The Impact of Upper Jaw Expansion Treatment on Vertical Craniofacial Characteristics and Upper Airway Dimensions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Craniofacial Characteristics Analysis
2.3. Upper Airway Dimensions Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Vertical Craniofacial Characteristics
3.2. Upper Airway Dimensions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McNamara, J.A. Maxillary transverse deficiency. Angle Orthod. 2000, 70, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunetto, D.P.; Sant’Anna, E.F.; Machado, A.W.; Moon, W. Non-surgical treatment of transverse deficiency in adults using Microimplant-assisted Rapid Palatal Expansion (MARPE). Dent. Press J. Orthod. 2017, 22, 110–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucci, R.; Montanaro, D.; Rongo, R.; Valletta, R.; Michelotti, A.; D’Antò, V. Effects of maxillary expansion on the upper airways: Evidence from systematic reviews and meta-analyses. J. Oral Rehabil. 2019, 46, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gungor, A.Y.; Turkkahraman, H. Effects of airway problems on maxillary growth: A review. Eur. J. Dent. 2009, 3, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin Dakhil, N.; Bin Salamah, F. The Diagnosis Methods and Management Modalities of Maxillary Transverse Discrepancy. Cureus 2021, 13, e20482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.H. Diagnosis of transverse problems. Semin. Orthod. 2019, 25, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanarsdall, R.L.; Blasi, I. Applying new knowledge to the correction of the transverse dimension. In Anecdote, Expertise and Evidence: Applying New Knowledge to Everyday Orthodontics; University of Michigan: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2017; pp. 167–193. [Google Scholar]
- Bucci, R.; D’Antò, V.; Rongo, R.; Valletta, R.; Martina, R.; Michelotti, A. Dental and skeletal effects of palatal expansion techniques: A systematic review of the current evidence from systematic reviews and meta-analyses. J. Oral Rehabil. 2016, 43, 543–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Vargas, J.A.; Silva, T.A.; Macari, S.; de Las Casas, E.B.; Garzón-Alvarado, D.A. Influence of interdigitation and expander type in the mechanical response of the midpalatal suture during maxillary expansion. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2019, 176, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, A.J. Long-term posttreatment evaluation of rapid palatal expansion. Angle Orthod. 1980, 50, 189–217. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, A.; Mathur, R. Maxillary Expansion. Int. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2010, 3, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, F.M.P.; Abi-Ramia, L.B.P.; Stuani, A.S.; Stuani, M.B.S.; Artese, F. Vertical growth control during maxillary expansion using a bonded Hyrax appliance. Dent. Press J. Orthod. 2012, 17, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garib, D.G.; Henriques, J.F.; Carvalho, P.E.; Gomes, S.C. Longitudinal effects of rapid maxillary expansion. Angle Orthod. 2007, 77, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilinç, A.S.; Arslan, S.G.; Kama, J.D.; Ozer, T.; Dari, O. Effects on the sagittal pharyngeal dimensions of protraction and rapid palatal expansion in Class III malocclusion subjects. Eur. J. Orthod. 2008, 30, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccetti, T.; Franchi, L.; Mucedero, M.; Cozza, P. Treatment and post-treatment effects of facemask therapy on the sagittal pharyngeal dimensions in Class III subjects. Eur. J. Orthod. 2010, 32, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, R.H.; de Assumpção, M.S.; Ribeiro, J.D.; Sakano, E. Impact of rapid maxillary expansion on mouth-breathing children and adolescents: A systematic review. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2021, 13, e1258–e1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, S.; Kalaskar, R.; Kalaskar, A. Rapid Maxillary Expansion and Upper Airway Volume: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis on the Role of Rapid Maxillary Expansion in Mouth Breathing. Int. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2022, 15, 617–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lione, R.; Balboni, A.; Di Fazio, V.; Pavoni, C.; Cozza, P. Effects of pendulum appliance versus clear aligners in the vertical dimension during Class II malocclusion treatment: A randomized prospective clinical trial. BMC Oral Health 2022, 22, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.H.; Font, B. Skeletal and dental changes in the sagittal, vertical, and transverse dimensions after rapid palatal expansion. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2004, 126, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozza, P.; Giancotti, A.; Petrosino, A. Rapid palatal expansion in mixed dentition using a modified expander: A cephalometric investigation. J. Orthod. 2001, 28, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutili, V.; Souki, B.Q.; Nieri, M.; Carlos, A.L.F.M.; Pavoni, C.; Cozza, P.; McNamara, J.A., Jr.; Giuntini, V.; Franchi, L. Long-term effects produced by early treatment of Class III malocclusion with rapid maxillary expansion and facemask followed by fixed appliances: A multicentre retro-prospective controlled study. Orthod. Craniofac. Res. 2024, 27, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muretić, Ž.; Rak, D. Promjene vrijednosti mandibularnoga kuta i njegovih segmenata tijekom rasta. Acta Stomatol. Croat. 1991, 25, 219–224. [Google Scholar]
- Hersberger-Zurfluh, M.A.; Papageorgiou, S.N.; Motro, M.; Kantarci, A.; Will, L.A.; Eliades, T. Vertical growth in mono-and dizygotic twins: A longitudinal cephalometric cohort study. Orthod. Craniofac. Res. 2020, 23, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouvelis, G.; Dritsas, K.; Doulis, I.; Kloukos, D.; Gkantidis, N. Effect of orthodontic treatment with 4 premolar extractions compared with nonextraction treatment on the vertical dimension of the face: A systematic review. Am. J. Orthod. 2018, 154, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skieller, V.; Bjork, A.; Lind-Hanse, T. Prediction of mandibular growth rotation evaluated from a longitudinal implant sample. Am. J. Orthod. 1984, 86, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faccioni, P.; Pardo, A.; Montini, E.; Bazzanella, S.; Pancera, P.; Beccherle, M.; Caroprese, M.; Lonardi, F.; Signoriello, A.; Montagna, P.; et al. Cephalometric variation of vertical dimension in patients treated with hyrax-type and McNamara-type rapid palatal expander. Study on latero-lateral teleradiography. Journal of Applied Cosmetology. J. Appl. Cosmetol. 2024, 42, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faccioni, P.; Sacchetto, L.; Sinigaglia, S.; Marchiori, M.; Pardo, A.; Zangani, A.; Luciano, U.; Melloni, F.; Albanese, M.; De Santis, D.; et al. An improvement of upper airway flow in patients treated with rapid maxillary expansion: A Cone Beam Computed Tomography study. J. Appl. Cosmetol. 2023, 41, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Measured Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| SNA | Position of the maxilla relative to the cranial base |
| SNB | Position of the mandible relative to the cranial base |
| ANB | Sagittal intermaxillary relationship |
| Wits | Linear measurement of the skeletal class |
| ANPG | Profile of the facial bone structures |
| SN:NL | Angle between the cranial base and the nasal line |
| IntermaxAngle | Intermaxillary angle |
| SArGo | Gonial angle |
| MeGoAr | Mandibular angle |
| Bjork | Björk’s polygon |
| NSGn | Y-axis angle |
| Sn:gogn | Angle between the cranial base and the mandibular plane |
| U1Mx | Angle of inclination of the upper incisors to the skeletal base of the maxilla |
| L1Md | Angle of inclination of the lower incisors to the skeletal base of the mandible |
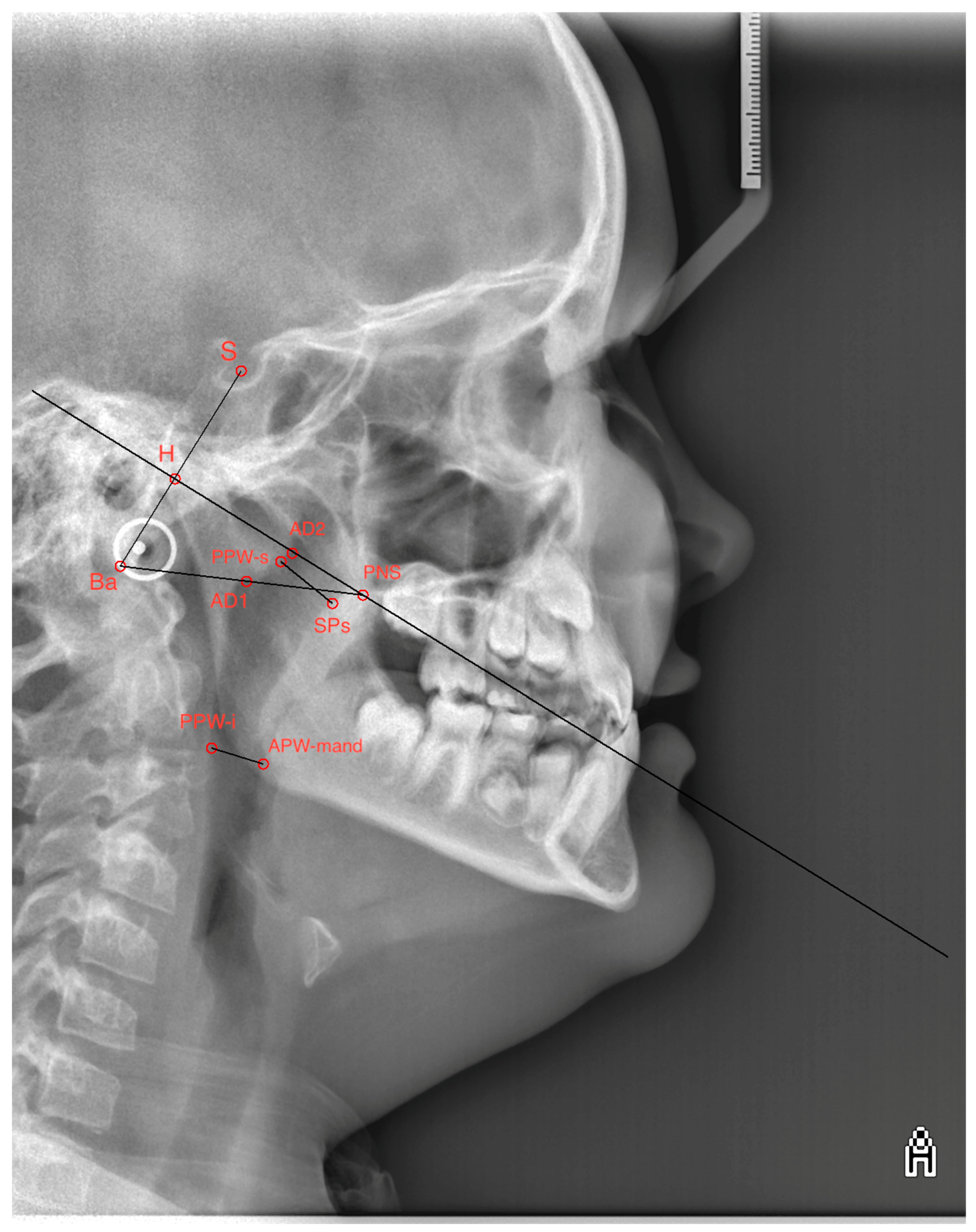
| Point, Lines and Measured Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| S (Sella turcica) | Central point of the sella turcica |
| Ba (Basion) | Point on the lower part of the occipital bone |
| PNS (Posterior Nasal Spine) | Spina nasalis posterior |
| H (Hormion) | Point on the posterior border of the foramen magnum |
| AD2 (Adenoid upper point) | Upper point of the adenoids |
| D1 (Adenoid lower point) | Lower point of the adenoids |
| SPs (Upper soft palate dorsum) | Upper part of the soft palate dorsum |
| PPW-s (Posterior pharynx wall, superior point) | Upper point of the posterior wall of the pharynx |
| APW-mand (Anterior pharynx wall at mandible) | Anterior wall of the pharynx at the level of the mandible. |
| PPW-i (Posterior pharynx wall, inferior point) | Lower point of the posterior wall of the pharynx |
| SBa line | Line defined by the points S and Ba |
| SBa line|PNS | Line perpendicular to the SBa line passing through the PNS point |
| BaPNS line | Line defined by the points Ba and PNS |
| Upper airway | Distance between the points AD2 and PNS |
| Upper adenoid | Distance between the points H and AD2 |
| Lower airway | Distance between the points AD1 and PNS |
| Lower adenoid | Distance between the points Ba and AD1 |
| Upper pharynx | Minimal distance between the point SPs and the closest point on the posterior pharyngeal wall (PPW-s) |
| Lower pharynx | Minimal distance between the point APW-mand and the closest point on the posterior pharyngeal wall (PPW-i) |
| Arithmetic Mean | Standard Deviation | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Par 1 | SNA1 | 79.66 | 3.96 |
| SNA2 | 80.23 | 3.84 | |
| Par 2 | SNB1 | 78.64 | 3.64 |
| SNB2 | 78.48 | 3.69 | |
| Par 3 | ANB1 | 1.02 | 3.42 |
| ANB2 | 1.74 | 2.69 | |
| Par 4 | Wits1 | −3.86 | 4.33 |
| Wits2 | −2.50 | 3.45 | |
| Par 5 | ANPG1 | 1.00 | 8.12 |
| ANPG2 | 2.14 | 6.68 | |
| Par 6 | SN:NL1 | 8.34 | 2.71 |
| SN:NL2 | 8.45 | 2.66 | |
| Par 7 | IntermaxAngle1 | 26.22 | 5.54 |
| IntermaxAngle2 | 25.97 | 4.73 | |
| Par 8 | SArGo1 | 143.87 | 6.96 |
| SArGo2 | 145.11 | 6.89 | |
| Par 9 | MeGoAr1 | 128.29 | 5.60 |
| MeGoAr2 | 126.53 | 6.13 | |
| Par 10 | Bjork1 | 394.56 | 5.29 |
| Bjork2 | 394.41 | 4.66 | |
| Par 11 | NSGn1 | 66.26 | 3.50 |
| NSGn2 | 66.76 | 3.33 | |
| Par 12 | Sn:gogn1 | 32.29 | 5.21 |
| Sn:gogn2 | 32.27 | 4.64 | |
| Par 13 | U1Mx1 | 109.86 | 6.69 |
| U1Mx2 | 111.04 | 7.26 | |
| Par 14 | L1Md1 | 88.97 | 6.15 |
| L1Md2 | 88.49 | 6.09 |
| HYRAX | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Start | End | |||||
| M ± SD (mm) | Median (IQR) (mm) | M ± SD (mm) | Median (IQR) (mm) | p Value | ||
| Upper airway | 14.1 ± 3.0 | 13.4 (12.4–16.1) | Upper airway | 14.9 ± 2.6 | 14.5 (12.2–16.6) | 0.048 * |
| Upper adenoid | 21.8 ± 2.7 | 23.3 (19.6–23.5) | Upper adenoid | 21.5 ± 2.6 | 22.1 (19.5–23.9) | 0.530 * |
| Lower airway | 18.3 ± 4.3 | 18.0 (14.7–20.7) | Lower airway | 17.5 ± 3.2 | 18.0 (14.5–20.5) | 0.386 ** |
| Lower adenoid | 22.5 ± 4.2 | 22.7 (18.3–26.1) | Lower adenoid | 23.0 ± 3.3 | 23.3 (19.4–24.7) | 0.589 * |
| Upper pharynx | 9.8 ± 2.9 | 9.2 (7.8–11.3) | Upper pharynx | 10.7 ± 3.0 | 9.8 (8.6–14.0) | 0.033 ** |
| Lower pharynx | 10.5 ± 2.1 | 10.5 (9.1–12.6) | Lower pharynx | 11.0 ± 2.6 | 12.1 (9.3–12.9) | 0.395 * |
| HYRAX + FACE MASK | ||||||
| Start | End | |||||
| Upper airway | 12.1 ± 1.5 | 11.7 (11.3–13.7) | Upper airway | 13.4 ± 1.7 | 13.4 (12.7–14.7) | 0.103 * |
| Upper adenoid | 23.8 ± 1.9 | 23.7 (22.4–25.1) | Upper adenoid | 23.6 ± 1.3 | 23.7 (23.1–24.4) | 0.740 * |
| Lower airway | 15.3 ± 2.6 | 13.9 (13.5–17.4) | Lower airway | 17.3 ± 3.2 | 17.3 (14.3–19.7) | 0.173 ** |
| Lower adenoid | 25.9 ± 3.1 | 26.6 (22.6–28.7) | Lower adenoid | 24.4 ± 3.6 | 24.0 (22.0–27.0) | 0.154 * |
| Upper pharynx | 7.9 ± 1.4 | 7.8 (6.7–8.7) | Upper pharynx | 9.3 ± 1.6 | 9.1 (8.1–10.5) | 0.016 ** |
| Lower pharynx | 10.9 ± 3.1 | 9.1 (8.6–13.9) | Lower pharynx | 12.0 ± 3.1 | 10.8 (9.8–1.4) | 0.234 * |
| Differences in Dependent Samples | t | ss | p Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aritmetic Mean | Standard Deviation | |||||
| Par 1 | SNA1–SNA2 | −0.57 | 1.74 | −2.01 | 37 | 0.05 |
| Par 2 | SNB1–SNB2 | 0.16 | 1.26 | 0.79 | 37 | 0.43 |
| Par 3 | ANB1–ANB2 | −0.73 | 1.66 | −2.71 | 37 | 0.01 |
| Par 4 | wits1–wits2 | −1.36 | 2.32 | −3.61 | 37 | 0.00 |
| Par 5 | ANPG1–ANPG2 | −1.13 | 3.25 | −2.16 | 37 | 0.04 |
| Par 6 | SN: NL1–SN: NL2 | −0.11 | 1.72 | −0.38 | 37 | 0.71 |
| Par 7 | IntermaxAngle1–IntermaxAngle2 | 0.26 | 2.86 | 0.56 | 37 | 0.58 |
| Par 8 | SArGo1–SArGo2 | −1.24 | 3.10 | −2.46 | 37 | 0.02 |
| Par 9 | MeGoAr1–MeGoAr2 | 1.76 | 2.73 | 3.98 | 37 | 0.00 |
| Par 10 | Bjork1–Bjork2 | 0.15 | 2.20 | 0.43 | 37 | 0.67 |
| Par 11 | NSGn1–NSGn2 | −0.50 | 1.25 | −2.46 | 37 | 0.02 |
| Par 12 | sn:gogn1–sn:gogn2 | 0.02 | 2.27 | 0.05 | 37 | 0.96 |
| Par 13 | U1Mx1–U1Mx2 | −1.18 | 5.00 | −1.45 | 37 | 0.16 |
| Par 14 | L1Md1–L1Md2 | 0.47 | 4.27 | 0.68 | 37 | 0.50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Crnković, S.; Šimac Pavičić, D.; Svirčić, A.; Trinajstić Zrinski, M.; Katić, V. The Impact of Upper Jaw Expansion Treatment on Vertical Craniofacial Characteristics and Upper Airway Dimensions. Oral 2025, 5, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/oral5020033
Crnković S, Šimac Pavičić D, Svirčić A, Trinajstić Zrinski M, Katić V. The Impact of Upper Jaw Expansion Treatment on Vertical Craniofacial Characteristics and Upper Airway Dimensions. Oral. 2025; 5(2):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/oral5020033
Chicago/Turabian StyleCrnković, Sara, Doris Šimac Pavičić, Anđelo Svirčić, Magda Trinajstić Zrinski, and Višnja Katić. 2025. "The Impact of Upper Jaw Expansion Treatment on Vertical Craniofacial Characteristics and Upper Airway Dimensions" Oral 5, no. 2: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/oral5020033
APA StyleCrnković, S., Šimac Pavičić, D., Svirčić, A., Trinajstić Zrinski, M., & Katić, V. (2025). The Impact of Upper Jaw Expansion Treatment on Vertical Craniofacial Characteristics and Upper Airway Dimensions. Oral, 5(2), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/oral5020033