New Insights into Hsp90 Structural Plasticity Revealed by cryoEM
Abstract
1. Molecular Chaperones, a Brief Overview
1.1. The Molecular Chaperones: Hsp40, Hsp70, Hsp100, and Hsp60
1.2. The Bright Start: Hsp90
2. Hsp90 Cochaperones
2.1. Hop
2.2. Aha-Type Cochaperone
2.3. p23
2.4. SGTs
3. The Importance of Hsp90
3.1. Proteosome Relationship
3.2. Foldosome
4. Hsp90 Structural Bases
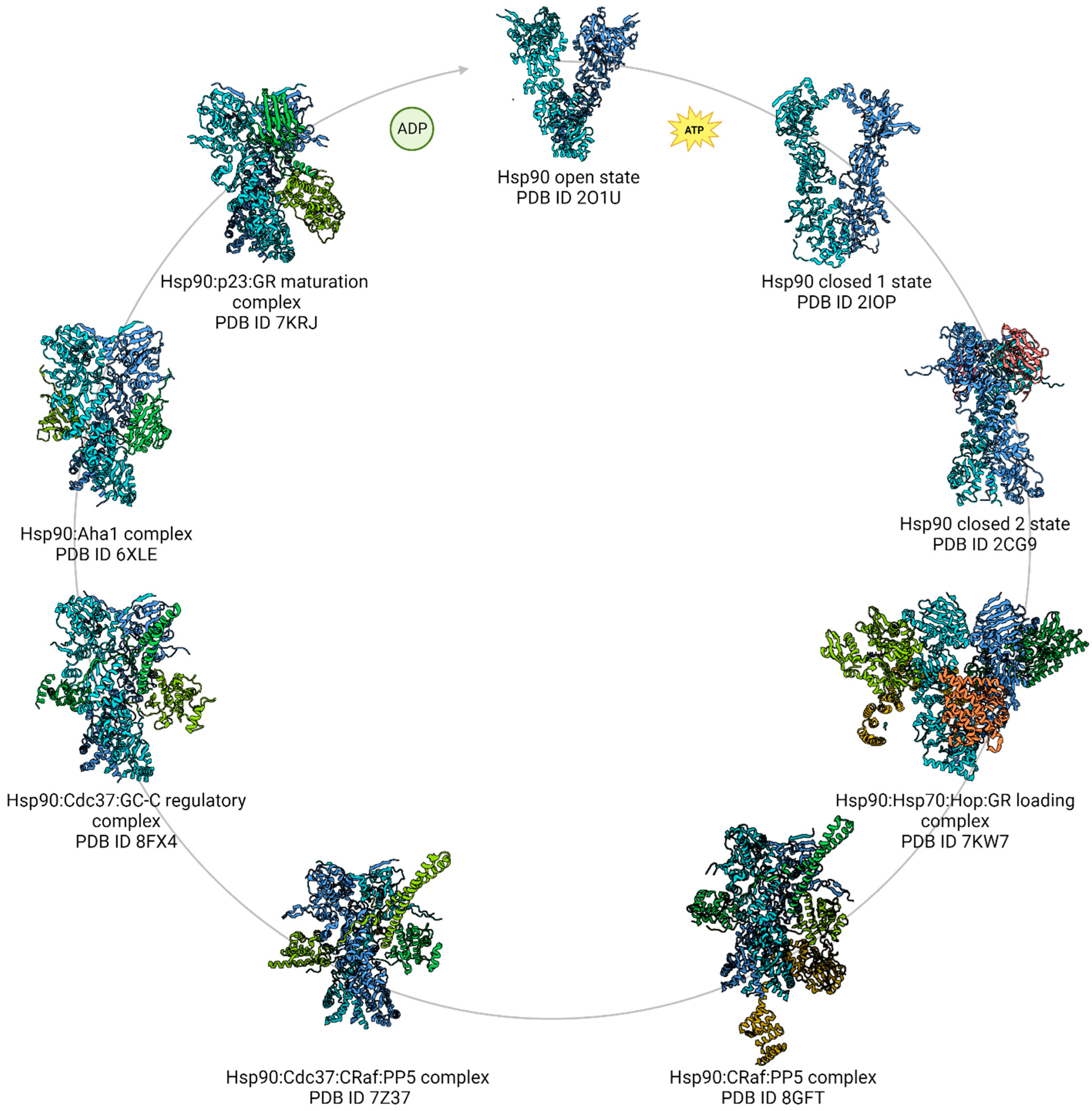
5. The Breakthrough in Hsp90 Complexes Analysis Using High-Resolution cryoEM
5.1. Polydispersity Analysis: TRAP1, Mitochondrion-Specific Hsp90
5.2. Hsp90: Kinase-Specific Cochaperone Complexes
5.3. Hsp90:Hop and the GR-Loading Complex
5.4. Hsp90:p23 Complex and the GR Maturation Complex
5.5. Hsp90:p23:FKBP51 Complex: An Extra Step in the Proposed Mechanism
5.6. Hsp90:Aha1 Cochaperone Complex
5.7. Hsp90:AHR:XAP2 Unusual Cochaperone Complex
5.8. Hsp90:R2TP Yeast Cochaperone Complex
6. Drug Discovery and Mechanistic
6.1. Cancer
6.2. Neurodegenerative Diseases
6.3. Infectious Diseases
7. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, Y.E.; Hipp, M.S.; Bracher, A.; Hayer-Hartl, M.; Ulrich Hartl, F. Molecular Chaperone Functions in Protein Folding and Proteostasis. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2013, 82, 323–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saibil, H. Chaperone Machines for Protein Folding, Unfolding and Disaggregation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 630–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartl, F.U.; Bracher, A.; Hayer-Hartl, M. Molecular Chaperones in Protein Folding and Proteostasis. Nature 2011, 475, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, J.C. Chaperones & Co: Roles in Protein/Nucleic Acid Homeostasis. Curr. Proteom. 2019, 16, 3–4. [Google Scholar]
- Heat Shock Protein 40—An Overview|ScienceDirect Topics. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/heat-shock-protein-40 (accessed on 24 November 2023).
- Qiu, X.-B.; Shao, Y.-M.; Miao, S.; Wang, L. The Diversity of the DnaJ/Hsp40 Family, the Crucial Partners for Hsp70 Chaperones. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2006, 63, 2560–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, J.C.; Seraphim, T.V.; Mokry, D.Z.; Almeida, F.C.L.; Cyr, D.M.; Ramos, C.H.I. Identification of Regions Involved in Substrate Binding and Dimer Stabilization within the Central Domains of Yeast Hsp40 Sis1. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Qian, X.; Sha, B. Heat Shock Protein 40: Structural Studies and Their Functional Implications. Protein Pept. Lett. 2009, 16, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, K.P.; Borges, J.C. The Molecular Chaperone Hsp70 Family Members Function by a Bidirectional Heterotrophic Allosteric Mechanism. Protein Pept. Lett. 2011, 18, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dores-Silva, P.R.; Beloti, L.L.; Minari, K.; Silva, S.M.O.; Barbosa, L.R.S.; Borges, J.C. Structural and Functional Studies of Hsp70-Escort Protein—Hep1—Of Leishmania Braziliensis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 79, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dores-Silva, P.R.; Minari, K.; Ramos, C.H.I.; Barbosa, L.R.S.; Borges, J.C. Structural and Stability Studies of the Human mtHsp70-Escort Protein 1: An Essential Mortalin Co-Chaperone. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 56, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, J.C.; Ramos, C.H. Protein folding assisted by chaperones. Protein Pept. Lett. 2005, 12, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, N.S.M.; Bertolino-Reis, D.E.; Dores-Silva, P.R.; Anneta, F.B.; Seraphim, T.V.; Barbosa, L.R.S.; Borges, J.C. Structural Studies of the Hsp70/Hsp90 Organizing Protein of Plasmodium Falciparum and Its Modulation of Hsp70 and Hsp90 ATPase Activities. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Proteins Proteom. 2020, 1868, 140282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heat Shock Protein 100—An Overview|ScienceDirect Topics. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/heat-shock-protein-100 (accessed on 24 November 2023).
- Seraphim, T.V.; Houry, W.A. AAA+ Proteins. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, R251–R257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.; Kim, R.S.; Lee, S.B.; Lee, S.; Tsai, F.T.F. Deciphering the Mechanism and Function of Hsp100 Unfoldases from Protein Structure. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2022, 50, 1725–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HSP60—An Overview|ScienceDirect Topics. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/biochemistry-genetics-and-molecular-biology/hsp60 (accessed on 24 November 2023).
- Bukau, B.; Horwich, A.L. The Hsp70 and Hsp60 Chaperone Machines. Cell 1998, 92, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayer-Hartl, M.; Bracher, A.; Hartl, F.U. The GroEL-GroES Chaperonin Machine: A Nano-Cage for Protein Folding. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2016, 41, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, T.K.; Verma, V.K.; Maheshwari, A. GroEL Assisted Folding of Large Polypeptide Substrates in Escherichia coli: Present Scenario and Assignments for the Future. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2009, 99, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schopf, F.H.; Biebl, M.M.; Buchner, J. The HSP90 Chaperone Machinery. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heat Shock Protein 90—An Overview|ScienceDirect Topics. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/heat-shock-protein-90 (accessed on 24 November 2023).
- Neckers, L.; Ivy, S.P. Heat Shock Protein 90. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2003, 15, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuehlke, A.D.; Moses, M.A.; Neckers, L. Heat Shock Protein 90: Its Inhibition and Function. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 373, 20160527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biebl, M.M.; Buchner, J. Structure, Function, and Regulation of the Hsp90 Machinery. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2019, 11, a034017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiosis, G.; Digwal, C.S.; Trepel, J.B.; Neckers, L. Structural and Functional Complexity of HSP90 in Cellular Homeostasis and Disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 24, 797–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, M.P.; Le Breton, L. Hsp90: Breaking the Symmetry. Mol. Cell 2015, 58, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genest, O.; Wickner, S.; Doyle, S.M. Hsp90 and Hsp70 Chaperones: Collaborators in Protein Remodeling. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 2109–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoter, A.; El-Sabban, M.E.; Naim, H.Y. The HSP90 Family: Structure, Regulation, Function, and Implications in Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, K.P.; Seraphim, T.V.; Borges, J.C. Structural and Functional Studies of Leishmania Braziliensis Hsp90. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Proteins Proteom. 2013, 1834, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minari, K.; de Azevedo, É.C.; Kiraly, V.T.R.; Batista, F.A.H.; de Moraes, F.R.; de Melo, F.A.; Nascimento, A.S.; Gava, L.M.; Ramos, C.H.I.; Borges, J.C. Thermodynamic Analysis of Interactions of the Hsp90 with Adenosine Nucleotides: A Comparative Perspective. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 130, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratzke, C.; Hellenkamp, B.; Hugel, T. Four-Colour FRET Reveals Directionality in the Hsp90 Multicomponent Machinery. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caplan, A.J. What Is a Co-Chaperone? Cell Stress. Chaperones 2003, 8, 105–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altinok, S.; Sanchez-Hodge, R.; Stewart, M.; Smith, K.; Schisler, J.C. With or without You: Co-Chaperones Mediate Health and Disease by Modifying Chaperone Function and Protein Triage. Cells 2021, 10, 3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, K.; Weidenauer, L.; Luengo, T.M.; Pieters, E.C.; Echeverría, P.C.; Bernasconi, L.; Wider, D.; Sadian, Y.; Koopman, M.B.; Villemin, M.; et al. The Hsp70-Hsp90 Co-Chaperone Hop/Stip1 Shifts the Proteostatic Balance from Folding towards Degradation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Masison, D.C. Independent Regulation of Hsp70 and Hsp90 Chaperones by Hsp70/Hsp90-Organizing Protein Sti1 (Hop1). J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 34178–34185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniel, S.; Söti, C.; Csermely, P.; Bradley, G.; Blatch, G.L. Hop: An Hsp70/Hsp90 Co-Chaperone That Functions Within and Beyond Hsp70/Hsp90 Protein Folding Pathways. In Networking of Chaperones by Co-Chaperones; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 26–37. ISBN 978-0-387-49308-4. [Google Scholar]
- LaPointe, P.; Mercier, R.; Wolmarans, A. Aha-Type Co-Chaperones: The Alpha or the Omega of the Hsp90 ATPase Cycle? Biol. Chem. 2020, 401, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Retzlaff, M.; Hagn, F.; Mitschke, L.; Hessling, M.; Gugel, F.; Kessler, H.; Richter, K.; Buchner, J. Asymmetric Activation of the Hsp90 Dimer by Its Cochaperone Aha1. Mol. Cell 2010, 37, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, P.; Prodromou, C.; Liao, C.; Hu, B.; Roe, S.M.; Vaughan, C.K.; Vlasic, I.; Panaretou, B.; Piper, P.W.; Pearl, L.H. Structural Basis for Recruitment of the ATPase Activator Aha1 to the Hsp90 Chaperone Machinery. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 1402–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Richter, K.; Reinstein, J.; Buchner, J. Integration of the Accelerator Aha1 in the Hsp90 Co-Chaperone Cycle. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, F.; Gadura, N.; Michels, C.A. Hsp90 Cochaperone Aha1 Is a Negative Regulator of the Saccharomyces MAL Activator and Acts Early in the Chaperone Activation Pathway*. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 13850–13862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seraphim, T.V.; Gava, L.M.; Mokry, D.Z.; Cagliari, T.C.; Barbosa, L.R.S.; Ramos, C.H.I.; Borges, J.C. The C-Terminal Region of the Human P23 Chaperone Modulates Its Structure and Function. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 565, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, F.A.H.; Almeida, G.S.; Seraphim, T.V.; Silva, K.P.; Murta, S.M.F.; Barbosa, L.R.S.; Borges, J.C. Identification of Two P23 Co-Chaperone Isoforms in Leishmania Braziliensis Exhibiting Similar Structures and Hsp90 Interaction Properties despite Divergent Stabilities. FEBS J. 2015, 282, 388–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Botër, M.; Li, K.; Kadota, Y.; Panaretou, B.; Prodromou, C.; Shirasu, K.; Pearl, L.H. Structural and Functional Coupling of Hsp90- and Sgt1-Centred Multi-Protein Complexes. EMBO J. 2008, 27, 2789–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coto, A.L.S.; Seraphim, T.V.; Batista, F.A.H.; Dores-Silva, P.R.; Barranco, A.B.F.; Teixeira, F.R.; Gava, L.M.; Borges, J.C. Structural and Functional Studies of the Leishmania Braziliensis SGT Co-Chaperone Indicate That It Shares Structural Features with HIP and Can Interact with Both Hsp90 and Hsp70 with Similar Affinities. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118, 693–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatima, K.; Naqvi, F.; Younas, H. A Review: Molecular Chaperone-Mediated Folding, Unfolding and Disaggregation of Expressed Recombinant Proteins. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2021, 79, 153–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, S.E. Hsp90: Structure and Function. Top. Curr. Chem. 2013, 328, 155–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearl, L.H.; Prodromou, C. Structure and Mechanism of the Hsp90 Molecular Chaperone Machinery. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2006, 75, 271–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Zhong, D.; Monteiro, A. Comparative Genomics and Evolution of the HSP90 Family of Genes across All Kingdoms of Organisms. BMC Genom. 2006, 7, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prodromou, C.; Panaretou, B.; Chohan, S.; Siligardi, G.; O’Brien, R.; Ladbury, J.E.; Roe, S.M.; Piper, P.W.; Pearl, L.H. The ATPase Cycle of Hsp90 Drives a Molecular ‘Clamp’ via Transient Dimerization of the N-Terminal Domains. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 4383–4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prodromou, C.; Roe, S.M.; Piper, P.W.; Pearl, L.H. A Molecular Clamp in the Crystal Structure of the N-Terminal Domain of the Yeast Hsp90 Chaperone. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1997, 4, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panaretou, B.; Prodromou, C.; Roe, S.M.; O’Brien, R.; Ladbury, J.E.; Piper, P.W.; Pearl, L.H. ATP Binding and Hydrolysis Are Essential to the Function of the Hsp90 Molecular Chaperone In Vivo. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 4829–4836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, R.; Inouye, M. GHKL, an Emergent ATPase/Kinase Superfamily. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2000, 25, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-T.; Graf, C.; Mayer, F.J.; Richter, S.M.; Mayer, M.P. Dynamics of the Regulation of Hsp90 by the Co-Chaperone Sti1. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 1518–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blundell, K.L.I.M.; Pal, M.; Roe, S.M.; Pearl, L.H.; Prodromou, C. The Structure of FKBP38 in Complex with the MEEVD Tetratricopeptide Binding-Motif of Hsp90. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lott, A.; Oroz, J.; Zweckstetter, M. Molecular Basis of the Interaction of Hsp90 with Its Co-Chaperone Hop. Protein Sci. 2020, 29, 2422–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsutsumi, S.; Mollapour, M.; Graf, C.; Lee, C.-T.; Scroggins, B.T.; Xu, W.; Haslerova, L.; Hessling, M.; Konstantinova, A.A.; Trepel, J.B.; et al. Hsp90 Charged-Linker Truncation Reverses the Functional Consequences of Weakened Hydrophobic Contacts in the N Domain. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2009, 16, 1141–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiau, A.K.; Harris, S.F.; Southworth, D.R.; Agard, D.A. Structural Analysis of E. Coli Hsp90 Reveals Dramatic Nucleotide-Dependent Conformational Rearrangements. Cell 2006, 127, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huai, Q.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Kim, H.-Y.; Toft, D.; Ke, H. Structures of the N-Terminal and Middle Domains of E. Coli Hsp90 and Conformation Changes upon ADP Binding. Structure 2005, 13, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, P.; Prodromou, C.; Hu, B.; Vaughan, C.; Roe, S.M.; Panaretou, B.; Piper, P.W.; Pearl, L.H. Structural and Functional Analysis of the Middle Segment of Hsp90: Implications for ATP Hydrolysis and Client Protein and Cochaperone Interactions. Mol. Cell 2003, 11, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soti, C.; Vermes, A.; Haystead, T.A.J.; Csermely, P. Comparative Analysis of the ATP-Binding Sites of Hsp90 by Nucleotide Affinity Cleavage: A Distinct Nucleotide Specificity of the C-Terminal ATP-Binding Site. Eur. J. Biochem. 2003, 270, 2421–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Devin, J.; Sullivan, W.P.; Toft, D.; Baulieu, E.E.; Catelli, M.G. Mutational Analysis of Hsp90 Alpha Dimerization and Subcellular Localization: Dimer Disruption Does Not Impede “in Vivo’ Interaction with Estrogen Receptor. J. Cell Sci. 1996, 109 Pt 7, 1677–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minami, Y.; Kawasaki, H.; Suzuki, K.; Yahara, I. The Calmodulin-Binding Domain of the Mouse 90-kDa Heat Shock Protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 9604–9610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bron, P.; Giudice, E.; Rolland, J.-P.; Buey, R.M.; Barbier, P.; Díaz, J.F.; Peyrot, V.; Thomas, D.; Garnier, C. Apo-Hsp90 Coexists in Two Open Conformational States in Solution. Biol. Cell 2008, 100, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.M.U.; Roe, S.M.; Vaughan, C.K.; Meyer, P.; Panaretou, B.; Piper, P.W.; Prodromou, C.; Pearl, L.H. Crystal Structure of an Hsp90–Nucleotide–P23/Sba1 Closed Chaperone Complex. Nature 2006, 440, 1013–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.-C.; Lin, T.-W.; Ko, T.-P.; Wang, A.H.-J. The Hexameric Structures of Human Heat Shock Protein 90. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moullintraffort, L.; Bruneaux, M.; Nazabal, A.; Allegro, D.; Giudice, E.; Zal, F.; Peyrot, V.; Barbier, P.; Thomas, D.; Garnier, C. Biochemical and Biophysical Characterization of the Mg2+-Induced 90-kDa Heat Shock Protein Oligomers. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 15100–15110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavery, L.A.; Partridge, J.R.; Ramelot, T.A.; Elnatan, D.; Kennedy, M.A.; Agard, D.A. Structural Asymmetry in the Closed State of Mitochondrial Hsp90 (TRAP1) Supports a Two-Step ATP Hydrolysis Mechanism. Mol. Cell 2014, 53, 330–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, J.C.; Seraphim, T.V.; Dores-Silva, P.R.; Barbosa, L.R.S. A Review of Multi-Domain and Flexible Molecular Chaperones Studies by Small-Angle X-Ray Scattering. Biophys. Rev. 2016, 8, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, N.S.M.; Torricillas, M.S.; Minari, K.; Barbosa, L.R.S.; Seraphim, T.V.; Borges, J.C. Solution Structure of Plasmodium Falciparum Hsp90 Indicates a High Flexible Dimer. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 690, 108468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elnatan, D.; Betegon, M.; Liu, Y.; Ramelot, T.; Kennedy, M.A.; Agard, D.A. Symmetry Broken and Rebroken during the ATP Hydrolysis Cycle of the Mitochondrial Hsp90 TRAP1. eLife 2017, 6, e25235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, M.; Elnatan, D.; Larson, A.G.; Agard, D.A. Cryo-EM Analysis of Human Mitochondrial Hsp90 in Multiple Tetrameric States. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodromou, C.; Bjorklund, D.M. Advances towards Understanding the Mechanism of Action of the Hsp90 Complex. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verba, K.A.; Wang, R.Y.-R.; Arakawa, A.; Liu, Y.; Shirouzu, M.; Yokoyama, S.; Agard, D.A. Atomic Structure of Hsp90-Cdc37-Cdk4 Reveals That Hsp90 Traps and Stabilizes an Unfolded Kinase. Science 2016, 352, 1542–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caveney, N.A.; Tsutsumi, N.; Garcia, K.C. Structural Insight into Guanylyl Cyclase Receptor Hijacking of the Kinase–Hsp90 Regulatory Mechanism. eLife 2023, 12, RP86784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaime-Garza, M.; Nowotny, C.A.; Coutandin, D.; Wang, F.; Tabios, M.; Agard, D.A. Hsp90 Provides a Platform for Kinase Dephosphorylation by PP5. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Alonso, S.; Mesa, P.; de la Puente Ovejero, L.; Aizpurua, G.; Lechuga, C.G.; Zarzuela, E.; Santiveri, C.M.; Sanclemente, M.; Muñoz, J.; Musteanu, M.; et al. Structure of the RAF1-HSP90-CDC37 Complex Reveals the Basis of RAF1 Regulation. Mol. Cell 2022, 82, 3438–3452.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Southworth, D.R.; Agard, D.A. Client-Loading Conformation of the Hsp90 Molecular Chaperone Revealed in the Cryo-EM Structure of the Human Hsp90:Hop Complex. Mol. Cell 2011, 42, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.Y.-R.; Noddings, C.M.; Kirschke, E.; Myasnikov, A.G.; Johnson, J.L.; Agard, D.A. Structure of Hsp90-Hsp70-Hop-GR Reveals the Hsp90 Client-Loading Mechanism. Nature 2022, 601, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, N.S.M.; Seraphim, T.V.; Minari, K.; Barbosa, L.R.S.; Borges, J.C. Comparative Studies of the Low-Resolution Structure of Two P23 Co-Chaperones for Hsp90 Identified in Plasmodium Falciparum Genome. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noddings, C.M.; Wang, R.Y.-R.; Johnson, J.L.; Agard, D.A. Structure of Hsp90-P23-GR Reveals the Hsp90 Client-Remodelling Mechanism. Nature 2022, 601, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biebl, M.M.; Lopez, A.; Rehn, A.; Freiburger, L.; Lawatscheck, J.; Blank, B.; Sattler, M.; Buchner, J. Structural Elements in the Flexible Tail of the Co-Chaperone P23 Coordinate Client Binding and Progression of the Hsp90 Chaperone Cycle. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkhivker, G.M. Conformational Dynamics and Mechanisms of Client Protein Integration into the Hsp90 Chaperone Controlled by Allosteric Interactions of Regulatory Switches: Perturbation-Based Network Approach for Mutational Profiling of the Hsp90 Binding and Allostery. J. Phys. Chem. B 2022, 126, 5421–5442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noddings, C.M.; Johnson, J.L.; Agard, D.A. Cryo-EM Reveals How Hsp90 and FKBP Immunophilins Co-Regulate the Glucocorticoid Receptor. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2023, 30, 1867–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, M.; Myasnikov, A.; Elnatan, D.; Delaeter, N.; Nguyenquang, M.; Agard, D. Cryo-EM Structures Reveal a Multistep Mechanism of Hsp90 Activation by Co-Chaperone Aha1. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruszczyk, J.; Grandvuillemin, L.; Lai-Kee-Him, J.; Paloni, M.; Savva, C.G.; Germain, P.; Grimaldi, M.; Boulahtouf, A.; Kwong, H.-S.; Bous, J.; et al. Cryo-EM Structure of the Agonist-Bound Hsp90-XAP2-AHR Cytosolic Complex. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Hang, Y.; Xu, L.; Chen, Y.; Xie, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, L.; Li, G.; et al. Cryo-EM Structure of the Cytosolic AhR Complex. Structure 2023, 31, 295–308.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maimoni Campanella, J.E.; Ramos Junior, S.L.; Rodrigues Kiraly, V.T.; Severo Gomes, A.A.; de Barros, A.C.; Mateos, P.A.; Freitas, F.Z.; de Mattos Fontes, M.R.; Borges, J.C.; Bertolini, M.C. Biochemical and Biophysical Characterization of the RVB-1/RVB-2 Protein Complex, the RuvBL/RVB Homologues in Neurospora Crassa. Biochimie 2021, 191, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seraphim, T.V.; Nano, N.; Cheung, Y.W.S.; Aluksanasuwan, S.; Colleti, C.; Mao, Y.-Q.; Bhandari, V.; Young, G.; Höll, L.; Phanse, S.; et al. Assembly Principles of the Human R2TP Chaperone Complex Reveal the Presence of R2T and R2P Complexes. Structure 2022, 30, 156–171.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seraphim, T.V.; Chakafana, G.; Shonhai, A.; Houry, W.A. Plasmodium Falciparum R2TP Complex: Driver of Parasite Hsp90 Function. Biophys. Rev. 2019, 11, 1007–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Calzada, A.; Pal, M.; Muñoz-Hernández, H.; Luque-Ortega, J.R.; Gil-Carton, D.; Degliesposti, G.; Skehel, J.M.; Prodromou, C.; Pearl, L.H.; Llorca, O. The Structure of the R2TP Complex Defines a Platform for Recruiting Diverse Client Proteins to the HSP90 Molecular Chaperone System. Structure 2017, 25, 1145–1152.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.-N.; Luo, Y. HSP90 Inhibitors and Cancer: Prospects for Use in Targeted Therapies (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2022, 49, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birbo, B.; Madu, E.E.; Madu, C.O.; Jain, A.; Lu, Y. Role of HSP90 in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tittelmeier, J.; Nachman, E.; Nussbaum-Krammer, C. Molecular Chaperones: A Double-Edged Sword in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 581374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lackie, R.E.; Maciejewski, A.; Ostapchenko, V.G.; Marques-Lopes, J.; Choy, W.-Y.; Duennwald, M.L.; Prado, V.F.; Prado, M.A.M. The Hsp70/Hsp90 Chaperone Machinery in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 257764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, W.; Sun, W.; Taldone, T.; Rodina, A.; Chiosis, G. Heat Shock Protein 90 in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Mol. Neurodegener. 2010, 5, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Bansal, A.; Hashimoto-Torii, K. HSP70 and HSP90 in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 716, 134678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumi, M.P.; Ghosh, A. Hsp90 in Human Diseases: Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Approaches. Cells 2022, 11, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubkowska, A.; Pluta, W.; Strońska, A.; Lalko, A. Role of Heat Shock Proteins (HSP70 and HSP90) in Viral Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, W. Heat Shock Proteins and Viral Infection. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 947789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, T.; Singh, H.; Edkins, A.L.; Blatch, G.L. Hsp90 and Associated Co-Chaperones of the Malaria Parasite. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahinas, D.; Folefoc, A.; Pillai, D.R. Targeting Plasmodium Falciparum Hsp90: Towards Reversing Antimalarial Resistance. Pathogens 2013, 2, 33–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
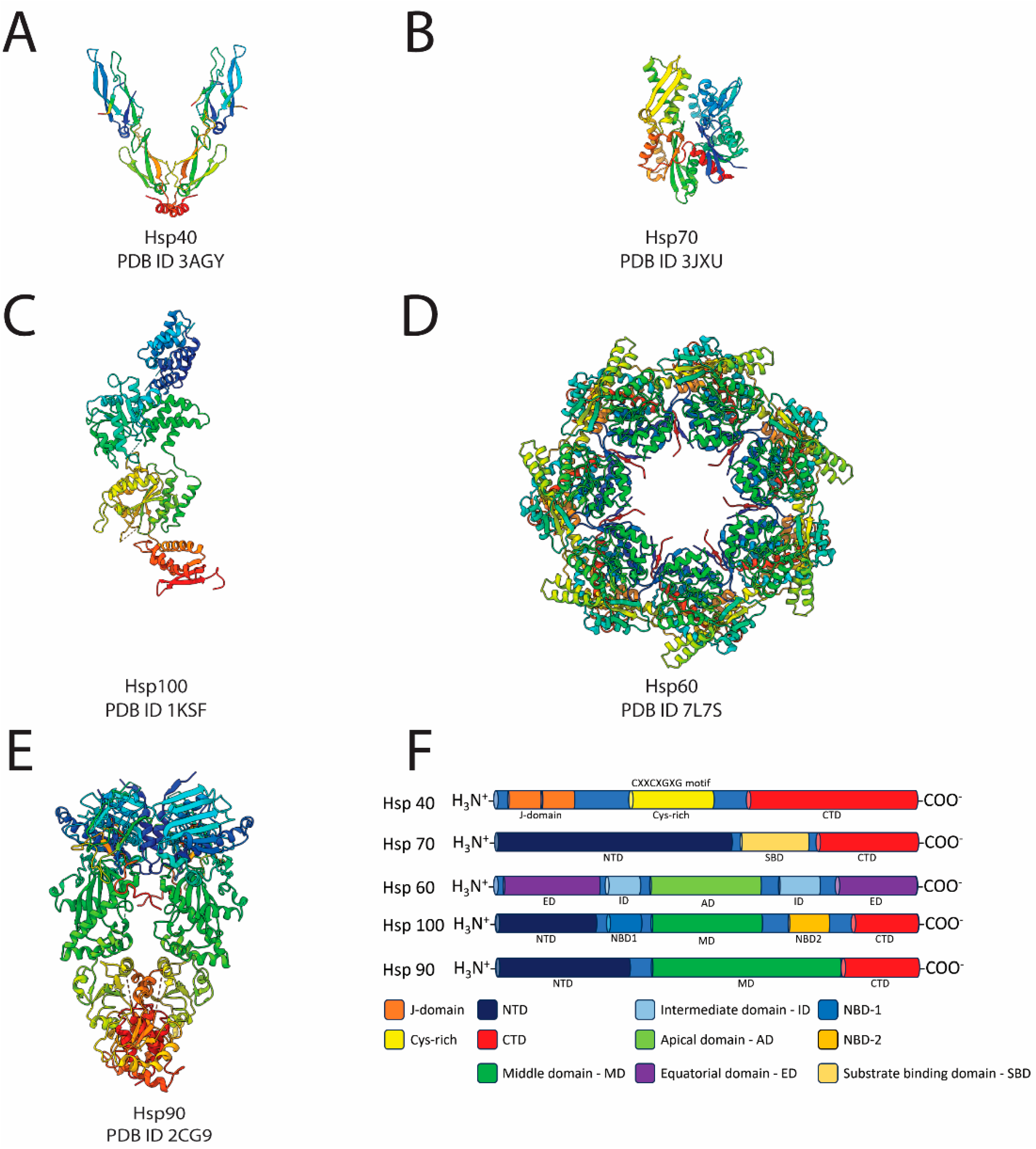
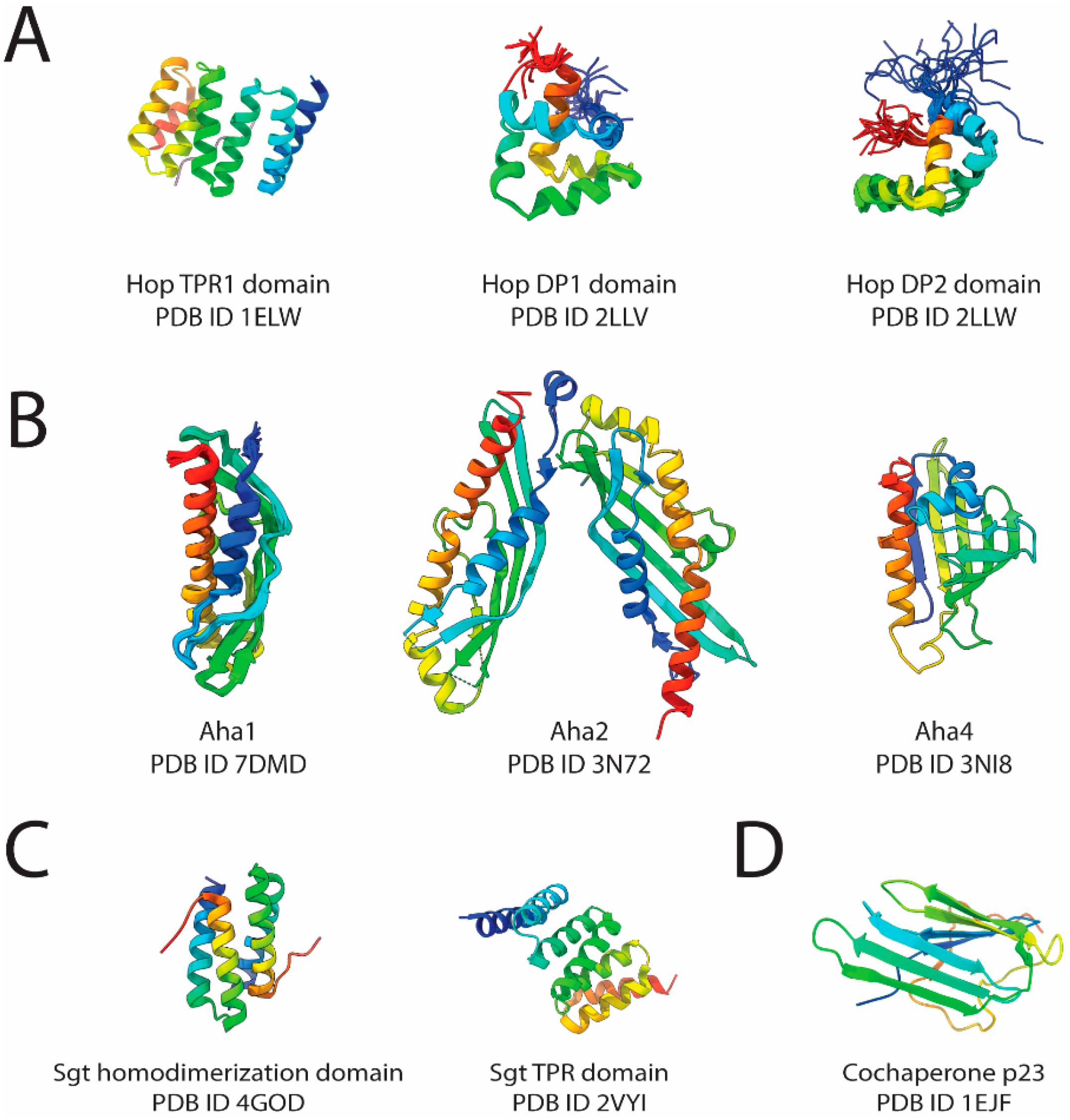
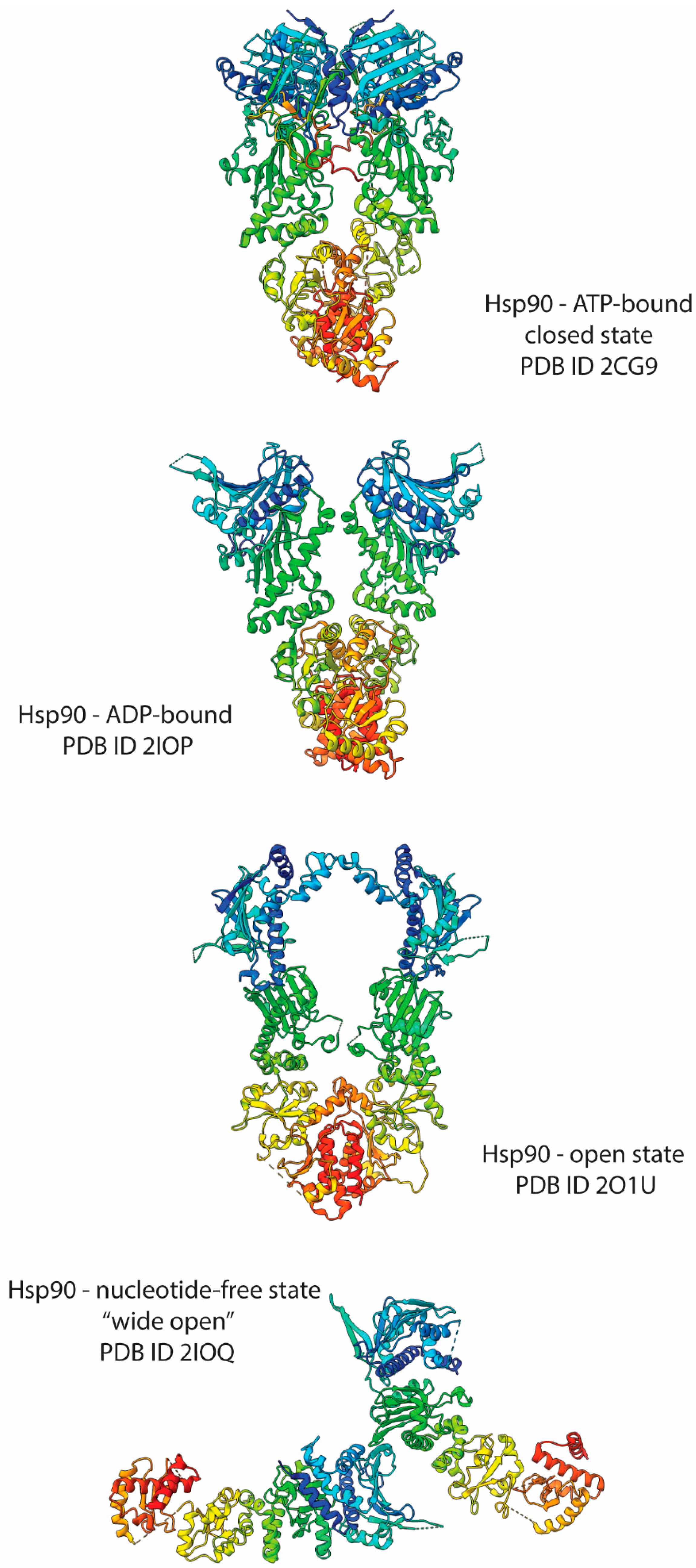
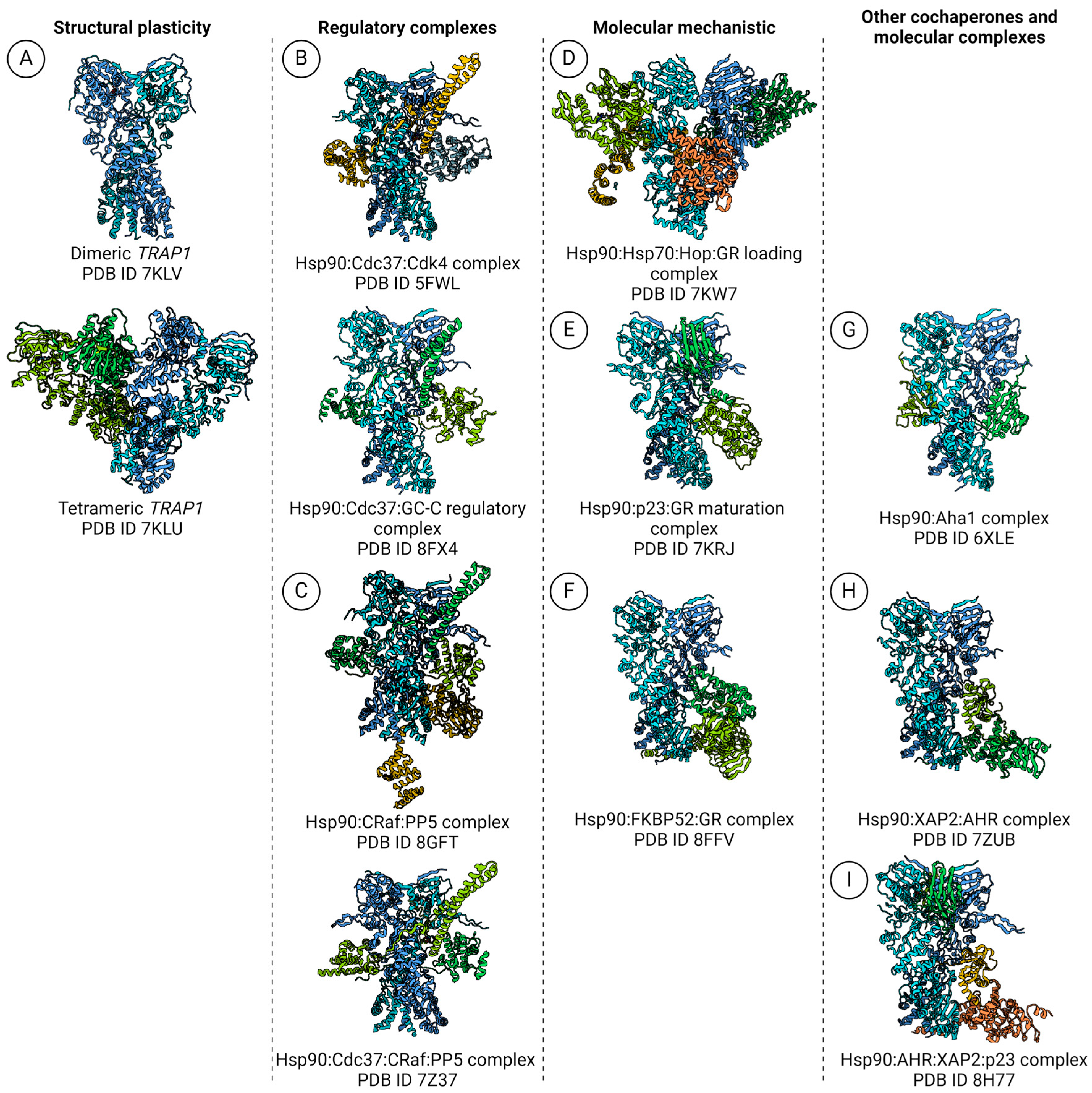
| Class | Nomenclature | PDB ID | Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chaperones and cochaperones | Hsp40—J-Domain Proteins | 3AGY | X-ray crystallography |
| Hsp70 | 3JXU | ||
| Hsp100—Clp or AAA+ proteins | 1KSF | ||
| Hsp60—GroEL | 7L7S | ||
| Hop TPR1 domain | 1ELW | ||
| Hop DP1 domain | 2LLV | NMR | |
| Hop DP2 domain | 2LLW | ||
| Aha1 | 7DMD | ||
| Aha2 | 3N72 | X-ray crystallography | |
| Aha4 | 3NI8 | ||
| Sgt—dimerization domain | 4GOD | ||
| Sgt TPR domain | 2VYI | ||
| Cochaperone p23 | 1EJF | ||
| Hsp90 | Hsp90—ATP-bound closed state | 2CG9 | |
| Hsp90—ADP-bound | 2IOP | ||
| Hsp90—open state | 2O1U | ||
| Hsp90—nucleotide-free wide open state | 2IOQ | ||
| TRAP1 | Dimeric TRAP1 | 7KLV | SPA-cryoEM |
| Tetrameric TRAP1 | 7KLU | ||
| Hsp90 complexes | Hsp90:Cdc37:Cdk4 complex | 5FWL | |
| Hsp90:Cdc37:GC-C regulatory complex | 8FX4 | ||
| Hsp90:CRaf:PP5 complex | 8GFT | ||
| Hsp90:Cdc37:CRaf:PP5 complex | 7Z37 | ||
| Hsp90:Hsp70:Hop:GR loading complex | 7KW7 | ||
| Hsp90:p23:GR maturation complex | 7KRJ | ||
| Hsp90:FKBP52:GR complex | 8FFV | ||
| Hsp90:Aha1 complex | 6XLE | ||
| Hsp90:XAP2:AHR complex | 7ZUB | ||
| Hsp90:AHR:XAP2:p23 complex | 8H77 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Minari, K.; Balasco Serrão, V.H.; Borges, J.C. New Insights into Hsp90 Structural Plasticity Revealed by cryoEM. BioChem 2024, 4, 62-89. https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem4020004
Minari K, Balasco Serrão VH, Borges JC. New Insights into Hsp90 Structural Plasticity Revealed by cryoEM. BioChem. 2024; 4(2):62-89. https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem4020004
Chicago/Turabian StyleMinari, Karine, Vitor Hugo Balasco Serrão, and Júlio César Borges. 2024. "New Insights into Hsp90 Structural Plasticity Revealed by cryoEM" BioChem 4, no. 2: 62-89. https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem4020004
APA StyleMinari, K., Balasco Serrão, V. H., & Borges, J. C. (2024). New Insights into Hsp90 Structural Plasticity Revealed by cryoEM. BioChem, 4(2), 62-89. https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem4020004






