Development and Validation of Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry Method for Quantification of Lithium in Whole Blood from Forensic Postmortem Cases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. Rinse Program Between Injections
2.4. Solutions
2.5. Quality Control Samples
2.6. Sample Preparation
2.7. Method Development
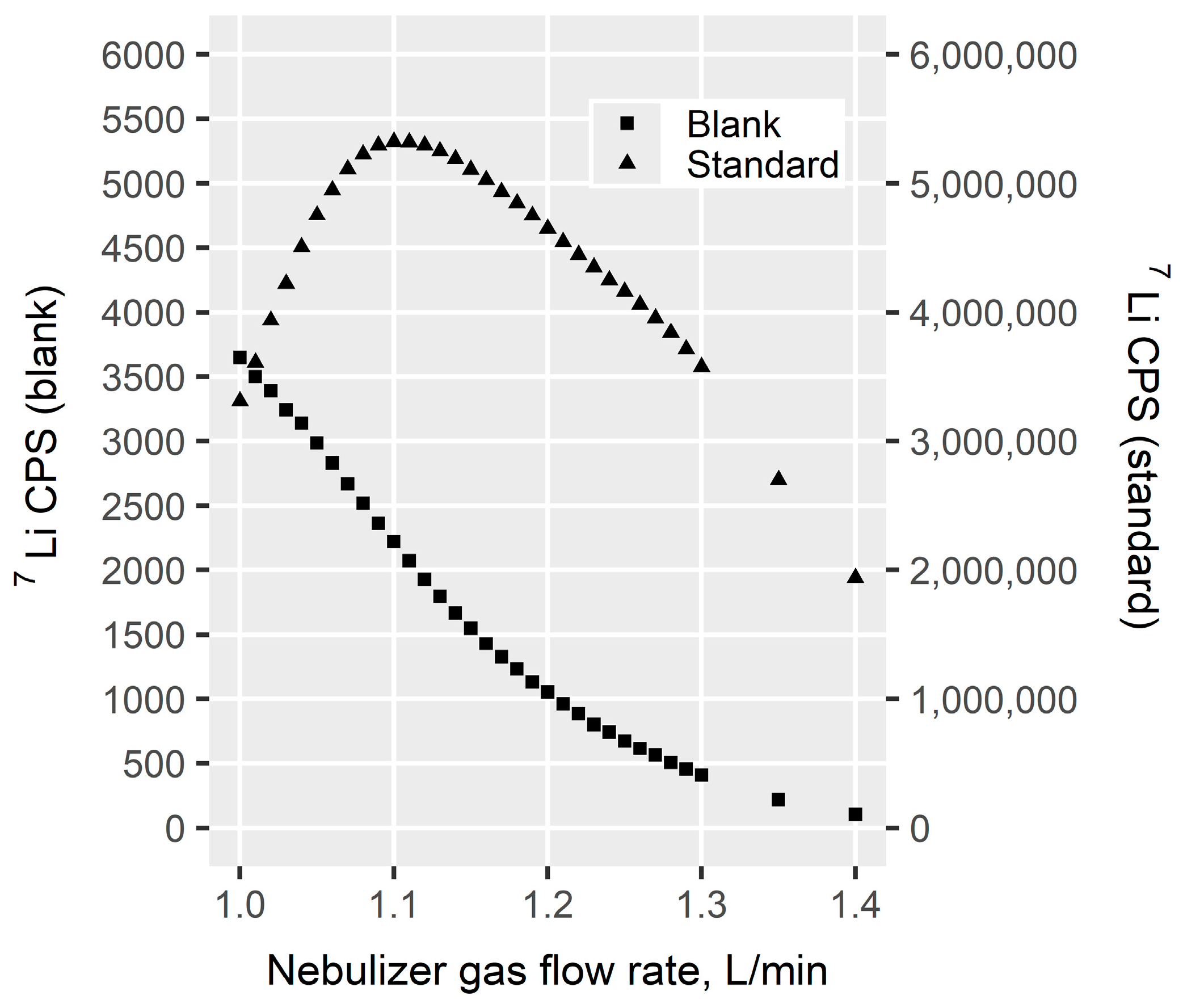
2.7.1. Nebulizer Gas Flow Rate
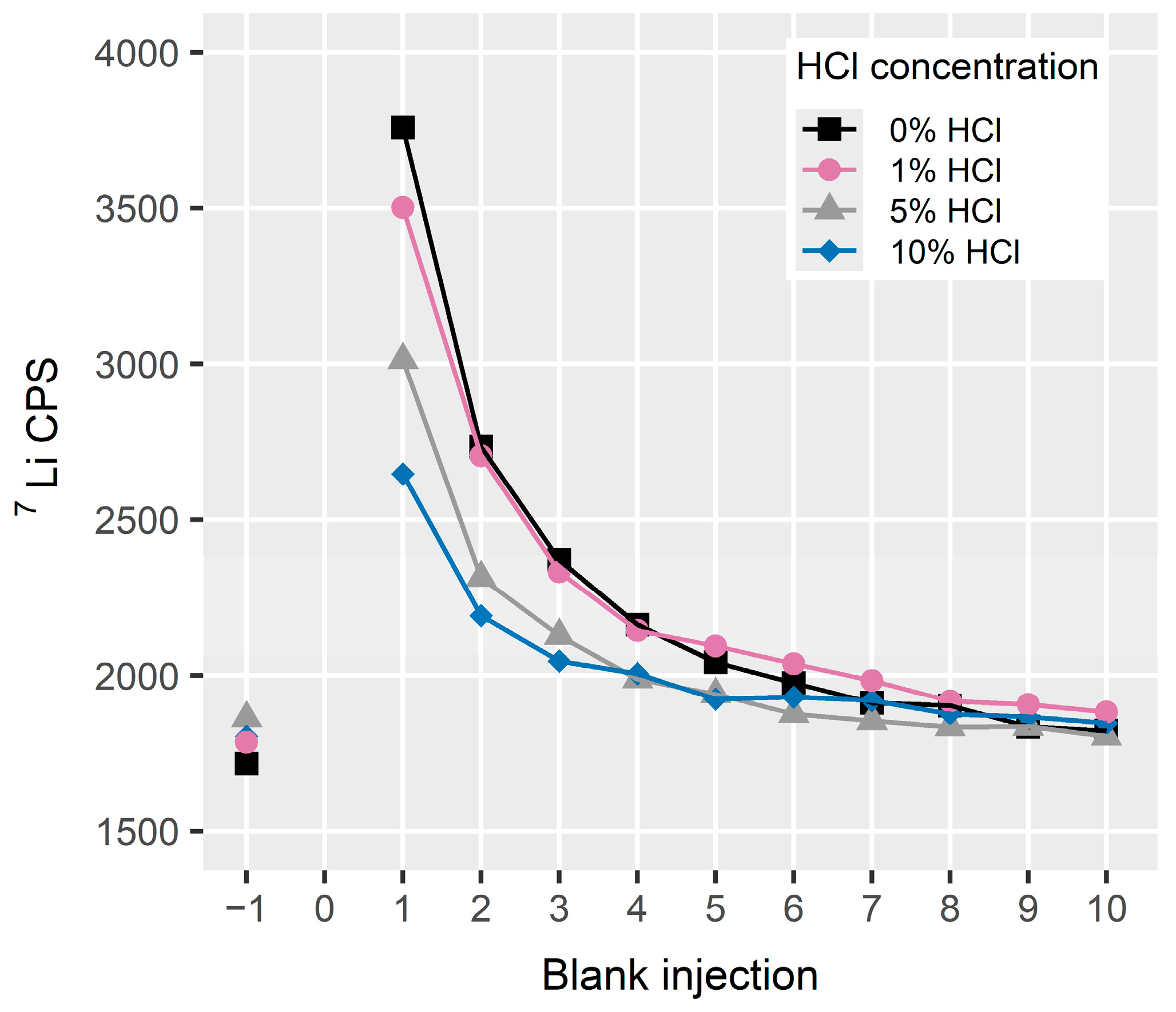
2.7.2. Carry-Over (Rinse Solution)
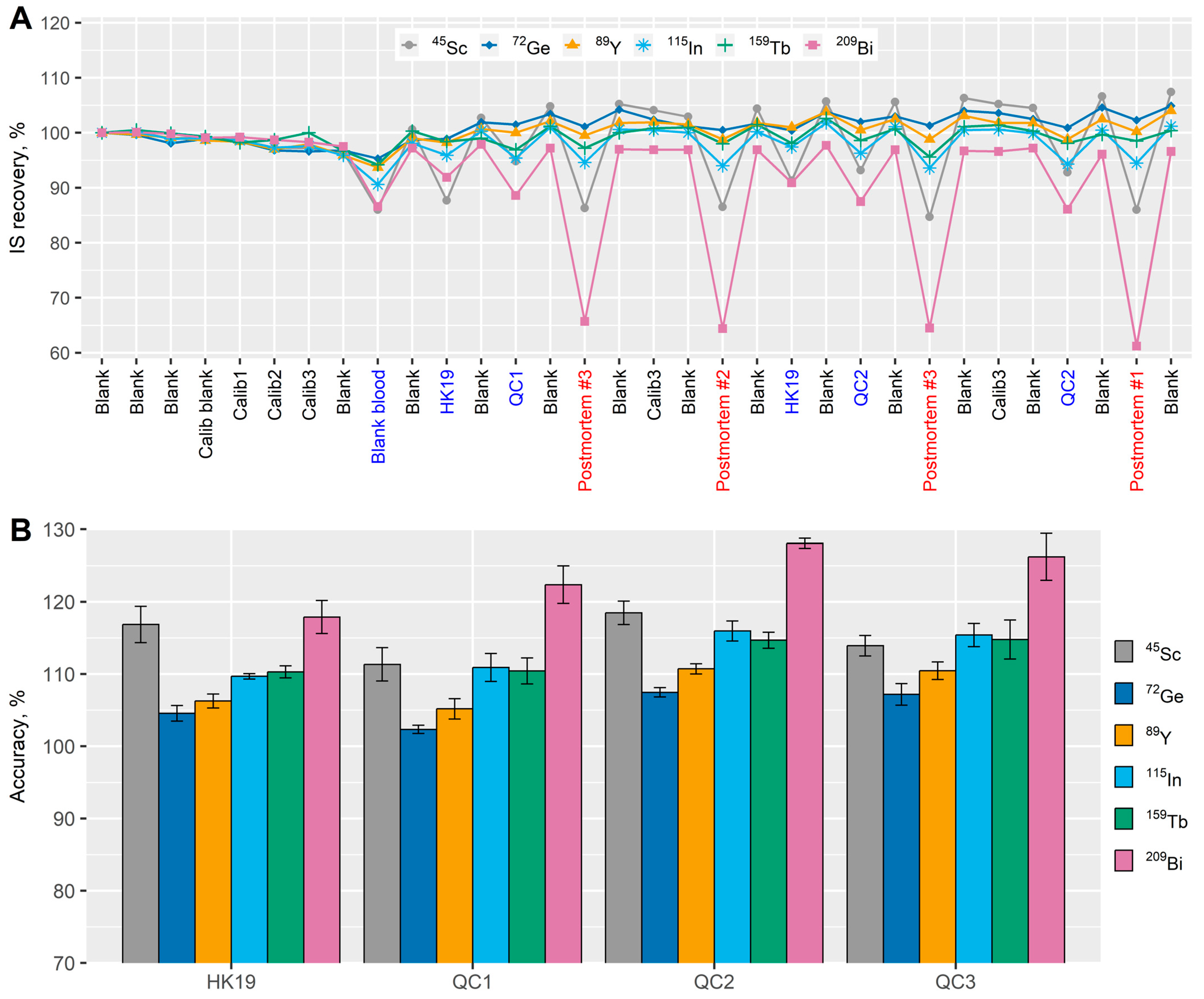
2.7.3. Selection of Internal Standard
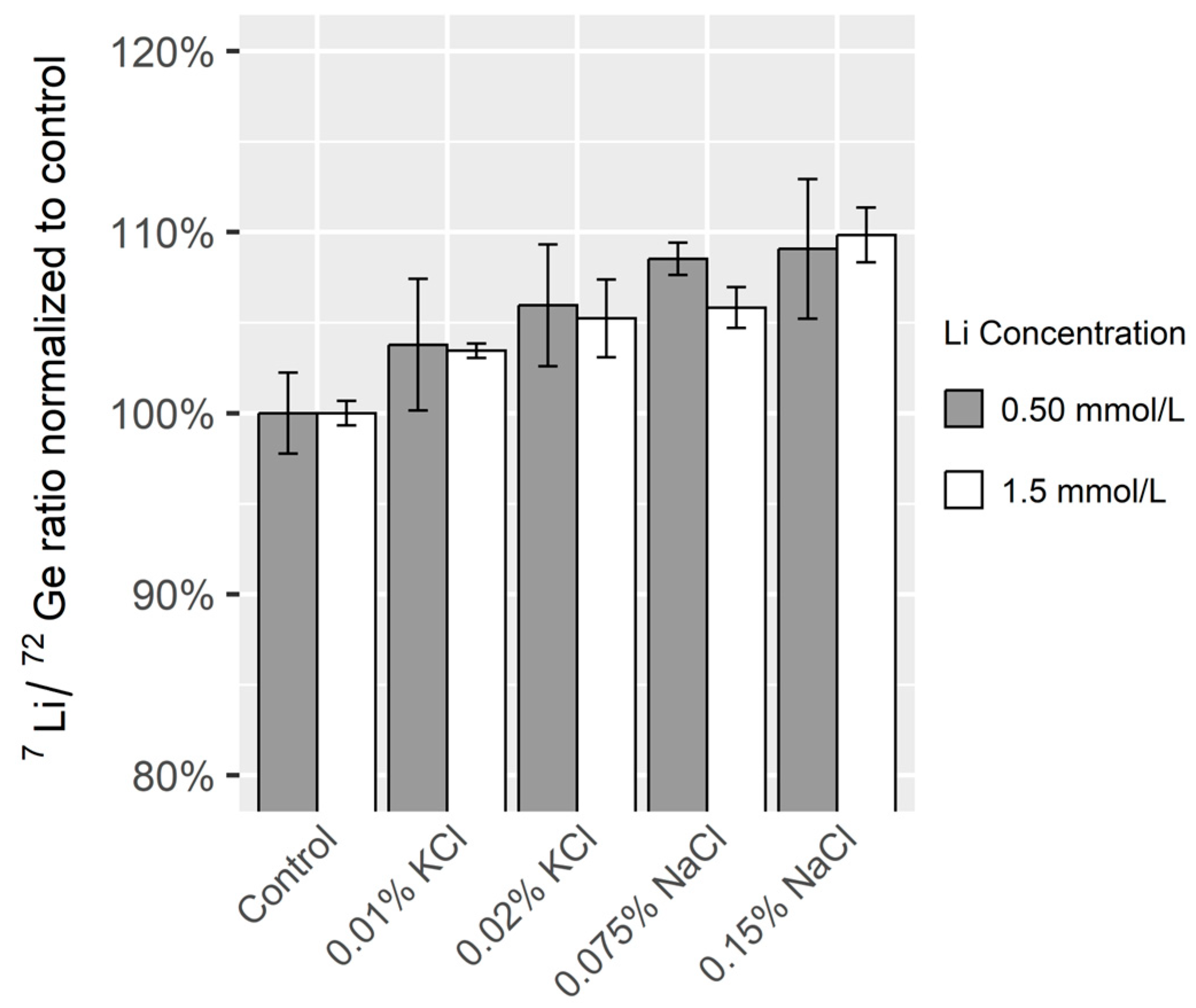
2.7.4. Effect of Sodium and Potassium on Accuracy
2.8. Method Validation
2.8.1. Linearity
2.8.2. Accuracy, Precision, LLOQ, and Dilution Integrity
2.8.3. Accuracy in Postmortem Whole Blood
2.9. Analysis of Whole Blood from 103 Consecutive Autopsy Cases
2.10. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Method Development
3.1.1. Nebulizer Gas Flow Rate
3.1.2. Effect of Hydrochloric Acid on Carry-Over
3.1.3. Selection of Internal Standard
3.1.4. Effect of Sodium and Potassium on Accuracy
3.2. Validation
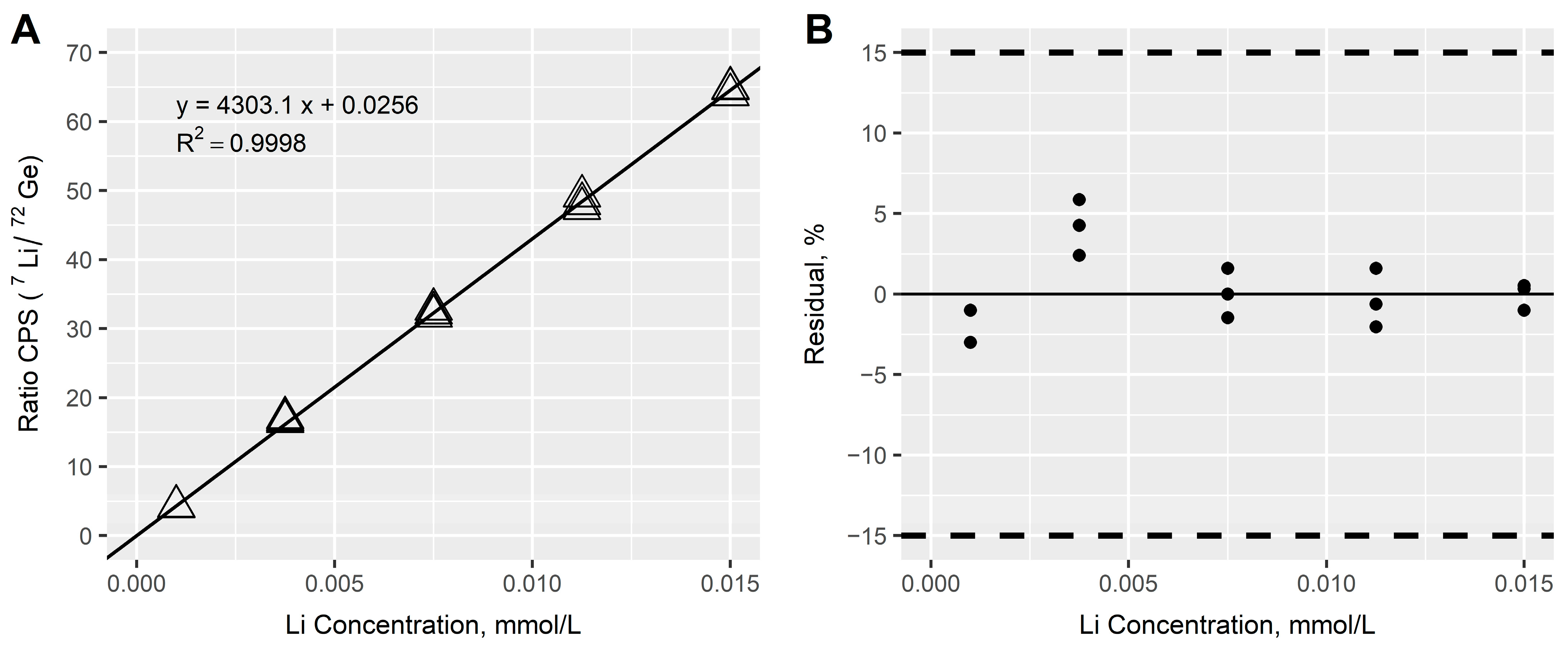
3.2.1. Linearity
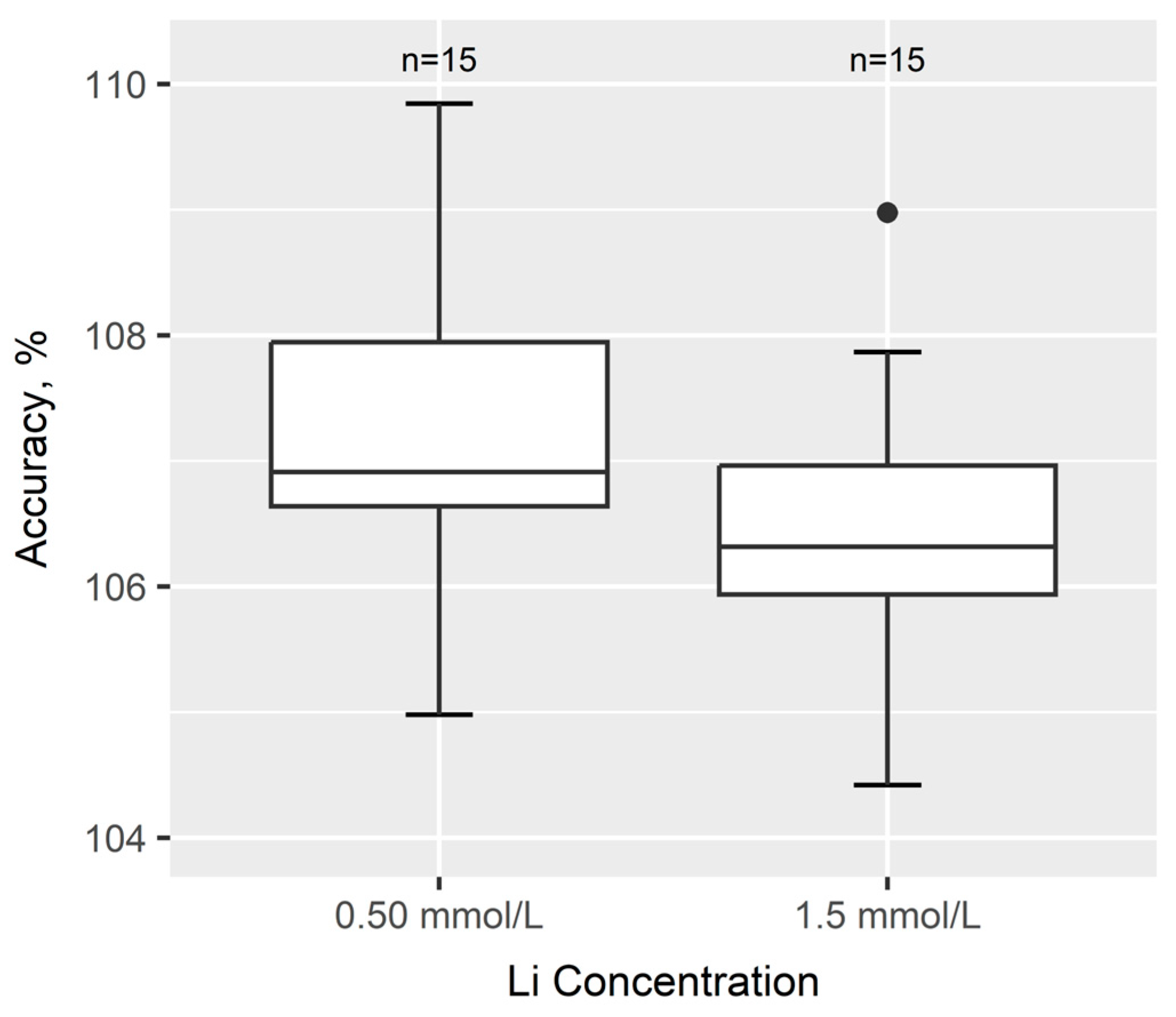
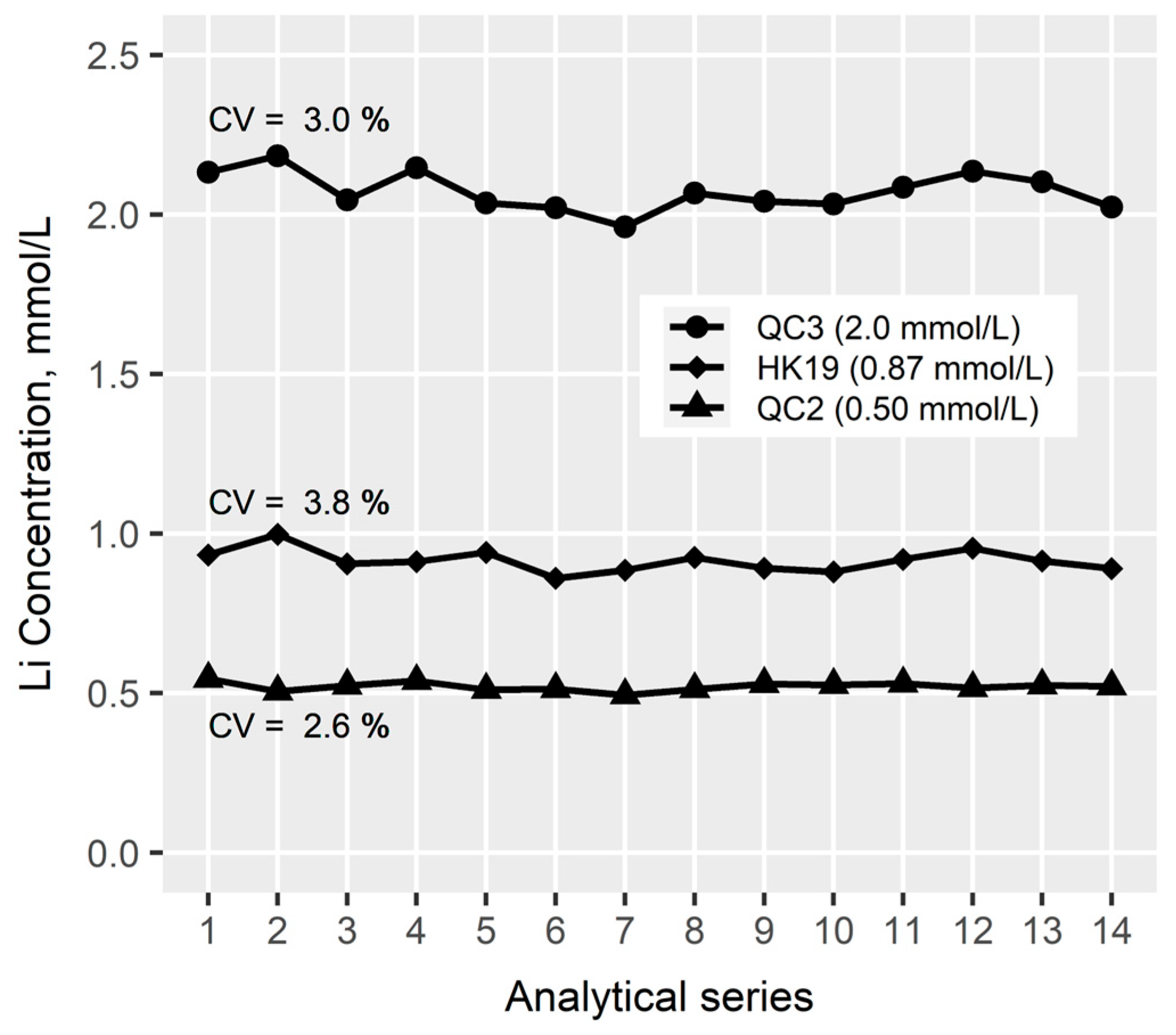
3.2.2. Precision and Accuracy
3.2.3. Dilution Integrity
3.2.4. Accuracy in Postmortem Whole Blood
3.3. Analysis of 103 Consecutive Autopsy Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ICP-MS | Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry |
| CPS | Counts per second |
| QC | Quality control |
| CV | Coefficient of variation |
| LLOQ | Lower limit of quantification |
| IS | Internal standard |
References
- Rakofsky, J.J.; Lucido, M.J.; Dunlop, B.W. Lithium in the treatment of acute bipolar depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 308, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mose, T.; Damkier, P.; Petersen, M.; Antonsen, S. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Lithium: A Study of the Accuracy and Analytical Variation Between Laboratories in Denmark. Ther. Drug Monit. 2015, 37, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söderberg, C.; Wernvik, E.; Jönsson, A.K.; Druid, H. Reference values of lithium in postmortem femoral blood. Forensic Sci. Int. 2017, 277, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saady, J.J. Metals. In Principles of Forensic Toxicology, 5th ed.; Levine, B.S., Kerrigan, S., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 569–581. [Google Scholar]
- Baselt, R.C. Lithium. In Disposition of Toxic Drugs and Chemicals in Man, 12th ed.; Biomedical Publications: Foster City, CA, USA, 2020; pp. 1170–1171. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, X.; Li, Q.; Lin, P.; Jin, Z.; Chen, M.; Ju, Y. A standard addition method to quantify serum lithium by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2022, 59, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, M.; Stegmayr, B.; Salander Renberg, E.; Werneke, U. Lithium intoxication: Incidence, clinical course and renal function—A population-based retrospective cohort study. J. Psychopharmacol. 2016, 30, 1008–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gitlin, M. Lithium side effects and toxicity: Prevalence and management strategies. Int. J. Bipolar Disord. 2016, 4, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oruch, R.; Elderbi, M.A.; Khattab, H.A.; Pryme, I.F.; Lund, A. Lithium: A review of pharmacology, clinical uses, and toxicity. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 740, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumbelow, B.; Peake, M. Performance of a novel spectrophotometric lithium assay on a routine biochemistry analyser. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2001, 38, 684–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R. Practical Guide to ICP-MS and Other Atomic Spectroscopy Techniques: A Tutorial for Beginners; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Abou-Shakra, F.R.; Havercroft, J.M.; Ward, N.I. Lithium and boron in biological tissues and fluids. Trace Elem. Med. 1989, 6, 142–146. [Google Scholar]
- Vanhoe, H.; Dams, R.; Versieck, J. Use of inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry for the determination of ultra-trace elements in human serum. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 1994, 9, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhoe, H.; Vandecasteele, C.; Versieck, J.; Dams, R. Determination of lithium in biological samples by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 1991, 244, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrer, R.; Gautschi, K.; Lutz, H. Simultaneous measurement of the trace elements Al, As, B, Be, Cd, Co, Cu, Fe, Li, Mn, Mo, Ni, Rb, Se, Sr, and Zn in human serum and their reference ranges by ICP-MS. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2001, 80, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goullé, J.P.; Mahieu, L.; Castermant, J.; Neveu, N.; Bonneau, L.; Lainé, G.; Bouige, D.; Lacroix, C. Metal and metalloid multi-elementary ICP-MS validation in whole blood, plasma, urine and hair. Reference values. Forensic Sci. Int. 2005, 153, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maynar, M.; Llerena, F.; Grijota, F.J.; Alves, J.; Robles, M.C.; Bartolomé, I.; Muñoz, D. Serum concentration of several trace metals and physical training. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2017, 14, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laur, N.; Kinscherf, R.; Pomytkin, K.; Kaiser, L.; Knes, O.; Deigner, H.P. ICP-MS trace element analysis in serum and whole blood. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesbron, A.; Saussereau, E.; Mahieu, L.; Couland, I.; Guerbet, M.; Goullé, J.P. Metallic profile of whole blood and plasma in a series of 106 healthy volunteers. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2013, 37, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Kippler, M.; Harari, F.; Grandér, M.; Palm, B.; Nordqvist, H.; Vahter, M. Alkali dilution of blood samples for high throughput ICP-MS analysis-comparison with acid digestion. Clin. Biochem. 2015, 48, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawi, M.A.; Chin, S.F.; Jamal, R. Simultaneous analysis of 25 trace elements in micro volume of human serum by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). Pract. Lab. Med. 2020, 18, e00142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Ma, W.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, H.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, Y. Circulating metal concentrations, inflammatory cytokines and gestational weight gain: Shanghai MCPC cohort. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 199, 110697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayawardene, I.; Paradis, J.F.; Bélisle, S.; Poddalgoda, D.; Macey, K. Multi-elemental determination of metals, metalloids and rare earth element concentrations in whole blood from the Canadian Health Measures Survey, 2009–2011. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2021, 68, 126830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goullé, J.P.; Le Roux, P.; Castanet, M.; Mahieu, L.; Guyet-Job, S.; Guerbet, M. Metallic Profile of Whole Blood and Plasma in a Series of 99 Healthy Children. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2015, 39, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Söderberg, C.; Rodushkin, L.; Johansson, A.; Kugelberg, F.C. Postmortem reference concentrations of 68 elements in blood and urine. Int. J. Legal Med. 2023, 137, 655–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Society of Forensic Toxicologists/American Academy of Forensic Sciences. SOFT/AAFS Forensic Toxicology Laboratory Guidelines; Society of Forensic Toxicologists/American Academy of Forensic Sciences: Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, F.T.; Drummer, O.H.; Musshoff, F. Validation of new methods. Forensic Sci. Int. 2007, 165, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnet, K. The between-run component of variation in internal quality control. Clin. Chem. 1989, 35, 1416–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanhaecke, F.; Dams, R.; Vandecasteele, C. ‘Zone model’ as an explanation for signal behaviour and non-spectral interferences in inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 1993, 8, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ilio, S.; Violante, N.; Di Gregorio, M.; Senofonte, O.; Petrucci, F. Simultaneous quantification of 17 trace elements in blood by dynamic reaction cell inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (DRC-ICP-MS) equipped with a high-efficiency sample introduction system. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 579, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.S.; Shin, H.S.; Kil, Y.W. Precise determination of lithium isotopes in seawater using MC-ICP-MS. Microchem. J. 2010, 95, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, C.J.; McCulloch, M.T.; Bennett, V.C. Impact of matrix effects on the accurate measurement of Li isotope ratios by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (MC-ICP-MS) under “cold” plasma conditions. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2003, 18, 734–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohlin, M.S.; Misra, S.; Lloyd, N.; Elderfield, H.; Bickle, M.J. High-precision determination of lithium and magnesium isotopes utilising single column separation and multi-collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass. Spectrom. 2018, 32, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hakkani, M.F. Guideline of inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry “ICP–MS”: Fundamentals, practices, determination of the limits, quality control, and method validation parameters. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juzer, S.; Tanwar, N.; Misra, S. Precise determination of lithium isotope ratios at the sub-nanogram level by QQQ-ICP-MS: Application to natural waters and carbonates. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2022, 37, 1541–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Yang, L.; Chen, K.; Chen, H.; Zong, K.; Gao, S. Accurate determination of lithium isotope ratios by MC-ICP-MS without strict matrix-matching by using a novel washing method. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2016, 31, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wille, M.R.S.; Coucke, W.; De Baere, T.; Peters, T.F. Update of Standard Practices for New Method Validation in Forensic Toxicology. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 5442–5454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilschefski, S.C.; Baxter, M.R. Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry: Introduction to Analytical Aspects. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2019, 40, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajek, R.; Barley, F.; She, J. Determination of essential and toxic metals in blood by ICP-MS with calibration in synthetic matrix. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 2193–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajek, R.; Choe, K.-Y. Determination of ultra-trace elements in human plasma or serum by ICP-MS using sodium in the presence of carbon as a single calibration matrix-match component. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2015, 30, 1142–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. Ionization Energy in the Periodic Table of Elements. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ptable/ionization-energy/ (accessed on 22 March 2024).
- Rammer, L.; Gerdin, B. Dilution of blood in fresh water drowning. Post-mortem determination of osmolarity and electrolytes in blood, cerebrospinal fluid and vitreous humor. Forensic Sci. 1976, 8, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Setting | Value |
|---|---|
| RF power | 1550 W |
| Nebulizer gas flow rate | 1.15 L/min |
| RF matching | 1.80 V |
| Sample depth | 10.0 mm |
| Nebulizer pump | 0.10 rps |
| S/C temp | 2 °C |
| Auxiliary gas | 0.90 L/min |
| Plasma gas | 15.0 L/min |
| OctP bias | −8.0 V |
| Data acquisition | |
| Peak pattern | 1 point |
| Replicates | 3 |
| Sweeps/replicate | 100 |
| Integration time | 1 s (7Li) 0.1 s (72Ge) |
| Samples | Matrix | Accuracy (%) Mean (Range) | Within-Run CV (%) | Between-Run CV (%) | Total CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QC1 (0.10 mmol/L) | Whole blood | 105 (101–108) | 1.5 | 1.7 | 2.3 |
| QC2 (0.50 mmol/L) | Whole blood | 108 (104–110) | 1.4 | 1.2 | 1.8 |
| QC3 (2.0 mmol/L) | Whole blood | 105 (103–109) | 2.1 | 0.0 | 2.1 |
| HK19 (0.87 mmol/L) | Serum | 105 (103–107) | 1.1 | 0.0 | 1.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, C.C.Y.; Johansen, S.S.; Rasmussen, B.S.; Linnet, K.; Thomsen, R. Development and Validation of Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry Method for Quantification of Lithium in Whole Blood from Forensic Postmortem Cases. Forensic Sci. 2025, 5, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci5020022
Chang CCY, Johansen SS, Rasmussen BS, Linnet K, Thomsen R. Development and Validation of Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry Method for Quantification of Lithium in Whole Blood from Forensic Postmortem Cases. Forensic Sciences. 2025; 5(2):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci5020022
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Cherrie Cheuk Yiu, Sys Stybe Johansen, Brian Schou Rasmussen, Kristian Linnet, and Ragnar Thomsen. 2025. "Development and Validation of Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry Method for Quantification of Lithium in Whole Blood from Forensic Postmortem Cases" Forensic Sciences 5, no. 2: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci5020022
APA StyleChang, C. C. Y., Johansen, S. S., Rasmussen, B. S., Linnet, K., & Thomsen, R. (2025). Development and Validation of Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry Method for Quantification of Lithium in Whole Blood from Forensic Postmortem Cases. Forensic Sciences, 5(2), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci5020022






