Abstract
The problem of dump recultivation associated with sulfide ore mining is always a challenge for ecologists. A special case is the Arctic, where the specific climate and short vegetative period mean that any traces of such activities can persist for many years. The Monchepluton massif is a Paleoproterozoic, layered Platinum Group Element (PGE) intrusion, which is located in NE Scandinavia, beyond the Arctic Circle. This intrusion is mainly composed of ultramafic and alkaline rocks, represented by dunites, harzburgites, orthopyroxenites, norites, and gabbronorites. In these rocks, there is mineralization of the oxide ores Cr, Fe, and Ti, as well as the sulfide ores Cu, Ni, Fe, and PGE. The massifs of this intrusion were mined in the 20th century. The traces of intensive mining in the area are still visible today. The purpose of this study was to demonstrate the state of the environment and propose its rehabilitation. The authors carried out an inventory of the mining facilities and studies of the area’s rocks, soils, plants, and waters. The results of these studies unequivocally show that the current condition of the site indicates the conditions for an ecological disaster. The most important polluting factor is the presence of metallurgical plants, which are responsible for acid rain and soil pollution. Another threat is uncontrolled mine water outflows. Due to the specific climatic conditions and the vegetation found in the area, the process of rehabilitating the area may be costly and lengthy.
1. Introduction
In NE Scandinavia, there are magmatic and metamorphic rocks that form the Fennoscandia craton [1,2,3,4,5]. Among these rocks are the Kola Series and the Belamorian Series [6], between which is the collisional series (the Lapland Granulite Belt) and a series of Paleoproterozoic PGE-Layered Intrusions, forming numerous occurrences [4,5,7,8]. They were formed during the breakup of the Kenorland Supercontinent [9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16], as a result of the impact of the long-lived hot spot and four magmatism activities [17,18]. Located in NE Scandinavia, the Monchepluton intrusion is one of the oldest in the region and has an age of 2500 million years [19,20,21,22,23]. It constitutes a series of small hills reaching up to 618 m above sea level (Figure 1). The area was glaciated during the Pleistocene period, which resulted in the weathering of the summit parts and their strong smoothing [24]. In the summit parts, there is a stone run, sheep rocks, and rock blocks with a spur character, often with visible signs of weathering [24]. Small ponds and swampy zones are also visible. Below are sharpened slopes with numerous rock walls, and in the valley bottoms there are thick deposits of sands, clays, and gravels of a glacial origin [25]. Small glacial cirques are visible in the Sopcha and Vurechuaivench massifs. The entire massif is surrounded by the large gutter lake Imandra to the east and Lake Moncheozero to the north. It is located in the Arctic zone, which influences specific climatic conditions and vegetation. The climate is cool, with annual averages ranging from +3 °C in the sheltered valley zones to −3 °C in the hills [26]. On average, snow accumulates from October to early May, and there can be perennial patches of snow in the gap zones [27]. The vegetation consists of an understory of a sparse spruce–pine forest with an admixture of birch thickets, sometimes heavily thinned due to acid rain caused by heavy industry [28,29,30]. In the summit areas, this gives way to tundra composed mainly of arctic–alpine plants [31,32,33,34].

Figure 1.
Landscape of the Monchepluton region with a visible metallurgical plant, an acidified lake, and a zone of plant succession in an area of forest destroyed by acid rain.
The Monchepluton intrusion, due to its location, is an area that was mined in the 20th century due to the presence of Cr–Ti–Fe oxide ores and Ni–Cu–Fe sulfides [35,36,37,38], along with the enrichment of PGE mineralization [39,40,41,42,43]. Currently, mining operations have stopped there, and the area is being developed for tourism [44,45,46,47]. However, due to the location of the massif behind the Arctic Circle and the numerous quarries, adits, and shafts, the area poses a threat to nature due to the lack of reclamation processes.
The purpose of this study is to characterize the state of the environment in the Monchepluton area and to identify possible avenues for the reclamation of the area.
2. Study Area Localization
The Monchepluton intrusion is located in NE Scandinavia and is surrounded to the north by Archean iron quartzites belonging to the Banded Iron Formation [2,3], to the west by the Monchetundra intrusion (age 2491 million years) [1,4,5], to the south by the Imandra intrusion (age 2410 million years) [1,4], and to the east by the Khibiny alkaline rock intrusion of a Paleozoic age [48] (Figure 2). The Monchepluton intrusion has an area of 55 km2 [4,5] and consists of two wings: the NKT (Nittis, Kumuzhia, Traviannaya, and several smaller ones including the Dunite Block) and SNP (formed by the massifs of Sopcha, Nyud, Poaz, and Vurechuaivench, located slightly south of them) ranges. The NKT range extends southward, and the SNP band extends latitudinally (Figure 2). The NKT range is built mainly of ultramafic rocks. The SNP band is mainly made up of alkaline rocks. All the ranges have sulfide mineralization, zones of so-called Critical Horizons [4,8], and are composed of intermixed ultramafic rocks, mafic rocks, and breccias of supracrustal rocks; additionally, younger mineral veins formations (mainly dolerite and younger prehnite-carbonatite veins), breccias, and mylonite are also present in the fault zones [3,36,37,38].
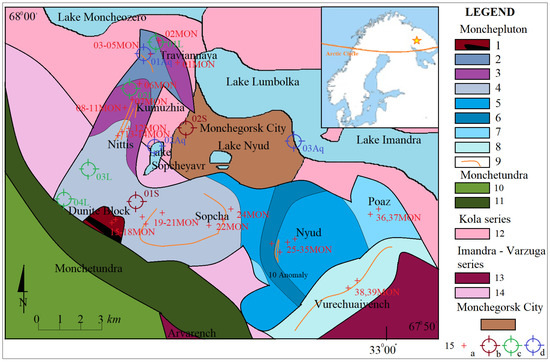
Figure 2.
Geological Sketch of the Monchepluton intrusion (generalized, based on [3,4,23]). Abbreviations: Monchepluton—1. Dunites and chromitites, 2. Harzburgites, 3. Other peridotites, 4. Orthopyroxenites, 5. Olivine norites, 6. Gabbro-norites, 7. Gabbro, 8. Gabbro–anorthosites, 9. Massive sulfide mineralization; Monchetundra—11. Gabbro-anorthosites, and 12. Peridotites; Kola series—12. Archean gneisses; Imandra Varzuga series—13. Hypersthene diorites, 14. Metasediments, and metavolcanites; 15 sample localization: a—rock, b—soil, c—plant, and d—water.
3. Characteristics of the Carried-Out Mining Operational Work
The mining activity in the area in question began in the first half of the 20th century after the re-discovery of sulfide Cu–Ni–Fe mineralization. At that time, intensive field work was carried out, combined with an exploration of deposits and an inventory of the geological structure of the area. This work was carried out in the 1930s by A.E. Fersman [4]. Then, numerous exploration adits and shafts were built. The work accelerated in the 1940s as a result of the war effort and the country’s needs for reconstruction after the war. That was also when a mine was built in the Nittis, Sopcha, and Traviannaya areas. There were also large quarries established in the northern slopes of Sopcha and Nyud [4,5]. There were processing plants in the northern slopes of Nittis and a non-ferrous metal smelter that operated in Monchegorsk (north of Sopcha). At the time, the Monchepluton area was also home to a development of small wooden houses, which served as housing for seconded employees of the mine plants. It is possible that GULAG (General Directorate of Correctional Labor Camps and Colonies in the Soviet Union) prisoners were also used for work, as was the case in Khibiny and elsewhere. Intensive mining operations were carried out until the 1970s. In the late 20th century, chromite deposits were also discovered in the Dunite Block massif area, where a small quarry was also located. During the 1990s, these processes were halted, and the mining equipment was devastated. The buildings left unattended began deteriorating. The same was also true of the line built for the chairlift to Nittis. At present, the Monchegorsk non-ferrous metals smelter (north of Sopcha) and the chairlift on the Nyud slope are in operation. Access to the mining facilities is free, but many adits have collapsed and the buildings are ruined in many places. A television (TV) relay station also operates in the Poaz Peak area. As a result of a community initiative, biking, climbing, and other trails are being created in the Nittis and Nyud areas.
4. Materials and Methods
The authors conducted detailed research in the Monchegorsk region (included Monchepluton) from 2008 to 2020. The study area focused on the NKT and SNP massifs. In particular, these are the areas of adits in the southwestern part of Traviannaya and in the eastern part of Kumuzhia, processing plants and other facilities in the Nittis and Sopcha areas, stone quarries and adits in the Nyud area, and facilities located in the Poaz area. During the fieldwork, the focus was on inventorying mining facilities, geological variability, determining the degree of the devastation of the environment by the earthworks, and where deep excavations were carried out. Collected rocks, along with lichens, were described in the field, where tomographic documentation was also conducted, and the location was determined using GPS. Thin, polished, and exposed plate preparations were made from selected rock samples as well as scrapings. The rock samples were pulverized and solubilized to determine their chemical composition. Plants were grouped and dried. Rock and plant samples were examined using a Leica DM2500P optical microscope in transmitted and reflected light and then tests were performed using a Hitachi SU6600 scanning electron microscope with an EDS (Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy) attachment [49,50,51,52,53,54]. The EDS analysis was performed on the “low-vacuum” setting, without sputtering with a conductive metal. The electron gun was set at 15 kV with an exposure time of 60 s. The scanning beam had a diameter of 2 μm. Geochemical investigations of rocks, soils, and plants were accomplished using ICP-OES (Inductively Coupled Plasma-Optical Emission Spectrometry) by Varian [55,56,57,58,59]. Selected samples were solubilized using a MARS microwave melter and then placed in an argon atmosphere; afterwards, they were fed to the ICP of Varian, where elemental composition analysis took place. Rocks samples were compared with the chondrite standard (as a reference material) [60]. The soil and plants analyses were performed using Loam Soil (7004) and San Joaqain Soil (0709) as reference materials. These studies were performed under the supervision of Dr. Lesia Lata. Water reaction and its electrolytic conductivity were measured using the meter WTW InoLab 1 firm compatible with the pH electrode Hanna Instrument and the conductometric electrode TetraC WTW. Bicarbonate content was determined by titration method with hydrochloric acid in the presence of bromocresol green. Concentrations of anions and cations were determined by ion chromatography (Metrohm MIC 3). Anions (sulphates, chlorides, and nitrates) were separated using the Metrosep A Supp 5-250 column. Cations (calcium, magnesium, sodium, potassium, strontium, and ammonium) were separated using the Metrosep C 2-150 column. In the analytic process, the following procedures and materials were employed: calibration by solutions Merck Anion multi-element standard I, Anion multi-element standard II, Cation multi-element standard VII, and analytical reference material Environment Canada MISSIPPI-14. Recovery of certified reference materials was in a range of 92–113% [61,62,63,64]. The EDS and ICP-MS (Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry) analyses of soils and rocks were carried out at the Department of Geology, Soil Science and Geoinformation; the water analyses were carried out at the Department of Hydrology and Climatology, Maria Curie-Skłodowska University, Lublin. The results of this research are described below.
5. Geology of the Monchepluton
Among the rocks found in Monchepluton are the ultra-basic types: dunites, chromitites, harzburgites, and orthopyroxenites [3,4]. The basic rocks are represented mainly by norites and gabbronorites and meta-anorthosite [3,4]. These rocks are accompanied by oxide and sulfide mineralization. Dunites and chromitites are exposed in the Dunite Block and in smaller amounts as inserts and lenses in Harzburgites in Traviannaya, Kumuzhia, and the northern slopes of Nittis. Dunites are gray-colored rocks with a coarse-crystalline structure and a clumped, disorderly texture. The olivines in these rocks form large crystals in contact with each other. Sometimes small crystals of chromite are also visible in the background of these minerals. Between the olivine crystals in the rock, there are a few, singular orthopyroxene crystals. In some zones of the rock, reaction crown zones composed of serpentine and talc minerals are visible (Figure 3A). Chromitites are steel-gray colored rocks, usually forming layers, between dunites. They are rocks with a coarse crystalline structure and a compact, disorderly texture. Alongside these minerals, talc crystals are also visible (Figure 3B). Small crystals of magnetite (mainly in zones close to serpentinization of olivine) and small sulfides (millerite) are also sometimes visible at these scales.
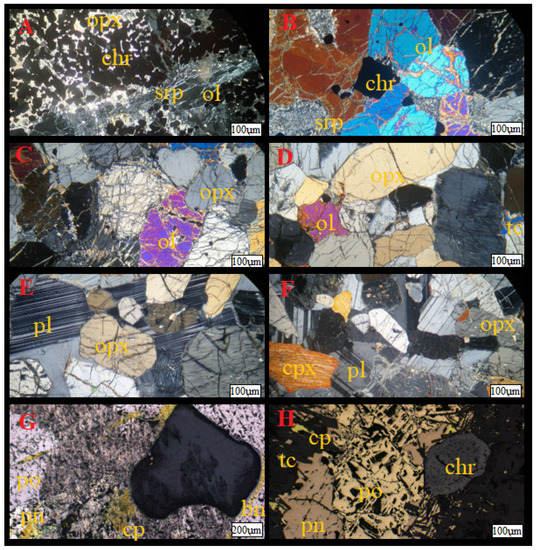
Figure 3.
Microphotograph of the selected rocks types ((A–F) polarizing microscope, (G,H) reflected light): (A)—chromitite with chromite (chr) crystals on the orthopyroxene (opx) and serpentinized (srp) olivines (ol); (B)—dunites with zonal olivines and chromites and serpentine; (C)—harzburgites with orthopyroxene and olivine; (D)—orthopyroxenites with talc (tc); (E)—norites with orthopyroxenes and plagioclases (pl); (F)—gabbronorites with ortho- and clinopyroxenes (cpx) with plagioclases; (G,H) sulfide ores with pentlandite (pn), pyrrhotite (po), chalcopyrite (cp), and sometimes with bornite (bn) accompanied by crystals of talc and zonal chromite.
Harzburgites are exposed mainly in the Traviannaya massif, Kumuzhia, and the northern slopes of Nittis, and as inserts and lenses in the Sopcha orthopyroxenites and the Critical Horizon area of Nyud. These rocks are black-colored, weathered in rusty-brown hues with a coarse-crystalline texture and a compact, disorderly texture. Visible in these rocks are olivines, often heavily fractured and serpentinized. Orthopyroxenes are visible next to these minerals. Small crystals of clinopyroxene, talc, and carbonates are also found. The sulfides present in these rocks are pyrrhotite, pentlandite, and chalcopyrite. In some zones, the sulfides are accompanied by PGE mineralization, represented by tellurides and bismuths of platinum and palladium.
Orthopyroxenites are exposed in the Nittis and Sopcha massifs. These rocks are gray in color, coarse crystalline in structure, and have a compact, disorderly texture. Orthopyroxenes are visible in the rock, which is mainly represented by bronzite. Sometimes, fine aggregates of talc and chromite inclusions are found in pyroxenes.
Norites and olivine norites are found in the Nyud massif. These are gray-colored rocks with a coarse crystalline texture and a compact, unstructured, ophitic texture. In this rock, orthopyroxenes form large crystals, sometimes approximated with each other. Pyroxenes are found against a background of plagioclase, creating an ophitic texture in the rock. Small crystals of sulfides, represented mainly by pentlandite, pyroxene, and chalcopyrite with associated PGE mineralization, can sometimes be seen in the rock.
Gabbronorite and gabbro are exposed in the Nyud and Poaz massifs. They are steel-gray-colored rocks, sometimes weathered in a rusty manner with a coarse-crystalline structure. Orthopyroxene and clinopyroxene are also visible. Next to them are plagioclases, which are numerous in the rock, forming an ophitic texture. There are small crystals of chromite in the pyroxenes. Scattered small crystals of sulfides and PGE mineralization can also be seen in the rock, as in norite.
The meta-anorthosites exposed in the Vurechuaivench massif are gray-colored rocks, with secondary gneissic structures sometimes visible. In this rock there are plagioclases, forming large anhedral crystals, which contact each other. Alongside these minerals, relics of clinopyroxene (diopside) can be seen, most often overgrown with common hornblende. These rocks also contain aggregates of phlogopite and accessory small addition of quartz crystals, featuring relict ilmenite with rutile and titanite. Sulfide mineralization containing PGE phases is also found in these rocks in less altered zones.
Chemical studies of the rock samples in question have been published in another paper (Huber 2021). The chemical composition of the selected samples is presented below (Table 1). The results of the analysis indicate a significant proportion of heavy metals, in particular, iron, titanium, copper, and nickel, and admixtures of zinc and lead. The content of these metals is mainly concentrated in sulfides, which are found in a dispersed form in the rocks in question.

Table 1.
Chemical composition of the selected rocks from Monchepluton (mine element in [wt.%], trace in [ppm]) (as standards, Loam 7004 and San Joaquill soil were used, see Table 2 and Table 4).
6. Results
The Monchepluton massif in question is an area that was mined in the 20th century. In addition, most of the infrastructure—including the tourist infrastructure—that was built there in the past is now devastated and deteriorating. Given the climatic and environmental conditions, the effects of these activities will be clear for a long time to come. The following describes the characteristics of the mining work carried out in Monchepluton and discusses the characteristics of the soils and vegetation therein.
6.1. Characteristics and Present Stage of Recultivation Process
The Monchepluton area was intensively mined in the first half of the 20th century. Numerous traces of mining work date from that time. Mining shafts are visible in the Nittis and Sopcha areas. In the NKT and Nyud massifs, adits, which are partially collapsed, are preserved in varying conditions. Quarries are also visible in these massifs (especially in the N slopes of Sopcha and Nyud) and on the slopes of Nittis, where sulfide veins were explored. In the aforementioned NKT and Nyud massifs, there are numerous heaps of rocks containing ores. In addition, in all of the Monchepluton massifs, earthworks of various scales were carried out, leading to the exposure of rocks and sampling. In the Nittis and Kumuzhia areas, there are ruins of processing plants. Precipitates of copper carbonate and sulfate are often visible in the areas of former adits. Streams flowing from the sites of former adits also often have a color indicative of the metal oxides and hydroxides found in the deposit. In addition, in the area of the northern slopes of Sopcha, a non-ferrous metal smelter still exists, which currently processes ore from Norilsk (Figure 4). The slag is dumped on a heap that enters the lake, strongly acidifying it, which is visible from a distance by the turquoise-greenish color of the water. The Nittis, Nyud, and Poaz massifs are also home to infrastructure features such as ski lifts and a TV station. In the Nittis area, the ski lift is closed and all its infrastructure is in the undergrowth, while parts of the lift (ropes and fragments of instrumentation) are scattered along the slope. The biggest threat to the environment comprises former adits from which streams leak and heaps of sulfide-containing ore. In addition, a major burden on the ecosystem is the smelter, which releases aerosols and causes acid rain in the area, thereby contributing to the death of forests.
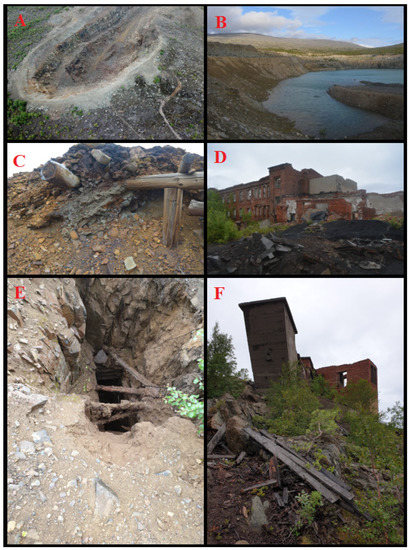

Figure 4.
Photographs from the site, showing various traces of mining activity in Monchepluton: (A)—stone quarry in Nyud area with visible mining levels; (B)—chromitite quarry in Dunite Block with acidified flooded level; (C)—shaft and collapsed adit with visible precipitates; (D)—ruined outbuildings; (E)—unprotected shaft; (F)—ruined mine shaft.
6.2. Results’ Analysis of Soils and Water Samples
In the massif in question, the initial soils are mostly formed as a result of the mechanical fragmentation of the rocks in the mountain slopes due to the action of frost [25,65]. There are also slag admixtures in the mining area, which were formed as a result of various engineering works, forming difficult, complex vitrified compounds [66,67,68]. Typically, soils in these areas have psammitic and psephitic fractions with varying degrees of clasts, being composed mainly of bedrock minerals possibly enriched with post-glacial material. Stone runes are visible in the summit areas (Figure 5).

Figure 5.
Photographs of soils from the Monchepluton area: (A)—initial soils based on regolith in the Kumuzhia area; (B)—a weathering cap over a chromite occurrence.
In the saddle zones, which locally drain due to the action of nivation, there are small ponds and, in their vicinity, there are soils formed by the accumulation of silty material. Among these formations, small soils containing fine aleuritic and pelitic facies retained by snow patches were encountered. Some warmer places form raised bogs. The slopes are dominated by rockfalls, landslides, colluviums, debris flows, and illuviums, especially in gullies, where the transport of rock crumbs occurs due to the action of rainwater. In slope break zones, which occur on rock shelves where crumb material can take hold, pioneer vegetation enters the rock, as well as taller vegetation, especially on slopes with southern exposure. In the valley bottoms, there are numerous accumulations of glacial, fluvioglacial, and fluvial characters. These include numerous moraines along with sands, interlocking with colluviums descending from gullies and stagnant forms. They usually produce podzolic soils with a poorly developed humus layer. The humus layer in the soils in question is usually severely reduced. Various types of boulders are visible throughout the massif, formed as a result of the disintegration of rocks on the slopes and occurring as erratics.
The soil samples that were examined (Figure 2) showed significant proportions of lead, cadmium, copper, chromium, and zinc (Table 2). These are heavy metals, which in these soils come from the decomposition of mainly admixed ores, which are found in the bedrock. Their presence in the soils taken in the area of valleys with fluvioglacial deposits indicates pollution from anthropogenic activities resulting from mining and processing operations [53,54,55,56,57]. The studies in the micro-area found that sample 01S is rich in plagioclase and possesses a small admixture of clay minerals and sulfates. In sample 02S, in addition to plagioclase and clay minerals, an admixture of nickel and titanium was also found. The content of these metals far exceeds the standards, indicating that this environment is highly polluted with metals [67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75]. The reference values of these metals in the soils, water, and plants in the UE are described in the UE Report [76] and other publications [77].

Table 2.
Elemental composition of soil samples from Monchepluton.
Three water samples from the massif were also examined for comparison. The first was collected near the mine water outflow in the area of the so-called Adit 5.1 in the Traviannaya massif; the second came from Lake Sopcheyavr, located in the central part of the intrusion; and the third from Lake Imandra in the Monchepluton area (Figure 2, Table 3). The relatively high pH may indicate that from the adit to the water intake site (at its outflow), these waters may have been enriched in carbonate components of Anthropogenic or Holocene origins.

Table 3.
Chemical composition of the water samples from Monchepluton.
The analyses of the water samples from the Monchepluton area were conducted to solve the problem of the influence of anthropogenic factors in the study area [27,29,30,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75]. The samples were collected from surface waters during the summer (13 July). The ions studied indicate calcium and magnesium content with a significant proportion of sulfate, indicating the influence of sulfide ores on the chemical composition of the waters. The sampling location was determined based on observations of possible exposure to pollutants. This was hypothesized to originate from melting snow, with water flowing from stagnant water and a water supply intake. The content of these components suggests the occurrence of anthropogenic pollution.
6.3. Result of the Analysis of the Plant Samples
The Monchepluton hills are small, flattened hills, with a character of separate isolated mountain ranges cut by wide valleys with numerous fleshy postglacial deposits. In the bottoms of these valleys, it is likely that taiga once grew, although due to human activity and the heavy pollution of the area today they are rather desolate wastelands not infrequently populated with stumps of dried trees and presenting numerous rusty patches on the surface of rocks. In the shaded zones of the massif (from the metallurgical combine), one can see a secondary succession of plants with visible small trees such as birch, pine, spruce, and juniper (Figure 6). The forestation of the farthest massif appears to be in a much better condition: in Vurechuaivench, a lush pine–spruce forest occurs in the valleys, transitioning higher into a forest–tundra with dwarf pine, spruce, birch, and rowan trees. Higher up, dwarf birch, veined willow, and the tundra floor appear. The mosses and lichens that occur in this area form accumulations throughout the area’s profile, and in the summit areas, they overgrow in areas where little if any relict soil has formed, while the lichens are usually directly adhered to rocks.

Figure 6.
Examples of vegetation in the Monchepluton area: (A)—destroyed forest in the Sopcha area; (B)—forest–tundra in the Vurechuaivench area.
These lichens often form quite extensive, characteristic mats covering almost the entire visible surface of the rock (Figure 7). Microscopically magnified preparations show numerous impurities, sometimes contributing to the discoloration of these organisms. Numerous structures of a taxonomic nature (protuberances, discoloration, etc.) are also visible. The mosses and lichens examined are mainly Rhizocarpon and Cladonia sp., which occur mainly on the surface of rocks [31,32,33].

Figure 7.
Examples of photographs of lichens from the study area: (A)—lichens of cladonia sp., in the vicinity of a clump of mosses and grasses; (B)—the lichen Cladonia chlorophaea.
Analyses of four lichen samples were performed (Figure 2). The samples are relatively geochemically diverse. Analyzing the following data (Table 4), it can be concluded that in the examined lichens, sometimes quite significant amounts of Ti and Fe, as well as Cu, Ni, Zn, Pb, and Cr, were found, significantly exceeding the background standards.

Table 4.
Results of ICP analyses of plant samples from the Monchepluton [ppm].
The cadmium content in one sample reaches 2 ppm, while the concentration of lead in these samples is more than 100 ppm. Elevated copper, chromium, and nickel contents of sometimes as much as 40–50 ppm were also found in these samples. The manganese content in the two samples is more than 100 ppm and the proportion of titanium can be determined in weight percentages, as in iron. Elevated contents of heavy metals, especially Cr, Ni, Cu, Cd, and Pb, are associated with the weathering zone of sulfides found in the heaps of the sites in question. These values correspond to the measured content of these metals in the soils (see Table 2). It seems that these elements can accumulate in the plants in question.
7. Discussion
The surveyed area requires a great deal of serious work to be rehabilitated. This contributes to some plant successions in previously devastated areas. Some shafts are still permeable. Their historical value may still be of interest; hence, it may be worth preserving them (so that a museum can be organized there in the future), but they need to be protected from water entering the mine. A major challenge remains regarding the soil. Its self-cleaning process will probably take many years. Another problem is the ruined infrastructure, which will have to be removed, as it poses a danger to both animals and people. Some of the buildings could be used for tourism purposes, but this would require a considerable amount of money for their renovation [45,47,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90]. Left to themselves, they will continue deteriorating. The minimum protection would be to clean the site of the remains of the infrastructure (cables, wires, steel cables, etc.). Securing former surface-mining operations seems to be a separate problem. Quarries could be adequately protected against natural wall-fall processes. With a relatively small financial outlay, they could be adapted for artistic purposes. Such a need is evidenced by the fact that in these mountains there are now numerous trails marked out independently by individuals (marked with paint, old tires, and ribbon trails, shown in Figure 8). In the massifs farthest from the city, wildlife appears, as evidenced by the tracks of bears and other animals visible in the field. Due to climatic conditions and the short vegetative period, the biological reclamation of the area will take many years.

Figure 8.
Examples of field trail delineation by residents’ initiative: bike trail marked with used tires (A) and paint-painted markings on rocks (B).
8. Conclusions
The Monchepluton area is a series of massifs containing alkaline and ultramafic rocks with Cr–Ti–Fe oxide mineralization and PGE-doped Cu–Ni–Fe sulfide mineralization. They were heavily mined in the 20th century, resulting in numerous mining operations that are still discernable on the ground today. Unprotected shafts, adits, and heaps as well as smoky non-ferrous metal-smelting plants caused an ecological disaster. The composition of the plants indicates elevated levels of heavy metals such as Pb, Ni, and Cu. Hydrological relations have also been disturbed, and due to the lack of proper protection works, they pose a constant threat. Some mitigation of the negative impact on nature was achieved via the installation of filters on the chimneys of the nonferrous metal smelter. However, further reclamation may be very costly. The most pressing problem seems to be securing the ruins, which pose a threat to humans and animals, as well as cleaning the area. The next step is to secure water relations. The accumulated contamination in the soil and plants will require many more years of work.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.H. and O.I.; methodology, M.H.; software, M.H. and S.C.; validation, M.H. and O.I.; formal analysis, M.H. and S.C.; investigation, M.H.; resources, M.H.; data curation, M.H. and O.I.; writing—original draft preparation, M.H.; writing—review and editing, M.H. and O.I.; visualization, M.H.; supervision, M.H.; project administration, M.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Lesa Lata for performing geochemical studies of soils and plants and Halas for isotopic analyses.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bayanova, T.B. Age of Benchmark Geological Complexes of the Kola Region and Magmatism Processes Action; Nauka: St. Petersburg, Russia, 2004; p. 174. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Glebovitsky, V.A. Early Precambrian of the Baltic Shield; Nauka: St. Petersburg, Russia, 2005; p. 710. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Huber, M. Evolution of the Kola-Lapland Mobile Belt in PGE-Bearning Paleoproterozoic Layered Intrussion of Monchepluton; Maria Curie-Sklodowska University Press: Lublin, Poland, 2021; p. 234. [Google Scholar]
- Pozhilienko, V.I.; Gavrilenko, B.V.; Zhirov, C.V.; Zhabin, S.V. Geology of mineral areas of the Murmansk Region. Apatity Russ. Acad. Sci. 2002, 360. [Google Scholar]
- Sharkov, E.V. Formation of Layered Intrusions and Related Mineralization; Scientific World: Moscow, Russia, 2006; p. 364. [Google Scholar]
- Mitrofanov, F.P. Geological characteristics of Kola Peninsula. Apatity Russ. Acad. Sci. 2000, 166. [Google Scholar]
- Hanski, E.; Huhma, H.; Smolkin, V.F.; Vaasjoki, M. The age of the ferropicritic volcanics and comagmatic Ni-bearing intrusions at Pechenga, Kola Peninsula, USSR. Bull. Geol. Soc. Finl. 1990, 62, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrofanov, F.P. Metallogeny of the Kola-Karelian Region, Baltic Shield. In Fundamental Geological Problems of Mineral Deposits Metallogeny; IGEM RAS: Moscow, Russia, 2010; p. 257. [Google Scholar]
- Lubnina, N.V.; Pasenko, A.M.; Novikova, M.A.; Bubnov, A.Y. The East European Craton at the End of the Paleoproterozoic: A New Paleomagnetic Pole of 1.79–1.75 Ga. Mosc. Univ. Geol. Bull. 2016, 71, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubnina, N.V.; Slabunov, A.I. Reconstruction of the Kenorland Supercontinent in the Neoarchean Based on Paleomagnetic and Geological Data. Mosc. Univ. Geol. Bull. 2011, 66, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozhko, N.A. Supercontinental Cyclicity in the Earth’s Evolution. Mosc. Univ. Geol. Bull. 2009, 64, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozhko, N.A. Intraplate Basic–Ultrabasic Magmatism Through Time in Terms of Supercontinental Cyclicity. Mosc. Univ. Geol. Bull. 2010, 65, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozhko, N.A. On Two Types of Supercontinental Cyclicity. Mosc. Univ. Geol. Bull. 2011, 66, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, R.; Bleeker, W. Large igneous provinces (LIPs), giant dyke swarms, and mantle plumes, significance for breakup events within Canada and adjacent regions from 2.5 Ga to the Present. Can. J. Earth Sci. 2010, 47, 695–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, R.E.; Srivastava, R.K. India’s place in the Proterozoic world, constraints from the large igneous provinces (LIP) record. In Indian Dyke Geochemistry, Geophysics, and Geochronology; Srivastava, R.K., Sivaji, C., Rao, N.V.C., Eds.; Narosa Publishing House Pvt. Ltd.: New Delhi, India, 2008; pp. 41–56. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, D.A.D.; Li, Z.X.; Murphy, J.B. Four-dimensional context of Earth’s supercontinent. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2016, 424, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baluev, A.S.; Zhuravlev, V.A.; Przhiyalgovskii, E.S. New Data on the Structure of the Central Part of the White Sea Paleorift System. Doklady Earth Sci. 2009, 427A, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayanova, T.B.; Kunakkuzin, E.L.; Serov, P.A.; Fedotov, D.A.; Borisenko, E.S.; Elizarov, D.V.; Larionov, A.V. Precise U-Pb (Id-Tims) and SHRIMP-II ages on single zircon and Nd-Sr signatures from Achaean TTG and high aluminum gneiss on the Fennoscandian Shield. In Proceedings of the 32nd Nordic Geological Winter Meeting, Helsinki, Finland, 13–15 January 2018; p. 172. [Google Scholar]
- Huber, M.; Halas, S.; Piestrzyński, A. Petrology of gabroides and isotope signature of sulfide mineralization from Fedorov-Pansky layered mafic intrusion, Kola Peninsula, Russia. Geochronometria 2009, 33, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, M.; Hałas, S.; Serov, P.A.; Ekimova, N.A.; Bayanova, T.B. Stable isotope geochemistry and Sm-Nd, U-Pb dating of sulphides from layered intrusions in the northern part of Baltic Shield. Cent. Eur. Geol. 2013, 56, 134–135. [Google Scholar]
- Bayanova, T.; Korchagin, A.; Mitrofanov, A.; Serov, P.; Ekimova, N.; Nitkina, E.; Kamensky, I.; Elizarov, D.; Huber, M. Long-Lived Mantle Plume and Polyphase Evolution of Palaeoproterozoic PGE Intrusions in the Fennoscandian Shield. Minerals 2019, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryshov, N.M.; Mokrushin, A.V. Mesoarchean gabbroanorthosite magmatism of the Kola region: Petrochemical, geochronological, and isotope-geochemical data. J. Petrol. 2011, 19, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrofanov, F.P.; Smolkin, V.F. Stratified Intrusions of the Monchegorsk ore Region: Petrology, Mineralization, Isotopes, Deep Structure, 2nd ed.; Kola Scientific Center, Russian Academy of Sciences: Apatity, Russia, 2004; p. 344. [Google Scholar]
- Korsakova, O.P. Pleistocene marine deposits in the coastal areas of the Kola Peninsula (Russia). Quat. Int. 2009, 206, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møer, J.J.; Yevzerov, V.Y.; Kolka, V.V.; Corner, G.D. Holocene raised-beach ridges and sea-ice-pushed boulders on the Kola Peninsula, northwest Russia: Indicators of climatic change. Holocene 2001, 12, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aune, S.; Hofgaard, A.; Söderström, L. Contrasting climate- and land-use-driven tree encroachment patterns of subarctic tundra in northern Norway and the Kola Peninsula. Can. J. For. Res. 2011, 41, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caritat, P.; Reimann, C.; Äyräs, M.; Niskavaara, H.; Chekushin, V.A.; Paclov, V.A. Stream water geochemistry from selected catchments on the Kola Peninsula (NW Russia) and in neighbouring areas of Finland and Norway: 1. Elements levels and sources. Aquati. Geochem. 1996, 2, 149–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aamlid, D.; Venn, K. Methods of monitoring the effects of air pollution on forest and vegetation of eastern Finnmark, Norway, Norw. J. Agr. Sci. 1993, 7, 71–87. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, A.; Patel, K.S.; Lata, L.; Huber, M.; Li, P.; Allen, J.; Corn, W. Contamination of water, soil and plant with arsenic and heavy metals. In Environmental Arsenic in a Changing World; Yong-Guan, Z., Huaming, G., Prosun, B., Jochen, B., Arslan, A., Ravi, N., Eds.; CRC Press/Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; pp. 386–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.S.; Yadav, A.; Sahu, Y.; Sahu, P.K.; Lata, L.; Huber, M.; Corns, W.T.; Martín-Ramos, P. Tree Bark as a Bioindicator for Arsenic and Heavy Metal Air Pollution in Rajnandgaon District, Chhattisgarh, India. J. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste 2020, 24, 05019006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinov, A.S.; Koryakin, O.A.; Makarova, V.V. Red Book of the Murmansk Region, 2nd ed.; Asia-Print: Kemerovo, Russia, 2014; p. 584. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Konstantinova, N.A. Flora and Vegetation of Murmansk Region; Kola Science Centre, Rusian Academy of Sciences: Apatity, Russia, 1999; p. 175. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Koroleva, N.E. Phytosociological survey of the tundra vegetation of the Kola Peninsula. J. Veget. Sci. 1994, 5, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trutnev, Y.P.; Kamelin, R.V. Red Book of the Russian Federation (Plants and Mushrooms); Partnership of scientific publications KMK; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 2008; p. 855. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Elizarova, I.R.; Bayanova, T.B. Mass-spectrometric REE analysis in sulphide minerals. J. Biol. Earth Sci. 2012, 2, E45–E49. [Google Scholar]
- Huber, M.; Hałas, S.; Lata, L.; Mitrofanov, F.P.; Neryadovski, Y.N.; Bayanova, T.B. Table isotope results of sulfides from old mafic intrusions in the Kola Peninsula (N Russia). J. Biol. Earth Sci. 2014, 4, 27–28. [Google Scholar]
- Huber, M.; Hałas, S.; Neradovski, Y.; Bayanova, T.; Mokrushin, A.; Lata, L. Stable isotope geochemistry of sulfides from intrusion in Monchegorsk, Northern part of Baltic Shield. Geochronometria 2016, 43, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolkin, V.F.; Mokrushin, A.V.; Bayanova, T.B.; Serov, P.A.; Ariskin, A.A. Magma feeding paleochannel in the Monchegorsk ore region: Geochemistry, isotope U-Pb and Sm-Nd analysis (Kola region, Russia). J. Min. Inst. 2022, 255, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayanova, T.B.; Ludden, J.; Mitrofanov, F.P. Timing and duration of Palaeoproterozoic events producing ore-bearing layered intrusions of the Baltic Shield: Metallogenic, petrological and geodynamic implications. Palaeoproterozoic Supercontinents Glob. Evol. 2009, 323, 165–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisenko, E.S.; Bayanova, T.B.; Nerovich, L.I.; Kunakkuzin, E.L. The Paleoproterozoic Monchetundra Mafic Massif (Kola Peninsula): New Geological and Geochronological Data. Dokl. Earth Sci. 2015, 465, 1107–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grebnev, R.A.; Rundkvist, T.V.; Pripachkin, P.V. Geochemistry of Mafic Rocks of the PGE -Bearing Vurechuaivench Massif (Monchegorsk Complex, Kola Region). Geochem. Int. 2014, 52, 726–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grokhovskaya, T.L.; Ivanchenko, V.N.; Karimova, O.V. Geology, mineralogy, and genesis of PGE mineralization in the South Sopcha Massif, Monchegorsk Complex, Russia. Geol. Ore Depos. 2012, 54, 347–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokrushin, A.V.; Kudyrashov, V.M.; Huber, M. First Discovery of sperrylite in archean patchemvarek gabroanorthosite (Kola region, Russia). In Proceedings of the 12th International Platinum Symposium, Yekaterinburg, Russia, 11–14 August 2014; pp. 307–308. [Google Scholar]
- Huber, M.; Zhigunova, G.; Menshakova, M.; Iakovleva, O.; Karimova, M. Geoheritage of the Monchegorsk Igneous Layered Paleoproterozoic Intrusion (Kola Peninsula, Arctic Russia): Evaluation and Geotourism Opportunities. Heritage 2021, 4, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, P.; Lauri, L.S.; Voytekhovsky, Y.L. Barents Tour for Geotourists; Kolarctic, Rovaniemi Finland Publishing House: Rovaniemi, Finland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Murmansk Visitor Center. Available online: https://visitmurmansk.info/en/ (accessed on 2 July 2022).
- Tourist Potential of Murmansk Region. Available online: www.gov-murman.ru (accessed on 5 July 2022).
- Arzamastsev, A.A.; Mitrofanov, F.P. Paleozoic Plume–Lithospheric Processes in Northeastern Fennoscandia: Evaluation of the Composition of the Parental Mantle Melts and Magma Generation Conditions. Petrology 2009, 17, 300–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizilkaya, R.; Askin, T.A.; Bayrakli, B.; Saglam, M. Microbiological characteristics of soils contaminated with heavy metals. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2004, 40, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colin, V.L.; Villegas, L.B.; Abate, C.M. Indigenous microorganisms as potential bioremediators for environments contaminated with heavy metals. International Biodeterioration et Biodegradation 2012, 69, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hseu, Z.Y. Evaluating heavy metal contents in nine composts using four digestion methods. Bioresour. Technol. 2004, 95, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydinalp, C.; Marinova, S. Distribution and Forms of Heavy Metals in Some Agricultural Soils. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2003, 12, 629–633. [Google Scholar]
- Puig, S.; Thiele, D.J. Molecular mechanisms of copper uptake and distribution. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2002, 6, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastre, J.; Sahuquillo, A.; Vidal, M.; Rauret, G. Determination of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn in environmental samples: Microwaveassisted total digestion versus aqua regia and nitric acid extraction. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 462, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipiak-Szok, A.; Kurzawa, M.; Szłyk, E. Determination of toxic metals by ICP-MS in Asiatic and European medicinal plants and dietary supplements. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2015, 30, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, I.C.H.; Chen, K.S.; Huang, Y.L.; Lee, P.N.; Lin, T.H. Determination of trace elements in some natural drugs by atomic absorption spectrometry. Biol Trace Elem. Res. 2000, 76, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moor, C.; Lymberopoulou, T.; Dietrich, V.L. Determination of Heavy Metals in Soils, Sediments and Geological Materials by ICP-AES and ICP-MS. Mikrochim. Acta 2001, 136, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewen, N.; Mathew, S.; Schenkenberger, M.; Raglione, T. A rapid ICP-MS screen for heavy metals in pharmaceutical compounds. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2004, 35, 739–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackley, K.L.; Sutton, K.L.; Caruso, J.A. The use of ICP–MS as a detector for elemental speciation studies. In Element Speciation–New Approaches for Trace Elemental Analysis. Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry; Caruso, J.A., Sutton, K.L., Ackley, K.L., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; Volume 33, p. 9. [Google Scholar]
- Rudnick, R.L.; Gao, S. Composition of the Continental Crust. In Treatise on Geochemistry; Turekian, K., Holland, H., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; Volume 3, pp. 1–64. [Google Scholar]
- Ammann, A.A. Speciation of heavy metals in environmental water by ion chromatography coupled to ICP–MS. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2002, 372, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malassa, H.; Al-Qutob, M.; Al-Khatib, M.; Al-Rimawi, F. Determination of Different Trace Heavy Metals in Ground Water of South West Bank/Palestine by ICP/MS. J. Environ. Prot. 2013, 4, 818–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sereshti, H.; Heravi, Y.E.; Samadi, S. Optimized ultra sound-assisted emulsification microextraction for.simultaneous trace multielement determination of heavy metals in real water samples by ICP-OES. Talanta 2012, 97, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayon, G.; Birot, D.; Bollinger, C.; Barrat, J.A. Multi-Element Determination of Trace Elements in Natural Water Reference Materials by ICP-SFMS after Tm Addition and Iron Co-precipitation. Geostandarts Geoanalytical Res. 2010, 35, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paszko, T.; Matysiak, J.; Kamiński, D.; Pasieczna–Patkowska, S.; Huber, M.; Król, B. Adsorption of bentazone in the profiles of mineral soils with low organic matter content. PLoS ONE 2020, 1, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jończy, I.; Huber, M.; Lata, L. Vitrified metallurgical wastes after zinc and lead production from the dump in Ruda Śląska in the aspect of mineralogical and chemical studies. Miner. Resour. Manag. 2014, 30, 161–174. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, A.; Sahu, P.K.; Patel, K.S.; Lata, L.; Huber, M.; Corns, W.T.; Allen, J.; Martín-Ramos, P. Assessment of Arsenic and Heavy Metal Pollution in Chhattisgarh, India. J. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste 2020, 24, 05019008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Yadav, A.; Ramteke, S.; Chakradhari, S.; Patel, K.S.; Lata, L.; Huber, M.; Li, P.; Allen, J.; Corns, W. Contamination of arsenic and heavy metals in coal exploitation area. In Environmental Arsenic in a Changing World; Zhu, Y.G., Guo, H., Bhattacharya, P., Bundschuh, J., Ahmad, A., Naidu, R., Eds.; CRC Press/Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; pp. 381–385. [Google Scholar]
- Koptsik, G.N.; Niedbaiev, N.P.; Koptsik, S.V.; Pavluk, I.N. Heavy metal pollution of forest soils by atmospheric emissions of Pechenganikel smelter. Eurasian Soil Sci. 1999, 32, 896–903. [Google Scholar]
- Koptsik, S.V.; Koptsik, G. Soil pollution in terrestial ecosystems of the Kola peninsula, Russia. In Proceedings of the 10th international Soil Conservation Organization Meeting, West Lafayette, Indiana, 24–29 May 1999; pp. 212–216. [Google Scholar]
- Pereverzev, V.N. Peat Soils of the Kola Peninsula. Eur. Soil Sci. 2005, 38, 457–464. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, R.; Yadav, A.; Ramteke, S.; Patel, K.S.; Lata, L.; Huber, M.; Corns, W.T.; Martín-Ramos, P. Heavy Metal Pollution in Surface Soil of Korba Basin, India. J. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste 2019, 23, 05019004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatyeva, M.; Yurak, V.; Pustokhina, N. Recultivation of Post-Mining Disturbed Land: Review of Content and Comparative Law and Feasibility Study. Resources 2020, 9, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paczynski, B. Influence of geogenic and anthropogenic groundwater. In The Changes of Water as a RESULT of Natural and Anthropogenic Processes; Dynowska, I., Ed.; Iagiellonian University Press: Krakow, Poland, 1993; pp. 211–270. [Google Scholar]
- Pekkaa, L.; Ingria, J.; Widerlund, A.; Mokrotovarova, O.; Riabtseva, M.; Öhlander, B. Geochemistry of the Kola River, northwestern Russia. Appl. Geochem. 2004, 19, 1975–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammel, M.; Holzwarth, F. Heavy Metals (Trace Elements) and Organic Matter Content of European Soils. 1999. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/environment/archives/waste/sludge/pdf/heavy_metals_feasibility_study.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Tóth, G.; Hermann, B.; Da Silva, M.R.; Montanarell, L. Heavy metals in agricultural soils of the European Union with implications for food safety. Environ. Int. 2016, 88, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Z.; Luan, F.; Xiong, H.; Wang, Z.; Shi, H. Analysis on spatial distribution characteristics and geographical factors of Chinese National Geoparks. Cent. Eur. J. Geosci. 2014, 6, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravis, I.; Német, H.K.; Twemlow, C.; Németh, B. The Case for Community-Led Geoheritage and Geoconservation Ventures in Māngere, South Auckland, and Central Otago, New Zealand. Geoheritage 2020, 12, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürer, A.; Gürer, Ö.F.; Sangu, E. Compound geotourism and mine tourism potentiality of Soma region, Turkey. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hose, T.A. 3G’s for Modern Geotourism. Geoheritage 2012, 4, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, M.; Iakovleva, O. Tourism, Scientific, and Didactic Potential of the Ultrabasic-Alkaline Intrusion in Afrikanda with Perovskite Mineral (Kola Peninsula, N Russia) and of the Related Built Heritage. Heritage 2021, 4, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, M.; Rusek, A.; Menshakova, M.; Zhigunova, G.; Chmiel, S.; Iakovleva, O. Possibilities of Sustainable Development including Improvement in Air Quality for the City of Murmansk-Examples of Best Practice from Scandinavia. Climate 2022, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinnyovsky, D.; Sachkov, D.; Tsvetkova, I.; Atanasova, N. Geomorphosite Characterization Method for the Purpose of an Aspiring Geopark Application Dossier on the Example of Maritsa Cirque Complex in Geopark Rila, Rila Mountain, SW Bulgaria. Geoheritage 2020, 12, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vdovets, M.S.; Silantiev, V.V.; Mozzherin, V.V. A National Geopark in the Republic of Tatarstan (Russia): A Feasibility Study. Geoheritage 2010, 2, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voytekhovsky, Y.L. Geological Outdoor Map 1:50,000 with a Guidebook; Kolarctic, Rovaniemi Finland Publishing House: Rovaniemi, Finland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, F. Safeguarding Geoheritage in Ethiopia: Challenges Faced, and the Role of Geotourism. Geoheritage 2020, 12, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, K.S.; Chun, S.S.; Moon, K.O. Outstanding Geoheritage Values of the Island-Type Tidal Flats in Korea. Geoheritage 2020, 12, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangmo, G.T.; Kagou, A.D.; Nkouathio, D.G.; Gountié, M.D.; Kamgang, P. The Volcanic Geoheritage of the Mount Bamenda Calderas (Cameroon Line): Assessment for Geotouristic and Geoeducational Purposes. Geoheritage 2017, 9, 255–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pactwa, K.; Woźniak, J.; Dudek, M. Coal mining waste in Poland in reference to circular economy principles. Fuel 2020, 270, 117493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).