Tracking Changes of Hidden Food: Spatial Pattern Learning in Two Macaw Species
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
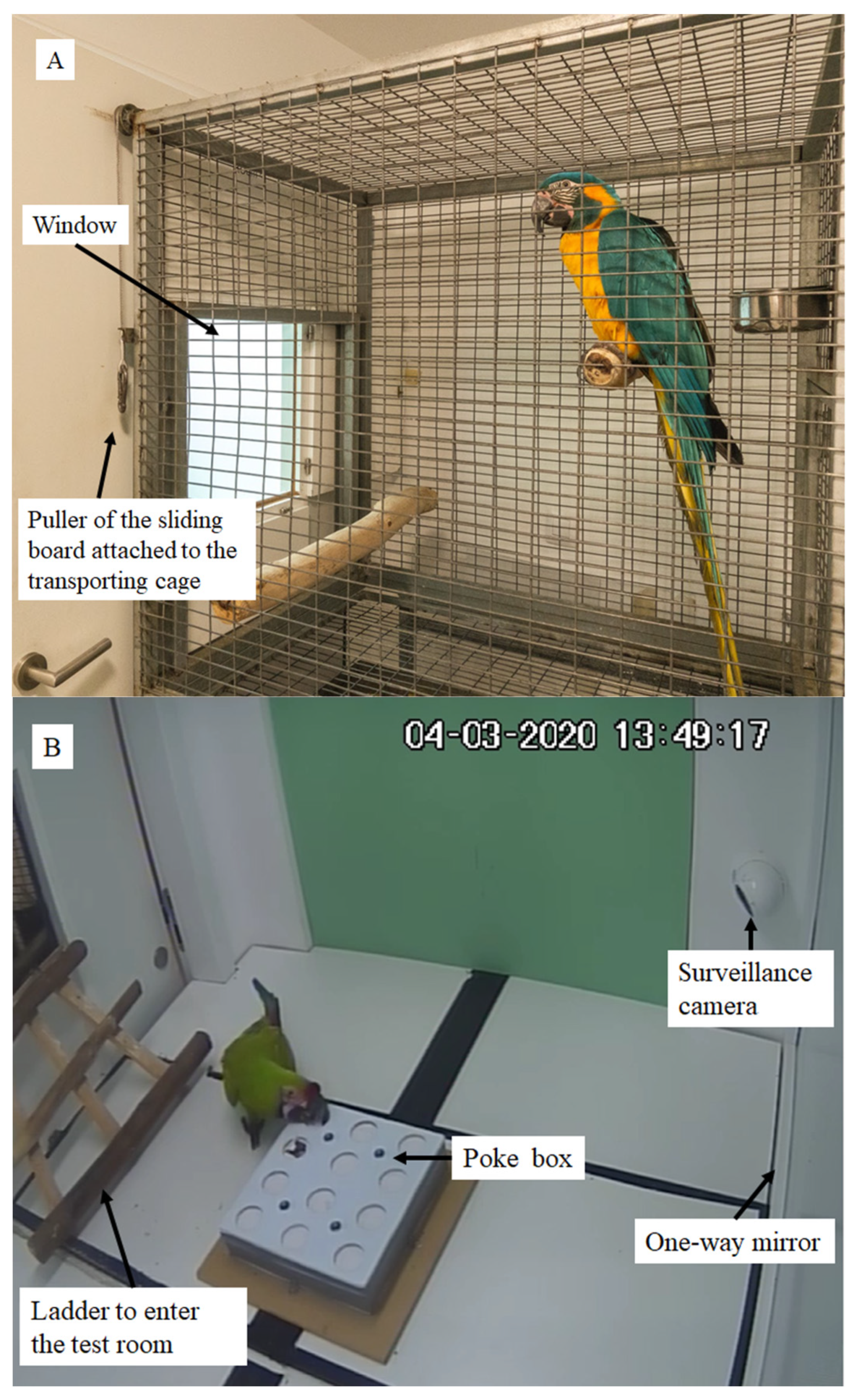
2.1. Study Species and Housing
2.2. Test Room Set Up
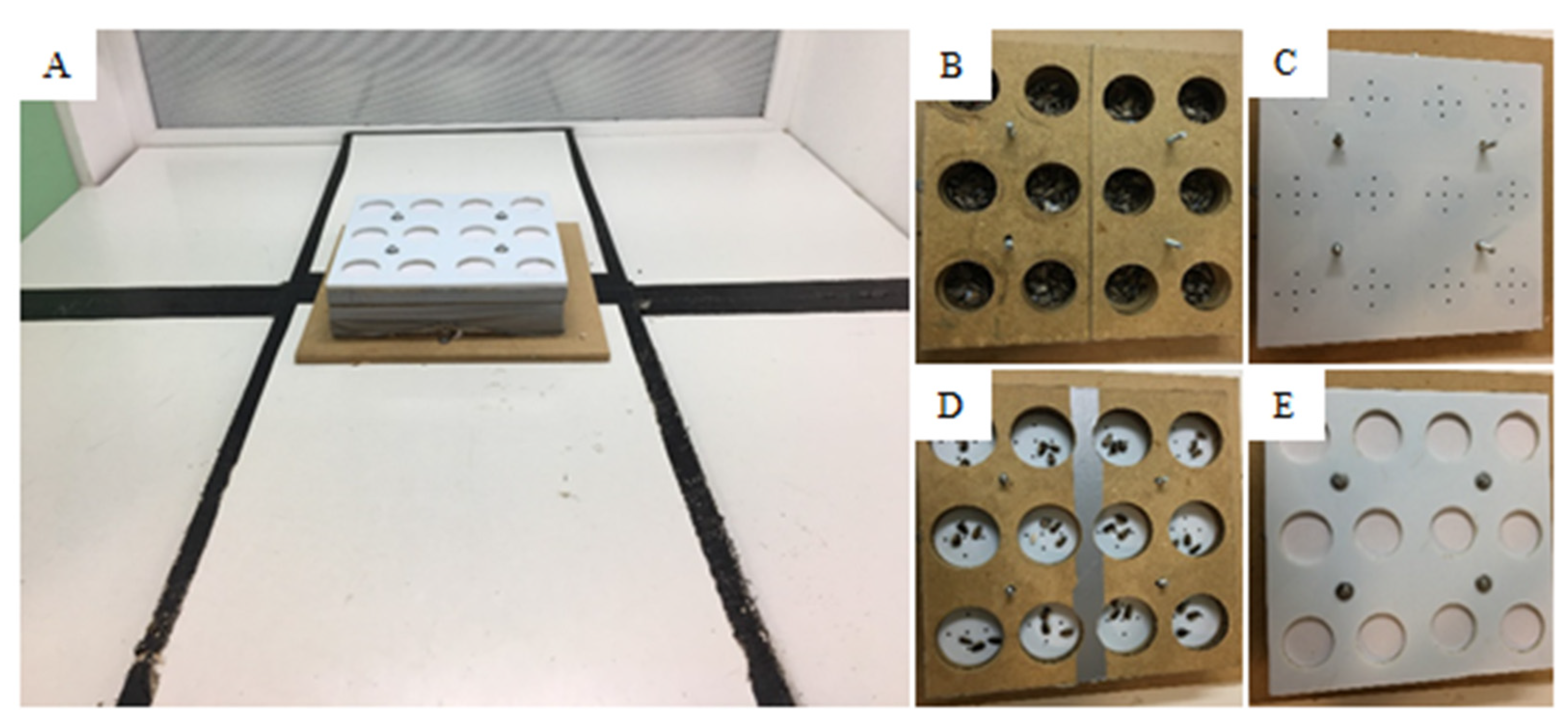
2.3. Experimental Apparatus
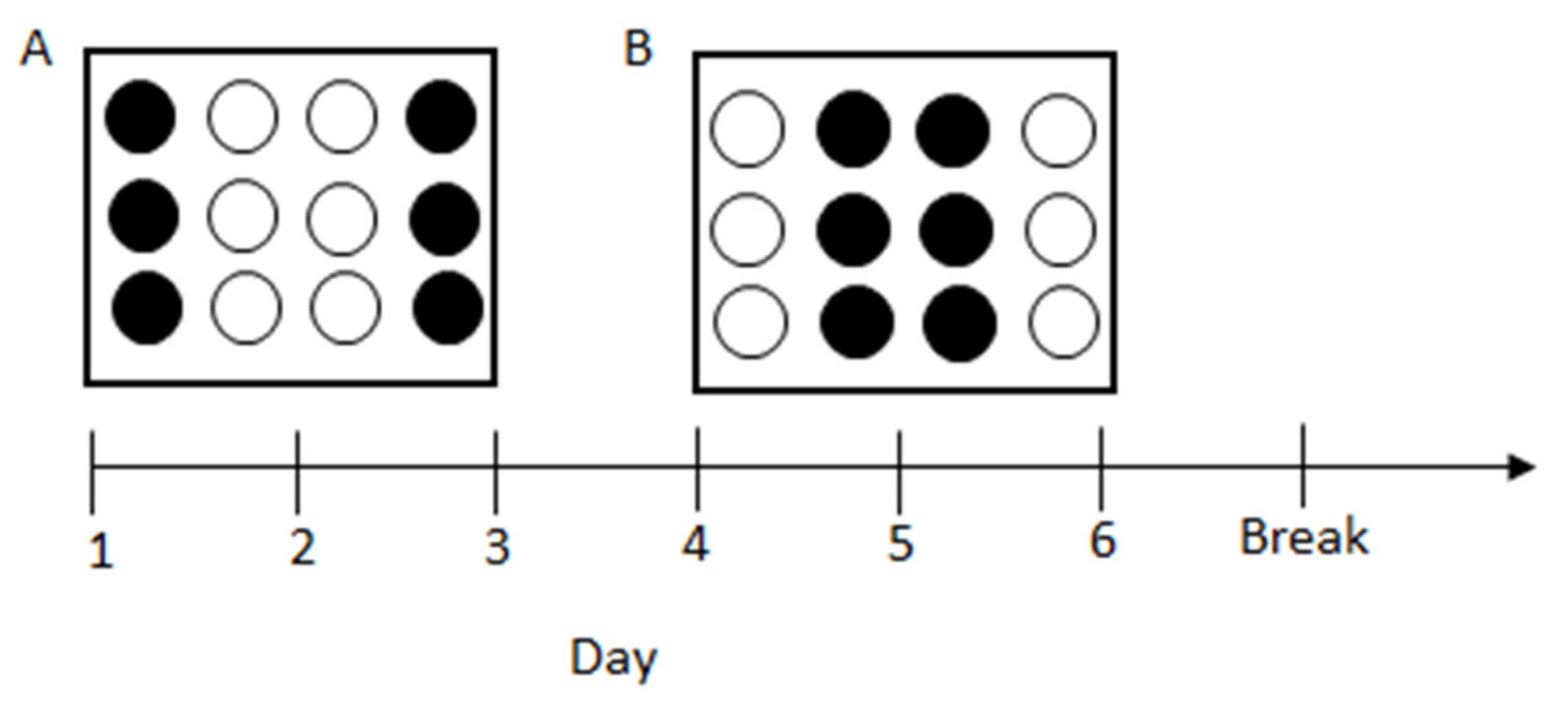
2.4. Procedures
Behavioural Measurements
2.5. Data Analyses
3. Results
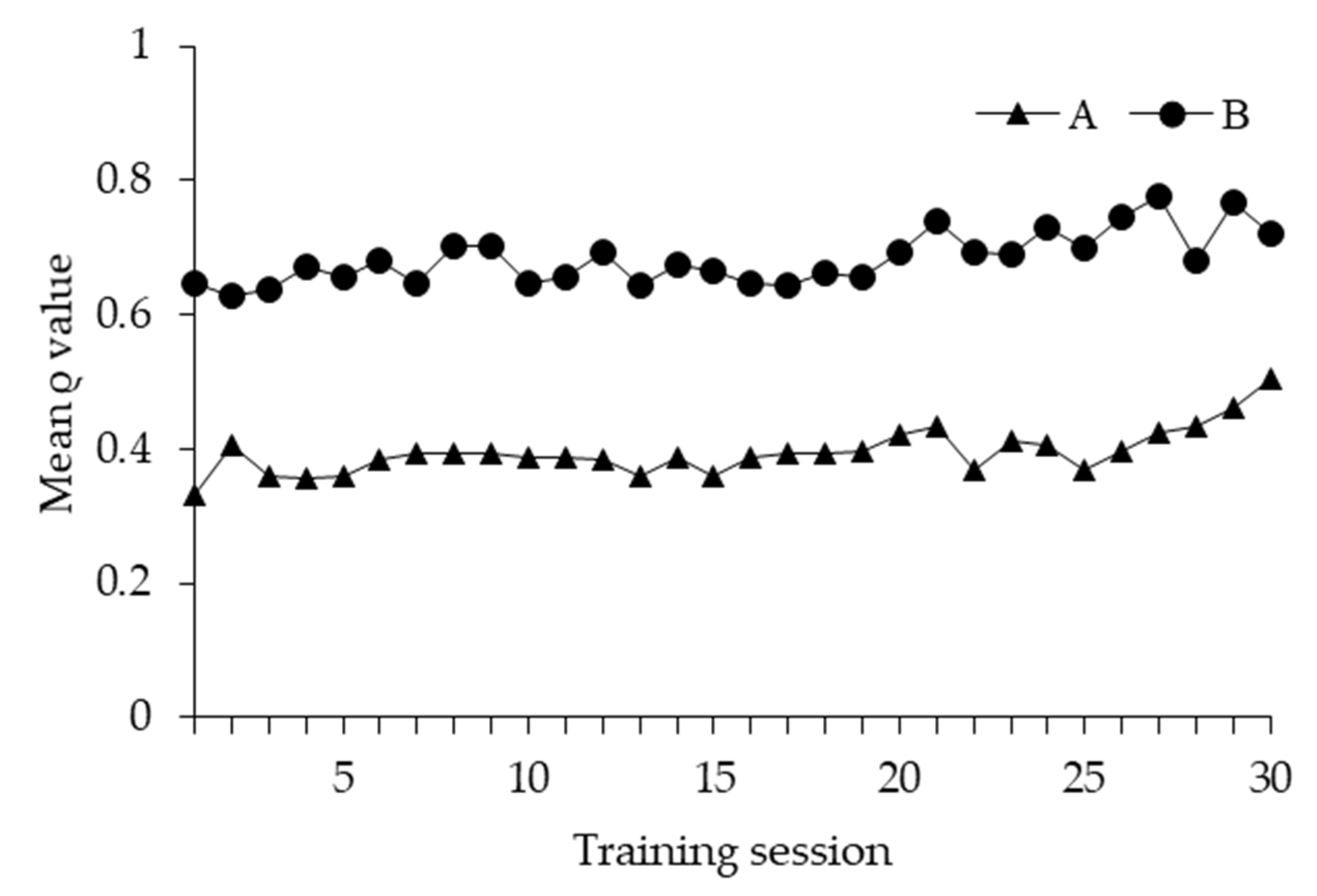
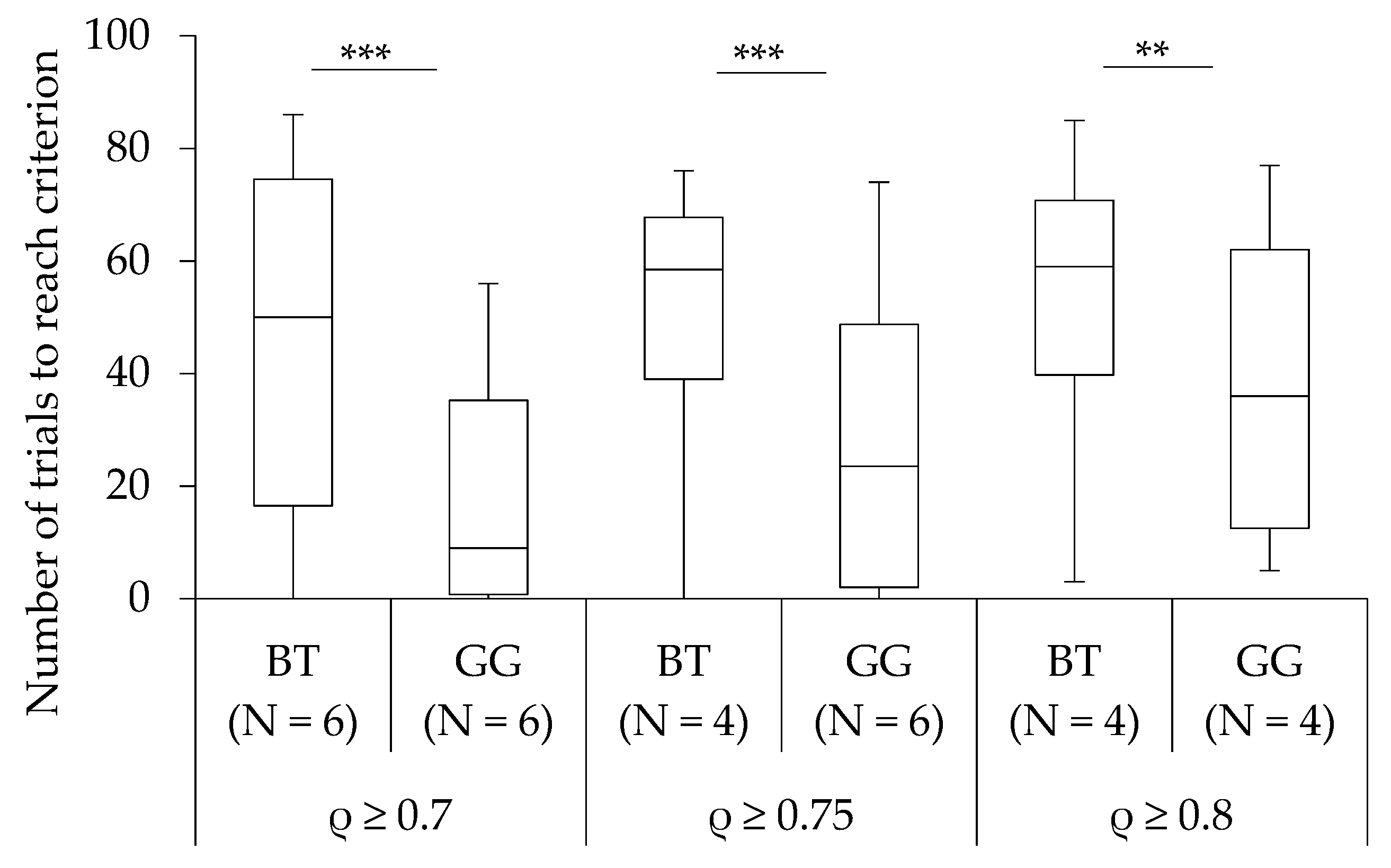
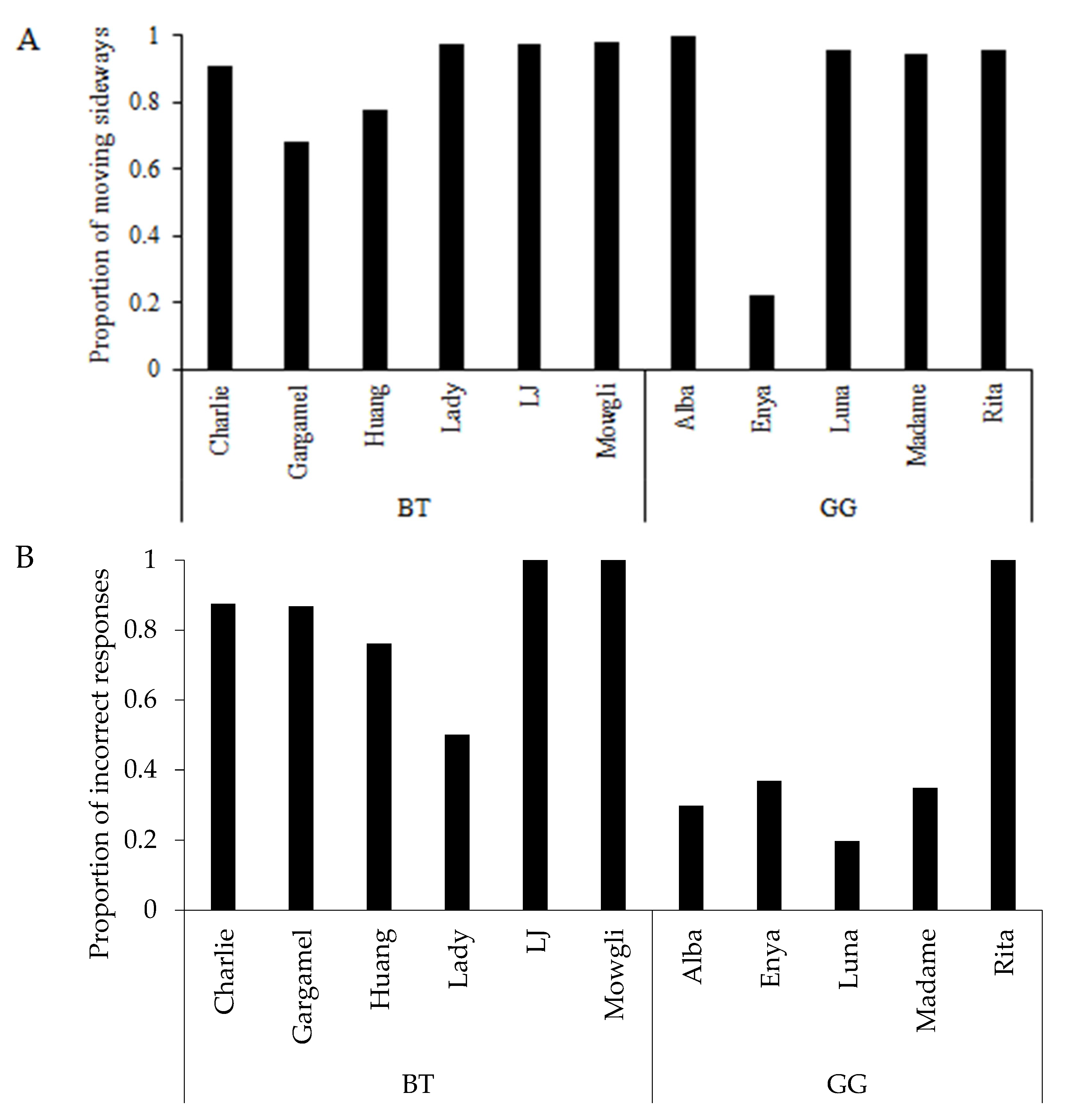
3.1. Learning Performance
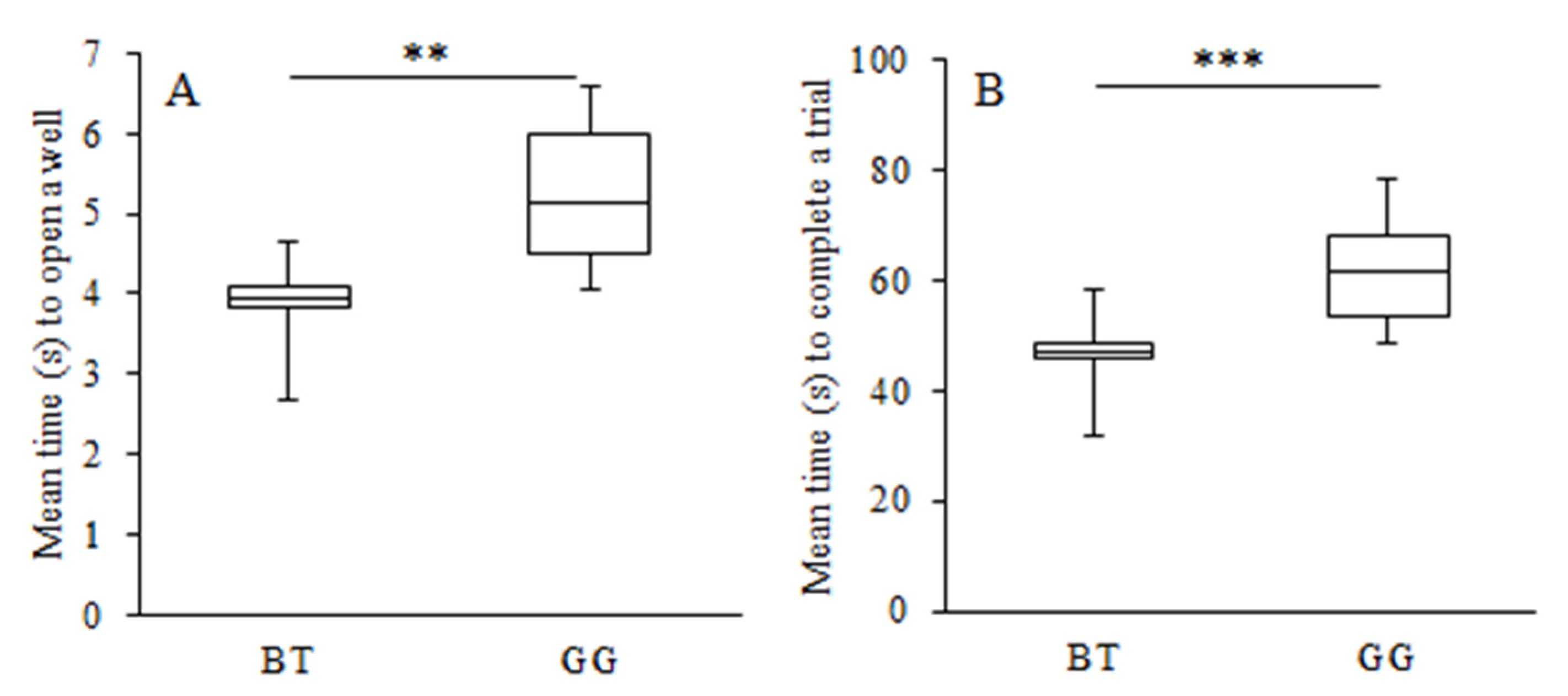
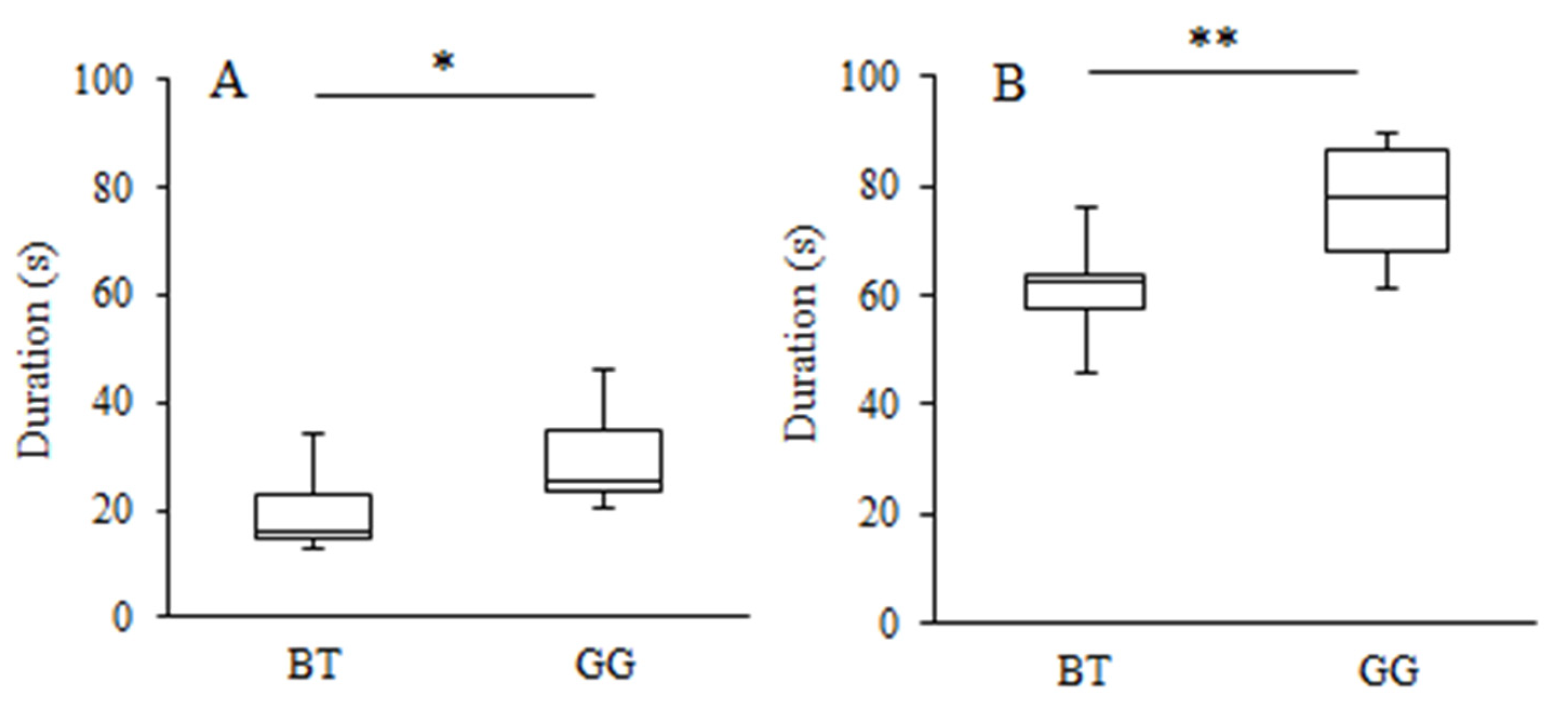
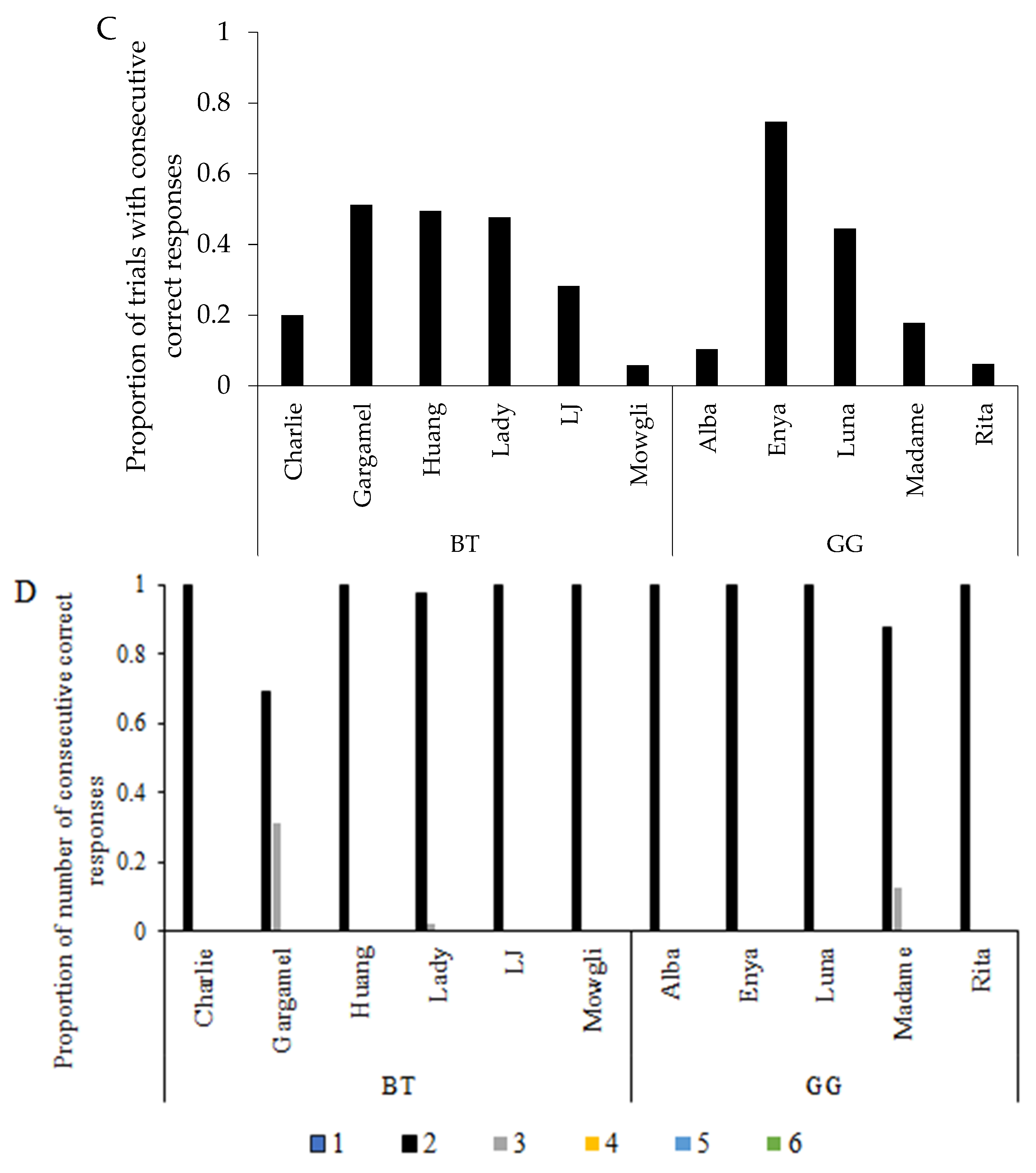
3.2. Learning Strategy and Exploratory Behaviour
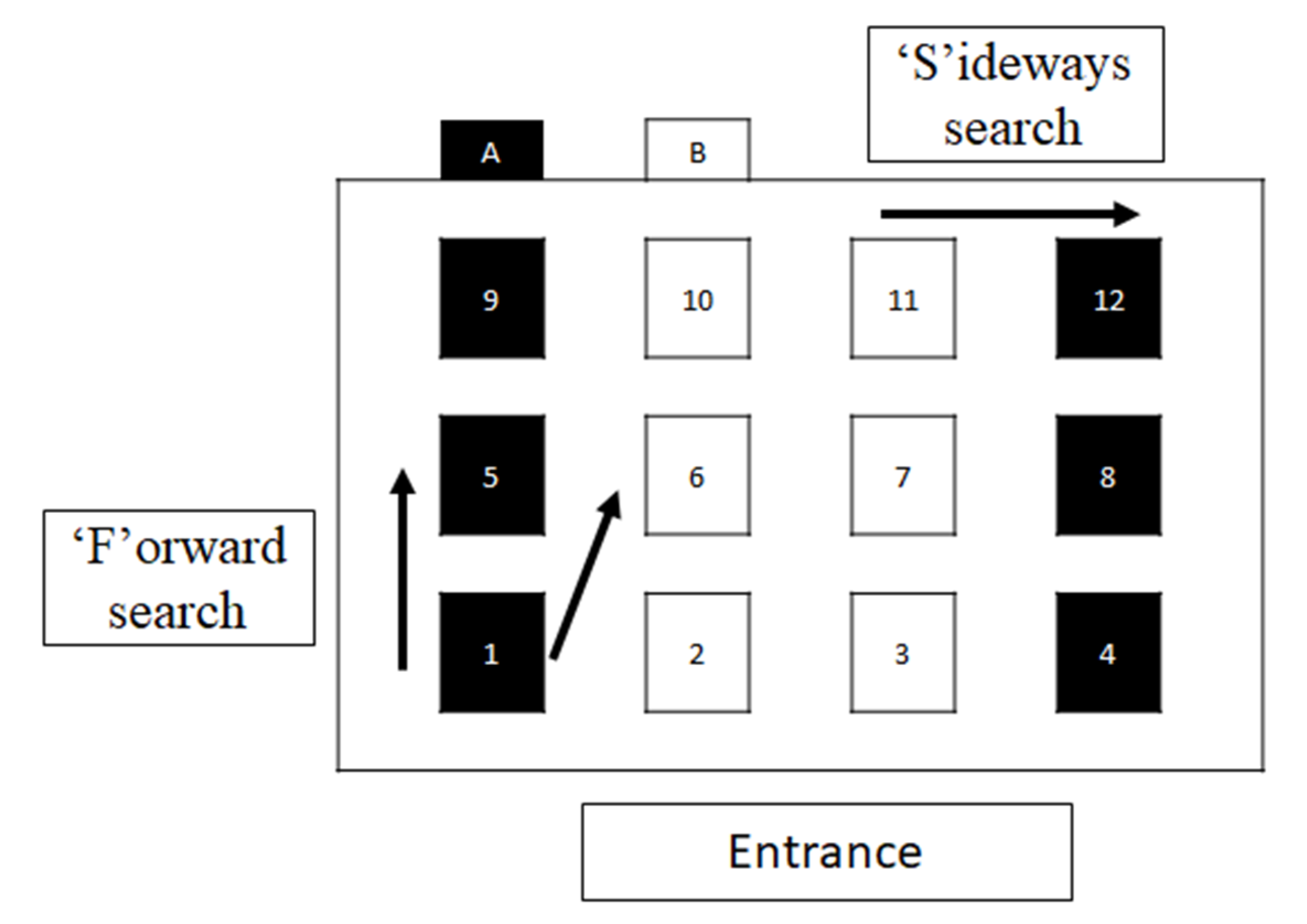
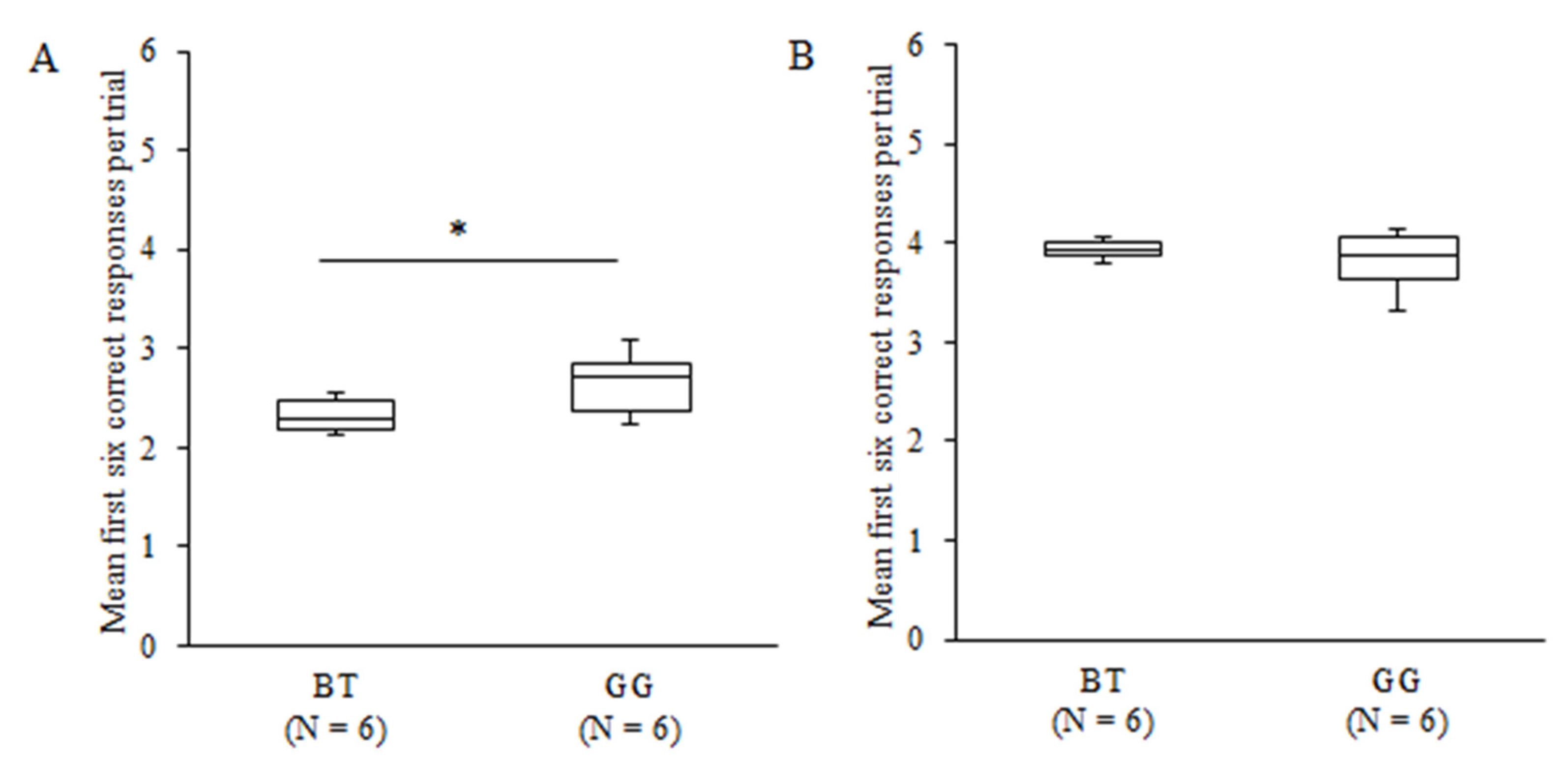
3.3. Search Order in Pattern A
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, K.; Spetch, M.L. Mechanisms of landmark use in mammals and birds. In Spatial Representation in Animals; Healy, S., Ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Bicca-Marques, J.C.; Garber, P.A. Use of spatial, visual, and olfactory information during foraging in wild nocturnal and diurnal anthropoids: A field experiment comparing Aotus, Callicebus, and Saguinus. Am. J. Primatol. 2004, 62, 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, D.M.; Spetch, M.L.; Donald, H.C. Pigeons’ (Columba livia) encoding of geometric and featural properties of a spatial environment. J. Comp. Psychol. 1998, 112, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamil, A.; Cheng, K. Way-finding and landmarks: The multiple-bearings hypothesis. J. Exp. Biol. 2001, 204, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernays, E.A.; Singer, M.S.; Rodrigues, D. Foraging in nature: Foraging efficiency and attentiveness in caterpillars with different diet breadths. Ecol. Entomol. 2004, 29, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavel, J.; Julliard, R.; Devictor, V. Worldwide decline of specialist species: Toward a global functional homogenization? Front. Ecol. Environ. 2011, 9, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terraube, J.; Arroyo, B.; Madders, M.; Mougeot, F. Diet specialisation and foraging efficiency under fluctuating vole abundance: A comparison between generalist and specialist avian predators. Oikos 2011, 120, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malsburg, J.H.; Fichtel, C. Are generalists more innovative than specialists? A comparison of innovative abilities in two wild sympatric mouse lemur species. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 180480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernays, E.A.; Funk, D.J. Specialists make faster decisions than generalists: Experiments with aphids. In Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences; The Royal Society: London, UK, 1999; Volume 266, pp. 151–156. [Google Scholar]
- Mettke-Hofmann, C.; Winkler, H.; Leisler, B. The Significance of Ecological Factors for Exploration and Neophobia in Parrots. Ethology 2002, 108, 249–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducatez, S.; Clavel, J.; Lefebvre, L. Ecological generalism and behavioural innovation in birds: Technical intelligence or the simple incorporation of new foods? J. Anim. Ecol. 2014, 84, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guido, J.M.; Biondi, L.M.; Vasallo, A.I.; Muzio, R.N. Neophobia is negatively related to reversal learning ability in females of a generalist bird of prey, the Chimango Caracara, Milvago chimango. Anim. Cogn. 2017, 20, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.F.; Digello, E.; Milewski, M.; Wilson, M.; Kozak, M. Spatial pattern learning in rats: Conditional control by two patterns. Anim. Learn. Behav. 2000, 28, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brown, M.F.; Zeiler, C.; John, A. Spatial pattern learning in rats: Control by an iterative pattern. J. Exp. Psychol. Anim. Behav. Process. 2001, 27, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Digello, E.; Brown, M.F.; Affuso, J. Negative information: Both presence and absence of spatial pattern elements guide rats’ spatial choices. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2002, 9, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sutherland, G.D.; Gass, C.L. Learning and remembering of spatial patterns by hummingbirds. Anim. Behav. 1995, 50, 1273–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Great Green Macaw (Ara ambiguus)-BirdLife Species Factsheet. In Press. Available online: http://datazone.birdlife.org/species/factsheet/great-green-macaw-ara-ambiguus (accessed on 9 June 2021).
- BirdLife International (BirdLife International). IUCN Red List of Threatened Species: Ara ambiguus. In IUCN Red List of Threatened Species; BirdLife International: Cambridge, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Blue-Throated Macaw (Ara glaucogularis)-BirdLife Species Factsheet. In Press. Available online: http://datazone.birdlife.org/species/factsheet/22685542 (accessed on 9 June 2021).
- BirdLife International (BirdLife International). IUCN Red List of Threatened Species: Ara glaucogularis. In IUCN Red List of Threatened Species; BirdLife International: Cambridge, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita, C.; Barros, Y.M. The Blue-throated Macaw Ara glaucogularis: Characterization of its distinctive habitats in savannahs of the Beni, Bolivia. Ararajuba 1997, 5, 141–150. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, K.S.; Socola, J.; Angel, R.R. Great Green Macaws and the annual cycle of their food plants in Ecuador. J. Field Ornithol. 2007, 78, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levins, R. Evolution in Changing Environments: Some Theoretical Explorations. (MPB-2); Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Chassot, O.; Monge-Arias, G. Connectivity conservation of the Great Green Macaw’s landscape in Costa Rica and Nicaragua (1994–2012). Parks Recreat 2012, 18, 61–69. [Google Scholar]
- Figueroa, P.G. Ecología y conservación de la lapa verde (Ara ambigua) en Costa Rica. Posgrado y Soc. 2009, 9, 58–80. [Google Scholar]
- Hesse, A.J.; Duffield, G.E. The status and conservation of the Blue-Throated Macaw Ara glaucogularis. Bird Conserv. Int. 2000, 10, 255–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuevo Dato en la Distribucion de la Paraba Barba Azul (Ara glaucogularis). In Press. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Herrera-Mauricio/publication/26575754_Nuevo_dato_en_la_distribucion_de_la_paraba_barba_azul_Ara_glaucogularis/links/5f0528a4299bf188160a3364/Nuevo-dato-en-la-distribucion-de-la-paraba-barba-azul-Ara-glaucogularis.pdf (accessed on 21 July 2021).
- Benavidez, A.; Palacio, F.; Rivera, L.O.; Echevarria, A.L.; Politi, N. Diet of Neotropical parrots is independent of phylogeny but correlates with body size and geographical range. Ibis 2018, 160, 742–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsos, E.A.; Matson, K.D.; Klasing, K.C. Nutrition of Birds in the Order Psittaciformes: A Review. J. Avian Med. Surg. 2001, 15, 257–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loro Parque Fundación/Asociación Armonía. Saving the Blue-Throated Macaw Ara glaucogularis: A Species Recovery Plan; Loro Parque Fundación/Asociación Armonía: Santa Cruz de la Sierra, Bolivia, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Baños-Villalba, A.; Blanco, G.; Díaz-Luque, J.A.; Dénes, F.; Hiraldo, F.; Tella, J.L. Seed dispersal by macaws shapes the landscape of an Amazonian ecosystem. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas-Retana, S.A.; Araya-H., D. Consumo de almendro de playa (Terminalia catappa) y uso de hojas como herramienta por parte del ave Ara ambiguus (Psittaciformes: Psittacidae) en Costa Rica. UNED Res. J. 2017, 9, 199–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- World Parrot Trust. Great Green Macaw. In Press. Available online: https://www.parrots.org/encyclopedia/great-green-macaw (accessed on 21 April 2021).
- van Roosmalen, C.; Rica-Tortuguero, C. The Great Green Macaw Project. 2018; unpublished. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, P.K.Y.; Leaver, L.A.; Wang, M.; Lea, S.E.G. Serial Reversal Learning in Gray Squirrels: Learning Efficiency as a Function of Learning and Change of Tactics. J. Exp. Psychol. Anim. Learn. Cogn. 2015, 41, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wills, A.J.; Lea, S.E.G.; Leaver, L.A.; Osthaus, B.; Ryan, C.M.E.; Suret, M.B.; Bryant, C.M.L.; Chapman, S.J.A.; Millar, L. A comparative analysis of the categorization of multidimensional stimuli: I. Unidimensional classification does not necessarily imply analytic processing; evidence from pigeons (Columba livia), squirrels (Sciurus carolinensis), and humans (Homo sapiens). J. Comp. Psychol. 2009, 123, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Team, R. RStudio: Integrated Development for R; RStudio, Inc.: Boston, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neill, L.; Picaud, A.; Hastings, R.; Buffenoir, N.; Gahr, M.; von Bayern, A.M.P. Causal Understanding of the Stone Dropping Task in Two Species of Macaw. bioRxiv 2020, 8, 264390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebbich, S.; Fessl, B.; Blomqvist, D. Exploration and ecology in Darwin’s finches. Evol. Ecol. 2009, 23, 591–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sol, D.; Timmermans, S.; Lefebvre, L. Behavioural flexibility and invasion success in birds. Anim. Behav. 2002, 63, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, R. The Role of Neophobia in Determining the Degree of Foraging Specialization in Some Migrant Warblers. Am. Nat. 1983, 122, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, R. Differences in feeding neophobia in the tropical migrant wood warblers Dendroica castanea and D. pensylvanica. J. Comp. Psychol. 1984, 98, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuck-Paim, C.; Alonso, W.; Ottoni, E. Cognition in an Ever-Changing World: Climatic Variability Is Associated with Brain Size in Neotropical Parrots. Brain Behav. Evol. 2008, 71, 200–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondi, L.M.; Bó, M.S.; Vassallo, A.I. Inter-individual and age differences in exploration, neophobia and problem-solving ability in a Neotropical raptor (Milvago chimango). Anim. Cogn. 2010, 13, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergman, T.J.; Kitchen, D.M. Comparing responses to novel objects in wild baboons (Papio ursinus) and geladas (Theropithecus gelada). Anim. Cogn. 2008, 12, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reader, S.M. Causes of Individual Differences in Animal Exploration and Search. Top. Cogn. Sci. 2015, 7, 451–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolnick, D.I.; Svanbäck, R.; Fordyce, J.A.; Yang, L.H.; Davis, J.M.; Hulsey, C.D.; Forister, M.L. The ecology of individuals: Incidence and implications of individual specialization. Am. Nat. 2003, 161, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceia, F.R.; Ramos, J. Individual specialization in the foraging and feeding strategies of seabirds: A review. Mar. Biol. 2015, 162, 1923–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimmer, P.C.; Houston, A.; Marshall, J.; Bogacz, R.; Paul, E.S.; Mendl, M.; McNamara, J.M. Mammalian choices: Combining fast-but-inaccurate and slow-but-accurate decision-making systems. Proc. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 2008, 275, 2353–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, J.G.; Dyer, A.G. Diversity of speed-accuracy strategies benefits social insects. Curr. Biol. 2008, 18, R953–R954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chittka, L.; Dyer, A.G.; Bock, F.; Dornhaus, A. Psychophysics: Bees trade off foraging speed for accuracy. Nature 2003, 424, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, A.S.; Guez, D.; Lermite, F.; Patience, M. Tracking Changing Environments: Innovators Are Fast, but Not Flexible Learners. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e84907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ducatez, S.; Audet, J.-N.; Lefebvre, L. Problem-solving and learning in Carib grackles: Individuals show a consistent speed–accuracy trade-off. Anim. Cogn. 2014, 18, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, B.T. Tradeoff Between Travel Speed and Olfactory Food Detection in Ring-Tailed Coatis (Nasua nasua). Ethology 2010, 116, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latty, T.; Beekman, M. Speed–accuracy trade-offs during foraging decisions in the acellular slime mould Physarum polycephalum. In Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences; The Royal Society: London, UK, 2011; Volume 278, pp. 539–545. [Google Scholar]
- Burns, J.G.; Thomson, J.D. A test of spatial memory and movement patterns of bumblebees at multiple spatial and temporal scales. Behav. Ecol. 2005, 17, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sturz, B.R.; Kelly, D.M.; Brown, M.F. Facilitation of learning spatial relations among locations by visual cues: Generality across spatial configurations. Anim. Cogn. 2009, 13, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.F.; Wintersteen, J. Spatial patterns and memory for locations. Learn. Behav. 2004, 32, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, L.; Rasyidi, R.; Hastings, R.; von Bayern, A.M.P. Innovative problem solving in macaws. Learn. Behav. 2021, 49, 106–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Great Green Macaws (Ara ambiguus) | Blue-Throated Macaws (A. glaucogularis) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Age | Sex | Weight (g) | Name | Age | Sex | Weight (g) |
| Hagrid | 5 | M | 1213 | Mowgli | 5 | M | 762 |
| Enya | 5 | F | 1160 | Charlie | 5 | M | 783 |
| Luna | 5 | F | 1129 | Long John | 6 | M | 746 |
| Madame | 5 | F | 1064 | Gargamel | 7 | M | 849 |
| Alba | 5 | F | 1153 | Lady | 5 | F | 728 |
| Rita | 5 | F | 1119 | Mr. Huang | 6 | M | 812 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chow, P.K.Y.; Davies, J.R.; Bapat, A.; von Bayern, A.M.P. Tracking Changes of Hidden Food: Spatial Pattern Learning in Two Macaw Species. Birds 2021, 2, 285-301. https://doi.org/10.3390/birds2030021
Chow PKY, Davies JR, Bapat A, von Bayern AMP. Tracking Changes of Hidden Food: Spatial Pattern Learning in Two Macaw Species. Birds. 2021; 2(3):285-301. https://doi.org/10.3390/birds2030021
Chicago/Turabian StyleChow, Pizza Ka Yee, James R. Davies, Awani Bapat, and Auguste M. P. von Bayern. 2021. "Tracking Changes of Hidden Food: Spatial Pattern Learning in Two Macaw Species" Birds 2, no. 3: 285-301. https://doi.org/10.3390/birds2030021
APA StyleChow, P. K. Y., Davies, J. R., Bapat, A., & von Bayern, A. M. P. (2021). Tracking Changes of Hidden Food: Spatial Pattern Learning in Two Macaw Species. Birds, 2(3), 285-301. https://doi.org/10.3390/birds2030021






