Abstract
As a vital transition metal species, cobalt ions (Co2+) play a critical role in industrial and medical fields. However, uncontrolled release into ecosystems via industrial effluents presents significant environmental risks. To address this, a prism-coupled surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensor chip was developed which enables simultaneous high sensitivity, wide detection range, and rapid detection of Co2+ under ultra-low detection limit conditions. By depositing a 50 nm Au film and AuNPs on a glass substrate, and integrating carboxyl-functionalized carbon quantum dots (CQDs), the chip achieved the detection range of 10−20 mol/L to 10−4 mol/L, and the response time was reduced from 21 min to 11 min under optimal electric field conditions (1.2 V, 0.15 mol/L electrolyte concentration). The sensor exhibits high selectivity, repeatability, and stability. It can be integrated with optofluidic technology to enable high-throughput microfluidic analysis, thereby facilitating further advancements in related research.
1. Introduction
Cobalt ions (Co2+), essential transition metal cations [1], serve critical functions in industrial and medical fields [2]. However, their release into ecosystems via industrial effluents poses significant environmental hazards. Presently, conventional analytical techniques are predominantly utilized for Co2+ detection, such as atomic absorption spectrometry (AAS) [3], inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) [4], colorimetry [5], and electrochemical analysis [6]. Although these techniques offer high accuracy, their reliance on costly instrumentation, complex sample preparation, and specialized operation limits their suitability for rapid detection on site, which hinders the widespread adoption of Co2+ detection in real-world applications. Thus, it is critically important to develop sensors which is highly sensitive and have the ability of rapid detection of Co2+ for environmental monitoring.
Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensors have emerged as a robust analytical platform for heavy metal ions detection and biomedical monitoring [7], primarily due to its unique combination of label-free operation, superior sensitivity, and real-time monitoring. According to their structure, SPR sensors are primarily categorized as fiber-optic.
SPR sensors, grating-coupled SPR sensors, and prism-coupled SPR sensors, each exhibiting unique advantages and inherent limitations. Emanuela Jin-Ho Park et al. [8] developed a simple, receptor-free, and regenerable Hg2+ detection system. However, this sensor faces challenges in implementing multi-channel detection and fails to meet the detection requirements for high-volume sample analysis. Xin Kang et al. [9] fabricated a graphene oxide/polydopamine-functionalized micro-tapered long-period fiber grating for label-free detection of heavy metal ions. While offering high sensitivity, compact dimensions, and simple optical integration, this sensor demonstrates reduced sensitivity at ultra-low ion concentrations and involves a complex fabrication procedure. Compared with other sensors, prism-coupled SPR sensors are widely employed due to their structural stability, excellent signal reproducibility, easy integrability and operational simplicity [10].
Owing to their limited sensitivity for low-concentration analysis, conventional prism-coupled SPR sensors face significant limitations in practical applications [11]. Typical sensitive materials for SPR sensors encompass noble metal nanoparticles [12,13], magnetic nanoparticles [14], and carbon nanomaterials [15]. Noble metal nanoparticles are extensively utilized owing to their exceptional optical properties, biocompatibility, chemical stability, and tunable characteristics [16]. The most common noble metal nanoparticles include Au, Ag, and Pt nanoparticles [17]. Among these, gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) dominate applications due to their unparalleled biocompatibility and exceptional chemical stability [18,19]. Moreover, conventional prism-coupled SPR sensors depend on passive ion diffusion, resulting in prolonged response times. To overcome this limitation, Saad et al. [20] reported developing a flow-through bioelectrochemical reactor for Co2+ removal, demonstrating that an applied planar electric field significantly enhances reaction efficiency, reduces reaction time, and offers advantages such as simplicity, high efficiency, and strong controllability. However, this approach lacks real-time detection capability and requires complex bioanode maintenance under stringent control conditions. These limitations severely restrict its utility for rapid detection applications. Fluorescent nanoparticles, particularly carbon dots, are commonly employed as probes in Co2+ sensors [21] due to their excellent water solubility [22], optimal size [23], low cost [24], biocompatibility [25], and tunable surface properties [26]. Carboxyl-functionalized CQDs offer high-density binding sites. For instance, Wanqiu Chen et al. [27] developed an NAC-CdTe quantum dot fluorescent probe for Co2+ detection, which exhibits excellent biocompatibility and selectivity but requires stringent pH and temperature control during operation. Depeng Kong et al. [28] used carbon dots as a sensitive and selective probe for the detection of Co2+, and Xinyi Zhao et al. [29] synthesized B,N-doped CQDs as a general-purpose fluorescent probe for the sensitive detection of Co2+ in environmental water and biological samples. Although both methods are facile to synthesize, their high detection limits remain inadequate for trace-level Co2+ detection and require further optimization. In our previous work [30], we developed a highly sensitive fiber-optic surface plasmon resonance sensor for label-free cobalt ion detection. However, this sensor exhibits a long response time of 20 min, poor integrability, and challenges in multi-channel implementation, thus limiting its suitability for high-throughput sample analysis.
Building on the above, this study reports the development of an electric field-enhanced prism-coupled SPR sensing chip, which enables simultaneous high sensitivity, wide detection range, and rapid detection of Co2+ under ultra-low detection limit conditions. The design achieves a significant improvement in detection efficiency through synergistic integration of coated Au film, modified AuNPs, and functionalized CQDs, combined with an applied planar electric field to facilitate directional migration of Co2+ and the occurrence of chelation reactions. Experimental results demonstrate that the design reduces the response time from 21 min to 11 min compared with our previous work. and the sensor exhibits excellent specificity, repeatability, and selectivity. Furthermore, this method is simple to operate, easy to control, and readily integrated, enabling high-throughput micro-total analysis [31].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Instruments
Glass substrates (size: 18 mm × 18 mm × 0.2 mm) were purchased from Wuqiang Laboratory Equipment Co., Ltd. (Guangzhou, China). Gold targets (99.99%) were purchased from Zhongnuo New Materials Technology Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China). Anhydrous ethanol (AR), Chloroauric acid (99.99%) and Sodium citrate (99.8%) were purchased from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). DL-lipoic acid (99%), triethylenetetramine (70%), dl-dithiothreitol (DTT, 99%), thioglycollic acid (98%), 1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide (EDC, 98%), N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS, MW 2000 Da) were purchased from Aladdin Reagent (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, 0.01 mol/L, pH = 7.4) were purchased from Beijing Dingguo Biotechnology (Beijing, China).
2.2. Preparation of Prismatic SPR Co2+ Sensing Chip
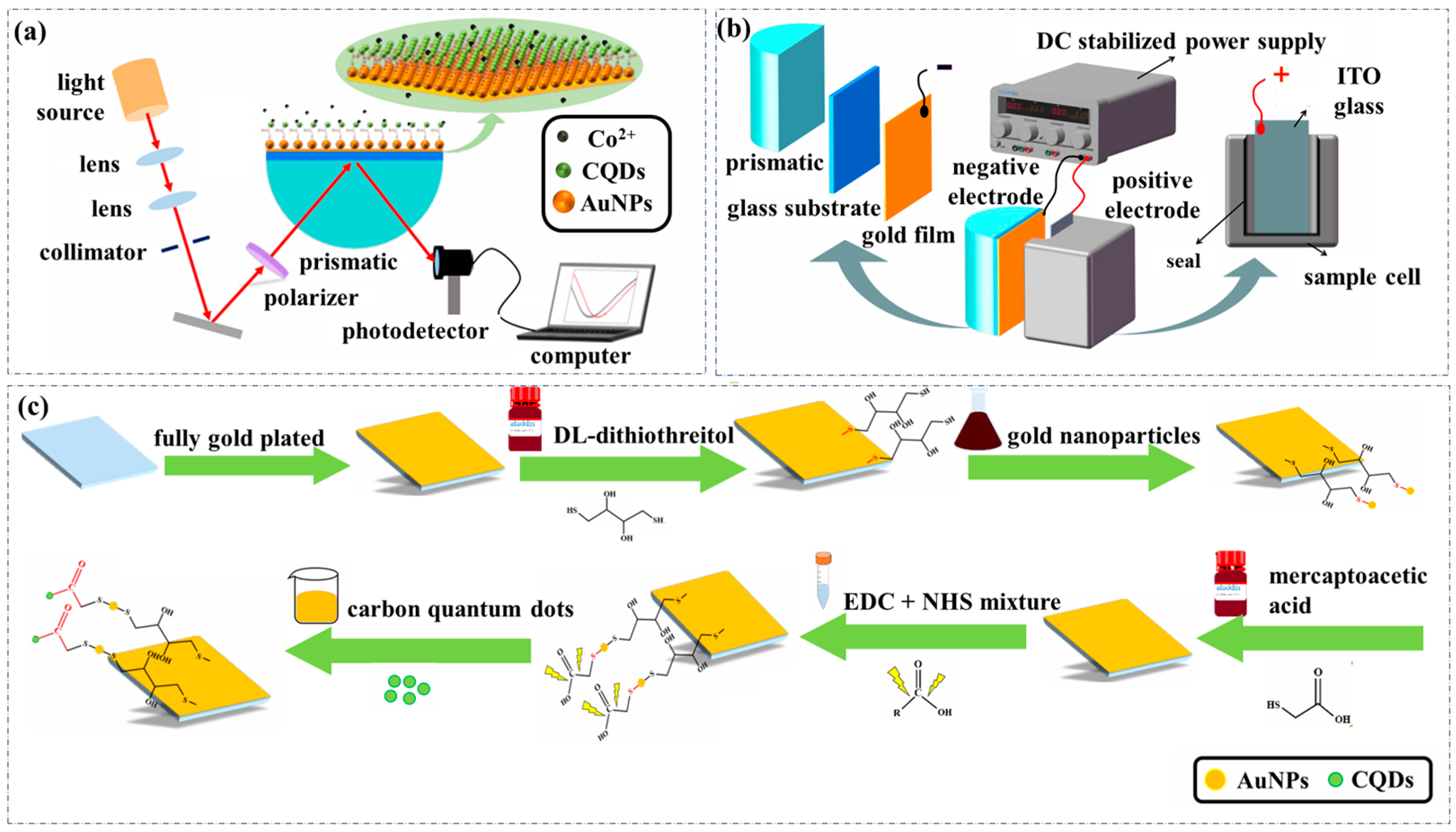
Figure 1a depicts a prismatic SPR Co2+ sensor coated Au film modified AuNPs and functionalized with carbon quantum dots (CQDs) employing angle modulation, which is based on a Kretschmann configuration [32]. Light emitted by the light source is collimated by the collimator and polarized by the polarizer to generate P-polarized light. Subsequently, the P-polarized light is incident into the center of the semi-cylindrical prism at a specific angle. The glass substrates were coated with Au film, and AuNPs were introduced as a synergistic sensitizing material for SPR via gold-sulfur bonding. Carboxyl-functionalized CQDs were introduced as sensing probes through an amide reaction. These steps finalized the preparation of the sensing chip through biofunctionalization of the glass substrate. The sensing chip coated with Au film is fixed on the surface of the semi-cylindrical prism using cedar oil, then total internal reflection is observed at the prism-metal film interface, leading to the generation of an evanescent wave. As the evanescent wave propagates through the metal film, it excites surface plasmon polaritons at the metal-sample interface, and subsequently, induces resonance with the surface plasma wave. The energy of the incident light is transferred to the plasma wave. Consequently, a substantial reduction in the intensity of the reflected light is observed, and an obvious absorption peak is presented in the transmission spectrum of the prism SPR sensing chip at the resonance angle. As a result, the sensing chip is highly sensitive to the changes in the effective refractive index (RI) of the surrounding medium. Co2+ is bound by CQDs with the chelating coordination reaction on the surface of the glass substrate coated Au film, resulting in the change in effective RI, which induces a shift in the resonance angle. Subsequently, the P-polarized light is emitted from the other side of the semi-cylindrical prism and enters the photodetector. The transmission spectrum was recorded and the Co2+ concentration was determined by measuring the change in the resonance angle.
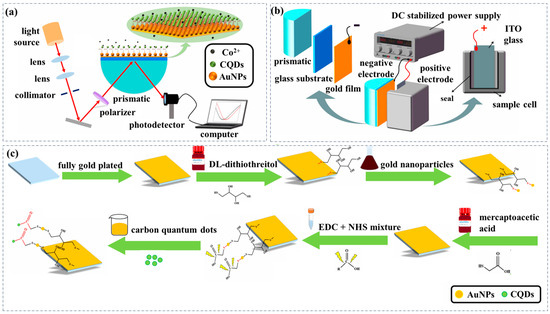
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic diagram of the prismatic SPR Co2+ sensing chip modified AuNPs and functionalized CQDs. (b) Schematic diagram of the device with an applied planar electric field of prismatic SPR sensing chip. (c) Preparation of prismatic SPR Co2+ sensing chip modified AuNPs and functionalized CQDs.
In the experiment, glass substrates (size: 18 mm × 18 mm, thickness: 0.2 mm) were prepared and then coated with a 50 nm-thick Au film. After washing with DI (Distilled) water and anhydrous ethanol several times, the glass substrates coated with Au film were fully immersed in a 0.5 mol/L DTT solution in the Petri dish, which was then sealed and incubated undisturbed for 1.5 h. After that, the glass substrate coated with Au film was completely submerged in the AuNPs solution with a similar process for 3 h. The glass substrates which were coated with Au film and modified with AuNPs were then incubated in 0.05 mol/L MAA solution for 9 h under light protection to complete the carboxyl modification and were activated in EDC/NHS mixed solution for 2 h. Finally, the prismatic SPR Co2+ sensing chip which was modified with AuNPs and functionalized with CQDs synergistic enhancement was obtained by immersing in CQDs solution for 3 h and the unbound reagents at each stage were removed by repeated DI water and anhydrous ethanol washing. AuNPs with a diameter of about 20 nm and CQDs were prepared with the same processes detailed in our previous work [30].
2.3. An Applied Planar Electric Field on Prismatic SPR Sensor Chip
To shorten the response time and enhance the detection performance of the prismatic SPR sensing chip, a planar electric field with an applied bias voltage was introduced to regulate the interaction between the substance to be measured and the probe in the sensing chip. Figure 1b illustrates the schematic diagram of the prismatic SPR sensing chip device with an applied planar electric field, which consists of two parts. On one side of the device, the glass substrate coated with Au film which is modified with AuNPs functionalized with CQDs is fixed to the surface of the semi-cylindrical prism using cedar oil and serves as the negative electrode. On the other side of the device, the Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) coated conducting glass was fixed in the inner side of the sample cell and served as the positive electrode. After that, a planar electric field is successfully applied to both ends of the sample to be measured using the DC stabilized power supply, which can adjust the strength of the field.
At the same distance, different voltages generate distinct electric fields, each exerting varying influences on the deflection of Co2+. To verify the impact of the electric field on Co2+, a prismatic SPR sensor was constructed, and a planar electric field simulation model was incorporated. The initial position of particle release was set to be uniformly distributed, and the initial velocity of particle release was set to 1000 μm/s. In the experiment, a 10−16 mol/L Co2+ standard solution, prepared from a 0.1 mol/L electrolyte solution (NaCl, PBS), was injected into the sample cell for detection. The voltage was then adjusted to 0 V, 0.4 V, 0.8 V, 1.2 V, 1.6 V, and 2.0 V in sequence, and the SPR angles under different voltages were recorded and averaged over three measurements. To investigate the effect of electrolyte concentration on the prismatic SPR sensing chip, the electrolyte solutions with different concentrations (0 mol/L, 0.05 mol/L, 0.1 mol/L, 0.15 mol/L, 0.2 mol/L, and 0.25 mol/L) and 10−16 mol/L Co2+ standard solutions were prepared, respectively. The voltage of the applied planar electric field was adjusted to 1.2 V. The Co2+ standard solution was then injected into the sample cell for detection and the SPR angle under different electrolyte concentrations was recorded and averaged over three measurements.
2.4. Characterization
The AuNPs on the glass substrate were characterized using scanning electron microscopy (SEM, Zeiss G300, Carl Zeiss AG, Oberkochen, Baden-Wurttemberg, Germany). X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS, Thermo Scientific K-Alpha, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) was employed to investigate the chemical composition of the CQDs and the binding of Co2+ on the glass substrate coated with Au film which was modified with AuNPs and functionalized with CQDs. The doped elements in the synthesized CQDs were analyzed by the SERS spectral tests using a Laser Confocal Micro-Raman Spectrometer (LabRAM Odyssey, Horiba, Paris, France) calibrated with a 532 nm laser beam.
2.5. Performance of Prismatic SPR Co2+ Sensing Chip
Co2+ standard solutions with different concentrations (10−20 mol/L, 10−16 mol/L, 10−12 mol/L, 10−8 mol/L, and 10−4 mol/L, prepared in PBS) were prepared, injected into the sample cell according to the order of concentration from low to high and contacted with the sample in the sample cell. After 15 min of testing, the changes in the SPR angles were recorded. Specificity experiments were conducted under the same experimental detection conditions and typical metal ions (Na+, K+, Mg2+, Fe2+, Fe3+, Ca2+, Zn2+, Cu2+, Al3+, Cl−, HCO3−, SO42− and the mixed solutions) at a uniform concentration of 1 × 10−16 mol/L were used as interfering ions. To verify the reusability of the sensor, the prismatic SPR sensing chip was tested for repeatability using Co2+ solutions with concentrations of 10−20 mol/L, 10−16 mol/L, 10−12 mol/L, 10−8 mol/L, and 10−4 mol/L, respectively. Additionally, to evaluate the stability of the prismatic SPR sensing chip, the sensing chip was exposed to different concentrations of Co2+ solutions (10−4 mol/L, 10−8 mol/L, 10−12 mol/L, 10−16 mol/L, 10−20 mol/L, PBS) for 8 h under the same experimental testing conditions.
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Prismatic SPR Co2+ Sensing Chip
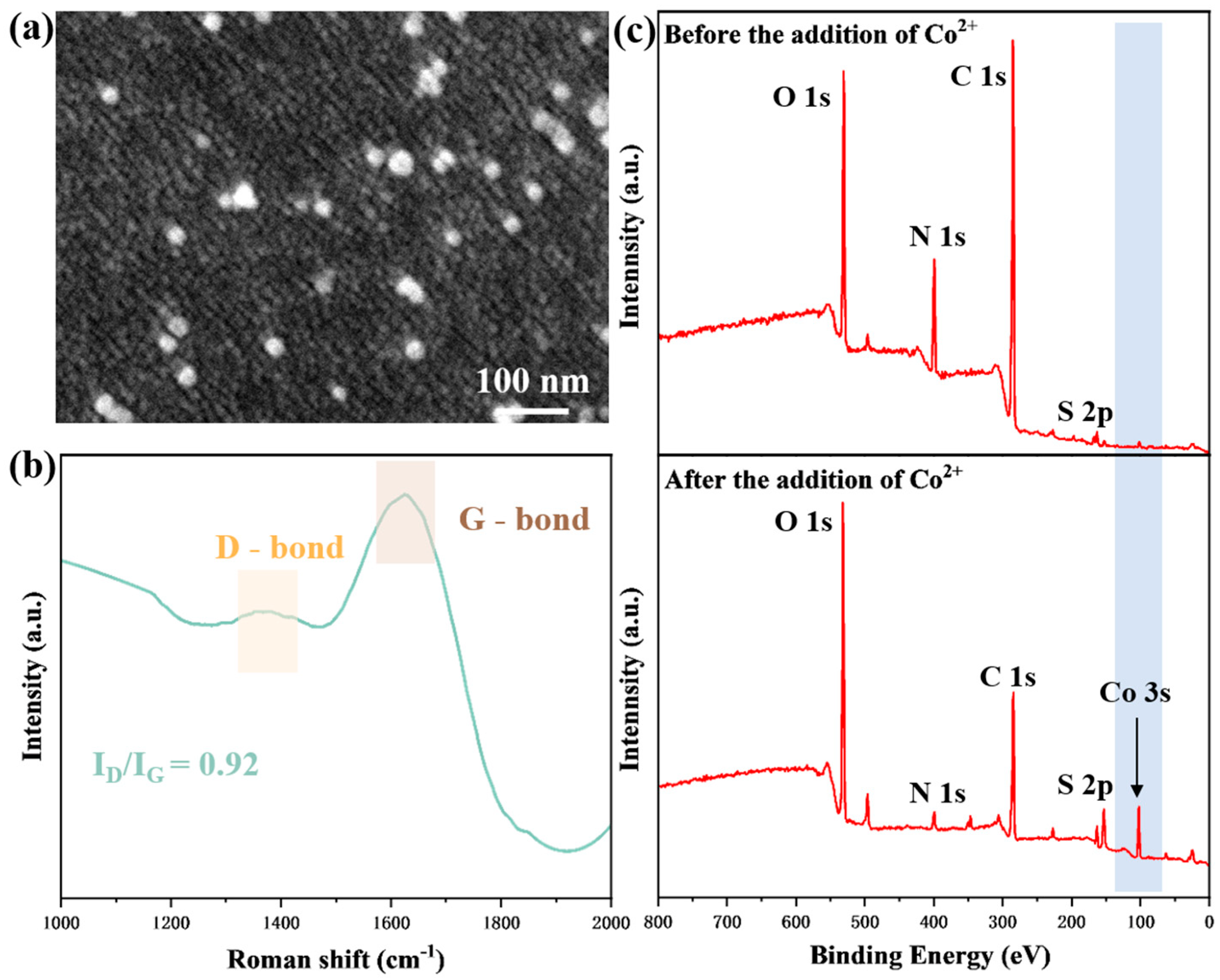
Figure 2a presents the SEM image of AuNPs, revealing a monolayer of uniformly dispersed spherical AuNPs on the glass substrate coated with Au film. This uniform distribution results from citrate ions adsorbed on the AuNPs surfaces during synthesis, inducing negative charges that promote dispersion via electrostatic repulsion. Figure 2b displays the Raman spectra of the CQDs, which exhibit two characteristic broad peaks at 1351.63 cm−1 (D-band) and 1632.28 cm−1 (G-band) [33], corresponding to disordered sp3 carbon and crystalline sp2 carbon vibrations, respectively [34,35]. The relative intensity ratio of the disordered D-band to the crystalline G-band (ID/IG) of the CQDs is approximately 0.92, indicating a graphite-like structure [36]. In our previous studies, transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images revealed that the CQDs exhibited uniform spherical distribution without agglomeration. High-resolution TEM (HRTEM) images further showed that the as-synthesized CQDs were highly crystalline, with a lattice spacing of approximately 0.27 nm and an average diameter of 7.61 ± 1.2 nm [30]. Figure 2c shows the XPS spectra of the CQDs and CQDs bonded with Co2+, which exhibit four peaks at 284.13, 398.54, 153.00, and 532.65 eV, corresponding to C 1s (46.35%), N 1s (14.28%), S 2p (6.41%), and O 1s (32.96%), respectively. The emergence of the N 1s and S 2p signals confirms the substantial doping of nitrogen and sulfur in the CQDs, which further validates the functionalization of CQDs by nitrogen-containing functional groups, and indicates the presence of a large number of amino and carboxyl groups on the surface of the CQDs. After the CQDs bonded to Co2+, the appearance of a new Co 3s peak at 103 eV indicates that Co2+ successfully underwent a chelating coordination reaction with the carboxyl-functionalized CQDs, enabling Co2+ capture.
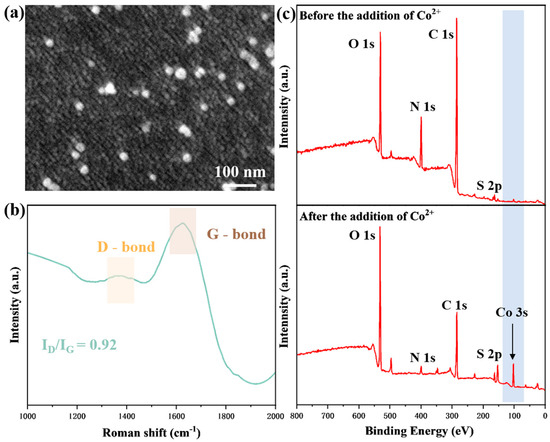
Figure 2.
Characterization of the functional CQDs and modified AuNPs on the gold substrate. (a) SEM characterization of the surface on the sensor; (b) Raman spectrum of CQDs; (c) XPS spectra of the surface of the sensor before and after the addition of Co2+.
3.2. Simulation of Prismatic SPR Sensing Chip with Planar Electric Field Applied
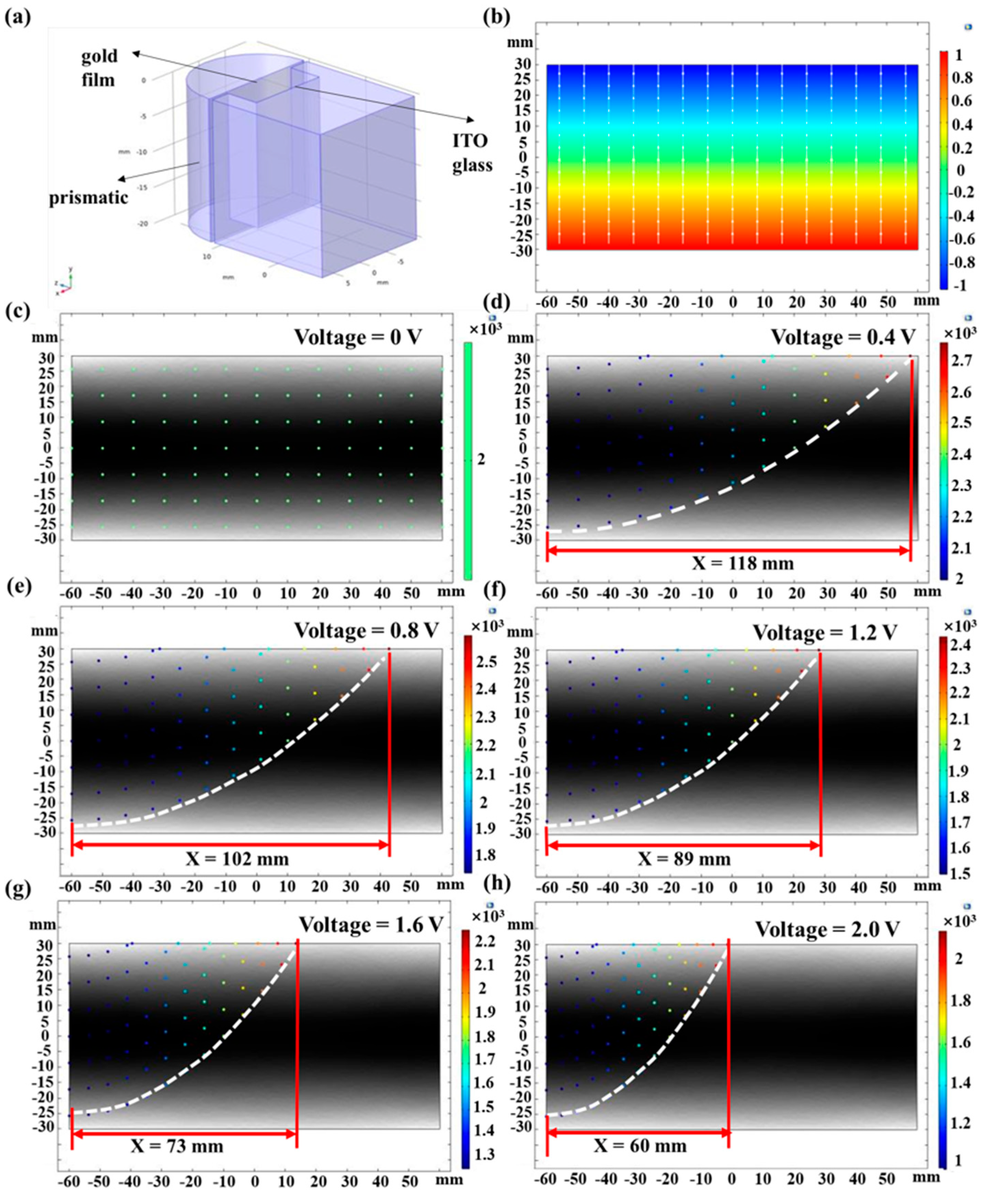
Figure 3a shows a schematic of the simulated and analyzed prismatic SPR sensor simulation model. In this sensor, the glass substrate coated with Au film which is modified with AuNPs and functionalized with CQDs, is adhered to the prism surface using cedar oil and connected to the negative electrode of the DC stabilized power supply. Meanwhile, the ITO glass embedded in the sample cell is connected to the positive electrode of the DC stabilized power supply. To simplify the theoretical model, the cross-section of the analyte was selected as the research object, and the analysis system was constructed based on this. Figure 3b shows the potential distribution of the applied planar electric field in this cross-section, which illustrates the Au film surface with a negative potential and the ITO glass surface with a positive potential from top to bottom. Figure 3c–h show the effects of different voltages covering 0 V, 0.4 V, 0.8 V, 1.2 V, 1.6 V and 2.0 V on the trajectories of the ions to be measured.
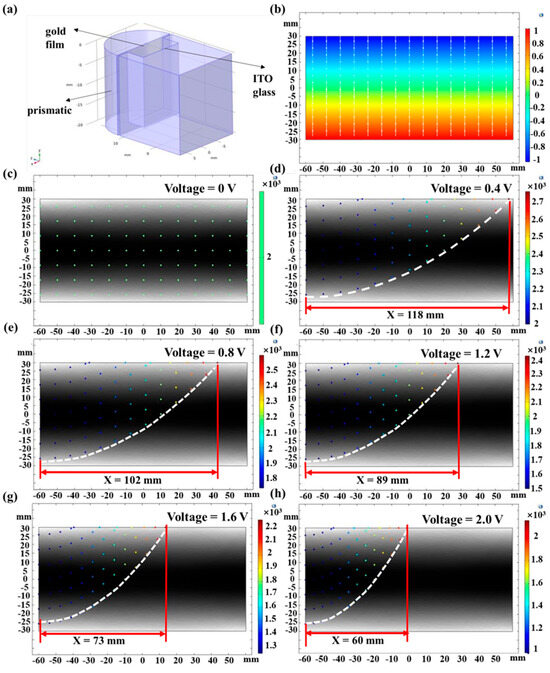
Figure 3.
(a) Schematic of the simulation model. (b) Potential distribution of the applied planar electric field. Effect of different voltages on the trajectories of ions to be measured. (c) 0 V; (d) 0.4 V; (e) 0.8 V; (f) 1.2 V; (g) 1.6 V; (h) 2.0 V.
As shown in Figure 3, when the voltage of the planar electric field is 0 V, the ions to be measured move in a straight line between the entrance and the exit at the initial release velocity and do not come into contact with the surface of the Au film above the cross-section. When the voltage of the planar electric field is 0.4 V, the ions to be measured are deflected and all make contact with the surface of the Au film, and the displacement along the direction of the Au film of the farthest contact point is 118 mm. With the increasing voltage, the displacement of the farthest point of contact of the ion to be measured from the upper cross-section decreases. At an applied voltage of 2 V, the displacement of the farthest point of contact reaches its minimum value of 60 mm. The initial particle release velocity is fixed, and the displacement of the contact point along the Au film direction indicates that the ion to be measured contacts the Au film surface in a shorter time. The response rate of the prismatic SPR sensing chip is increased by about 49% when a 2.0 V planar electric field is applied compared to a 0.4 V field.
3.3. Response Time and Resonance Angle of Prismatic SPR Chip Under Different Voltages
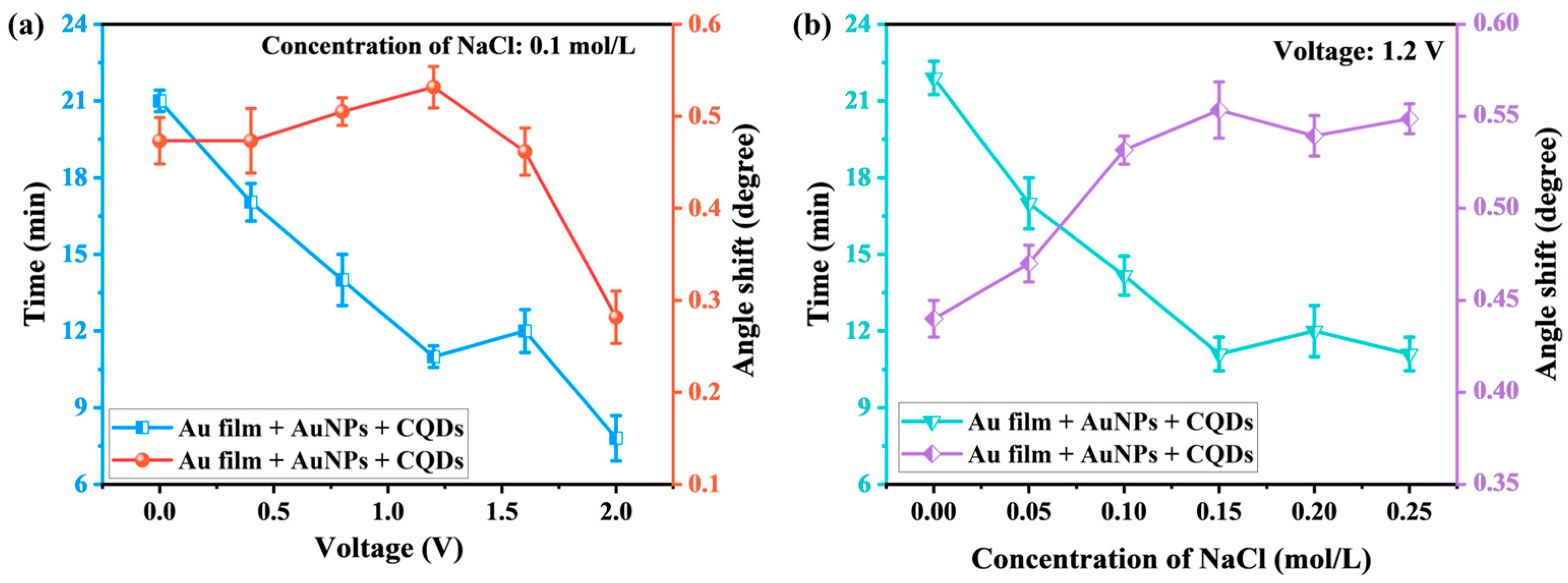
As shown in Figure 4a, the response time of the prismatic SPR sensing chip gradually decreased from 21 min to 11 min as the voltage was increased from 0 V to 1.2 V. This shortening of response time is primarily attributed to the accelerated directional migration of Co2+ induced by the planar electric field, which leads to the directional movement of Co2+ toward the surface of the sensing chip under the influence of the electric field force to chelate and connect with the CQDs probe to complete the detection. The resonance angle shift also was increased from 0.473° to 0.533°. When an electric field is exerted on a sensor within a Kretschmann configuration, the variation in the refractive index on the sensor’s surface adheres to the equation presented below. . E represents the electric field that is induced on the surface of the gold thin film. is the component of the electro-optic (EO) coefficient, and denotes the refractive index of the prism without an applied electric field. From this equation, it is evident that as the magnitude of the applied electric field increases, the change in the refractive index becomes more pronounced [37]. Therefore, the applied planar electric field enhanced the sensor’s detection signal and effectively improved its detection accuracy and sensitivity. Upon adjustment of the applied voltage to 1.6 V, the response time of the prismatic SPR sensing chip increased marginally to 12 min. This is because the solution under measuring initiates an electrolytic water reaction [38], generating a small amount of gas bubbles. These bubbles impede the movement of Co2+ toward the sensor. Upon adjustment of the voltage to 2.0 V, following 8 min, the resonance angle of the prismatic SPR sensor chip remained unchanged, and the shift in the resonance angle was merely 0.278°. This indicates that at a voltage of 2.0 V, water molecules begin to decompose into hydrogen and oxygen, forming bubbles. The higher the voltage, the faster the electrolysis speed and the more bubbles are generated, attaching to the electrode surface and reducing the effective contact area between the electrode and the electrolyte, resulting in a decrease in current [39]. Moreover, the chelation reaction between Co2+ and CQDs is hindered, thus greatly reducing the sensor′s detection sensitivity. Consequently, the sensor was incapable of accurately detecting Co2+ during this period. Thus, the optimal voltage for the applied planar electric field is determined to be 1.2 V.
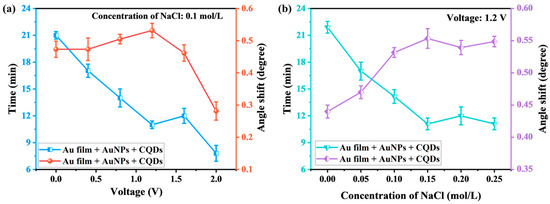
Figure 4.
Variation in response time and resonance angle of the prismatic SPR sensing chip. (a) Response time and angle variation at different voltages; (b) Response time and angle variation for different electrolyte concentrations.
3.4. Response Time and Resonance Angle of Prismatic SPR Chip Under Different Electrolyte Concentrations
Figure 4b illustrates that the response time of the prismatic SPR sensing chip decreased from 21 min to 11 min as the electrolyte concentration in the Co2+ solution was increased from 0 mol/L to 0.15 mol/L. This reduction in response time can be attributed to the increase in electrolyte concentration. As the concentration of the electrolyte increases, the quantity of free ions (such as Na+ and Cl−) present in the solution rises proportionally. In the presence of an external electric field, these free ions generate a stronger localized electric field. Within this enhanced field, Co2+ experiences a greater electrostatic force, accelerating its migration toward the sensor surface [40]. The resonance angle shift in the prismatic SPR sensing chip is increased from 0.447° to 0.553° as the electrolyte concentration in the Co2+ solution is increased from 0 mol/L to 0.15 mol/L. Higher electrolyte concentrations induce more significant changes in the effective refractive index of the solution surrounding the sensor. These changes lead to a more pronounced resonance angle shift, effectively enhancing the sensor′s sensitivity [41]. As the electrolyte concentration increased from 0.15 mol/L to 0.20 mol/L, the response time of the prismatic SPR sensing chip slightly increased while the resonance angle shift decreased. This phenomenon arises from the accumulation of Na+ and Cl− near the electrode surface during migration, which induces polarization at both electrode ends. This generates a potential difference opposing the original electromotive force, thereby blocking ion flow, increasing solution equivalent resistance, and causing measurement errors [42]. As the electrolyte concentration increased from 0.2 mol/L to 0.25 mol/L, the response time of the prismatic SPR sensing chip slightly decreased while the resonance angle shift increased. This phenomenon can be attributed to the thickness of the bilayer decreasing with increasing NaCl concentration. As the ionic strength rises, the electrical double layer is electrostatically compressed, reducing the diffusion layer thickness and driving bilayer thinning. Some counterions dissociate from the electrical double layer and migrate into the bulk solution, becoming free-charged carriers that contribute to ionic conductivity in the short term [43,44]. The electrolyte conductivity attains its maximum at an electrolyte solution concentration of 0.15 mol/L, with the electric field-driven reaction rate showing a positive correlation to this conductivity. Consequently, the prism-based SPR sensing chip demonstrates the shortest response time and the greatest resonance angular shift under this optimal concentration.
3.5. Detection of Co2+
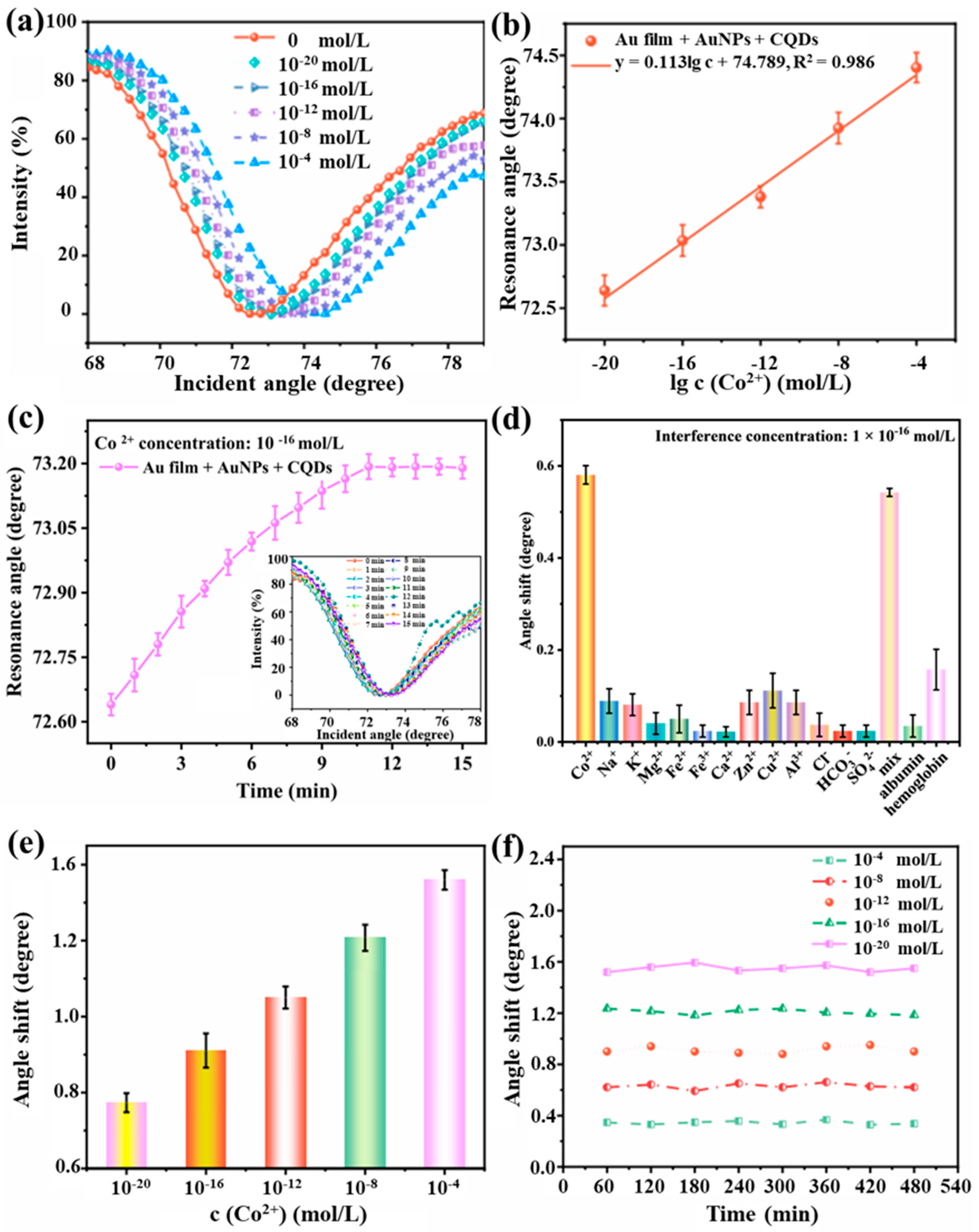
To investigate the performance of the prismatic SPR sensor chip in the detection of Co2+, the sensor was used to measure Co2+ solutions of varying concentrations. As shown in Figure 5a, the resonance angle of the SPR spectra of Co2+ was gradually increased by a total of about 2.101° as the concentration ranged from 10−20 mol/L to 10−4 mol/L. Figure 5b shows the relationship between resonance angle shift and Co2+ concentration. The resonance angle shift was measured by the prismatic SPR sensor chip coated Au film which modified AuNPs and functionalized with CQDs for signal enhancement. The calibration curve exhibited a linear relationship between the resonance angle shift and the concentration of Co2+, with a linear correlation coefficient of 0.986. The enhancement in sensitivity can be attributed to the electric field coupling effect between AuNPs and the gold film. When P-polarized light is incident on the substrate-metal interface, the energy of the evanescent wave (EW) decays, inducing surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs) to propagate along the metal layer’s surface. The evanescent wave penetrates both the substrate and the metal, exciting surface plasmon waves (SPW) at the gold film interface and localized surface plasmon waves (LSPW) at the AuNP interface. When their frequencies match, they induce SPR and LSPR effects, thereby redistributing charges. When the frequencies of LSPR and SPR align, plasmonic coupling between AuNPs and the Au thin film enhances refractive index (RI) sensitivity through electric field coupling [45,46,47]. The detection limit of a sensor device represents the concentration of an analyte that can be detected at concentrations approaching zero. Mathematically, it can be expressed as . Here, LOD denotes the sensor’s detection limit. The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is 3. represents the variance of the resonance angle shift in a 0.15 mol/L electrolyte solution. The sensor was tested 5 times on blank specimens to calculate the standard deviation. s represents the sensor sensitivity at near-blank concentrations. The average resonance angle shift is 0.347° at a Co2+ concentration of 10−20 mol/L. Therefore, the near-zero concentration sensitivity is 3.47 × 1019°/M.
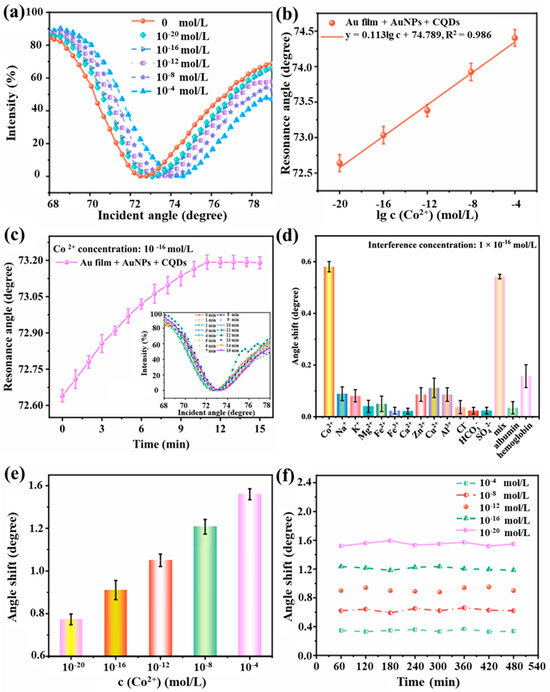
Figure 5.
Response of the prismatic SPR sensing chip to Co2+. (a) SPR spectra of prismatic SPR sensing chip based on photoelectric synergistic enhancement at different Co2+ concentrations. (b) Relationship between SPR spectral resonance angle and Co2+ concentration. (c) Response time of prismatic SPR sensing chip based on optimal electric field conditions. (d) Selectivity of prismatic SPR Co2+ sensing chips. (e) Repeatability of prismatic SPR Co2+ sensing chips. (f) Stability of prismatic SPR Co2+ sensing chips.
Since the standard deviation is 0.574° and the sensitivity of the sensor near zero concentration is 3.47 × 1019°/M, the calculated value of LOD of the sensor is 4.96 × 10−20 mol/L.
3.6. Selectivity, Repeatability, and Stability of the Prismatic SPR Sensing Chips
Under optimal electric field conditions, that is at a voltage of 1.2 V with a concentration of 10−16 mol/L Co2+ (0.15 mol/L electrolyte concentration), the relationship between the resonance angle and response time of the prismatic SPR sensing chip was recorded. As shown in Figure 5c, a total of 16 sets of SPR spectra were measured and recorded over a period of 15 min from 0 to 15 min and at 11 min, the resonance angle stays constant. The Co2+ adsorbed by the CQDs probes on the prismatic SPR sensing chip reaches saturation. At this moment, the effective refractive index sensitivity no longer changes. Therefore, under the defined optimal electric field conditions, the response time of the prismatic SPR Co2+ sensing chip coated Au film which modified AuNPs and was functionalized with CQDs enhanced was determined to be 11 min.
As shown in Figure 5d, the prismatic SPR sensing chip exhibited the most significant response to Co2+, with a resonance angle shift of 0.582°. Cu2+ showed the resonance angle shift was 0.11°. The resonance angle shifts in albumin and hemoglobin were 0.036° and 0.16°, respectively. The resonance angle shifts in Na+, K+, Mg2+, Fe2+, Fe3+, Ca2+, Zn2+, Al3+, Cl−, HCO3−, and SO42− were all less than 0.1°. The shifts in the interfering substances are significantly smaller than those of Co2+. The resonance angle shift in the prismatic SPR sensing chip in response to the mixed-ion solution is 0.543°. This indicates that the prismatic SPR sensing chip modified AuNPs and functionalized CQDs synergistic enhancement, exhibits good selectivity for Co2+.
To evaluate the repeatability of the prismatic SPR sensing chip, six repetitions of the test were conducted using Co2+ solutions at concentrations of 10−20 mol/L, 10−16 mol/L, 10−12 mol/L, 10−8 mol/L, and 10−4 mol/L. Figure 5e presents the results of the repeated tests performed on one identical sensor using Co2+ solutions at concentrations of 10−20 mol/L, 10−16 mol/L, 10−12 mol/L, 10−8 mol/L, and 10−4 mol/L. The resonance angle shift in the prismatic SPR sensing chip remained stable within 0.07°. These results indicate the consistent repeatability of the prismatic SPR sensing chip in detecting Co2+ under various measurements of the same concentration.
Stability is a crucial indicator for sensors in practical applications, as shown in Figure 5f. At a Co2+ concentration of 10−4 mol/L, the maximum resonance angle shift was measured as 0.08°. At a Co2+ concentration of 10−8 mol/L, the maximum resonance angle shift was measured as 0.05°. At a Co2+ concentration of 10−12 mol/L, the maximum resonance angle shift was measured as 0.07°. At a Co2+ concentration of 10−16 mol/L, the maximum resonance angle shift was measured as 0.04°. At a Co2+ concentration of 10−20 mol/L, the maximum resonance angle shift was measured as 0.04°. Consequently, the sensor exhibits excellent stability.
4. Discussion
The proposed biosensor in this work is compared with typical Co2+-detecting sensors, as shown in Table 1. Ning Wang et al. [48] developed fluorescent BSA-templated silver nanoparticles as probes for Co2+ detection. Lili Sun et al. [49] synthesized nitrogen and sulfur co-doped carbon dots using a simple hydrothermal method with L-cysteine as the precursor, leveraging their fluorescence quenching properties for Co2+ detection. These sensors offer simple structures and straightforward preparation processes, ensuring good stability and repeatability. However, their relatively high LODs and narrow linear ranges limit their use for detecting low-concentration Co2+ in practical applications. Xin Kang et al. [9] developed a micro-tapered long-period fiber grating sensor functionalized with polydopamine-graphene oxide, enabling highly sensitive Co2+ detection. Changiz Karami et al. [50] developed colorimetric sensors using glycyrrhizic acid-functionalized AuNPs, where Co2+ detection relies on nanoparticle color changes upon interaction. These sensors exhibit low detection limits, wide dynamic ranges, high sensitivity, and good reproducibility. However, their clinical application is constrained by structural complexity, demanding modification control, laborious preparation, material reproducibility issues, and inconsistent batch—to-batch performance.

Table 1.
Comparison of different methods for the detection of Co2+.
In contrast, our sensor achieves ultra-low detection limits for Co2+ through a simple preparation process, with a wide dynamic range. Although employing functionalized AuNPs and Au film, our sensor maintains cost-effectiveness due to industrial-scale magnetron sputtering production, and the system remains economically viable. The prismatic SPR platform enables label-free and ultrasensitive Co2+ detection, featuring a simple yet stable structure with excellent selectivity, low cost, and operational simplicity. Optimization of the external planar electric field directs Co2+ ions to move towards the sensor chip surface under the influence of the electric field force, optimizing the conditions for chelation with CQD probes and significantly reducing detection time. Additionally, the sensor features simple operation, high controllability, and strong integrability, thereby enabling a chip-based detection approach. When integrated with optofluidic technology, it enables high-throughput micro-total analysis, showing significant potential for multi-sample detection applications.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, this study presents a prismatic SPR Co2+ sensing chip with optoelectronic synergistic enhancement, aiming to achieve rapid, label-free detection of ultra-low concentrations of Co2+ through the integration of a planar electric field. To address the shortcomings of Conventional Co2+ sensor regarding low response rate and long detection time, it was first verified that when a planar electric field with a voltage of 2.0 V was introduced, the response rate of the prismatic SPR sensing chip increased by 49% compared to that with a voltage of 0.4 V. Subsequent experiments demonstrated that the optimal experimental conditions for a planar field were a voltage of 1.2 V and an electrolyte concentration of 0.15 mol/L. Under these conditions, the response time was reduced from 21 min to 11 min, while the chip exhibited an ultra-low detection limit of 4.96 × 10−20 mol/L and a wide detection range from 10−20 mol/L to 10−4 mol/L, alongside excellent selectivity, repeatability, and stability. The proposed prismatic SPR Co2+ sensing chip, based on optoelectronic synergistic enhancement, provides a simple and feasible strategy to accelerate reaction rates and reduce detection time, offering valuable insights for rapid multi-sample detection of Co2+ in environmental and biological matrices.
Author Contributions
X.J.: Conceptualization, formal analysis, visualization. M.C.: Conceptualization, formal analysis. X.M.: Methodology. X.X.: Data curation, visualization. N.W.: Writing—review and editing, supervision, funding acquisition, project administration. K.N.: Supervision, review. X.C.: Data curation. Y.W.: Data curation. J.Z.: Visualization. J.H.: Visualization. Z.W.: Visualization. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 62375208); Science and Technology Major Project of Hubei Province, China (Grant No. 2023BCA003) and Hubei Optical Fundamental Research Center.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author (privacy).
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 62375208); Science and Technology Major Project of Hubei Province, China (Grant No. 2023BCA003) and Hubei Optical Fundamental Research Center.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Abdelbasir, S.M.; El-Shewaikh, A.M.; El-Sheikh, S.M.; Ali, O.I. Novel modified chitosan nanocomposites for Co(II) ions removal from industrial wastewater. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 41, 102008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, A.; Tamang, S.; Rethinasabapathy, M.; Ranjith, K.S.; Safarkhani, M.; Kwak, C.H.; Roh, C.; Huh, Y.S.; Han, Y.-K. Eco-friendly synthesis of rod-like hydroxyapatite on spherical carbon: A dual-function composite for selective cobalt removal and enhanced oxygen evolution reaction. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 487, 137164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Zhu, J.; Li, X.; Weng, G.-J.; Li, J.-J.; Zhao, J.-W. Surface etching-dependent geometry tailoring and multi-spectral information of Au@AuAg yolk-shell nanostructure with asymmetrical pyramidal core: The application in Co2+ determination. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 625, 340–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Lu, C.; Yan, D.; Ma, L. High selectivity sensing of cobalt in HepG2 cells based on necklace model microenvironment-modulated carbon dot-improved chemiluminescence in Fenton-like system. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 45, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashisht, D.; Kaur, K.; Jukaria, R.; Vashisht, A.; Sharma, S.; Mehta, S.K. Colorimetric chemosensor based on coumarin skeleton for selective naked eye detection of cobalt (II) ion in near aqueous medium. Sens. Actuators B 2019, 280, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.M.; Asiri, A.M.; Arshad, M.N.; Rahman, M.M. Development of selective Co2+ ionic sensor based on various derivatives of benzenesulfonohydrazide (BSH) compound: An electrochemical approach. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 339, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravets, V.G.; Strudwick, A.; Grigorenko, A.N. Ultrathin Gold for Robust Multi-Element Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensing. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2025, 12, 2400925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H.; Byun, J.-Y.; Yim, S.-Y.; Kim, M.-G. A Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance (LSPR)-based, simple, receptor-free and regeneratable Hg2+ detection system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 307, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, X.; Wang, R.; Jiang, M.; Li, E.; Li, Y.; Yan, X.; Wang, T.; Ren, Z. Polydopamine functionalized graphene oxide for high sensitivity micro-tapered long period fiber grating sensor and its application in detection Co2+ ions. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2022, 68, 102807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhou, X.; Ma, R.; He, M.; Shi, H.; Yi, Q. High-throughput biomolecular interaction analysis probing by an array fluorescent biosensor platform. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 259, 888–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravets, V.G.; Wu, F.; Yu, T.; Grigorenko, A.N. Metal-Dielectric-Graphene Hybrid Heterostructures with Enhanced Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensitivity Based on Amplitude and Phase Measurements. Plasmonics 2022, 17, 973–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Lu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chi, M.; Cheng, Q.; Yin, Y. Highly Stable Silver Nanoplates for Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensing. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 5629–5633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stebunov, Y.V.; Yakubovsky, D.I.; Fedyanin, D.Y.; Arsenin, A.V.; Volkov, V.S. Superior Sensitivity of Copper-Based Plasmonic Biosensors. Langmuir 2018, 34, 4681–4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Peng, Y.; Bai, J.; Zhang, X.; Cui, Y.; Ning, B.; Cui, J.; Gao, Z. Magnetic nanoparticle enhanced surface plasmon resonance sensor for estradiol analysis. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 254, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.G.; Park, K.M.; Jeong, J.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Baek, J.E.; Lee, H.W.; Jung, J.K.; Chung, B.H. Carbon nanotube-assisted enhancement of surface plasmon resonance signal. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 408, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubé, A.; Charbonneau, D.M.; Pelletier, J.N.; Masson, J.-F. Response Monitoring of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Patients Undergoing l-Asparaginase Therapy: Successes and Challenges Associated with Clinical Sample Analysis in Plasmonic Sensing. ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 1358–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wei, J. Recent advances in surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy (SERS): Finite-difference time-domain (FDTD) method for SERS and sensing applications. Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 75, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Choudhary, K.; Kumar, S. Photonic crystal fiber-based SPR sensor for broad range of refractive index sensing applications. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2022, 73, 103030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Zhong, S. High-mode spoof SPP of periodic metal grooves for ultra-sensitive terahertz sensing. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 25149–25160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saad, D.R.; Alismaeel, Z.T.; Abbar, A.H. Cobalt Removal from Simulated Wastewaters Using a Novel Flow-by Fixed Bed Bio-electrochemical Reactor. Chem. Eng. Process. 2020, 156, 108097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, V.N.; Desai, M.L.; Basu, H.; Kumar Singhal, R.; Kailasa, S.K. Recent developments on fluorescent hybrid nanomaterials for metal ions sensing and bioimaging applications: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 333, 115950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, P.; Saini, S.; Kim, K.-H. The advanced role of carbon quantum dots in nanomedical applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 141, 111158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, G.; Li, L.; Wang, D.; Chen, M.; Zeng, Z.; Xiong, W.; Wu, X.; Guo, C. Carbon dots: Synthesis, properties and biomedical applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 6553–6575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Chaudhary, A.; Mehta, P.; Dwivedi, C.; Khan, S.; Verma, N.C.; Nandi, C.K. Nitrogen-doped, thiol-functionalized carbon dots for ultrasensitive Hg(ii) detection. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 10750–10753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Z.; Shan, X.; Chai, L.; Chen, J.; Feng, H. Simultaneous Detection of Multiple DNA Targets by Integrating Dual-Color Graphene Quantum Dot Nanoprobes and Carbon Nanotubes. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 16065–16069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowery, J.L.; Chen, J. Recent Biomedical Applications of Carbon Quantum Dots in Cancer Treatment. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2024, 128, 16291–16301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Chen, T.; Fang, M.; Zhu, W.; Li, C. Continuous Detection of Cobalt Ions and Pyrophosphates by NAC-CdTe Quantum Dots Fluorescence Probes. J. Fluoresc. 2025, 35, 2261–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Yan, F.; Han, Z.; Xu, J.; Guo, X.; Chen, L. Cobalt(ii) ions detection using carbon dots as an sensitive and selective fluorescent probe. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 67481–67487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, L.; Liu, Q.; Chen, M.; Chen, X. Facile synthesis of B,N-doped CQDs as versatile fluorescence probes for sensitive detection of cobalt ions in environmental water and biological samples. Microchem. J. 2021, 163, 105888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Xia, B.; Niu, K.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Wang, N. Ultrasensitive optical fiber SPR sensor enhanced by Au-NPs-film modified with functionalized CQDs for label-free detecting cobalt (II) ion. Anal. Chim. Acta 2024, 1320, 343030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salihoglu, O.; Balci, S.; Kocabas, C. Plasmon-polaritons on graphene-metal surface and their use in biosensors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 213110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretschmann, E.; Raether, H. Notizen: Radiative Decay of Non Radiative Surface Plasmons Excited by Light. Naturforsch. A 1968, 23, 2135–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, M.; Das, T.; Dihingia, N.; Fan, X.; Silva, L.F.O.; Saikia, B.K. Formation of carbon quantum dots and graphene nanosheets from different abundant carbonaceous materials. Diamond Relat. Mater. 2020, 106, 107813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, J.; Peng, R.; Wei, S.; Chen, J.; Peng, X.; Xiao, B. Ethanol-Precipitation-Assisted Highly Efficient Synthesis of Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots from Chitosan. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 22574–22580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Duan, J.; Yang, W.; Li, X.; Mo, J.; Yang, P.; Tang, Q. Nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots from biomass via simple one-pot method and exploration of their application. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 434, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Wang, X.; Lu, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, L. A Biocompatible Fluorescent Ink Based on Water-Soluble Luminescent Carbon Nanodots. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 12215–12218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahyuni, S.; Riswan, M.; Adrianto, N.; Dharmawan, M.Y.; Tumbelaka, R.M.; Cuana, R.; Istiqomah, N.I.; Jiananda, A.; Garcia, S.; Suharyadi, E. Localized surface plasmon resonance properties dependence of green-synthesized Fe3O4/Ag composite nanoparticles on Ag concentration and an electric field for biosensor application. Photonics Nanostruct. Fundam. Appl. 2023, 57, 101191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Huang, J.; Xiang, D.; Deng, A.; Du, J.; Liu, H. Decoupled water electrolysis: Flexible strategy for pure hydrogen production with small voltage inputs. J. Energy Chem. 2024, 94, 340–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Yao, J.; Feng, Z.; Huang, B.; Luo, Z.; Wang, L. Enhancing Water Electrolysis Performance by Bubble Behavior Management. Small Methods 2025, 9, 2402105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Wu, M.; Zhou, L.; Chen, W.; Han, L.; Gao, G.; Cui, Y.; Sun, Z.; Cabot, A. Enhancing Electrocatalytic Activity Through Targeted Local Electrolyte Micro-Environment. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2419328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, K.E.; Uddin, N.; Kim, T.H.; Fan, Q.H.; Yoon, H.J. Highly sensitive detection of biological substances using microfluidic enhanced Fabry-Perot etalon-based optical biosensors. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 277, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, B.; Yue, Y.; Sun, M.; Li, J.; Jia, D. Design of a Real-Time Salinity Detection System for Water Injection Wells Based on Fuzzy Control. Sensors 2021, 21, 3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantaramethakul, J.; Choophun, N.; Chokradjaroen, C.; Watthanaphanit, A.; Saito, N.; Panomsuwan, G. Morphological Evolution of Gold Nanoparticles Synthesized via Solution Plasma Sputtering: Effect of Sodium Chloride Concentration and Storage Time. J. Phys. Chem. C 2023, 127, 3184–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.A.; Goel, A.; Abbas, Z. Effect of Electrolyte Concentration on the Stern Layer Thickness at a Charged Interface. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 3790–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubeen, S.; Zhang, S.; Kim, N.; Lee, S.; Krämer, S.; Xu, H.; Moskovits, M. Plasmonic Properties of Gold Nanoparticles Separated from a Gold Mirror by an Ultrathin Oxide. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 2088–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, X.-Z.; Song, H.; Zhao, W.-M.; Jing, J.-Y. A dual channel self-compensation optical fiber biosensor based on coupling of surface plasmon polariton. Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 124, 106002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhao, C.; Xia, B.; Wang, N.; Chen, X.; Jing, X.; Chen, M.; Xu, X. An enhanced SPR optical fiber biosensor using Ti3C2Tx MXene/AuNPs for label-free and sensitive detection of human IgG. Nanoscale 2024, 16, 18477–18487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Ga, L.; Ai, J. Synthesis of fluorescent BSA templated silver nanomaterials and it’s application of detection of Zn2+ and Co2+. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 5, 105703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Xiong, Z.; Zhao, X.; Xia, Y. Nitrogen and sulfur Co-doped carbon dots as selective and visual sensors for monitoring cobalt ions. Opt. Mater. 2021, 112, 110787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, C.; Taher, M.A. Colorimetric Sensor of Cobalt Ions in Aqueous Solution Using Gold Nanoparticles Modified with Glycyrrhizic Acid. Plasmonics 2018, 13, 1315–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.; Zhu, F.; Zhao, X.; Yang, H.; Chen, X. A reusable P, N-doped carbon quantum dot fluorescent sensor for cobalt ion. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 260, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Lou, T.; Pan, D.; Chen, L.; Qu, C.; Chen, Z. Label-free colorimetric sensing of cobalt(ii) based on inducing aggregation of thiosulfate stabilized gold nanoparticles in the presence of ethylenediamine. Analyst 2012, 137, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazur, F.; Liu, L.; Li, H.; Huang, J.; Chandrawati, R. Core-satellite gold nanoparticle biosensors for monitoring cobalt ions in biological samples. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 268, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).