Interplay Between Protein Phosphatase 2A (PP2A) and SE Translocation (SET) as Macromolecular Target of Anticancer Compounds: A Combined Computational and Experimental Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Computational Studies
2.2. Biological Studies
2.2.1. Patient Cohort and Ethical Approval
2.2.2. Isolation and Purification of CLL Cells
2.2.3. Tumor Cell Lines
2.2.4. Apoptosis Assay and Flow Cytometry Analysis
2.2.5. Western Blot Analysis
2.2.6. PP2A Activity Assay
2.2.7. Immunoprecipitation Assays
2.2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
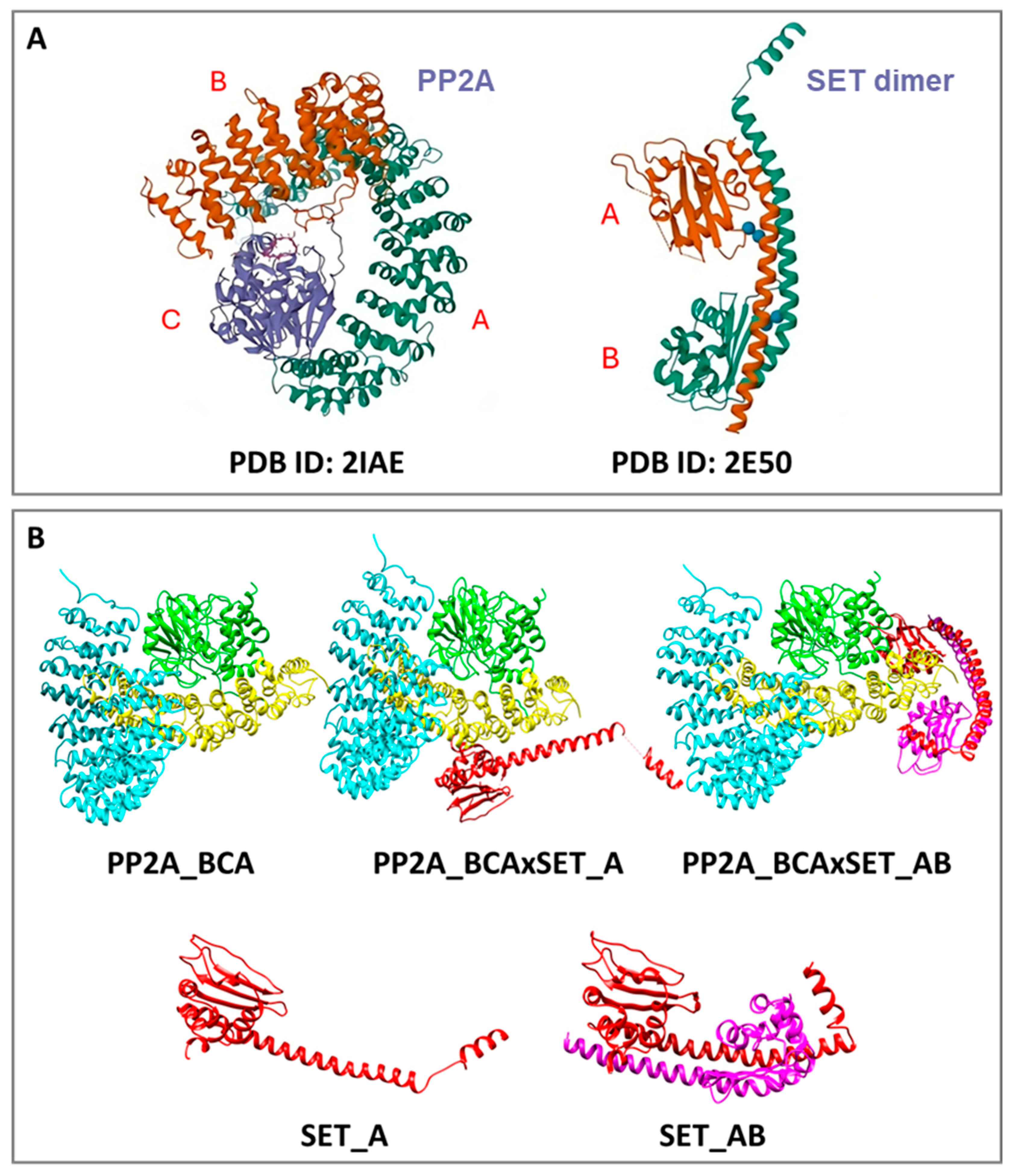
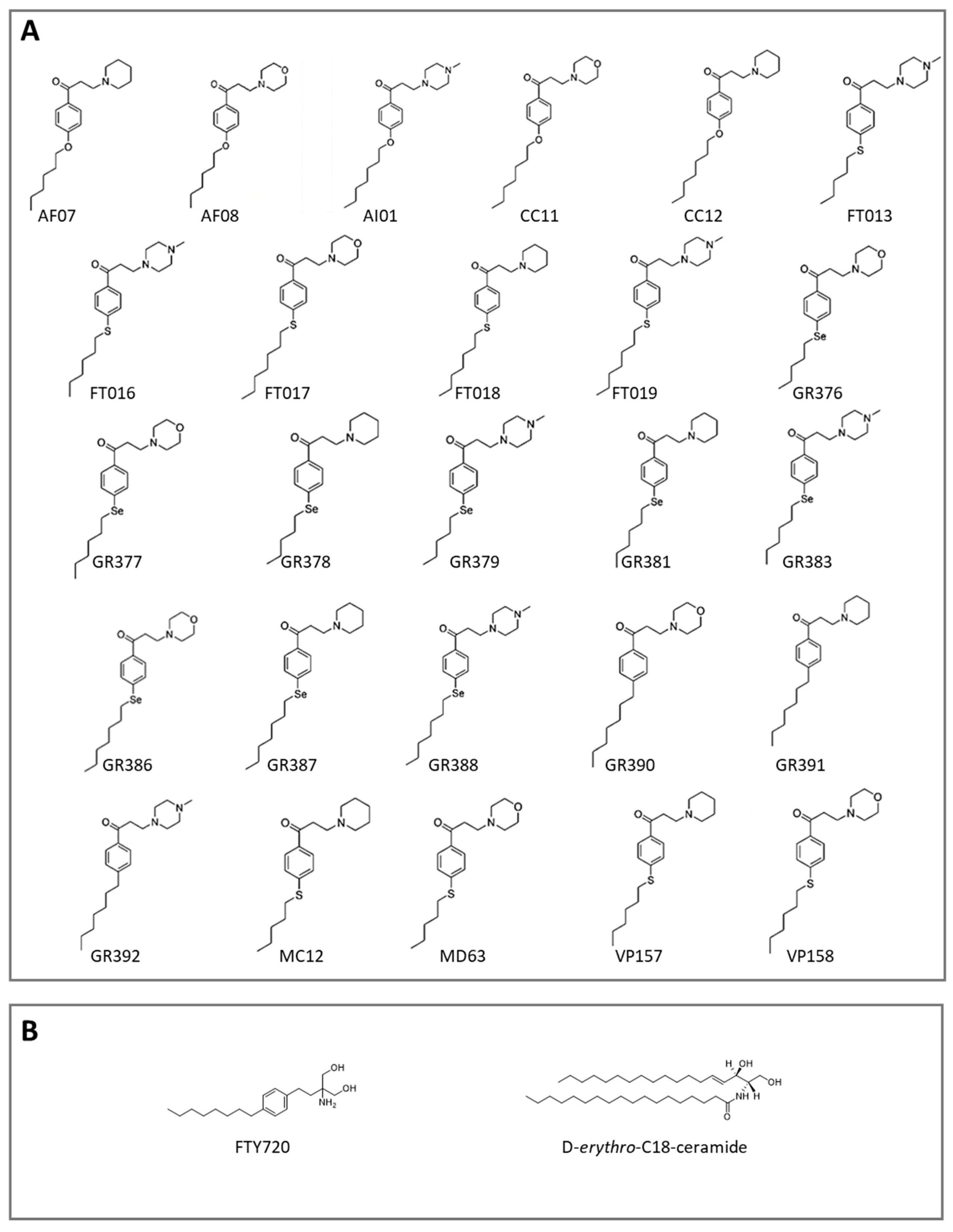
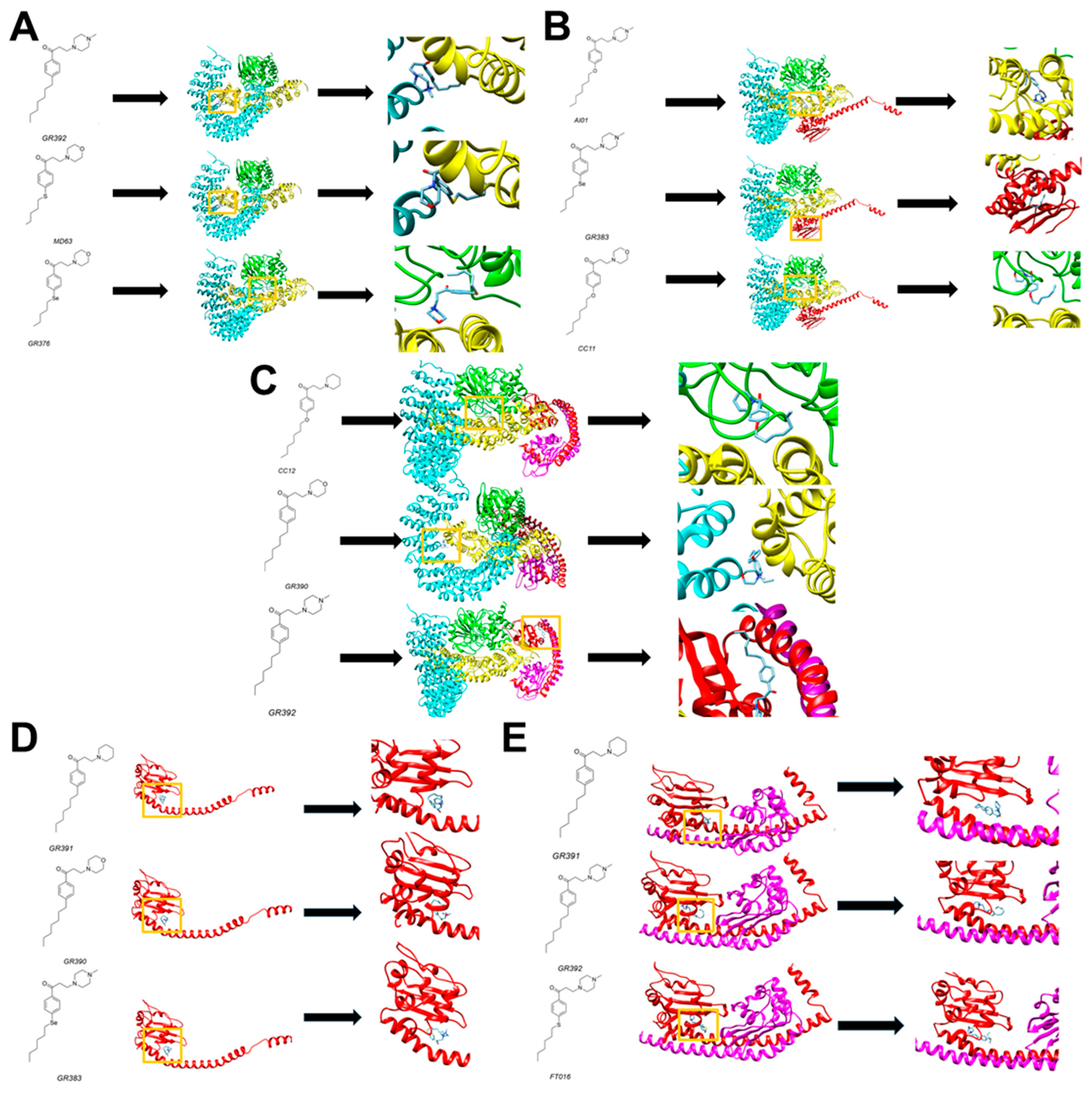
3.1. Computational Studies
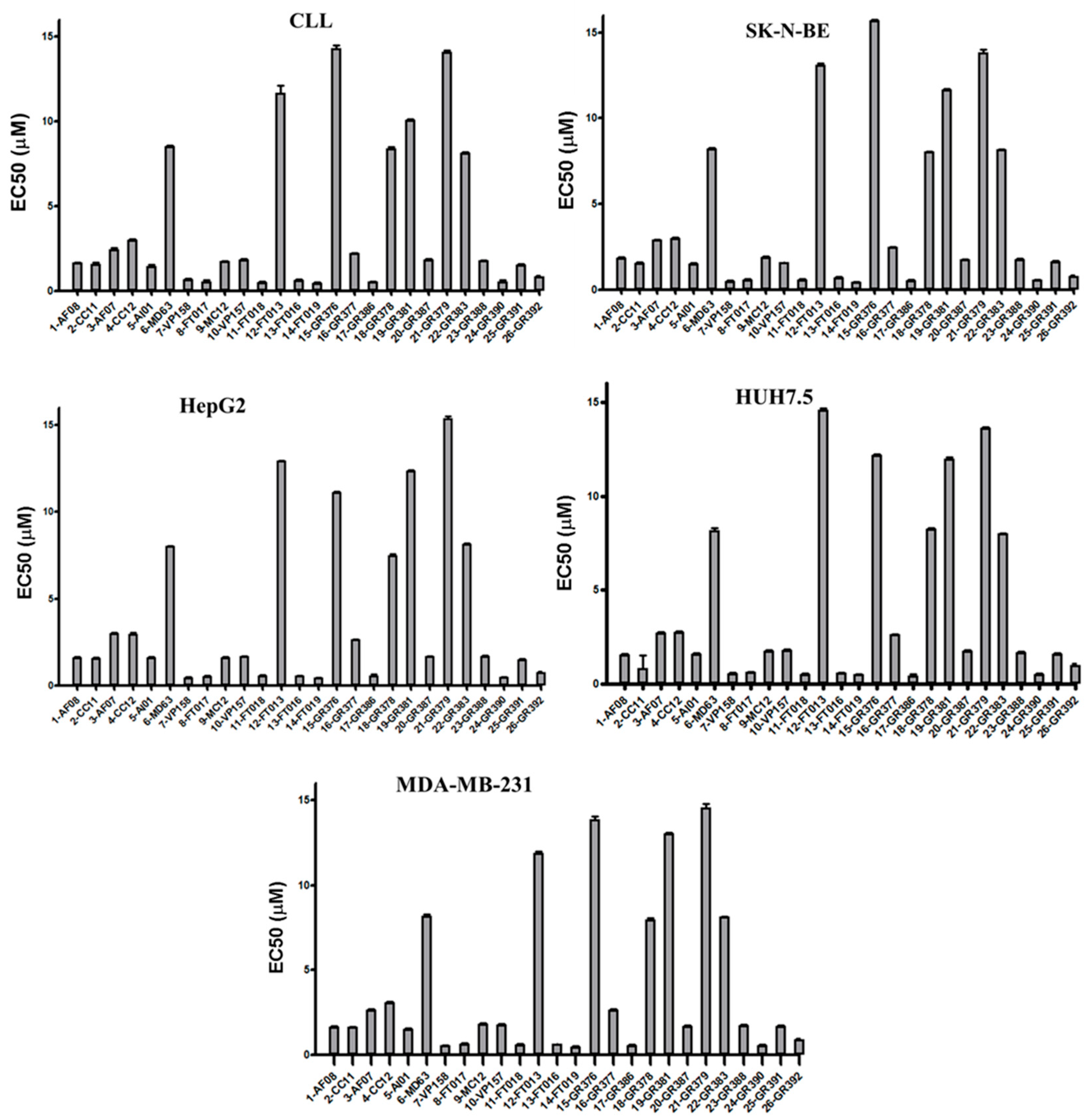
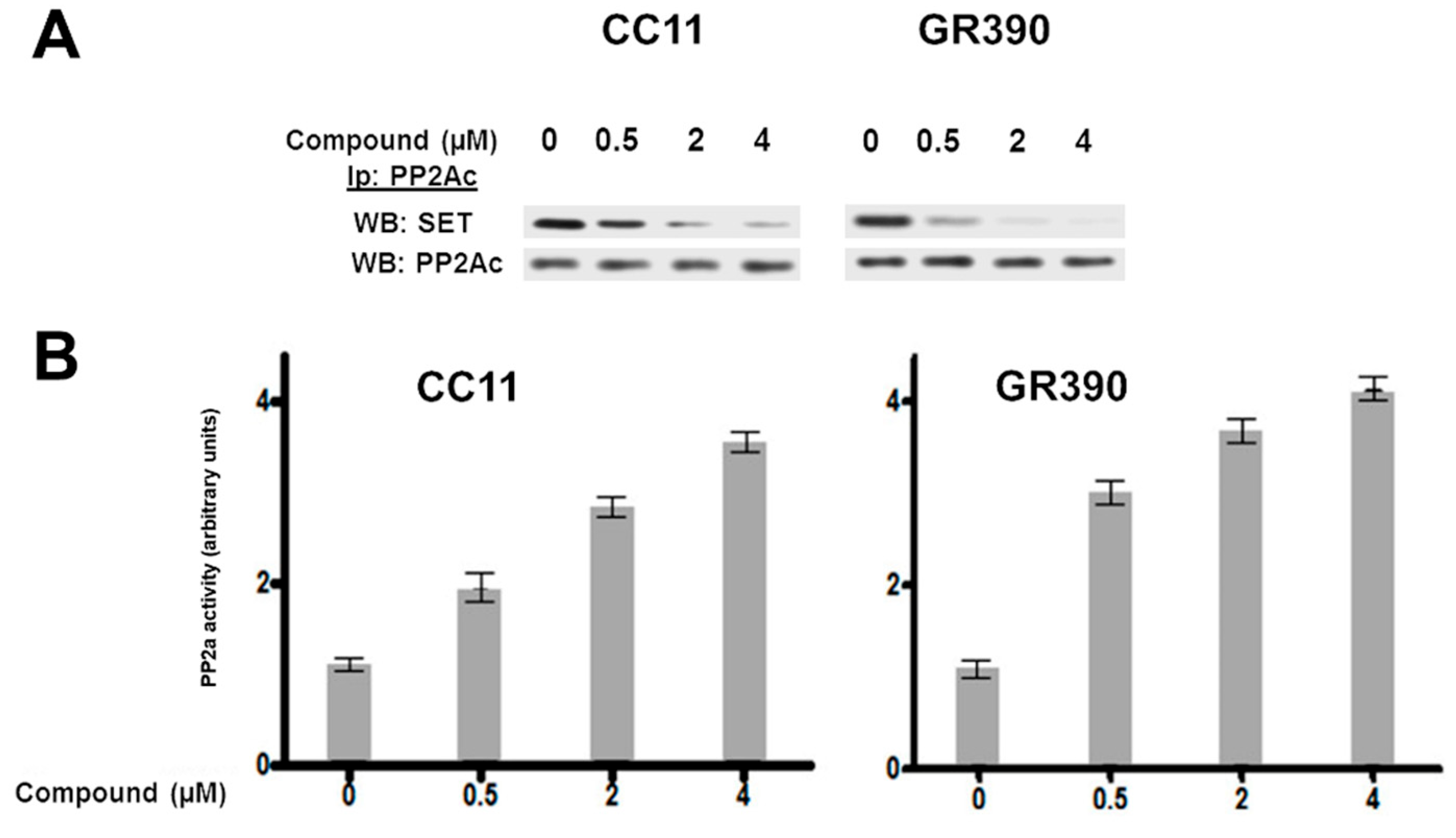
3.2. Biological Studies and ADME Prediction
3.3. Computational and Biological Data Integration
4. Conclusions
5. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sangodkar, J.; Farrington, C.C.; McClinch, K.; Galsky, M.D.; Kastrinsky, D.B.; Narla, G. All Roads Lead to PP 2A: Exploiting the Therapeutic Potential of This Phosphatase. FEBS J. 2016, 283, 1004–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orgad, S.; Brewis, N.D.; Alphey, L.; Axton, J.M.; Dudai, Y.; Cohen, P.T.W. The Structure of Protein Phosphatase 2A Is as Highly Conserved as That of Protein Phosphatase I. FEBS Lett. 1990, 275, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westermarck, J.; Hahn, W.C. Multiple Pathways Regulated by the Tumor Suppressor PP2A in Transformation. Trends Mol. Med. 2008, 14, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y. Serine/Threonine Phosphatases: Mechanism through Structure. Cell 2009, 139, 468–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichhorn, P.J.A.; Creyghton, M.P.; Bernards, R. Protein Phosphatase 2A Regulatory Subunits and Cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Rev. Cancer 2009, 1795, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, V.; Goris, J. Protein Phosphatase 2A: A Highly Regulated Family of Serine/Threonine Phosphatases Implicated in Cell Growth and Signalling. Biochem. J. 2001, 353, 417–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seshacharyulu, P.; Pandey, P.; Datta, K.; Batra, S.K. Phosphatase: PP2A Structural Importance, Regulation and Its Aberrant Expression in Cancer. Cancer Lett. 2013, 335, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wlodarchak, N.; Xing, Y. PP2A as a Master Regulator of the Cell Cycle. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 51, 162–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jong, C.J.; Merrill, R.A.; Wilkerson, E.M.; Herring, L.E.; Graves, L.M.; Strack, S. Reduction of Protein Phosphatase 2A (PP2A) Complexity Reveals Cellular Functions and Dephosphorylation Motifs of the PP2A/B′δ Holoenzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 5654–5668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccone, M.; Calin, G.A.; Perrotti, D. From the Biology of PP2A to the PADs for Therapy of Hematologic Malignancies. Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrotti, D.; Neviani, P. Protein Phosphatase 2A: A Target for Anticancer Therapy. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, e229–e238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haesen, D.; Sents, W.; Lemaire, K.; Hoorne, Y.; Janssens, V. The Basic Biology of PP2A in Hematologic Cells and Malignancies. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, U.S.; Xu, W. Crystal Structure of a Protein Phosphatase 2A Heterotrimeric Holoenzyme. Nature 2007, 445, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Jeffrey, P.D.; Chao, Y.; Lin, Z.; Li, Z.; Strack, S.; Stock, J.B.; Shi, Y. Structure of Protein Phosphatase 2A Core Enzyme Bound to Tumor-Inducing Toxins. Cell 2006, 127, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brewer, A.; Sathe, G.; Pflug, B.E.; Clarke, R.G.; Macartney, T.J.; Sapkota, G.P. Mapping the Substrate Landscape of Protein Phosphatase 2A Catalytic Subunit PPP2CA. iScience 2024, 27, 109302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaswamy, K.; Spitzer, B.; Kentsis, A. Therapeutic Re-Activation of Protein Phosphatase 2A in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowle, H.; Zhao, Z.; Graña, X. PP2A Holoenzymes, Substrate Specificity Driving Cellular Functions and Deregulation in Cancer. In Advances in Cancer Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 144, pp. 55–93. ISBN 978-0-12-817155-4. [Google Scholar]
- Janssens, V.; Jordens, J.; Stevens, I.; Van Hoof, C.; Martens, E.; De Smedt, H.; Engelborghs, Y.; Waelkens, E.; Goris, J. Identification and Functional Analysis of Two Ca2+-Binding EF-Hand Motifs in the B“/PR72 Subunit of Protein Phosphatase 2A. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 10697–10706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssens, V.; Longin, S.; Goris, J. PP2A Holoenzyme Assembly: In Cauda Venenum (the Sting Is in the Tail). Trends Biochem. Sci. 2008, 33, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, W.; Chen, M.; He, F.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Feng, M.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Striatins Contain a Noncanonical Coiled Coil That Binds Protein Phosphatase 2A A Subunit to Form a 2:2 Heterotetrameric Core of Striatin-Interacting Phosphatase and Kinase (STRIPAK) Complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 9651–9661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, V.; Goris, J.; Van Hoof, C. PP2A: The Expected Tumor Suppressor. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2005, 15, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruediger, R.; Pham, H.T.; Walter, G. Disruption of Protein Phosphatase 2A Subunit Interaction in Human Cancers with Mutations in the Aα Subunit Gene. Oncogene 2001, 20, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard, D.; Huang, W.; Izadmehr, S.; O’Connor, C.M.; Wiredja, D.D.; Wang, Z.; Zaware, N.; Chen, Y.; Schlatzer, D.M.; Kiselar, J.; et al. Selective PP2A Enhancement through Biased Heterotrimer Stabilization. Cell 2020, 181, 688–701.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Okkeri, J.; Pavic, K.; Wang, Z.; Kauko, O.; Halonen, T.; Sarek, G.; Ojala, P.M.; Rao, Z.; Xu, W.; et al. Oncoprotein CIP 2A Is Stabilized via Interaction with Tumor Suppressor PP 2A/B56. EMBO Rep. 2017, 18, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dacol, E.C.; Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; Lepique, A.P. The Interaction of SET and Protein Phosphatase 2A as Target for Cancer Therapy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Rev. Cancer 2021, 1876, 188578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, H.K.; Sears, R.C. A Tumor Suppressor Role for PP2A-B56α Through Negative Regulation of c-Myc and Other Key Oncoproteins. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2008, 27, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruvolo, P.P.; Qui, Y.H.; Coombes, K.R.; Zhang, N.; Ruvolo, V.R.; Borthakur, G.; Konopleva, M.; Andreeff, M.; Kornblau, S.M. Low Expression of PP2A Regulatory Subunit B55α Is Associated with T308 Phosphorylation of AKT and Shorter Complete Remission Duration in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patients. Leukemia 2011, 25, 1711–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverstein, A.M.; Barrow, C.A.; Davis, A.J.; Mumby, M.C. Actions of PP2A on the MAP Kinase Pathway and Apoptosis Are Mediated by Distinct Regulatory Subunits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 4221–4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauko, O.; Laajala, T.D.; Jumppanen, M.; Hintsanen, P.; Suni, V.; Haapaniemi, P.; Corthals, G.; Aittokallio, T.; Westermarck, J.; Imanishi, S.Y. Label-Free Quantitative Phosphoproteomics with Novel Pairwise Abundance Normalization Reveals Synergistic RAS and CIP2A Signaling. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruvolo, P.P. The Broken “Off” Switch in Cancer Signaling: PP2A as a Regulator of Tumorigenesis, Drug Resistance, and Immune Surveillance. BBA Clin. 2016, 6, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurimchak, A.; Graña, X. PP2A Holoenzymes Negatively and Positively Regulate Cell Cycle Progression by Dephosphorylating Pocket Proteins and Multiple CDK Substrates. Gene 2012, 499, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Shi, J.; Yin, X.; Iqbal, K.; Grundke-Iqbal, I.; Gong, C.-X.; Liu, F. PP2A Regulates Tau Phosphorylation Directly and Also Indirectly via Activating GSK-3β. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2010, 19, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shentu, Y.-P.; Huo, Y.; Feng, X.-L.; Gilbert, J.; Zhang, Q.; Liuyang, Z.-Y.; Wang, X.-L.; Wang, G.; Zhou, H.; Wang, X.-C.; et al. CIP2A Causes Tau/APP Phosphorylation, Synaptopathy, and Memory Deficits in Alzheimer’s Disease. Cell Rep. 2018, 24, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xia, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shentu, Y.; Zeng, K.; Mahaman, Y.A.R.; Huang, F.; Wu, M.; Ke, D.; Wang, Q.; et al. CK2 Phosphorylating I2PP2A/SET Mediates Tau Pathology and Cognitive Impairment. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, A.R.; Ohlmeyer, M. Protein Phosphatase 2A as a Therapeutic Target in Inflammation and Neurodegeneration. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 201, 181–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharabi, A.; Kasper, I.R.; Tsokos, G.C. The Serine/Threonine Protein Phosphatase 2A Controls Autoimmunity. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 186, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, C.M.; Perl, A.; Leonard, D.; Sangodkar, J.; Narla, G. Therapeutic Targeting of PP2A. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 96, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, A.; Pan, L.; Groen, R.W.J.; Baleydier, F.; Kentsis, A.; Marineau, J.; Grebliunaite, R.; Kozakewich, E.; Reed, C.; Pflumio, F.; et al. Phenothiazines Induce PP2A-Mediated Apoptosis in T Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 644–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastrinsky, D.B.; Sangodkar, J.; Zaware, N.; Izadmehr, S.; Dhawan, N.S.; Narla, G.; Ohlmeyer, M. Reengineered Tricyclic Anti-Cancer Agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 6528–6534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westermarck, J.; Neel, B.G. Piecing Together a Broken Tumor Suppressor Phosphatase for Cancer Therapy. Cell 2020, 181, 514–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang-Schulz, A.; Zacharopoulou, M.; Yilmaz, S.Z.; Banerjee, A.; Saha, S.; Nietlispach, D.; Ohlmeyer, M.; Gur, M.; Itzhaki, L.S.; Bahar, I.; et al. Direct Observation of Small Molecule Activator Binding to Single PR65 Protein. Npj Biosens. 2025, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bownes, L.V.; Julson, J.R.; Quinn, C.H.; Hutchins, S.C.; Erwin, M.H.; Markert, H.R.; Stewart, J.E.; Mroczek-Musulman, E.; Aye, J.; Yoon, K.J.; et al. The Effects of Protein Phosphatase 2A Activation with Novel Tricyclic Sulfonamides on Hepatoblastoma. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2023, 58, 1145–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Lindern, M.; Van Baal, S.; Wiegant, J.; Raap, A.; Hagemeijer, A.; Grosveld, G. Can, a Putative Oncogene Associated with Myeloid Leukemogenesis, May Be Activated by Fusion of Its 3‣ Half to Different Genes: Characterization of the Set. Gene. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1992, 12, 3346–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, K.; Saito, S.; Okuwaki, M.; Kawase, H.; Furuya, A.; Kusano, A.; Hanai, N.; Okuda, A.; Kikuchi, A. Cellular Localization and Expression of Template-Activating Factor I in Different Cell Types. Exp. Cell Res. 1998, 240, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, Y.; Pavlakis, G.N.; Copeland, T.D. Identification and Characterization of SET, a Nuclear Phosphoprotein Encoded by the Translocation Break Point in Acute Undifferentiated Leukemia. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 2258–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Yan, T.; Feng, Y.; Liu, X.; Xia, Y.; Luo, H.; Wang, J.-Z.; Wang, X. Ser9 Phosphorylation Causes Cytoplasmic Detention of I2PP2A/SET in Alzheimer Disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2013, 34, 1748–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, S.; Miyaji-Yamaguchi, M.; Shimoyama, T.; Nagata, K. Functional Domains of Template-Activating Factor-I as a Protein Phosphatase 2A Inhibitor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 259, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muto, S.; Senda, M.; Akai, Y.; Sato, L.; Suzuki, T.; Nagai, R.; Senda, T.; Horikoshi, M. Relationship between the Structure of SET/TAF-Iβ/INHAT and Its Histone Chaperone Activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 4285–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Gu, Y.; Wang, H.; Yin, J.; Zheng, G.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, M.; Wang, C.; He, Z. Overexpression of PP2A Inhibitor SET Oncoprotein Is Associated with Tumor Progression and Poor Prognosis in Human Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 14913–14925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristobal, I.; Garcia-Orti, L.; Cirauqui, C.; Cortes-Lavaud, X.; Garcia-Sanchez, M.A.; Calasanz, M.J.; Odero, M.D. Overexpression of SET Is a Recurrent Event Associated with Poor Outcome and Contributes to Protein Phosphatase 2A Inhibition in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Haematologica 2012, 97, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappos, L.; Antel, J.; Comi, G.; Montalban, X.; O’Connor, P.; Polman, C.H.; Haas, T.; Korn, A.A.; Karlsson, G.; Radue, E.W. Oral Fingolimod (FTY720) for Relapsing Multiple Sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 1124–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horga, A.; Montalban, X. FTY720 (Fingolimod) for Relapsing Multiple Sclerosis. Expert. Rev. Neurother. 2008, 8, 699–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neviani, P.; Santhanam, R.; Oaks, J.J.; Eiring, A.M.; Notari, M.; Blaser, B.W.; Liu, S.; Trotta, R.; Muthusamy, N.; Gambacorti-Passerini, C.; et al. FTY720, a New Alternative for Treating Blast Crisis Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia and Philadelphia Chromosome–Positive Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 2408–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, K.G.; Smith, A.M.; McDougall, F.; Carpenter, H.; Horan, M.; Neviani, P.; Powell, J.A.; Thomas, D.; Guthridge, M.A.; Perrotti, D.; et al. Essential Requirement for PP2A Inhibition by the Oncogenic Receptor C-KIT Suggests PP2A Reactivation as a Strategy to Treat c-KIT+ Cancers. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 5438–5447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, H.-D.; Ji, X.-J.; Cong, Z.-X.; Zhu, J.-H.; Zhou, Y. FTY720 for Cancer Therapy (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 2571–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, C.; Alshaker, H.; Cooper, C.; Winkler, M.; Pchejetski, D. The Emerging Role of FTY720 (Fingolimod) in Cancer Treatment. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 23106–23127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Roy, S.G.; McMonigle, R.J.; Keebaugh, A.; McCracken, A.N.; Selwan, E.; Fransson, R.; Fallegger, D.; Huwiler, A.; Kleinman, M.T.; et al. Azacyclic FTY720 Analogues That Limit Nutrient Transporter Expression but Lack S1P Receptor Activity and Negative Chronotropic Effects Offer a Novel and Effective Strategy to Kill Cancer Cells in Vivo. ACS Chem. Biol. 2016, 11, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagano, M.A.; Tibaldi, E.; Molino, P.; Frezzato, F.; Trimarco, V.; Facco, M.; Zagotto, G.; Ribaudo, G.; Leanza, L.; Peruzzo, R.; et al. Mitochondrial Apoptosis Is Induced by Alkoxy Phenyl-1-Propanone Derivatives Through PP2A-Mediated Dephosphorylation of Bad and Foxo3A in CLL. Leukemia 2019, 33, 1148–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zonta, F.; Pagano, M.A.; Trentin, L.; Tibaldi, E.; Frezzato, F.; Trimarco, V.; Facco, M.; Zagotto, G.; Pavan, V.; Ribaudo, G.; et al. Lyn Sustains Oncogenic Signaling in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia by Strengthening SET-Mediated Inhibition of PP2A. Blood 2015, 125, 3747–3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, L.A.; Kosinski, A.; Estébanez-Perpiñá, E.; Guy, R.K. Inhibitors of the Interaction of a Thyroid Hormone Receptor and Coactivators: Preliminary Structure−Activity Relationships. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 5269–5280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, D.; Wang, X.; Xie, Y. Dyclonine and Alverine Citrate Enhance the Cytotoxic Effects of Proteasome Inhibitor MG132 on Breast Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2009, 23, 205–209. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, M.-H.; Chen, Y.-L.; Chu, P.-Y.; Shih, C.-T.; Yu, H.-C.; Tai, W.-T.; Shiau, C.-W.; Chen, K.-F. Upregulation of the Oncoprotein SET Determines Poor Clinical Outcomes in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Shows Therapeutic Potential. Oncogene 2016, 35, 4891–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leopoldino, A.M.; Squarize, C.H.; Garcia, C.B.; Almeida, L.O.; Pestana, C.R.; Sobral, L.M.; Uyemura, S.A.; Tajara, E.H.; Silvio Gutkind, J.; Curti, C. SET Protein Accumulates in HNSCC and Contributes to Cell Survival: Antioxidant Defense, Akt Phosphorylation and AVOs Acidification. Oral Oncol. 2012, 48, 1106–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, S.; Chiang, C.-L.; Zapolnik, K.; Nunes, J.; Ventura, A.; Mo, X.; Xie, Z.; Lee, L.J.; Baskar, S.; Rader, C.; et al. ROR1 Targeted Immunoliposomal Delivery of OSU-2S Shows Selective Cytotoxicity in t(1;19)(Q23;P13) Translocated B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2022, 118, 106872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.B.; Oh, Y.S.; Kim, K.J.; Cho, S.W.; Park, S.K.; Baek, D.J.; Park, E.-Y. Synthesis of PP2A-Activating PF-543 Derivatives and Investigation of Their Inhibitory Effects on Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Molecules 2022, 27, 3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, U.S.; Morrone, S.; Sablina, A.A.; Arroyo, J.D.; Hahn, W.C.; Xu, W. Structural Basis of PP2A Inhibition by Small t Antigen. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scorsato, V.; Lima, T.B.; Righetto, G.L.; Zanchin, N.I.T.; Brandão-Neto, J.; Sandy, J.; Pereira, H.D.; Ferrari, Á.J.R.; Gozzo, F.C.; Smetana, J.H.C.; et al. Crystal Structure of the Human Tip41 Orthologue, TIPRL, Reveals a Novel Fold and a Binding Site for the PP2Ac C-Terminus. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A Visualization System for Exploratory Research and Analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanwell, M.D.; Curtis, D.E.; Lonie, D.C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Zurek, E.; Hutchison, G.R. Avogadro: An Advanced Semantic Chemical Editor, Visualization, and Analysis Platform. J. Cheminform. 2012, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the Speed and Accuracy of Docking with a New Scoring Function, Efficient Optimization, and Multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A Free Web Tool to Evaluate Pharmacokinetics, Drug-Likeness and Medicinal Chemistry Friendliness of Small Molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zonta, F.; Borgo, C.; Quezada Meza, C.P.; Masgras, I.; Rasola, A.; Salvi, M.; Pinna, L.A.; Ruzzene, M. Contribution of the CK2 Catalytic Isoforms α and α’ to the Glycolytic Phenotype of Tumor Cells. Cells 2021, 10, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masola, V.; Carraro, A.; Zaza, G.; Bellin, G.; Montin, U.; Violi, P.; Lupo, A.; Tedeschi, U. Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in the Liver Field: The Double Face of Everolimus in Vitro. BMC Gastroenterol. 2015, 15, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamoto, M.; Yamaji, T.; Saito, K.; Shirasago, Y.; Satomura, K.; Endo, T.; Fukasawa, M.; Hanada, K.; Osada, N. Identification of Characteristic Genomic Markers in Human Hepatoma HuH-7 and Huh7.5.1-8 Cell Lines. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 546106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberle, C.-A.; Zayas, M.; Stukalov, A.; Pichlmair, A.; Alvisi, G.; Müller, A.C.; Bennett, K.L.; Bartenschlager, R.; Superti-Furga, G. The Lysine Methyltransferase SMYD3 Interacts with Hepatitis C Virus NS5A and Is a Negative Regulator of Viral Particle Production. Virology 2014, 462–463, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, F.; Sasso, M.; Turdo, F.; Beretta, G.L.; Casalini, P.; Ghirelli, C.; Sfondrini, L.; Ménard, S.; Tagliabue, E.; Campiglio, M. Fhit Nuclear Import Following EGF Stimulation Sustains Proliferation of Breast Cancer Cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2015, 230, 2661–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagotto, G.; Ribaudo, G.; Brunati, A.M.; Pagano, M.A.P.; Tibaldi, E.; Trentin, L. 1-Phenylpropanone Compounds and Use Thereof. WO2018060947A1, 4 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Saddoughi, S.A.; Gencer, S.; Peterson, Y.K.; Ward, K.E.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Oaks, J.; Bielawski, J.; Szulc, Z.M.; Thomas, R.J.; Selvam, S.P.; et al. Sphingosine Analogue Drug FTY720 Targets I2PP2A/SET and Mediates Lung Tumour Suppression via Activation of PP2A-RIPK1-dependent Necroptosis. EMBO Mol. Med. 2013, 5, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipinski, C.A. Drug-like Properties and the Causes of Poor Solubility and Poor Permeability. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2000, 44, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ribaudo, G.; Pagano, M.A.; Anyanwu, M.; Giannangeli, M.; Vezzoli, M.; Visentin, A.; Frezzato, F.; Trentin, L.; Brunati, A.M.; Gianoncelli, A. Interplay Between Protein Phosphatase 2A (PP2A) and SE Translocation (SET) as Macromolecular Target of Anticancer Compounds: A Combined Computational and Experimental Study. Macromol 2025, 5, 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol5030043
Ribaudo G, Pagano MA, Anyanwu M, Giannangeli M, Vezzoli M, Visentin A, Frezzato F, Trentin L, Brunati AM, Gianoncelli A. Interplay Between Protein Phosphatase 2A (PP2A) and SE Translocation (SET) as Macromolecular Target of Anticancer Compounds: A Combined Computational and Experimental Study. Macromol. 2025; 5(3):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol5030043
Chicago/Turabian StyleRibaudo, Giovanni, Mario Angelo Pagano, Margrate Anyanwu, Matteo Giannangeli, Marika Vezzoli, Andrea Visentin, Federica Frezzato, Livio Trentin, Anna Maria Brunati, and Alessandra Gianoncelli. 2025. "Interplay Between Protein Phosphatase 2A (PP2A) and SE Translocation (SET) as Macromolecular Target of Anticancer Compounds: A Combined Computational and Experimental Study" Macromol 5, no. 3: 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol5030043
APA StyleRibaudo, G., Pagano, M. A., Anyanwu, M., Giannangeli, M., Vezzoli, M., Visentin, A., Frezzato, F., Trentin, L., Brunati, A. M., & Gianoncelli, A. (2025). Interplay Between Protein Phosphatase 2A (PP2A) and SE Translocation (SET) as Macromolecular Target of Anticancer Compounds: A Combined Computational and Experimental Study. Macromol, 5(3), 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol5030043









