Salivary Biomarkers for Early Detection of Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Scoping Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
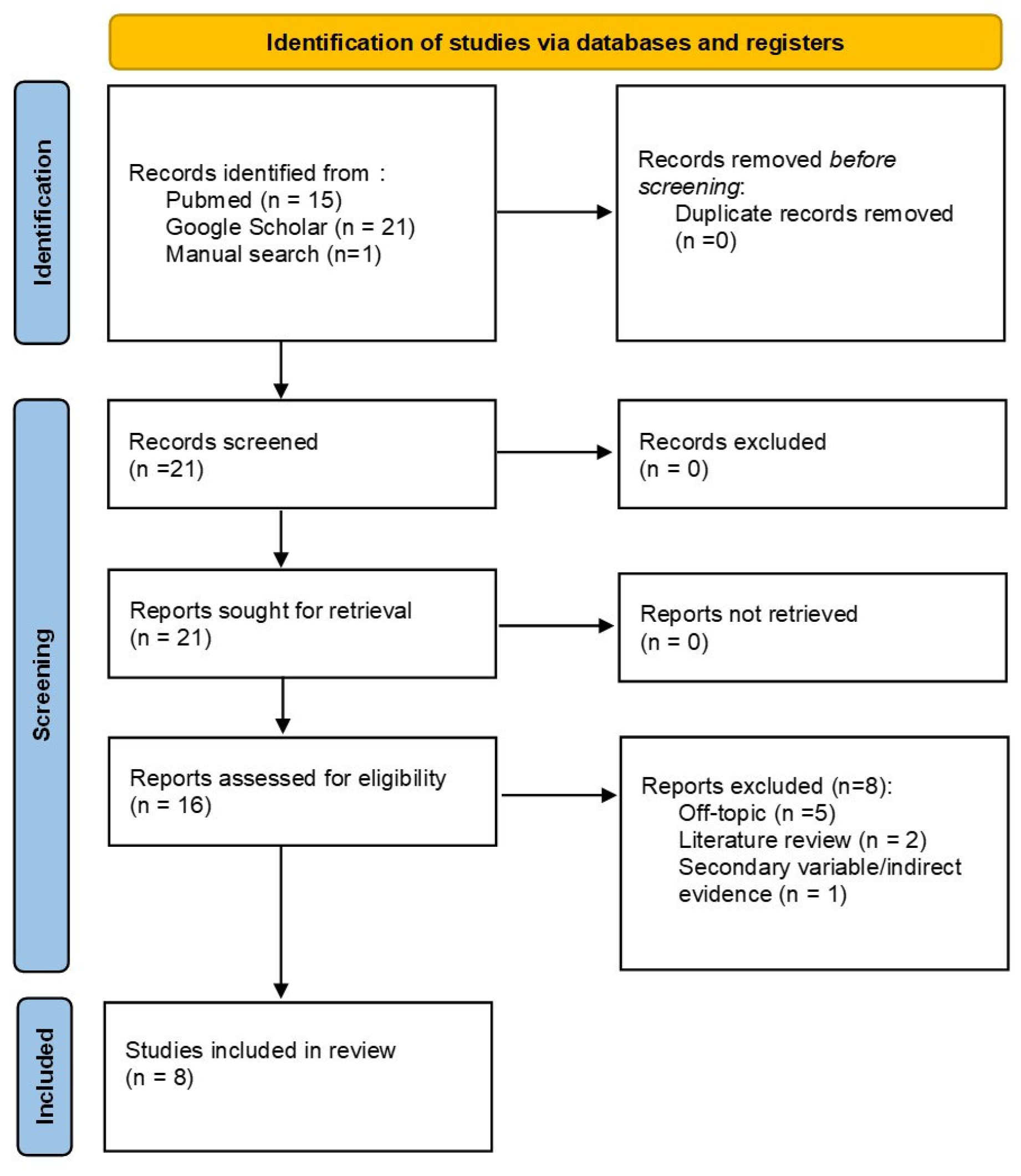
2. Materials and Methods
Screening, Eligibility and Synthesis Processes
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Salivary Biosensors in ASD Diagnosis
| Authors | Journal | Years | Study Design | Sample Size | Age | Biomarker | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
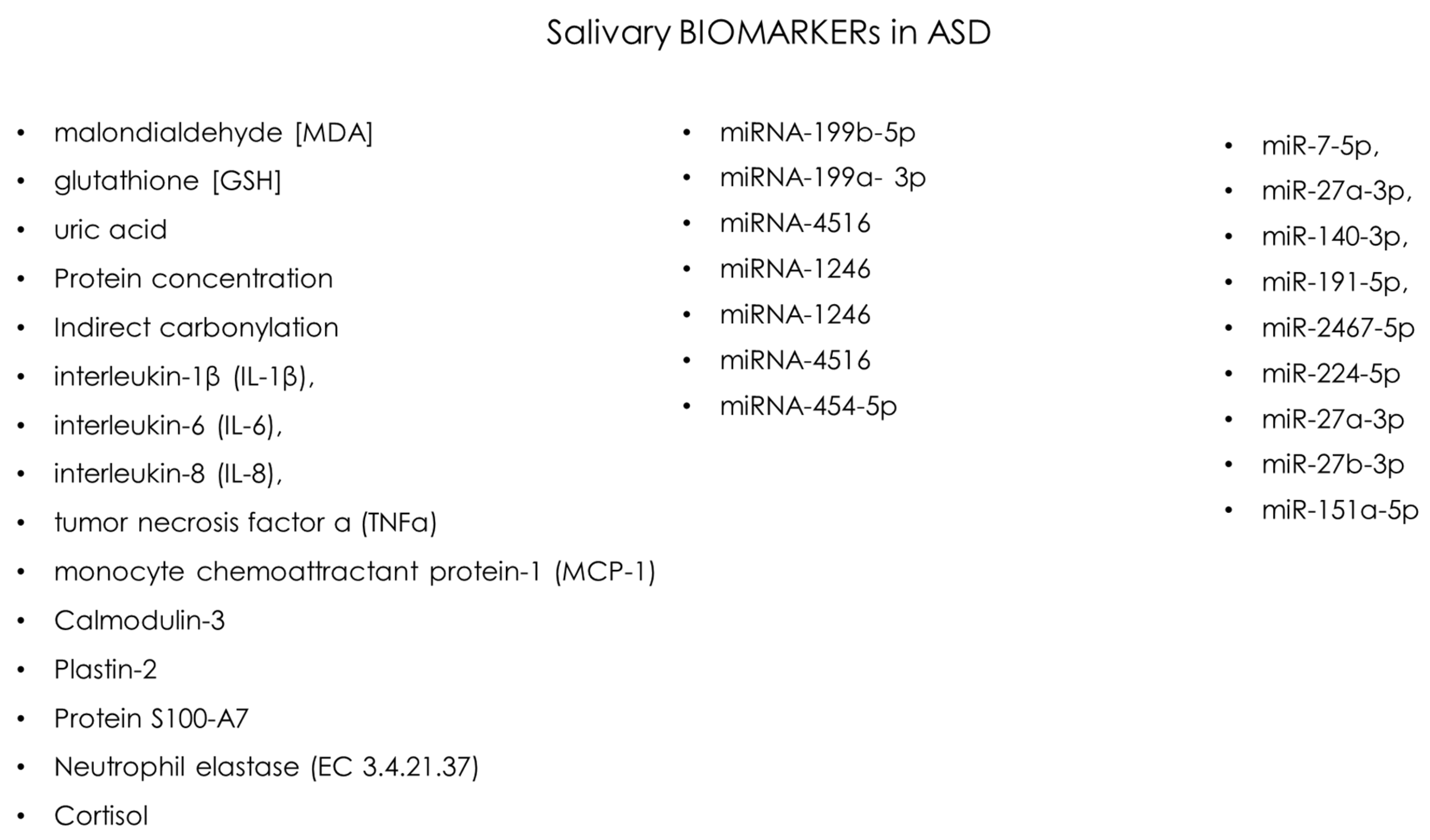
| SS Mahmood | Cureus | 2024 | case-control study | 96 | 5–12 yr | malondialdehyde [MDA] glutathione [GSH] uric acid | [31] |
| Z Kalemaj | Front Neurosci | 2022 | Pilot Study | 10 | 3–7 yr | miRNA-199b-5p (inv. with AUTS2 gene) miRNA-199a- 3p (inv. with CB1 receptor (Cannabinoid receptor type 1) miRNA-4516 miRNA-1246 inv. With SYN II Synapsin II) miRNA-1246 miRNA-4516 miRNA-454-5p | [32] |
| MMD Souza | Rev. Odontol. | 2021 | cross-sectional | 24 | 5–11 yr | Protein concentration uric acid Indirect carbonylation | [33] |
| Hicks SD | BMC Pediatr. | 2016 | cross-sectional | 24 | 5–13 yr | miR-7-5p, miR-27a-3p, miR-140-3p, miR-191-5p, miR-2467-5p | [13] |
| Samborska-Mazur J | J. Clin. Med. | 2020 | cross-sectional | 38 | 3–13 yr | interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-8 (IL-8), tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα), monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), Regulated on Activation, Normal T-cell Expressed and Secreted (RANTES), Eotaxin | [15] |
| Beversdorf DQ | Front Psychiatry | 2022 | cohort study | 898 | 18–73 months | miR-224-5p miR-27a-3p miR-27b-3p miR-151a-5p | [34] |
| Mota FSB | Int. J. Biol. Macromol. | 2022 | case-control study | 75 | 35.47 ± 10.42 months | severe ASD vs. Healthy: Calmodulin-3, Plastin-2 and Protein S100-A7 present in the mild/moderate ASD in the control group; Cysteine-rich secretory protein 3, CRISP-3 and Neutrophil elastase (EC 3.4.21.37) | [35] |
| Abdulla AM | J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. | 2015 | case-control study | 100 | 6–12 yr | Cortisol | [36] |
- Ionization: The molecules present in the saliva sample are ionized, i.e., transformed into ions (electric charges).
- Separation: Ions are separated according to their mass/charge ratio (m/z).
- Detection: Spectrometry measures the abundance of each separate ion, creating a spectrum that represents the molecular composition of the sample [40].
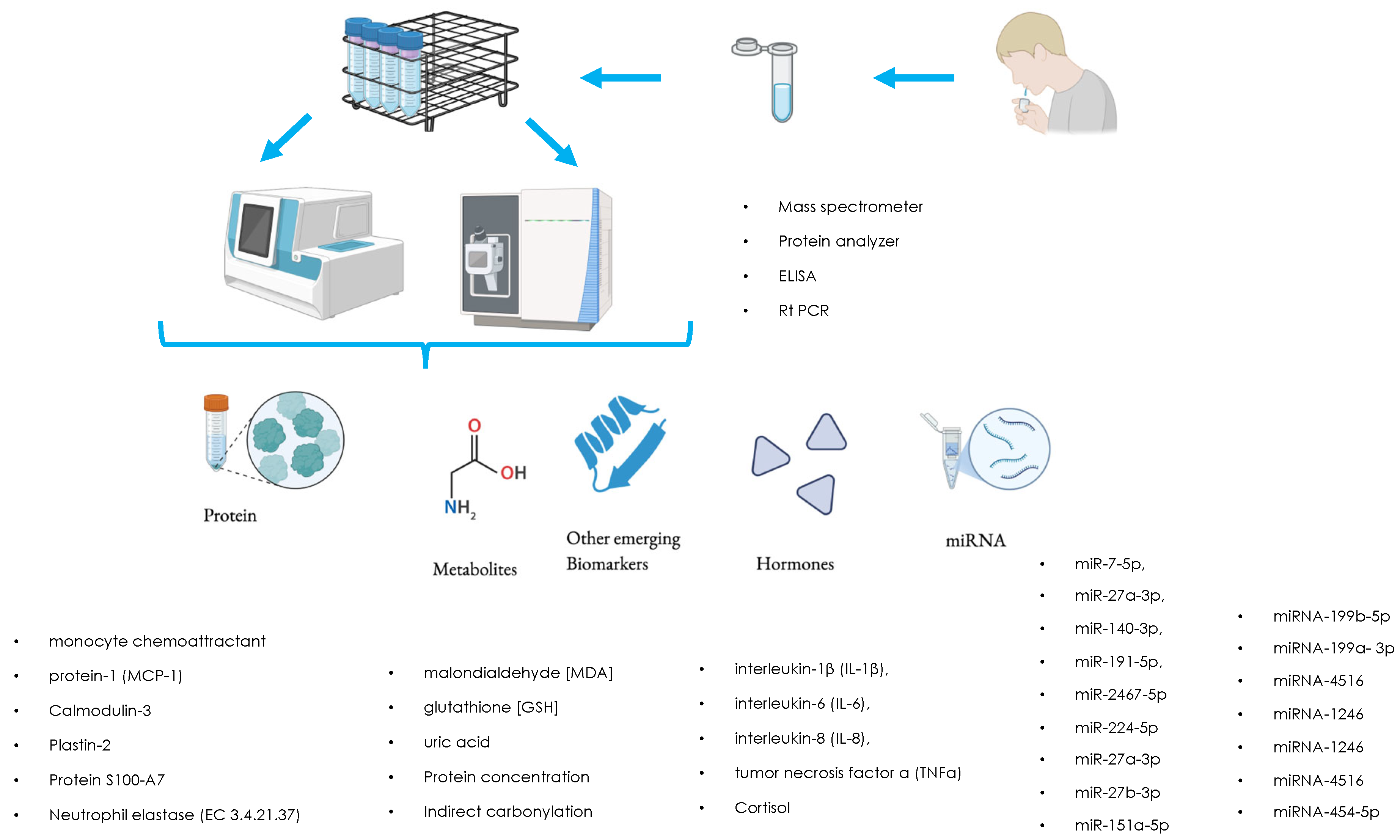
3.2. MicroRNA (miRNA) Profiling
- RNA extraction: The first step is to extract RNA from saliva. This can be done using RNA-specific extraction techniques.
- MiRNA analysis: Once the RNA has been extracted, the microRNA profile can be analyzed through techniques such as quantitative PCR or high-capacity sequencing.
- qPCR (quantitative PCR): Uses specific primers to amplify the microRNAs of interest and measure their abundance.
- Next Generation Sequencing (NGS): Allows to obtain a detailed profile of all the microRNAs present in the sample.
3.3. Proteomics
- Protein identification: Using techniques such as mass spectrometry (which we have discussed) or Western blot, it is possible to identify the proteins present in saliva and determine their levels.
- Quantification: The identified proteins are then quantified to determine if there are any significant differences between children with autism and those with neurotypical condition.
3.4. Metabolomics
3.5. Limits and Future Directions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Campisi, L.; Imran, N.; Nazeer, A.; Skokauskas, N.; Azeem, M.W. Autism Spectrum Disorder. Br. Med. Bull. 2018, 127, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faras, H.; Al Ateeqi, N.; Tidmarsh, L. Autism Spectrum Disorders. Ann. Saudi Med. 2010, 30, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulter, R.A. Understanding the Visual Symptoms of Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). Optom. Vis. Dev. 2009, 40, 164. [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher-Watson, S.; McConnell, F.; Manola, E.; McConachie, H. Interventions Based on the Theory of Mind Cognitive Model for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 2014, CD008785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rescorla, L.; Safyer, P. Lexical Composition in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). J. Child Lang. 2013, 40, 47–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Frith, U.; Happé, F. Autism Spectrum Disorder. Curr. Biol. 2005, 15, R786–R790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, J.; Eigsti, I.-M.; Naigles, L.; Barton, M.; Kelley, E.; Fein, D. Narrative Performance of Optimal Outcome Children and Adolescents with a History of an Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2014, 44, 1681–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsia, Y.; Wong, A.Y.; Murphy, D.G.; Simonoff, E.; Buitelaar, J.K.; Wong, I.C. Psychopharmacological Prescriptions for People with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): A Multinational Study. Psychopharmacology 2014, 231, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachibana, Y.; Miyazaki, C.; Ota, E.; Mori, R.; Hwang, Y.; Kobayashi, E.; Terasaka, A.; Tang, J.; Kamio, Y. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Comprehensive Interventions for Pre-School Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoner, J.B.; Angell, M.E.; House, J.J.; Bock, S.J. Transitions: Perspectives from Parents of Young Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). J. Dev. Phys. Disabil. 2007, 19, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paquet, A.; Olliac, B.; Golse, B.; Vaivre-Douret, L. Current Knowledge on Motor Disorders in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). Child Neuropsychol. 2016, 22, 763–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogay, H.S.; Adeli, H. Machine Learning (ML) for the Diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Using Brain Imaging. Rev. Neurosci. 2020, 31, 825–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, S.D.; Rajan, A.T.; Wagner, K.E.; Barns, S.; Carpenter, R.L.; Middleton, F.A. Validation of a Salivary RNA Test for Childhood Autism Spectrum Disorder. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forsyth, A.; Raslan, K.; Lyashenko, C.; Bona, S.; Snow, M.; Khor, B.; Herrman, E.; Ortiz, S.; Choi, D.; Maier, T. Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: Pilot Studies Examining the Salivary Microbiome and Implications for Gut Metabolism and Social Behavior. Hum. Microbiome J. 2020, 15, 100066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samborska-Mazur, J.; Kostiukow, A.; Miechowicz, I.; Sikorska, D.; Rutkowski, R.; Wyganowska-Świątkowska, M.; Błochowiak, K. Salivary Cytokine Profile as a Possible Predictor of Autism Spectrum Disorder. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dongiovanni, P.; Meroni, M.; Aiello, G.; D’Amato, A.; Cenzato, N.; Casati, S.; Damiani, G.; Fenoglio, C.; Galimberti, D.; Grossi, E.; et al. Salivary Proteomic Profile of Young Healthy Subjects. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1327233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wormwood, K.L.; Charette, L.; Ryan, J.P.; Darie, C.C.; Woods, A.G. A Proteomics Investigation of Salivary Profiles as Potential Biomarkers for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). Protein J. 2023, 42, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.N.; Kato, H.; Masuda, K.; Yamaza, H.; Hirofuji, Y.; Sato, H.; Pham, T.T.M.; Takayama, F.; Sakai, Y.; Ohga, S.; et al. Impaired Neurite Development Associated with Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Dopaminergic Neurons Differentiated from Exfoliated Deciduous Tooth-Derived Pulp Stem Cells of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2018, 16, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roi, A.; Roi, C.; Negruțiu, M.L.; Rusu, L.C.; Riviș, M. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived from Human Periapical Cysts and Their Implications in Regenerative Medicine. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.J.; Colombo, J.; Unruh, K.E. Pupil and Salivary Indicators of Autonomic Dysfunction in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Dev. Psychobiol. 2013, 55, 465–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutton, B.; Salanti, G.; Caldwell, D.M.; Chaimani, A.; Schmid, C.H.; Cameron, C.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Straus, S.; Thorlund, K.; Jansen, J.P.; et al. The PRISMA Extension Statement for Reporting of Systematic Reviews Incorporating Network Meta-Analyses of Health Care Interventions: Checklist and Explanations. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldoni, R.; Scolaro, A.; Boccalari, E.; Dolci, C.; Scarano, A.; Inchingolo, F.; Ravazzani, P.; Muti, P.; Tartaglia, G. Malignancies and Biosensors: A Focus on Oral Cancer Detection through Salivary Biomarkers. Biosensors 2021, 11, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.K.; Koo, J.; Lee, Y.K.; Rogers, J.A. Advanced Materials and Devices for Bioresorbable Electronics. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 988–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nath, N.; Chakroborty, S.; Vishwakarma, D.P.; Goga, G.; Yadav, A.S.; Mohan, R. Recent advances in sustainable nature-based functional materials for biomedical sensor technologies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2024, 31, 57289–57313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini, E.S.; Dervin, S.; Ganguly, P.; Dahiya, R. Biodegradable Materials for Sustainable Health Monitoring Devices. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 163–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, Y.J.; Ryu, B.; Ahn, S.; Koh, W.-G. A Colorimetric Biosensor Based on a Biodegradable Fluidic Device Capable of Efficient Saliva Sampling and Salivary Biomarker Detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 396, 134601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldoni, R.; Farronato, M.; Connelly, S.T.; Tartaglia, G.M.; Yeo, W.-H. Recent Advances in Graphene-Based Nanobiosensors for Salivary Biomarker Detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 171, 112723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, S.; Abdul Manap, A.S.; Attiq, A.; Albokhadaim, I.; Kandeel, M.; Alhojaily, S.M. From Imbalance to Impairment: The Central Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in Oxidative Stress-Induced Disorders and Therapeutic Exploration. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1269581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataramani, V.; Tanev, D.I.; Strahle, C.; Studier-Fischer, A.; Fankhauser, L.; Kessler, T.; Körber, C.; Kardorff, M.; Ratliff, M.; Xie, R.; et al. Glutamatergic Synaptic Input to Glioma Cells Drives Brain Tumour Progression. Nature 2019, 573, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takiguchi, M.; Sato, I.; Ueda, Y.; Kawata, S.; Natsuyama, Y.; Yakura, T.; Li, Z.-L.; Itoh, M. Structural and CBCT Analysis of Mandibular Canal Microvessels Expressing Neurotransmitters in Human Cadavers. Surg. Radiol. Anat. SRA 2023, 45, 975–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, S.S.; Alzubaidee, A.F.; Hussein, V.M. Assessment of Saliva Oxidative Stress Biomarkers and Gingival Health Status in a Sample of High-Functioning Autistic Children in Erbil City. Cureus 2024, 16, e73717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalemaj, Z.; Marino, M.M.; Santini, A.C.; Tomaselli, G.; Auti, A.; Cagetti, M.G.; Borsello, T.; Costantino, A.; Inchingolo, F.; Boccellino, M.; et al. Salivary microRNA Profiling Dysregulation in Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Pilot Study. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 945278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, M.M.D.; Rodrigues, J.V.S.; Gonçalves, M.E.C.; Rossato, A.C.P.; Stein, M.C.R.V.; Poli, M.C.F.; Theodoro, L.H.; Nakamune, A.C.D.M.S. Gender Influence on Antioxidant Capacity and Oxidative Damage in Saliva of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Preliminary Study. Rev. Odontol. UNESP 2021, 50, e20210057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beversdorf, D.Q.; Sohl, K.; Levitskiy, D.; Tennant, P.; Goin-Kochel, R.P.; Shaffer, R.C.; Confair, A.; Middleton, F.A.; Hicks, S.D. Saliva RNA Biomarkers of Gastrointestinal Dysfunction in Children with Autism and Neurodevelopmental Disorders: Potential Implications for Precision Medicine. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 824933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, F.S.B.; Nascimento, K.S.; Oliveira, M.V.; Osterne, V.J.S.; Clemente, J.C.M.; Correia-Neto, C.; Lima-Neto, A.B.; Van Tilburg, M.F.; Leal-Cardoso, J.H.; Guedes, M.I.F.; et al. Potential Protein Markers in Children with Autistic Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Revealed by Salivary Proteomics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 199, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulla, A.; Hegde, A. Salivary Cortisol Levels and Its Implication on Behavior In Children with Autism during Dental Treatment. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2015, 39, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnoni, A.; Lippolis, R.; Zanotti, F.; Papa, S.; Palese, L.L. A Two-Dimensional Electrophoresis and Mass Spectrometry Protein Analysis of the Antibiotic Producer Nonomuraea Sp. ATCC 39727 in Different Growth Conditions. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2007, 274, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongiovanni, P.; Meroni, M.; Casati, S.; Goldoni, R.; Thomaz, D.V.; Kehr, N.S.; Galimberti, D.; Del Fabbro, M.; Tartaglia, G.M. Salivary Biomarkers: Novel Noninvasive Tools to Diagnose Chronic Inflammation. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2023, 15, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay, S.; Rawat, M.; Sharma, A. Mass Spectrometry Based Proteomic Analysis of Salivary Glands of Urban Malaria Vector Anopheles Stephensi. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 686319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Nuttall, P.A. Comparison of the Proteins in Salivary Glands, Saliva and Haemolymph of Rhipicephalus Appendiculatus Female Ticks during Feeding. Parasitology 1994, 109 Pt.4, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Hirata, M.; Shinonome, S.; Torii, M.; Nezasa, K.-I.; Tanaka, H. Distribution Analysis of Epertinib in Brain Metastasis of HER2-Positive Breast Cancer by Imaging Mass Spectrometry and Prospect for Antitumor Activity. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitskiy, D.; Confair, A.; Wagner, K.E.; DeVita, S.; Shea, N.; McKernan, E.P.; Kopec, J.; Russo, N.; Middleton, F.A.; Hicks, S.D. Longitudinal Stability of Salivary microRNA Biomarkers in Children and Adolescents with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Res. Autism Spectr. Disord. 2021, 85, 101788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tumedei, M.; Mancinelli, R.; Di Filippo, E.S.; Marrone, M.; Iezzi, G.; Piattelli, A.; Fulle, S. Osteogenic Potential of Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells Co-Cultured with Equine Bone Substitute Combined with Melatonin. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2022, 42, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcà, B.; Colantoni, A.; Fiorillo, C.; Severini, F.; Benes, V.; Di Luca, M.; Calogero, R.A.; Lombardo, F. MicroRNAs from Saliva of Anopheline Mosquitoes Mimic Human Endogenous miRNAs and May Contribute to Vector-Host-Pathogen Interactions. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulzele, A.; Malgundkar, S.A.; Govekar, R.B.; Patil, A.; Kane, S.V.; Chaturvedi, P.; D’Cruz, A.K.; Zingde, S.M. Proteomic Profile of Keratins in Cancer of the Gingivo Buccal Complex: Consolidating Insights for Clinical Applications. J. Proteom. 2013, 91, 242–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghazadeh, A.; Rezaei, N. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Levels in Autism: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2017, 47, 1018–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xia, J.; Yin, H.; Qiu, Z.; Wang, H.; Xu, W.; Xu, Z.; Xie, J. Analysis of Salivary Steroid Hormones in Boys with Autism Spectrum Disorder. BMC Psychiatry 2023, 23, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasue, H.; Domes, G. Oxytocin and Autism Spectrum Disorders. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 35, 449–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagnola, M.; Messana, I.; Inzitari, R.; Fanali, C.; Cabras, T.; Morelli, A.; Pecoraro, A.M.; Neri, G.; Torrioli, M.G.; Gurrieri, F. Hypo-Phosphorylation of Salivary Peptidome as a Clue to the Molecular Pathogenesis of Autism Spectrum Disorders. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 5327–5332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glinton, K.E.; Elsea, S.H. Untargeted Metabolomics for Autism Spectrum Disorders: Current Status and Future Directions. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussap, M.; Noto, A.; Fanos, V. Metabolomics of Autism Spectrum Disorders: Early Insights Regarding Mammalian-Microbial Cometabolites. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2016, 16, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siracusano, M.; Arturi, L.; Riccioni, A.; Noto, A.; Mussap, M.; Mazzone, L. Metabolomics: Perspectives on Clinical Employment in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ansary, A.; Chirumbolo, S.; Bhat, R.S.; Dadar, M.; Ibrahim, E.M.; Bjørklund, G. The Role of Lipidomics in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2020, 24, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Tang, X.; Xing, A.; Lin, J.; Li, J.; Ji, J.; Cai, T.; Zheng, K.; Lingampelly, S.S. Causal Metabolomic and Lipidomic Analysis of Circulating Plasma Metabolites in Autism: A Comprehensive Mendelian Randomization Study with Independent Cohort Validation. Metabolites 2024, 14, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, C.X.; Henders, A.K.; Alvares, G.A.; Giles, C.; Huynh, K.; Nguyen, A.; Wallace, L.; McLaren, T.; Yang, Y.; Hernandez, L.M. Interactions between the Lipidome and Genetic and Environmental Factors in Autism. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 936–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tumedei, M.; Cenzato, N.; Panda, S.; Goker, F.; Del Fabbro, M. Salivary Biomarkers for Early Detection of Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Scoping Review. Oral 2025, 5, 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/oral5030056
Tumedei M, Cenzato N, Panda S, Goker F, Del Fabbro M. Salivary Biomarkers for Early Detection of Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Scoping Review. Oral. 2025; 5(3):56. https://doi.org/10.3390/oral5030056
Chicago/Turabian StyleTumedei, Margherita, Niccolò Cenzato, Sourav Panda, Funda Goker, and Massimo Del Fabbro. 2025. "Salivary Biomarkers for Early Detection of Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Scoping Review" Oral 5, no. 3: 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/oral5030056
APA StyleTumedei, M., Cenzato, N., Panda, S., Goker, F., & Del Fabbro, M. (2025). Salivary Biomarkers for Early Detection of Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Scoping Review. Oral, 5(3), 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/oral5030056









