Development of a Fluorescent Ionic Liquid Nanosensor for the Onsite Detection of Gamma-Hydroxybutyrate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
Materials
3. Experimental Procedures
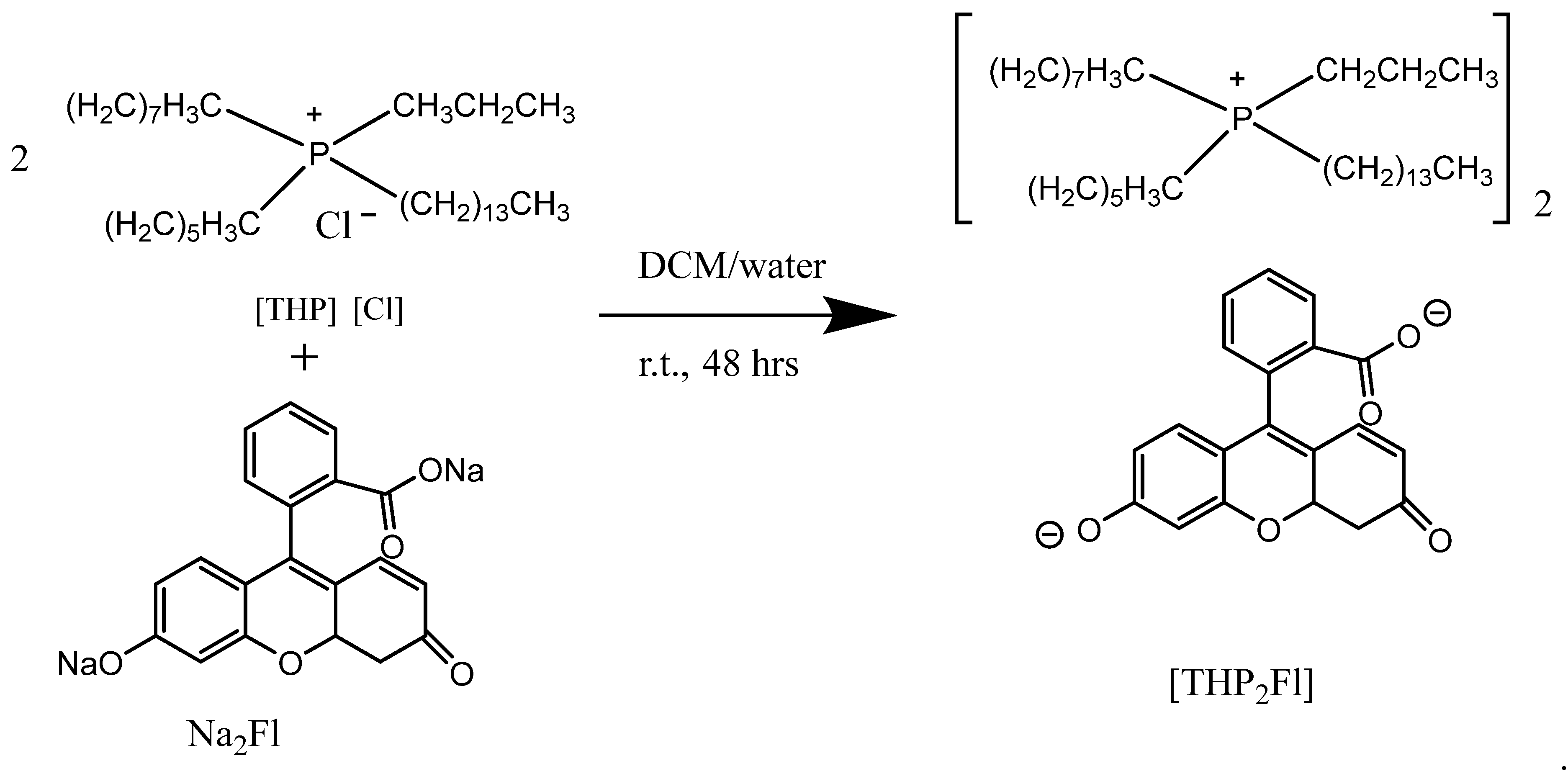
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of THP2FL Ionic Liquid
3.2. Synthesis of THP2FL Nanoparticles
3.3. Preparation of THP2FL Samples for Absorbance and Fluorescence Measurements
3.4. Characterization of Size and Zeta Potential of the Nanoparticles
3.5. GHB Detection Using THP2FL Nanoparticles
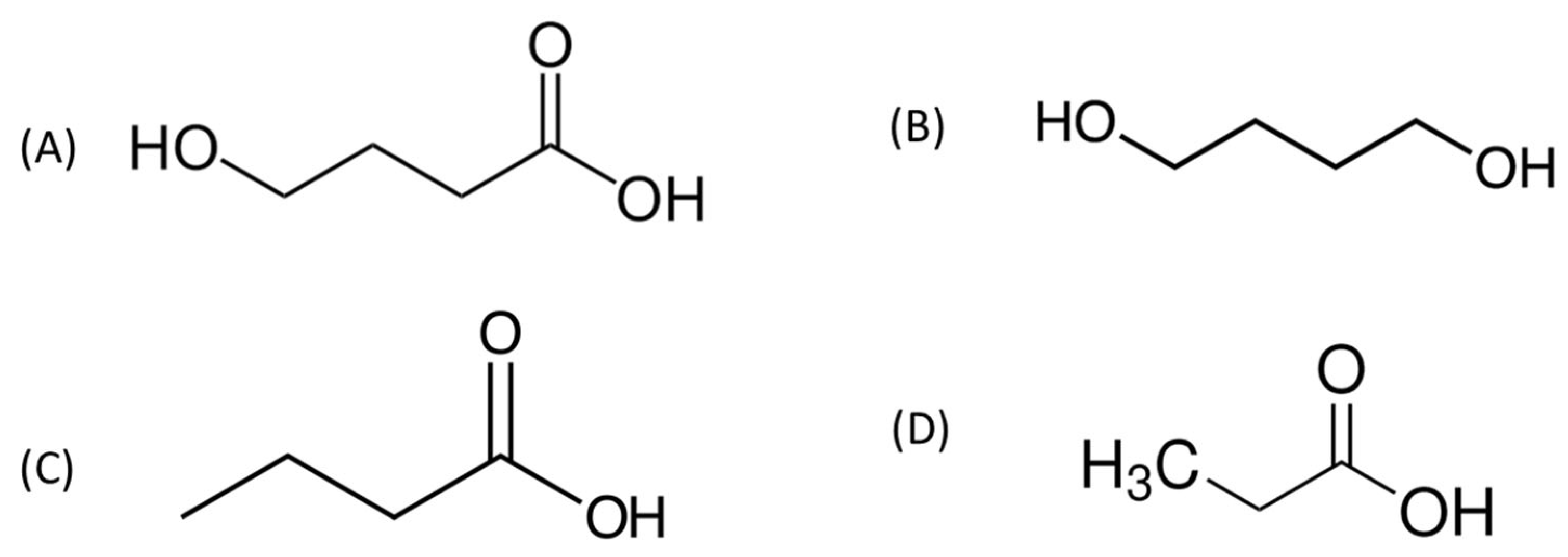
3.6. Testing Selectivity of the GHB Nanosensor Using Potential Interfering Species with Similar Chemical Structures
3.7. Testing Selectivity of the GHB Nanosensor Using Potential Interfering Species in Drinks and Beverages
4. Results and Discussion
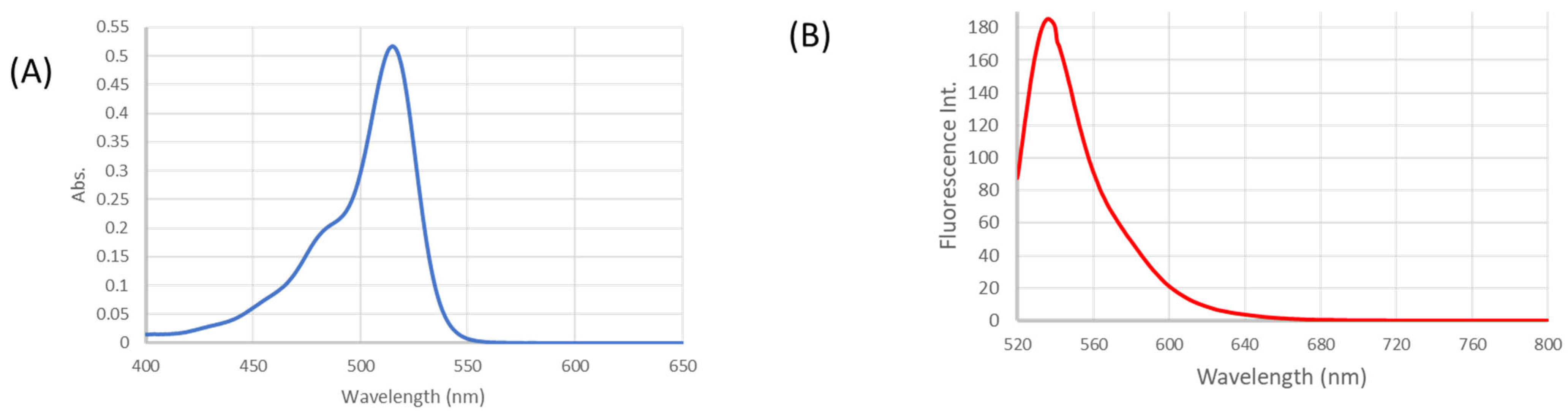
4.1. Photophysical Characterization of THP2FL
4.2. Characterization of THP2FL Nanoparticles
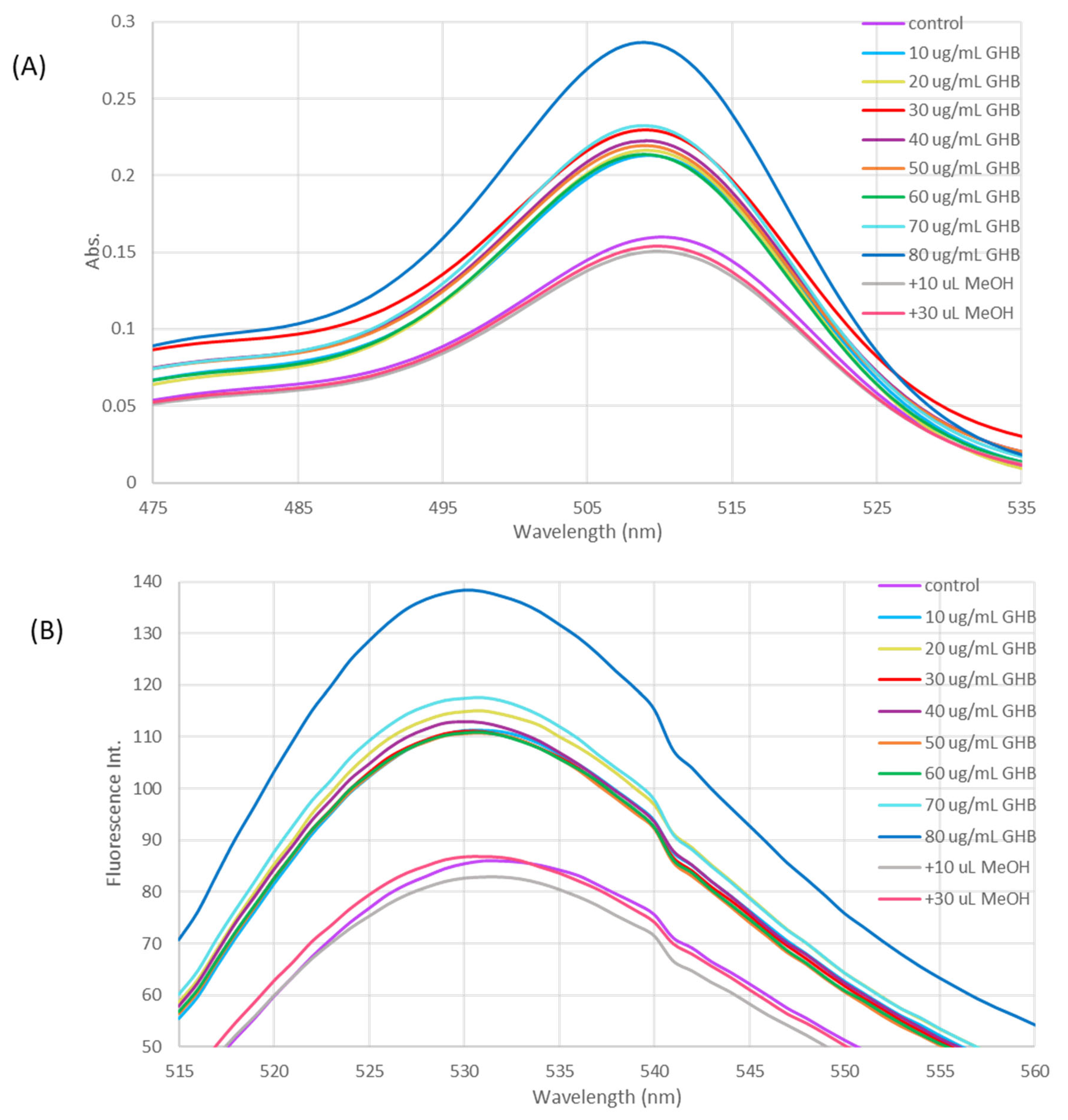
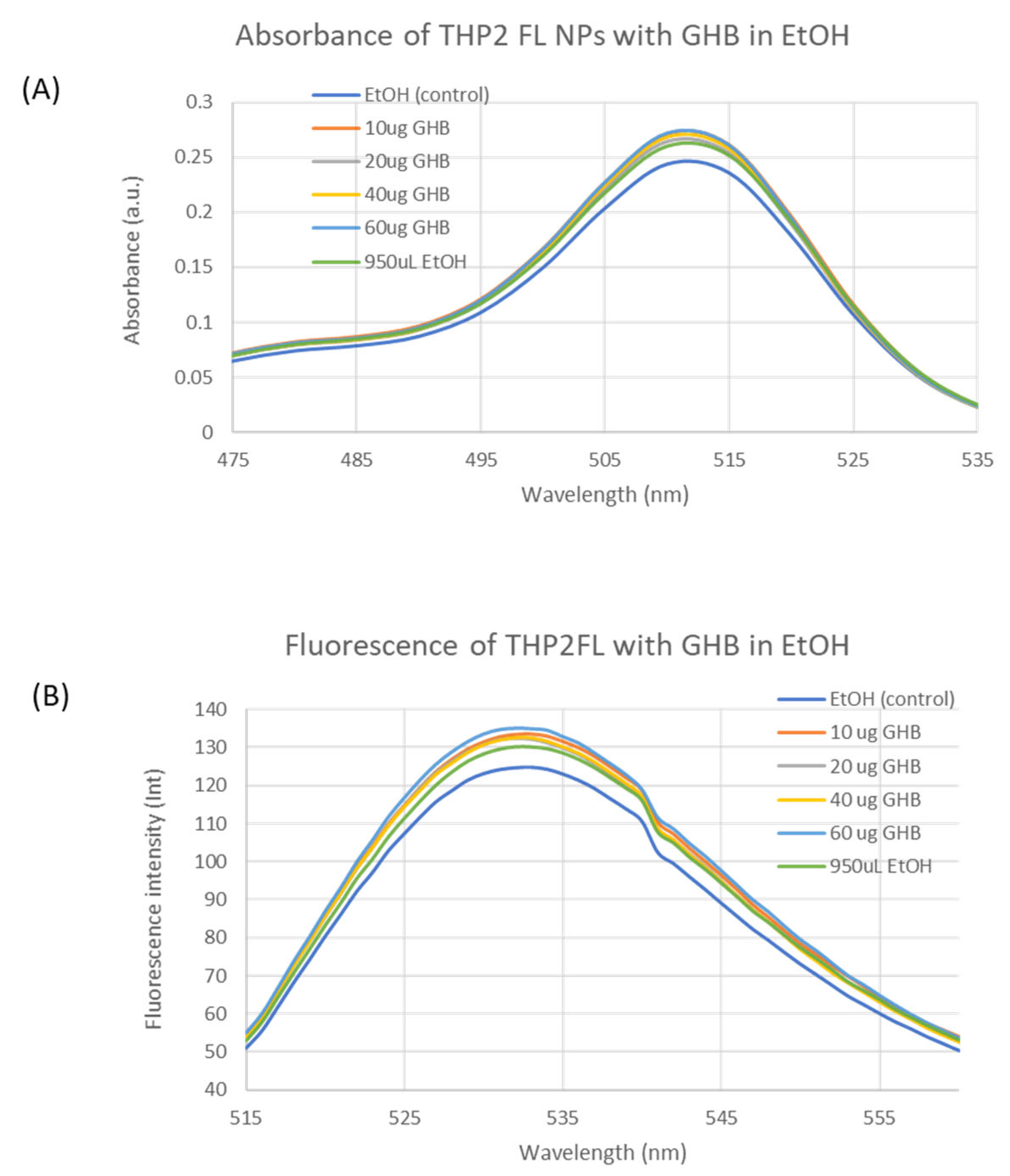
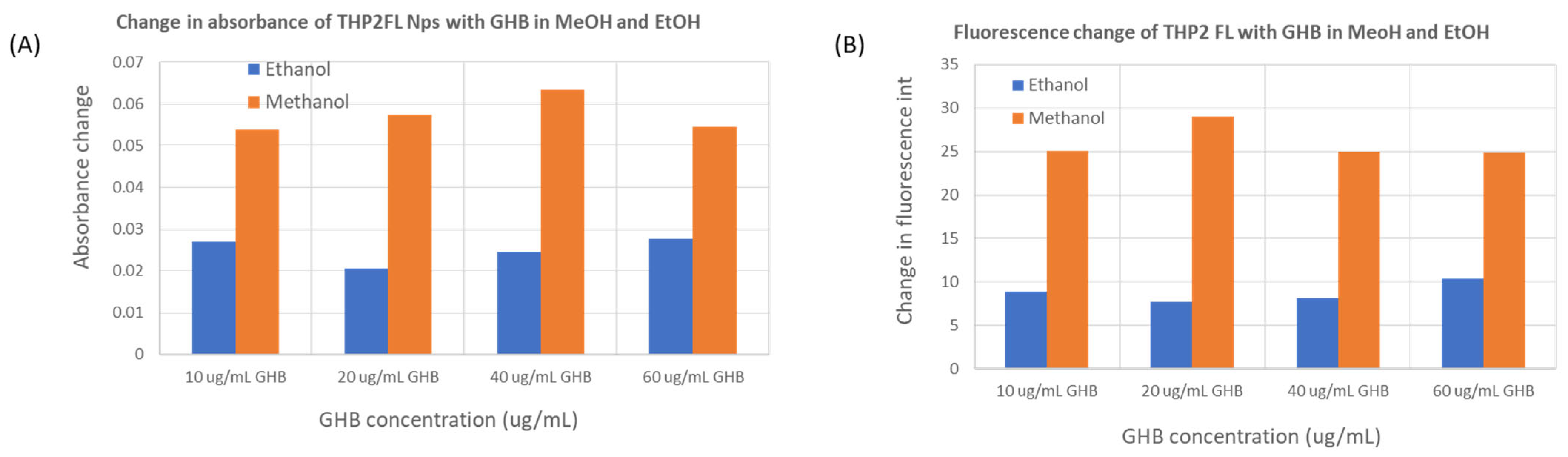
4.3. GHB Sensing Using THP2FL Nanoparticles
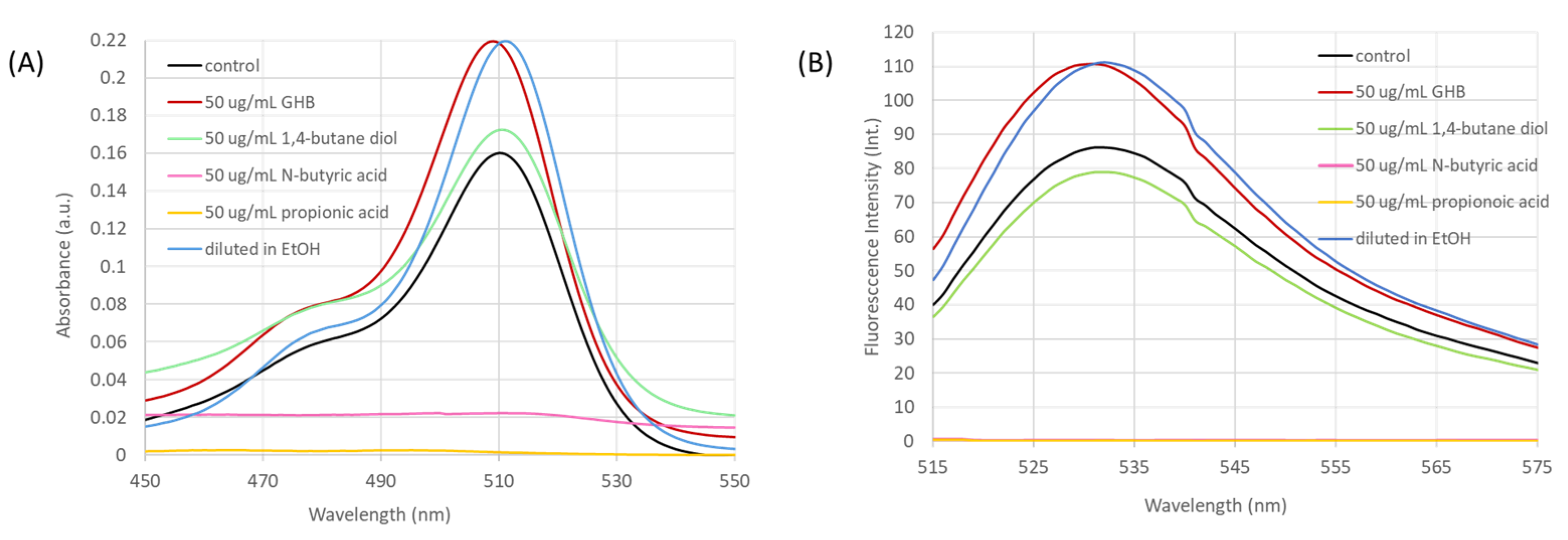
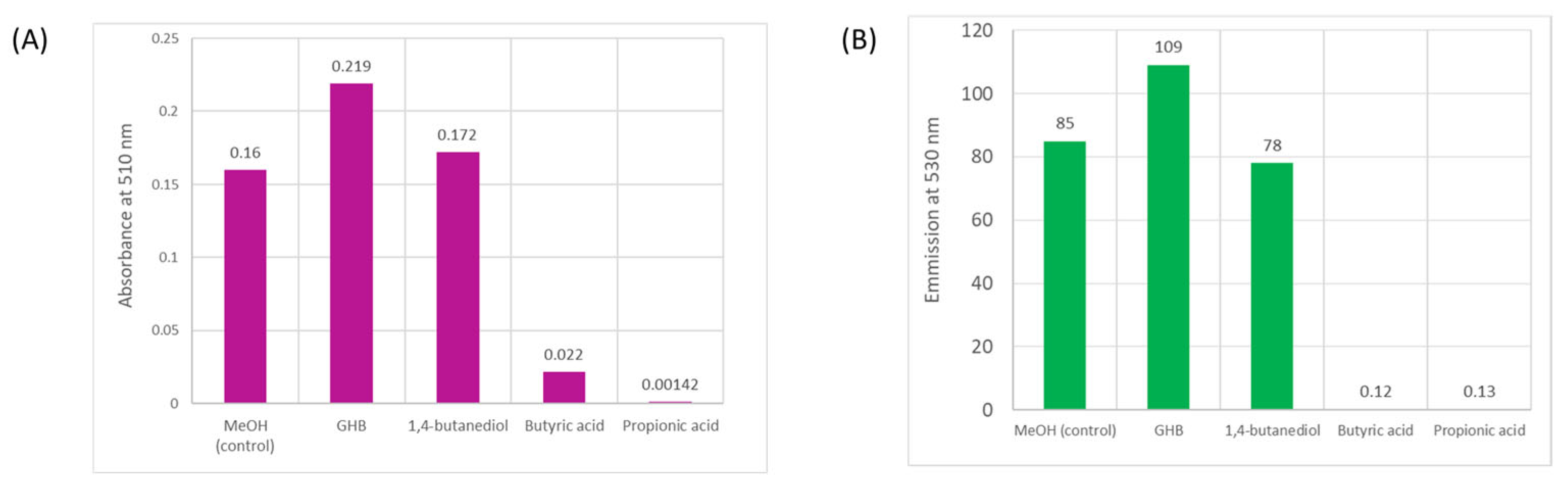
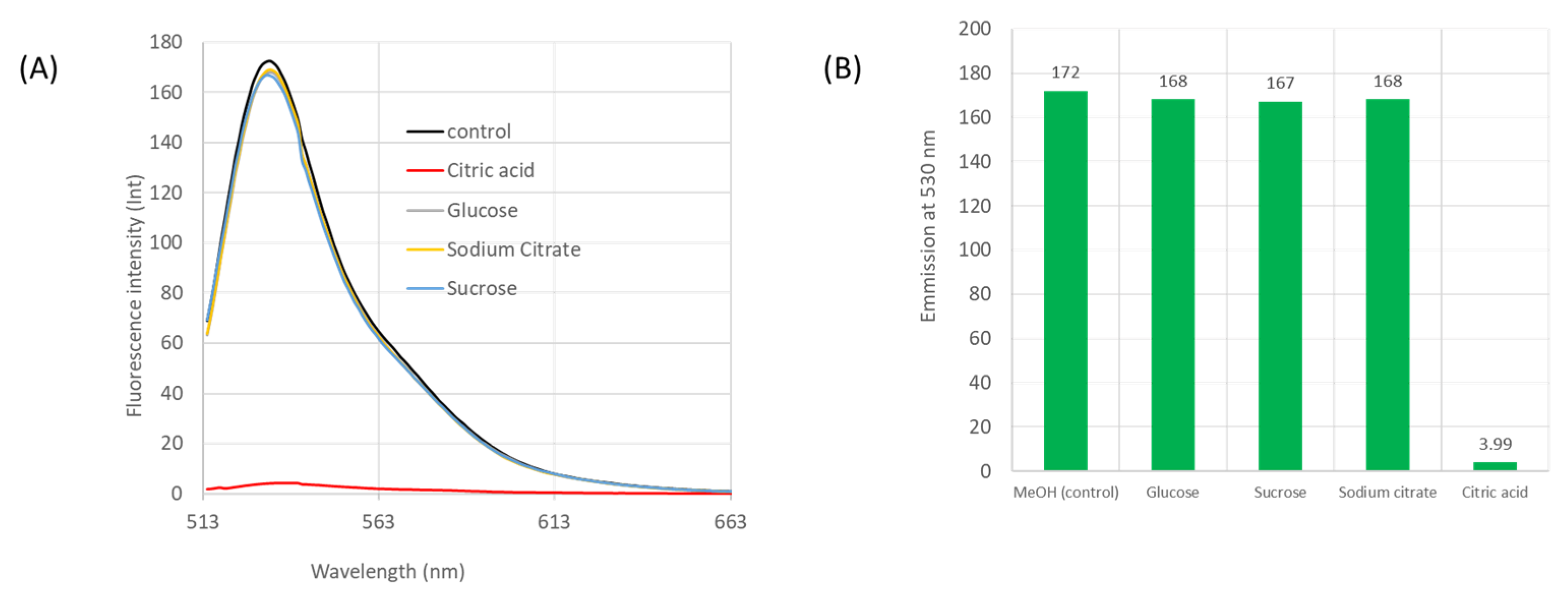
4.4. Testing for Interfering Species
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cooper, F.J.; Marinetti, L.J. γ-hydroxybutyrate (GHB)—Effects on human performance and behavior. Forensic Sci. Rev. 2002, 14, 101–121. [Google Scholar]
- Berretta, P.; Varì, M.R. The overwhelming issue of drug facilitated sexual assaults (DFSA): The case of GHB. Clin Ter. 2020, 170, e44–e45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Drug Enforcement Administration, Diversion Control Division, Drug & Chemical Evaluation Section. Gamma Hydroxybutyric Acid. Available online: https://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/drug_chem_info/ghb.pdf (accessed on 3 January 2025).
- García, M.G.; Pérez-Cárceles, M.D.; Osuna, E.; Legaz, I. Drug-facilitated sexual assault and other crimes: A systematic review by countries. J. Forensic Leg. Med. 2021, 79, 102151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapitány-Fovény, M.; Zacher, G.; Posta, J.; Demetrovics, Z. GHB-involved crimes among intoxicated patients. Forensic Sci. Int. 2017, 275, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickers, M. Gammahydroxybutyric acid. Int. Anesthesiol. Clin. 1969, 7, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galloway, G.P.; Frederick, S.L.; Staggers, F.E.; Gonzales, M.; Stalcup, S.A.; Smith, D.E. Gamma-hydroxybutyrate: An emerging drug of abuse that causes physical dependence. Addiction 1997, 92, 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, D.; Keatin, G.M. Sodium oxybate: A review of its use in the management of narcolepsy. CNS Drugs 2007, 21, 337–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscolo-Berto, R.; Viel, G.; Montagnese, S.; Raduazzo, D.I.; Ferrara, S.D.; Dauvilliers, Y. Narcolepsy and effectiveness of gammahydroxybutyrate. (GHB): A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Sleep Med. Rev. 2012, 16, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busardò, F.P.; Jones, A.W. GHB pharmacology and toxicology: Acute intoxication, concentrations in blood and urine in forensic cases and treatment of the withdrawal syndrome. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2015, 13, 47–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busardo, F.P.; Jones, A.W. Interpreting γ-hydroxybutyrate concentrations for clinical and forensic purposes. Clin. Toxicol. 2019, 57, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Németh, Z.; Kun, B.; Demetrovics, Z. Review: The involvement of gamma-hydroxybutyrate in reported sexual assaults: A systematic review. J. Psychopharmacol. 2010, 24, 1281–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, L.; Richards, B.; Mintzer, M.; Griffiths, R.R. Relative abuse liability of GHB in humans: A comparison of psychomotor, subjective, and cognitive effects of supratherapeutic doses of Triazolam, Pentobarbital, and GHB. NPP 2006, 31, 2537–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, R.R.; Walker, G.S. Rapid screening for the detection and differentiation of gamma-hydroxybutyrate using ion-chromatography. J. Forensic Sci. 2011, 56, 1256–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumes, L.A.; Buaki Sogo, M.; Montes-Navajas, P.; Corma, A.; Garcia, H. A colorimetric sensor array for the detection of the date-rape drug γ-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB): A supramolecular approach. Chemistry 2010, 16, 4489–4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casey, T.; Lesar, C.T.; Decatur, J.; Lukasiewicz, E.; Champeil, E. Report on the analysis of common beverages spiked with gamma-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) and gamma-butyrolactone (GBL) using NMR and the PURGE solvent-suppression technique. Forensic Sci. Int. 2011, 212, e40–e45. [Google Scholar]
- Frison, G.; Tedeschi, L.; Maietti, S.; Ferrara, S.D. Determination of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) in plasma and urine by headspace solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography/positive ion chemical ionization mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass. Spectrom. 2000, 14, 2401–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crookes, C.E.; Faulds, M.C.; Forrest, A.R.; Galloway, J.H. A reference range for endogenous gamma-hydroxybutyrate in urine by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2004, 28, 644–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kintz, P.; Goullé, J.P.; Cirimele, V.; Ludes, B. Window of detection of gamma-hydroxybutyrate in blood and saliva. Clin. Chem. 2001, 47, 2033–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; Kim, Y. Overcoming interferences in the colorimetric and fluorimetric detection of γ-hydroxybutyrate in spiked beverages. Sensor Actuat. B Chem. 2022, 364, 131861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, E.; Lo, W.K.W.; Murnion, B. Current insights on the impact of gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB) abuse. Subst. Abuse Rehabil. 2022, 13, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alston II, W.C.; Ng, K. Rapid colorimetric screening test for γ-hydroxybutyric acid (liquid X) in human urine. Forensic Sci. Int. 2002, 126, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, D.; Tan, Y.Q.; Xu, W.; Chang, Y.T. Development of a fluorescent sensor for illicit date rape drug GHB. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 2904–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Nuévalos, S.; Costero, A.M.; Parra, M.; Gil, S.; Arroyo, P.; Sáez, J.A.; Gaviña, P.; Ceroni, P.; Fermi, A. Colorimetric and fluorescent hydrazone-BODIPY probes for the detection of γ-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) and cathinones. Dyes Pigm. 2022, 207, 110757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahiwadkar, R.; Kumar, H.; Kanvah, S. Detection of illicit GHB using AIE active fluorene containing α-Cyanostilbenes. JPPA 2022, 427, 113844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonzo, M.; Alder, R.; Clancy, L.; Fu, S. Portable testing techniques for the analysis of drug materials. WIREs Forensic Sci. 2022, 4, e1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Chen, B.; Moo, Y.; MacFarlane, D.R. Introduction: Ionic liquids. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 6633–6635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordness, O.; Brennecke, F.J. Ion dissociation in ionic liquids and ionic liquid solutions. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 12873–12902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Magut, P.K.S.; de Rooy, S.L.; Hasan, F.; Warner, I.M. Ionic liquid-based fluorescein colorimetric pH nanosensors. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 21054–21061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Bwambok, D.; El-Zahab, B.; Monk, J.; de Rooy, S.L.; Challa, S.; Li, M.; Hung, F.R.; Baker, G.A.; Warner, I.M. Nontemplated approach to tuning the spectral properties of cyanine-based fluorescent nanoGUMBOS. Langmuir 2010, 26, 12867–12876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huller, C.; Thai, D.; Jacob III, P.; Dyer, J.E. GHB urine concentrations after single-dose administration in humans. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2006, 30, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moss, J.E.R.; Hamory, K.; Moreland, R.; Oakley, C.B.; Bwambok, D.K.; Fernand Narcisse, V.E. Development of a Fluorescent Ionic Liquid Nanosensor for the Onsite Detection of Gamma-Hydroxybutyrate. Forensic Sci. 2025, 5, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci5030028
Moss JER, Hamory K, Moreland R, Oakley CB, Bwambok DK, Fernand Narcisse VE. Development of a Fluorescent Ionic Liquid Nanosensor for the Onsite Detection of Gamma-Hydroxybutyrate. Forensic Sciences. 2025; 5(3):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci5030028
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoss, Joel E. R., Kathryn Hamory, Robert Moreland, Carolyn B. Oakley, David K. Bwambok, and Vivian E. Fernand Narcisse. 2025. "Development of a Fluorescent Ionic Liquid Nanosensor for the Onsite Detection of Gamma-Hydroxybutyrate" Forensic Sciences 5, no. 3: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci5030028
APA StyleMoss, J. E. R., Hamory, K., Moreland, R., Oakley, C. B., Bwambok, D. K., & Fernand Narcisse, V. E. (2025). Development of a Fluorescent Ionic Liquid Nanosensor for the Onsite Detection of Gamma-Hydroxybutyrate. Forensic Sciences, 5(3), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci5030028




