Application of Annealed Bambara Starch as a Stabilizer in Ice Cream Production
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Extraction and Annealing of Bambara Starch
2.3. Ice Cream Mix Formulation and Production
2.4. Percentage Overrun
2.5. Foam Stability
2.6. Viscosity
2.7. Meltdown Rate
2.8. Sensory Evaluation
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
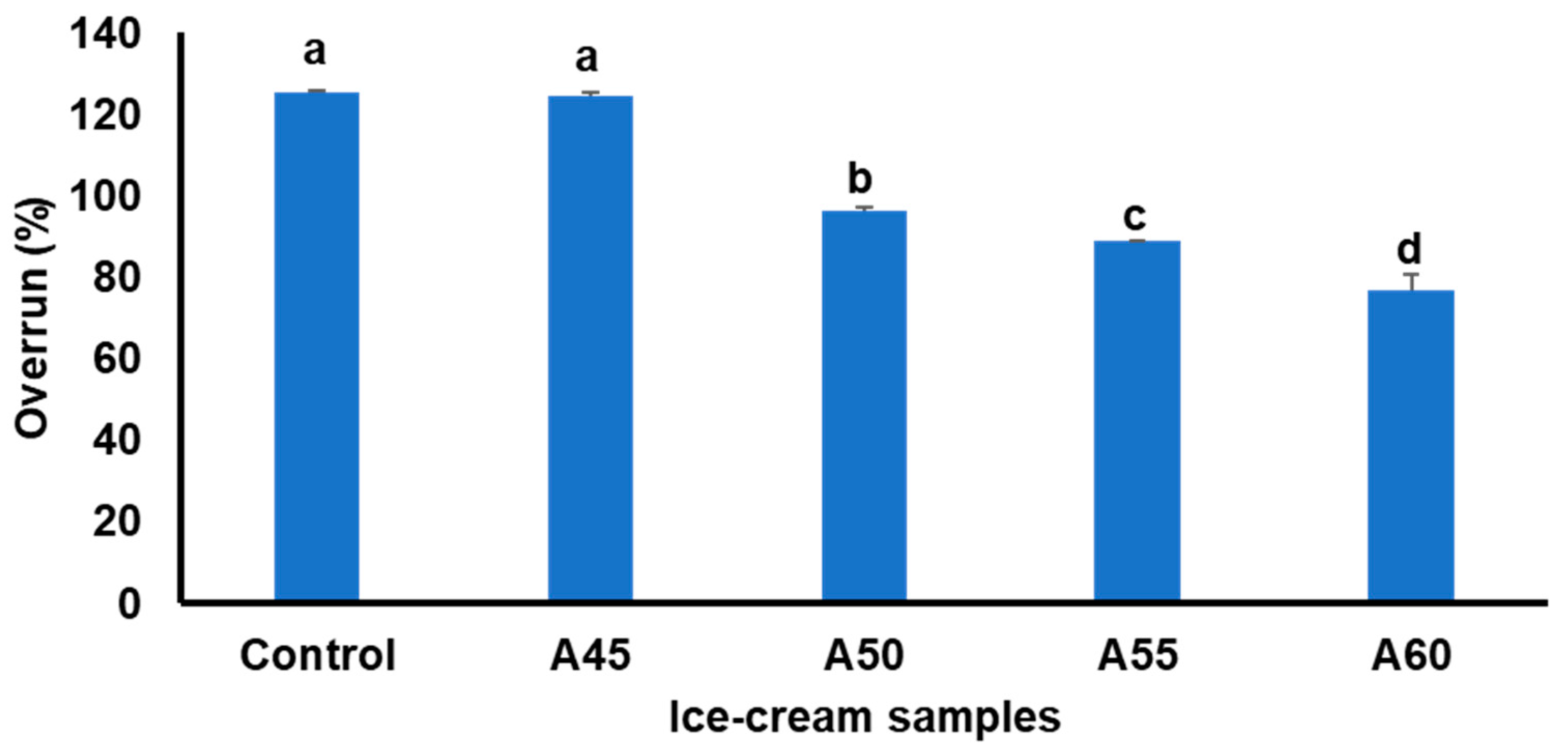
3.1. Effect of Annealed Bambara Starch on Overrun of Ice Creams
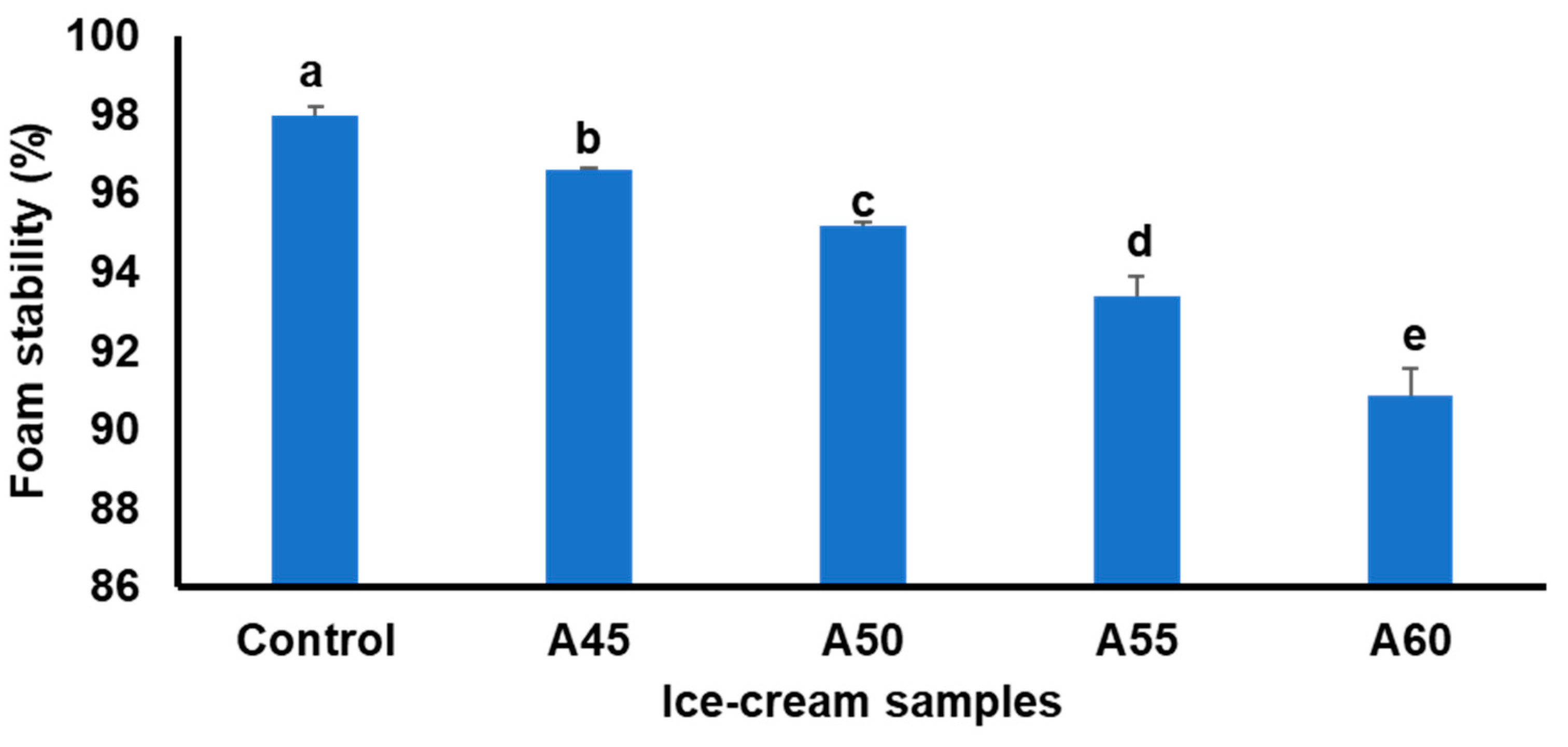
3.2. Effect of Annealed Bambara Starch on Foam Stability of Ice Creams
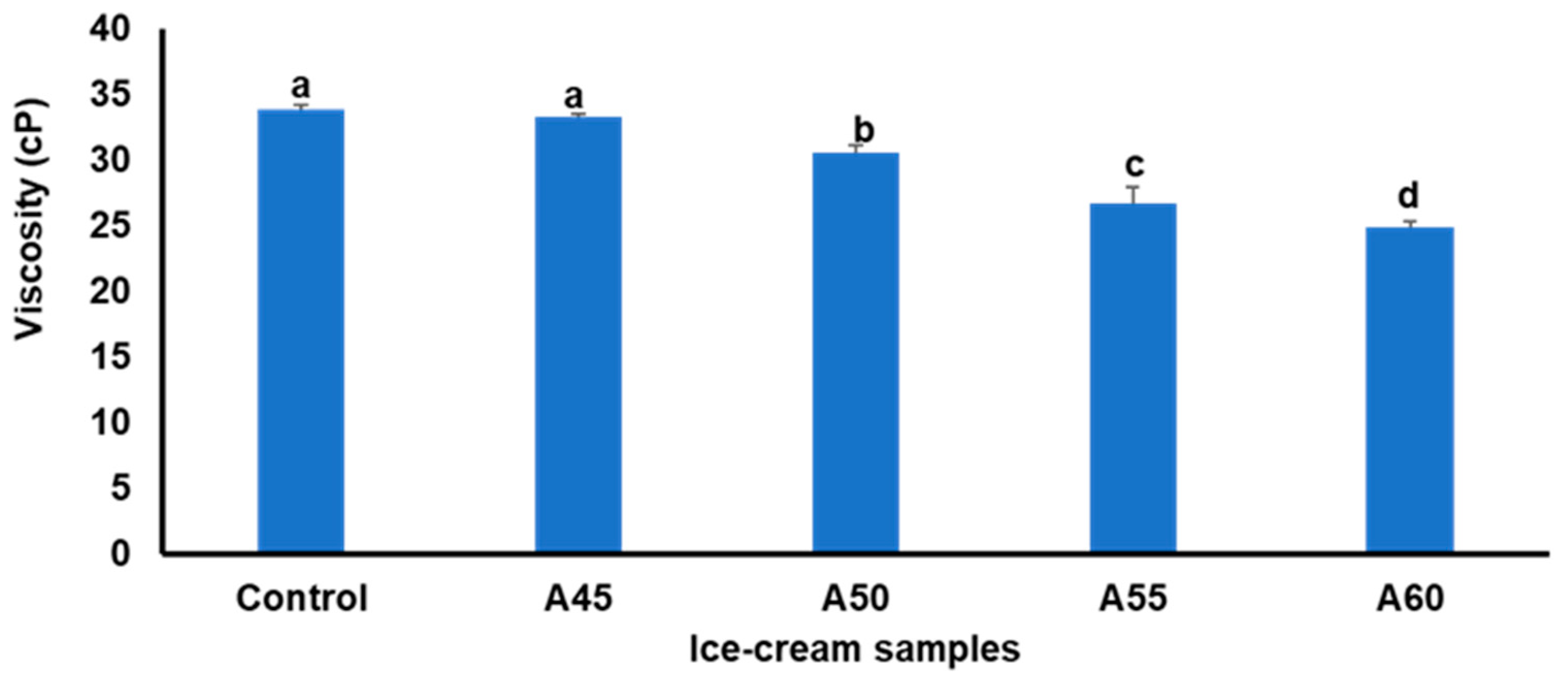
3.3. Effect of Annealed Bambara Starch on Viscosity of Ice Creams
3.4. Effect of Annealed Bambara Starch on Meltdown Rate of Ice Creams
3.5. Sensory Characteristics of Annealed Bambara Starch-Stabilized Ice Creams
3.6. Pearson Correlation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murevanhema, Y.Y.; Jideani, V.A. Potential of bambara groundnut (Vigna subterranea (L.) Verdc) milk as a probiotic beverage—A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 53, 954–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyeyinka, S.A.; Singh, S.; Amonsou, E.O. Physicochemical properties of starches extracted from bambara groundnut landraces. Starch-Stärke 2017, 69, 1600089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temegne, N.; Gouertoumbo, W.; Wakem, G.; Nkou, F.; Youmbi, E.; Ntsomboh-Ntsefong, G. Origin and ecology of Bambara groundnut (Vigna subterranea (L.) Verdc): A review. J. Ecol. Nat. Res. 2018, 2, 000140. [Google Scholar]
- Oyeyinka, S.A.; Oyeyinka, A.T. A review on isolation, composition, physicochemical properties and modification of Bambara groundnut starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 75, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaptso, K.G.; Njintang, Y.N.; Nguemtchouin, M.M.G.; Scher, J.; Hounhouigan, J.; Mbofung, C.M. Physicochemical and micro-structural properties of flours, starch, and proteins from two varieties of legumes: Bambara groundnut (Vigna subterranea). J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 4915–4924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyeyinka, S.A.; Singh, S.; Adebola, P.O.; Gerrano, A.S.; Amonsou, E.O. Physicochemical properties of starches with variable amylose contents extracted from bambara groundnut genotypes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 133, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyeyinka, S.A.; Singh, S.; Ma, Y.; Amonsou, E.O. Effect of high-pressure homogenization on structural, thermal and rheological properties of bambara starch complexed with different fatty acids. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 80174–80180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyeyinka, S.A.; Singh, S.; Ma, Y.; Amonsou, E.O. Influence of high-pressure homogenization on the physicochemical properties of bambara starch complexed with lysophosphatidylcholine. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 74, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.Y.; Woo, K.S.; Chung, H.J. Starch characteristics of cowpea and mungbean cultivars grown in Korea. Food Chem. 2018, 263, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashogbon, A.O. Current research addressing physical modification of starch from various botanical sources. Glob. Nutr. Diet. 2018, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, B.; Ariffin, F.; Bhat, R.; Karim, A.A. Progress in starch modification in the last decade. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 26, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwaogazie, F.O.; Akinwande, B.A.; Oyyinka, S.A. Physicochemical properties of Bambara groundnut (Vigna subterranea) starch annealed at different temperatures. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2022, 46, e17183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebowale, K.; Afolabi, T.; Olu-Owolabi, B. Hydrothermal treatments of Finger millet (Eleusine coracana) starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2005, 19, 974–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyeyinka, S.A.; Adegoke, R.; Oyeyinka, A.T.; Salami, K.O.; Olagunju, O.F.; Kolawole, F.L.; Joseph, J.K.; Bolarinwa, I.F. Effect of annealing on the functionality of Bambara groundnut (Vigna subterranea) starch–palmitic acid complex. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikegwu, O.; Odo, M.; Okoli, E. Effect of annealing on the physicochemical properties of some under-utilised legume starches. Nig. Food J. 2011, 29. Available online: https://www.ajol.info/index.php/nifoj/article/view/73643 (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- Afolabi, T.A.; Opara, A.O.; Kareem, S.O.; Oladoyinbo, F.O. In vitro digestibility of hydrothermally modified Bambara groundnut (Vigna subterranea L.) starch and flour. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 6, 36–46. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.; Saleh, A.S.; Gong, B.; Li, B.; Jing, L.; Gou, M.; Jiang, H.; Li, W. The effect of repeated versus continuous annealing on structural, physicochemical, and digestive properties of potato starch. Food Res. Int. 2018, 111, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, A.G.; Banerjee, S. Variants of ice creams and their health effects. MOJ Food Process. Technol. 2017, 4, 58–64. [Google Scholar]
- Marimon-Valverde, S.; Lainez-Ramirez, S.; Sepúlveda-Valencia, J.-U.; Mejia-Villota, A.; Rodriguez-Sandoval, E. Quality characteristics of low-fat ice cream mixtures as affected by modified cassava starch and hydrocolloids. Int. J. Food Prop. 2024, 27, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, Q.A.; Shah, M.S.U. Impact of stabilizers on ice cream quality characteristic. MOJ Food Process. Technol. 2016, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Soukoulis, C.; Chandrinos, I.; Tzia, C. Study of the functionality of selected hydrocolloids and their blends with κ-carrageenan on storage quality of vanilla ice cream. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 41, 1816–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaiudom, S.; Singchan, K.; Saeli, T. Comparison of commercial stabilizers with modified tapioca starch on foam stability and overrun of ice cream. Asian J. Food Agro-Ind. 2008, 1, 51–61. [Google Scholar]
- Perez Navarro, O.; Ley Chong, N.; Gonzalez Suarez, E.; Valdes Valmaseda, C. Hydrothermal modification of cassava starch for use as ice cream stabilizer. AFINIDAD 2017, 74, 275–281. [Google Scholar]
- Surapat, S.; Rugthavon, P. Use of modified starch as a fat replacer in reduced fat coconut milk ice cream. Kasetsart J. 2003, 37, 484–492. [Google Scholar]
- Surendra Babu, A.; Parimalavalli, R.; Jagan Mohan, R. Effect of modified starch from sweet potato as a fat replacer on the quality of reduced fat ice creams. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2018, 12, 2426–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W. General Steps of Ice Cream Processing. Snowball Machinery, Ice Cream Solutions Provider. Dalian, China. 2014. Available online: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/general-steps-ice-cream-processing-william-wang (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- Otutu, O.L.; Ade-Omowaye, B.I.O.; Akinwade, A.B. Stability and sensory evaluation of ice cream prepared from acetylated cassava starches. Futa J. Res. Sci. 2017, 13, 483–492. [Google Scholar]
- Alakali, J.; Okonkwo, T.; Uwu, L. Effect of food binders on the textual and sensory characteristics of ice cream. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 8, 2853–2856. [Google Scholar]
- Singo, T.; Beswa, D. Effect of roselle extracts on the selected quality characteristics of ice cream. Int. J. Food Prop. 2019, 22, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, S.; Leong, S.; Henna, L.F. Physicochemical and sensory properties of ice cream formulated with virgin coconut oil. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2010, 16, 531–541. [Google Scholar]
- Bahramparvar, M.; Mazaheri Tehrani, M. Application and functions of stabilizers in ice cream. Food Rev. Int. 2011, 27, 389–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofjan, R.P.; Hartel, R.W. Effects of overrun on structural and physical characteristics of ice cream. Int. Dairy J. 2004, 14, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, F.Y.; White, C. Effect of ultrafiltration retentates and whey protein concentrates on ice cream quality during storage. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 1170–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, M.; Azizi-Lalabadi, M.; Kheirouri, S. Impact of using stevia on physicochemical, sensory, rheology and glycemic index of soft ice cream. Food Nutr. Sci. 2014, 2014, 42783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.T.; Ting, Y.; Hu, J.Y.; Hsieh, S.C. Techniques and methods to study functional characteristics of emulsion systems. J. Food Drug Anal. 2017, 25, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwood, F.; Smallfield, H. Factors influencing the viscosity of cream and ice cream. J. Dairy Sci. 1926, 9, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muse, M.; Hartel, R.W. Ice cream structural elements that affect melting rate and hardness. J. Dairy Sci. 2004, 87, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Saleh, A.S.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, K.; Ge, X.; Zhang, Q.; Li, W. Changes in structural, physicochemical, and digestive properties of normal and waxy wheat starch during repeated and continuous annealing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 247, 116675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sala, G.; Scholten, E. Impact of soy protein dispersibility on the structural and sensory properties of fat-free ice cream. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 147, 109340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsalee, N.; Meerasri, J.; Sothornvit, R. Enhancing ice cream qualities with novel rice husk cellulose nanocrystal applications. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 2495–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goff, H.D.; Davidson, V.J. Flow characteristics and holding time calculations of ice cream mixes in HTST holding tubes. J. Food Prot. 1992, 55, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koxholt, M.M.; Eisenmann, B.; Hinrichs, J. Effect of the fat globule sizes on the meltdown of ice cream. J. Dairy Sci. 2001, 84, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Freire, D.O.; Hartel, R.W. The effect of overrun, fat destabilization, and ice cream mix viscosity on entire meltdown behavior. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 2562–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Zhao, J.; Fan, H.; Qin, W.; Wu, Z. Enhancing starch nanocrystal production and evaluating their efficacy as fat replacers in ice cream: Investigating the influence of high pressure and ultrasonication. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 251, 126385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Khalesi, H.; He, J.; Fang, Y. Application of different hydrocolloids as fat replacer in low-fat dairy products: Ice cream, yogurt and cheese. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 138, 108493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, M.; Eskandari, M.H.; Davoudi, Z. Application and functions of fat replacers in low-fat ice cream: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 86, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sensory Descriptors | Range of Sensory Descriptors |
|---|---|
| Color | Off-white, white, and cream |
| Aroma | Plain, mild, and intense |
| Mouthfeel | Gritty, slightly smooth, and smooth |
| Body | Unstable, slightly firm, and very firm |
| Taste | Bland, slightly sweet, and very sweet |
| Melting Time (min) | Control | A45 | A50 | A55 | A60 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 1.90 ± 0.00 a | 1.89 ± 0.00 a | 1.77 ± 0.00 b | 1.55 ± 0.00 c | 1.53 ± 0.03 c |
| 10 | 3.72 ± 0.00 a | 3.70 ± 0.00 b | 2.44 ± 0.00 c | 2.24 ± 0.00 d | 2.24 ± 0.00 d |
| 15 | 4.05 ± 0.00 a | 3.99 ± 0.00 b | 3.64 ± 0.00 c | 2.41 ± 0.00 d | 2.40 ± 0.00 e |
| 20 | 4.09 ± 0.00 a | 4.08 ± 0.00 b | 4.07 ± 0.00 c | 3.63 ± 0.00 d | 2.39 ± 0.00 e |
| 25 | 4.32 ± 0.00 a | 4.31 ± 0.00 b | 4.29 ± 0.00 c | 3.14 ± 0.00 d | 2.34 ± 0.00 e |
| 30 | 4.56 ± 0.00 a | 4.55 ± 0.00 b | 4.32 ± 0.00 c | 3.23 ± 0.00 d | 2.28 ± 0.00 e |
| 35 | 4.62 ± 0.00 a | 4.59 ± 0.00 b | 4.38 ± 0.00 c | 3.19 ± 0.00 d | 2.19 ± 0.00 e |
| 40 | 4.65 ± 0.00 a | 4.65 ± 0.00 a | 4.65 ± 0.00 a | 3.08 ± 0.00 b | 2.08 ± 0.06 c |
| 45 | 4.67 ± 0.00 a | 4.65 ± 0.00 b | 4.51 ± 0.00 c | 3.00 ± 0.00 d | 2.08 ± 0.00 e |
| Samples | Taste | Aroma | Mouthfeel | Body | Color |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSI 101 | 13.32 ± 0.29 a | 14.65 ± 0.13 a | 14.92 ± 0.12 a | 14.98 ± 0.04 a | 13.78 ± 0.21 a |
| ASI 201 | 13.30 ± 0.29 a | 14.55 ± 0.21 ab | 14.31 ± 0.21 b | 14.28 ± 0.24 b | 13.67 ±0.19 ab |
| ASI 202 | 13.21 ± 0.22 a | 14.28 ± 0.24 bc | 12.23 ± 0.44 c | 11.93 ± 0.12 c | 13.58 ± 0.31 b |
| AS1 203 | 13.33 ± 0.26 a | 14.43 ± 0.17 c | 8.87 ± 0.41 d | 8.41 ± 0.22 d | 13.38 ± 0.16 c |
| ASI 204 | 13.13 ± 0.23 a | 14.08 ± 0.16 d | 7.50 ± 0.49 e | 6.73 ± 0.37 e | 12.98 ± 0.06 d |
| 5 min | 10 min | 15 min | 20 min | 25 min | 30 min | 35 min | 40 min | 45 min | FS (%) | Viscosity (cP) | Overrun (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 min | 1 | |||||||||||
| 10 min | 0.902 ** | 1 | ||||||||||
| 15 min | 0.992 ** | 0.855 ** | 1 | |||||||||
| 20 min | 0.787 ** | 0.601 * | 0.788 ** | 1 | ||||||||
| 25 min | 0.923 ** | 0.718 ** | 0.937 ** | 0.946 ** | 1 | |||||||
| 30 min | 0.935 ** | 0.762 ** | 0.941 ** | 0.950 ** | 0.997 ** | 1 | ||||||
| 35 min | 0.935 ** | 0.758 ** | 0.940 ** | 0.950 ** | 0.997 ** | 1.000 ** | 1 | |||||
| 40 min | 0.925 ** | 0.713 ** | 0.940 ** | 0.940 ** | 1.000 ** | 0.995 ** | 0.995 ** | 1 | ||||
| 45 min | 0.943 ** | 0.751 ** | 0.954 ** | 0.932 ** | 0.999 ** | 0.997 ** | 0.998 ** | 0.998 ** | 1 | |||
| FS (%) | 0.938 ** | 0.857 ** | 0.916 ** | 0.889 ** | 0.931 ** | 0.952 ** | 0.951 ** | 0.927 ** | 0.939 ** | 1 | ||
| Viscosity (cP) | 0.976 ** | 0.895 ** | 0.968 ** | 0.837 ** | 0.934 ** | 0.951 ** | 0.949 ** | 0.931 ** | 0.949 ** | 0.963 ** | 1 | |
| Overrun (%) | 0.945 ** | 0.968 ** | 0.905 ** | 0.774 ** | 0.847 ** | 0.883 ** | 0.880 ** | 0.841 ** | 0.868 ** | 0.948 ** | 0.951 ** | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nwaogazie, F.O.; Akinwande, B.A.; Adebo, O.A.; Oyeyinka, S.A. Application of Annealed Bambara Starch as a Stabilizer in Ice Cream Production. Macromol 2024, 4, 533-543. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol4030031
Nwaogazie FO, Akinwande BA, Adebo OA, Oyeyinka SA. Application of Annealed Bambara Starch as a Stabilizer in Ice Cream Production. Macromol. 2024; 4(3):533-543. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol4030031
Chicago/Turabian StyleNwaogazie, Faith O., Bolanle A. Akinwande, Oluwafemi A. Adebo, and Samson A. Oyeyinka. 2024. "Application of Annealed Bambara Starch as a Stabilizer in Ice Cream Production" Macromol 4, no. 3: 533-543. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol4030031
APA StyleNwaogazie, F. O., Akinwande, B. A., Adebo, O. A., & Oyeyinka, S. A. (2024). Application of Annealed Bambara Starch as a Stabilizer in Ice Cream Production. Macromol, 4(3), 533-543. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol4030031







