Increased Expression of CD169 on Monocytes in Adult-Onset Kikuchi–Fujimoto Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
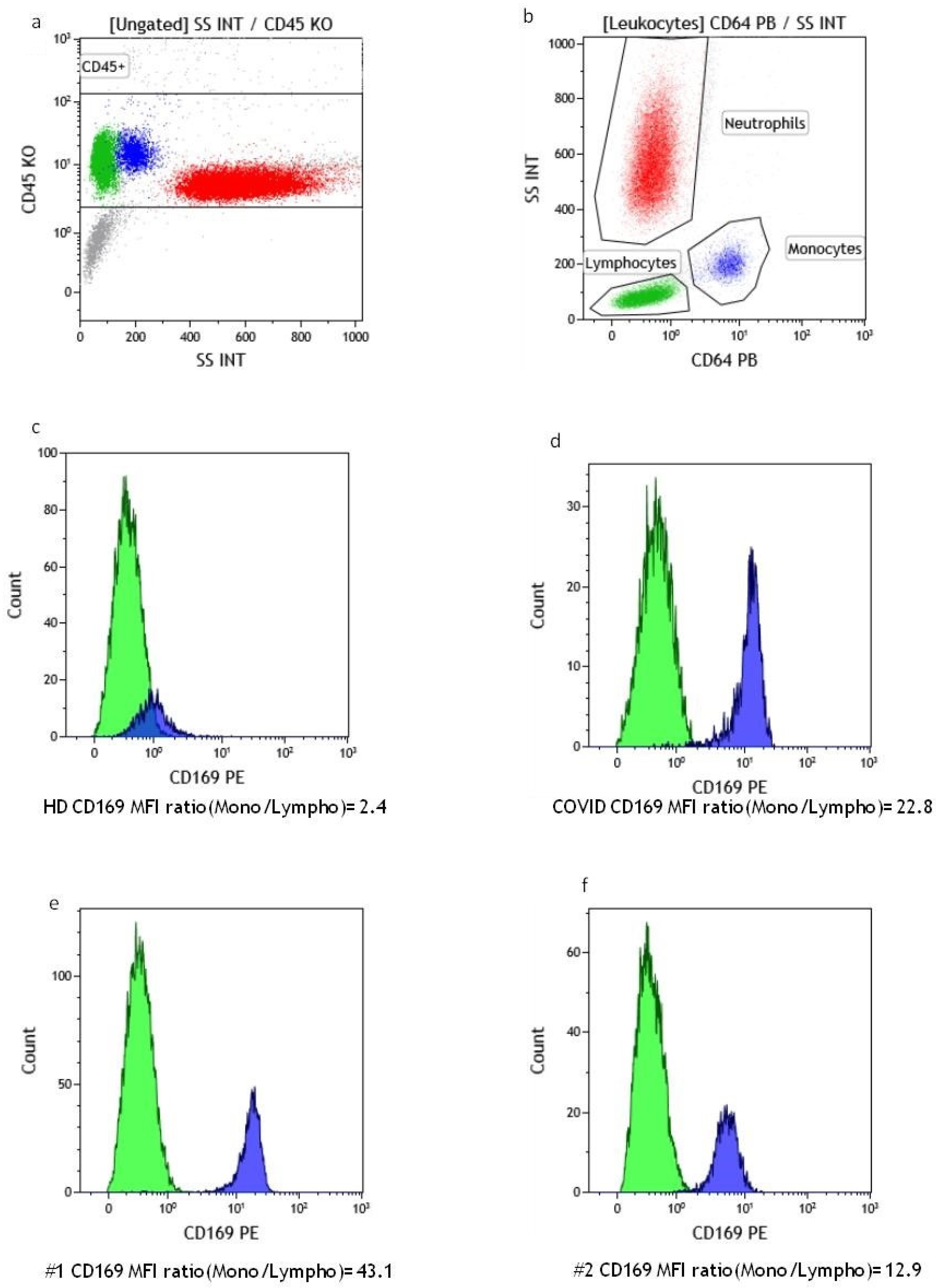
2.1. Flow Cytometry Evaluation of Monocyte CD169 Expression
2.2. Suspensions and Biopsy Immunophenotyping via Flow Cytometry
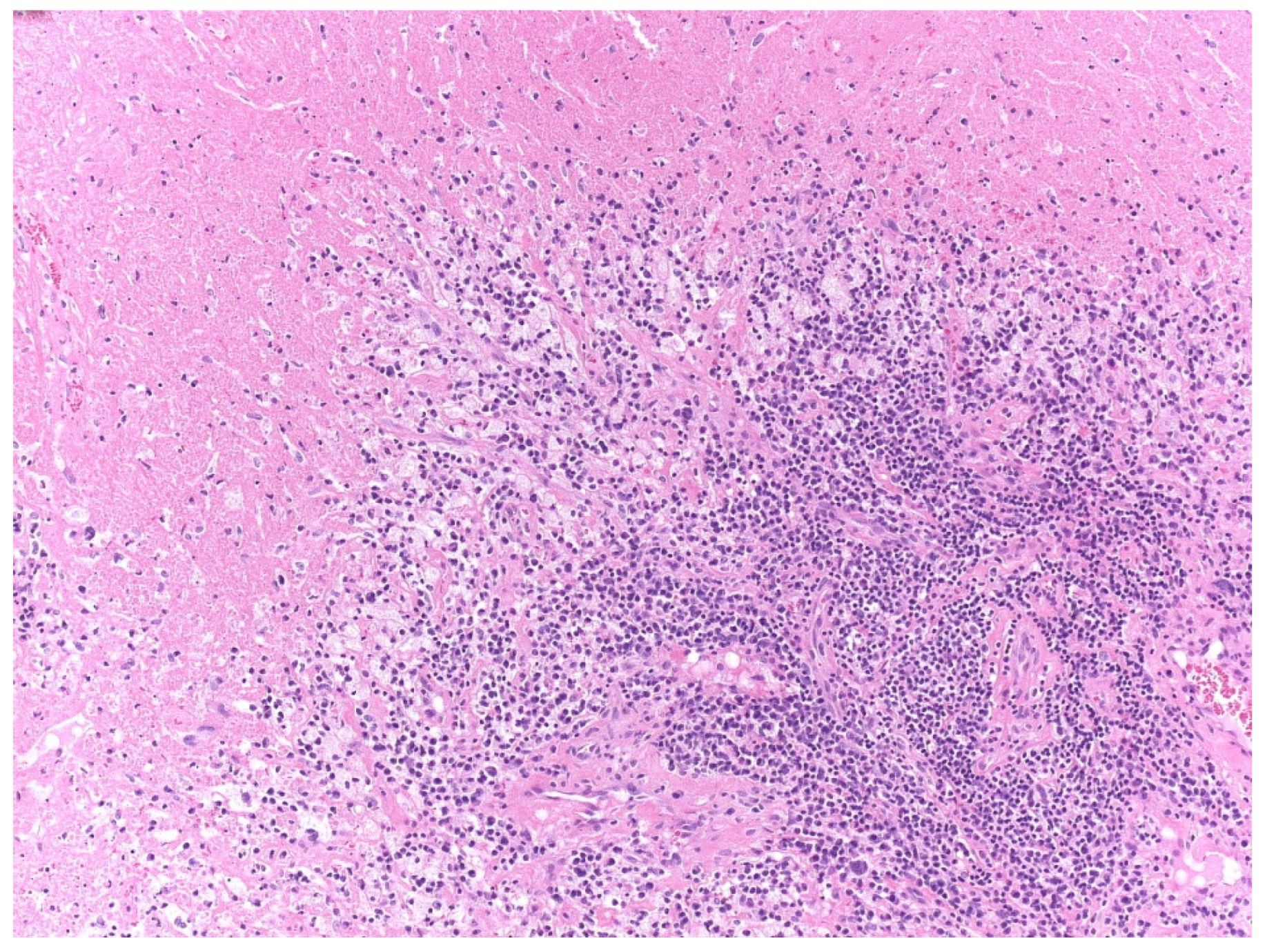
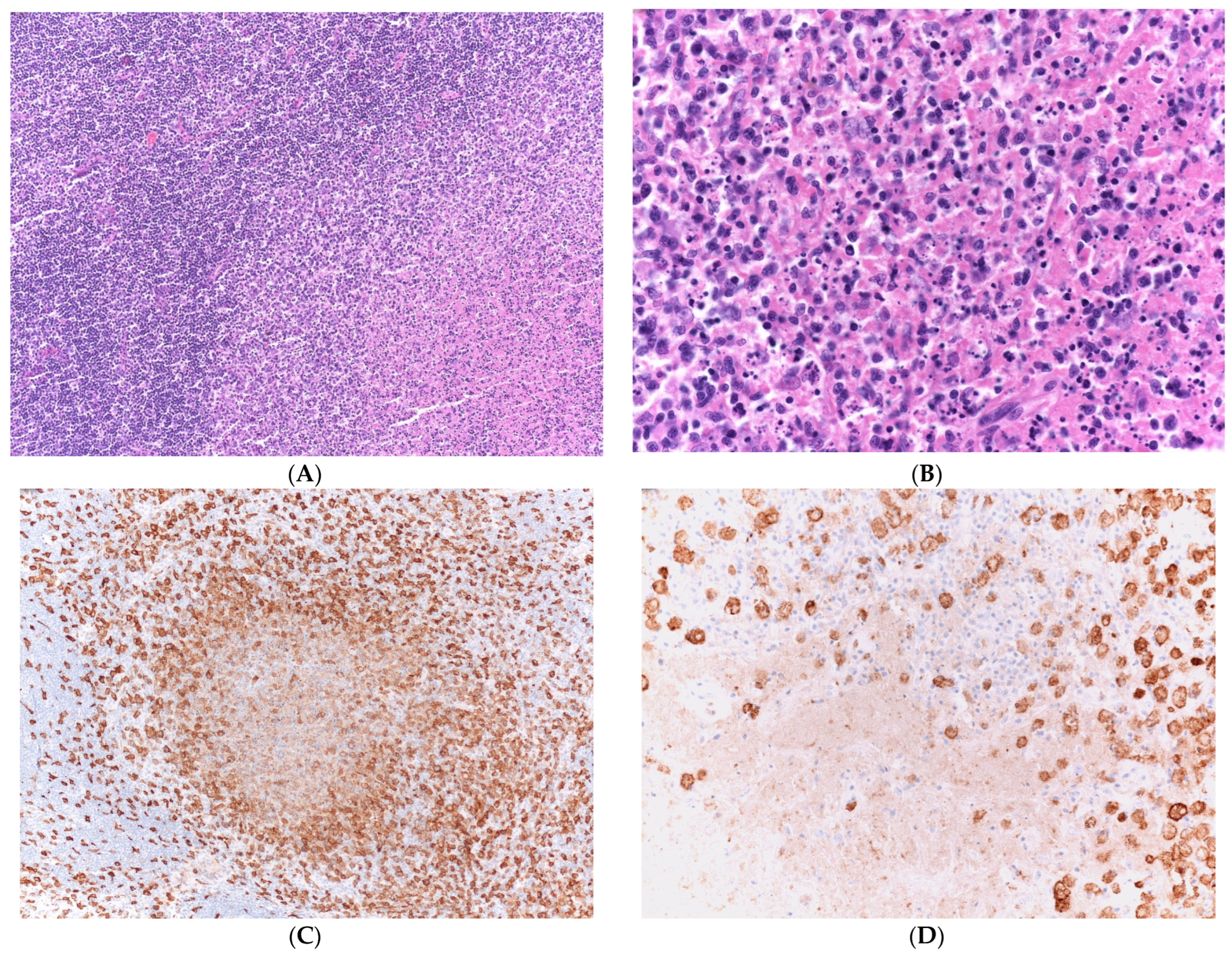
2.3. Pathological Analysis
2.4. Case Reports
2.4.1. Case 1
2.4.2. Case 2
3. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
Abbreviations
| ANA | Antinuclear Antibodies |
| CD | Cluster of Differentiation |
| CRP | C-reactive Protein |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| ED | Emergency Department |
| FDC | Follicular Dendritic Cell |
| HLH | Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis |
| INFα | Interferon Alpha |
| ISG | INF-stimulated genes |
| KFD | Kikuchi–Fujimoto disease |
| MFI | Mean Fluorescence Intensity |
| SSC | Side Scatter |
| SSc | Systemic Sclerosis |
| SIADs | Systemic Inflammatory Autoimmune Diseases |
| SIGLEC-1 | Sialic Acid-Binding Ig-like Lectin 1 |
| pDC | Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cell |
References
- Kikuchi, M. Lymphadenitis showing focal reticulum cell hyperplasia with nuclear debris and phagocytosis. Nippon Ketsueki Gakkai Zasshi 1972, 35, 379–380. [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto, Y.; Kozima, Y.; Yamaguchi, K. Cervical subacute necrotizing lymphadenitis. A new clinicopathological entity. Naika 1972, 20, 920–927. [Google Scholar]
- Dumas, G.; Prendki, V.; Haroche, J.; Amoura, Z.; Cacoub, P.; Galicier, L.; Meyer, O.; Rapp, C.; Deligny, C.; Godeau, B.; et al. Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease: Retrospective study of 91 cases and review of the literature. Medicine 2014, 93, 372–382, Erratum in Medicine 2014, 93, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaccarelli, F.; de Vincentiis, M.; D’Erme, G.; Greco, A.; Natalucci, F.; Fusconi, M. Kikuchi-Fujimoto Disease: A Distinct Pathological Entity but also an “Overlap” Autoimmune Syndrome—A systematic review. Curr. Rheumatol. Rev. 2022, 19, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, F.; Disma, S.; Teodoro, C.; Pepe, P.; Magro, G. Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease: A clinicopathologic update. Pathologica 2016, 108, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pileri, S.A.; Facchetti, F.; Ascani, S.; Sabattini, E.; Poggi, S.; Piccioli, M.; Rondelli, D.; Vergoni, F.; Zinzani, P.L.; Piccaluga, P.P.; et al. Myeloperoxidase expression by histiocytes in Kikuchi’s and Kikuchi-like lymphadenopathy. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 159, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukswai, N.; Jung, H.R.; Amr, S.S.; Ng, S.B.; Sheikh, S.S.; Lyapichev, K.; El Hussein, S.; Loghavi, S.; Agbay, R.L.M.C.; Miranda, R.N.; et al. Immunopathology of Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease: A reappraisal using novel immunohistochemistry markers. Histopathology 2020, 77, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, H.; Asano, S.; Mori, K.; Yamazaki, K.; Wakasa, H. Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells Producing Interferon-α (IFN-α) and Inducing Mx1 Play an Important Role for CD4(+) Cells and CD8(+) Cells in Necrotizing Lymphadenitis. J. Clin. Exp. Hematop. 2015, 55, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.W.; Liu, T.Y.; Lin, C.J.; Hsu, S.M. Oligoclonal T cells in histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenopathy are associated with TLR9+ plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Lab. Investig. 2005, 85, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabata, T.; Takata, K.; Miyata-Takata, T.; Sato, Y.; Ishizawa, S.; Kunitomo, T.; Nagakita, K.; Ohnishi, N.; Taniguchi, K.; Noujima-Harada, M.; et al. Characteristic Distribution Pattern of CD30-positive Cytotoxic T Cells Aids Diagnosis of Kikuchi-Fujimoto Disease. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2018, 26, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishimoto, K.; Tate, G.; Kitamura, T.; Kojima, M.; Mitsuya, T. Cytologic features and frequency of plasmacytoid dendritic cells in the lymph nodes of patients with histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis (Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease). Diagn. Cytopathol. 2010, 38, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, S.; Sato, H.; Mori, K.; Yamazaki, K.; Naito, H.; Suzuki, H. Necrotizing lymphadenitis may be induced by overexpression of Toll-like receptor7 (TLR7) caused by reduced TLR9 transport in plasmacytoid dendritic cells (PDCs). J. Clin. Exp. Hematop. 2021, 61, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, E.Y.; Xu, J.; Nelson, N.D.; Teachey, D.T.; Tan, K.; Romberg, N.; Behrens, E.; Pillai, V. Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease is mediated by an aberrant type I interferon response. Mod. Pathol. 2022, 35, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- York, M.R.; Nagai, T.; Mangini, A.J.; Lemaire, R.; van Seventer, J.M.; Lafyatis, R. A macrophage marker, Siglec-1, is increased on circulating monocytes in patients with systemic sclerosis and induced by type I interferons and toll-like receptor agonists. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 1010–1020, Erratum in Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorn-Pauly, L.; von Stuckrad, A.S.L.; Klotsche, J.; Rose, T.; Kallinich, T.; Enghard, P.; Ostendorf, L.; Burns, M.; Doerner, T.; Meisel, C.; et al. Evaluation of SIGLEC1 in the diagnosis of suspected systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology 2022, 61, 3396–3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graf, M.; von Stuckrad, S.L.; Uruha, A.; Klotsche, J.; Zorn-Pauly, L.; Unterwalder, N.; Buttgereit, T.; Krusche, M.; Meisel, C.; Burmester, G.R.; et al. SIGLEC1 enables straightforward assessment of type I interferon activity in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. RMD Open 2022, 8, e001934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerkvaleekul, B.; Veldkamp, S.R.; van der Wal, M.M.; Schatorjé, E.J.H.; Kamphuis, S.S.M.; van den Berg, J.M.; Hissink Muller, P.C.E.; Armbrust, W.; Vastert, S.J.; Wienke, J.; et al. Siglec-1 expression on monocytes is associated with the interferon signature in juvenile dermatomyositis and can predict treatment response. Rheumatology 2022, 61, 2144–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comins-Boo, A.; Gutiérrez-Larrañaga, M.; Roa-Bautista, A.; Guiral Foz, S.; Renuncio García, M.; González López, E.; Irure Ventura, J.; Fariñas-Álvarez, M.C.; San Segundo, D.; López Hoyos, M. Validation of a Quick Flow Cytometry-Based Assay for Acute Infection Based on CD64 and CD169 Expression. New Tools for Early Diagnosis in COVID-19 Pandemic. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 655785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgoin, P.; Soliveres, T.; Ahriz, D.; Arnoux, I.; Meisel, C.; Unterwalder, N.; Morange, P.E.; Michelet, P.; Malergue, F.; Markarian, T. Clinical research assessment by flow cytometry of biomarkers for infectious stratification in an Emergency Department. Biomark. Med. 2019, 13, 1373–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedin, A.S.; Makinson, A.; Picot, M.C.; Mennechet, F.; Malergue, F.; Pisoni, A.; Nyiramigisha, E.; Montagnier, L.; Bollore, K.; Debiesse, S.; et al. Monocyte CD169 Expression as a Biomarker in the Early Diagnosis of Coronavirus Disease 2019. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 223, 562–567, Erratum in J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 225, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Hoogen, F.; Khanna, D.; Fransen, J.; Johnson, S.R.; Baron, M.; Tyndall, A.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Naden, R.P.; Medsger, T.A., Jr.; Carreira, P.E.; et al. 2013 classification criteria for systemic sclerosis: An American College of Rheumatology/European League against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 2737–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Huang, S.; Nong, L.; Li, X.; Li, D.; Zhang, B.; Li, T. Clinicopathologic Analysis of Kikuchi-Fujimoto Disease and Etiologic Exploration Using Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequencing. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2022, 147, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, K.; Kakehi, E.; Adachi, S.; Kotani, K. Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease following SARS-CoV-2 vaccination. BMJ Case Rep. 2022, 15, e250601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiśniewska, K.; Pawlak-Buś, K.; Leszczyński, P. Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease associated with primary Sjögren’s syndrome—Literature review based on a case report. Reumatologia 2020, 58, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, B.M.; Bernardes, M.; Barroca, H.; Costa, L. Kikuchi-Fujimoto Disease Associated With Mixed Connective Tissue Disease: A Late Recurrence Case. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 27, S779–S780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Zamalloa, A.; Taboada-Gomez, J.; Bernardo-Galán, P.; Magdalena, F.M.; Zaldumbide-Dueñas, L.; Ugarte-Maiztegui, M. Bilateral pleural effusion and interstitial lung disease as unusual manifestations of Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease: Case report and literature review. BMC Pulm. Med. 2010, 10, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Stefano, P.; Chizzolini, C.; Lalive, P.H.; Lascano, A.M. Limbic encephalitis associated with systemic sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2018, 24, 142–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabana, M.; Warnack, W. An atypical neurologic complication of Kikuchi-Fujimoto Disease. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 7, e707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gism Elseed, I.; Osman, H.; Ahmedfiqi, O.; Najmi, F.; Al-Hebshi, A. Kikuchi-Fujimoto Disease: A Rare Benign Cause of Lymphadenopathy That Mimics Malignant Lymphoma. Cureus 2022, 14, e23177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Ba, X.; Yang, H.; Huang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xu, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; et al. Kikuchi disease with an exuberant proliferation of large T-cells: A study of 25 cases that can mimic T-Cell lymphoma. Histopathology 2023, 82, 340–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, E. (Ed.) PART II • Normal and Reactive Conditions of Hematopoietic Tissues, Kikuchi’s Lymphadenitis. In Hematopathology, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Perry, A.M.; Choi, S.M. Kikuchi-Fujimoto Disease: A Review. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2018, 142, 1341–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohshima, K.; Shimazaki, K.; Kume, T.; Suzumiya, J.; Kanda, M.; Kikuchi, M. Perforin and Fas pathways of cytotoxic T-cells in histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis. Histopathology 1998, 33, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, N.D.; Meng, W.; Rosenfeld, A.M.; Bullman, S.; Sekhar Pedamallu, C.; Nomburg, J.L.; Wertheim, G.B.; Paessler, M.E.; Pinkus, G.; Hornick, J.L.; et al. Characterization of Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells, Microbial Sequences, and Identification of a Candidate Public T-Cell Clone in Kikuchi-Fujimoto Disease. Pediatr. Dev. Pathol. 2021, 24, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilichowska, M.E.; Pinkus, J.L.; Pinkus, G.S. Histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis (Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease): Lesional cells exhibit an immature dendritic cell phenotype. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2009, 131, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, G.D.; Kumar, J.; Oak, J.S.; Boyd, S.D.; Raess, P.W.; Gratzinger, D.A. Histology-Independent Signature Distinguishes Kikuchi-Fujimoto Disease/Systemic Lupus Erythematosus-Associated Lymphadenitis From Benign and Malignant Lymphadenopathies. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2020, 154, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.C.; Huang, H.H.; Chen, C.N.; Chen, T.C.; Yang, T.L. Blood cell and marrow changes in patients with Kikuchi disease. Haematologica 2022, 107, 1981–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Liang, L.; Li, D.; Bai, Y.; Li, X. Analysis of the clinical manifestations and 18F-FDG PET-CT findings in 40 patients with histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis. Medicine 2021, 100, e27189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimura, M.; Yamamoto, H.; Mizuno, Y.; Takada, H.; Goto, M.; Doi, T.; Hoshina, T.; Ohga, S.; Ohshima, K.; Hara, T. A non-invasive diagnosis of histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis by means of gene expression profile analysis of peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J. Clin. Immunol. 2013, 33, 1018–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, U.; Güner, S.; Eşkazan, T.; Demiröz, A.S.; Kurtuluş, G.; Bahar, F.; Uğurlu, S.; Eşkazan, A.E. Kikuchi Fujimoto disease as the presenting component of VEXAS syndrome: A case report of a probable association. Clin. Rheumatol. 2022, 41, 3589–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.M.S.; Fan, B.E.; Lim, J.H.; Goh, L.L.; Lee, J.S.S.; Koh, L.W. A case of VEXAS syndrome manifesting as Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease, relapsing polychondritis, venous thromboembolism and macrocytic anaemia. Rheumatology 2021, 60, e304–e306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prenzler, S.; Rudrawar, S.; Waespy, M.; Kelm, S.; Anoopkumar-Dukie, S.; Haselhorst, T. The role of sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like-lectin-1 (siglec-1) in immunology and infectious disease. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 42, 113–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, K.; Chen, Q.; Shi, D.; Huang, S.; Wang, C.; Ai, Z.; Jiang, J. Sialylation-dependent interaction between PD-L1 and CD169 promotes monocyte adhesion to endothelial cells. Glycobiology 2023, 33, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Affandi, A.J.; Olesek, K.; Grabowska, J.; Nijen Twilhaar, M.K.; Rodríguez, E.; Saris, A.; Zwart, E.S.; Nossent, E.J.; Kalay, H.; de Kok, M.; et al. CD169 Defines Activated CD14+ Monocytes With Enhanced CD8+ T Cell Activation Capacity. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 697840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakumura, N.; Yokoyama, T.; Usami, M.; Hosono, Y.; Inoue, N.; Matsuda, Y.; Tasaki, Y.; Wada, T. CD169 expression on monocytes as a marker for assessing type I interferon status in pediatric inflammatory diseases. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 250, 109329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabowska, J.; Lopez-Venegas, M.A.; Affandi, A.J.; den Haan, J.M.M. CD169+ Macrophages Capture and Dendritic Cells Instruct: The Interplay of the Gatekeeper and the General of the Immune System. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gkirtzimanaki, K.; Kabrani, E.; Nikoleri, D.; Polyzos, A.; Blanas, A.; Sidiropoulos, P.; Makrigiannakis, A.; Bertsias, G.; Boumpas, D.T.; Verginis, P. IFNα Impairs Autophagic Degradation of mtDNA Promoting Autoreactivity of SLE Monocytes in a STING-Dependent Fashion. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 921–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caielli, S.; Cardenas, J.; de Jesus, A.A.; Baisch, J.; Walters, L.; Blanck, J.P.; Balasubramanian, P.; Stagnar, C.; Ohouo, M.; Hong, S.; et al. Erythroid mitochondrial retention triggers myeloid-dependent type I interferon in human SLE. Cell 2021, 184, 4464–4479.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trombetta, A.C.; Soldano, S.; Contini, P.; Tomatis, V.; Ruaro, B.; Paolino, S.; Brizzolara, R.; Montagna, P.; Sulli, A.; Pizzorni, C.; et al. A circulating cell population showing both M1 and M2 monocyte/macrophage surface markers characterizes systemic sclerosis patients with lung involvement. Respir. Res. 2018, 19, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hénault, J.; Robitaille, G.; Senécal, J.L.; Raymond, Y. DNA topoisomerase I binding to fibroblasts induces monocyte adhesion and activation in the presence of anti-topoisomerase I autoantibodies from systemic sclerosis patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, L.; Marcondes, N.A.; Hax, V.; da Silva Moreira, I.F.; Ueda, C.Y.; Piovesan, R.R.; Xavier, R.; Chakr, R. Flow cytometry evaluation of CD14/CD16 monocyte subpopulations in systemic sclerosis patients: A cross sectional controlled study. Adv. Rheumatol. 2021, 61, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höppner, J.; Casteleyn, V.; Biesen, R.; Rose, T.; Windisch, W.; Burmester, G.R.; Siegert, E. SIGLEC-1 in Systemic Sclerosis: A Useful Biomarker for Differential Diagnosis. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmey, B.; Boix, C.; Barbaroux, J.B.; Dieu-Nosjean, M.C.; Diebold, J.; Audouin, J.; Fridman, W.H.; Mueller, C.G.; Molina, T.J. CD14 and CD169 expression in human lymph nodes and spleen: Specific expansion of CD14+CD169− monocyte-derived cells in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Hum. Pathol. 2006, 37, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malipiero, G.; Machin, P.; Ermacora, A.; Pratesi, C.; Carbone, A.; Fontana, D.E.; Vattamattathil, K.P.; De Rosa, R.; Doretto, P. Increased Expression of CD169 on Monocytes in Adult-Onset Kikuchi–Fujimoto Disease. Hemato 2023, 4, 273-284. https://doi.org/10.3390/hemato4030022
Malipiero G, Machin P, Ermacora A, Pratesi C, Carbone A, Fontana DE, Vattamattathil KP, De Rosa R, Doretto P. Increased Expression of CD169 on Monocytes in Adult-Onset Kikuchi–Fujimoto Disease. Hemato. 2023; 4(3):273-284. https://doi.org/10.3390/hemato4030022
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalipiero, Giacomo, Piernicola Machin, Anna Ermacora, Chiara Pratesi, Antonino Carbone, Desre’ Ethel Fontana, Kathreena Paul Vattamattathil, Rita De Rosa, and Paolo Doretto. 2023. "Increased Expression of CD169 on Monocytes in Adult-Onset Kikuchi–Fujimoto Disease" Hemato 4, no. 3: 273-284. https://doi.org/10.3390/hemato4030022
APA StyleMalipiero, G., Machin, P., Ermacora, A., Pratesi, C., Carbone, A., Fontana, D. E., Vattamattathil, K. P., De Rosa, R., & Doretto, P. (2023). Increased Expression of CD169 on Monocytes in Adult-Onset Kikuchi–Fujimoto Disease. Hemato, 4(3), 273-284. https://doi.org/10.3390/hemato4030022







