Abstract
The main purpose of the study was the absorption of heavy metals in the leaves of forest tree species, which were planted in two different plots for forestry use and environmental restoration. Four species were studied Pinus brutia, Robinia pseudoacaccia, Quercus trojana and Fraxinus ornus. Forty-eight leaf samples were collected which consisted of six samples from each species at each plot. The heavy metal concentrations in the leaves were measured for the following nine heavy metals: iron (Fe), copper (Cu), chromium (Cr), nickel (Ni), cadmium (Cd), manganese (Mn), zinc (Zn), cobalt (Co) and lead (Pd). The determinative estimation of metal concentration was carried out in the clear filtrate, using ICP-OES. Statistically significant differences in the concentrations of the heave metals were found among the species, as well as between the two plots. It was only in Robinia peudoacacia’s leaves that the cadmium concentration showed a statistical difference among the other species. The same applied for manganese in Quercus trojana’s leaves and zinc for Pinus brutia. The careful selection and planting of the appropriate forest tree species provides for an overall improvement in the environment in heavy metal polluted sites, such as those resulting from thermal power plants.
1. Introduction
Lignite is the most common type of coal in Greece, occurring in more than 60 sedimentary basins [1]. Lignite is exclusively used in Greece for electrical power regeneration and has led to the production of the most cost-effective kilowatt hour within the European Community [2]. Four Thermal Power Stations (TPSs) with more than 4000 MW total installed capacity are located in the Ptolemais-Amynteon basin, which is the most important natural lignite basin in south Europe and is located in west Macedonia, Greece [3].
The main potential source of air and soil pollution in this area are the four TPSs, which release fly ash into the atmosphere [4]. Fly ash is the main waste residue produced during pulverized lignite combustion and is collected by electrostatic precipitators. Despite the fact that most thermal power plants have been equipped with electrostatic precipitators in recent years, significant amounts of fly ash are still emitted into the atmosphere because of the high rate of lignite combustion [5]. Several studies have demonstrated the environmental impacts of fly ash air pollution [5,6,7,8,9,10,11]. This fly ash contains heavy metals in concentrations comparable to, and in some cases greater than, those found in the upper continental crust [4].
With the construction and operation of the four TPSs, the vegetation of the area has been exposed to pollution emissions. As a result, the environmental situation has been additionally complicated by the designation of special areas with reclaimed soils where lignite has been exhausted. Such reclaimed soils have led to extremely harsh stress conditions for plant survival [12].
The restoration of old mine areas, where lignite has been exhausted, is one of the goals of the Public Power Corporation (PPC). To achieve this, the PPC has selected woody species to remove pollutants from the environment or to render them harmless [11]. The absorption and accumulation of heavy metals in plants are the result of the influence of some external factors, such as the concentration of heavy metals in fly ash, atmospheric deposition, rainfall, plant growth stage, and soil properties. The solubility of heavy metals generally increases with the decrease in the pH of soil; the high values of soil pH could represent a reduced metal transfer from soil to plants [13].
Table 1 represents the concentrations of important heavy metals in fly ashes and soils that were measured in the same area [2,14,15,16]. The pollution of the area’s soils from fugitive fly ash emissions is minimized, however, due to the alkalinity of the Greek soils and the alkalinity of the fly ash [14]. The main pathway of heavy metal accumulation by plants is via atmospheric position.

Table 1.
Concentrations, in ppm, of heavy metals of environmental interest in fly ashes and reclaimed soils.
Uptake and accumulation of heavy metals in woody species follow two different pathways, one via the root system and the second via the leaves [11,17,18,19].
Trees via their leaves reduce air pollution in two ways: with direct removal of pollutants from the air, and with indirect reduction through preventing the creation of secondary air pollutants. Direct reduction is carried out through pollutant absorption by the stomata of leaves. In addition, the crown of the trees stops pollutant movement and diffusion [20] by absorbing them, via the wet surface of their leaves [21]. Indirect pollution reduction occurs due to the tree’s cooling effect of the atmospheric temperature (via shading and evapotranspiration mechanisms), which in turn leads to lower rates of chemical reactions in the atmosphere and reduces secondary pollutant production by interfering with VOC production by the leaves/needles [22,23].
The aim of this study was to determine the levels of airborne heavy metal contamination (Cu, Fe, Mn, Zn, Cd, Co, Cr, Ni, Pb) in trees leaves at reforestation locations (four forest species and two planting distances) with reclaimed soils in post-mining landscapes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The Ptolemais region is in northwest Greece, where the biggest lignite deposits of Greece are found. Four Thermal Power Stations (TPSs) are located in this basin. About 64 Mt of lignite, produced by open-cast mining, is used in the TPSs. Knowing that around 15% of the fuel is converted to ash, and assuming 99.9% collection efficiency for the electrostatic precipitators, the total amount of fly ash which is released into the atmosphere is about 9.6 Kt annually [5,24,25].
The climate is continental Mediterranean, characterized by low temperatures during winter (−1.3 °C to 6.3 °C) and high temperatures during summer (20.1 °C to 28.5 °C). Prevailing winds are weak to moderate, and their direction is NW/SE [8,26,27].
2.2. Methods
The research was conducted in the main lignite field of PPC-Ptolemais. There were two different plantation locations, with one being utilized for forestry and the second for environmental restoration. The main purpose of plantations in the first area was the production of timber. Three broad-leaved trees were planted there: Robinia pseudoacaccia L. (Black Locust), Quercus trojana Webb. (Macedonian Oak) and Fraxinus ornus L. (Flowering Ash). These were planted in a 2.5 m × 2.5 m planting joint, and one conifer species Pinus brutia Ten. (Calabria or Turkish Pine) was planted in a 2 m × 3 m planting joint.
The main purpose of plantations in the second area was for environmental restoration, in order to shape the landscape of the area in such a way that it is directly related to its natural features. The forest tree species used for the creation of areas for the purpose of environmental restoration was the conifer Pinus brutia in a 5 m × 5 m planting joint, the broadleaf species Robinia pseudoacaccia L., Quercus trojana Webb. and Fraxinus ornus L. in a 5 m × 5 m planting joint. It is important that in such plantations, the species selected for planting (in addition to forestry use or ecological-aesthetic restoration) is firstly to survive, and secondly to have the ability to retain pollutants.
A variety of forest species have been planted in the past in the study area. However, three species, Pinus brutia, Quercus trojana Webb. and Fraxinus ornus L. were planted for the first time. Therefore, we decided to study these species. The leaf morphology differs among the four species, i.e., Pinus brutia’s needles are rough, while Robinia pseudoacaccia and Fraxinus ornus leaves are compound and Pinus brutia’s leaves are lamina [27,28,29,30,31,32,33].
We collected leaves from six trees of each species at each plot (n = 48). The samples were collected from the same part of the plants, since the content in heavy metals varies depending on the part of the plants [34]. Leaves were sampled uniformly around the lower foliage (1.5 to 2.0 m) [26] and from the four points of the horizon [35,36].
The sampled trees were selected using systematic sampling [37]. The repetitions are of vital importance, since pollutant concentration may vary among different species and even for the same species [34]. The sampling was carried out after a prolonged rainless period (end of summer), [37,38].
All samples were collected following Kovác’s suggestion [37]. At both plantation locations, 48 foliage samples were taken, with 24 samples from each location and 6 samples taken from each species. Leaves were sampled uniformly from the four points of the horizon [35,36] and at a fixed height of around 2 m from the ground [26]. Leaf samples (approximately 200 g) were collected in the morning, placed in paper bags and oven-dried at 80 °C for 24 h. All samples were washed with distilled water, desiccated at room temperature to constant weight, ground and sieved with a 2 mm mesh (0.2 mm Culatti 220 Model, 301122). All measurements were carried out on fully developed leaves, undamaged by insects, and with no color differentiations. For evergreen coniferous species, biennial needles were selected [39,40,41,42].
Chemical analyses were carried out to determine of copper (Cu), iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), zinc (Zn), cadmium (Cd), cobalt (Co), chromium (Cr), nickel (Ni) and lead (Pb) levels. Specifically, 1 gr of sieved foliage matter samples were heated overnight (16 h) at 550 °C in a muffle furnace and cooled in a desiccator to room temperature. Afterwards, 5 mL HCl 6N was added to the samples to dissolve the ash. The supernatant was placed in 50 mL volumetric flasks, topped up with water. The metal concentration was determined in the diluted ash by using an ICP-OES (Perkin Elmer Optical Emission Spectrometry, Optima 2100 DV), an inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer [15,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46]. The respective wave lengths which were used and the lowest detectable metal concentration according to instrument’s specifications were: (1) for Cu 0.0097 ppm, (2) for Fe 0.0046 ppm, (3) for Mn 0.0014 ppm, (4) for Zn 0.0059 ppm, (5) for Cd 0.0027 ppm, (6) for Cu 0.0097 ppm, (7) for Cr 0.0071 ppm, (8) for Ni 0.015 ppm and (9) for Pb 0.042 ppm, respectively.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
A statistical analysis was conducted to determine the differences in the heavy metal levels of the samples using analysis of variance/General Linear Models [39,40]. The experimental design was a 2 × 4 factorial completely randomized design (two plots × four tree species). Significant differences among means were detected by the Tukey’s test. The Tukey test was chosen to reduce the expansion Error Type I cumulative rate [41]. Statistical analysis was performed using the SPSS statistical package v 17.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Prior to analysis, the metal concentrations of Mn, Zn, Cd, Ni and Pb were log transformed, in order to homogenize error variances. A value of p < 0.05 was considered significant.
3. Results
Metal Retention
The mean concentrations of copper, iron, manganese, zinc, cadmium, cobalt, chromium, nickel, and lead of the tree leaves and needles are given in Table 2.

Table 2.
Heavy metal concentration in forestry use landscape and in the environmental area (ppm) 1.
The concentrations of the heavy metals depended on the species and the plot from which they were collected.
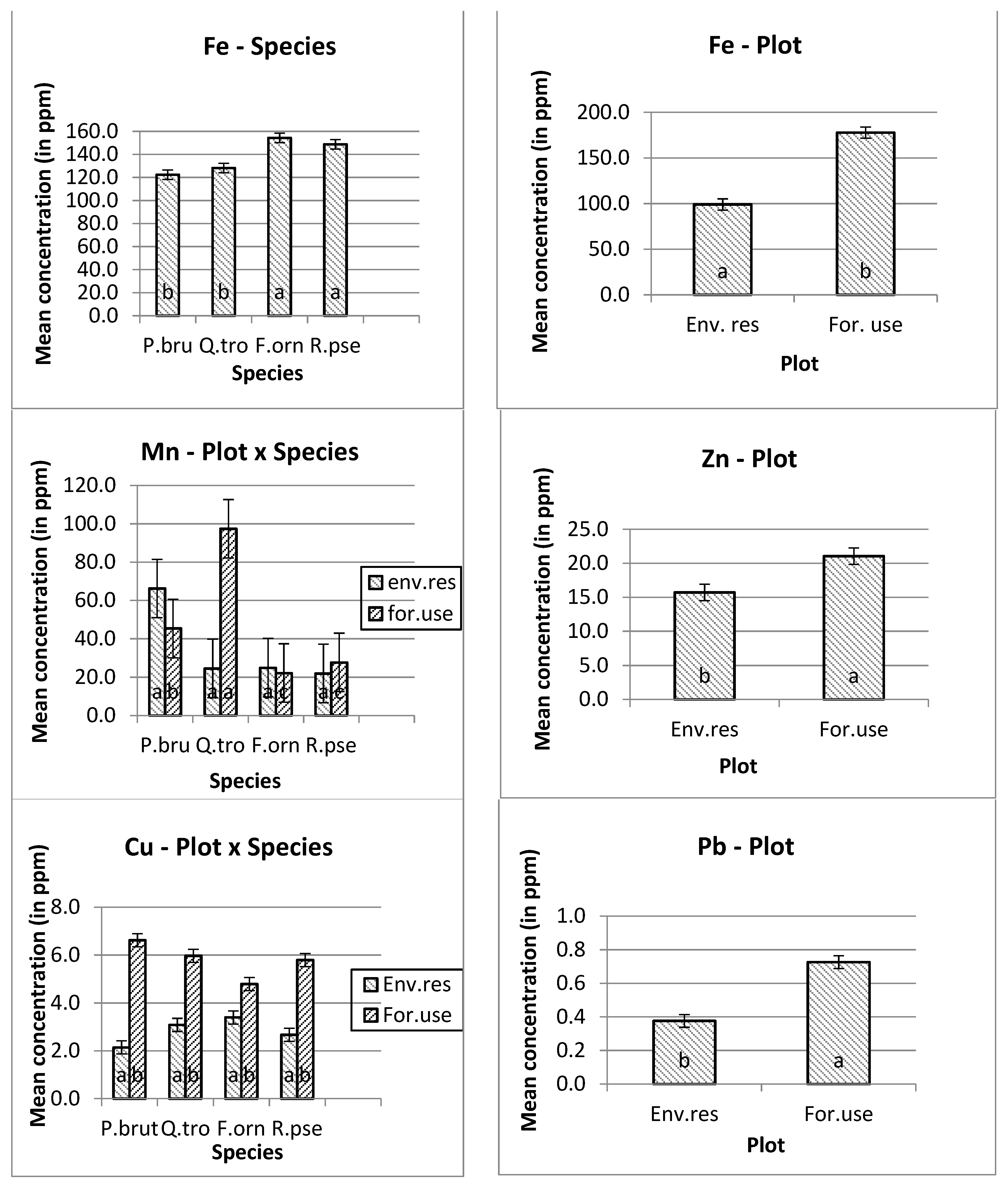
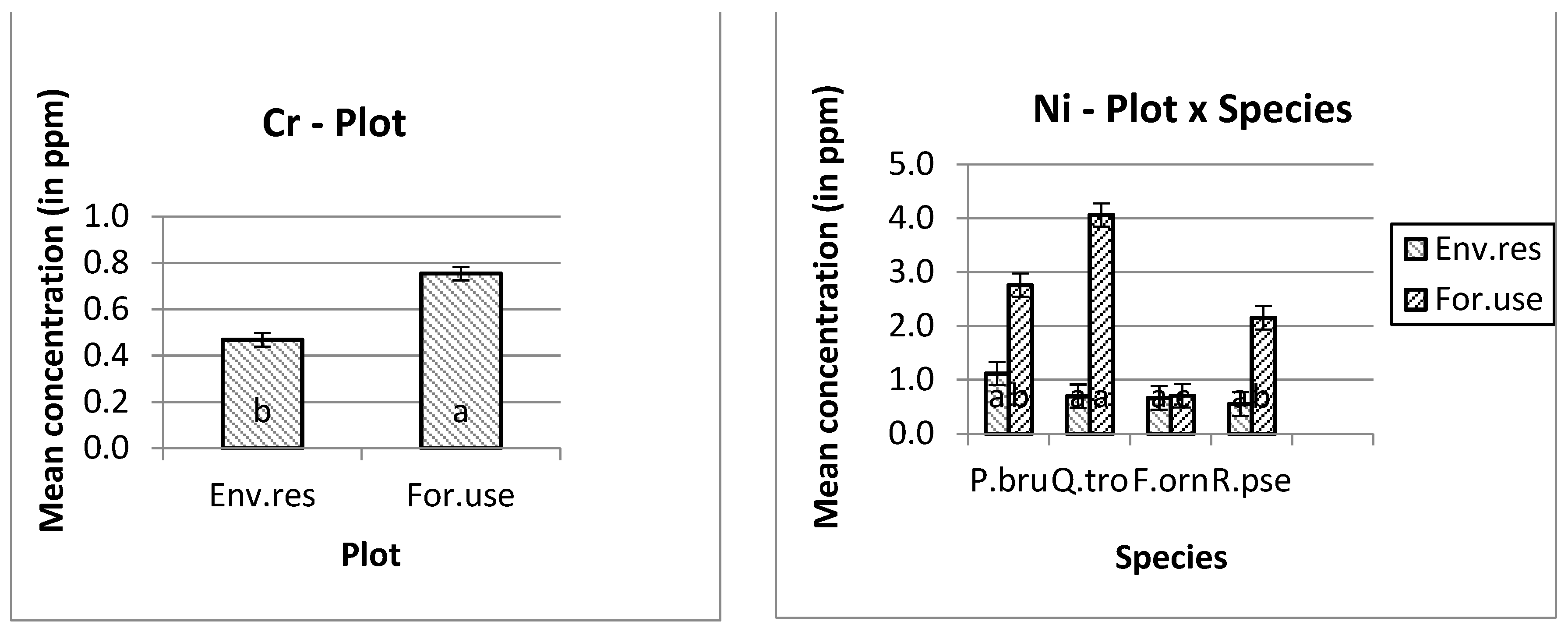
The higher manganese (Mn) and nickel (Ni) mean concentrations were measured in Quercus trojana’s leaves, and the higher copper (Cu) concentration was measured in Pinus brutia’s leaves at the forestry use plot. In addition, the higher concentrations of iron (Fe), zinc (Zn), chromium (Cr) and lead (Pb) were measured at the forestry use plot. Furthermore, the higher concentration of iron (Fe) was measured on the leaves of Fraxinus ornus trees (Figure 1).
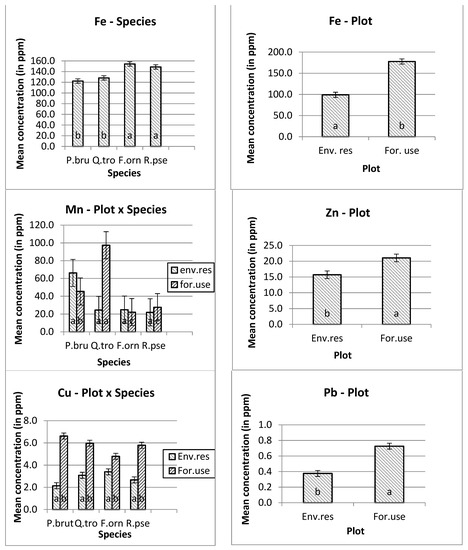
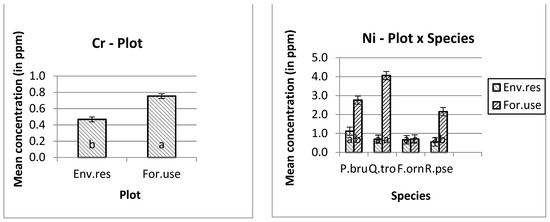
Figure 1.
Mean and s.e. of the studied heavy metals concentrations. The differences in the mean values of the heavy metal concentration with different letters are significantly (ANOVA, p ˂ 0.05 and the Bonferroni Test of multiple comparisons.
Except for nickel, all the other heavy metals showed higher concentrations in the leaves of the trees that were planted for environmental use. For example, the mean copper concentration in the tree leaves that were planted in the forestry use plot was 2.821 ppm, rather than 5.793 ppm in the environmental use plot. The corresponding concentrations for iron was 98.983 ppm (first plot) and 177.780 ppm (second plot), for manganese 34.394 ppm and 48.146 ppm, for zinc 15.707 and 21.041 ppm, for cadmium 0.164 and 0.275 ppm, for cobalt 0.089 and 0.098 ppm, for chromium 0.468 ppm and 0.754 ppm, and for lead 0.376 and 0.726 ppm, respectively.
4. Discussion
An environmentally sustainable development approach for coal mining activities, reclamation, and reforestation of depleted and/or abandoned coal mines is essential. The concentration of heavy metals in the fly ashes and their solubility in water in the reclaimed soils, hence their absorption or retention by plants, are of great importance. Although there are many studies about the presence of heavy metals in the fly ashes originating from Greek power stations [46,47,48,49,50,51], there are few studies on the retention of heavy metals by plants [11,52].
Plant biomonitoring and retention of heavy metals has been widely applied as a complementary approach to conventional methods [53,54,55]. Trees are very efficient at trapping atmospheric particles. Leaves of various tree species, both evergreen and deciduous, have been studied for this purpose [11,56,57].
In the present research, the average concentration of heavy metals in the leaves of the forest species was Fe > Mn > Zn > Ni for all of the species. The descending order for the rest metals was Cr > Pb > Cd > Co for Pinus brutia and Fraxinus ornus. For Quercus trojana the descending order was Pb > Cr > Cd > Co and for Robinia pseudoacacia was Cd > Cr > Pb > Co. Similar results were also obtained in other studies on trees and other vegetation types (mosses, lichens, sea plants) [29,58,59,60,61,62].
Likewise, not one species that displayed the maximum concentration for all of the measured heavy metals. Pinus brutia, for example, showed the highest copper, zinc, and cobalt concentration. As in most coniferous trees, the needles of Pinus brutia remain in the tree from two to five years. Therefore, they are exposed to the polluted air for a longer period in relation to the leaves of deciduous trees. The sunken stomata of Pinus brutia borne in longitudinal bands and its rough surface are among the reasons for the high heavy metal concentration in its leaves [30].
Beckett et al. [62] stated that coniferous trees have higher air pollutant concentration than broad-leaved trees, but in this study the broadleaves species showed maximum concentrations for some of the heavy metals that were studied. Oak leaves remain on the trees during winter, whereas the other broadleaves trees lose their leaves in the winter season. During this period the leaves are dry and accumulate heavy metals in a high capacity, derived from dry and wet deposition from the atmosphere [63]. Quercus trojana’s leaves retained the highest manganese and nickel concentration.
Fraxinus ornus is a tall tree species which is readily distinguished by its light-grey bark and its large compound leaves. It is also considered to be a pioneer tree due to the fact that it is tolerant to the wide ranges of most environmental factors, except a shortage of light [64]. Fraxinus ornus is the only species that didn’t display the maximum concentration of any of the studied heavy metals. The reason for this may be due to the fact that Fraxinus sp., such as Alnus sp. and Sorbus sp. can be considered to be heavy metal excluders. These three plant species may have a mechanism to avoid metal uptake by stabilizing it in the rhizosphere or excluding it from their above-ground tissues by keeping it in their roots [65,66,67]. Thus, the other three species that were studied could potentially uptake metals from the soil and translocate them to their above-ground tissues like leaves. Unfortunately, root analyses could not be performed at that stage of the experiment. This suggests that the heavy metal concentrations that were measured in Fraxinus ornus leaves may have originated primarily from atmospheric deposition.
Robinia pseudoacacia is used as a pioneer species to reforest the degraded land where other species fail to succeed [68,69]. It also has good adaptability to dryness, fast growth, and the ability to fix nitrogen [70]. It can survive under a wide temperature range and grows in almost any type of soil [64]. Tzvetkova and Petkova [71] suggested that Robinia pseudoacacia may be considered a bioaccumulator species for Pb, Zn and Cd, and can be used as a bioindicator of pollution with these metals. The strong correlation between the degree of contamination and concentrations in all plant leaves that were assessed, demonstrate that the leaves of Robinia pseudoacacia reflect the environmental changes accurately and that they seem to act as an effective biomonitor of environmental quality in areas subjected to industrial and traffic pollution [68]. The Robinia pseudoacacia showed the highest concentrations of iron, cadmium, chromium and lead. Leaf accumulation for lead and chromium only depends on the direct uptake of atmosphere particulates by foliar absorption, rather than from their translocation from the soil to the leaves [72]. In many cases, plants seem to accumulate high concentrations of heavy metals such as lead in their cell walls [63].
Cadmium concentrations of tree leaves range between 0.015 to 1.686 ppm. All the studied species had a cadmium concentration below 1 ppm except for Robinia pseudoacacia.
Copper concentrations ranged between 1.672 and 8.083 ppm with no strong differences among the studied species. It must be noted that copper concentrations in all of the trees studied are in adverse proportion to iron, because these heavy metals show an antagonistic interaction.
Iron was the heavy metal with the highest concentration in all the studied species, a maximum being observed in the case of Robinia pseudoacacia (337.574 ppm) while Pinus brutia (50.699 ppm) accounted for minimum values. The systematically higher iron concentration in Pinus brutia in relation to the other species makes it a satisfactory indicator of iron pollution [4]. Iron concentrations are, as a rule, in inverse proportion to manganese concentrations, which can be attributed to the antagonistic action of the two elements. This is especially evident for Fraxinus ornus and Robinia pseudoacacia.
Foliar zinc concentrations in the studied area ranged from 9.022 ppm to 40.164 ppm which is within the normal range [17].
The manganese concentrations of tree leaves ranged from 9.632 and 224.016 ppm with strong differences among the studied species. Pinus brutia and Quercus trojana had manganese concentrations above 100 ppm, while Fraxinus ornus and Robinia pseudoacacia had less than 38 ppm. The same differences were shown between species measured by Sawidis et al. [52] for the same area studied.
The average chromium concentration varies between 0.256 ppm and 1.669 ppm. The highest values of chromium in Robinia pseudoacacia were accompanied by low values for Mn and Ni, which is normal since these elements have an antagonistic relation with chromium [4]. The same matter could not be confirmed for Cu where Robinia pseudoacacia retained high concentrations. It is important to note that in none of the studied species did the chromium concentration exceed the toxicity limits which range from 5–30 ppm [17].
The nickel average concentration ranged from 0.356 ppm in Robinia pseudoacacia to 6.191 ppm in Quercus trojana. The toxicity limits for nickel in plants ranges from 10–100 ppm [17]. Concentrations higher than 10 ppm have not been observed.
Average cobalt concentration varied between 0.042 ppm and 0.179 ppm. The maximum cobalt concentration was observed in Pinus brutia, while Quercus trojana displayed minimum cobalt concentration values.
Finally, lead concentrations of tree leaves range between 0.046 ppm for Quercus trojana and 1.328 ppm for Robinia pseudoacacia. Lead is one of the heavy metals which has very low translocation capability from soil to leaves. Thus, leaf accumulation for lead only depends on the direct uptake from the atmosphere rather than translocation from the soil [19]. For this reason, in descending order lead holds one of the last positions.
The differences that were observed between the two plots may be due to the different planting joints in which the trees were planted. The higher concentrations of heavy metals found in the tree leaves of the second plot suggests that this may be due to much easier air flow between the crowns of the trees.
5. Conclusions
The Ptolemais basin region is in the northwest of Greece. The lignite beds of this basin are under intense exploitation by open cast mining [4]. The depleted or abandoned mines are reclaimed and revegetated after being filled with a mixture of fly ash, overburden and inter-bedded sentiments removed from the working mines [25,73]. Before a plantation is initiated, it is essential to consider the existing vegetation, ecological and climatic factors. It is important to note that the trees not only play only important role in the retention of heavy metals on their leaves, but also plays an important role in protecting the terrain from wind erosion [12].
It was only in Robinia peudoacacia leaves that the cadmium concentration showed a statistical difference among the other species. The same applied for manganese in Quercus trojana’s leaves and zinc for Pinus brutia. Therefore, the selection of forest species for plantations in the post-mining area of Ptolemais basin should be with different forest species (coniferous and broad-leaved) which contributes to the enhancement of the environment and the remediation of post-mining areas.
Only three (Mn, Cd, Co) of the nine heavy metals didn’t show a statistical difference between the two plots. The two plots were planted with the same species but with different planting joints. Thus, further research must be carried out to determine the effect of the planting joints in the ability of forest trees to retain heavy metals.
Overall, the selection and planting of the appropriate forest species is critical in order to ensure improvement in the environment in the vicinity of thermal power plants.
Author Contributions
“Heavy metal retention by different forest species used for restoration of post-mining landscapes, N. Greece” conception and experiment design: T.S., I.S., P.P. and T.G.P. Laboratory chemical analyses and analyses and interpretation of the data: T.S. Critical revision of the article: I.S., P.P. and T.G.P. T.S. takes responsibility for the integrity of the work from the inception to the finished article. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received funding from Public Power Company (PPC) of Greece (Contract No 435/2010) within the research program ‘Woody species selection for environmental restoration at Ptolemais area mines of “PPC”’ and the Forest Research Institute of Thessaloniki (TGP was the scientific coordinator).
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank E. Havales for his help with field data. The authors are grateful to Psoma P. and Mpountla A. of chemical analysis in the laboratory of Soil Science Institute of Thessaloniki, ELGO-DEMETER, and Menexes G. for his advice on statistical analyses of data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Georgakopoulos, A.; Valceva, S. Petrographic Characteristics of Neogene Lignites from the Ptolemais and Servia Basins, Northern Greece. Energy Sources 2000, 22, 587–602. [Google Scholar]
- Pentari, D.; Typou, J.; Goodarzi, F.; Foscolos, A.E. Comparison of elements of environmental concern in regular and reclaimed soils, near abandoned coal mines Ptolemais-Amynteon, northern Greece: Impact on wheat crops. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2006, 65, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petaloti, C.; Triantafyllou, A.; Kouimtzis, T.; Samara, C. Trace elements in atmospheric particulate matter over a coal burning power production area of western Macedonia, Greece. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 2233–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsikritzis, L.; Ganatsios, S.; Duliu, O.G.; Sawidis, T. Heavy metals distribution in some lichens, mosses, and trees in the vicinity of lignite power plants from West Macedonia, Greece. J. Trace Microprobe Tech. 2002, 20, 395–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iordanidis, A.; Buckman, J.; Triantafyllou, A.G.; Asvesta, A. Fly ash-airborne particles from Ptolemais-Kozani area, northern Greece, as determined by ESEM-EDX. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2008, 73, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stalikas, C.D.; Chaidou, C.I.; Pilidis, G.A. Enrichment of PAHs and heavy metals in soils in the vicinity of the lignite-fired power plants of West Macedonia (Greece). Sci. Total Environ. 1997, 204, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallithrakas-Kontos, N.; Zoumi, K.; Nikolaki, S.; Kritidis, P. Trace elements and radioactivity in aerosol particles, produced in the area of Ptolemais (Greece). J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 1998, 227, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllou, G.A. PM10 pollution episodes as a function of synoptic climatology in a mountainous industrial area. Environ. Pollut. 2001, 112, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samara, C. Chemical mass balance source apportionment of TSP in lignite-burning area of Western Macedonia, Greece. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 6430–6443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllou, A.G.; Zoras, S.; Evagelopoulos, V. Particulate matter over the last 7 years in urban and rural areas within, proximal and far from mining and power station operations in Greece. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2006, 122, 41–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samara, T.; Spanos, I.; Platis, P.; Papachristou, T. Heavy metal retention by different forest species used for restoration of post-mining landscapes, N. Greece. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovic, P.; Mitrovic, M.; Djurdjevic, L. An Ecophysiological Study of Plants Growing on the Fly Ash Deposits from the “Nicola Tesla-A” Thermal Power Station in Serbia. Environ. Manag. 2004, 33, 654–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delia, N.B. Assessing the degree of dispersion and distribution of heavy metals in soil and plants associated with area of influence of coal power plant. J. Environ. Prot. Ecol. 2015, 16, 453–460. [Google Scholar]
- Gerouki, F.; Foscolos, A.E.; Dimitroula, M. Environmental impact of trace elements encountered in fly ashes from power stations located in the wider area of Ptolemais basin. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Environmental Pollution, Toronto, ON, Canada, 16–20 September 1996; University of Thessaloniki: Thessaloniki, Greece, 1996; pp. 213–218. [Google Scholar]
- Foscolos, A.E.; Goodarzi, F.; Koukouzas, C.N.; Hatziyannis, G. Assessment of environmental impact of coal exploration and exploitation in the Drama basin, Northeastern Greek-Macedonia. Energy Sources 1998, 20, 795–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fillipidis, A.; Georgokopoulos, A. Mineralogical and chemical investigation of fly ash from the Main and Northern lignite fields in Ptolemais, Greece. Fuel 1992, 71, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabata-Pedias, A. Trace Elements in Soils and Plants; CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Alfani, A.; Batrol, G.; Rutigliano, F.A.; Maisto, G.; Virzo De Santo, A. Trace metal biomonitoring in the soil and the leaves of Quercus Ilex in the urban area of Naples. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 1996, 51, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawidis, T.; Metentzoglou, E.; Mitrakas, M. A study of chromium, cooper and lead distribution from lignite fuels using cultivated and non-cultivated plants as biological monitors. Water Air Soil Poll. 2011, 220, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckett, K.P.; Free-Smith, P.; Taylor, G. Urban Woodlands: Their role in reducing the effect of particulate pollution. Environ. Poll. 1998, 99, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, D.J. Air pollution removal by Chicago’s urban forest. In Chicago’s Urban Forest Ecosystem: Results of the Chicago’s Urban Forest Climate Project, General Technical Report NE-186; McPherson, E.G., Nowak, D.J., Rowntree, R.A., Eds.; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Radnor, PA, USA, 1994; pp. 63–84. [Google Scholar]
- Taha, H. Modeling impacts of in the South Coast Air Basin. Atmos. Environ. 1996, 30, 3423–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, D.J.; Dwyer, J.F. Understanding the benefits and costs of urban forest ecosystems. In Handbook of Urban and Community Forestry in the Northeast; Kuser, J.E., Ed.; Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 11–22. [Google Scholar]
- Batzias, B.A.; Roumpos, C.P. Optimal policy for lignite fly ash management. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Environmental Pollution, Kittilä, Finland, 29 August–1 September 2000; pp. 849–856. [Google Scholar]
- Georgakopoulos, A.; Filippidis, A.; Kassoli-Fournaraki, A.; Iordanidis, A.; Fernández-Turiel, J.L.; Llorens, J.F.; Gimeno, D. Environmentally important elements in fly ashes and their leachates of the power stations of Greece. Energy Source 2002, 24, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllou, G.A. Levels and trends of suspended particles around large lignite power stations. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2003, 89, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, W.H.; Staskawawicz, B.J. Removal of atmospheric particles by leaves and twings of urban trees: Some preliminary observations and assessment of research needs. Environ. Manag. 1977, 1, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.H.; Coughtrey, P.J. Biological Monitoring of Heavy Metal Pollution. Land and Air; Applied Science Publishers: London, UK, 1982; p. 475. [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson, N.M.; Turner, A.P.; Lepp, N.W. Survival of trees in a metal-contaminated environment, Part III. Water Air Soil Poll. 1991, 57–58, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawidis, T.; Marnasidis, A.; Zachariadis, G.; Stratis, J. A study of air-pollution with heavy-metals in Thessaloniki City (Greece) using trees as biological indicators. Arch. Environ. Con. Tox. 1995, 28, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckett, K.P.; Free-Smith, P.; Taylor, G. The capture of particulate pollution by trees at five contrasting urban sites. Arbor. J. 2000, 24, 209–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, A.; Kulshreshtha, K.; Ahmad, K.J.; Behl, H.M. Do leaf surface characters play a role in plant resistance to auto-exhaust pollution? Flora 2002, 197, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourkhabbaz, A.; Rastin, N.; Olbrich, A.; Langenfeld-Heyser, R.; Polle, A. Influence of environmental pollution on leaf properties of urban plane trees, Platanus orientalis L. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 85, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, H.J.; Ashmore, M.R.; Bell, J.N.B. Air Pollution Injury to Vegetation; IEHO: London, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Shayed, S.M.; Al-Rajhi, M.A.; Seaward, M.R.D. The date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) as a biomonitor of lead and other elements in arid environments. Sci. Total Environ. 1995, 168, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-alawi, M.; Mandiwana, K. The use of Alepo pine as a bio-monitor of heavy metals in atmosphere. J. Hazard Mater. 2007, 148, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, M. Trees as Biological Indicators. In Biological Indicators in Environmental Protection; Kovács, M., Ed.; Ellis Horwood: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen, P.E.; Mierle, G.; Nriagu, J.O. The Analysis of Vegetation for Total Mercury. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1991, 56, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceburnis, D.; Steinnes, E. Conifer needles as bio-monitors of atmospheric heavy metal deposition: Comparison with mosses and precipitation, role of the canopy. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 4265–4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holoubek, I.; Korinek, P.; Seda, Z.; Schneiderova, E.; Holoubkova, I.; Pacl, A.; Triska, J.; Cudlin, P.; Caslavsky, J. The use of mosses and pine needles to detect persistent organic pollutants at local and regional scales. Environ. Pollut. 2000, 109, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migaszewski, Z.M.; Galuszka, A.; Paslawski, P. Polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons, phenols and trace metals in selected soil profiles and plant bio-indicators in the Holy Cross Mountains, South-Central Poland. Environ. Int. 2002, 28, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, H.D.; Pratt, P.F. Methods of Analysis for Soils, Plants and Waters; University of California Berkeley, Division of Agriculture Sciences, Ed.; Priced Publication 4034: Berkley, CA, USA, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Rencher, A. Linear Models in Statistics; John Willey & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Toothaker, L. Multiple Comparison Procedures; Sage Publications, Inc.: Newbury Park, CA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson, D.R.; Townsend, W.N. The amelioration and revegetation of pulverized fuel ash. In Ecology and Reclamation of Devastated Land; Huntnik, R.J., Davis, G., Eds.; Gordon and Breach: London, UK, 1973; Volume 2, pp. 247–270. [Google Scholar]
- Foscolos, A.E.; Goodarzi, F.; Koukouzas, C.N.; Hatziyannis, G. Reconnaissance study of mineral matter and trace elements in Greek lignites. Chem. Geol. 1989, 76, 107–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakorafa, V.; Michailidis, K.; Burragato, F. Mineralogy geochemistry and physical properties of fly ash from the Megapolis lignite fields, Peloponese, Southern Greece. Fuel 1996, 75, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentzis, T.; Goodarzi, F.; Koukouzas, C.N.; Foscolos, A.E. Petrology mineralogy and geochemistry of lignites from Crete, Greece. Int. J. Coal Geol. 1996, 30, 131–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentzis, T.; Goodarzi, F.; Foscolos, A.E. Geochemistry and mineralogy of Greek lignites from the Ioannina basin. Energy Sources 1997, 19, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pentari, D.; Foscolos, A.E. Geochemistry of Florina and Ellasona Coal Basins with Emphasis on Trace Elements and Elements of Environmental Concern 2004. In Proceedings of the Chania Conference on the Advances in Mineral Resources Management and Environmenta Geotechnology, Chania, Greece, 7–9 June 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Papanikolaou, C.; Kotis, T.; Foscolos, A.; Goodarzi, F. Coals of Greece: A review of properties, uses and future perspectives. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2004, 58, 147–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawidis, T.; Chettri, A.; Papaioannou, A.; Zachariadis, G.; Stratis, J. A study of metal distribution from lignite fuels using trees as biological indicators. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Stud. 2001, 48, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Market, B. Instrumental analysis of plants. In Plants as Biomonitors, Indicators for Heavy Metals in Terrestial Environment; Market, B., Ed.; VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 1993; pp. 65–103. [Google Scholar]
- Bargagli, R. Trace Elements in Terrestrial Plants: An Ecophysiological Approach to Biomonitoring and Biorecovery; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, P.; Offenthaler, I.; Ohlinger, R.; Wimmer, J. Higher Plants as Accumulative Bioindicators. In Bioindicators & Biomonitors, Principles, Concepts and Applications; Market, B., Breure, A.M., Zechmeister, H.G., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; Volume 6, pp. 465–500. [Google Scholar]
- Stratis, J.A.; Tsitouridou, R.D.; Simeonov, V.D. Chemometrical data treatment to study the environment pollution around lignite power plants. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 1995, 47, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasevic, M.; Anicic, M.; Jovanovic, L.; Peric-Grujic, A.; Ristic, M. Deciduous tree leaves in trace elements biomonitoring: A contribution to methodology. Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 1689–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawidis, T.; Zachariadis, G.; Stratis, J.; Ladukakis, E. Mosses as biological indicators for monitoring of heavy-metal pollution. Fresenius. Environ. Bull. 1993, 2, 193–199. [Google Scholar]
- Sawidis, T.; Chettri, A.; Zachariadis, G.; Stratis, J. Heavy metals in aquatic plants and sediments from water system in Macedonia, Greece. Exotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1995, 32, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawidis, T.; Chettri, A.; Zachariadis, G.; Stratis, J.; Seaward, M.R.D. Heavy metal bioaccumulation in lichens from Macedonia in northern Greece. Toxical. Environ. Chem. 1995, 50, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samara, T.; Tsitsoni, T. Selection of forest species for use in urban environment in relation to their potential capture to heavy metals. Glob. NEST J. 2014, 16, 966–974. [Google Scholar]
- Beckett, K.P.; Free-Smith, P.; Taylor, G. Effective tree species for local air-quality management. Arboric. J. 2000, 26, 12–19. [Google Scholar]
- Vassileva, E.; Velev, V.; Daiev, C.; Stoichev, T.; Martin, M.; Robin, D.; Haerdi, W. Assessment of heavy metals air pollution in urban and industrial environments using oak leaves as bioindicators. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2000, 78, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoy, A.; Ozturk, M.A. Nerium oleader N. as a biomonitor of lead and other heavy metal pollution in Mediterranean environments. Sci. Total Environ. 1997, 205, 145–150. [Google Scholar]
- Blaylock, M.J.; Huang, J.W. Phytoextraction of metals. In Phytoremidation of Toxic Metals-Using Plants to Clean up the Environment; Raskin, I., Ensley, B.D., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 53–70. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.G. Relationships between chromium biomagnification ratio, accumulation factor, and mycorrhizae in plants growing on tannery effluent-polluted soil. Environ. Int. 2001, 26, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosselli, W.; Keller, C.; Boschi, K. Phytoextraction capacity of trees growing on a metal contaminated soil. Plant Soil 2003, 256, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, A.; Aslihan, A.; Kartal, A.; Kaska, Y. Determining the heavy metal pollution in Denizli (Turkey) by using Robinia pseudoacacia L. Environ. Intern. 2005, 31, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corneanu, C.G.; Gracium, C.; Corneanu, M.; Tripon, S. The ultrastructural features of the Robinia pseudoacacia var. Oltenica leaves, cultivated on degraded soils (sterile waste dumps). An. Univ. Din Craiova Ser. Agric.-Montanologie-Cadastru 2009, 39, 104–115. [Google Scholar]
- Converse, T.E.; Betters, D.R. Biomass yield equation for short rotation black locust plantations in the Central Great Plains. Biomass Bioenergy 1995, 8, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzvetkova, N.; Petkova, K. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals by the leaves of Robinia pseudoacacia as a bioindicator tree in industrial zones. J. Environ. Biol. 2015, 36, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maisto, G.; Alfani, A.; Baldantoni, D.; De Marco, A.; Virzo De Santo, A. Trace metals in the soil and in Quercus ilex L. leaves at anthropic and remote sites of the Campania Region of Italy. Geoderma 2004, 122, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papazafeiriou, A.; Alifragis, D.; Lakis, C.; Stefanou, S.; Yialoulaki, M.; Papanikolaou, K. Heavy Metal Transfer to Forage Material in Amended Soils in the Area of Ptolemais-Greece. Dry Grasslands of Europe: Grazing and Ecosystem Services; Vrahnakis, M., Kyriakopoulos, A.P., Chournavas, D., Fotiadis, G., Eds.; Thessaloniki, Greece; pp. 246–251. Available online: https://silo.tips/download/dry-grasslands-of-europe-grazing-and-ecosystem-services (accessed on 30 July 2022).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).