Comparative Taxonomic Study of Launaea Cass. (Asteraceae, Cichorioideae) in Egypt
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Specimens
2.2. Macromorphological Characters and Numerical Analysis
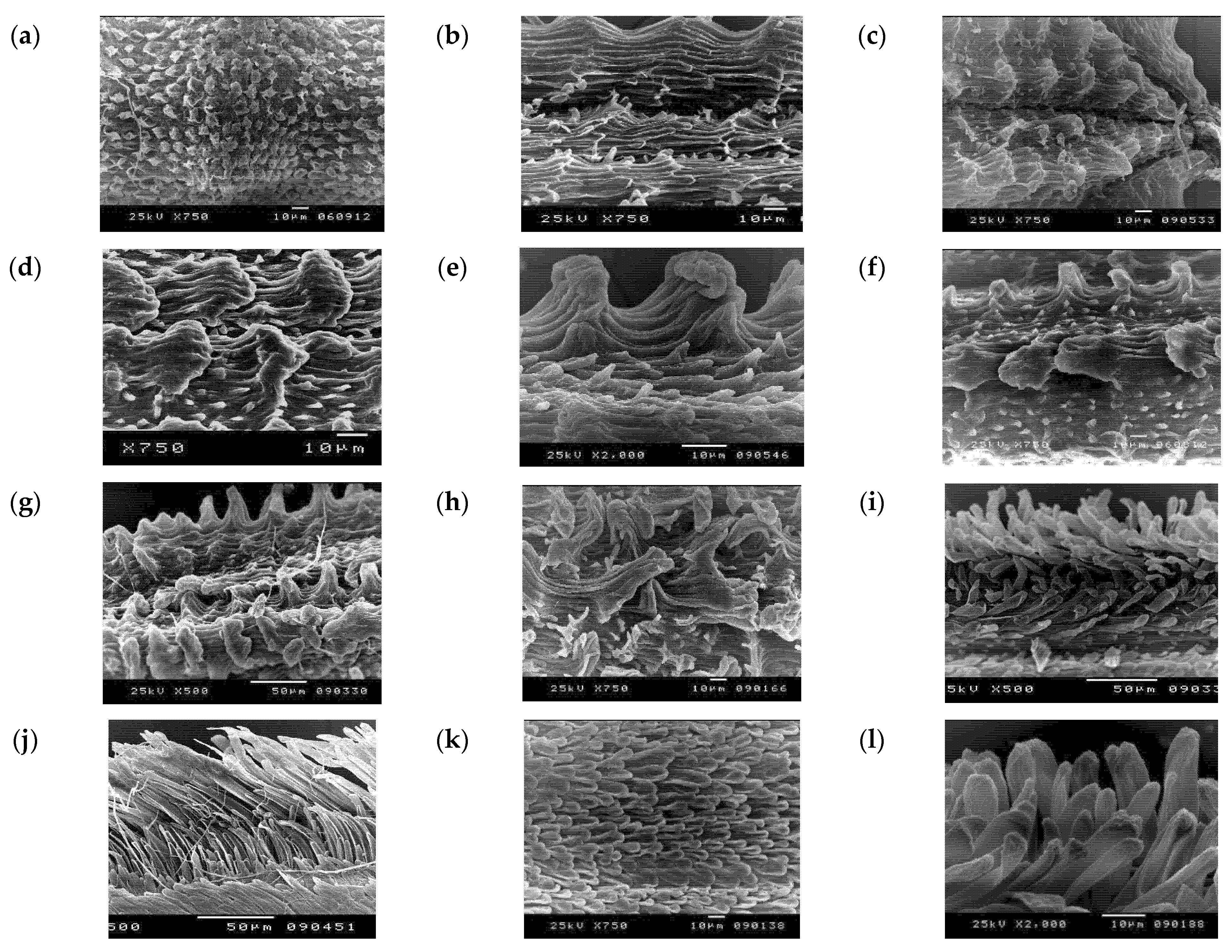
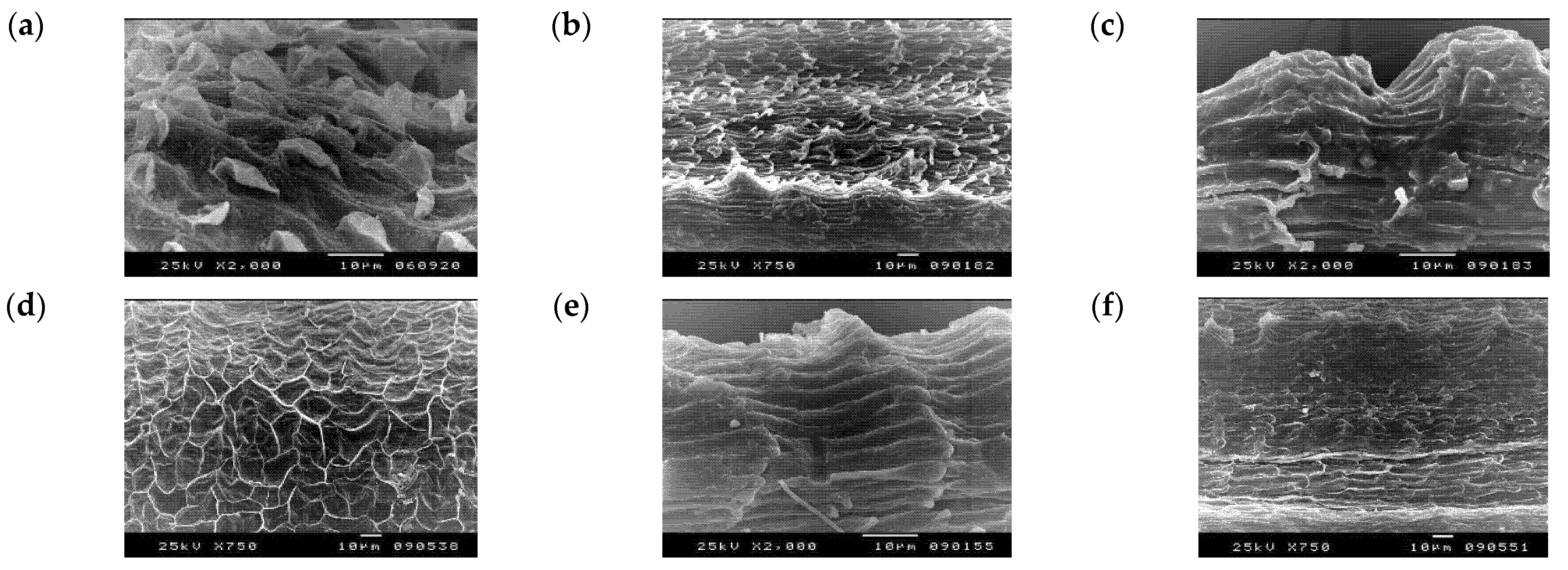
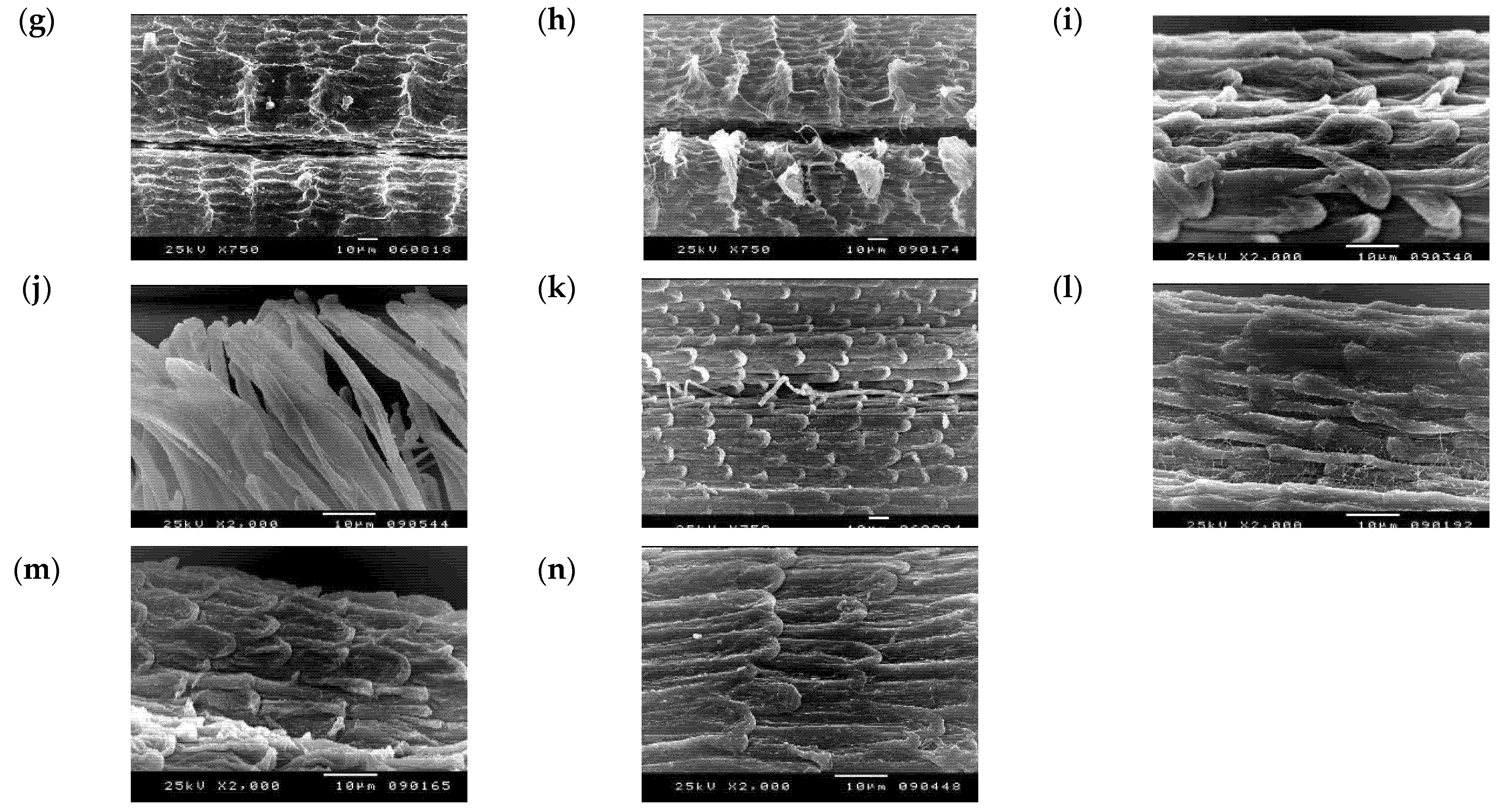
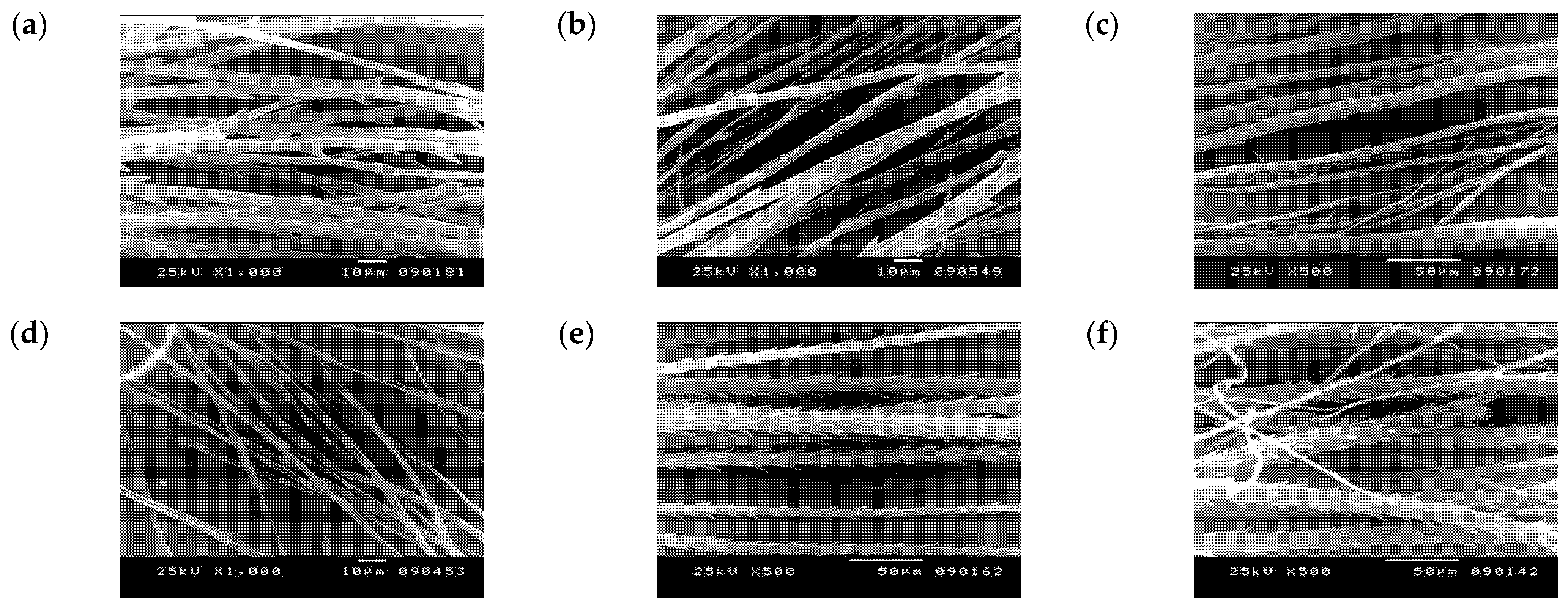
2.3. Micromorphological Characters (SEM) and Numerical Analysis
3. Results
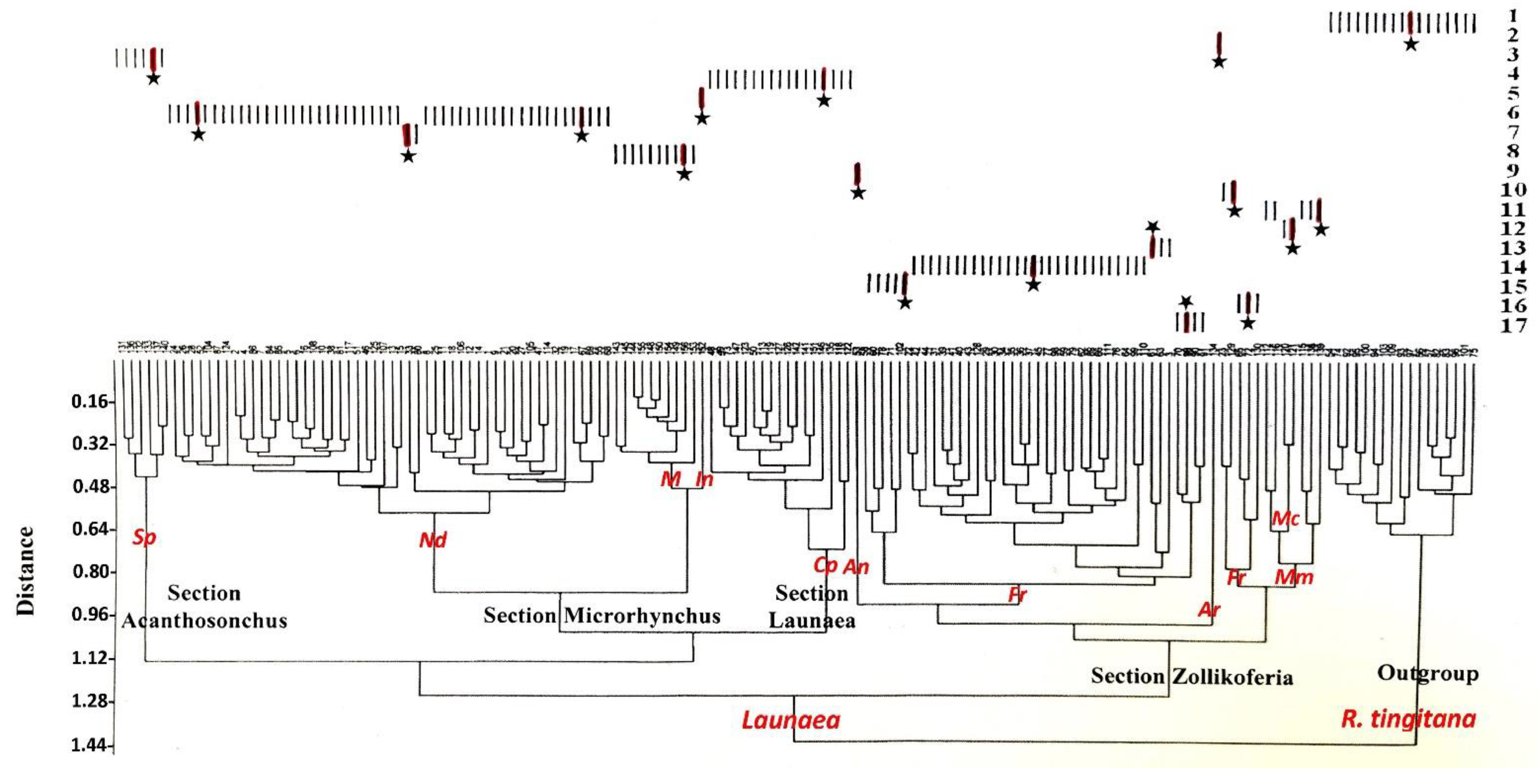
3.1. Numerical Analysis of Macromorphological Characters
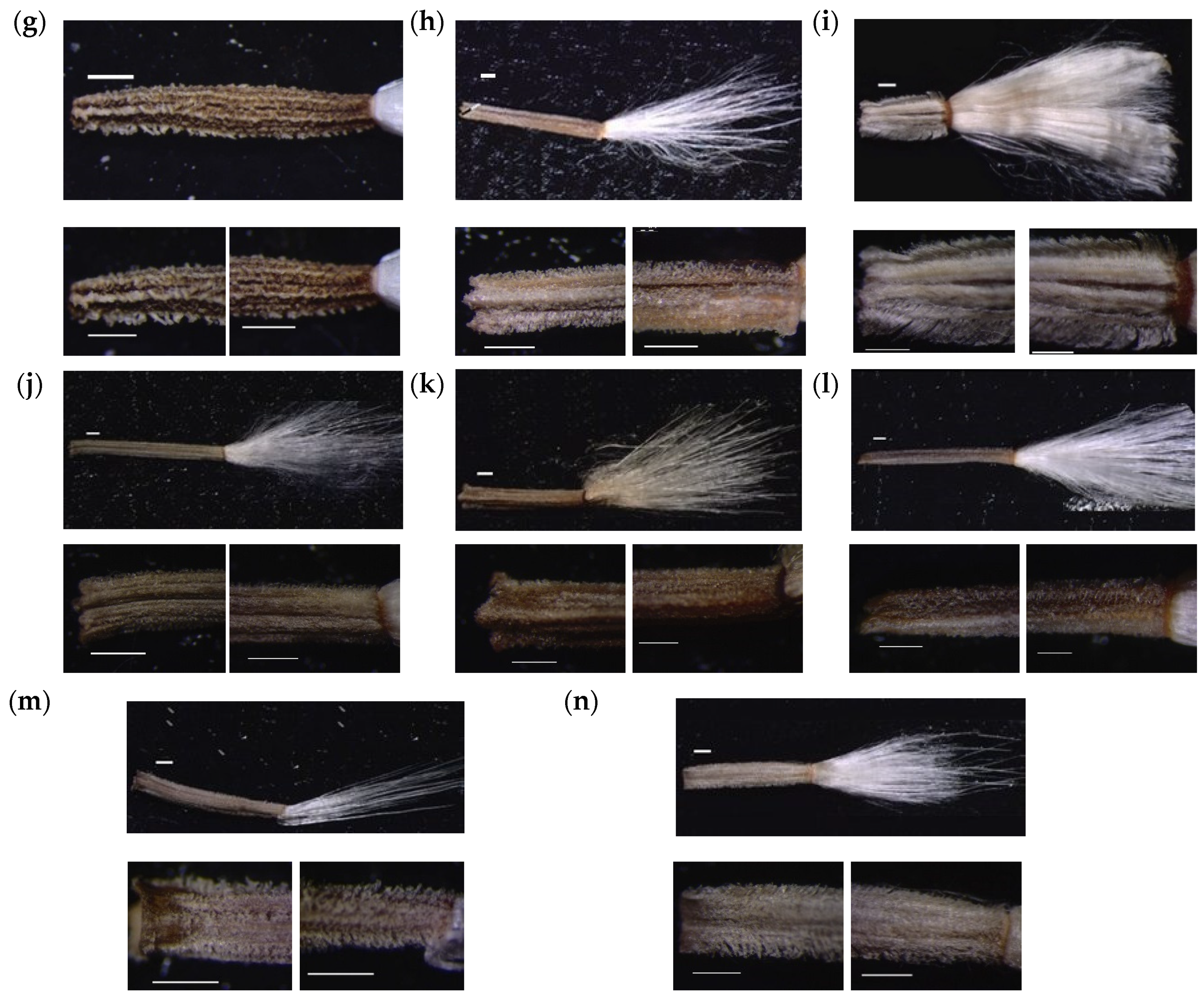
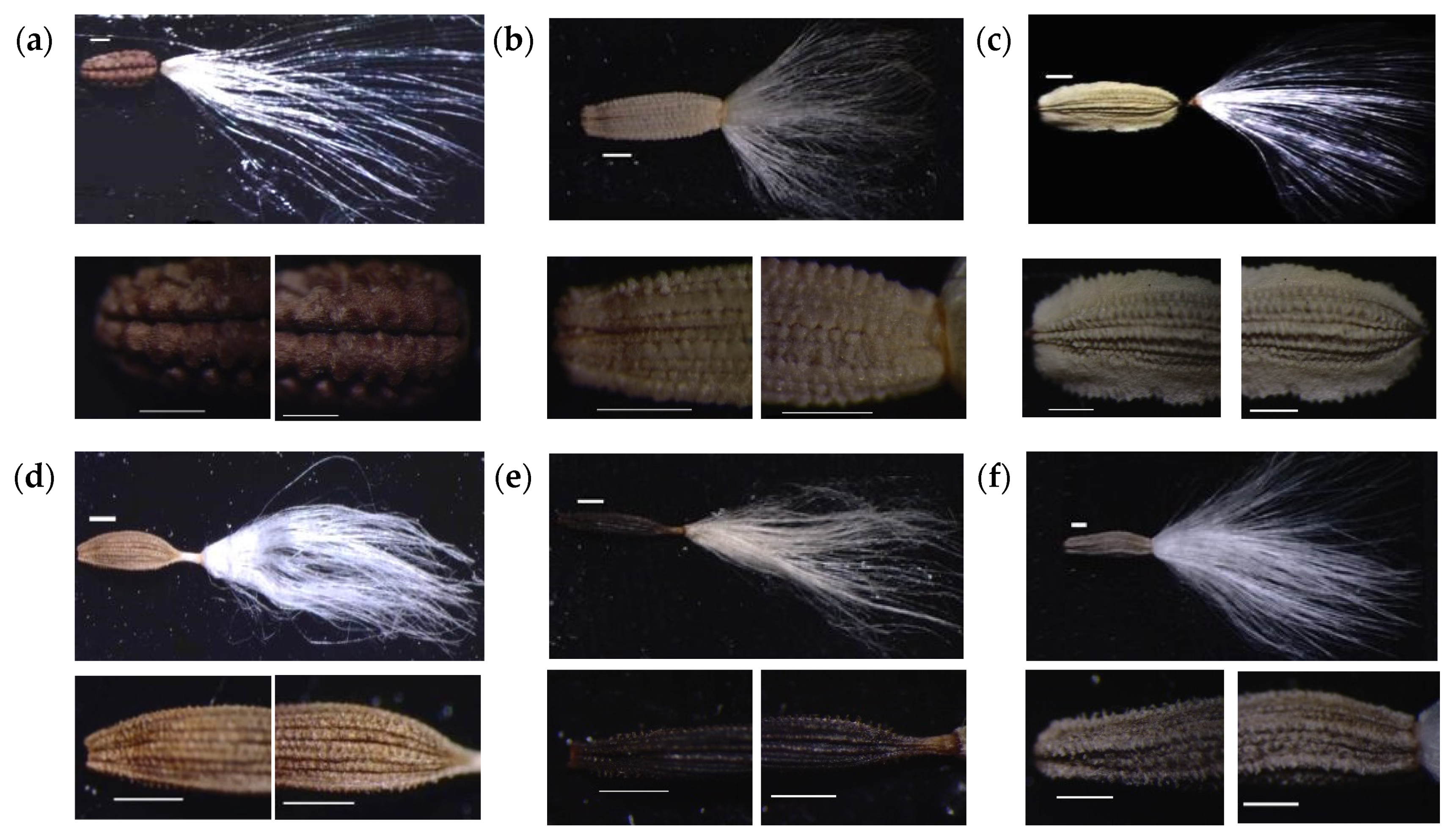
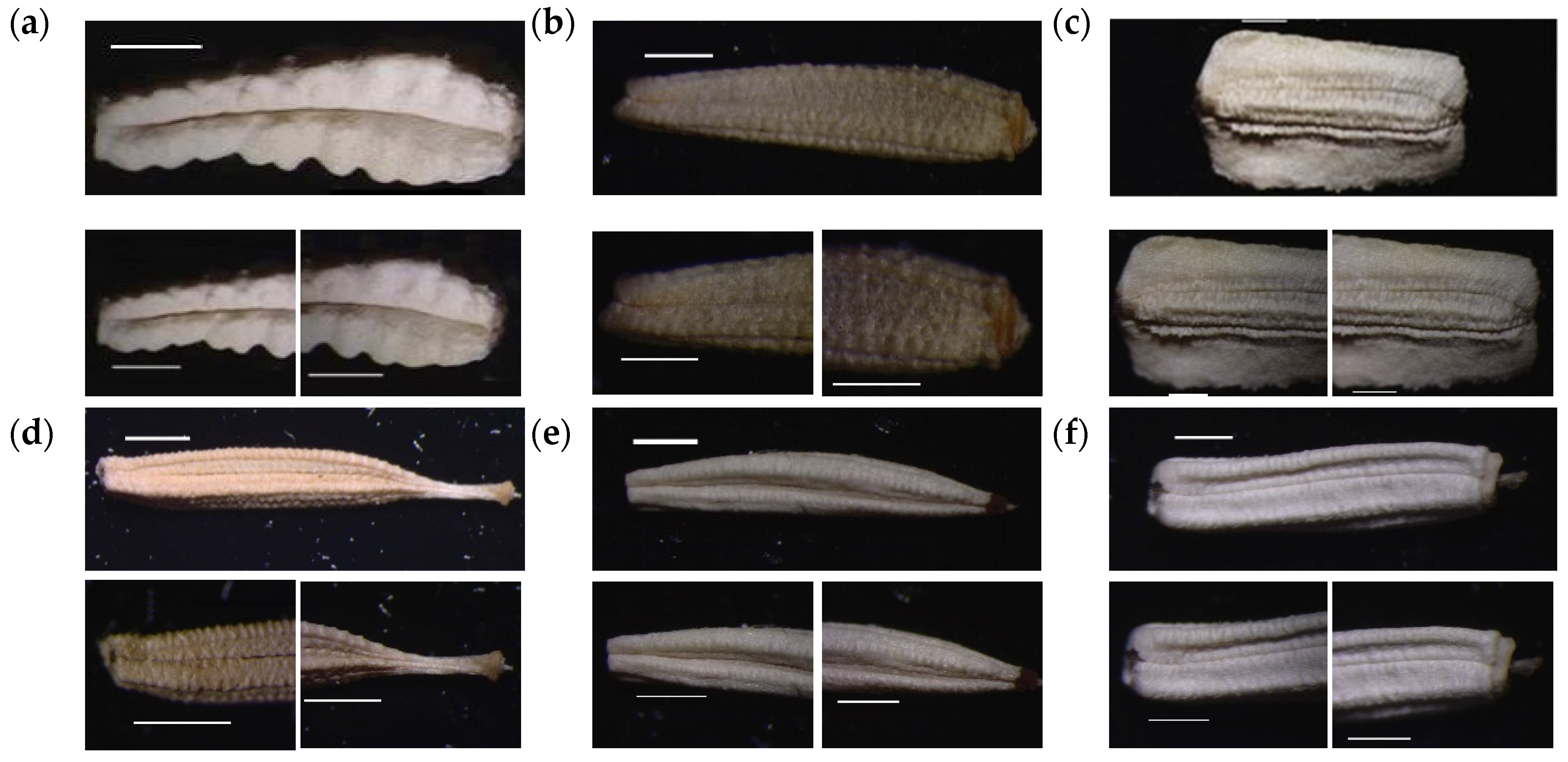
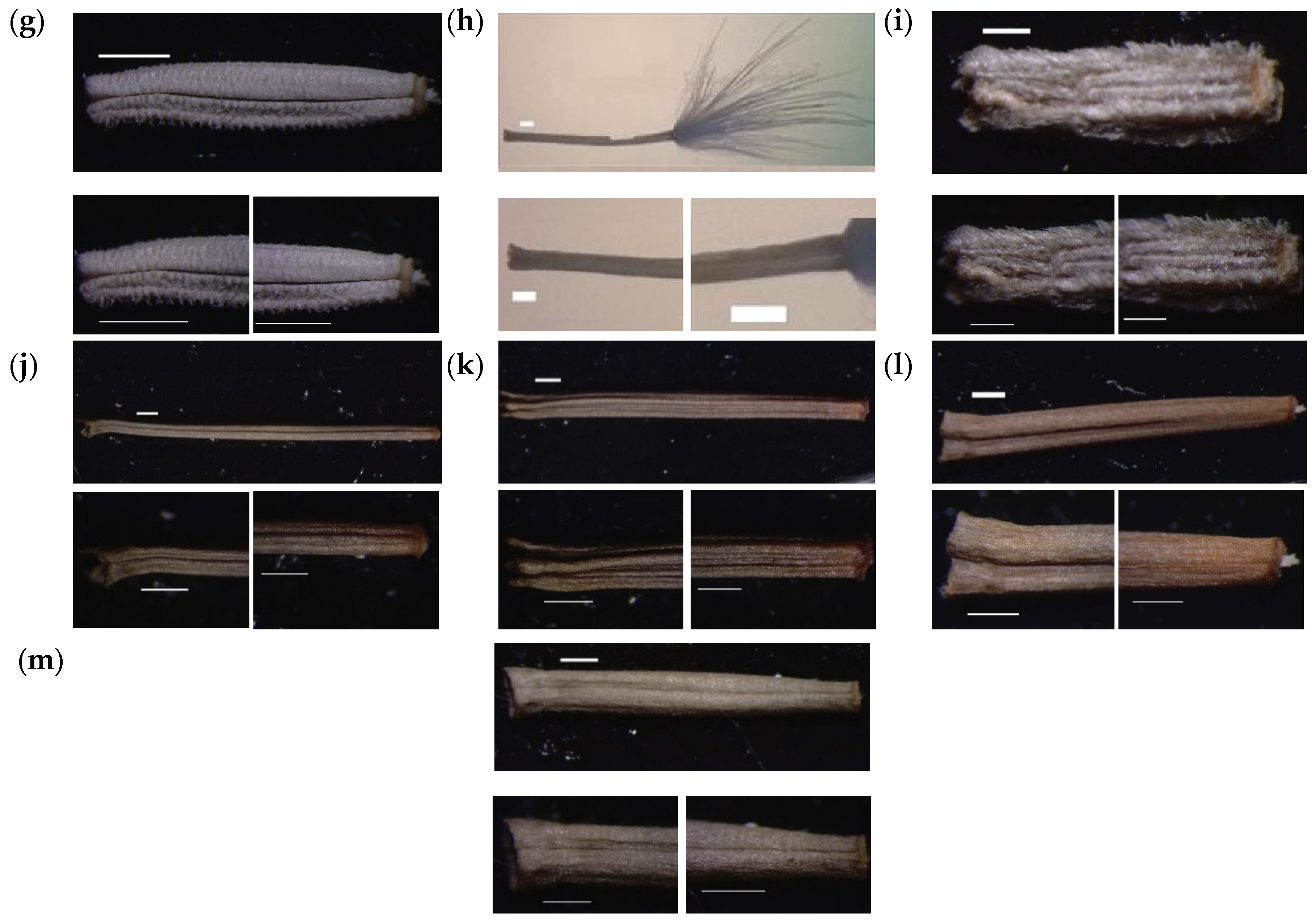
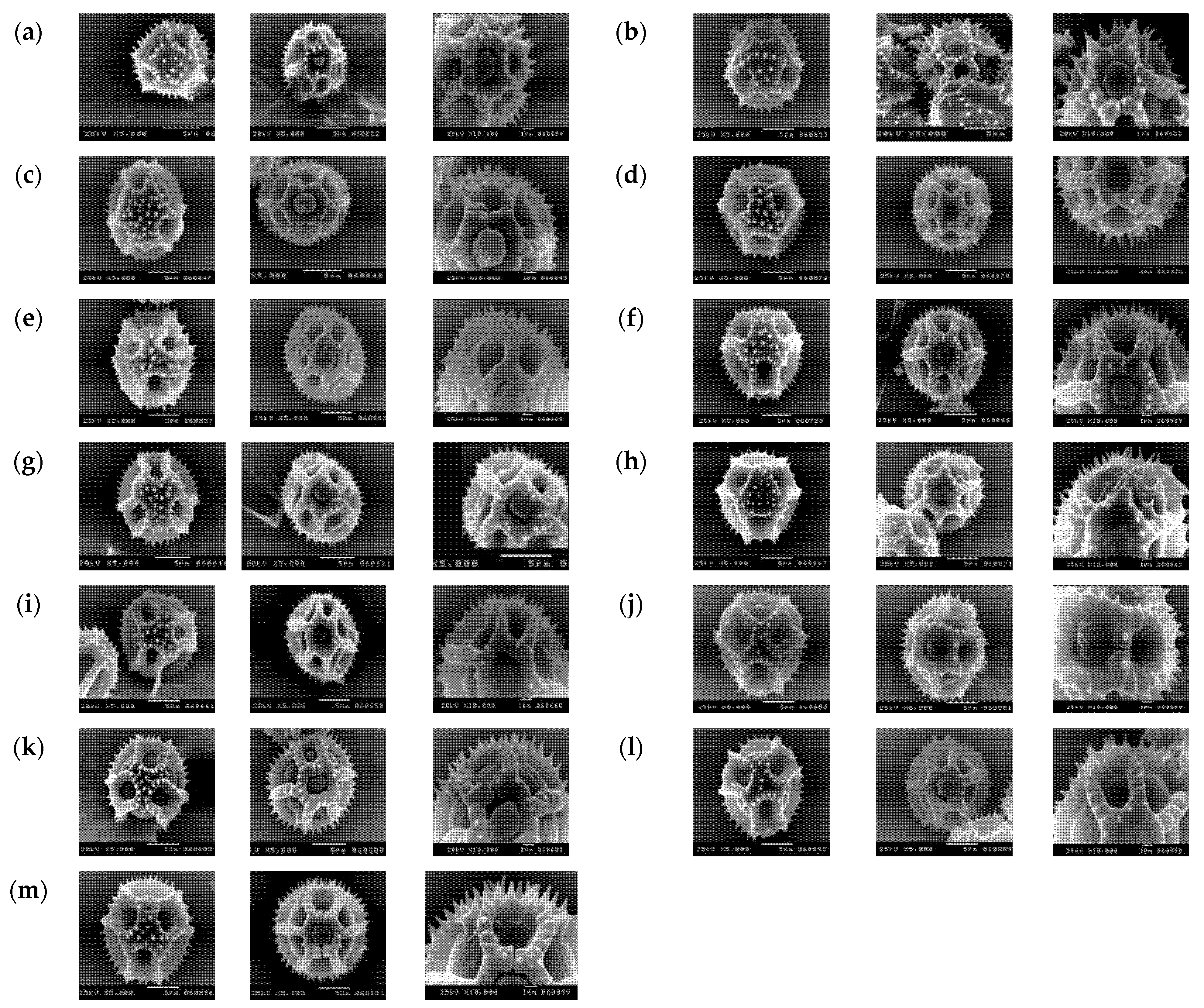
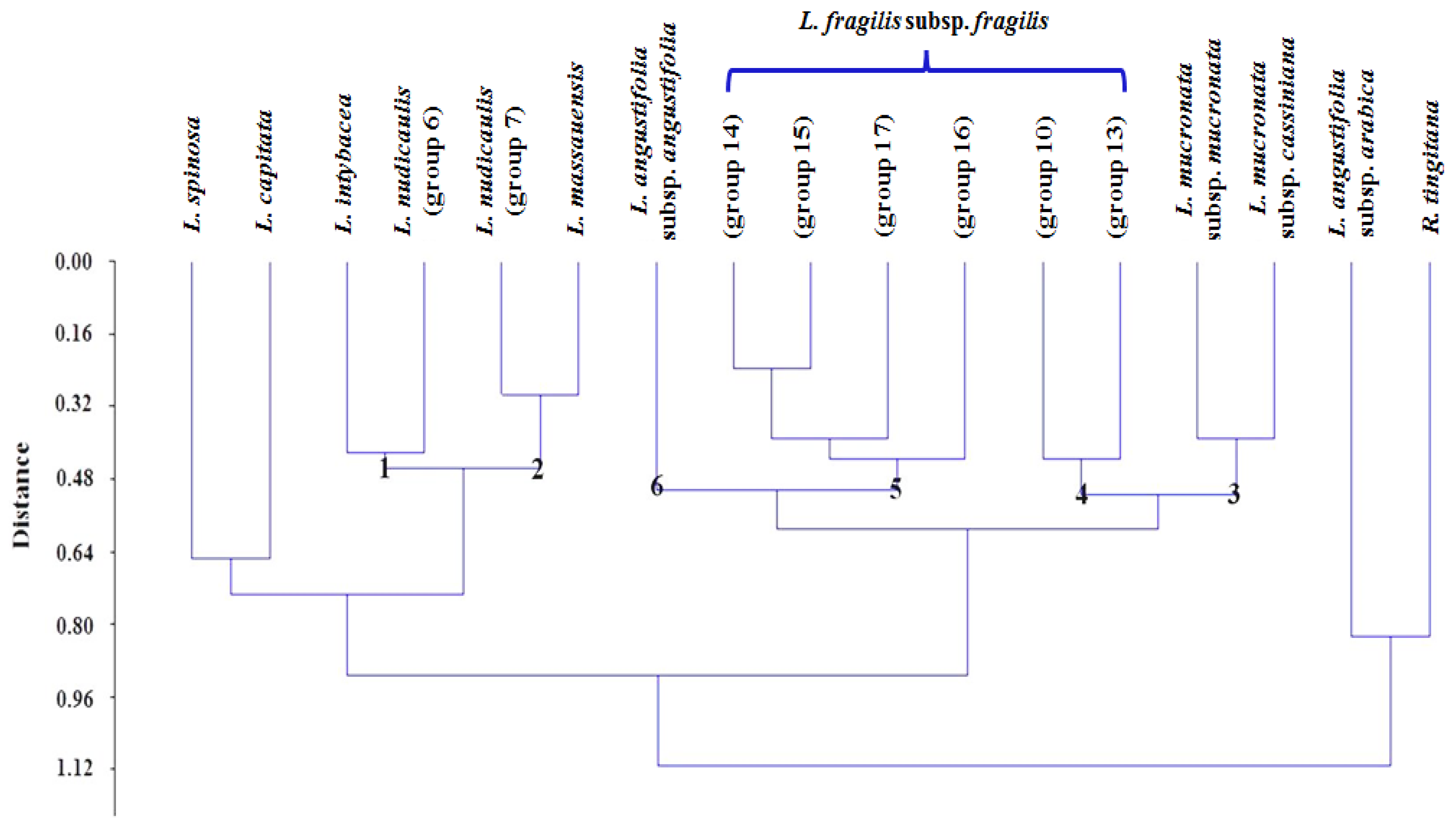
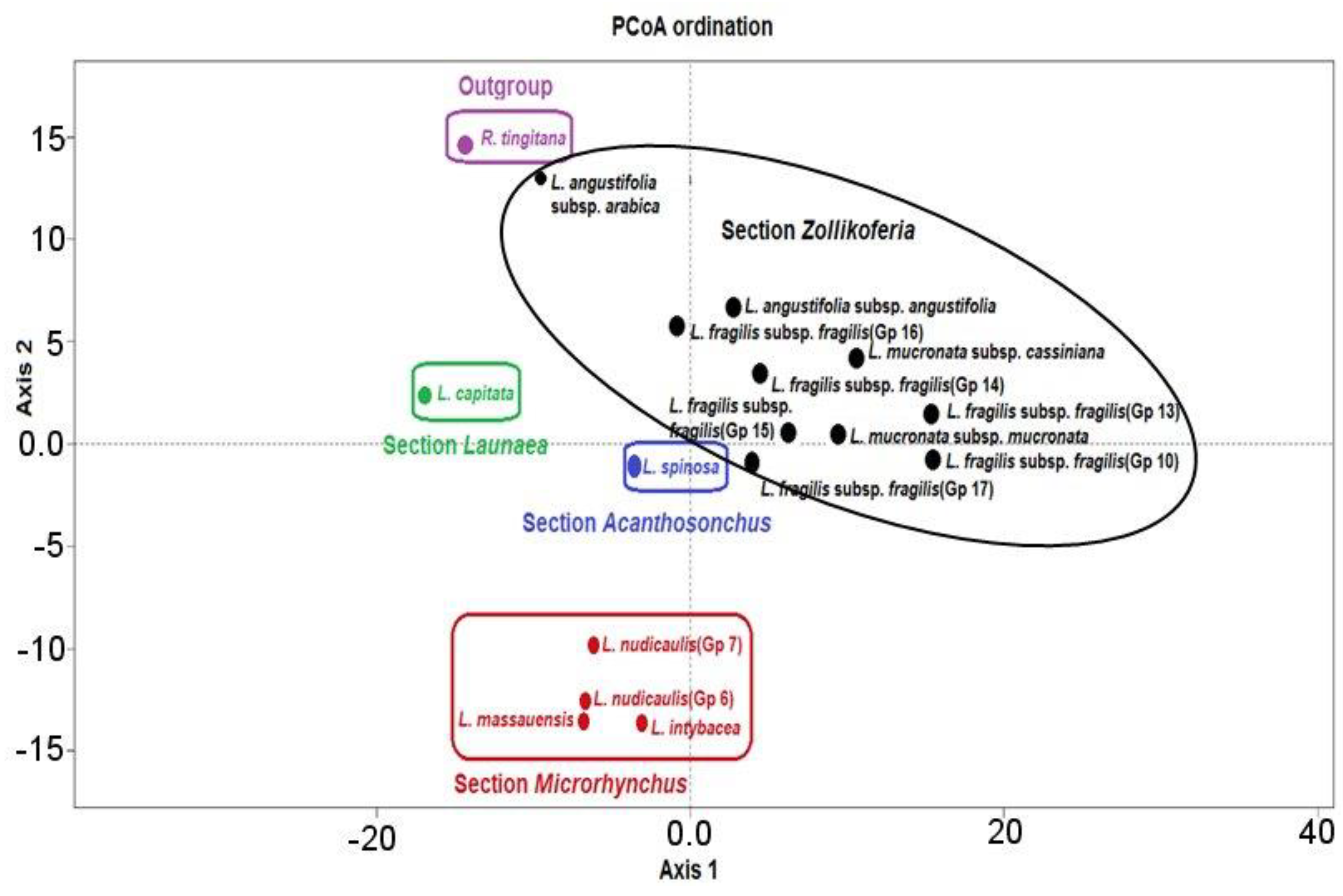
3.2. Numerical Analysis of Micromorphological Characters (SEM)
4. Discussion
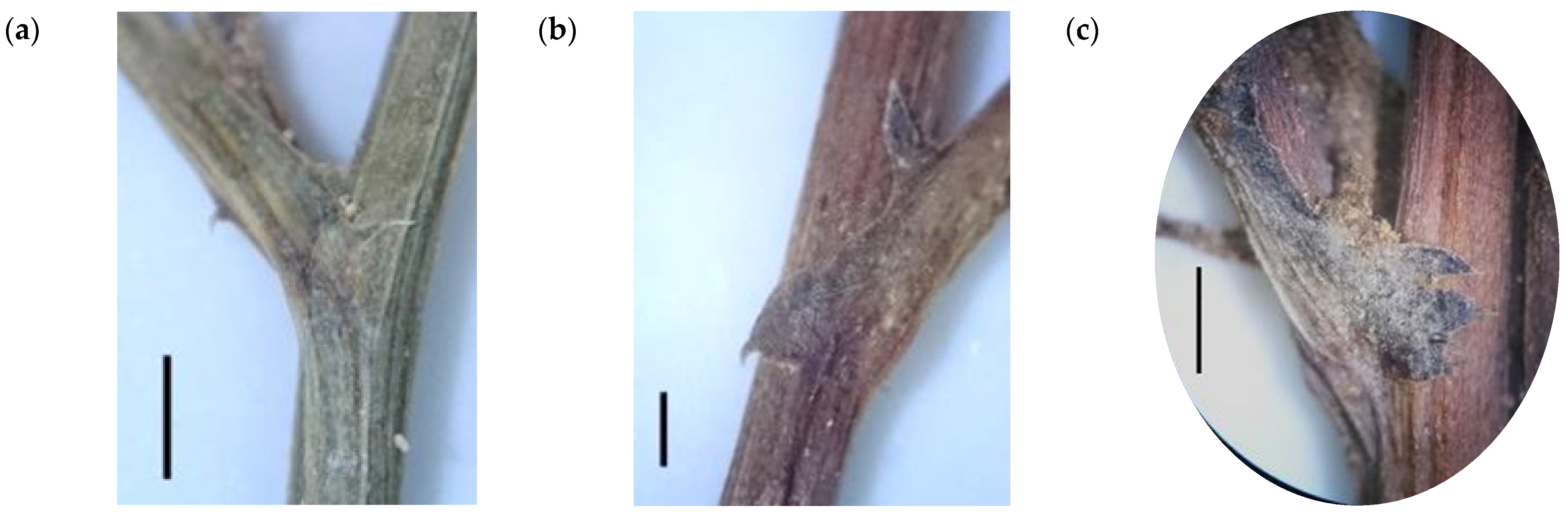
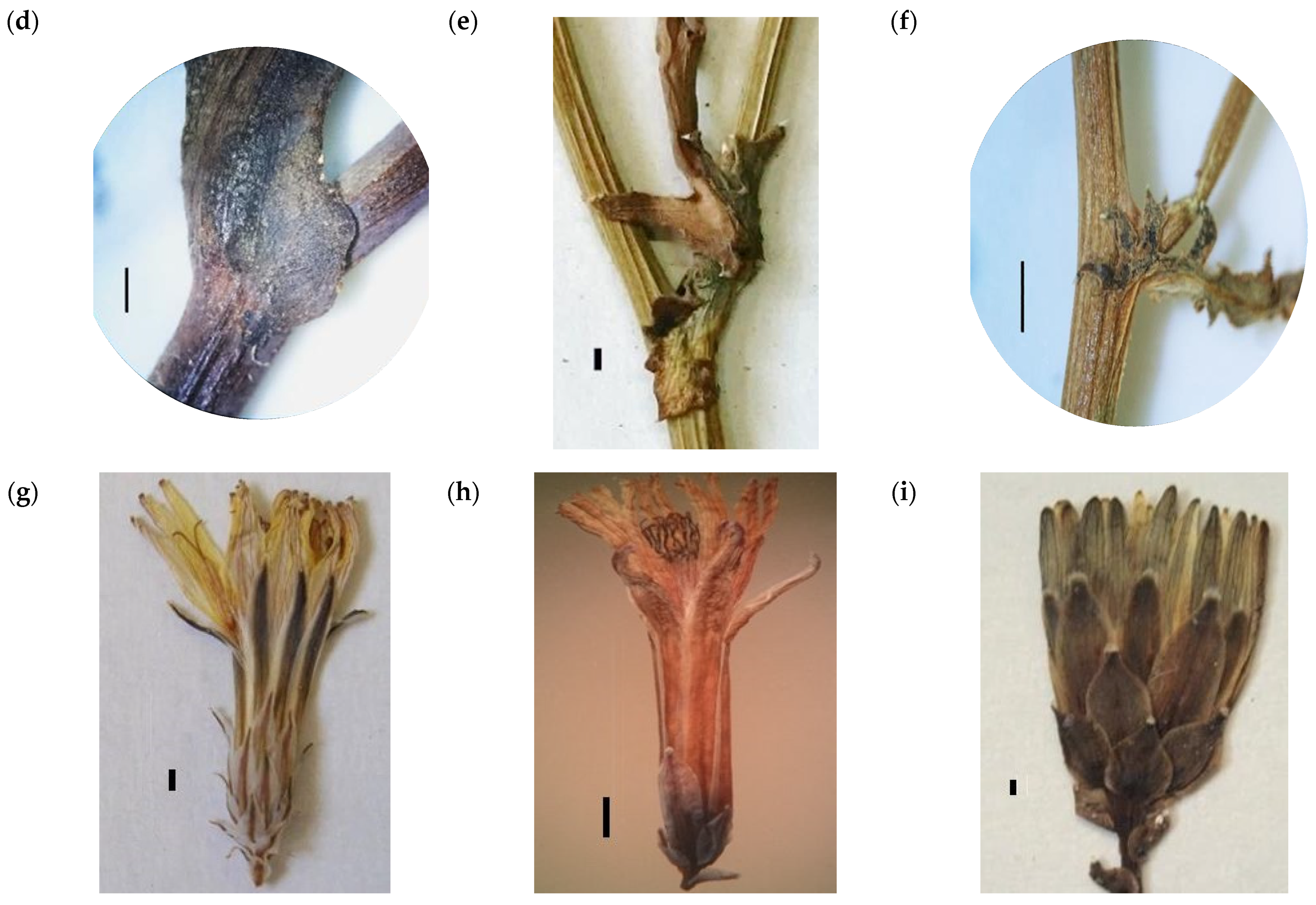
4.1. Section Acanthosonchus
4.2. Section Launaea
4.3. Section Microrhynchus
4.4. Section Zollikoferia
- 1.
- Spinescent branches; early deciduous cauline and rosette leaves, leaf lobes 4; achenes subhomomorphic, inner achene with 5 main ribs……………………………………………………………………………………………. L. spinosa
- 1.
- Spineless branches; persistent rosette leaves, leaf lobes more than 5; achenes heteromorphic, inner achene with 4 main ribs………………………………………………………………………………………….…………………………… 2
- 2.
- Leaf fragile; marginal achene apex rostrate and beaked……………………………….………………………………… 3
- 2.
- Leaf normal; marginal achene apex truncate and not beaked…………………………….……………………………… 4
- 3.
- Leaf lobe shape ovate; capitulescence divaricate; capitulum width less than 2 mm; inner achene shape columnar and creamy white with apex cuspidate…………………………………………………………………… L. massauensis
- 3.
- Leaf lobe shape oblong; capitulescence virgate; capitulum width more than 2.5 mm; inner achene shape cylindrical and straw with apex rostrate……………………………………………………………………………… L. intybacea
- 4.
- Capitulescence glomerate; ligule whitish-yellow; winged achenes, pappus deciduous………………… L. capitata
- 4.
- Capitulescence diffused, divaricate, or divaricate with cluster; ligule yellow; unwinged achenes, pappus persistent……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 5
- 5.
- Cauline leaves non-auriculated, rosette leaves runcinate; involucre scales not gradual in length, capitulum shape ellipsoid or lanceoloid; marginal achene shape subcuneate or subfusiform with wrinkled surface, inner achene creamy white………………………………………………………………………………………………… L. nudicaulis
- 5.
- Cauline leaves auriculated, rosette leaves spathulate; involucre scales gradual in length; capitulum shape obovoid; marginal achene cylindrical or columnar or obcolumnar with papillose surface, inner achene brown…………… 6
- 6.
- Rosette leaf lobed, leaf lobe shape ovate; peduncle length less than 1 cm; marginal achene length (2.37–2.5 mm), inner achene length (2.56–2.73 mm), marginal and inner achenes papillose with long and linear connate papillae (hyaline papillae), pappus homomorphic of cottony rays…………………………………………………… L. arabica
- 6.
- Rosette leaf partite or dissected, leaf lobe shape oblong to linear; peduncle length more than 1.5 cm; marginal achene length (3.20–7.73 mm), inner achene length (3.47–8.40 mm), marginal achenes only papillose with short and clavate or long and linear unconnate papillae, pappus dimorphic or subhomomorphic of setaceous bristles……………… 7
- 7.
- Ligule shape linear; marginal achenes with long and linear unconnate papillae; polar area to pollen area ratio >40%, spinules number on polar area from 16 to 20…………………………………………………… L. angustifolia
- 7.
- Ligule shape oblong to linear-lanceolate; marginal achenes with short and clavate papillae; polar area to pollen area ratio <40%, spinules or spines number on polar area from 3 to 14………………………………………………… 8
- 8.
- Auricle margin entire or dentate; inner achene with conspicuous secondary ribs and 4-horned (toothed) base………………………………………………………………………………………………… L. fragilis subsp. fragilis
- 8.
- Auricle margin dissected; inner achene with conspicuous or inconspicuous secondary ribs and ventricose truncate base…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 9
- 9.
- Ligule yellow with green abaxial surface; marginal achene length (2.95–4.0 mm), marginal achene length to width from 5.1 to 7.0, inner achene length (3.40–4.60 mm), inner achene uncompressed with conspicuous secondary ribs, pappus dimorphic; spines number on polar area from 10 to 14…………………… L. mucronata subsp. mucronata
- 9.
- Ligule yellow; marginal achene length (4.10–4.65 mm), marginal achene length to width from 9.5 to 13, inner achene length (5.10–5.60 mm), inner achene compressed with inconspicuous secondary ribs, pappus subhomomorphic of setaceous bristles; spines number on polar area from 3 to 5…………… L. mucronata subsp. cassiniana
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mandel, J.R.; Barker, M.S.; Bayer, R.J.; Dikow, R.B.; Gao, T.G.; Jones, K.E.; Keeley, S.; Kilian, N.; Ma, H.; Siniscalchi, C.M.; et al. The Compositae Tree of Life in the age of phylogenomics. J. Syst. Evol. 2017, 55, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susanna, A.; Baldwin, B.G.; Bayer, R.J.; Bonifacino, J.M.; Garcia-Jacas, N.; Keeley, S.C.; Mandel, J.R.; Ortiz, S.; Robinson, H.; Stuessy, T.F. The classification of the Compositae: A tribute to Vicki Ann Funk (1947–2019). Taxon 2020, 69, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chase, M.W.; Christenhusz, M.J.M.; Fay, M.F.; Byng, J.W.; Judd, W.S.; Soltis, D.E.; Mabberley, D.J.; Sennikov, A.N.; Soltis, P.S.; Stevens, P.F.; et al. An update of the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group classification for the orders and families of flowering plants: APG IV. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2016, 181, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Täckholm, V. Students’ Flora of Egypt, 2nd ed.; Cooperative Printing Company: Cairo, Egypt, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Boulos, L. Flora of Egypt; Al-Hadara Publishing: Cairo, Egypt, 2002; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, A.A. A taxonomic revision of the genus Launaea (Compositae.) I. General considerations. Taeckholmia 1978, 9, 111–117. [Google Scholar]
- Kilian, N. Revision of Launaea Cass. (Compositae, Lactuceae, Sonchinae). Englera 1997, 17, 1–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mahrezi, J.A.; Al-Sabahi, J.N.; Akhtar, M.S.; Selim, D.; Weli, A.M. Essential oil composition and antimicrobial screening of Launaea Nudicaulis grown in Oman. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2011, 2, 3166–3169. [Google Scholar]
- Khidr, Z.A.; Ebad, F.A.; El-Khawaga, H.A. Osmoregulation and antimicrobial activity of two egyptian true xerophytes; Launaea spinosa (Forssk.) and Leptadenia. Egypt. J. Desert Res. 2017, 67, 327–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.; Saadullah, M.; Yaseen, H.S.; Saleem, M.Y.; Ousaf, H.M.; Khan, I.U.; Yaseen, M.; Shams, M.U. Evaluation of in vivo anti-inflammatory and anti-angiogenic attributes of methanolic extract of Launaea spinosa. Inflammopharmacology 2020, 1, 993–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emad, F.; Khalafalah, A.K.; El Sayed, M.A.; Mohamed, A.E.H.; Stadler, M.; Helaly, S.E. Three new polyacetylene glycosides (PAGs) from the aerial part of Launaea capitata (Asteraceae) with anti-biofilm activity against Staphylococcus aureus. Fitoterapia 2020, 143, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulos, L. Flora of Egypt. Checklist; All-Hadara Publishing: Cairo, Egypt, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Thiers, B. Index Herbariorum: A Global Directory of Public Herbaria and Associated Staff. Available online: http://sweetgum.nybg.org/science/ih/ (accessed on 8 January 2021).
- Kilian, N.; Gemeinholzer, B.; Lack, H.W. Cichorieae. In Systematics, Evolution, and Biogeography of Compositae; Funk, V., Susanna, A., Stuessy, T., Bayer, R., Eds.; International Association for Plant Taxonomy: Vienna, Austria, 2009; pp. 343–383. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vogel, E. Manual of Herbarium Taxonomy; UNESCO: Jakarta, Indonesia, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, M.G. Plant Systematics; Elsevier Academic Press: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Roque, N.; Keil, D.J.; Susanna, A. Illustrated glossary of Compositae. In Systematics, Evolution, and Biogeography of Compositae; Funk, V., Susanna, A., Stuessy, T., Bayer, R., Eds.; International Association for Plant Taxonomy: Vienna, Austria, 2001; pp. 781–806. [Google Scholar]
- Hammer, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D.; Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.T. Past: Paleontological Statistics Software Package for Education and Data Analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Barthlott, W. Epidermal and seed surface characters of plants: Systematic applicability and some evolutionary aspects. Nord. J. Bot. 1981, 1, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Boufford, D.E.; Sun, H. Systematic significance of achene morphology in Soroseris, Syncalathium and Parasyncalathium (Asteraceae: Cichorieae). Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2013, 173, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hussein, H.A.; Eldemerdash, M.M. Comparative Morphology and Surface Microsculpture of Cypsela in Some Taxa of the Asteraceae and Their Taxonomic Significance. Egypt J. Bot. 2017, 56, 409–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Punt, W.; Hoen, P.P.; Blackmore, S.; Nilsson, S.; Le Thomas, A. Glossary of pollen and spore terminology. Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 2007, 143, 1–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, E.B.; Cavalcanti, P.P.; Nogueira, D.A. ExpDes: An R Package for ANOVA and Experimental Designs. Appl. Math. 2014, 5, 2952–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjer, K.M.; Simon, C.; Yavorskaya, M.; Beutel, R.G. Progress, pitfalls and parallel universes: A history of insect phylogenetics. J. R. Soc. Interface 2016, 13, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zareh, M.M.; Faried, A.M.; Mohamed, M. Revision of Launaea Cass. (Compositae) in Egypt with special references to cypselar diversity. Feddes Repert. 2016, 127, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zareh, M.M. Synopsis of the Family Asteraceae in Egypt. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2005, 7, 832–844. [Google Scholar]
- Osman, A.K.E. Pollen types of the Egyptian species of tribe Lactuceae (subfamily Cichorioideae-Compositae). Acta Bot. Croat 2006, 65, 161–180. [Google Scholar]
- Soliman, M.I.; Samaan, L.S.; Ghoniem, G.T.; El-Saied, F.M. Genetic diversity of some Launaea Cass. species in Egypt. Mansoura J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 43, 79–96. [Google Scholar]
- Montasir, A.H.; Hassib, M. Illustrated Manual Flora of Egypt; Part 1; Imprimeri Misr, S.A.E.: Cairo, Egypt, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Boissier, E. Flora Orientalis Sive Enumeratio Plantarum in Oriente a Graecia et Aegypto ad Indiae Fines Hucusque Observatarum; Apud H. Georg.: Genevae, Switzerland, 1875; Volume III. [Google Scholar]
- Alavi, S.A. Asteraceae. In Flora of Libya; Jafri, S.M.H., El-Gadi, A., Eds.; Al-Faateh University: Trípoli, Libya, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi, S.J.; Awan, A.G.; Khan, M.; Bano, S. Taxonomic study of the Genus Launaea L. from Pakistan. J. Biol. Sci. 2002, 2, 315–319. [Google Scholar]
- Abou El-Naga, A.Z. Taxonomic and Palynological Studies of Some Species of Compositae in Egypt; Unpublished; El-Mansoura University: Cairo, Egypt, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, A.A. Taxonomic Studies in the Genus Launaea; Unpublished; Cairo University: Cairo, Egypt, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Zareh, M.M.; Faried, A.M.; Mohamed, M. Achene wall anatomy and surface sculpturing of Launaea Cass. (Compositae: Cichorieae) with notes on their systematic significance. Korean J. Plant Taxon. 2016, 46, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muschler, K.; Muschler, R.C. A Manual Flora of Egypt; R. Friedlaender & sohn: Berlin, Germany, 1912; Volume II. [Google Scholar]
- Maire, R. Contributions a l’etude de la flore de l’Afrique du Nord. Bull. Société d’Histoire Nat. L’Afrique Nord 1937, 28, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Quezel, P.; Santa, S. Nouvelle flore de l’Algérie et des régions désertiques méridionales; Éditions du Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique: Paris, France, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, A.A. Cytological studies on some Egyptian plants. United Arab Repub. J. Bot. 1973, 16, 501–506. [Google Scholar]
- Boissier, E.; Reuter, G.F. Pugillus Plantarum Novarum Africae Borealis Hispaniaeque Australis; Ramboz: Genevae, Switzerland, 1852. [Google Scholar]
- Bonnet, E.; Barratte, G. Catalogue Raisonné des Plantes Vasculaires de la Tunisie; Imprimerie Nationale: Paris, France, 1896. [Google Scholar]
- González, G.L. Launaea fragilis (Asso) Pau, nombre correcto para L. resedifolia Auct. Plur. Non (L.) Kuntze. An. Jardín Botánico Madr. 1979, 36, 135–138. [Google Scholar]
- Feinbrun-Dothan, N. Flora Palaestina, Part 3: Text, Ericaceae to Labiatae; Palestine Academy of Sciences and Humanities: Palestine, Jerusalem, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Kilian, N.; Oberprieler, C.; Vogt, R. Chromosome numbers of North African phanerogams. V. some counts in Launaea (Compositae, Lactuceae). Willdenowia 1995, 25, 273–281. [Google Scholar]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marzouk, R.I.; El-Darier, S.M.; Kamal, S.A.; Nour, I.H. Comparative Taxonomic Study of Launaea Cass. (Asteraceae, Cichorioideae) in Egypt. Taxonomy 2021, 1, 192-209. https://doi.org/10.3390/taxonomy1030014
Marzouk RI, El-Darier SM, Kamal SA, Nour IH. Comparative Taxonomic Study of Launaea Cass. (Asteraceae, Cichorioideae) in Egypt. Taxonomy. 2021; 1(3):192-209. https://doi.org/10.3390/taxonomy1030014
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarzouk, Ream I., Salama M. El-Darier, Sania A. Kamal, and Iman H. Nour. 2021. "Comparative Taxonomic Study of Launaea Cass. (Asteraceae, Cichorioideae) in Egypt" Taxonomy 1, no. 3: 192-209. https://doi.org/10.3390/taxonomy1030014
APA StyleMarzouk, R. I., El-Darier, S. M., Kamal, S. A., & Nour, I. H. (2021). Comparative Taxonomic Study of Launaea Cass. (Asteraceae, Cichorioideae) in Egypt. Taxonomy, 1(3), 192-209. https://doi.org/10.3390/taxonomy1030014






