The Role of Digital Innovations in Shaping Contemporary Fixed Prosthodontics: A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A data acquisition unit, which collects data from the prepared area and surrounding structures to create virtual impressions.
- A designing unit, which uses software to design virtual restorations.
- A manufacturing unit, which fabricates the prosthesis through milling or 3D printing.
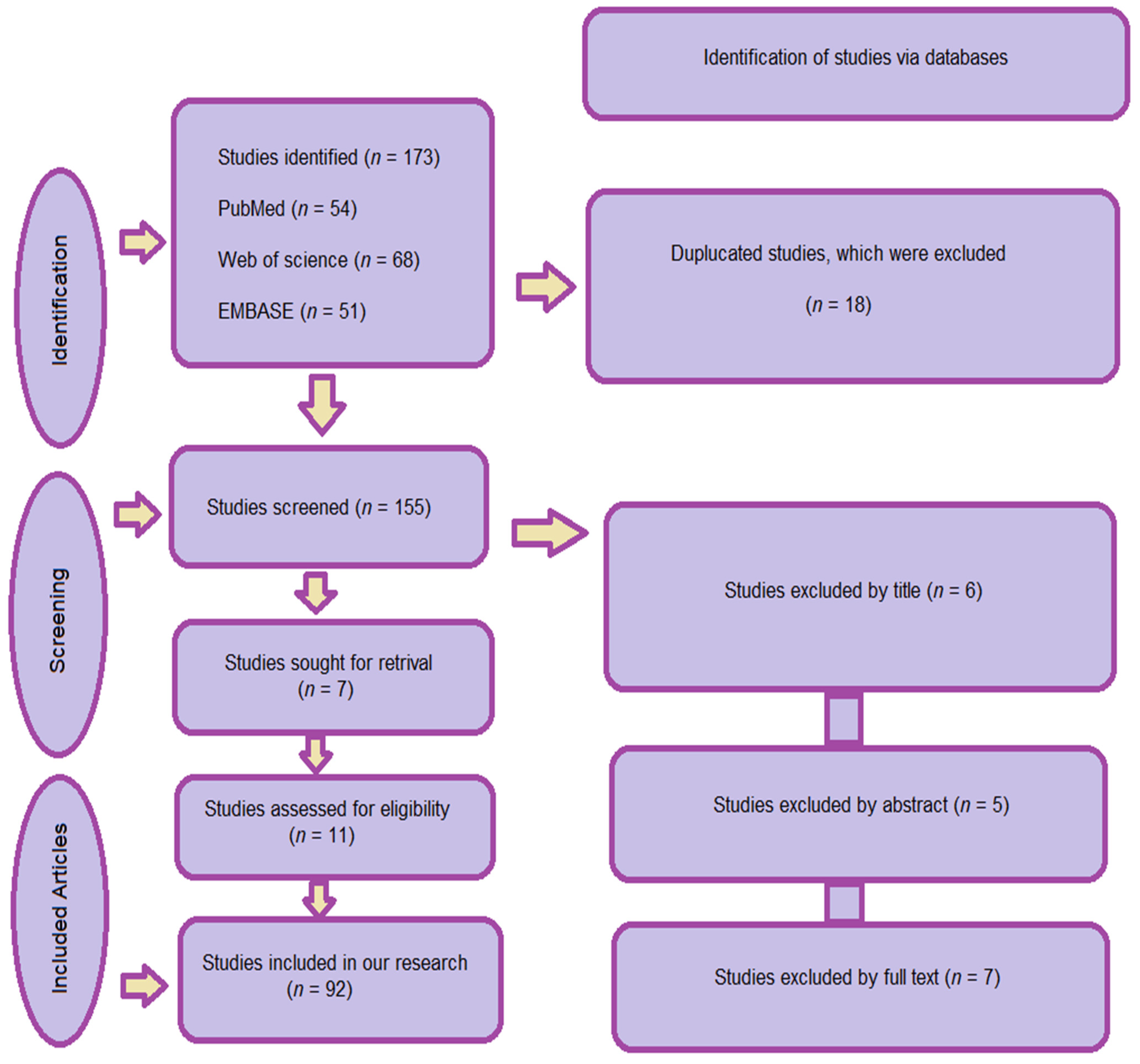
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
- Database Search:
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
- Published in English between January 2000 and May 2024
- Addressed fixed prosthetic restorations using additive or subtractive manufacturing
- Included peer-reviewed in vitro studies, observational clinical studies, case reports, systematic reviews, or RCTs
- Reported outcomes related to accuracy, fit, clinical performance, or workflow efficiency
- Articles were excluded if they:
- They were unrelated to fixed prosthodontics
- Did not involve digital manufacturing methods
- Duplicated previously included data
2.3. Data Categorization and Evaluation
3. Digital Protocol for Fixed Prosthetic Restorations
3.1. Digital Scanning and Impression Techniques
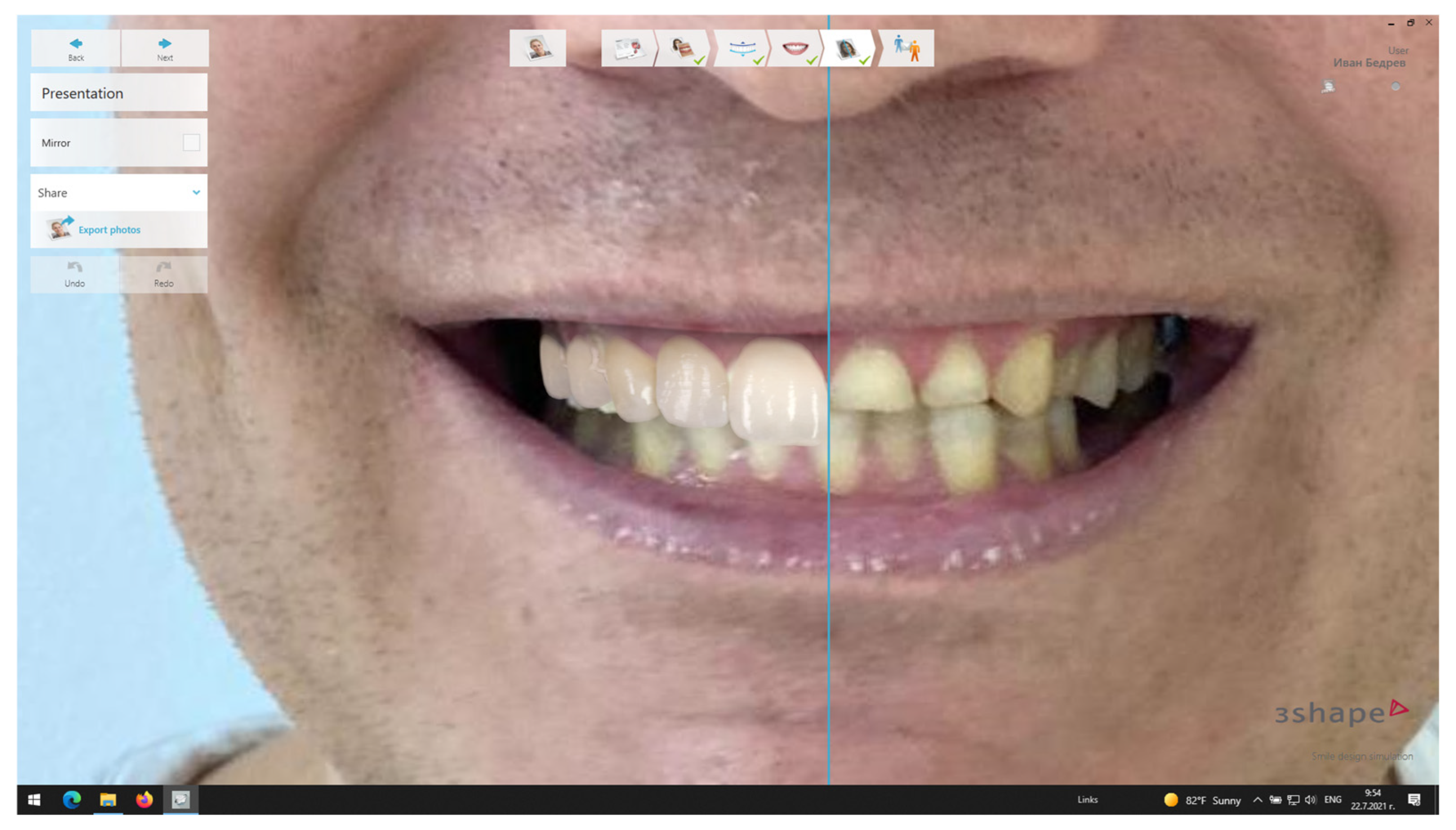
3.2. Digital Smile Design
3.3. Digital Design and Fabrication of the Provisional Restorations
3.4. Fabrication Techniques in Digital Fixed Prosthodontics
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
- Hybrid Manufacturing
3.5. Quality Control and Dimensional Evaluation
3.6. Advantages of Digital Workflow
4. Disadvantages and Limitations of CAD/CAM Technology in Fixed Prosthodontics
5. Critical Appraisal and Future Directions
6. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AM | Additive manufacturing |
| CAD/CAM | Computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing |
| CNC Milling | Computer Numerical Control Milling |
| DSD | Digital smile design |
| IOS | Intraoral scanner |
| FPD | Fixed partial denture |
| SM | Subtractive manufacturing |
| STL | Stereolithography, standard triangle language, standard tessellation language |
| 3D | Three-dimensional |
References
- Pan, S.; Guo, D.; Zhou, Y.; Jung, R.E.; Hämmerle, C.H.F.; Mühlemann, S. Time efficiency and quality of outcomes in a model-free digital workflow using digital impression immediately after implant placement: A double-blind self-controlled clinical trial. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2019, 30, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Jiang, X.; Lin, Y.; Di, P. Crown Accuracy and Time Efficiency of Cement-Retained Implant-Supported Restorations in a Complete Digital Workflow: A Randomized Control Trial. J. Prosthodont. 2022, 31, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Tian, J.; Wei, D.; Di, P.; Lin, Y. Quantitative clinical adjustment analysis of posterior single implant crown in a chairside digital workflow: A randomized controlled trial. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2019, 30, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gintaute, A.; Weber, K.; Zitzmann, N.U.; Brägger, U.; Ferrari, M.; Joda, T. A Double-Blind Crossover RCT Analyzing Technical and Clinical Performance of Monolithic ZrO2 Implant Fixed Dental Prostheses (iFDP) in Three Different Digital Workflows. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gintaute, A.; Zitzmann, N.U.; Brägger, U.; Weber, K.; Joda, T. Patient-reported outcome measures compared to professional dental assessments of monolithic ZrO2 implant fixed dental prostheses in complete digital workflows: A double-blind crossover randomized controlled trial. J. Prosthodont. 2023, 32, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, A.M.; Hashemi, H.M.; Siadat, H.; Shamshiri, A.; Afrashtehfar, K.I.; Alikhasi, M. Fully Digital versus Conventional Workflows for Fabricating Posterior Three-Unit Implant-Supported Reconstructions: A Prospective Crossover Clinical Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joda, T.; Gintaute, A.; Brägger, U.; Ferrari, M.; Weber, K.; Zitzmann, N.U. Time-efficiency and cost-analysis comparing three digital workflows for treatment with monolithic zirconia implant fixed dental prostheses: A double-blinded RCT. J. Dent. 2021, 113, 103779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.W.; Ye, S.Y.; Chien, C.H.; Chen, C.J.; Papaspyridakos, P.; Ko, C.C. Randomized clinical trial of a conventional and a digital workflow for the fabrication of interim crowns: An evaluation of treatment efficiency, fit, and the effect of clinician experience. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2021, 125, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddadi, Y.; Bahrami, G.; Isidor, F. Accuracy of crowns based on digital intraoral scanning compared to conventional impression-a split-mouth randomised clinical study. Clin. Oral Investig. 2019, 23, 4043–4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mühlemann, S.; Benic, G.I.; Fehmer, V.; Hämmerle, C.H.F.; Sailer, I. Clinical quality and efficiency of monolithic glass ceramic crowns in the posterior area: Digital compared with conventional workflows. Int. J. Comput. Dent. 2018, 21, 215–223. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.S.; Lim, Y.J.; Kim, B.; Kim, M.J.; Kwon, H.B. Clinical Evaluation of Time Efficiency and Fit Accuracy of Lithium Disilicate Single Crowns between Conventional and Digital Impression. Materials 2020, 13, 5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sailer, I.; Benic, G.I.; Fehmer, V.; Hämmerle, C.H.F.; Mühlemann, S. Randomized controlled within-subject evaluation of digital and conventional workflows for the fabrication of lithium disilicate single crowns. Part II: CAD-CAM versus conventional laboratory procedures. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2017, 118, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakornwimon, N.; Leevailoj, C. Clinical marginal fit of zirconia crowns and patients’ preferences for impression techniques using intraoral digital scanner versus polyvinyl siloxane material. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2017, 118, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeltner, M.; Sailer, I.; Mühlemann, S.; Özcan, M.; Hämmerle, C.H.; Benic, G.I. Randomized controlled within-subject evaluation of digital and conventional workflows for the fabrication of lithium disilicate single crowns. Part III: Marginal and internal fit. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2017, 117, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capparé, P.; Ferrini, F.; Ruscica, C.; Pantaleo, G.; Tetè, G.; Gherlone, E.F. Digital versus Traditional Workflow for Immediate Loading in Single-Implant Restoration: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Biology 2021, 10, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanozin, B.; Li Manni, L.; Lecloux, G.; Bacevic, M.; Lambert, F. Digital vs. conventional workflow for one-abutment one-time immediate restoration in the esthetic zone: A randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2022, 8, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alauddin, M.S.; Baharuddin, A.S.; Mohd Ghazali, M.I. The Modern and Digital Transformation of Oral Health Care: A Mini Review. Healthcare 2021, 9, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joda, T.; Yeung, A.W.K.; Hung, K.; Zitzmann, N.U.; Bornstein, M.M. Disruptive Innovation in Dentistry: What It Is and What Could Be Next. J. Dent. Res. 2021, 100, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Noort, R. The future of dental devices is digital. Dent. Mater. 2012, 28, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsy, N.; El Kateb, M. Accuracy of intraoral scanners for static virtual articulation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of multiple outcomes. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2022, 132, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joda, T.; Brägger, U. Digital vs. conventional implant prosthetic workflows: A cost/time analysis. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2015, 26, 1430–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joda, T.; Zarone, F.; Ferrari, M. The complete digital workflow in fixed prosthodontics: A systematic review. BMC Oral Health 2017, 17, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernauer, S.A.; Zitzmann, N.U.; Joda, T. The Use and Performance of Artificial Intelligence in Prosthodontics: A Systematic Review. Sensors 2021, 21, 6628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, N.; Abbasi, M.S.; Zuberi, F.; Qamar, W.; Halim, M.S.B.; Maqsood, A.; Alam, M.K. Artificial Intelligence Techniques: Analysis, Application, and Outcome in Dentistry-A Systematic Review. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 9751564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revilla-León, M.; Gómez-Polo, M.; Vyas, S.; Barmak, B.A.; Gallucci, G.O.; Att, W.; Özcan, M.; Krishnamurthy, V.R. Artificial intelligence models for tooth-supported fixed and removable prosthodontics: A systematic review. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2023, 129, 276–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, R.; Galli, M.; Chen, Z.; Mendonca, G.; Meirelles, L.; Wang, H.L.; Chan, H.L. Intraoral scanning reduces procedure time and improves patient comfort in fixed prosthodontics and implant dentistry: A systematic review. Clin. Oral Investig. 2021, 25, 6517–6531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSimone, J.M.; Ermoshkin, A.; Ermoshkin, N.; Samulski, E.T. Continuous Liquid Interphase Printing. U.S. Patent 9,205,601 B2, 8 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Alghazzawi, T.F. Advancements in CAD/CAM Technology: Applications of Recent Developments for CAD/CAM Generated Restorations. Br. Dent. J. 2008, 204, 505–511. [Google Scholar]
- Bernauer, S.A.; Zitzmann, N.U.; Joda, T. The Complete Digital Workflow in Fixed Prosthodontics Updated: A Systematic Review. Healthcare 2023, 11, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlholm, P.; Sipilä, K.; Vallittu, P.; Jakonen, M.; Kotiranta, U. Digital Versus Conventional Impressions in Fixed Prosthodontics: A Review. J. Prosthodont. 2018, 27, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ting-Shu, S.; Jian, S. Intraoral Digital Impression Technique: A Review. J. Prosthodont. 2015, 24, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, P.A.; Krishnamoorthi, D.; Mohan, J.; Raju, R.; Rajajayam, S.; Venkatesan, S. Digital Smile Design. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2022, 14, S43–S49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervino, G.; Fiorillo, L.; Arzukanyan, A.V.; Spagnuolo, G.; Cicciù, M. Dental Restorative Digital Workflow: Digital Smile Design from Aesthetic to Function. Dent. J. 2019, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diwan, K.; Rathee, M.; Tomar, S.S.; Singh, S.; Divakar, S.; Chahal, S. Applications of 3D Printing in Prosthodontics: A Review. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2016, 60, 72–84. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, S.; Sayed, M.E.; Shetty, M.; Alqahtani, S.M.; Al Wadei, M.H.D.; Gupta, S.G.; Othman, A.A.; Alshehri, A.H.; Alqarni, H.; Mobarki, A.H.; et al. Physical and Mechanical Properties of 3D-Printed Provisional Crowns and Fixed Dental Prosthesis Resins Compared to CAD/CAM Milled and Conventional Provisional Resins: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Polymers 2022, 14, 2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakinuma, H.; Izumita, K.; Yoda, N.; Egusa, H.; Sasaki, K. Comparison of the Accuracy of Resin-Composite Crowns Fabricated by Three-Dimensional Printing and Milling Methods. Dent. Mater. J. 2022, 41, 808–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baghani, M.T.; Shayegh, S.S.; Johnston, W.M.; Shidfar, S.; Hakimaneh, S.M.R. In vitro evaluation of the accuracy and precision of intraoral and extraoral complete-arch scans. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2021, 126, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gintaute, A.; Keeling, A.J.; Osnes, C.A.; Zitzmann, N.U.; Ferrari, M.; Joda, T. Precision of maxillo-mandibular registration with intraoral scanners in vitro. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2020, 64, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, D.; Gallucci, G.; Lin, W.S.; Pjetursson, B.; Polido, W.; Roehling, S.; Sailer, I.; Aghaloo, T.; Albera, H.; Bohner, L.; et al. Group 2 ITI Consensus Report: Prosthodontics and implant dentistry. Clin. Oral. Implants Res. 2018, 29 (Suppl. 16), 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sailer, I.; Mühlemann, S.; Kohal, R.J.; Spies, B.C.; Pjetursson, B.E.; Lang, N.P.; Gotfredsen, K.L.; Ellingsen, J.E.; Francisco, H.; Özcan, M.; et al. Reconstructive aspects: Summary and consensus statements of group 3. The 5th EAO Consensus Conference 2018. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2018, 29 (Suppl. 18), 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhambhani, R.; Bhattacharya, J.; Sen, S.K. Digitization and Its Futuristic Approach in Prosthodontics. J. Indian Prosthodont. Soc. 2013, 13, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kihara, H.; Hatakeyama, W.; Komine, F.; Takafuji, K.; Takahashi, T.; Yokota, J.; Oriso, K.; Kondo, H. Accuracy and practicality of intraoral scanner in dentistry: A literature review. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2020, 64, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.; Chugh, A.; Kumar, A.; Rathee, M.; Jain, P. Comparative Evaluation of Fracture Resistance of Anterior Provisional Restorations Fabricated Using Conventional and Digital Techniques—An In Vitro Study. J. Indian Prosthodont. Soc. 2022, 22, 361–367. [Google Scholar]
- Czigola, A.; Róth, I.; Vitai, V.; Fehér, D.; Hermann, P.; Borbély, J. Comparing the Effectiveness of Shade Measurement by Intraoral Scanner, Digital Spectrophotometer, and Visual Shade Assessment. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2021, 33, 1166–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweiger, J.; Edelhoff, D.; Güth, J.F. Update digitale Zahnheilkunde 2020—Aktuelle Möglichkeiten und Limitationen. Bayer. Zahnärzte Bl. 2020, 57, 42–52. [Google Scholar]
- Schweiger, J.; Güth, J.F. Neue Entwicklungen in der additiven und subtraktiven Fertigung Teamwork. J. Cont. Dent. Educ. 2020, 23, 82–90. [Google Scholar]
- Betriebe—Beschäftigte—Auszubildende im Zahntechniker-Handwerk. Available online: https://www.vdzi.de/Ausbildungsverg%C3%BCtungen-2025 (accessed on 20 May 2024).
- Campbell, S.D.; Cooper, L.; Craddock, H.; Hyde, T.P.; Nattress, B.; Pavitt, S.H.; Seymour, D.W. Removable Partial Dentures: The Clinical Need for Innovation. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2017, 118, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, R.A.; Micheelis, W. Fünfte Deutsche Mundgesundheitsstudie (DMS V); Deutscher Zahnärzte: Köln, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Horn, T.J.; Harryson, O.L.A. Overview of Current Additive Manufacturing Technologies and Selected Applications. Sci. Prog. 2012, 95, 255–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawood, A.; Marti, B.; Sauret Jackson, V.; Darwood, A. 3D Printing in Dentistry. Br. Dent. J. 2015, 219, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caviezel, C.; Grünwald, R.; Ehrenberg-Silies, S.; Kind, S.; Jetzke, T.; Bovenschulte, M. Additive Fertigungsverfahren (3D-Druck)—Innovationsanalyse; TAB Arbeitsbereicht: Berlin, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kessler, A.; Hickel, R.; Reymus, M. 3D Printing in Dentistry—State of the Art. Oper. Dent. 2020, 45, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, Y.; Koizumi, H.; Furuchi, M.; Sato, Y.; Ohkubo, C.; Matsumura, H. Use of Digital Impression Systems with Intraoral Scanners for Fabricating Restorations and Fixed Dental Prostheses. J. Oral Sci. 2018, 60, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathee, M.; Alam, M.; Divakar, S.; Malik, S. Resin-Bonded Bridge as a Simplified Approach to Restore Missing Teeth in Esthetic Zone by Conventional and Digital Techniques. Dent. Res. J. 2022, 19, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuer, F.; Schweiger, J.; Edelhoff, D. Digital Dentistry: An Overview of Recent Developments for CAD/CAM Generated Restorations. Br. Dent. J. 2008, 204, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quante, K.; Ludwig, K.; Kern, M. Marginal and internal fit of metal-ceramic crowns fabricated with a new laser melting technology. Dent. Mater. 2008, 24, 1311–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Xiang, N.; Wie, B. The marginal fit of selective laser melting-fabricated metal crowns: An in vitro study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2014, 112, 1437–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, X. Clinical marginal and internal fit of metal ceramic crowns fabricated with a selective laser melting technology. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2015, 113, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lövgren, N.; Roxner, R.; Klemendz, S.; Larsson, C. Effect of production method on surface roughness, marginal and internal fit, and retention of cobalt-chromium single crowns. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2017, 118, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, K.M.; Hellwig, E.; Wenz, H.J. Zahnärztliche Propädeutik; Deutscher Zahnärzte: Köln, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Stark, H. Ist die Modellgussprothese adäquater Zahnersatz für den älteren Menschen? Quintessenz 2005, 56, 367–373. [Google Scholar]
- Tumbletone, J.R.; Shirvanyants, D.; Ermoshkin, N.; Janusziewicz, R.; Johnson, A.R.; Kelly, D.; Chen, K.; Pinschmidt, R.; Rolland, J.P.; Ermoshkin, A.; et al. Additive Manufacturing: Continuous Liquid Interface Production of 3D Objects. Science 2015, 347, 1349–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweiger, J.; Kieschnick, A. CAD/CAM in der Digitalen Zahnheilkunde; Teamwork Media: Fuchstal, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Alifui-Segbaya, F.; Williams, R.J.; George, R. Additive manufacturing: A novel method for fabricating cobalt-chromium removable partial denture frameworks. Eur. J. Prosthodont. Restor. Dent. 2017, 25, 73–78. [Google Scholar]
- Laverty, D.P.; Thomas, M.B.M.; Clark, P.; Addy, L.D. The use of 3D metal printing (direct metal laser sintering) in removable prosthodontics. Dent. Update 2016, 43, 826–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, J.M.; Anami, L.C.; Araujo, R.M.; Pavanelli, C.A. Removable partial dentures: Use of rapid prototyping. J. Prosthodont. 2014, 23, 588–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kieschnick, A.; Schweiger, J.; Edelhoff, D.; Güth, J.F. Status Präsens 2020: Additive CAD/CAM-Gestützte Fertigungstechnologien im Zahntechnischen Labor. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/341990852_Status_Prasens_2020_Additive_CADCAM-gestutzte_Fertigungstechnologien_im_zahntechnischen_Labor#fullTextFileContent (accessed on 24 April 2024).
- Joda, T.; Bragger, U. Time-Efficiency Analysis Comparing Digital and Conventional Workflows for Implant Crowns: A Prospective Clinical Crossover Trial. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2015, 30, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar]
- Kollenberg, W. Keramik und Multimaterial 3D-Druck. Keram. Z. 2014, 66, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO/ASTM 52900; Additive Manufacturing—General Principles—Terminology. Beuth: Berlin, Germany, 2017.
- ISO/ASTM 17296–2; Additive Manufacturing—General Principles—Part 2: Overview of Process Categories and Feedstock. Beuth: Berlin, Germany, 2016.
- Gartner Hype Cycle. Available online: https://www.gartner.com/en/research/methodologies/gartner-hype-cycle (accessed on 28 April 2024).
- Dolabdjian, H.; Strietzel, R. Verfahren zur Herstellung von Zahnersatz und dentalen Hilfsteilen. EP 1 021 997 B2, 26 July 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Revilla-León, M.; Meyer, M.J.; Özcan, M. Metal additive manufacturing technologies. Int. J. Comput. Dent. 2019, 22, 55–67. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, J.; Stawarczyk, B.; Trottmann, A.; Hämmerle, C.H.F. Festigkeit lasergesinterter Brückengerüste aus einer CoCr-legierung. Quintessenz Zahntech. 2008, 34, 140–149. [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph, M.; Setz, J. Ein CAD/CAM-System mit aufbauender Lasertechnologie. Quintessenz Zahntech. 2007, 33, 582–587. [Google Scholar]
- Tregermann, I.; Renne, W.; Kelly, A.; Wilson, D. Evaluation of removable partial denture frameworks fabricated using 3 different techniques. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2019, 122, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Zeghbroeck, L.; Boons, E. Evaluation of technicians working time in the fabrication of removable partial dentures: Cad/Cam versus tradition. In Proceedings of the 14th Biennial Meeting of the International College of Prosthodontics, Waikoloa Village, HI, USA, 7–12 September 2011; p. 63. [Google Scholar]
- Schweiger, J.; Güth, J.F.; Erdelt, K.J.; Edelhoff, D.; Schubert, O. Internal porosities, retentive force, and survival of cobalt-chromium alloy clasps fabricated by selective laser sintering. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2019, 64, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torii, M.; Nakata, T.; Takahashi, K.; Kawamura, N.; Shimpo, H.; Ohkubo, C. Fitness and retentive force of cobalt-chromium alloy clasps fabricated with repeated laser sintering and milling. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2018, 62, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakata, T.; Shimpo, H.; Ohkubo, C. Clasp fabrication using one-process molding by repeated laser sintering and high-speed milling. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2017, 61, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revilla-León, M.; Özcan, M. Additive manufacturing technologies used for processing polymers: Current status and potential application in prosthetic dentistry. J. Prosthodont. 2019, 28, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jockusch, J.; Özcan, M. Additive manufacturing of dental polymers: An overview on processes, materials, and applications. Dent. Mater. J. 2020, 39, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, H.; Zhang, T.; Xu, H.; Luo, S.; Nie, J.; Zhu, X. Photo-curing 3D-printing technique and its challenges. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 22, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, C.A.; Ender, A.; Baumgartner, S.; Mehl, A. A validation study of reconstructed rapid prototyping models produced by two technologies. Angle Orthod. 2017, 87, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.B.; Currier, G.F.; Kadioglu, O.; Kierl, J.P. Accuracy of 3-dimensional printed dental models reconstructed from digital intraoral impressions. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2018, 154, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Shin, Y.S.; Jund, H.D.; Hwang, C.J.; Baik, H.S.; Cha, J.Y. Precision and trueness of dental models manufactured with different 3-dimensional printing technologies. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2018, 153, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallweit, D.; Mönch, W.; Zappe, H. Kontrolliert kippen: Silizium-Mikrospiegel mit integriertem optischen Feedback. Photonik 2006, 4, 62–65. [Google Scholar]
- Viereck, V.; Li, Q.; Jäkel, A.; Hillmer, H. Großflächige Anwendung von optischen MEMS: Mikrospiegel-Arrays zur Tageslichtlenkung. Photonik 2009, 2, 28–29. [Google Scholar]



| Author’s Name | Topic | Article Type | Year of Publication | Reference Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Morsy, N.; El Kateb, M. | Intraoral scanners | Systematic review and meta-analysis | 2022 | [21] |
| Joda, T.; Brägger, U. | Digital vs. conventional implant prosthetic workflows | Cost/time analysis | 2015 | [22] |
| Joda, T.; Zarone, F.; Ferrari, M. | The complete digital workflow in fixed prosthodontics | Systematic review | 2017 | [23] |
| Bernauer, S.A.; Zitzmann, N.U.; Joda, T. | Artificial intelligence in prosthodontics | Systematic review | 2021 | [24] |
| Ahmed, N.; et al. | Artificial intelligence techniques in dentistry | Systematic review | 2021 | [25] |
| Revilla-León, M.; et al. | Artificial intelligence models for fixed and removable prosthodontics | Systematic review | 2023 | [26] |
| Siqueira, R.; et al. | Intraoral scanning in fixed prosthodontics and implant dentistry | Systematic review | 2021 | [27] |
| DeSimone, J.M.; et al. | Continuous Liquid Interface Printing | US Patent | 2015 | [28] |
| Alghazzawi, T.F. | Advancements in CAD/CAM Technology | Literature review | 2008 | [29] |
| Bernauer, S.A.; et al. | The complete digital workflow in fixed prosthodontics (updated) | Systematic review | 2023 | [30] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dimitrova, M. The Role of Digital Innovations in Shaping Contemporary Fixed Prosthodontics: A Narrative Review. Oral 2025, 5, 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/oral5040084
Dimitrova M. The Role of Digital Innovations in Shaping Contemporary Fixed Prosthodontics: A Narrative Review. Oral. 2025; 5(4):84. https://doi.org/10.3390/oral5040084
Chicago/Turabian StyleDimitrova, Mariya. 2025. "The Role of Digital Innovations in Shaping Contemporary Fixed Prosthodontics: A Narrative Review" Oral 5, no. 4: 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/oral5040084
APA StyleDimitrova, M. (2025). The Role of Digital Innovations in Shaping Contemporary Fixed Prosthodontics: A Narrative Review. Oral, 5(4), 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/oral5040084






