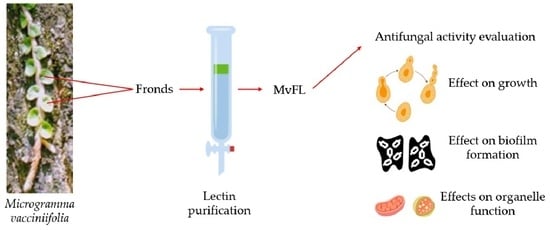
Evaluation of the Antifungal Activity of Microgramma vacciniifolia Frond Lectin (MvFL) Against Pathogenic Yeasts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. Isolation of MvFL
2.3. Antifungal Activity
2.3.1. Broth Microdilution Assay
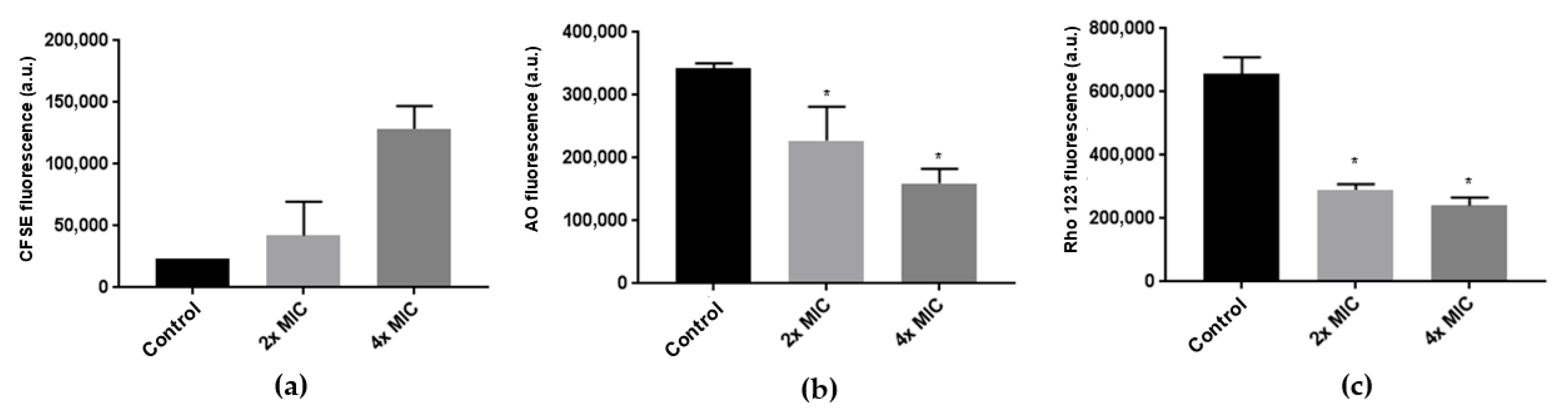
2.3.2. Cell Proliferation Assessment
2.3.3. Evaluation of Lysosomal Stability and Mitochondrial Membrane Potential
2.3.4. Antibiofilm Activity
2.3.5. Assessment of Combinatory Effects of MvFL and Fluconazole on Yeast Growth
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garcia-Marin, L.E.; Juarez-Moreno, K.; Vilchis-Nestor, A.R.; Castro-Longoria, E. Highly antifungal activity of biosynthesized copper oxide nanoparticles against Candida albicans. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadi, S.; Azizipour, E.; Amani, A.M.; Vaez, A.; Zareshahrabadi, Z.; Abbaspour, A.; Firuzyar, T.; Dortaj, H.; Kamyab, H.; Chelliapan, S.; et al. Antifungal activity of Fe3O4@SiO2/Schiff-base/Cu(II) magnetic nanoparticles against pathogenic Candida species. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padmavathi, A.R.; Murthy, P.S.; Das, A.; Priya, A.; Sushmitha, T.J.; Pandian, S.K.; Toleti, S.R. Impediment to growth and yeast-to-hyphae transition in Candida albicans by copper oxide nanoparticles. Biofouling 2020, 36, 56–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badrane, H.; Cheng, S.; Dupont, C.L.; Hao, B.; Driscoll, E.; Morder, K.; Liu, G.; Newbrough, A.; Fleres, G.; Kaul, D.; et al. Genotypic diversity and unrecognized antifungal resistance among populations of Candida glabrata from positive blood cultures. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Duran, J.; Torres, R.; Stashenko, E.E.; Ortiz, C. Antifungal and antibiofilm activity of Colombian essential oils against different Candida strains. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappas, P.G.; Lionakis, M.S.; Arendrup, M.C.; Ostrosky-Zeichner, L.; Kullberg, B.J. Invasive candidiasis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 18026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talattof, Z.; Azad, A.; Zahed, M.; Shahradnia, N. Antifungal activity of xylitol against Candida albicans: An in vitro study. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2018, 19, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinea, J. Global trends in the distribution of Candida species causing candidemia. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Escobar, A.; Reyes-López, S.Y. Antifungal susceptibility of Candida species to copper oxide nanoparticles on polycaprolactone fibers (PCL-CuONPs). PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.; Heitman, J. On fruits and fungi: A risk of antifungal usage in food storage and distribution in driving drug resistance in Candida auris. mBio 2022, 13, e00739-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meagher, R.B.; Lewis, Z.A.; Ambati, S.; Lin, X. DectiSomes: C-type lectin receptor-targeted liposomes as pan-antifungal drugs. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2023, 196, 114776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabino, R.; Veríssimo, C.; Pereira, Á.A.; Antunes, F. Candida auris, an agent of hospital-associated outbreaks: Which challenging issues do we need to have in mind? Microorganisms 2020, 8, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revie, N.M.; Iyer, K.R.; Robbins, N.; Cowen, L.E. Antifungal drug resistance: Evolution, mechanisms and impact. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2018, 45, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, T.F.; Thompson, G.R., III; Denning, D.W.; Fishman, J.A.; Hadley, S.; Herbrecht, R.; Kontoyiannis, D.P.; Marr, K.A.; Morrison, V.A.; Nguyen, M.H.; et al. Practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of aspergillosis: 2016 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, e1–e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, N.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yang, D.; Weng, L.; Zhao, B.; Wang, L. Efficient click chemistry towards fatty acids containing 1,2,3-triazole: Design and synthesis as potential antifungal drugs for Candida albicans. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 136, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.R.; Malveira, E.A.; Aguiar, T.K.; Neto, N.A.; Roma, R.R.; Santos, M.H.C.; Santos, A.L.E.; Silva, A.F.B.; Freitas, C.D.T.; Rocha, B.A.M.; et al. DVL, lectin from Dioclea violacea seeds, has multiple mechanisms of action against Candida spp. via carbohydrate recognition domain. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2023, 348, 109649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Rio, M.; Radicioni, M.B.; Mello, É.O.; Ribeiro, S.F.; Taveira, G.B.; Carvalho, A.O.; la Canal, L.; Gomes, V.M.; Regente, M. A plant mannose-binding lectin and fluconazole: Key targets combination against Candida albicans. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 132, 4310–4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coriolano, M.C.; Brito, J.S.; Ferreira, G.R.S.; Moura, M.C.; Melo, C.M.L.; Soares, A.K.A.; Lorena, V.M.B.; Figueiredo, R.C.B.Q.; Paiva, P.M.G.; Napoleão, T.H.; et al. Antibacterial lectin from Moringa oleifera seeds (WSMoL) has differential action on growth, membrane permeability and protease secretory ability of Gram-positive and Gram-negative pathogens. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2020, 129, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, W.S.F.L.; Amorim, P.K.; Ferreira, G.R.S.; Alves, R.R.V.; Silva, C.E.S.; Santos, P.E.M.; Paiva, P.M.G.; Ingmer, H.; Silva, S.P.; Silva, P.M.; et al. Moringa oleifera seed preparations containing the lectin WSMoL inhibit growth, cell aggregation, and biofilm production of Listeria monocytogenes. Microb. Pathog. 2025, 204, 107600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, F.E.V.; Lima, D.B.; Santos, A.L.E.; Sousa, V.C.; Carvalho, R.D.C.V.; Alves, M.M.M.; Lima, M.A.P.; Souza, R.O.S.; Silva, C.G.L.; Teixeira, C.S. Dioclea violacea lectin has potent in vitro leishmanicidal activity against Leishmania infantum via carbohydrate recognition domain. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 280, 135665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, N.D.L.; Santos, P.E.M.; Lira, T.L.S.; Santos, A.R.S.; Silva, J.N.O.; Santos, A.N.S.; Amorim, M.M.R.; Barros, M.R.; Coelho, L.C.B.B.; Paiva, P.M.G.; et al. Insecticidal activity of lectin preparations from Moringa oleifera Lam. (Moringaceae) seeds against Alphitobius diaperinus (Panzer) (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). Plants 2025, 14, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesquita, J.X.; Brito, T.V.; Fontenelle, T.P.C.; Damasceno, R.O.S.; Souza, M.H.L.P.; Lopes, J.L.S.; Beltramini, L.M.; Barbosa, A.L.R.; Freitas, A.L.P. Lectin from red algae Amansia multifida Lamouroux: Extraction, characterization and anti-inflammatory activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 170, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, J.S.; Marinho, A.O.; Coelho, L.C.B.B.; Oliveira, A.M.; Paiva, P.M.G.; Patriota, L.L.S.; Napoleão, T.H. Toxicity and antitumor activity of the water-soluble lectin from Moringa oleifera Lam. seeds (WSMoL) in sarcoma 180-bearing mice. Toxicon 2023, 234, 107306. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, L.R.D.; Silva, A.F.; Siqueira, J.S.; Santos, R.C.; Lima, V.S.; Oliveira, A.M.; Soares, L.A.L.; Silva, G.C. Estudo do perfil fitoquímico e avaliação dos efeitos citotóxicos do rizoma da Microgramma vacciniifolia. Braz. J. Health Rev. 2020, 3, 1185–1202. [Google Scholar]
- Tryon, R.M.; Tryon, A.F. Family Pteridaceae: From Ferns and Allied Plants; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, M.G.; Sylvestre, L.D.S. Floristics and economics aspects of the pteridophytes of rocky outcrop from Rio de Janeiro State, Brazil. Acta Bot. Bras. 2006, 20, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agra, M.F.; Silva, K.N.; Basílio, I.J.L.D.; Freitas, P.F.; Barbosa-Filho, J.M. Survey of medicinal plants used in the region Northeast of Brazil. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2008, 18, 472–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, M.T.L.P.; Simionatto, E.; Hess, S.C.; Bonani, V.F.L.; Candido, A.C.S.; Castelli, C.; Poppi, N.R.; Honda, N.K.; Cardoso, C.A.L.; Faccenda, O. Chemical and biological studies of Microgramma vacciniifolia (Langsd. & Fisch.) Copel (Polypodiaceae). Quim. Nova 2009, 32, 897–901. [Google Scholar]
- Patriota, L.L.S.; Procópio, T.F.; Brito, J.S.; Sebag, V.; Oliveira, A.P.S.; Soares, A.K.A.; Moreira, L.R.; Lima, T.A.; Soares, T.; Silva, T.D.; et al. Microgramma vacciniifolia (Polypodiaceae) fronds contain a multifunctional lectin with immunomodulatory properties on human cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 103, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patriota, L.L.S.; Ramos, D.B.M.; Silva, Y.A.; Santos, A.C.L.A.; Araujo, M.T.M.F.; Brito, J.S.; Torres, D.J.L.; Oliveira, A.M.; Silva, D.C.N.; Lorena, V.M.B.; et al. Microgramma vacciniifolia frond lectin (MvFL) exhibits antitumor activity against sarcoma 180 in mice. Phytomed. Plus 2021, 1, 100013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, L.M.S.; Alves, M.M.M.; Sobrinho Júnior, E.P.C.; Paiva, P.M.G.; Carvalho, F.A.A.; Albuquerque, L.P.; Patriota, L.L.S.; Napoleão, T.H. Microgramma vacciniifolia Frond Lectin: In Vitro Anti-leishmanial Activity and Immunomodulatory Effects Against Internalized Amastigote Forms of Leishmania amazonensis. Acta Parasitol. 2023, 68, 869–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procópio, T.F.; Patriota, L.L.S.; Moura, M.C.; Silva, P.M.; Oliveira, A.P.S.; Carvalho, L.V.N.; Lima, T.A.; Soares, T.; Silva, T.D.; Coelho, L.C.B.B.; et al. CasuL: A new lectin isolated from Calliandra surinamensis leaf pinnulae with cytotoxicity to cancer cells, antimicrobial activity and antibiofilm effect. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 98, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharan, M.; Dhaka, P.; Bedi, J.S.; Mehta, N.; Singh, R. Assessment of biofilm-forming capacity and multidrug resistance in Staphylococcus aureus isolates from animal-source foods: Implications for lactic acid bacteria intervention. Ann. Microbiol. 2024, 74, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, S.K.; Moellering, R.C.; Eliopoulos, G.M. Antimicrobial combinations. In Antibiotics in Laboratory Medicine; Lorian, V., Ed.; The Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Co.: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2005; pp. 365–440. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, P.M.; Silva, B.R.; Silva, J.N.O.; Moura, M.C.; Soares, T.; Feitosa, A.P.S.; Brayner, F.A.; Alves, L.C.; Paiva, P.M.G.; Damborg, P.; et al. Punica granatum sarcotesta lectin (PgTeL) has antibacterial activity and synergistic effects with antibiotics against β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 135, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios, J.L.; Recio, M.C. Medicinal plants and antimicrobial activity. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 100, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.M.M.; Silva, P.M.; Moura, M.C.; Junior, A.C.; Amorim, P.K.; Procópio, T.F.; Coelho, L.C.B.B.; Silva, L.C.N.; Paiva, P.M.G.; Santos, N.D.L.; et al. Anti-Candida activity of the water-soluble lectin from Moringa oleifera seeds (WSMoL). J. Med. Mycol. 2021, 31, 101074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lašt’ovička, J.; Budinsky, V.; Spisek, R.; Bartunkova, J. Assessment of lymphocyte proliferation: CFSE kills dividing cells and modulates expression of activation markers. Cell. Immunol. 2009, 256, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, B.; Hwang, J.-S.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.-K.; Kim, S.R.; Kim, Y.; Lee, D.G. Induction of yeast apoptosis by an antimicrobial peptide, Papiliocin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 408, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.R.; Neto, J.B.A.; Campos, R.S.; Figueiredo, N.S.; Sampaio, L.S.; Magalhães, H.I.F.; Cavalcanti, B.C.; Gaspar, D.M.; Andrade, G.M.; Lima, I.S.P.; et al. Synergistic effect of the flavonoid catechin, quercetin, or epigallocatechin gallate with fluconazole induces apoptosis in Candida tropicalis resistant to fluconazole. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 1468–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, J.B.; Silva, C.R.; Neta, M.A.; Campos, R.S.; Siebra, J.T.; Silva, R.A.; Gaspar, D.M.; Magalhães, H.I.F.; Moraes, M.O.; Lobo, M.D.P.; et al. Antifungal activity of naphthoquinoidal compounds in vitro against fluconazole-resistant strains of different Candida species: A special emphasis on mechanisms of action on Candida tropicalis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, G.R.S.; Brito, J.S.; Procópio, T.F.; Santos, N.D.L.; De Lima, B.J.R.C.; Coelho, L.C.B.B.; Navarro, D.M.A.F.; Paiva, P.M.G.; Soares, T.; Moura, M.C.; et al. Antimicrobial potential of Alpinia purpurata lectin (ApuL): Growth inhibitory action, synergistic effects in combination with antibiotics, and antibiofilm activity. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 124, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaller, M.A.; Amaral, R.C.R.; Biasi, R.P.; Guilhermetti, E.; Svidzinski, T.I.E.; Baeza, L.C. Antifungal resistance: Mechanisms, epidemiology and consequences for treatment. Am. J. Med. 2012, 125, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoraj, A.; Thevanesam, V.; Bandara, B.M.R.; Ekanayake, A.; Liyanapathirana, V. Synergistic activity between Triphala and selected antibiotics against drug resistant clinical isolates. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2019, 19, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayaz, M.; Ullah, F.; Sadiq, A.; Ullah, F.; Ovais, M.; Ahmed, J.; Devkota, H.P. Synergistic interactions of phytochemicals with antimicrobial agents: Potential strategy to counteract drug resistance. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2019, 308, 294–303. [Google Scholar]
- Bollenbach, T. Antimicrobial interactions: Mechanisms and implications for drug discovery and resistance evolution. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2015, 27, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaachouay, N. Synergy, Additive Effects, and Antagonism of Drugs with Plant Bioactive Compounds. Drugs Drug Candidates 2025, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, T.H.D.; Labedzka-Dmoch, K. RetroGREAT signaling: The lessons we learn from yeast. IUBMB Life 2024, 76, 26–37. [Google Scholar]
- Napoleão, T.H.; Lira, T.L.S.; Pontual, E.V.; Ferreira, G.R.S.; Silva, P.M. Lectins as Natural Antibiofilm Agents in the Fight Against Antibiotic Resistance: A Review. Molecules 2025, 30, 3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Svarovsky, M.J.; Karlsson, A.J.; Wagner, J.P.; Marchillo, K.; Oshel, P.; Andes, D.; Palecek, S.P. Eap1p, an adhesin that mediates Candida albicans biofilm formation in vitro and in vivo. Eukaryot. Cell 2007, 6, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Yeasts | Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (µg/mL) |
|---|---|
| Candida albicans | 20.00 |
| Candida krusei | 1.25 |
| Candida parapsilosis | 40.00 |
| Candida tropicalis | 40.00 |
| Nakaseomyces glabratus | 0.625 |
| Yeasts | MIC (Alone/Combination) | FICI | Combination Effect | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MvFL | Fluconazole | |||
| C. albicans | 20/ND | 0.25/ND | NC | Antagonistic |
| C. krusei | 1.25/0.002 | 32.0/32.0 | 1.0 | Additive |
| C. parapsilosis | 40.0/0.625 | 64.0/8.0 | 0.14 | Synergism |
| C. tropicalis | 40.0/0.078 | 4.0/4.0 | 1.0 | Additive |
| N. glabratus | 0.625/ND | 64.0/ND | NC | Antagonistic |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Oliveira, R.M.V.V.; Junior, A.R.C.; da Silva, P.M.; Ferreira, G.R.S.; Amorim, P.K.; Paiva, P.M.G.; da Silva, L.C.N.; Patriota, L.L.d.S.; Pontual, E.V.; Napoleão, T.H. Evaluation of the Antifungal Activity of Microgramma vacciniifolia Frond Lectin (MvFL) Against Pathogenic Yeasts. Macromol 2025, 5, 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol5040044
de Oliveira RMVV, Junior ARC, da Silva PM, Ferreira GRS, Amorim PK, Paiva PMG, da Silva LCN, Patriota LLdS, Pontual EV, Napoleão TH. Evaluation of the Antifungal Activity of Microgramma vacciniifolia Frond Lectin (MvFL) Against Pathogenic Yeasts. Macromol. 2025; 5(4):44. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol5040044
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Oliveira, Rayanne Maria Vitória Vasconcelos, Alexsander Rodrigues Carvalho Junior, Pollyanna Michelle da Silva, Gustavo Ramos Salles Ferreira, Poliana Karla Amorim, Patrícia Maria Guedes Paiva, Luís Cláudio Nascimento da Silva, Leydianne Leite de Siqueira Patriota, Emmanuel Viana Pontual, and Thiago Henrique Napoleão. 2025. "Evaluation of the Antifungal Activity of Microgramma vacciniifolia Frond Lectin (MvFL) Against Pathogenic Yeasts" Macromol 5, no. 4: 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol5040044
APA Stylede Oliveira, R. M. V. V., Junior, A. R. C., da Silva, P. M., Ferreira, G. R. S., Amorim, P. K., Paiva, P. M. G., da Silva, L. C. N., Patriota, L. L. d. S., Pontual, E. V., & Napoleão, T. H. (2025). Evaluation of the Antifungal Activity of Microgramma vacciniifolia Frond Lectin (MvFL) Against Pathogenic Yeasts. Macromol, 5(4), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol5040044