Genomic Characterization of Linezolid-Resistant Clostridioides difficile Harboring cfr Variants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Data Analysis
3. Results
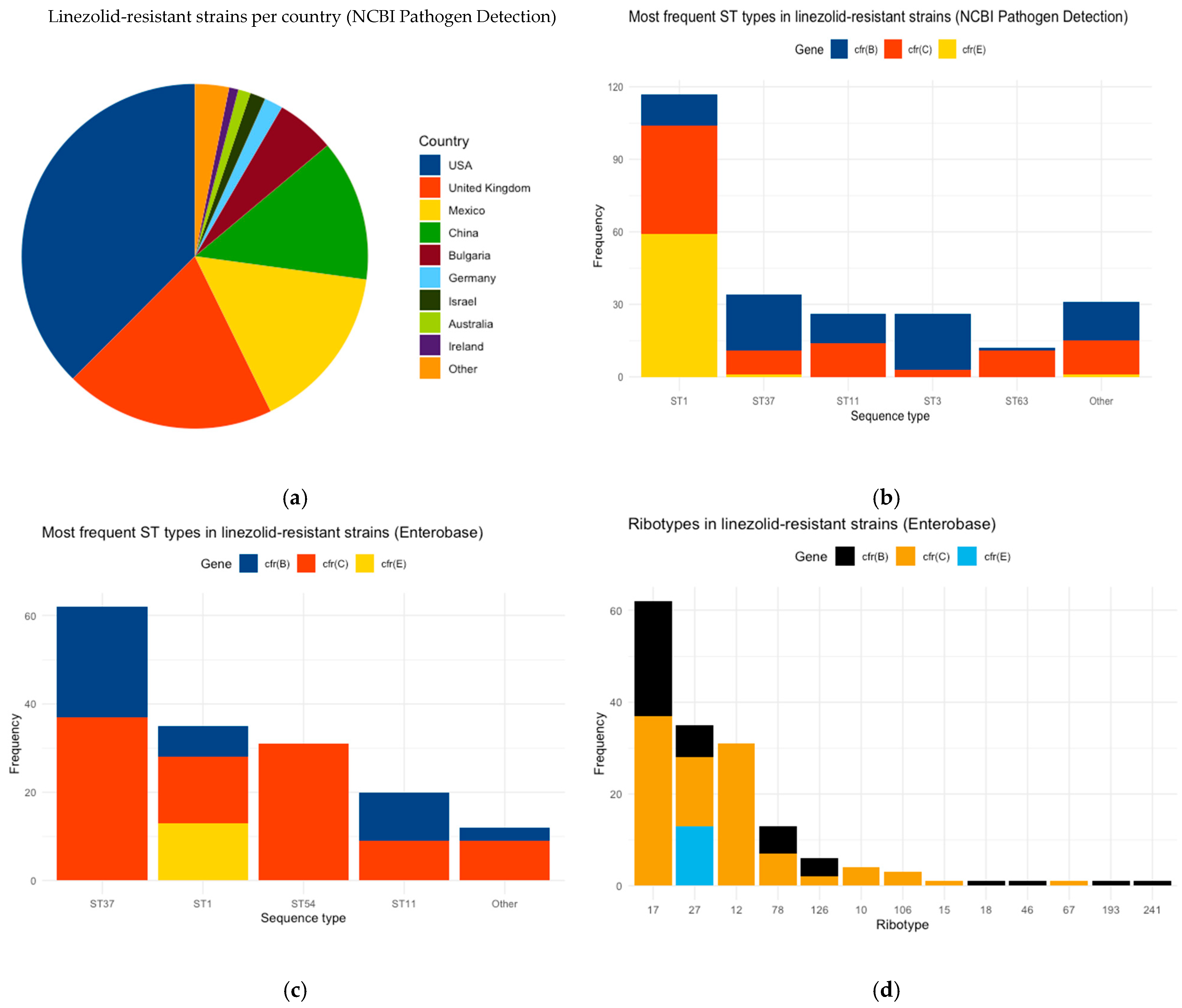
3.1. Description of Linezolid-Resistant C. difficile Strains
3.2. Comparison Between Linezolid-Resistant and Susceptible C. difficile Strains of NCBI
3.3. Mutation Analysis of EnteroBase C. difficile Strains
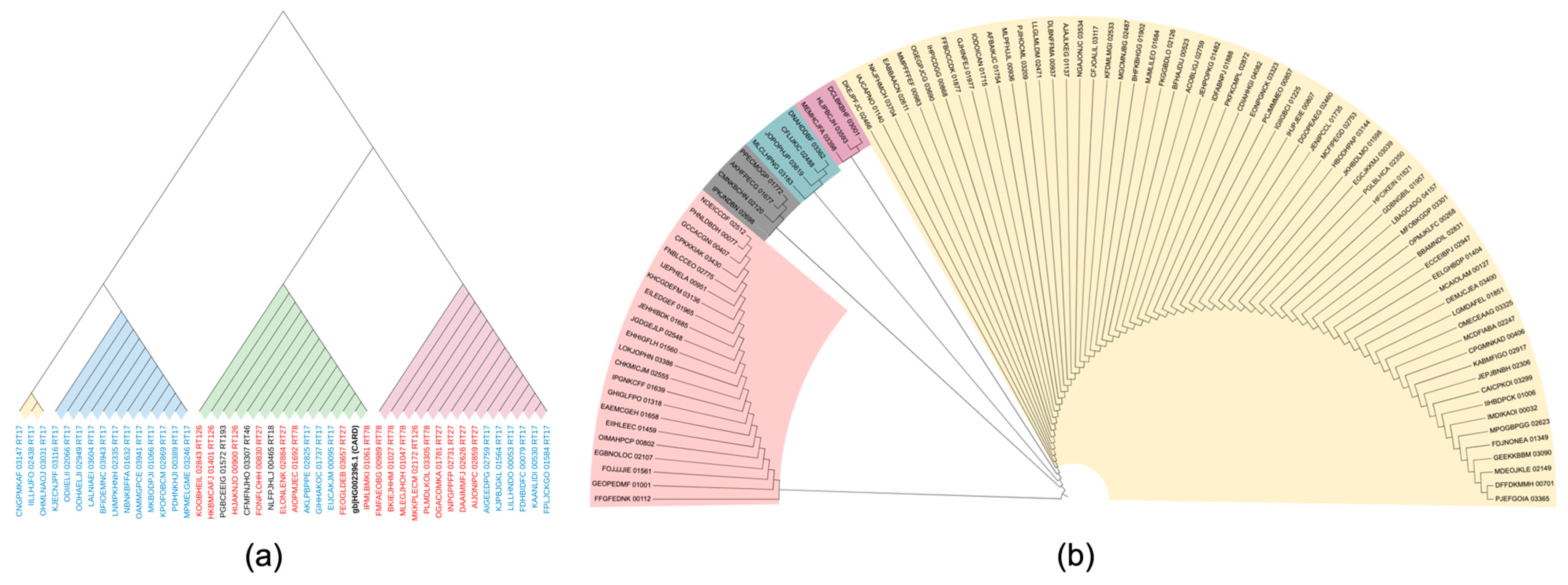
3.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
3.5. Presence of Other AMR Genes
4. Discussion
5. Limitations of the Study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smits, W.K.; Lyras, D.; Lacy, D.B.; Wilcox, M.H.; Kuijper, E.J. Clostridium Difficile Infection. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Bella, S.; Ascenzi, P.; Siarakas, S.; Petrosillo, N.; di Masi, A. Clostridium Difficile Toxins A and B: Insights into Pathogenic Properties and Extraintestinal Effects. Toxins 2016, 8, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehgal, K.; Khanna, S. Gut Microbiome and Clostridioides Difficile Infection: A Closer Look at the Microscopic Interface. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2021, 14, 1756284821994736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, C.; Zhang, C.; Mao, X.; Lizhe, A. Complete Genome Sequence of the Clostridium Difficile LCL126. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerding, D.N.; Johnson, S.; Rupnik, M.; Aktories, K. Clostridium Difficile Binary Toxin CDT: Mechanism, Epidemiology, and Potential Clinical Importance. Gut Microbes 2013, 5, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czepiel, J.; Dróżdż, M.; Pituch, H.; Kuijper, E.J.; Perucki, W.; Mielimonka, A.; Goldman, S.; Wultańska, D.; Garlicki, A.; Biesiada, G. Clostridium Difficile Infection: Review. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 38, 1211–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vindigni, S.M.; Surawicz, C.M.C. C. Difficile Infection: Changing Epidemiology and Management Paradigms. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2015, 6, e99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Emerging Infections Program, Healthcare-Associated Infections—Community Interface Surveillance Report, Clostridioides Difficile Infection (CDI); Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Khanna, S.; Pardi, D.S.; Aronson, S.L.; Kammer, P.P.; Orenstein, R.; St Sauver, J.L.; Harmsen, W.S.; Zinsmeister, A.R. The Epidemiology of Community-Acquired Clostridium Difficile Infection: A Population-Based Study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 107, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupnik, M.; Wilcox, M.H.; Gerding, D.N. Clostridium Difficile Infection: New Developments in Epidemiology and Pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spigaglia, P.; Mastrantonio, P.; Barbanti, F. Antibiotic Resistances of Clostridium Difficile. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1050, 137–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawes, T.; Lopez-Lozano, J.M.; Nebot, C.A.; Macartney, G.; Subbarao-Sharma, R.; Wares, K.D.; Sinclair, C.; Gould, I.M. Effect of a National 4C Antibiotic Stewardship Intervention on the Clinical and Molecular Epidemiology of Clostridium Difficile Infections in a Region of Scotland: A Non-Linear Time-Series Analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, L.C.; Gerding, D.N.; Johnson, S.; Bakken, J.S.; Carroll, K.C.; Coffin, S.E.; Dubberke, E.R.; Garey, K.W.; Gould, C.V.; Kelly, C.; et al. Clinical Practice Guidelines for Clostridium Difficile Infection in Adults and Children: 2017 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA). Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 66, e1–e48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debast, S.B.; Bauer, M.P.; Kuijper, E.J.; Allerberger, F.; Bouza, E.; Coia, J.E.; Cornely, O.A.; Fitzpatrick, F.; Guery, B.; Wilcox, M.; et al. European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases: Update of the Treatment Guidance Document for Clostridium Difficile Infection. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20 (Suppl. 2), S1–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcalá, L.; Martín, A.; Marín, M.; Sánchez-Somolinos, M.; Catalán, P.; Peláez, T.; Bouza, E.; Spanish Clostridium difficile Study Group. The Undiagnosed Cases of Clostridium Difficile Infection in a Whole Nation: Where Is the Problem? Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, E204–E213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spigaglia, P.; Barbanti, F.; Mastrantonio, P.; Ackermann, G.; Balmelli, C.; Barbut, F.; Bouza, E.; Brazier, J.; Delmée, M.; Drudy, D.; et al. Multidrug Resistance in European Clostridium Difficile Clinical Isolates. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2011, 66, 2227–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemian, S.M.R.; Farhadi, T.; Ganjparvar, M. Linezolid: A Review of Its Properties, Function, and Use in Critical Care. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2018, 12, 1759–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalewicz, C.; Timmermans, M.; Fretin, D.; Wattiau, P.; Boland, C. An In-House 45-Plex Array for the Detection of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in Gram-Positive Bacteria. MicrobiologyOpen 2023, 12, e1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candela, T.; Marvaud, J.C.; Nguyen, T.K.; Lambert, T. A Cfr-like Gene Cfr(C) Conferring Linezolid Resistance Is Common in Clostridium Difficile. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 50, 496–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojković, V.; Ulate, M.F.; Hidalgo-Villeda, F.; Aguilar, E.; Monge-Cascante, C.; Pizarro-Guajardo, M.; Tsai, K.; Tzoc, E.; Camorlinga, M.; Paredes-Sabja, D.; et al. Cfr(B), Cfr(C), and a New Cfr-Like Gene, Cfr(E), in Clostridium Difficile Strains Recovered across Latin America. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e01074-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plankaova, A.; Brajerova, M.; Capek, V.; Balikova Novotna, G.; Kinross, P.; Skalova, J.; Soltesova, A.; Drevinek, P.; Krutova, M. Clostridioides Difficile Infections Were Predominantly Driven by Fluoroquinolone-Resistant Clostridioides Difficile Ribotypes 176 and 001 in Slovakia in 2018–2019. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2023, 62, 106824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Alikhan, N.-F.; Mohamed, K.; Fan, Y.; Achtman, M. The EnteroBase User’s Guide, with Case Studies on Salmonella Transmissions, Yersinia Pestis Phylogeny, and Escherichia Core Genomic Diversity. Genome Res. 2020, 30, 138–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, M.V.; Cosentino, S.; Rasmussen, S.; Friis, C.; Hasman, H.; Marvig, R.L.; Jelsbak, L.; Sicheritz-Pontén, T.; Ussery, D.W.; Aarestrup, F.M.; et al. Multilocus Sequence Typing of Total-Genome-Sequenced Bacteria. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 1355–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharat, A.; Petkau, A.; Avery, B.P.; Chen, J.C.; Folster, J.P.; Carson, C.A.; Kearney, A.; Nadon, C.; Mabon, P.; Thiessen, J.; et al. Correlation between Phenotypic and In Silico Detection of Antimicrobial Resistance in Salmonella Enterica in Canada Using Staramr. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolaia, V.; Kaas, R.S.; Ruppe, E.; Roberts, M.C.; Schwarz, S.; Cattoir, V.; Philippon, A.; Allesoe, R.L.; Rebelo, A.R.; Florensa, A.F.; et al. ResFinder 4.0 for Predictions of Phenotypes from Genotypes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 3491–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carattoli, A.; Zankari, E.; García-Fernández, A.; Voldby Larsen, M.; Lund, O.; Villa, L.; Møller Aarestrup, F.; Hasman, H. In Silico Detection and Typing of Plasmids Using PlasmidFinder and Plasmid Multilocus Sequence Typing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid Prokaryotic Genome Annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, F.; Higgins, D.G. Clustal Omega, Accurate Alignment of Very Large Numbers of Sequences. 2014, 1079, 105–116. Methods Mol. Biol. [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL) v6: Recent Updates to the Phylogenetic Tree Display and Annotation Tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, W78–W82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stothard, P. The Sequence Manipulation Suite: JavaScript Programs for Analyzing and Formatting Protein and DNA Sequences. BioTechniques 2000, 28, 1102–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, A.M.; Procter, J.B.; Martin, D.M.A.; Clamp, M.; Barton, G.J. Jalview Version 2—A Multiple Sequence Alignment Editor and Analysis Workbench. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1189–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, R.; Lacy, D.B. The Role of Toxins in Clostridium Difficile Infection. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 723–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar-Zamora, E.; Weimer, B.C.; Torres, R.C.; Gómez-Delgado, A.; Ortiz-Olvera, N.; Aparicio-Ozores, G.; Barbero-Becerra, V.J.; Torres, J.; Camorlinga-Ponce, M. Molecular Epidemiology and Antimicrobial Resistance of Clostridioides Difficile in Hospitalized Patients From Mexico. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 787451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

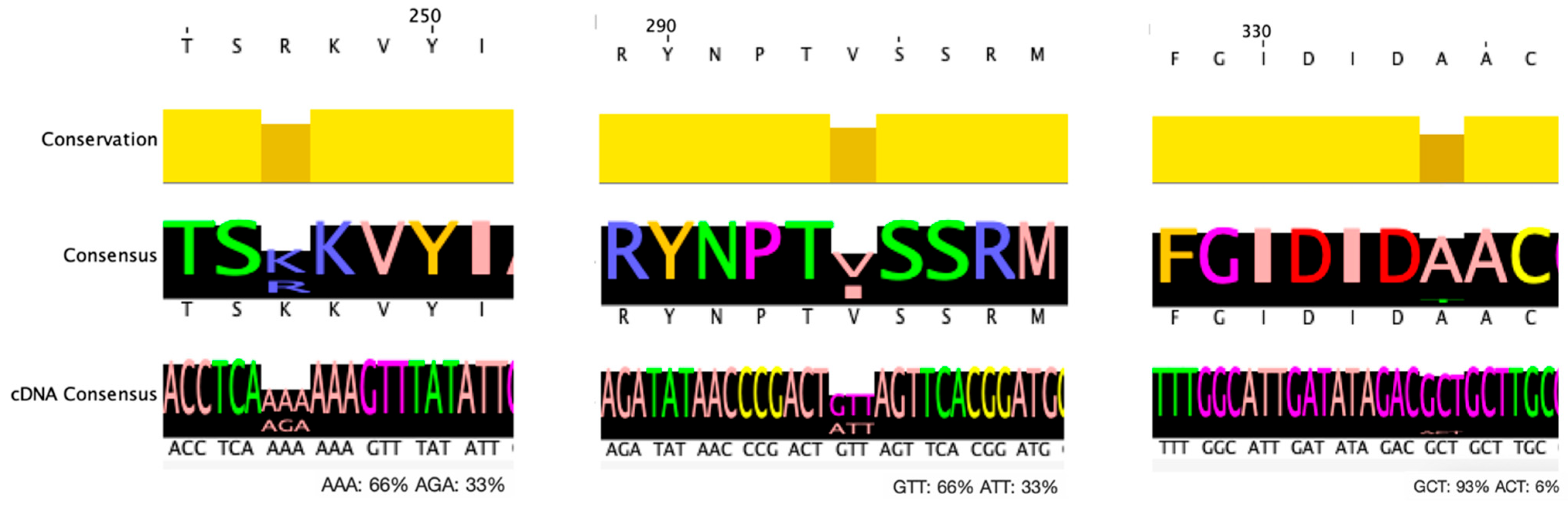
| Amino Acid Mutations of cfr(B) Gene | Number of Strains | ST11 | ST1 | ST17 | ST37 | no ST |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p.R247K | 14/44 | 6 (RT78, RT126, RT193) | 3 (RT27) | 1 (RT18) | 3 (RT17) | 1 (RT46) |
| p.V294I | 29/44 | 11 (RT78, RT126, RT193) | 7 (RT27) | 1 (RT18) | 9 (RT17) | 1 (RT46) |
| p.R247K & p.V294I | 14/44 | 6 (RT78, RT126, RT193) | 3 (RT27) | 1 (RT18) | 3 (RT17) | 1 (RT46) |
| p.A334T | 3/44 | - | - | - | 3 (RT17) | - |
| All three mutations | 3/44 | - | - | - | 3 (RT17) | - |
| AMR Gene | Antibiotic of Resistance | Coexistence with cfr Gene | No. of Strains per Gene | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cfr(B) | cfr(c) | cfr(E) | |||
| erm(B) | Erythromycin, Azithromycin | 43 | 69 | 68 | 195 |
| erm(Q) | Erythromycin, Azithromycin | 2 | 2 | - | |
| erm(A) | Erythromycin, Azithromycin | 10 | 1 | - | |
| tet(m) | Tetracycline | 66 | - | - | 76 |
| tet(32) | Tetracycline | 10 | - | - | |
| aac(6′)-aph(2″) | Amikacin, Gentamicin, Tobramycin | 42 | 12 | 6 | 60 |
| ant(6)-Ia | Streptomycin | 41 | 35 | 1 | 77 |
| fosB3 | Fosfomycin | - | - | 8 | 8 |
| catP | Chloramphenicol | 16 | - | - | 16 |
| qnrB19 | Ciprofloxacin I/R | - | - | 3 | 3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Panou, A.; Malousi, A.; Kachrimanidou, M. Genomic Characterization of Linezolid-Resistant Clostridioides difficile Harboring cfr Variants. BioTech 2025, 14, 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech14020042
Panou A, Malousi A, Kachrimanidou M. Genomic Characterization of Linezolid-Resistant Clostridioides difficile Harboring cfr Variants. BioTech. 2025; 14(2):42. https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech14020042
Chicago/Turabian StylePanou, Aikaterini, Andigoni Malousi, and Melina Kachrimanidou. 2025. "Genomic Characterization of Linezolid-Resistant Clostridioides difficile Harboring cfr Variants" BioTech 14, no. 2: 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech14020042
APA StylePanou, A., Malousi, A., & Kachrimanidou, M. (2025). Genomic Characterization of Linezolid-Resistant Clostridioides difficile Harboring cfr Variants. BioTech, 14(2), 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech14020042









