New Trends in Composite Coagulants for Water and Wastewater Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Natural Coagulants
Natural Coagulants with Flocculants Added
3. Inorganic Coagulants
Inorganic Coagulants with Flocculants Added
4. Organic Coagulants
5. Hybrid Coagulants/Flocculants
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Naraghi, B.; Baneshi, M.M.; Amiri, R.; Dorost, A.; Biglari, H. Removal of Reactive Black 5 Dye from Aqueous Solutions by Coupled Electrocoagulation and Bio-Adsorbent Process. Electron. Physician 2018, 10, 7086–7094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolkou, A.K.; Mitropoulos, A.C.; Kyzas, G.Z. Removal of Anthraquinone Dye from Wastewaters by Hybrid Modified Activated Carbons. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 73688–73701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolkou, A.K.; Tsoutsa, E.K.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Katsoyiannis, I.A. Sustainable Use of Low-Cost Adsorbents Prepared from Waste Fruit Peels for the Removal of Selected Reactive and Basic Dyes Found in Wastewaters. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 14662–14689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoong, H.N.J.; Ismail, N. Removal of Dye in Wastewater by Adsorption-Coagulation Combined System with Hibiscus Sabdariffa as the Coagulant. In Proceedings of the MATEC Web of Conferences, 9th International Engineering Research Conference (Eureca 2017), Selango, Malaysia, 6 December 2017; EDP Sciences: Les Ulis, France, 2018; Volume 152. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Luo, X.B.; Ding, L.; Luo, S.L. Application of Nanotechnology in the Removal of Heavy Metal from Water; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; ISBN 9780128148389. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Tayawi, A.N.; Sisay, E.J.; Beszédes, S.; Kertész, S. Wastewater Treatment in the Dairy Industry from Classical Treatment to Promising Technologies: An Overview. Processes 2023, 11, 2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.K.; Aggarwal, I.; Kumar, H.; Prasad, L.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, A.; Vo, D.V.N.; Van Thuan, D.; Mishra, V. Magnetite Nanoparticles as Sorbents for Dye Removal: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 2487–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Mu, B.; Zhang, T.; Dong, C.; Zhu, Y.; Zong, L.; Wang, A. Synthesis of Biochar/Clay Mineral Nanocomposites Using Oil Shale Semi-Coke Waste for Removal of Organic Pollutants. Biochar 2023, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Li, S.; Ding, Z.; Li, J.; Yu, A.; Wen, S.; Bai, S. Treatment Technology and Research Progress of Residual Xanthate in Mineral Processing Wastewater. Minerals 2023, 13, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wantoputri, N.I.; Notodarmojo, S.; Helmy, Q. Reactive Black-5 Removal by Ozonation as Post Treatment. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; Institute of Physics; International Conference on Science and Innovated Engineering (I-COSINE), Aceh, Indonesia, 21–22 October 2018; IOP Science: Bristol, UK, 2019; Volume 536. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Da, Y.; Xie, F.; Wang, J. Advanced Treatment of Landfill Leachate Using Integrated Coagulation/Photo-Fenton Process through in-Situ Generated Nascent Al3+ and H2O2 by Cl, N Co-Doped Aluminum-Graphite Composite. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2022, 304, 121003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, R.; Liu, L.; Su, X.; Gong, W.; Luo, X.; Gao, H. Facile Preparation of Cellulose Beads with Tunable Graded Pores and High Mechanical Strength. Polymers 2024, 16, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadadi, A.; Imessaoudene, A.; Bollinger, J.C.; Cheikh, S.; Assadi, A.A.; Amrane, A.; Kebir, M.; Mouni, L. Parametrical Study for the Effective Removal of Mordant Black 11 from Synthetic Solutions: Moringa Oleifera Seeds’ Extracts Versus Alum. Water 2022, 14, 4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daud, Z.; Awang, H.; Latif, A.A.A.; Nasir, N.; Ridzuan, M.B.; Ahmad, Z. Suspended Solid, Color, COD and Oil and Grease Removal from Biodiesel Wastewater by Coagulation and Flocculation Processes. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 195, 2407–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azamzam, A.A.; Rafatullah, M.; Yahya, E.B.; Ahmad, M.I.; Lalung, J.; Alam, M.; Siddiqui, M.R. Enhancing the Efficiency of Banana Peel Bio-Coagulant in Turbid and River Water Treatment Applications. Water 2022, 14, 2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoutsa, E.K.; Tolkou, A.K.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Katsoyiannis, I.A. An Update on Agricultural Wastes Used as Natural Adsorbents or Coagulants in Single or Combined Systems for the Removal of Dyes from Wastewater. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 2024, 235, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, J.; Domingues, E.; Fernandes, E.; Castro, L.; Martins, R.C.; Quinta-Ferreira, R.M. Coagulation and Biofiltration by Corbicula Fluminea for COD and Toxicity Reduction of Swine Wastewater. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 42, 102145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, M.; El-Tanany, S.S.; Moatasim, Y.; Moniem, S.M.A.; Hemdan, B.A.; Ammar, N.S.; El-Taweel, G.E.; Ashmawy, A.M.; Badawy, M.I.; Lasheen, M.R.; et al. Assessment of Toxicity and Antimicrobial Performance of Polymeric Inorganic Coagulant and Evaluation for Eutrophication Reduction. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.E.M.; Moniem, S.M.A.; Hemdan, B.A.; Ammar, N.S.; Ibrahim, H.S. Innovative Polymeric Inorganic Coagulant-Flocculant for Wastewater Purification with Simultaneous Microbial Reduction in Treated Effluent and Sludge. South African J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 42, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaharia, C.; Musteret, C.-P.; Afrasinei, M.-A. The Use of Coagulation–Flocculation for Industrial Colored Wastewater Treatment—(I) The Application of Hybrid Materials. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, N.C.; Yel, E. Synthesis of a New Flocculant from Waste Polystyrene: Plastic Recycling Industry Wastewater Treatability. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, H.; Sun, C.; Yuan, W.; Li, H.; Jiang, W.; Dong, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H. Preparation of Inorganic–Organic Composite Coagulant and Its Mechanism in Destroying Emulsified Oil in Oilfield Sewage. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 330, 125446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Xu, H.; Wang, Z.; Chen, H.; Yang, L.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, C.; Wang, D. Effect of Surface Functional Groups of Polystyrene Micro/Nano Plastics on the Release of NOM from Flocs during the Aging Process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 472, 134421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimalaweera, I.P.; Wei, Y.; Ritigala, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, H.; Weerasooriya, R.; Jinadasa, S.; Weragoda, S. Enhanced Pretreatment of Natural Rubber Industrial Wastewater Using Magnetic Seed Coagulation with Ca(OH)2. Water 2024, 16, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, T.; Ladeia Janz, F.J.; Vizibelli, D.; Borges, J.C.Â.; Borssoi, J.A.; Fukumoto, A.A.F.; Bergamasco, R.; Ueda Yamaguchi, N.; Pereira, E.R. Magnetic Natural Coagulants for Plastic Recycling Industry Wastewater Treatability. Water 2023, 15, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumky, J.; Bandina, E.; Repo, E. Behavior of Sludge Dewaterability and Nutrient Contents after Treatment with Cellulose-Based Flocculants with Combined PTS and Catalytic Behavior of Sludge towards Tetracycline Degradation. Resources 2023, 12, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Huang, C.; Huang, J.; Yan, Y.; Liu, G.; Yu, X.; Liu, W.; Cao, H.; Liu, A. Mechanism for the Synergistic Removal of Sb(III) and Sb(V) from Printing and Dyeing Wastewater by Polyferric Sulfate. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoutsa, E.K.; Tolkou, A.K.; Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Kyzas, G.Z. Composite Activated Carbon Modified with AlCl3 for the Effective Removal of Reactive Black 5 Dye from Wastewaters. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Kurniawan, S.B.; Ahmad, J.; Alias, J.; Marsidi, N.; Said, N.S.M.; Yusof, A.S.M.; Buhari, J.; Ramli, N.N.; Rahim, N.F.M.; et al. Dosage-Based Application versus Ratio-Based Approach for Metal- and Plant-Based Coagulants in Wastewater Treatment: Merits, Limitations, and Applicability. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 334, 130245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Chen, F.; Xu, B.; Ma, G.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Z.; Liu, R.; Sun, C.; Cheng, X.; Guo, N.; et al. Iron-Based Technology Coupling Moderate Preoxidation with Hybrid Coagulation for Highly Effective Removal and Moderate Growth Inhibition of Oscillatoria in Drinking Water Treatment Plants. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, J.N.; Kapelyushin, Y.; Mishra, D.P.; Ghosh, P.; Sahoo, B.K.; Trofimov, E.; Meikap, B.C. Utilization of Ferrous Slags as Coagulants, Filters, Adsorbents, Neutralizers/Stabilizers, Catalysts, Additives, and Bed Materials for Water and Wastewater Treatment: A Review. Chemosphere 2023, 325, 138201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Long, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhu, G. Preparation and Application of Polymeric Silicate Coagulant: A Short Review. Environ. Eng. Res. 2024, 29, 230672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Huang, X.; Luan, Z.; Tang, W.; Xu, Z.; Xu, W. Suitability of Inorganic Coagulants for Algae-Laden Water Treatment: Trade-off between Algae Removal and Cell Viability, Aggregate Properties and Coagulant Residue. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 471, 134314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamira Shaharom, M.; Siti Quraisyah Abg Adenan, D. Potential of Orange Peel as a Coagulant for Water Treatment. Infrastruct. Univ. Kuala Lumpur Res. J. 2019, 7, 63–72. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, L.d.L.C.d.; Silva, J.B.M.; Neves, L.S.; Renato, N.d.S.; Moltó, J.; Conesa, J.A.; Borges, A.C. Life Cycle Assessment of a Vegetable Tannin-Based Agent Production for Waters Treatment. Water 2024, 16, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasi, I.T.; Machado, C.A.; Boaventura, R.A.R.; Botelho, C.M.S.; Santos, S.C.R. Tannin-Based Coagulants: Current Development and Prospects on Synthesis and Uses. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 822, 153454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolkou, A.K.; Tsoutsa, E.K.; Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Kyzas, G.Z. Simultaneous Removal of Anionic and Cationic Dyes on Quaternary Mixtures by Adsorption onto Banana, Orange and Pomegranate Peels. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 685, 133176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcés-Gómez, Y.A.; Pacheco-Gonzalez, S.I. Method for Extraction and Evaluation of Heliocarpus Popayanensis and Triumfetta Bogotensis as Natural Coagulants for the Treatment of Wastewater. Methods Protoc. 2023, 6, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-David, E.A.; Habibi, M.; Haddad, E.; Sammar, M.; Angel, D.L.; Dror, H.; Lahovitski, H.; Booth, A.M.; Sabbah, I. Mechanism of Nanoplastics Capture by Jellyfish Mucin and Its Potential as a Sustainable Water Treatment Technology. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 869, 161824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristianto, H.; Angelina Kurniawan, M.; M Soetedjo, J.N. Utilization of Papaya Seeds as Natural Coagulant for Synthetic Textile Coloring Agent Wastewater Treatment. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2018, 8, 2071–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abujazar, M.S.S.; Karaağaç, S.U.; Abu Amr, S.S.; Alazaiza, M.Y.D.; Fatihah, S.; Bashir, M.J.K. Recent Advancements in Plant-Based Natural Coagulant Application in the Water and Wastewater Coagulation-Flocculation Process: Challenges and Future Perspectives. Glob. Nest J. 2022, 24, 687–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abujazar, M.S.S.; Karaağaç, S.U.; Abu Amr, S.S.; Alazaiza, M.Y.D.; Bashir, M.J. Recent Advancement in the Application of Hybrid Coagulants in Coagulation-Flocculation of Wastewater: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 345, 131133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Huang, X.; Yu, Z.; Chen, P.; Cao, X. Application Progress of Enhanced Coagulation in Water Treatment. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 20231–20244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang, W.L.; Mohammad, A.W. State of the Art and Sustainability of Natural Coagulants in Water and Wastewater Treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 262, 121267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibiya, N.P.; Amo-Duodu, G.; Tetteh, E.K.; Rathilal, S. Magnetic Field Effect on Coagulation Treatment of Wastewater Using Magnetite Rice Starch and Aluminium Sulfate. Polymers 2023, 15, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, R.R.; Ketabachi, M.R.; McKay, G. Combined Magnetic Field and Adsorption Process for Treatment of Biologically Treated Palm Oil Mill Effluent (POME). Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 243, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Hasan, H.A.; Othman, A.R.; Kurniawan, S.B. Aquaculture Wastewater Treatment Using Plant-Based Coagulants: Evaluating Removal Efficiency through the Coagulation-Flocculation Process. Results Chem. 2024, 7, 101390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouj, N.; Majbar, Z.; Abelouah, M.R.; Ben Hamou, A.; Chaoui, A.; Hafid, N.; Benafqir, M.; El Alem, N.; Jada, A.; Ouachtak, H.; et al. Eco-Friendly Wastewater Treatment Using a Crab Shell-Based Liquid Bio-Coagulant: Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis Related to Different Pollutants Separation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benalia, A.; Chaibraa, W.; Djeghar, S.; Derbal, K.; Khalfaoui, A.; Mahfouf, A.; Bouchareb, R.; Panico, A.; Pizzi, A. Use of Extracted Proteins from Oak Leaves as Bio-Coagulant for Water and Wastewater Treatment: Optimization by a Fractional Factorial Design. Water 2023, 15, 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsergany, M. The Potential Use of Moringa Peregrina Seeds and Seed Extract as a Bio-Coagulant for Water Purification. Water 2023, 15, 2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otálora, M.C.; Wilches-Torres, A.; Lara, C.R.; Díaz-Gómez, J.; Gómez Castaño, J.A.; Cifuentes, G.R. Assessment of Prickly Pear Fruit Peel Mucilage in Form of Gel as a Green Coagulant for the Tertiary Treatment of Domestic Wastewater. Gels 2023, 9, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, A.; Jorge, N.; Teixeira, A.; Peres, J.A.; Lucas, M.S. Cattle Wastewater Treatment Using Almond Hull and Cherry Pit as Coagulants–Flocculants. Eng. Proc. 2023, 56, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Gaayda, J.; Titchou, F.E.; Barra, I.; Karmal, I.; Afanga, H.; Zazou, H.; Yap, P.S.; Abidin, Z.Z.; Hamdani, M.; Akbour, R.A. Optimization of Turbidity and Dye Removal from Synthetic Wastewater Using Response Surface Methodology: Effectiveness of Moringa Oleifera Seed Powder as a Green Coagulant. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 106988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naruka, A.K.; Suganya, S.; Kumar, P.S.; Amit, C.; Ankita, K.; Bhatt, D.; Kumar, M.A. Kinetic Modelling of High Turbid Water Flocculation Using Native and Surface Functionalized Coagulants Prepared from Shed-Leaves of Avicennia Marina Plants. Chemosphere 2021, 272, 129894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovuoraye, P.E.; Okpala, L.C.; Ugonabo, V.I.; Nwokocha, G.F. Clarification Efficacy of Eggshell and Aluminum Base Coagulant for the Removal of Total Suspended Solids (TSS) from Cosmetics Wastewater by Coag-Flocculation. Chem. Pap. 2021, 75, 4759–4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayavenkataraman, S.; Iniyan, S.; Goic, R. A Review of Solar Drying Technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 2652–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benalia, A.; Derbal, K.; Khalfaoui, A.; Bouchareb, R.; Panico, A.; Gisonni, C.; Crispino, G.; Pirozzi, F.; Pizzi, A. Use of Aloe Vera as an Organic Coagulant for Improving Drinking Water Quality. Water 2021, 13, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, A.; Agamuthu, P.; Hassan, A.; Auta, H.S.; Fauziah, S.H. Green Coagulant from Dillenia Indica for Removal of Bis(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate and Phenol, 4,4’-(1-Methylethylidene)Bis- from Landfill Leachate. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 102061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Al-Gheethi, A.; Asharuddin, S.M.; Othman, N. Potential of Cassava Peels as a Sustainable Coagulant Aid for Institutional Wastewater Treatment: Characterisation, Optimisation and Techno-Economic Analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 127642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauricio, M.; Flores, A.; Emmanuel, O.; Miranda, R.; Andr, N.; Omar, S. Evaluation of the Potential of a Biocoagulant Produced from Prickly Pear Peel Waste Valorization for Wastewater Treatment. Water 2024, 16, 1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wei, S.; Li, G.; Guo, B. Advanced Removal of Phosphorus from Urban Sewage Using Chemical Precipitation by Fe-Al Composite Coagulants. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 4918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chang, F.; Zheng, M. Advanced Treatment of Coking Wastewater by Polyaluminum Silicate Sulfate for Organic Compounds Removal. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 6342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, H.H.; Younis, S.A.; El-Fawal, E.M.; Ali, H.R.; Moustafa, Y.M.; Mohamed, G.G. Synthesis of Polyaluminum Chloride Coagulant from Waste Aluminum Foil and Utilization in Petroleum Wastewater Treatment. Separations 2023, 10, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Song, Q.; He, J. Preparation and Coagulation Performance of Polyaluminum Lanthanum Silicate Coagulant. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Gong, Z.; Qi, W.; Li, E.; Shen, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, H. Coagulation Performance and Floc Characteristics of Poly-Ferric-Titanium-Silicate-Chloride in Coking Wastewater Treatment. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 642, 128413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; An, G.; Lin, L.; Demissie, H.; Yang, X.; Jiao, R.; Wang, D. Design and Coagulation Mechanism of a New Functional Composite Coagulant in Removing Humic Acid. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 292, 121016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolkou, A.K.; Zouboulis, A.I.; Samaras, P.E. Synthesis and Coagulation Performance of Composite Poly-Aluminum-Ferric-Silicate-Chloride Coagulants in Water and Wastewater Treatment and Their Potentially Use to Alleviate the Membrane Fouling in MBRs. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 53, 3309–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolkou, A.K.; Zouboulis, A.I. Application of Composite Pre-Polymerized Coagulants for the Treatment of High-Strength Industrial Wastewaters. Water 2020, 12, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolkou, A.K.; Mitrakas, M.; Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Ernst, M.; Zouboulis, A.I. Fluoride Removal from Water by Composite Al/Fe/Si/Mg Pre-Polymerized Coagulants: Characterization and Application. Chemosphere 2019, 231, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartal, O.; Madinzi, A.; Khattabi Rifi, S.; Haddaji, C.; Agustiono Kurniawan, T.; Anouzla, A.; Souabi, S. Optimization of Coagulation-Flocculation Process for Wastewater Treatment from Vegetable Oil Refineries Using Chitosan as a Natural Flocculant. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2024, 22, 100957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khumalo, S.M.; Bakare, B.F.; Tetteh, E.K.; Rathilal, S. Application of Response Surface Methodology on Brewery Wastewater Treatment Using Chitosan as a Coagulant. Water 2023, 15, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Qian, J.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, B. Cationic Surfactant-Mediated Coagulation for Enhanced Removal of Toxic Metal-Organic Complexes: Performance, Mechanism, and Validation. ACS EST Eng. 2022, 2, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
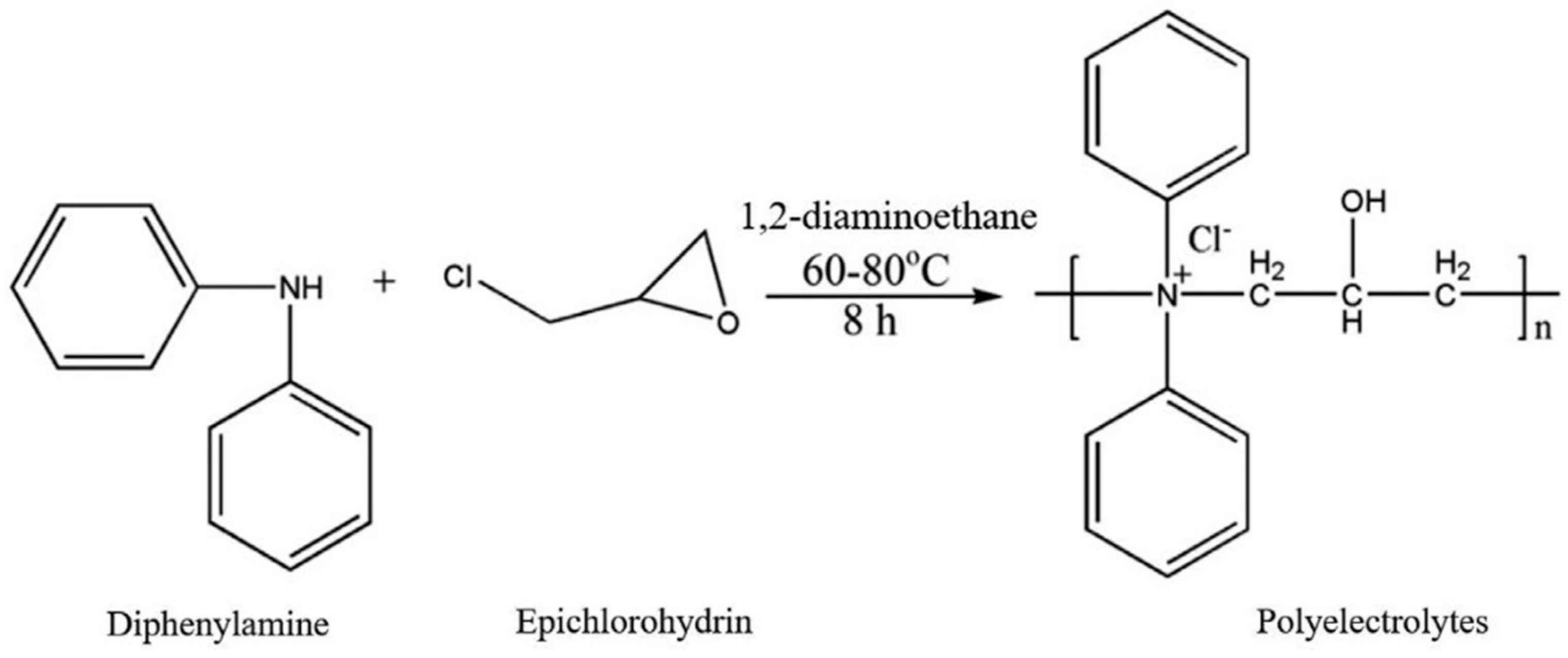
- Jabin, S.; Kapoor, J.K.; Jadoun, S.; Chandna, N.; Chauhan, N.P.S. Synthesis and Characterization of Polyamine-Based Polyelectrolytes for Wastewater Treatment in the Sugar Industry. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1275, 134573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, E.; Li, J.; Du, Z.; Cheng, F. Preparation and Coagulation-Flocculation Performance of Covalently Bound Organic Hybrid Coagulant with Excellent Stability. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 600, 124966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latour, I.; Miranda, R.; Carceller, R.; Blanco, A. Efficiency of Polyaluminum Nitrate Sulfate–Polyamine Hybrid Coagulants for Silica Removal. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 17973–17984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Fu, Y.; Su, M.M.; Cai, S.S.; Chen, Q.F. Coagulation Performance of Organic Modified Poly-Polyacrylamide-Al-Zn-Fe (PPAZF) Coagulant. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 848, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

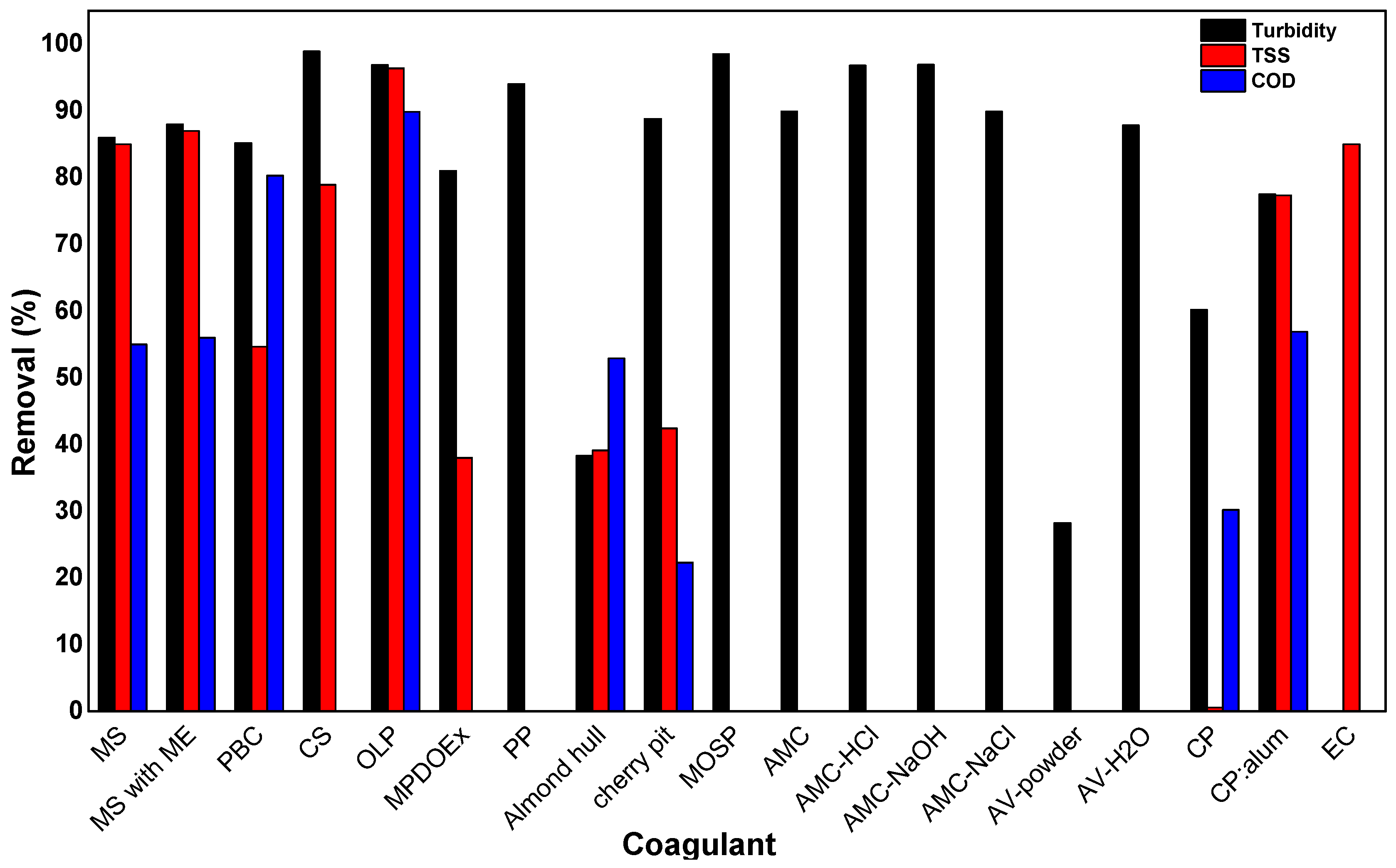
| Coagulants | Remove | Initial Conditions | pH | Coagulant Dosage | Removal | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MS 1 | Rice Starch-Containing Effluent | 11.78 NTU turbidity | 7.2 | 300 mg/L | 86.00% turbidity | [45] |
| 85.00% TSS | ||||||
| 73 mg/L COD | 55.00% COD | |||||
| MS 1 with magnetic exposure | 88.00% turbidity | |||||
| 6.5 mg/L TSS | 87.00% TSS | |||||
| 56.00% COD | ||||||
| PBC 2 | General Wastewater | 392.67–657.33 NTU turbidity | 7.13–7.21 | 0.79 mg/L | 85.17% turbidity | [47] |
| 711.00–727.33 mg/L COD | 54.63% COD | |||||
| 776–876 mg/L TSS | 80.28% TSS | |||||
| 1736–1789 ADM Color | 59.42% Color | |||||
| CS 3 bio-coagulant | Fish Processing Wastewater (FPW) | >1000 NTU Turbidity | 11.3 | 31.6 mL/L | 98.91% turbidity | [48] |
| 3735 mg O2/L COD | 78.92% COD | |||||
| 2345.5 mg O2/L BOD5 | 92.05% BOD5 | |||||
| oak leaves protein | Industrial Oily Wastewater | 187 NTU Turbidity | 12 | 0.538 mg/L | 96.87% turbidity | [49] |
| 969 mg/L COD | 96.39% COD | |||||
| 784.45 mg/L TSS | 89.86% TSS | |||||
| MPDOEx 4 | Synthetic water | 99.1 NTU Turbidity | 9 | 400 mg/L | 81.00% Turbidity | [50] |
| 188 mg/L COD | 38.00% COD | |||||
| 71.8 mg/L Mo | 200 mg/L | 97.40% Mo | ||||
| 8.1 mg/L Cu | 66.50% Cu | |||||
| 2.1 mg/L Cd | 51.80% Cd | |||||
| 11.0 mg/L Cr | 50.30% Cr | |||||
| 3.1 mg/L Co | 45.80% Co | |||||
| 10.1 mg/L Mn | 12.00% Mn | |||||
| 3.8 mg/L Ni | 10.50% Ni | |||||
| PP 5 fruit peel mucilage gel | Domestic Wastewater | 88 NTU Turbidity | 13 | 12 mg/L | 94.00% turbidity | [51] |
| 671 TCU color | 85.00% color | |||||
| Almond hull (Prunus dulcis) | Cattle Wastewater | 7207 NTU turbidity | 3 | 0.1 g/L | 38.30% turbidity | [52] |
| 39.10% COD | ||||||
| 21178 mg O2/L COD | 52.90% TSS | |||||
| cherry pit (Prunus avium) | 88.80% turbidity | |||||
| 6930 mg/L TSS | 42.40% COD | |||||
| 22.30% TSS | ||||||
| MOSP 6 | Synthetic Wastewater | Turbidity | 6.93 | 0.34 mg/L | 98.50% turbidity | [53] |
| 7.88 mg/L Amido Black 10B dye | 92.20% Amido Black 10B | |||||
| AMC 7 | Starch wastewater | 16.36 NTU turbidity | 7.90 | 1.0 g/L | 89.88% turbidity | [54] |
| Mud Wastewater | 15.15 NTU turbidity | 7.82 | 89.74% turbidity | |||
| HCl treated AMC 7 | Starch wastewater | 16.36 NTU turbidity | 7.90 | 96.77% turbidity | ||
| Mud Wastewater | 15.15 NTU turbidity | 7.82 | 95.87% turbidity | |||
| NaOH treated AMC 7 | Starch wastewater | 16.36 NTU turbidity | 7.90 | 96.90% turbidity | ||
| Mud Wastewater | 15.15 NTU turbidity | 7.82 | 94.73% turbidity | |||
| NaCl treated AMC 7 | Starch wastewater | 16.36 NTU turbidity | 7.90 | 89.87% turbidity | ||
| Mud Wastewater | 15.15 NTU turbidity | 7.82 | 94.66% turbidity | |||
| EC 8 | - | 232 mg/L TSS | 6 | 0.2 g/L | 85.00% TSS | [55] |
| AV 9-powder | General Wastewater | 13 NTU turbidity | 6 | 10 mg/L | 28.23% turbidity | [57] |
| AV 9-H2O | 7.5 | 0.1 mL/L | 87.84% turbidity | |||
| Dillenia indica | Leachate | 31 mg/L Bisphenol A | 8.5 | 1066 mg/L | 60.00% Bisphenol A | [58] |
| 15 mg/L DEHP | 958 mg/L | 55.00% DEHP | ||||
| CPS 10 | Water with Initial Turbidity, TSS, and COD | 194 NTU turbidity | 6.0 | 448.58 mg/L | 60.19% turbidity | [59] |
| 57.79% TSS | ||||||
| 284 mg/L TSS | 30.19% COD | |||||
| CPS 10:alum (4:1) | 8.0 | 80% of CPS 20% of alum | 77.48% turbidity | |||
| 296.248 mg/L COD | 77.34% TSS | |||||
| 56.89% COD |
| Coagulant | Flocculant | Initial Conditions | pH | Coagulant Dosage (mg/L) | Flocculant Dosage (mg/L) | Removal | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prickly pear peel waste | Anionic polymer | 45.39 NTU Turbidity | 4 | 100 | 1 | 76.10% turbidity | [60] |
| 7.8 | 250 | 51.70% turbidity | |||||
| 30% prickly pear peel waste and 70% aluminum sulfate | 58.10% turbidity |
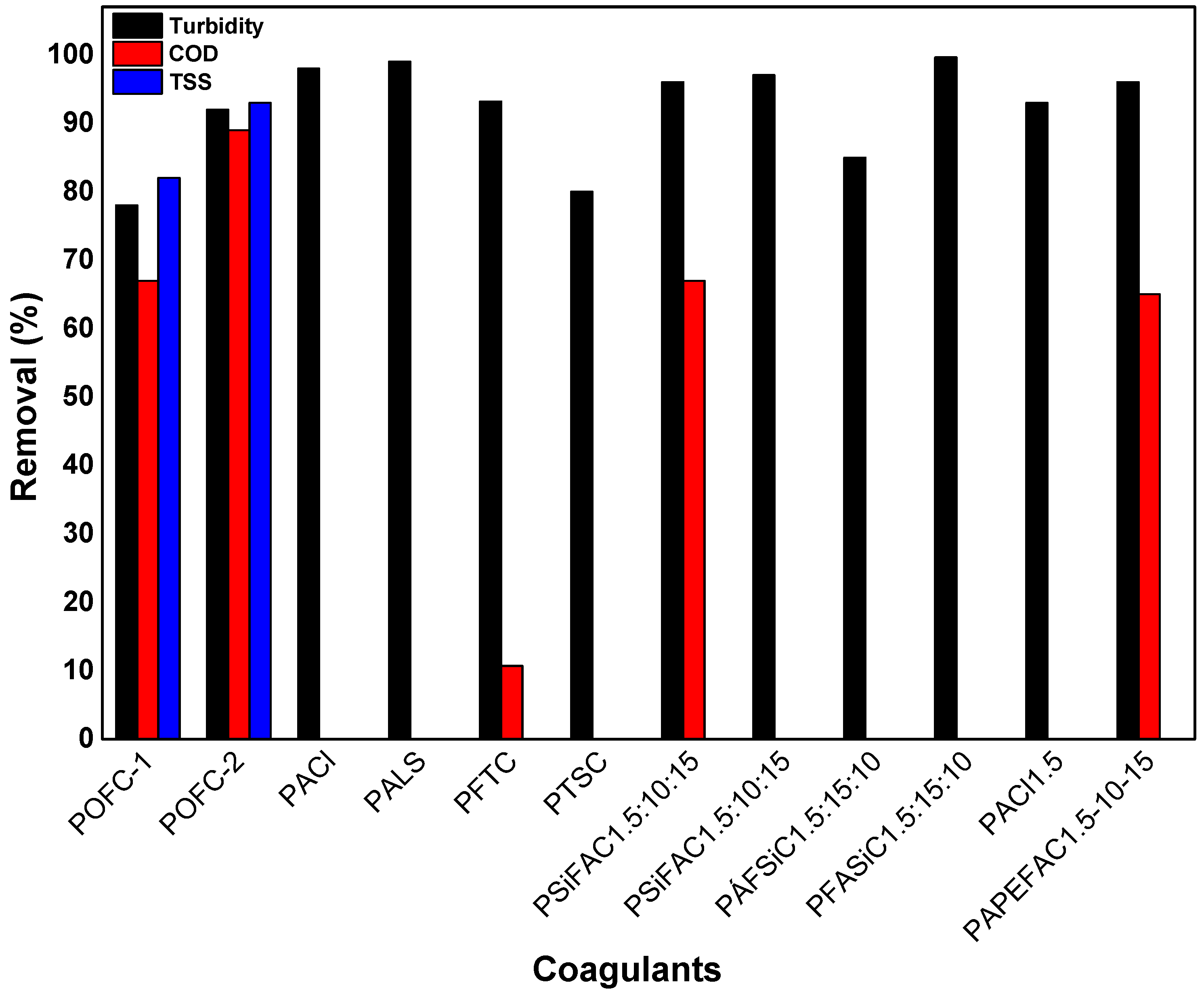
| Coagulants | Remove | Initial Conditions | pH | Coagulant Dosage | Removal | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| POFC-1 1 | Domestic Wastewater | 86 NTU turbidity | 6–8 | 10 mg/L | 78.00% turbidity | [19] |
| 67.00% COD | ||||||
| 342 mg/L COD | 82.00% TSS | |||||
| POFC-2 2 | 92.00% turbidity | |||||
| 300 mg/L TSS | 89.00% COD | |||||
| 93.00% TSS | ||||||
| PFS 3 | printing and dyeing wastewater | 1 mg/L Sb | 5 | 60 mg/L | 95.00% Sb(III), 90.00% Sb(V) | [27] |
| 0.085 mg/L Sb(III), and 0.1 mg/L Sb(V) | 97.50% total Sb | |||||
| FeCl3–AlCl3 4 | – | 0.519 mg/L Total P | 5 | 21.85 mg/L | 91.31% Total P | [61] |
| FeSO4–Al2(SO4)3 5 | 7 | 15 mg/L | 86.82% Total P | |||
| PASS 6 | Coking Wastewater | 196.67 mg/L CODCr | 7.0 | 7 mmol/L | 69.50% CODCr | [62] |
| PACl 7 | Domestic Wastewater | 270 NTU turbidity | 6.5 | 25 mg/L | 98.00% turbidity | [63] |
| 100 mg/L DOC | 69.80% DOC | |||||
| PALS 8 | Simulate Wastewater | 28.6–30.2 NTU Turbidity | 8 | 12 mg/L | 99.00% turbidity | [64] |
| 2 mg/L total phosphorus | 6 | 8.0 mg/L | 99.60% phosphate | |||
| 29.68–30.42 mg/L DOC | 3–7 | 14 mg/L | 69.57% DOC | |||
| PFTC 9 | Coking Wastewater | 40 NTU turbidity | 9 | 800 mg/L | 93.20% turbidity | [65] |
| 480 mg/L DOC | 10.10% DOC | |||||
| 2000 mg/L COD | 10.70% COD | |||||
| PTSC 10 | 80.00% turbidity | |||||
| Fe-PAA-1:0.1 11 | Humid acid | TOC | 5.0 | 0.1 mM Fe | ~80.00% TOC | [66] |
| Fe-PAA-1:1 12 | >80.00% TOC | |||||
| Fe-PAA-1:2 13 | <80.00% TOC | |||||
| PSiFAC1.5:10:15 14 | Tanner Wastewater | 668 NTU turbidity | 7.8 | 80 | 96.00% turbidity | [67,68] |
| 6800 mg/L COD | 67.00% COD | |||||
| 1.76 mg/L phosphates | 62.00% phosphates | |||||
| 2.981 UV254nm | 10.00% UV254nm | |||||
| Yeast wastewater after aerobic treatment | 418 NTU turbidity | 14.00% turbidity | ||||
| 11455 mg/L COD | 22.00% COD | |||||
| 3.49 mg/L phosphates | 38.00% phosphates | |||||
| 3.748 UV254nm | 15.00% UV254nm | |||||
| Yeast manufacturing wastewater without preliminary anaerobic treatment | 143 NTU turbidity | 40.00% turbidity | ||||
| 4590 mg/L COD | 56.00% COD | |||||
| 2.40 mg/L phosphates | 43.00% phosphates | |||||
| 3.307 UV254nm | 25.00% UV254nm | |||||
| PSiFAC1.5:10:15 14 | Simulated surface water | 17.2 NTU turbidity | 7.0 | 2 mg/L | 97.00% turbidity | [67] |
| 0.153 UV254nm | 3 mg/L | 93.00% UV254nm | ||||
| Tanner wastewater | >2000 turbidity | 100 mg/L | 99.60% turbidity | |||
| PAFSiC1.5:15:10 15 | Simulated surface water | 17.2 NTU turbidity | 2 mg/L | ~95.00% UV254nm | ||
| 0.153 UV254nm | 3 mg/L | ~85.00% turbidity | ||||
| Tanner wastewater | >2000 turbidity | 100 mg/L | 99.70% UV254nm | |||
| PFASiC1.5:15:10 16 | Simulated surface water | 17.2 NTU turbidity | 2 mg/L | ~95.00% turbidity | ||
| 0.153 UV254nm | 3 mg/L | >90.00% UV254nm | ||||
| Tanner wastewater | >2000 turbidity | 100 mg/L | 99.6.00% turbidity | |||
| PACl1.5 17 | Simulated surface water | 17.2 NTU turbidity | 2 mg/L | 93.00% turbidity | ||
| 0.153 UV254nm | 3 mg/L | 78.00% UV254nm | ||||
| PAPEFAC1.5-10-15 18 | Tanner Wastewater | 668 NTU turbidity | 7.8 | 80 mg Al/L | ~96.00% turbidity | [68] |
| 6800 mg/L COD | ~65.00% COD | |||||
| 1.76 mg/L phosphates | <65.00% phosphates | |||||
| Yeast wastewater after aerobic treatment | 418 NTU turbidity | ~20.00% turbidity | ||||
| 11455 mg/L COD | ~5.00% COD | |||||
| 3.49 mg/L phosphates | <30.00% phosphates | |||||
| Yeast manufacturing wastewater without preliminary anaerobic treatment | 143 NTU turbidity | ~40.00% turbidity | ||||
| 4590 mg/L COD | ~15.00% COD | |||||
| 2.40 mg/L phosphates | ~57.00% phosphates | |||||
| PSiFAC-Mg30-10-15 19 | Industrial Wastewater | 5 mg F/L fluoride | 7.0 | 30 mg Al/L | Q1.5 170 mg F/g Al | [69] |
| PSiFAC-Na1.5-10-15 20 | Q1.5 94 mg F/g Al |
| Coagulant | Flocculant | Remove | Initial Conditions | pH | Coagulant Dosage | Flocculant Dosage | Removal | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FeCl3 1 | chitosan | Vegetable oil refinery wastewater | 3753 NTU turbidity | 6.0 | 1.6 g/L | 13.4 mg/L | 100.00% turbidity | [70] |
| 7680 mg/L COD | 86.00% COD | |||||||
| 168.36 mg/L polyphenols | 90.00% polyphenol |
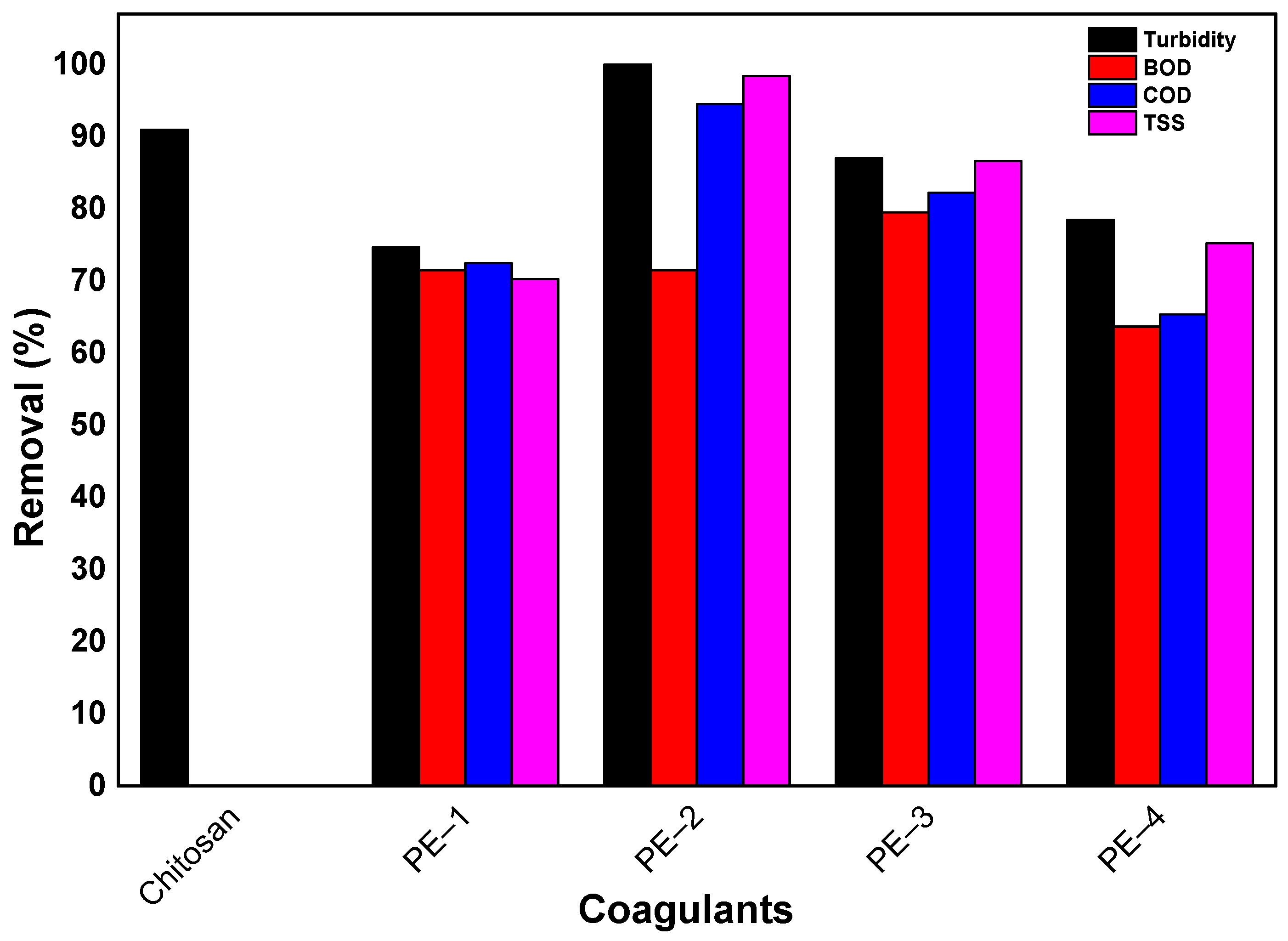
| Coagulants | Remove | Initial Conditions | pH | Coagulant Dosage (mg/L) | Removal | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chitosan | Brewery Wastewater | 160 NTU turbidity | 8 | 2000 | 91.00% turbidity | [71] |
| 176 mg/L TOC | 89.00% TOC | |||||
| 139 mg/L orthophosphate | 65.00% orthophosphate | |||||
| CTAB 1 | Toxic Metal−Organic Complexes | 10.4 mg/L Cr(III) | 10.5 | 57 | 98.00% Cr(III) | [72] |
| 10.4 mg/L Ni(II) | 92.69% Ni(II) | |||||
| 10.4 mg/L Cu(II) | 96.63% Cu(II) | |||||
| 10.4 mg/L Zn(II) | 99.35% Zn(II) | |||||
| 10.4 mg/L Cd(II) | 99.52% Cd(II) | |||||
| PE-1 2 | Sugar industry wastewater | 83 NTU Turbidity | 6.1 | 2.0 | 74.68% turbidity | [73] |
| 1.0 | 70.25% TSS | |||||
| 1.5 | 72.48% COD | |||||
| 1.5 | 71.47% BOD | |||||
| PE-2 3 | 1120 mg/L TSS | 1.0 | 100% turbidity | |||
| 1.0 | 98.40% TSS | |||||
| 1.5 | 94.50% COD | |||||
| 1.5 | 71.47% BOD | |||||
| PE-3 4 | 991 mg/L COD | 1.0 | 87.00% turbidity | |||
| 1.0 | 86.59% TSS | |||||
| 1.5 | 82.25% COD | |||||
| 1.5 | 79.52% BOD | |||||
| PE-4 5 | 543 mg/L BOD | 2.0 | 78.50% turbidity | |||
| 1.0 | 75.20% TSS | |||||
| 1.5 | 65.36% COD | |||||
| 1.5 | 63.67% BOD |
| Coagulants | Remove | Initial Conditions | pH | Coagulant Dosage (mg/L) | Removal | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PAAP0.1,0.5 1 | Raw coking wastewater | 105 NTU turbidity | 9.98 | 600 | 82.05% turbidity | [74] |
| 4654 mg/L COD | 24.16% COD | |||||
| 1138.45 mg/L DOC | 9.34% DOC | |||||
| 22.75 UV254nm | 12.09% UV254nm | |||||
| Biologically treated coking wastewater | 128 NTU turbidity | 8.13 | 300 | 97.84% turbidity | ||
| 109.03 mg/L COD | 63.39% COD | |||||
| 41.86 mg/L DOC | 29.97% DOC | |||||
| 2.197 UV254nm | 37.72% UV254nm | |||||
| PANS 2 | Raw water | 11.4 NTU turbidity | 10.5 | 500 | 14.00% silica | [75] |
| 1500 | 71.00% silica | |||||
| 2000 | 83.00% silica | |||||
| 1990 mg/L Total Solids (raw water) | 2500 | 90.00% silica | ||||
| PANS-PA1-Z 3 | 500 | ~86.00% silica | ||||
| 1000 | 50.00% silica | |||||
| 0.52 meq/L Cationic Demand | 1500 | 70.00% silica | ||||
| 2000 | 80.00% silica | |||||
| 2500 | 90.00% silica | |||||
| PANS-PA2-Z 4 | 1890 mg/L TOTAL Solids (dissolved fraction) | 500 | 31.00% silica | |||
| 1000 | 50.00% silica | |||||
| 1500 | 70.00% silica | |||||
| 256 mg/L COD | 2000 | 80.00% silica | ||||
| 2500 | 90.00% silica | |||||
| PANS-PA3-Z 5 | 500 | 16.00% silica | ||||
| 145 mg/L SiO2 Silica | 1000 | 50.00% silica | ||||
| Dissolved Fraction | 1500 | 70.00% silica | ||||
| 2000 | 80.00% silica | |||||
| 2500 | 90.00% silica | |||||
| PANS-PA1-5 6 | 8.4 | 1000 | ~40.00% silica | |||
| PANS-PA1-10 7 | 1500 | ~40.00% silica | ||||
| PANS-PA1-15 8 | 33.7 mg/L Calcium | 2000 | ~40.00% silica | |||
| PANS-PA1-20 9 | 2500 | 47.00% silica | ||||
| PANS-PA2-5 10 | 500 | 39.00% silica | ||||
| 2500 | ~50.00% silica | |||||
| PANS-PA2-10 11 | 500 | 35.00% silica | ||||
| 2500 | ~50.00% silica | |||||
| PANS-PA2-15 12 | 2.8 mg/L Magnesium | 500 | 26.00% silica | |||
| PANS-PA2-20 13 | 500 | 23.00% silica | ||||
| 2500 | 40.00% silica | |||||
| PANS-PA3-5 14 | 500 | 42.00% silica | ||||
| 2500 | 51.00% silica | |||||
| PANS-PA3-20 15 | 2500 | 40.00% silica | ||||
| PPAZF 16 | Domestic sewage | 232 NTU turbidity | 7.71 | 148 | ~98% turbidity | [76] |
| 661.51 mg/L COD | ~96% COD | |||||
| Pharmaceutical wastewater | 265 NTU turbidity | 4.48 | ~73% turbidity | |||
| 10,025 mg/L COD | ~47% COD |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsoutsa, E.K.; Tolkou, A.K.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Katsoyiannis, I.A. New Trends in Composite Coagulants for Water and Wastewater Treatment. Macromol 2024, 4, 509-532. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol4030030
Tsoutsa EK, Tolkou AK, Kyzas GZ, Katsoyiannis IA. New Trends in Composite Coagulants for Water and Wastewater Treatment. Macromol. 2024; 4(3):509-532. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol4030030
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsoutsa, Eleftheria K., Athanasia K. Tolkou, George Z. Kyzas, and Ioannis A. Katsoyiannis. 2024. "New Trends in Composite Coagulants for Water and Wastewater Treatment" Macromol 4, no. 3: 509-532. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol4030030
APA StyleTsoutsa, E. K., Tolkou, A. K., Kyzas, G. Z., & Katsoyiannis, I. A. (2024). New Trends in Composite Coagulants for Water and Wastewater Treatment. Macromol, 4(3), 509-532. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol4030030









