On the RE2TiAl3 (RE = Y, Gd–Tm, Lu) Series—The First Aluminum Representatives of the Rhombohedral Mg2Ni3Si Type Structure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
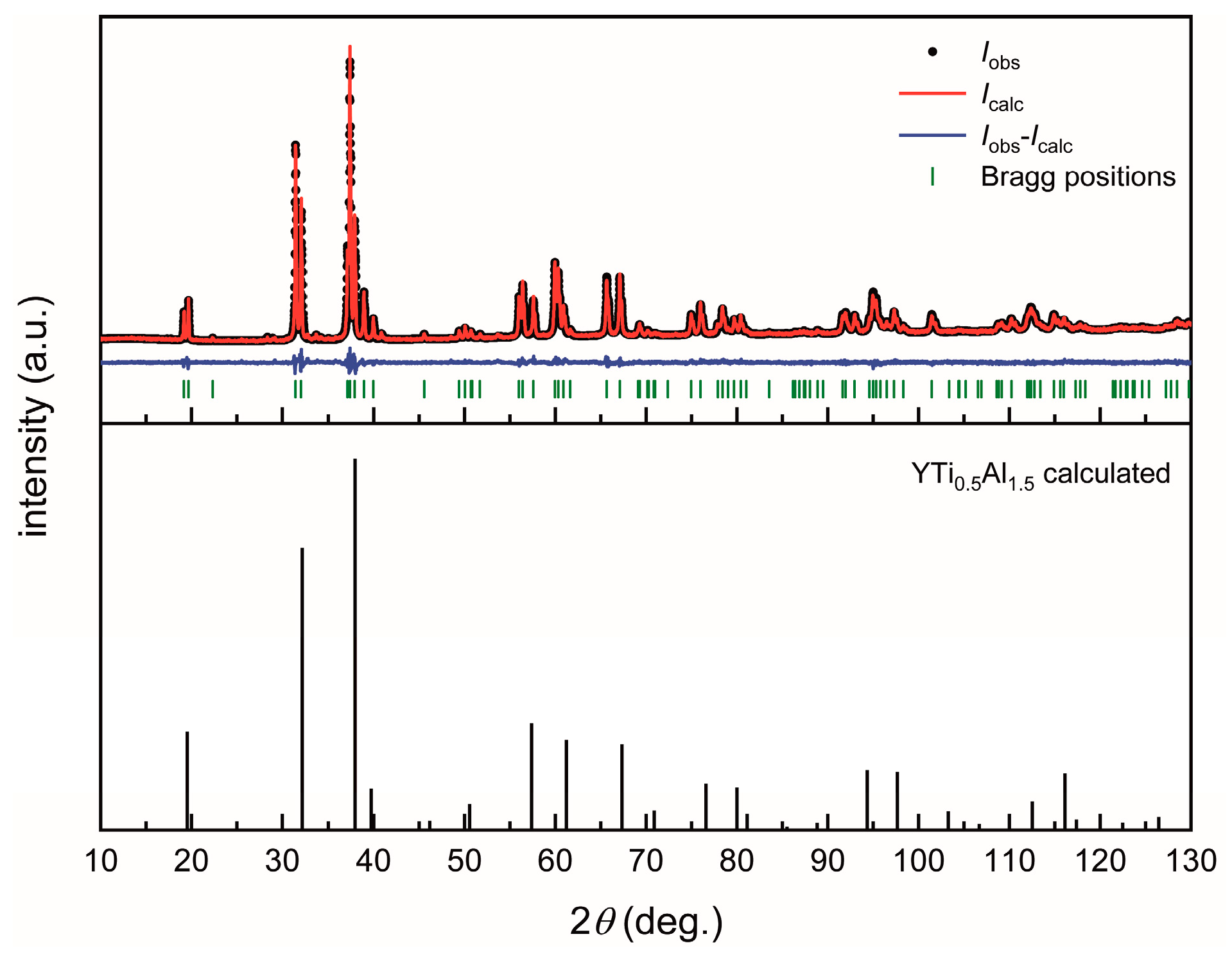
3.1. Structure Refinement
3.2. SEM-EDX Data
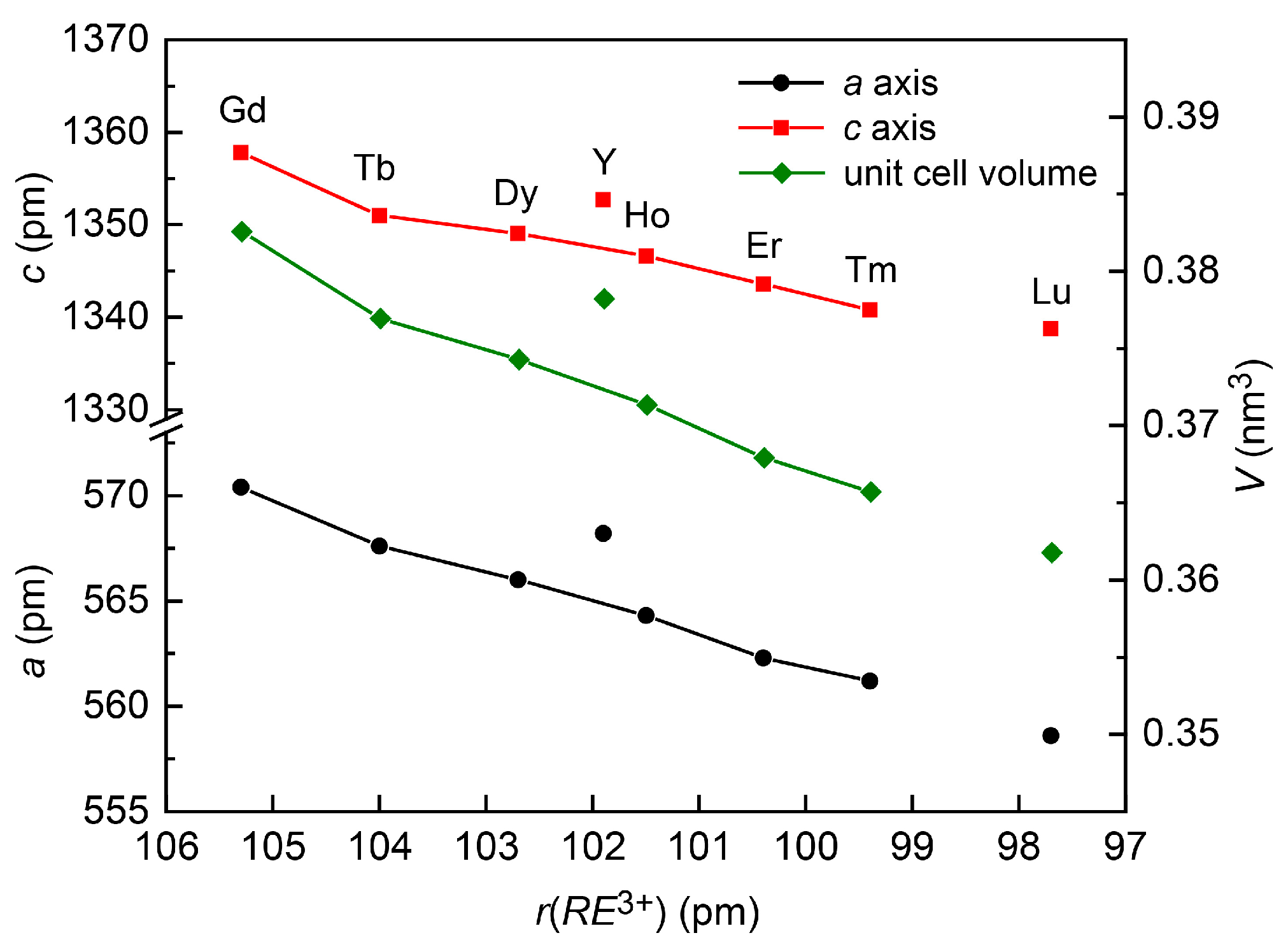
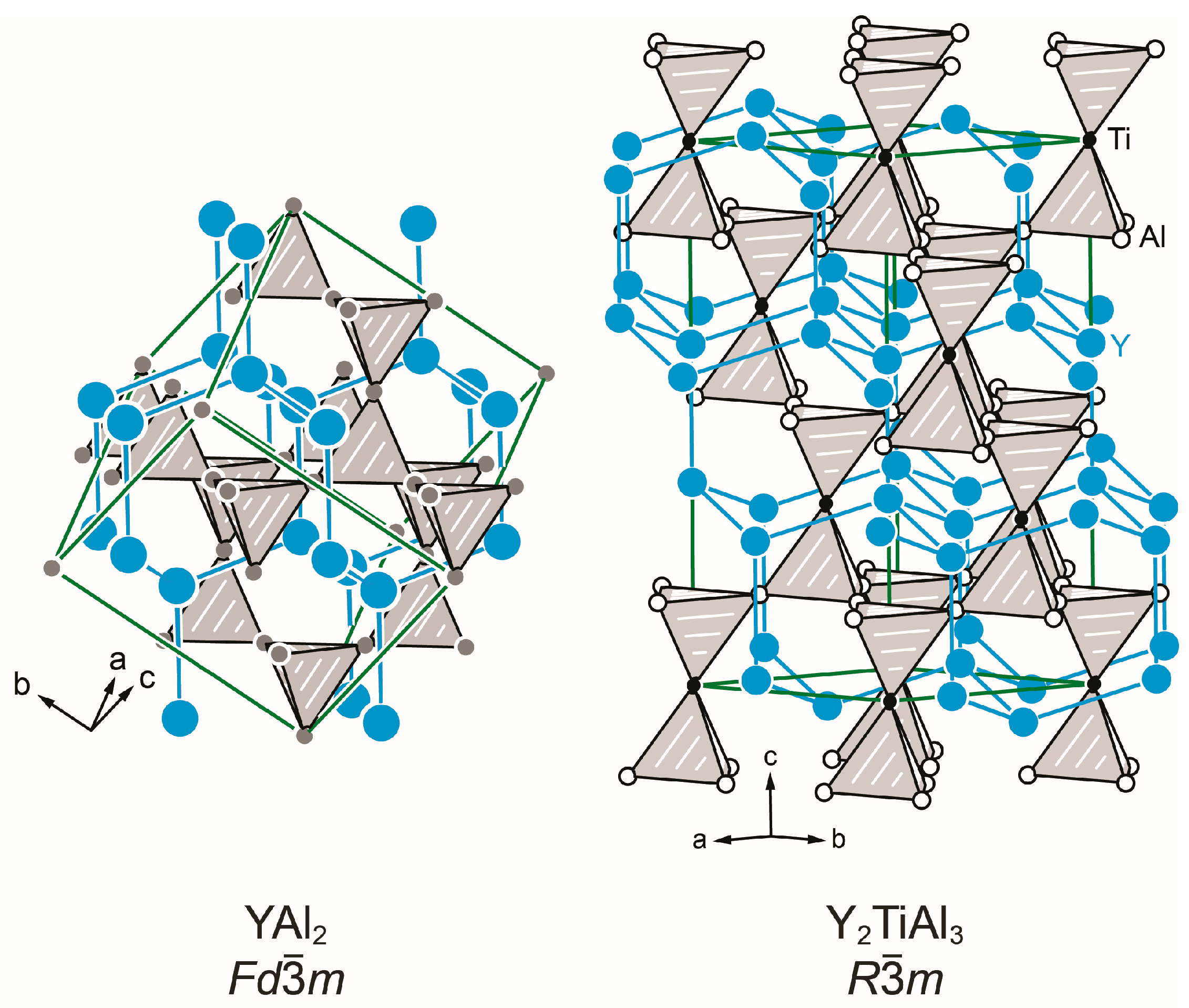
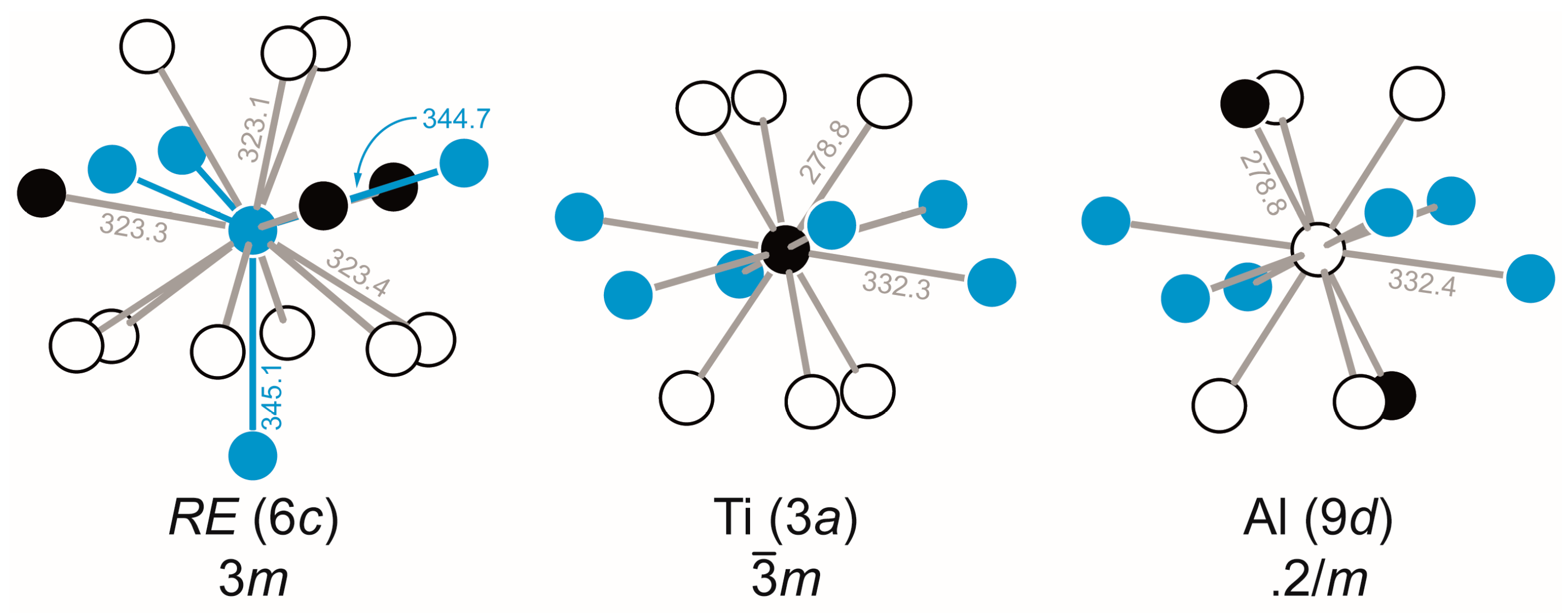
3.3. Crystal Chemistry
| Formula | Y2TiAl3 | Gd2TiAl3 | Tb2TiAl3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| CCDC number | 1939725 | 1939727 | 1939726 |
| Molar mass, g mol−1 | 306.6 | 443.3 | 446.7 |
| Lattice parameters | see Table 6 | ||
| Density calc., g cm−3 | 4.04 | 5.77 | 5.90 |
| Crystal size, µm | 50 × 40 × 35 | 30 × 25 × 10 | 40 × 40 × 20 |
| Diffractometer | IPDS-II | IPDS-II | Bruker CCD |
| Wavelength; λ, pm | MoKα; 71.073 | MoKα; 71.073 | MoKα; 71.073 |
| Transmission ratio (min/max) | 0.2943/0.4102 | 0.5295/0.7673 | 0.3054/0.5561 |
| Detector distance, mm | 60 | 70 | 40 |
| Exposure time, min | 10 | 30 | 0.167 |
| Integr. param. A, B, EMS | 14.0; −1.0; 0.030 | 16.0; –4.0; 0.030 | – |
| F(000), e | 417 | 567 | 573 |
| Range in hkl | ±9; −8, +9, ±21 | ±8; ±8, ±20 | ±7; ±8, −17, +20 |
| θmin, θmax, deg | 4.4/34.9 | 4.4/33.3 | 4.4/32.0 |
| Linear absorption coeff., mm−1 | 24.7 | 27.6 | 29.7 |
| Total no. of reflections | 2889 | 1579 | 826 |
| Independent reflections/Rint | 229/0.0510 | 212/0.0696 | 190/0.0143 |
| Reflections with I ≥ 3σ(I)/Rσ | 191/0.0168 | 175/0.0275 | 181/0.0122 |
| Data/parameters | 229/11 | 212/11 | 190/11 |
| R1/wR2 for I ≥ 3σ(I) | 0.0177/0.0357 | 0.0208/0.0214 | 0.0105/0.0259 |
| R1/wR2 for all data | 0.0286/0.0393 | 0.0317/0.0221 | 0.0111/0.0260 |
| Goodness-of-fit on F2 | 1.23 | 1.16 | 1.03 |
| Extinction scheme | Lorentzian isotropic [61] | ||
| Extinction coefficient | 160(50) | 58(19) | 350(20) |
| Diff. Fourier residues /e– Å−3 | −1.32/+1.01 | −1.81/+1.40 | −0.37/+1.06 |
| Atom | Wyckoff Position | x | y | z | Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y2TiAl3 | |||||
| Y | 6c | 0 | 0 | 0.37244(4) | 89(1) |
| Ti | 3a | 0 | 0 | 0 | 75(2) |
| Al | 9d | 1/2 | 0 | 1/2 | 88(3) |
| Gd2TiAl3 | |||||
| Gd | 6c | 0 | 0 | 0.37333(3) | 81(1) |
| Ti | 3a | 0 | 0 | 0 | 67(5) |
| Al | 9d | 1/2 | 0 | 1/2 | 84(7) |
| Tb2TiAl3 | |||||
| Tb | 6c | 0 | 0 | 0.37348(1) | 64(1) |
| Ti | 3a | 0 | 0 | 0 | 54(2) |
| Al | 9d | 1/2 | 0 | 1/2 | 69(3) |
| Atom | U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y2TiAl3 | ||||||
| Y | 86(2) | U11 | 94(2) | 43(1) | 0 | U13 |
| Ti | 79(3) | U11 | 66(4) | 40(1) | 0 | U13 |
| Al | 84(3) | 86(4) | 95(5) | 43(2) | 5(2) | 10(1) |
| Gd2TiAl3 | ||||||
| Gd | 79(2) | U11 | 84(2) | 40(1) | 0 | U13 |
| Ti | 74(5) | U11 | 54(9) | 37(3) | 0 | U13 |
| Al | 77(6) | 80(11) | 95(10) | 40(5) | 4(6) | 8(13) |
| Tb2TiAl3 | ||||||
| Tb | 62(1) | U11 | 69(1) | 31(1) | 0 | U13 |
| Ti | 55(3) | U11 | 52(4) | 28(1) | 0 | U13 |
| Al | 74(3) | 68(5) | 64(4) | 34(2) | 2(2) | 5(3) |
| Y2TiAl3 | Gd2TiAl3 | Tb2TiAl3 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y: | 3 | Al | 323.1 | Gd: | 3 | Al | 325.4 | Tb: | 3 | Al | 324.1 |
| 3 | Ti | 332.3 | 6 | Al | 333.1 | 6 | Al | 331.3 | |||
| 6 | Al | 332.4 | 3 | Ti | 333.8 | 3 | Ti | 332.1 | |||
| 3 | Y | 344.7 | 1 | Gd | 344.1 | 1 | Tb | 342.2 | |||
| 1 | Y | 345.1 | 3 | Gd | 346.8 | 3 | Tb | 345.1 | |||
| Ti: | 6 | Al | 278.8 | Ti: | 6 | Al | 279.9 | Ti: | 6 | Al | 278.6 |
| 6 | Y | 332.3 | 6 | Gd | 333.8 | 6 | Tb | 332.1 | |||
| Al: | 2 | Ti | 278.8 | Al: | 2 | Ti | 279.9 | Al: | 2 | Ti | 278.6 |
| 4 | Al | 284.1 | 4 | Al | 285.2 | 4 | Al | 283.7 | |||
| 2 | Y | 323.1 | 2 | Gd | 325.4 | 2 | Tb | 324.1 | |||
| 4 | Y | 332.4 | 4 | Gd | 333.1 | 4 | Tb | 331.3 | |||
| Compound | RE (at.-%) | Ti (at.-%) | Al (at.-%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ideal composition | 33.3 | 16.7 | 50.0 |
| Single crystal data | |||
| Y2TiAl3 | 36 | 16 | 48 |
| Gd2TiAl3 | 34 | 16 | 50 |
| Bulk sample data | |||
| Er2TiAl3 | 36 | 14 | 50 |
| Tm2TiAl3 | 32 | 16 | 52 |
| Lu2TiAl3 | 37 | 15 | 48 |
| Compound | a (pm) | c (pm) | V (nm³) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Y2TiAl3 P | 568.29(4) | 1353.0(1) | 0.3784 |
| Y2TiAl3 SC | 568.22(7) | 1352.9(2) | 0.3783 |
| Gd2TiAl3 P | 569.81(5) | 1359.6(2) | 0.3823 |
| Gd2TiAl3 SC | 570.45(5) | 1358.0(1) | 0.3827 |
| Tb2TiAl3 P | 567.55(6) | 1351.0(3) | 0.3769 |
| Tb2TiAl3 SC | 567.39(6) | 1352.4(2) | 0.3771 |
| Dy2TiAl3 P | 565.90(6) | 1349.1(2) | 0.3742 |
| Ho2TiAl3 P | 564.86(3) | 1347.5(1) | 0.3723 |
| Er2TiAl3 P | 563.10(3) | 1344.3(1) | 0.3691 |
| Tm2TiAl3 P | 559.61(9) | 1341.3(3) | 0.3638 |
| Lu2TiAl3 P | 558.37(4) | 1338.2(1) | 0.3613 |
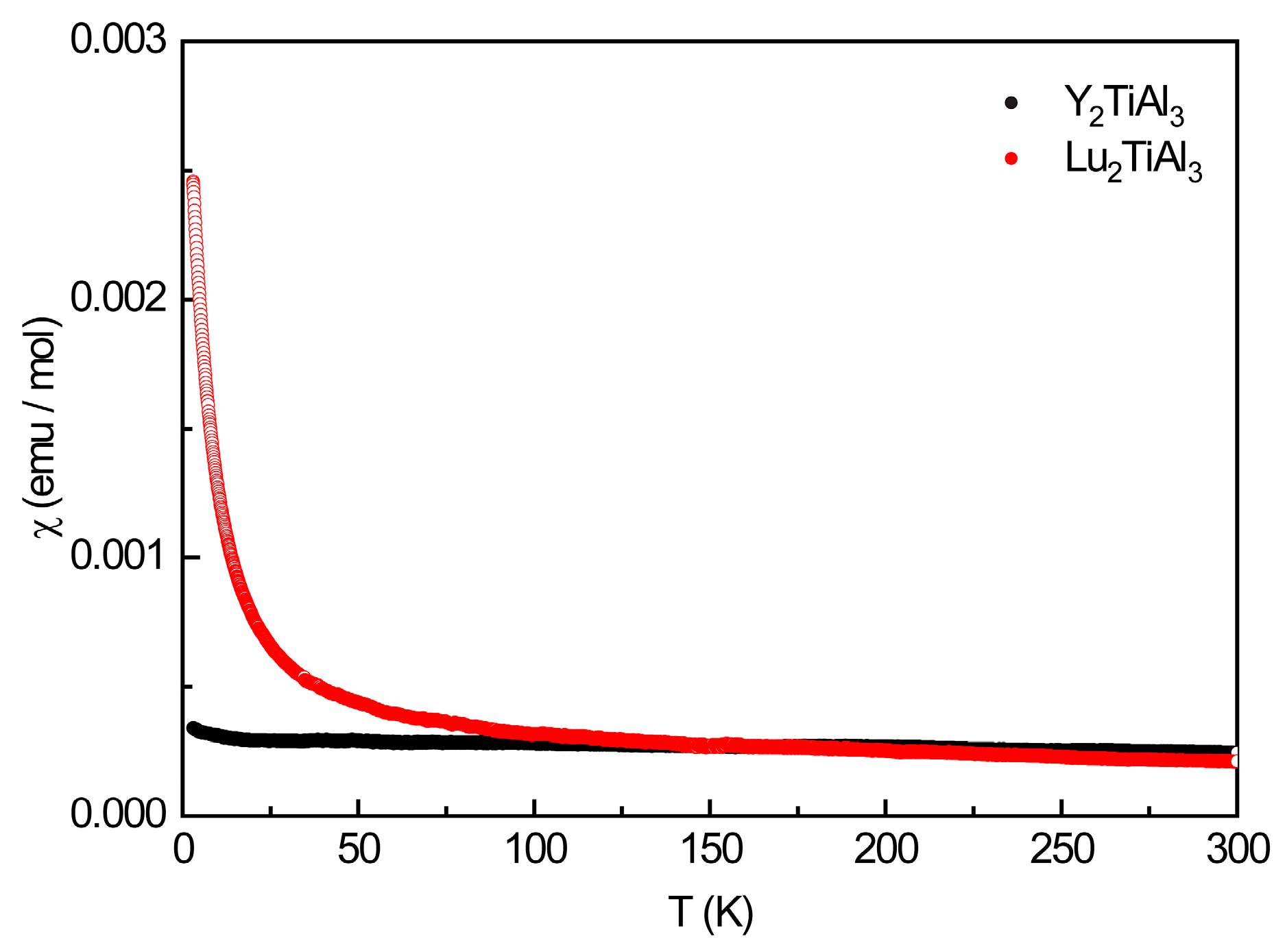
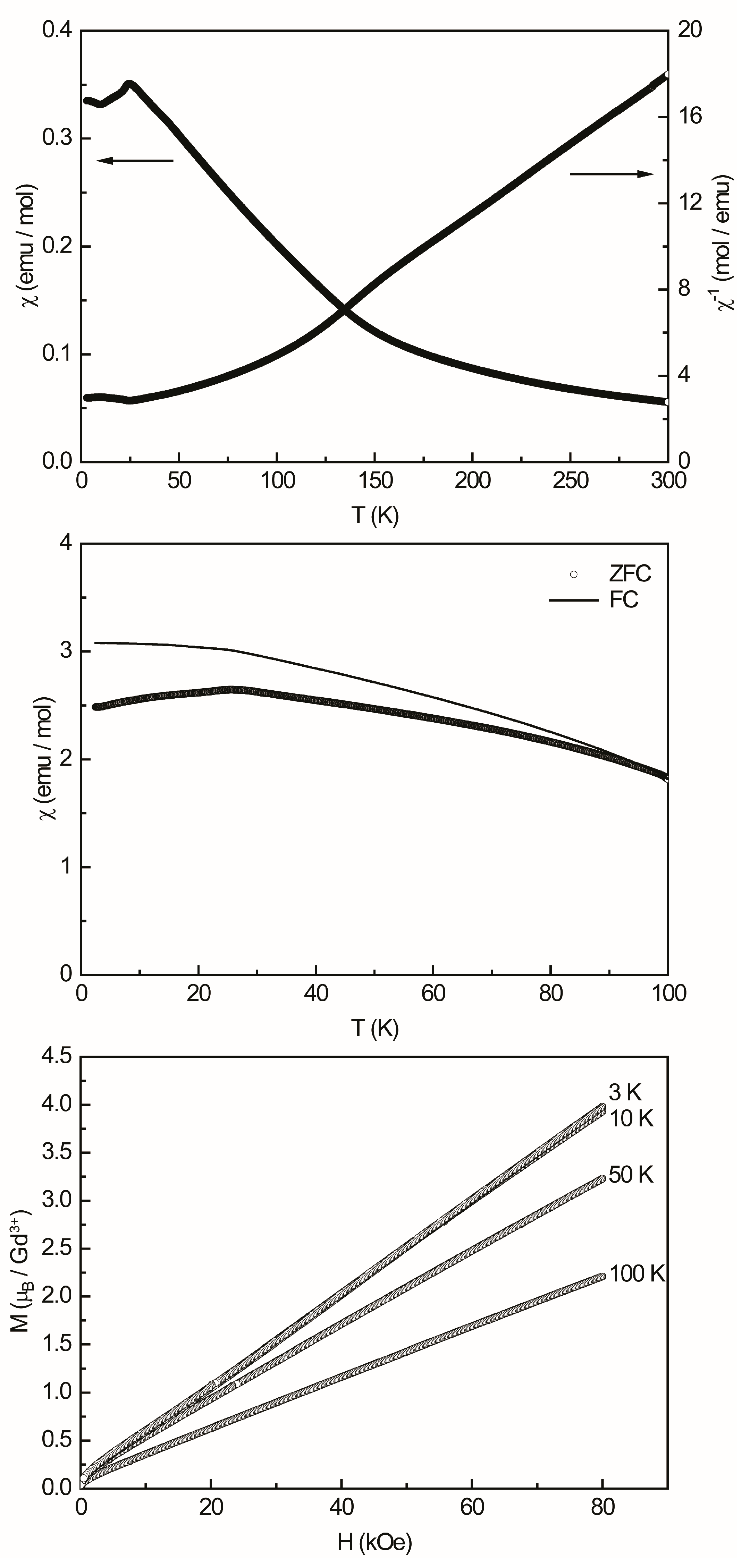
3.4. Physical Properties
| Compound | TN (K) | µexp (µB) | µeff (µB) | θP (K) | µsat (µB per RE3+) | gJ × J (µB per RE3+) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y2TiAl3 | Pauli-paramagnetic, non-superconducting, χ(300 K) = +2.48(1) × 10−4 emu mol−1 | |||||
| Gd2TiAl3 | 26.1(1) | 7.98(1) | 7.94 | +20.8(1) | 3.98(1) | 7 |
| Tb2TiAl3 | 24.0(1) | 10.04(1) | 9.72 | +31.7(1) | 3.58(1) | 9 |
| Dy2TiAl3 | 26.1(1) | 11.14(1) | 10.65 | −0.29(1) | 7.98(1) | 10 |
| Ho2TiAl3 | 10.3(1) | 10.85(1) | 10.61 | +0.72(1) | 7.36(1) | 10 |
| Er2TiAl3 | 17.6(1) | 9.73(1) | 9.58 | −6.5(1) | 4.46(1) | 9 |
| Tm2TiAl3 | 10.8(1) | 7.69(1) | 7.61 | −7.3(1) | 3.46(1) | 7 |
| Lu2TiAl3 | Pauli-paramagnetic, non-superconducting, χ(300 K) = +2.14(1) × 10−4 emu mol−1 | |||||
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paufler, P.; Gustav, E.R. Schulze’s pioneering work on Laves phases. Z. Kristallogr. 2006, 221, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, W.; Fritz, H. Laves—An ideal for generations. Z. Kristallogr. 2006, 221, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthé, E.; Fritz, H. Laves—100 years young. Z. Kristallogr. 2006, 221, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villars, P.; Cenzual, K. (Eds.) Pearson’s Crystal Data: Crystal Structure Database for Inorganic Compounds; (release 2022/23); ASM International®: Materials Park, OH, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Laves, F.; Witte, H. Der Einfluß von Valenzelektronen auf die Kristallstruktur ternärer Magnesiumlegierungen. Metallwirtsch. Metallwiss. Metalltech. 1936, 15, 840–842. [Google Scholar]
- Gschneidner, K.A., Jr.; Pecharsky, V.K. Binary rare earth Laves phases—An overview. Z. Kristallogr. 2006, 221, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, H.; Hirao, N.; Ohishi, Y.; Baron, A.Q.R. Compressional behavior of solid NeHe2 up to 90 GPa. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2010, 22, 095401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewaele, A.; Rosa, A.D.; Guignot, N. Argon-neon binary diagram and ArNe2 Laves phase. J. Chem. Phys. 2019, 151, 124708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Goncharov, A.F.; Shukla, V.; Jena, N.K.; Popov, D.; Li, B.; Wang, J.; Meng, Y.; Prakapenka, V.B.; Smith, J.S.; et al. Stability of Ar(H2)2 to 358 GPa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 3596–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laniel, D.; Weck, G.; Loubeyre, P. Xe(N2)2 compound to 150 GPa: Reluctance to the formation of a xenon nitride. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 94, 174109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komura, Y.; Kitano, Y. Long-period stacking variants and their electron-concentration dependence in the Mg-base Friauf-Laves phases. Acta Crystallogr. 1977, B33, 2496–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, H. Untersuchungen im System Magnesium-Kupfer-Silicium mit besonderer Berücksichtigung des Schnittes MgCu2-MgSi2. Z. Angew. Mineral. 1938, 1, 255–268. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, T.; Hoffmann, R.-D.; Schwickert, C.; Pöttgen, R. Structure Refinement and Magnetic Properties of Ce2RuAl3 and a Group-Subgroup Scheme for Ce5Ru3Al2. Z. Naturforsch. 2011, 66b, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eustermann, F.; Stegemann, F.; Gausebeck, S.; Janka, O. Structural and Magnetic Investigations of the Pseudo Ternary RE2TAl3 series (RE = Sc, Y, La–Nd, Sm, Gd–Lu; T = Ru, Rh, Ir)—Size Dependent Formation of Two Different Structure Types. Z. Naturforsch. 2018, 73b, 819–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazina, Z.; Ban, Z. The Crystal Structures of U2Cu3Al and UCuAl2, and their Relationship with Some Other Phases in the System U-Cu-Al. Z. Naturforsch. 1981, 35b, 1162–1165. [Google Scholar]
- Huneau, B.; Rogl, P.; Zeng, K.; Schmid-Fetzer, R.; Bohn, M.; Bauer, J. The ternary system Al–Ni–Ti Part I: Isothermal section at 900 °C; Experimental investigation and thermodynamic calculation. Intermetallics 1999, 7, 1337–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelinskii, A.V.; Fedorchuk, A.O.; Zelinska, O.Y. Synthesis and crystal structure of the compounds UMn1.43Ga0.57 and U2Fe3Ga. Visn. Lviv. Derzh. Univ. Ser. Khim. 2013, 54, 92–97. [Google Scholar]
- Sichevych, O.; Prots, Y.; Schnelle, W.; Schmidt, M.; Grin, Y. Crystal structure of dieuropium trigallium iridium, Eu2Ga3Ir. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 2006, 221, 263–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mykhalichko, O.; Gladyshevskii, E.I.; Hlukhyy, V.; Fässler, T.F. Synthesis and crystal structure of the compound Nb2Cu1.10Ga2.90. Visn. Lviv. Derzh. Univ. Ser. Khim. 2009, 50, 89–93. [Google Scholar]
- Myakush, O.R.; Fedorchuk, A.A. Crystal structure and electrical properties of HoRuGa compound. Visn. Lviv. Derzh. Univ. Ser. Khim. 2004, 44, 62–66. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.L.; Chen, X.-Q.; Grytsiv, A.; Witusiewicz, V.T.; Rogl, P.; Podloucky, R.; Giester, G. On the ternary Laves phases {Sc,Ti}2M3Si (M = Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni) with MgZn2-type. J. Alloys Compd. 2007, 429, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotur, B.Y. Crystal structure of Sc2M3Si (where M = Fe, Co, Ni) compounds. Dopov. Akad. Nauk Ukr. RSR 1977, A39, 164–165. [Google Scholar]
- Bardos, D.I.; Gupta, K.P.; Beck, P.A. Ternary Laves Phases with Transition Elements and Silicon. Trans. Metall. Soc. AIME 1961, 221, 1087–1088. [Google Scholar]
- Henriques, M.S.; Berthebaud, D.; Lignie, A.; El Sayah, Z.; Moussa, C.; Tougait, O.; Havela, L.; Gonçalves, A.P. Isothermal section of the ternary phase diagram U–Fe–Ge at 900 °C and its new intermetallic phases. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 639, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, R.-D.; Pöttgen, R.; Chevalier, B.; Gaudin, E.; Matar, S.F. The ternary germanides UMnGe and U2Mn3Ge. Solid State Sci. 2013, 21, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soudé, A.; Tougait, O.; Pasturel, M.; Kaczorowski, D.; Noël, H.; Roisnel, T. Characterization of the novel intermetallic compounds U2Co3Ge, U6Co12Ge4 and U6Co12Ge4C. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 5447–5452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, M.S.; Tougait, O.; Noel, H.; Pereira, L.C.J.; Waerenborgh, J.C.; Gonçalves, A.P. Evidence of uranium magnetic ordering on U2Fe3Ge. Solid State Commun. 2008, 148, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teslyuk, M.Y.; Gladyshevskii, E.I. Crystal structure of MnCu1.5Ge0.5 ternary compound. Visn. Lviv. Derzh. Univ. Ser. Khim. 1963, 6, 42–45. [Google Scholar]
- Kuz’ma, Y.B.; Gladyshevskii, E.I. Crystal structure of the compound Mn2Co3Ge. Dopov. Akad. Nauk Ukr. RSR 1963, A25, 205–208. [Google Scholar]
- Gladyshevskii, E.I.; Krypyakevych, P.I.; Teslyuk, M.Y. Crystal structure of the ternary phase Cu4MgSn. Dokl. Akad. Nauk. SSSR 1952, 85, 81–84. [Google Scholar]
- Zaremba, V.I.; Baranyak, V.M.; Kalychak, Y.M. Crystal structure of the RNi4In compounds. Visn. Lviv. Derzh. Univ. Ser. Khim. 1984, 25, 18–19. [Google Scholar]
- Felner, I. Magnetic properties of RAuNi4 rare earth compounds. Solid State Commun. 1977, 21, 267–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwight, A.E. Crystal structure of RENi4Au compounds and unitcell constants in the YCo5-YNi5-YCu5 series. J. Less-Common Met. 1975, 43, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshita, T.; Malik, S.K.; Wallace, W.E. Crystal structure of RCu4Ag and RCu4Al (R = Rare Earth) intermetallic compounds. J. Solid State Chem. 1978, 23, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, T.; Arai, S.; Abe, S.; Kamigaki, K. Magnetic properties of cubic RAuCu4 (R = Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho and Er) intermetallic compounds. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1986, 55, 4441–4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, S.; Pöttgen, R. Yb6Ir5Ga7—A MgZn2 Superstructure. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2017, 643, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eustermann, F.; Pominov, A.; Pöttgen, R. Rare Earth (RE) Gallides with Closely Related Compositions: REIrGa and RE6Ir5Ga7. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2018, 644, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eustermann, F.; Stegemann, F.; Radzieowski, M.; Janka, O. Intermetallic RE6T5Al7 Phases (RE = Sc, Y, Ce–Nd, Sm, Gd–Lu, T = Ru, Ir)—Diversity in their Magnetic, Magnetocaloric and Critical Properties. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 16211–16226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noréus, D.; Eriksson, L.; Göthe, L.; Werner, P.E. Structure determination of Mg2SiNi3. J. Less-Common Met. 1985, 107, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, S.; Janka, O.; Benndorf, C.; Mausolf, B.; Haarmann, F.; Eckert, H.; Heletta, L.; Pöttgen, R. Ternary rhombohedral Laves phases RE2Rh3Ga (RE = Y, La–Nd, Sm, Gd–Er). Z. Naturforsch. 2017, 72b, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cenzual, K.; Chabot, B.; Parthé, E. Y2Rh3Ge, a rhombohedral substitution variant of the MgCu2 type. J. Solid State Chem. 1987, 70, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipatov, A.; Gribanov, A.; Grytsiv, A.; Safronov, S.; Rogl, P.; Rousnyak, J.; Seropegin, Y.; Giester, G. The ternary system cerium–rhodium–silicon. J. Solid State Chem. 2010, 183, 829–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczorowski, D.; Lipatov, A.; Gribanov, A.; Seropegin, Y. Low-temperature magnetic and electrical transport properties of some ternary Ce–Rh–Si compounds. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 6518–6521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernière, A.; Lejay, P.; Bordet, P.; Chenavas, J.; Brison, J.P.; Haen, P.; Boucherle, J.X. Crystal structures and physical properties of some new ternary compounds U2T3X (T = Ru, Os; X = Si, Ge). J. Alloys Compd. 1994, 209, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozkin, A.V. New ternary compounds in the Sm–Rh–Ge system. J. Alloys Compd. 2004, 385, L1–L2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doverbratt, I.; Ponou, S.; Lidin, S. Ca2Pd3Ge, a new fully ordered ternary Laves phase structure. J. Solid State Chem. 2013, 197, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gießelmann, E.; Pöttgen, R.; Janka, O. Laves phases: Superstructures induced by coloring and distortions. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2023, e202300109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janka, O. Metallic Light-Weight Alloys: Al, Ti, Mg; Pöttgen, R., Jüstel, T., Strassert, C., Eds.; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany; Boston, MA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Massalski, T.B.; Okamoto, H.; Subramanian, P.R.; Kacprzak, L. Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams, 2nd ed.; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto, H. Al-Ti (aluminum-titanium). J. Phase Equilibria 1993, 14, 120–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, V. Al-Ti-V (Aluminum-Titanium-Vanadium). J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. 2005, 26, 276–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batalu, D.; Coşmeleaţǎ, G.; Aloman, A. Critical analysis of the Ti-Al phase diagrams. U.P.B. Sci. Bull. Ser. B 2006, 68, 77–90. [Google Scholar]
- Schuster, J.C.; Palm, M. Reassessment of the binary Aluminum-Titanium phase diagram. J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. 2006, 27, 255–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.; Hemptenmacher, J.; Kumpfert, J.; Leyens, C. Structure and Properties of Titanium and Titanium Alloys in Titanium and Titanium Alloys: Fundamentals and Applications; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH: Weinheim, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Sauthoff, G. Intermetallics in Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH: Weinheim, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pöttgen, R.; Gulden, T.; Simon, A. Miniaturisierte Lichtbogenapperatur für den Laborbedarf. GIT Labor-Fachz. 1999, 43, 133–136. [Google Scholar]
- Palatinus, L.; Chapuis, G. SUPERFLIP—A computer program for the solution of crystal structures by charge flipping in arbitrary dimensions. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2007, 40, 786–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petříček, V.; Dušek, M.; Palatinus, L. (Eds.) The Crystallographic Computing System; JANA 2006; Institute of Physics of the Czech Academy of Sciences: Praha, Czech Republic, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Petříček, V.; Dušek, M.; Palatinus, L. Crystallographic Computing System JANA2006: General features. Z. Kristallogr. 2014, 229, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emsley, J. The Elements; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, P.J.; Coppens, P. Extinction within the limit of validity of the Darwin transfer equations. I. General formalism for primary and secondary extinction and their applications to spherical crystals. Acta Crystallogr. 1974, A30, 129–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duwez, P.E.; Taylor, J.L. Crystal Structure of TiAl. Trans. Am. Inst. Min. Metall. Pet. Eng. 1952, 194, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ence, E.; Margolin, H. Compounds in the Titanium-Rich Region of the Ti-Al System. Trans. Am. Inst. Min. Metall. Pet. Eng. 1957, 209, 484–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemann, S.; Jeitschko, W. Ternary aluminides A6T4Al43 with A = Y, Nd, Sm, Gd-Lu, Th, U and T = Cr, Mo, W. Z. Metallkd. 1994, 85, 345–349. [Google Scholar]
- Frank, F.C.; Kasper, J.S. Complex alloy structures regarded as sphere packings. II. Analysis and classification of representative structures. Acta Crystallogr. 1959, 12, 483–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, F.C.; Kasper, J.S. Complex alloy structures regarded as sphere packings. I. Definitions and basic principles. Acta Crystallogr. 1958, 11, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compton, V.B.; Matthias, B.T. Laves phase compounds of rare earths and hafnium with noble metals. Acta Crystallogr. 1959, 12, 651–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gießelmann, E.C.J.; Engel, S.; Kostusiak, W.; Zhang, Y.; Herbeck-Engel, P.; Kickelbick, G.; Janka, O. Raman and NMR spectroscopic and theoretical investigations of the cubic Laves-phases REAl2 (RE = Sc, Y, La, Yb, Lu). Dalton Trans. 2023, 52, 3391–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.F.; Bakker, H. Mechanically induced structural and magnetic changes in the GdAl2 Laves phase. Phys. Rev. B 1995, 52, 9437–9445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janka, O.; Hoffmann, R.D.; Heying, B.; Pöttgen, R. Structural phase transitions in YPtGe2 and GdPtGe2. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 6075–6088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eustermann, F.; Eilers-Rethwisch, M.; Renner, K.; Hoffmann, R.-D.; Pöttgen, R.; Janka, O. Magnetic properties of the germanides RE3Pt4Ge6 (RE = Y, Pr, Nd, Sm, Gd–Dy). Z. Naturforsch. 2017, 72b, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staliński, B.; Pokrzywnicki, S. Magnetic Properties of Gadolinium-Aluminium Intermetallic Compounds. Phys. Status Solidi B 1966, 14, K157–K160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eustermann, F.; Stegemann, F.; Renner, K.; Janka, O. Platinum Triangles in the Pt/Al Framework of the Intermetallic REPt6Al3 (RE = Ce-Nd, Sm, Gd, Tb) Series. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2017, 643, 1836–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gießelmann, E.C.J.; Engel, S.; El Saudi, I.M.; Schumacher, L.; Radzieowski, M.; Gerdes, J.M.; Janka, O. On the RE2TiAl3 (RE = Y, Gd–Tm, Lu) Series—The First Aluminum Representatives of the Rhombohedral Mg2Ni3Si Type Structure. Solids 2023, 4, 166-180. https://doi.org/10.3390/solids4030011
Gießelmann ECJ, Engel S, El Saudi IM, Schumacher L, Radzieowski M, Gerdes JM, Janka O. On the RE2TiAl3 (RE = Y, Gd–Tm, Lu) Series—The First Aluminum Representatives of the Rhombohedral Mg2Ni3Si Type Structure. Solids. 2023; 4(3):166-180. https://doi.org/10.3390/solids4030011
Chicago/Turabian StyleGießelmann, Elias C. J., Stefan Engel, Israa M. El Saudi, Lars Schumacher, Mathis Radzieowski, Josef Maximilian Gerdes, and Oliver Janka. 2023. "On the RE2TiAl3 (RE = Y, Gd–Tm, Lu) Series—The First Aluminum Representatives of the Rhombohedral Mg2Ni3Si Type Structure" Solids 4, no. 3: 166-180. https://doi.org/10.3390/solids4030011
APA StyleGießelmann, E. C. J., Engel, S., El Saudi, I. M., Schumacher, L., Radzieowski, M., Gerdes, J. M., & Janka, O. (2023). On the RE2TiAl3 (RE = Y, Gd–Tm, Lu) Series—The First Aluminum Representatives of the Rhombohedral Mg2Ni3Si Type Structure. Solids, 4(3), 166-180. https://doi.org/10.3390/solids4030011







