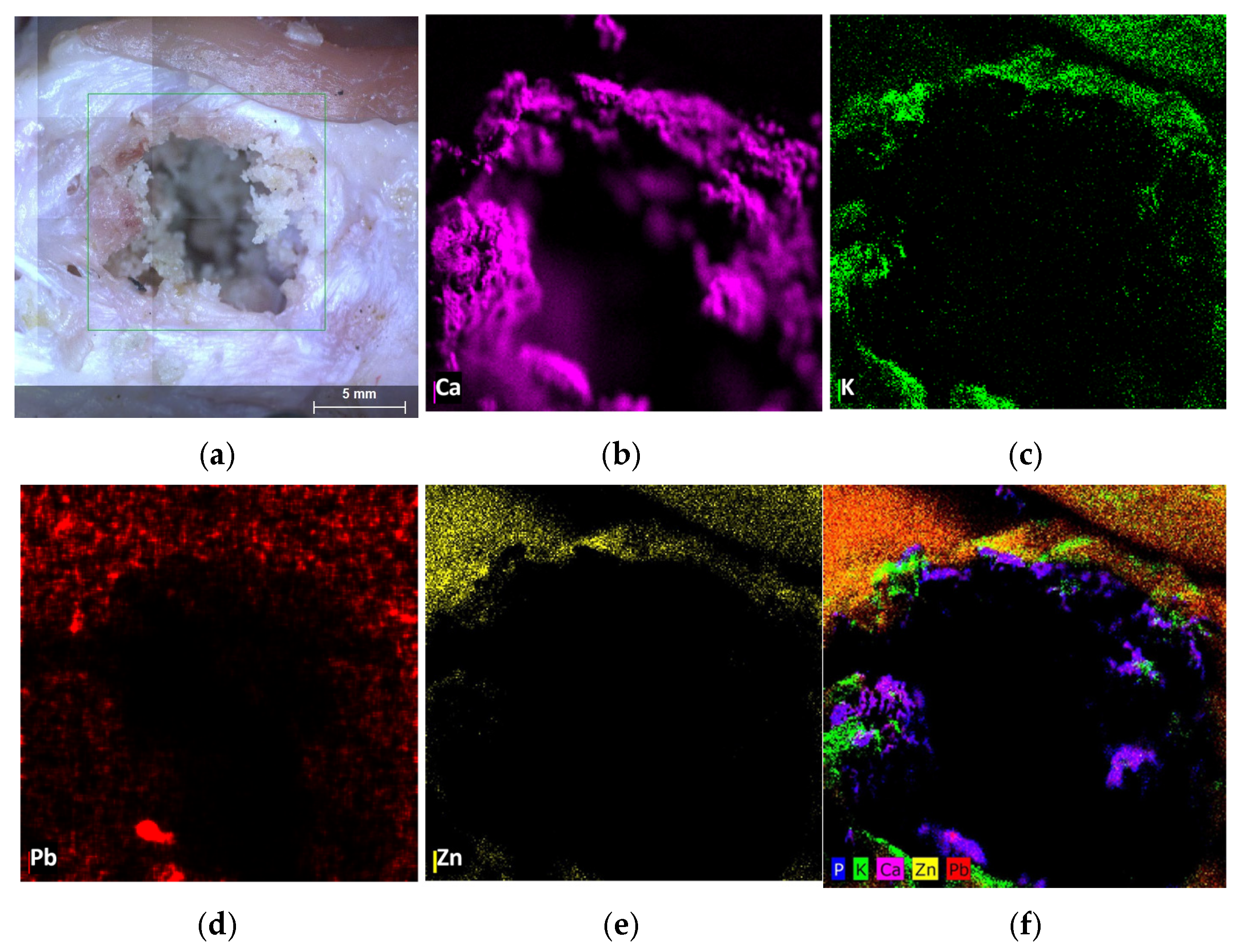
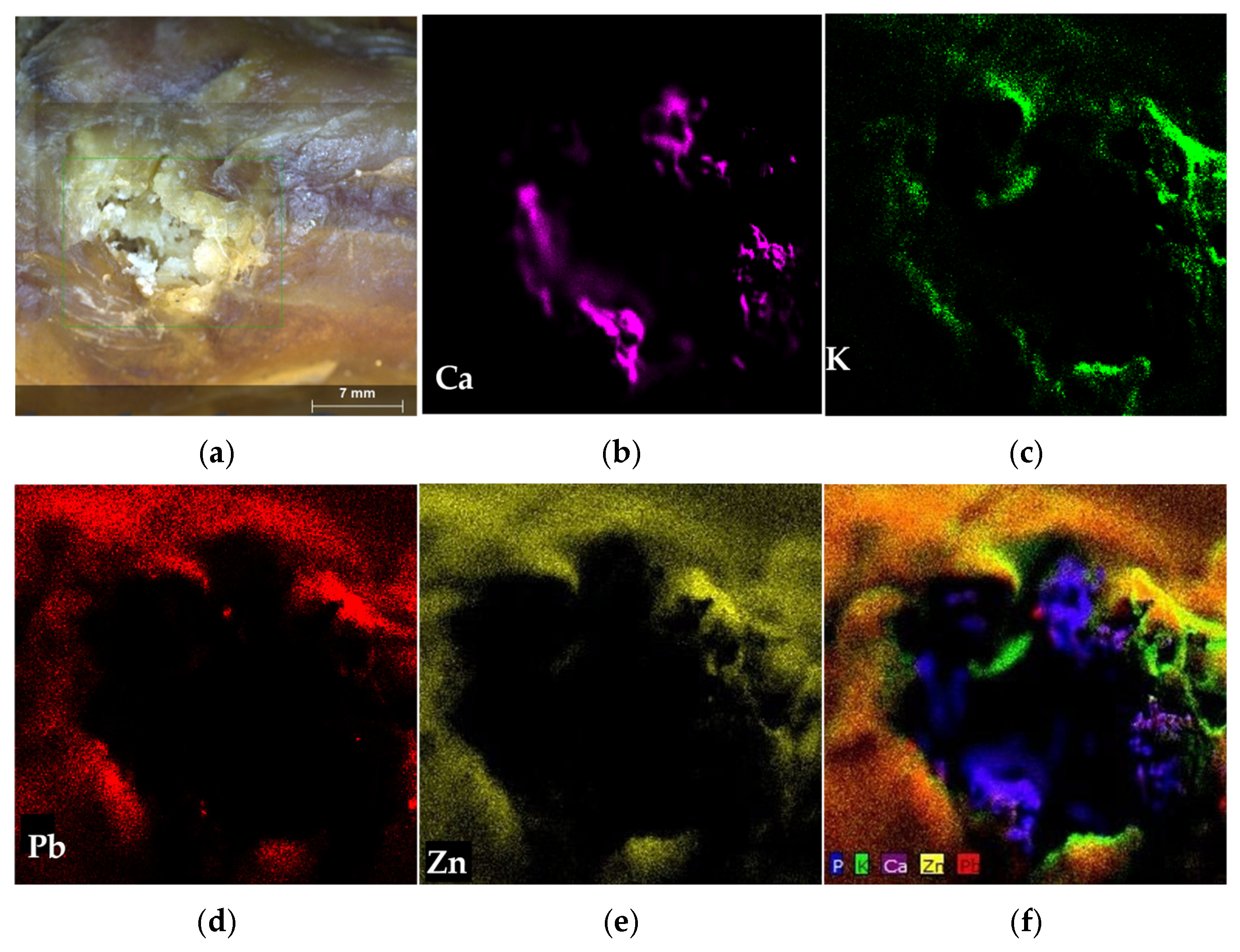
3.2. Transfer of Bullet Traces onto Target Surfaces
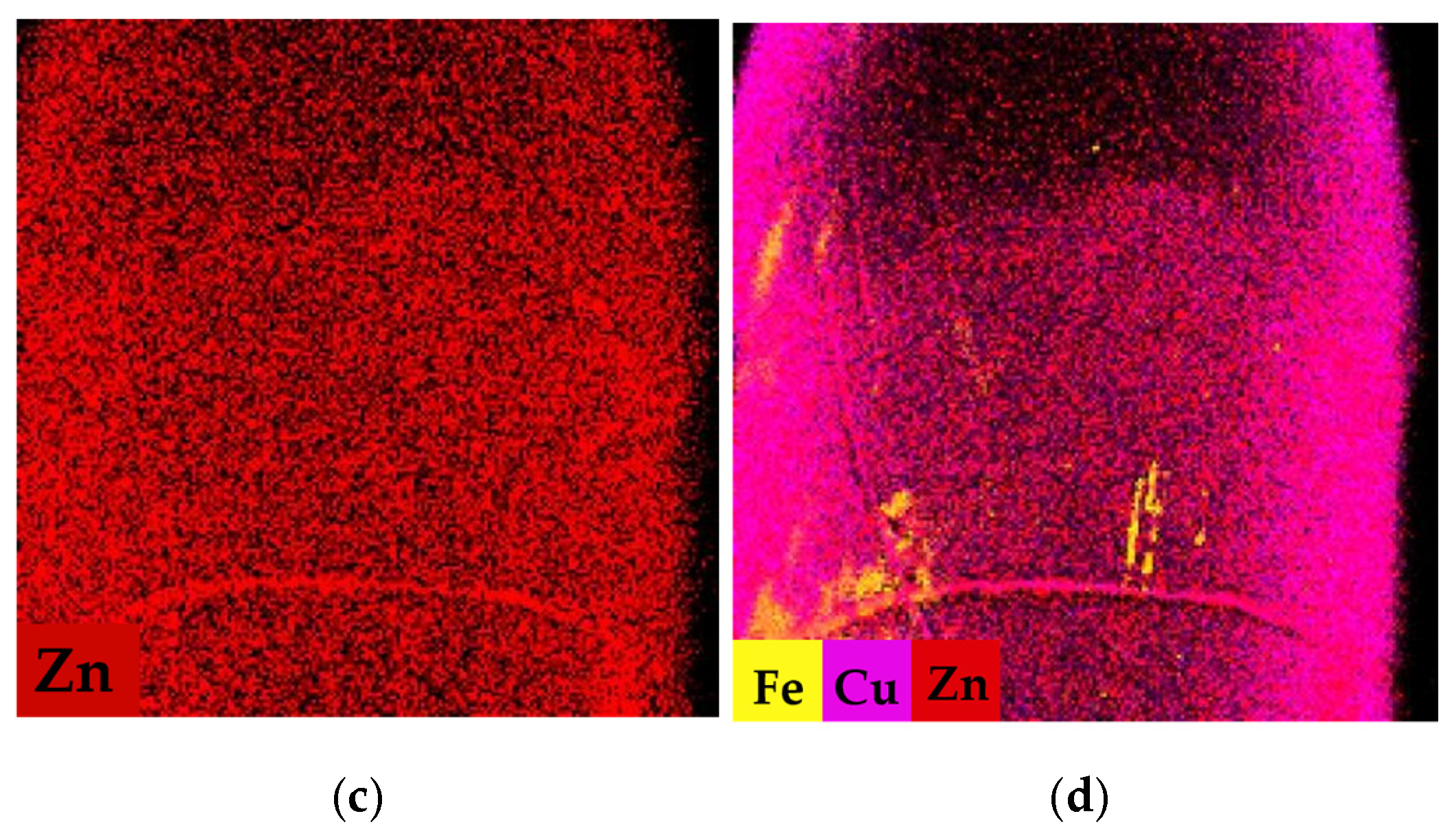
3.2.1. Results of Elemental Mapping Using XRF M4
3.2.2. Semi-Quantitative Comparison and Instrument Performance
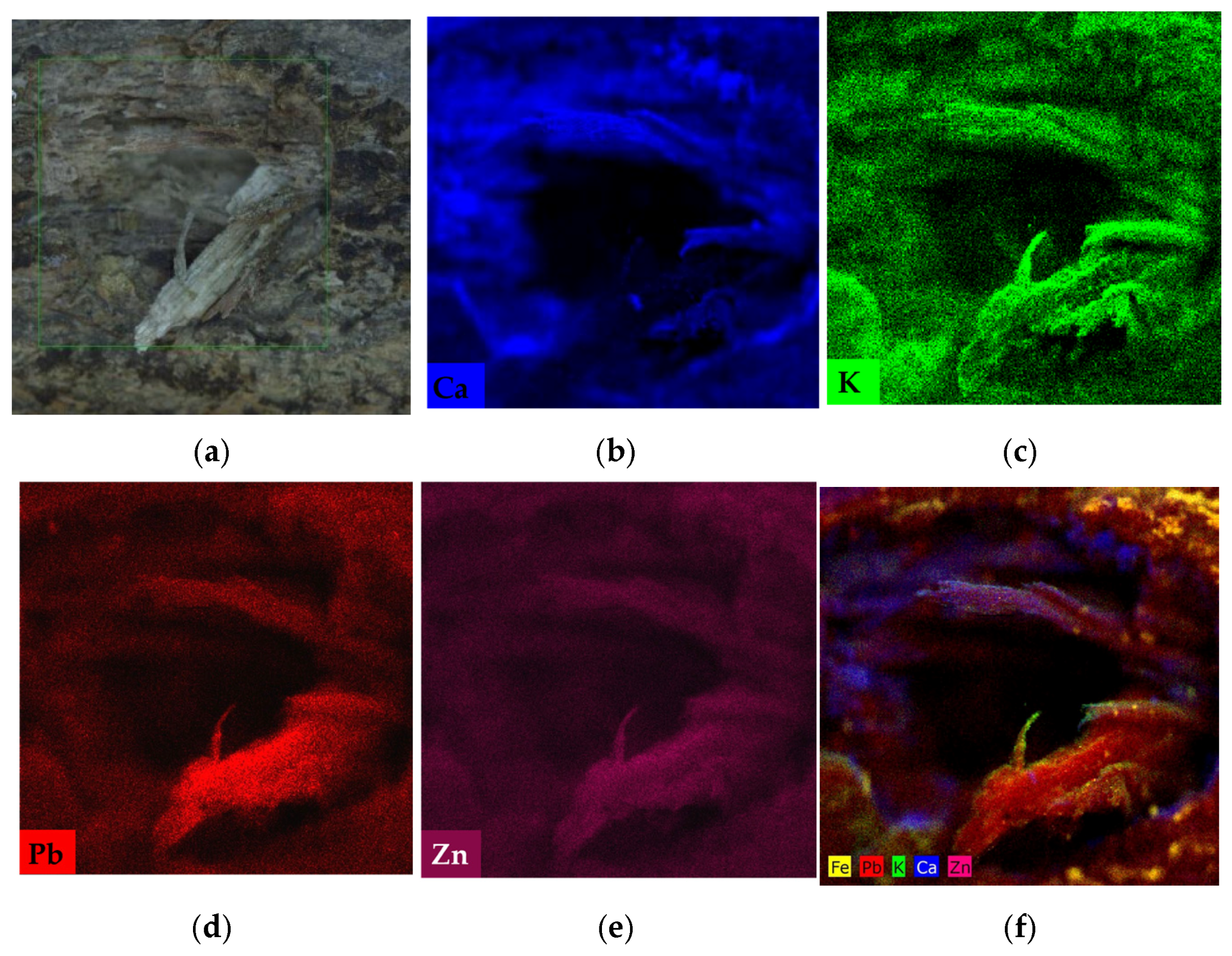
3.2.3. Forensic Taphonomy: Trace Persistence on Air-Dried Tissue
4. Discussion
4.1. Different Trace Transfer Mechanisms and Taphonomic Persistence
4.2. Comparative Performance of XRF Techniques in Forensic Trace Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LRN | Lead Round Nose |
| FMJ | Full Metal Jacketed |
| XRF | X-ray Fluorescence |
| Elio | Energy Dispersive Micro-X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometer (Commercial model by Bruker) |
| Pb | Lead |
| Sb | Antimony |
| Cu | Copper |
| Zn | Zinc |
| Sn | Tin |
| Fe | Iron |
References
- Abd Malik, S.A.; Nordin, F.A.D.; Ali, S.F.M.; Abdullah, A.F.L.; Chang, K.H. Distinctive bullet impact holes by 9-mm caliber projectile on sheet metal surfaces. J. Forensic Sci. Med. 2022, 8, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeij, E.; Rijnders, M.; Pieper, P.; Hermsen, R. Interaction of bullets with intermediate targets: Material transfer and damage. Forensic Sci. Int. 2012, 223, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, N.; Parmar, H. Exploring the capabilities of Micro-XRF to study the dispersion of GSR in firearms cases. Forensic Sci. Med. Pathol. 2025, 21, 1230–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, O.; Smith, S.C.; Roper, C. Advances and limitations in the determination and assessment of gunshot residue in the environment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonizzoni, L.; Mazzarelli, D.; Franceschetti, L.; Vitali, C.; Amadasi, A.; Cattaneo, C. Investigating gunshot wounds in charred bone with XRF spectroscopy: A technical note. Int. J. Legal Med. 2024, 138, 2587–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrivastava, P.; Jain, V.K.; Nagpal, S. Gunshot residue detection technologies—A review. Egypt. J. Forensic Sci. 2021, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serol, M.; Ahmad, S.M.; Quintas, A.; Família, C. Chemical analysis of gunpowder and gunshot residues. Molecules 2023, 28, 5550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, H.H.; Chen, Y.L. Energy dispersive X-ray analysis of bullets commonly encountered in Taiwan. Forensic Sci. J. 2006, 5, 21–34. [Google Scholar]
- Ovide, O.; Corzo, R.; Trejos, T. The analysis of glass from portable electronic devices and glass accessories using µ-XRF for forensic investigations. Forensic Sci. Int. 2023, 343, 111550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, L.G.; Martiny, A.; Pinto, A.L. Nano characterization of gunshot residues from Brazilian ammunition. Forensic Sci. Int. 2014, 240, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merli, D.; Di Trocchio, C.; Capucciati, A.; Fabbris, S.; Profumo, A.; Cucca, L.; Donghi, M. Bullet contribution to inorganic residue on targets. Talanta Open 2021, 4, 100067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, P.; Neff, C.; Hess, S.; Weis, P.; Günther, D. Forensic float glass fragment analysis using single-pulse laser ablation inductively coupled plasma time of flight mass spectrometry. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2020, 35, 2248–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobylarz, D.; Michalska, A.; Jurowski, K. Field portable X-ray fluorescence (FP-XRF) as powerful, rapid, non-destructive and ‘white analytical tool’ for forensic sciences-State of the art. Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 169, 117355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leatherland, L.; Andrews, Z.; Neumann, C.; Chester, J.; de Bruin-Hoegee, M.; Ernst, T.; Trejos, T. Assessing the expanded capacity of modern μ-XRF SDD systems for forensic analysis through an interlaboratory study: Part I—Electrical tapes. Forensic Chem. 2025, 47, 100719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pringle, J.K.; Jeffery, A.J.; Ruffell, A.; Stimpson, I.G.; Pirrie, D.; Bergslien, E.; Partridge, J. The use of portable XRF as a forensic geoscience non-destructive trace evidence tool for environmental and criminal investigations. Forensic Sci. Int. 2022, 332, 111175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sýkora, J.; Komendová, R. Field determination of trace concentrations of hazardous metals in waters by portable EDXRF. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łach, B.; Fiutowski, T.; del Hoyo-Meléndez, J.M.; Koperny, S.; Krupska-Wolas, P.; Mindur, B.; Dąbrowski, W. Application of a Full-Field macro-XRF imaging spectrometer to non-invasive investigation of elemental composition in three-dimensional artworks. npj Herit. Sci. 2025, 13, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricca, M.; Alberghina, M.F.; Randazzo, L.; Schiavone, S.; Donato, A.; Albanese, M.P.; La Russa, M.F. A combined non-destructive and micro-destructive approach to solving the forensic problems in the field of cultural heritage: Two case studies. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bominathan, U.R.; Abd Malik, S.A.; Abdullah, A.F.L.; Chang, K.H. Determination of elemental ratios correlating to the projectiles of conventional and non-toxic ammunitions. Malays. J. Anal. Sci. 2025, 29, 1361. [Google Scholar]
- Romolo, F.S.; Margot, P. Identification of gunshot residue: A critical review. Forensic Sci. Int. 2001, 119, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Target Surface | Elemental Signature | XRF M4 Median (Min-Max) (wt%) | Elio Median (Min-Max) (wt%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LRN | FMJ | LRN | FMJ | ||
| Fresh pork leg (bone/tissue) | Pb | 10.39 (1.57–40.58) | 2.21 (1.16–2.86) | 7.34 (3.99–16.11) | 0.27 (0.00–1.01) |
| Cu | 0.06 (0.00–0.21) | 0.24 (0.13–0.53) | n.d. | 0.24 (0.10–1.09) | |
| Zn | 0.64 (0.14–0.96) | 0.59 (0.00–0.89) | n.d. | n.d. | |
| Mango branch (Entrance surface) | Pb | 3.00 (0.46–3.77) | 0.53 (0.46–0.79) | 1.40 (0.27–1.71) | 0.06 (0.00–0.14) |
| Cu | 0.13 (0.11–0.13) | 0.15 (0.12–0.24) | 0.03 (0.00–0.08) | 0.07 (0.03–0.19) | |
| Zn | 0.31 (0.20–0.50) | 0.24 (0.12–0.50) | n.d. | n.d. | |
| Elemental Signature | Fresh Pork Leg (Bone/Tissue) (wt%) | Air-Dried Pork Leg (Bone/Tissue) (wt%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LRN | FMJ | LRN | FMJ | |
| Pb | 10.39 (1.57–40.58) | 2.21 (1.16–2.86) | 6.74 (1.20–59.48) | 0.31 (0.10–0.33) |
| Cu | 0.06 (0.00–0.21) | 0.24 (0.13–0.53) | n.d. | n.d. |
| Zn | 0.64 (0.14–0.96) | 0.59 (0.00–0.89) | 0.41 (0.09–0.62) | 0.48 (0.34–0.71) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Leasen, S.; Lorwongtragool, P.; Chaiwan, S.; Donphoongpri, M. Comparative Elemental Signatures of Full Metal Jacket (FMJ) and Lead Round Nose (LRN) Projectiles on Complex Biological Targets Using Micro-XRF and Portable XRF. Forensic Sci. 2026, 6, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci6010011
Leasen S, Lorwongtragool P, Chaiwan S, Donphoongpri M. Comparative Elemental Signatures of Full Metal Jacket (FMJ) and Lead Round Nose (LRN) Projectiles on Complex Biological Targets Using Micro-XRF and Portable XRF. Forensic Sciences. 2026; 6(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci6010011
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeasen, Suthisa, Panida Lorwongtragool, Sittichoke Chaiwan, and Montri Donphoongpri. 2026. "Comparative Elemental Signatures of Full Metal Jacket (FMJ) and Lead Round Nose (LRN) Projectiles on Complex Biological Targets Using Micro-XRF and Portable XRF" Forensic Sciences 6, no. 1: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci6010011
APA StyleLeasen, S., Lorwongtragool, P., Chaiwan, S., & Donphoongpri, M. (2026). Comparative Elemental Signatures of Full Metal Jacket (FMJ) and Lead Round Nose (LRN) Projectiles on Complex Biological Targets Using Micro-XRF and Portable XRF. Forensic Sciences, 6(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci6010011







