Simple Summary
Radiotherapy continues to be a key treatment for breast cancer after surgery, but daily changes in anatomy and breathing can reduce treatment accuracy, especially when targeting internal mammary or axillary lymph nodes near the heart and lungs. Adaptive radiotherapy allows for plan adjustments at each session based on the patient’s current anatomy, which improves target coverage while protecting organs. In this case report, daily adaptation reliably improved coverage of the breast and regional lymph nodes without exceeding dose limits for the heart, lungs, or thyroid. The treatment was well tolerated, and no acute side effects were seen. These results demonstrate the feasibility and potential benefits of adaptive radiotherapy in complex breast cancer cases and emphasize the need for future studies to determine its role in routine practice.
Abstract
Online adaptive radiotherapy mitigates errors in absorbed dose delivery due to daily anatomical changes during hypofractionated breast treatment, particularly when comprehensive nodal therapy includes the internal mammary chain. To illustrate this, we present a case of a 65-year-old woman with left-sided luminal B invasive carcinoma, who underwent segmentectomy and level 1–2 dissection. Pathology revealed an 18 × 15 × 13 mm primary tumor with lymphovascular invasion, two of eleven axillary nodes positive, and intramammary metastasis, staged pT1cN1a. She received adjuvant docetaxel–cyclophosphamide followed by letrozole. Hypofractionated radiotherapy (40 Gy in 15 fractions) was administered in an inspiration breath-hold setting using a CBCT-guided online-adaptive platform. Adaptive planning improved V95% coverage over the planned treatment for all targets: on average, whole breast coverage increased from 88.4% to 96.3%, supraclavicular from 93.0% to 97.1%, axilla from 90.6% to 96.7%, and internal mammary from 91.8% to 95.9%. Organ-at-risk metrics remained within limits: the mean heart dose increased slightly (from an average of 0.12 Gy in scheduled to 0.15 Gy in adaptive plans). At the same time, the LAD D0.03 cm3 decreased, and the heart V4 Gy fell modestly (from 13.3% in the scheduled plan to 8.2% in the adaptive plan), reflecting low-dose redistribution without exceeding constraints. Lung and thyroid mean doses remained comparable. The patient tolerated treatment well, with no acute toxicity or local recurrence. This case highlights the importance of daily adaptation for complex left-sided radiation treatment involving internal mammary nodes, demonstrating target recovery without exceeding absorbed dose constraints and supporting future studies on control, toxicity, and quality of life.
1. Introduction
Conserving surgery and in some post-mastectomy cases. Over the last decade, guidance has focused on two main themes: consistent, anatomy-based delineation of targets for regional nodal irradiation and the routine use of shorter, evidence-supported hypofractionated schedules. The European Society for Radiotherapy and Oncology (ESTRO) consensus aimed to minimize variability among observers in defining breast targets by establishing clinical target volumes for the breast and regional lymph nodes based on detailed anatomical boundaries; version 1.1 remains a commonly referenced standard for elective irradiation in early breast cancer [1].
Randomized trials clarified indications and expected benefits of comprehensive regional nodal irradiation. The EORTC 22922/10925 trial, which specifically examined internal mammary and medial supraclavicular irradiation, has demonstrated sustained reductions in breast cancer mortality and recurrences over long-term follow-up, although with limited impact on overall survival [2]. These findings support the current practice of selectively including the internal mammary chain, especially in left-sided tumors with nodal involvement or medial location, while acknowledging that covering the internal mammary chain increases technical complexity. Technically, comprehensive nodal irradiation on the left involves a narrow anatomical corridor, as the internal mammary chain is adjacent to the sternum and the anterior heart. Meanwhile, the axillary and supraclavicular regions are near the brachial plexus and lung apices. Even with conformal planning, internal mammary irradiation yields higher doses to the heart and lungs compared to tangential fields alone, underscoring the importance of meticulous planning and verification [3]. The inspiration breath-hold has therefore become a key technique; multiple studies and meta-analyses have shown meaningful reductions in mean heart dose and coronary exposure without compromising target coverage [4].
Concurrently, hypofractionation has progressed from selective use to a standard recommendation for most women after lumpectomy. The START-B trial demonstrated that 40 Gy in 15 fractions provides tumor control and late effects comparable to 50 Gy in 25 fractions, with durable 10-year results. The FAST-Forward trial later showed non-inferiority for 26 Gy in 5 fractions over one week [5,6]. Hypofractionation increases the need for precise geometric accuracy because each fraction has a greater biological impact, and daily variations in the lumpectomy cavity, chest wall contour, breast volume, arm position, and nodal-level junctions can compromise the planned coverage, especially for internal mammary volumes located near moving soft tissues. Breast volume itself may fluctuate over the course of treatment due to factors such as postoperative healing or hormonal influences, including menstrual cycle–related changes, further underscoring the rationale for online adaptive radiotherapy.
Online adaptive radiotherapy (oART) has become a practical solution to this variability. Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) guided oART platforms enable daily assessment of “influencer” structures, automated target propagation, per-fraction dose recalculation, and re-optimization when anatomy deviates from the plan. Early breast-specific studies and workflow research using the Varian Ethos system show technical feasibility, accurate auto-segmentation for most breast targets, and potential for improved plan quality [7]. Although strong prospective clinical outcome data are still being collected, these advancements make comprehensive nodal irradiation, including the internal mammary chain, a promising use for oART, where consistent per-fraction conformity may be most impactful.
This case report presents left-sided, node-positive breast cancer treated with hypofractionated adjuvant radiotherapy using daily online adaptation, intentionally targeting internal mammary, axillary, and supraclavicular regions. It also includes a brief narrative review to explain how changing guidelines, hypofractionated practices, and new adaptive technologies come together to address ongoing challenges in regional nodal coverage and breast radiotherapy.
2. Case Description
A 65-year-old postmenopausal woman was recalled in November 2024 following screening; breast MRI revealed a highly suspicious lesion in the left breast with abnormal axillary and intramammary lymph nodes. The largest intraglandular focus measured 18 mm. Ultrasound-guided core biopsy confirmed invasive carcinoma of no special type with a luminal B profile. Estrogen receptor expression was 70%, progesterone receptor was absent, HER2 was negative, and the Ki-67 proliferation index was 27%. Her medical history included contralateral right-sided breast cancer in 2012, treated with breast-conserving surgery and axillary dissection, followed by adjuvant doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide chemotherapy, whole-breast irradiation of 50 Gy in 25 fractions with a tumor-bed boost of 12.5 Gy in 5 fractions, and 10 years of tamoxifen, with durable disease control on that side. Significant cardiovascular comorbidity was present, most notably prior percutaneous coronary intervention of the left anterior descending coronary artery in 2020.
The current primary tumor was managed with left breast segmentectomy and level 1 and 2 axillary dissection in January 2025, with an uncomplicated recovery. Definitive histopathology showed a moderately differentiated invasive carcinoma of no special type measuring 18 × 15 × 13 mm with clear surgical margins. A small component of ductal carcinoma in situ was present and comprised less than 5% of the tumor volume. Lymphovascular invasion was identified, while perineural invasion was not observed. One intramammary lymph node measuring 5 mm was entirely replaced by carcinoma. Among 11 axillary lymph nodes, 2 contained metastatic deposits. The largest metastatic focus measured 7 mm, with extranodal extension observed in 1 lymph node. Immunohistochemistry on the resection specimen demonstrated strong and diffuse estrogen receptor expression approaching 100%, persistent absence of progesterone receptor, negative HER2 status, and a Ki-67 index of 5%. Pathologic staging was pT1cN1a according to the eighth edition of the AJCC system. Germline BRCA1/2 testing was negative. The intramammary nodal metastasis was considered clinically significant because it implies a higher probability of occult disease along the internal mammary chain. Adjuvant systemic therapy consisted of 6 cycles of docetaxel and cyclophosphamide with primary granulocyte colony-stimulating factor support. The course was complicated by symptomatic cytopenias, and the cumulative dose intensity was reduced by approximately 35%, yet all six cycles were completed without hospitalization. Endocrine therapy with letrozole was initiated after chemotherapy. At the radiation oncology consultation, the patient had an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status of 0–1, was afebrile, and had no clinical or radiologic evidence of distant metastasis.
Adjuvant radiotherapy was indicated and initiated in June, delivered as 40 Gy in 15 fractions, consistent with the START-B randomized trial. Simulation was performed on a photon-counting Computed Tomography (CT) platform, namely the Siemens Healthineers NAEOTOM Alpha system. A custom vacuum immobilization cradle was molded to the torso and ipsilateral shoulder girdle. Because of postoperative pain and restricted range of motion, the right arm was positioned alongside the body to prioritize comfort and reproducibility. A stable inspiration breath-hold was established through coaching and visual feedback and adopted for planning and treatment. Image guidance consisted of kilovoltage CBCT acquired before and during every fraction to verify target and organ-at-risk (OAR) geometry. In addition, continuous surface guidance with AlignRT (VisionRT) provided non-ionizing real-time verification of patient position and breath-hold quality, enabling immediate interruption and correction when predefined thresholds were exceeded. Treatment was delivered on a Varian Ethos linear accelerator equipped with HyperSight CBCT.
Target volumes were delineated according to contemporary ESTRO consensus recommendations, together with a vessel-based atlas for regional lymph nodes. Planning target volumes (PTVs) were labeled as follows: PTV1d encompassed the whole left breast parenchyma, derived from a clinical target volume cropped 5 mm beneath the skin surface and subsequently expanded by a 5 mm margin, with the resulting PTV again cropped 5 mm from the skin anteriorly, while posterior borders respected the chest wall and overall conformation followed glandular anatomy., PTV2s encompassed the supraclavicular region consistent with level 4 nodal stations, PTV3 encompassed the axillary nodal regions across levels 1 through 3, including the interpectoral space. Also, PTVIMN encompassed the internal mammary chain along the internal thoracic vessels within the first three intercostal spaces with a narrow perivascular margin to limit exposure of adjacent critical structures while maintaining proximity to the nodal basin.
A single-isocenter nine-field Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) plan was created on the simulation scan as the reference plan, using six megavolt flattening-filter-free (6 MV FFF) photon beams. The selected geometry provided adequate coverage with balanced integral dose and acceptable ipsilateral lung exposure, as illustrated in Figure 1. For each fraction, CBCT imaging was obtained, and key influencer structures such as lungs and heart were reviewed to support the reliable propagation of target contours. Dose calculation employed a synthetic CT (synCT) derived from the CBCT data and registered to the planning scan. The scheduled plan was recalculated on the synthetic dataset to display day-specific OAR doses. When the daily anatomy warranted, an online adaptive plan was generated with optimization driven by predefined clinical goals. We have chosen the adaptive plan for every fraction because daily synCT recalculations consistently showed it effectively restored V95% to ≥95% for all targets, especially the whole breast, axilla, and IMN (Figure 2). In contrast, the scheduled plan often undercovers and displays lower coverage for these volumes (Figure 3). Across all 15 fractions, OAR dosimetry remained well within institutional constraints, confirming the safety of daily adaptive re-optimization. At our institution, the mean heart dose constraint for left-sided breast irradiation in IBH is 2 Gy, with stricter attention given to the LAD for patients with pre-existing cardiac conditions. In this case, the mean heart dose increased only marginally, from an average of 0.12 Gy in scheduled to 0.15 Gy in adaptive plans—far below the 2 Gy threshold and therefore clinically insignificant. Conversely, the LAD D0.03 cm3 consistently decreased with adaptation, indicating improved sparing of the most radiosensitive cardiac substructure. The heart V4 Gy, a low-dose spread indicator, was reduced from 13.3% to 8.2%, demonstrating that adaptation effectively limited unnecessary low-dose exposure while maintaining high target conformity. Collectively, these findings confirm that adaptive planning did not compromise OAR protection despite tighter conformity and improved PTV coverage achieved through daily anatomical optimization (Figure 4).
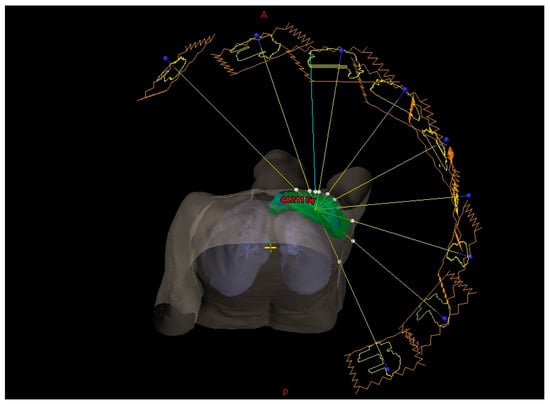
Figure 1.
Beam geometry of the nine-field IMRT plan used for comprehensive left-sided breast and nodal irradiation (beam angles: 320°, 345°, 10°, 35°, 60°, 85°, 110°, 135°, and 160°). Yellow lines represent beam central axes; green contours denote the planning target volume; gray structures depict the patient surface and lungs; red isodose region indicates the high-dose area.
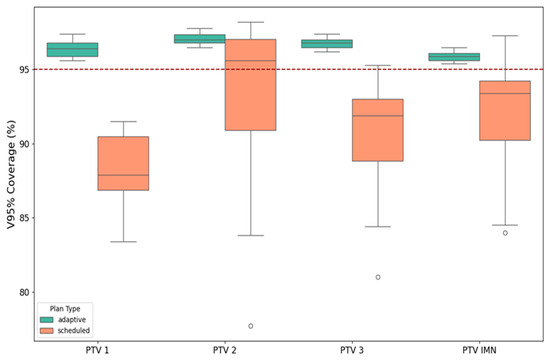
Figure 2.
Fraction-level V95% coverage (%) for each planning target volume comparing scheduled (orange) and adaptive (teal) plans. Boxes represent interquartile ranges with medians; whiskers indicate the distribution outside the IQR; isolated points denote outliers. The red dashed line marks the planning objective of 95% coverage. Adaptive planning consistently achieves and stabilizes V95% ≥ 95% across all targets, while scheduled plans frequently fall below the threshold with greater variability.
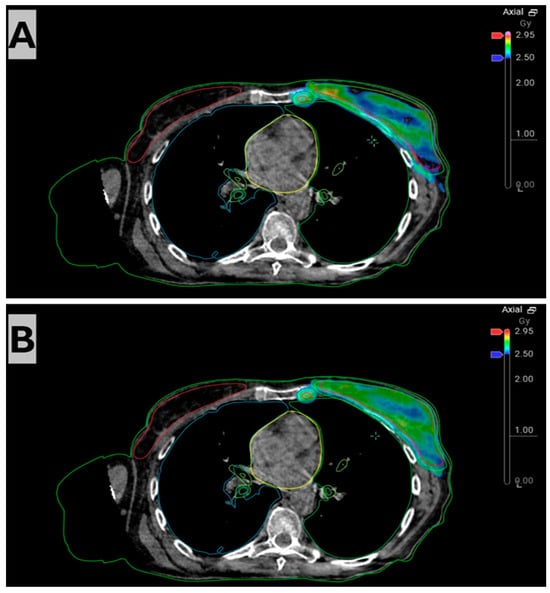
Figure 3.
Session 3 axial slice visualizing absorbed dose distribution of the scheduled plan (A) and the online-adapted plan (B). The scheduled plan displays under-coverage at the medial breast and partial coverage of the internal mammary target. The adapted plan re-establishes complete V95% coverage of both the breast PTV and the internal mammary PTV with more conformal dose around each volume.
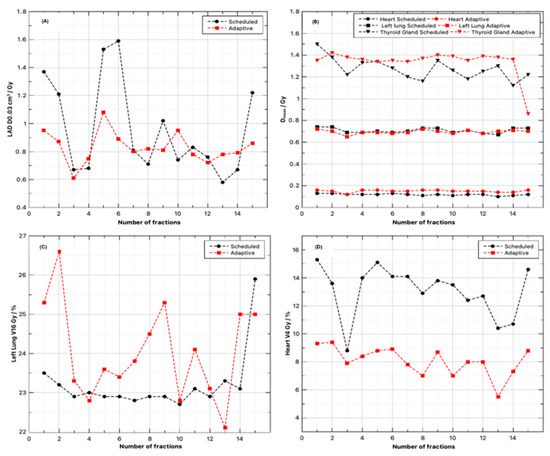
Figure 4.
Per-fraction OAR metrics for scheduled (black) versus online-adapted (red) delivery over 15 fractions. (A) Maximum left anterior descending coronary artery dose (LAD D0.03 cm3), (B) composite mean absorbed dose for the heart, left lung, and thyroid gland, (C) percentage volume of left lung that received 16 Gy of absorbed dose (V16 Gy), and (D) percentage volume of heart that received absorbed dose of 4 Gy (V4 Gy). Across the course, online adaptation produces lower and less variable high-dose surrogates to critical structures—most visibly, lower LAD D0.03 cm3 (A) and lower heart V4 Gy (D)—while left-lung dose metrics are consistently the same or lower than the scheduled plans (C). The absorbed dose to the Thyroid gland remains stable and low throughout treatment. An increase in the mean absorbed dose to the heart is observed in adaptive treatment; however, its influence remains clinically modest and within institutional limits (B).
From the patient’s perspective, the immobilization method and coached breath-hold were well tolerated, providing reassurance regarding cardiac protection, given the history of coronary intervention. At the first post-treatment review, three months after completing radiotherapy, she reported no new symptoms; there were no clinical or imaging signs of local recurrence, and no acute radiation-related adverse effects were observed.
3. Discussion: Online Adaptive Radiotherapy in Breast Cancer
3.1. Adaptive Radiotherapy Platforms
oART denotes the systematic adjustment of a treatment plan to the patient’s daily anatomy, to preserve target coverage and OAR sparing despite intrafraction change. Modern implementations range from offline re-planning to same-session online OART that acquires volumetric images, propagates or recontours targets and OARs, recalculates dose on the day’s anatomy, and if needed re-optimizes a deliverable plan within the treatment slot [7,8]. oART is delivered today on two main platform families, CBCT/CT-guided linacs and MR-linacs [9]. CBCT-guided oART workflows on ring-gantry linacs typically use daily CBCT to review “influencer” structures like the heart and lungs, auto-propagate targets from the reference plan, and perform same-session dose recalculation on a synthetic CT. For each fraction, the system automatically generated both the scheduled and the adaptive plan, and the physician reviewed plan quality and clinical goals to decide which plan to deliver [8]. In breast cancer specifically, early clinical experience with Ethos has shown feasibility, practical on-couch times, and acceptable plan quality for online adaptation [7]. Automated segmentation performance on Ethos for breast targets has also been reported as clinically usable, with manual edits still required for select subvolumes such as the boost [10]. Technical advances in imaging further support CBCT-only workflows: HyperSight iterative CBCT has shown high Hounsfield-unit fidelity and accurate dose calculation compared with conventional CBCT, including multi-site clinical validation. This enhances the dosimetric foundation of CBCT-guided adaptation [11,12]. Magnetic resonance image (MRI) guidance provides superior soft-tissue contrast, cine imaging for motion assessment, and on-table adaptation without added ionizing dose [9]. For breast cancer, MR-guided programs have reported technical feasibility and favorable early toxicity for prone whole-breast approaches and, notably, for stereotactic MR-guided adaptive partial-breast irradiation, where per-fraction visualization of the lumpectomy cavity enables tight margins and excellent cosmesis in prospective series [13]. CBCT-guided adaptive partial breast irradiation (PBI) has likewise shown improved delivered-plan quality versus scheduled plans with manageable online times, underscoring that breast oART is feasible across modalities when workflows are optimized [14]. The clinical challenge in left-sided cases arises from a narrow anatomic corridor: internal mammary nodes parallel the sternum and sit adjacent to the anterior heart. At the same time, axillary and supraclavicular basins abut lung apices and neurovascular structures. Day-to-day changes in breast shape, seroma behavior, arm position, and nodal-level junctions can reduce planned conformity and V95% coverage effects that hypofractionation might enhance because each fraction has a greater biological impact [8]. oART addresses these issues through daily geometric verification, offering the clinician a choice between the scheduled plan—where anatomic changes may reduce target coverage below clinical goals—and a reoptimized adaptive plan that accounts for the anatomy of the day [7].
3.2. Technical Challenges-Platform-Driven Considerations
On CBCT-guided systems like Varian Ethos, the adapt-to-shape workflow depends on accurate influencer segmentation, target propagation, and quick re-optimization. The practical implication for breast cases is that beam geometry needs to be “optimization-friendly” to keep on-couch times reasonable. In comparative simulations, IMRT with multiple static fields was favored over Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT) because VMAT increased optimization times to an impractical level for daily adaptation. Although the Ethos platform offers a predefined field set for IMRT plans, at our institution a patient-specific set of tangential fields is generated to best match individual anatomy, yielding plans of comparable quality while preserving workflow efficiency [15]. Multi-institution validations show dose-volume histogram (DVH) agreement with simulation CT (CT-sim) that meets standards for clinical use, though small deviations remain in high-dose gradients, requiring ongoing quality assurance (QA) [16]. Daily adaptation is especially beneficial when neighboring nodal targets (levels I–IV and IMN) are in contact with touch mobile influencers or when chest-wall–breast contact and seroma changes cause shape alterations that reduce planned coverage. Ethos feasibility studies show consistent improvements in PTV D95–V95 coverage with adapted plans without raising OAR doses on the same anatomy [17]. However, auto-propagation accuracy is structure-dependent: breast and nodal clinical target volumes (CTVs) generally meet coverage goals with minimal edits, whereas the tumor bed/boost often requires manual correction, prompting centers to anchor the boost CTV to surgical clips to reduce edit time [7,8]. For left-sided comprehensive irradiation, especially when the IMN is included, inspiration breath-hold remains a fundamental heart-sparing technique, lowering mean heart and LAD doses across different methods and fractionation schemes; oART does not eliminate this physiological separation and is best viewed as complementary to IBH [18,19]. Contemporary guidance notes that the vast majority of breast patients can maintain 25–30-s breath-holds, facilitating repeated CBCT and gated delivery within a single adaptive session [20]. While some patients derive limited benefit from IBH or cannot perform it reliably, the overall evidence still supports IBH for left-sided whole-breast and regional nodal irradiation, especially when the IMN is treated. Selection tools based on predicted heart–chest wall distance and lung expansion can help identify cases where free-breathing plus adaptation may be sufficient [18]. In short, oART addresses geometric variability, but it does not replace the anatomic displacement that IBH provides for cardiac sparing. Real-world CBCT-oART programs report total session durations of about 30–35 min from the first image to the end of treatment, with roughly 20 min attributed to the adaptive component. This matches department throughput when workflows and goals are standardized [21]. Motion-monitoring analyses across approximately 2000 oART fractions show sessions usually lasting 20 to −45 min, reinforcing the value of surface guidance for continuous motion monitoring and efficient re-verification without restarting the session [22]. In MR-linac programs, per-fraction times are generally longer; feasibility studies set thresholds of less than 80 min for adaptive delivery, and recent series still report median times of about 50 to −60 min for stereotactic, magnetic resonance (MR)-guided online-adaptive radiotherapy (SMART). However, patient-reported tolerance is high and acute grade ≥ 3 toxicity is uncommon [23,24]. Combining IBH with daily adaptation involves multiple short breath-holds for image acquisition and beam delivery. However, over 90% of patients can achieve the necessary breath-hold durations, and surface-guided coaching enhances reproducibility throughout the longer oART session [20]. Multi-field IMRT geometries commonly used for CBCT-oART can increase the very-low-dose exposure to the lungs compared to traditional tangential beams, even as adapted plans enhance high-dose conformity to complex targets such as the IMN [8]. MR-linac strategies, including precise prone positioning and stereotactic partial-breast techniques, offer superior soft-tissue visualization. However, they require longer optimization and gating times and may limit beam-angle options in certain setups [25]. Because plan selection occurs daily, programs focus on comprehensive QA that covers CBCT acquisition, synCT or direct CBCT dose recalculation, optimization stability, and delivery checks. Early Ethos breast studies reported excellent portal-dosimetry gamma pass rates for adapted plans, but widespread adoption still depends on institution-specific commissioning of HyperSight dose pipelines and regular cross-checks against CT-sim [7,16].
3.3. Clinical Evidence to Date
Clinical evidence for online adaptive breast radiotherapy is gradually evolving across different platforms, with variable degrees of clinical maturity depending on indication and imaging technology. Early MRI-guided, on-table adaptive partial-breast approaches have demonstrated technical feasibility with favorable early tolerance and cosmetic outcomes. A prospective series of MRI-guided adaptive PBI targeting the prone position reported that all patients completed treatment with target coverage and OAR constraints met, and no grade 2 or higher acute toxicity occurred, supporting the practicality of daily adaptation for cavity-focused targets [25]. Similarly, the phase II PARLOB study has reported outcomes for a magnetic–resonance–guided adaptive PBI strategy in low-risk breast cancer, showing acceptable toxicity and patient-reported cosmesis at early follow-up, confirming feasibility within a modern MR-linac program [13]. While these MRI-based experiences are valuable for demonstrating adaptive workflow robustness, they represent low-risk partial-breast indications with limited direct relevance to comprehensive adjuvant irradiation. In contrast, for whole-breast and nodal irradiation—especially left-sided cases that include the internal mammary chain—the clinical rationale for adaptation lies in day-to-day anatomic variability that can significantly impact target coverage and heart dose. Outside MRI platforms, a linac-based online-adaptive (APBI) series using cone-beam CT guidance showed improved plan quality and dosimetry compared to non-adaptive plans, indicating that same-session re-optimization can be leveraged even without MRI when daily anatomy differs from the reference plan [13]. In the adjuvant setting, CBCT-guided oART studies on the Ethos platform have demonstrated that automated segmentation and plan adaptation systematically improve breast and nodal target coverage without increasing OAR doses, highlighting the potential for real-time dose optimization in DIBH protocols. Hypofractionated schedules are now established standards, emphasizing the importance of per-fraction geometric accuracy when targets are near critical structures. The UK START-B randomized trial validated 40 Gy in 15 fractions as safe and effective compared to 50 Gy in 25 fractions. In contrast, FAST-Forward demonstrated the non-inferiority of 26 Gy in 5 fractions over one week versus 40 Gy in 15 fractions, with similar typical tissue effects at 5 years [5,6]. For selected patients with complex or evolving anatomy—such as preoperative, inoperable, or locally advanced disease—adaptive strategies with higher single-fraction doses continue to be explored, primarily in research settings, to extend the principles of precision adaptation beyond conventional postoperative radiotherapy. Five-year results from the prospective single-arm ABLATIVE trial of preoperative, single-dose MRI-guided PBI showed durable oncologic outcomes and preserved quality of life, demonstrating how daily soft-tissue visualization and adaptive planning can support unconventional timing or dose levels as targets evolve [26]. In summary, oART becomes clinically necessary when day-to-day anatomical or positional variations threaten target coverage or organ-at-risk sparing—most notably in left-sided comprehensive nodal irradiation, where conventional image guidance cannot reliably maintain heart and IMN dose constraints. In contrast, in stable, low-risk partial breast cases, it remains a primarily technically feasible option.
3.4. Perspective and Ongoing Studies
Near-term priorities include prospective comparisons of oART versus non-adaptive hypofractionated standards with endpoints in locoregional control, acute and late toxicity, and patient-reported outcomes, along with predefined subgroup analyses for internal mammary and axillary coverage in comprehensive nodal irradiation (Table 1 and Table 2) [27].

Table 1.
Ongoing and announced clinical trials investigating CBCT-guided oART in breast cancer.

Table 2.
Prospective and completed studies of MRI-guided oART, including partial-breast irradiation and preoperative approaches.
3.5. Cardiac Dose Considerations in Adaptive Breast Cancer Radiotherapy
Left-sided breast radiotherapy with comprehensive nodal irradiation, including internal mammary nodes, inevitably exposes a portion of the heart to radiation because of the close anatomical relationship [1]. To reduce long-term toxicity, planning guidelines stress minimizing both the dose and volume of cardiac irradiation. For instance, keeping the heart volume receiving ≥20 Gy below 10% and ≥40 Gy below 5% is recommended to lower the risk of radiation-induced cardiac death. The risk of radiation-related heart disease increases linearly with dose, with no clear threshold [35]. A landmark analysis by Darby et al. showed a 7.4% relative increase in major cardiac events per Gray of mean heart dose, highlighting the importance of the mean heart dose as a predictor of late cardiotoxicity. Advanced techniques like DIBH have significantly improved cardiac sparing by increasing the distance between the heart and chest wall during treatment [36]. In modern practice, routine DIBH has reduced the average mean heart dose for left-sided breast radiation to around 3–4 Gy, down from approximately 5 Gy in earlier eras [37,38]. DIBH not only lowers the mean dose but also greatly reduces high-dose exposure to the heart substructures. For instance, one dosimetric study reported that a 6 mm breath-hold expansion of the thorax reduced mean heart dose by ~1 Gy and shrank the high-dose heart volume (V25Gy) to ~1% [38,39]. The recent SAVE-HEART trial confirmed these benefits in a large cohort: surface-guided DIBH lowered the mean and maximum doses to the heart and left anterior descending coronary artery by approximately 36–42% compared with free-breathing, without compromising target coverage. This corresponded to an estimated 5% reduction in 10-year cardiovascular disease risk with DIBH (3.41% vs. 3.59%, p < 0.001) [37]. Similarly, Bruzzaniti et al. observed that DIBH produced statistically significant reductions in heart mean dose and LAD hotspots relative to free-breathing, while maintaining equal tumor control probability. These findings reinforce that DIBH should be the standard heart-sparing technique for left-sided breast cancer irradiation. Within this context, oART provides an additional tool to minimize cardiac exposure, especially in complex cases with comprehensive nodal targets. By re-optimizing the plan daily to account for anatomical changes, oART can tighten high-dose conformality around the targets and avoid incidental irradiation of the heart [6]. In our case, daily adaptation reduced the volume of heart receiving low doses (heart V4 Gy) and lowered the near-maximum dose to the LAD, at the cost of a slight increase in mean heart dose. This raises a pertinent radiobiological question: Is a small increase in mean heart dose more detrimental than a larger low-dose volume to the heart? Epidemiological evidence suggests that the mean heart dose is the strongest driver of late cardiac risk [2]. Therefore, a modest increase in mean dose—especially if the absolute mean remains low (on the order of a few Gy)—is unlikely to negate the benefit gained by reducing high-dose regions. In fact, keeping the mean heart dose below 3–4 Gy and heart V25Gy under 5–10% is associated with very low rates of radiation-induced cardiac events at 10 years [35]. Moreover, limiting point doses to critical structures, such as the LAD, is important, as high doses to small coronary segments can precipitate localized stenosis and ischemia [36]. From this perspective, our oART approach prioritized mitigating higher-dose exposure to the most sensitive cardiac substructures, while ensuring any increase in widely distributed low doses stayed within safe limits. It is also worth noting that the cumulative low-dose exposure over 15 fractions in an adaptive regimen is distributed across different cardiac regions depending on daily anatomy. There is no clinical evidence that such spatial–temporal dose variation worsens outcomes when all fractional doses remain well below tolerance. On the contrary, avoiding consistently high doses to the same cardiac region (which a non-adaptive plan might deliver if anatomy shifts unfavorably) could be protective [6]. Crucially, oART is complementary to, not a replacement for, DIBH in left-sided breast radiotherapy [35,38,39]. Breath-hold provides a fundamental geometric advantage by physically displacing the heart, yielding baseline dose reductions that adaptation cannot achieve through re-optimization alone. DIBH establishes a low-heart-dose baseline each day, and oART fine-tunes the plan to correct for daily variations (such as chest wall, heart position, or arm setup) without compromising target coverage. This combined approach minimizes high-dose spillage into the heart every fraction, marrying the strengths of both techniques. Early feasibility studies support this synergy: CBCT-guided adaptive plans in breath-hold have maintained heart doses within strict constraints while significantly improving target coverage in left-sided IMN cases [39]. In summary, by adhering to published cardiac dose thresholds and combining DIBH and oART, clinicians can achieve excellent nodal coverage and superior cardiac sparing, addressing the rationale that motivated the use of oART in comprehensive left-sided irradiation.
4. Conclusions
Online adaptive radiotherapy has evolved from an initially promising idea into a practical clinical workflow that recalculates and, when necessary, re-optimizes treatment based on the patient’s anatomy of the day. This approach maintains target coverage while respecting OAR constraints. Modern CBCT-guided platforms, equipped with high-fidelity imaging and structured goal sets, used together with inspiration breath-hold, are especially effective for left-sided breast cancer when regional nodal irradiation includes the internal mammary chain, where small daily geometric shifts can reduce conformity. The presented case highlights the clinical importance of this capability: over 15 fractions, the adaptive plan consistently outperformed the scheduled plan in V95% coverage for every planning target volume, with approximate mean improvements of 8% percentage points for the whole breast, 4% points for the supraclavicular region, 6% points for the axilla, and 4% points for the internal mammary chain, all while maintaining a manageable workflow and patient experience. These results align with emerging feasibility reports, which show improved on-table plan quality and consistent per-fraction coverage without increasing normal tissue damage. They also demonstrate why adaptation is most valuable when nodal junctions and internal mammary coverage are priorities. However, significant limitations remain: this is a single-patient case; most published evidence focuses on feasibility or dosimetric data rather than definitive oncologic outcomes; auto-segmentation still requires expert oversight; and adaptive sessions increase treatment time, demanding disciplined quality assurance and trained staff, which may limit widespread use. Future prospective studies, ideally randomized or conducted through multi-center registries, should investigate whether daily online adaptation can lead to better locoregional control, lower cardiac and pulmonary doses over the entire course, improved patient-reported quality of life, and sustainable throughput compared to non-adaptive hypofractionated protocols.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.V., D.K., M.L. and V.L.; methodology, M.M., G.U., H.K. and V.L.; validation, M.M., D.K. and H.K.; formal analysis, G.U., M.M. and K.S.; investigation, K.S. and M.L.; resources, M.M.; data curation, N.Š., writing—original draft preparation, V.L., N.Š. and D.V.; writing—review and editing, N.Š., M.M., H.K., G.U., M.L. and D.V.; visualization, N.Š.; supervision, D.S. and D.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable to this study. This study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The patient provided written informed consent for treatment and the publication of their anonymized data in this case study.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from the patient involved in the study, and written informed consent was obtained from the patient to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results. The study received no external funding.
References
- Offersen, B.V.; Boersma, L.J.; Kirkove, C.; Hol, S.; Aznar, M.C.; Sola, A.B.; Kirova, Y.M.; Pignol, J.P.; Remouchamps, V.; Verhoeven, K.; et al. ESTRO consensus guideline on target volume delineation for elective radiation therapy of early stage breast cancer, version 1.1. Radiother. Oncol. 2016, 118, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poortmans, P.M.; Collette, S.; Kirkove, C.; Van Limbergen, E.; Budach, V.; Struikmans, H.; Collette, L.; Fourquet, A.; Maingon, P.; Valli, M.; et al. Internal Mammary and Medial Supraclavicular Irradiation in Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finazzi, T.; Nguyen, V.T.; Zimmermann, F.; Gkika, E.; Aebersold, D.M.; Riesterer, O.; Klöck, S. Impact of patient and treatment characteristics on heart and lung dose in adjuvant radiotherapy for left-sided breast cancer. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 14, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, J.; Hu, S.; Luo, Y.; Zheng, R.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, P.; Chi, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, F.; Long, X. Meta-analysis of deep inspiration breath hold (DIBH) versus free breathing (FB) in postoperative radiotherapy for left-side breast cancer. Breast Cancer 2020, 27, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haviland, J.S.; Owen, J.R.; Dewar, J.A.; Agrawal, R.K.; Barrett, J.; Barrett-Lee, P.J.; Dobbs, H.J.; Hopwood, P.; Lawton, P.A.; Magee, B.J.; et al. The UK Standardisation of Breast Radiotherapy (START) trials of radiotherapy hypofractionation for treatment of early breast cancer: 10-year follow-up results of two randomised controlled trials. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 1086–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray Brunt, A.; Haviland, J.S.; Wheatley, D.A.; Sydenham, M.A.; Alhasso, A.; Bloomfield, D.J.; Chan, C.; Churn, M.; Cleator, S.; Coles, C.E.; et al. Hypofractionated breast radiotherapy for 1 week versus 3 weeks (FAST-Forward): 5-year efficacy and late normal tissue effects results from a multicentre, non-inferiority, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2020, 395, 1613–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galand, A.; Prunaretty, J.; Mir, N.; Morel, A.; Bourgier, C.; Aillères, N.; Azria, D.; Fenoglietto, P. Feasibility study of adaptive radiotherapy with Ethos for breast cancer. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1274082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-Colle, C.; Kirby, A.; Russell, N.; Shaitelman, S.F.; Currey, A.; Donovan, E.; Hahn, E.; Han, K.; Anandadas, C.N.; Mahmood, F.; et al. Adaptive radiotherapy for breast cancer. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 39, 100564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henke, L.E.; Contreras, J.A.; Green, O.L.; Cai, B.; Kim, H.; Roach, M.C.; Olsen, J.R.; Fischer-Valuck, B.; Mullen, D.F.; Kashani, R.; et al. Magnetic Resonance Image-Guided Radiotherapy (MRIgRT): A 4.5-Year Clinical Experience. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 30, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prunaretty, J.; Mekki, F.; Laurent, P.I.; Morel, A.; Hinault, P.; Bourgier, C.; Azria, D.; Fenoglietto, P. Clinical feasibility of Ethos auto-segmentation for adaptive whole-breast cancer treatment. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1507806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, N.; Oare, C.; Nelson, G.; Martin, T.; Huang, J.; Zhao, H. Feasibility of HyperSight CBCT for adaptive radiation therapy: A phantom benchmark study of dose calculation accuracy and delivery verification on the Halcyon. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2025, 26, e70245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reverberi, C.; Facondo, G.; Prisco, A.; Ceschia, T.; Moretti, E.; Scalchi, P.; Pegolo, E.; Orsaria, M.; Zuiani, C.; Seriau, L.; et al. Preoperative Single Fraction Stereotactic Partial Breast Irradiation for Early-Stage Breast Cancer Patients With GammaPod Technology: Pathologic Findings and Ki-67 Evaluation. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2025, 122, 1158–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vliet, C.; Tetar, S.U.; van den Bongard, H.J.G.D.; Fraikin, T.; Jeulink, M.; Palacios, M.A.; van den Tol, M.P.; Slotman, B.J.; Bruynzeel, A.M.E. Partial Breast Radiation Therapy in Low-Risk Breast Cancer Using a Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Guided Adaptive Approach; Results of the Phase 2 PARLOB Study. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2025, 15, e434–e443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, B.; Song, Y.; Chia-Ko, W.; Hsu, H.Y.; Zhai, X.; Tamas, P.; Powell, S.; Cahlon, O.; McCormick, B.; Khan, A.; et al. Accuracy and Efficiency of Patient Setup Using Surface Imaging Versus Skin Tattoos for Accelerated Partial Breast Irradiation. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 8, 101183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasun, P.; Kharade, V.; Pal, V.; Gupta, M.; Das, S.; Pasricha, R. Dosimetric Comparison of Hypofractionated Regimen in Breast Cancer Using Two Different Techniques: Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) and Volumetric-Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT). Cureus 2023, 15, e38045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Pogue, J.A.; Stanley, D.N.; Shen, S.; Viscariello, N.N.; Cardenas, C.E.; Popple, R.A.; Harms, J. Assessing HyperSight iterative CBCT for dose calculation in online adaptive radiotherapy for pelvis and breast patients compared to synthetic CT. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2025, 26, e70038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Timmeren, J.E.; Chamberlain, M.; Krayenbuehl, J.; Wilke, L.; Ehrbar, S.; Bogowicz, M.; Hartley, C.; Zamburlini, M.; Andratschke, N.; Garcia Schüler, H.; et al. Treatment plan quality during online adaptive re-planning. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 15, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaál, S.; Kahán, Z.; Paczona, V.; Kószó, R.; Drencsényi, R.; Szabó, J.; Rónai, R.; Antal, T.; Deák, B.; Varga, Z. Deep-inspirational breath-hold (DIBH) technique in left-sided breast cancer: Various aspects of clinical utility. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 16, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudat, V.; Zhao, R.; Wang, B.; Fakhrian, K.; Obeid, S.; Schramm, O.; Ahmed, M. Impact of deep inspiration breath hold, surface-guided radiotherapy, and daily CBCT on the organs at risk in breast cancer radiotherapy. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 27814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aznar, M.C.; Carrasco de Fez, P.; Corradini, S.; Mast, M.; McNair, H.; Meattini, I.; Persson, G.; van Haaren, P. ESTRO-ACROP guideline: Recommendations on implementation of breath-hold techniques in radiotherapy. Radiother. Oncol. 2023, 185, 109734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, D.N.; Harms, J.; Pogue, J.A.; Belliveau, J.G.; Marcrom, S.R.; McDonald, A.M.; Dobelbower, M.C.; Boggs, D.H.; Soike, M.H.; Fiveash, J.A.; et al. A roadmap for implementation of kV-CBCT online adaptive radiation therapy and initial first year experiences. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2023, 24, e13961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, D.N.; Covington, E.; Harms, J.; Pogue, J.; Cardenas, C.E.; Popple, R.A. Evaluation and correlation of patient movement during online adaptive radiotherapy with CBCT and a surface imaging system. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2023, 24, e14133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henke, L.; Kashani, R.; Robinson, C.; Curcuru, A.; DeWees, T.; Bradley, J.; Green, O.; Michalski, J.; Mutic, S.; Parikh, P. Phase I trial of stereotactic MR-guided online adaptive radiation therapy (SMART) for the treatment of oligometastatic or unresectable primary malignancies of the abdomen. Radiother. Oncol. 2018, 126, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mol van Otterloo, S.R.; Westerhoff, J.M.; Leer, T.; Rutgers, R.H.A.; Meijers, L.T.C.; Daamen, L.A.; Intven, M.P.W.; Verkooijen, H.M. Patient expectation and experience of MR-guided radiotherapy using a 1.5T MR-Linac. Tech. Innov. Patient Support Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 29, 100224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, J.; Pennell, R.; Formenti, S.C. The initial experience of MRI-guided precision prone breast irradiation with daily adaptive planning in treating early stage breast cancer patients. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1048512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civil, Y.A.; Vasmel, J.E.; Charaghvandi, R.K.; Houweling, A.C.; Vreuls, C.P.H.; van Diest, P.J.; Witkamp, A.J.; Doeksen, A.; van Dalen, T.; Felderhof, J.; et al. Preoperative Magnetic Resonance Guided Single-Dose Partial Breast Irradiation: 5-Year Results of the Prospective Single-Arm ABLATIVE Trial. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2025, 121, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunt, A.M.; Cafferty, F.H.; Wheatley, D.; Sydenham, M.A.; Kirby, A.M.; Coles, C.E.; Patel, J.; Alhasso, A.; Chan, C.; Cleator, S.; et al. Patient- and clinician-assessed five-year normal tissue effects following one-week versus three-week axillary radiotherapy for breast cancer: Results from the phase III FAST-Forward trial randomised nodal sub-study. Radiother. Oncol. 2025, 207, 110915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Hypofractionated Online Adaptive Radiotherapy of Breast Cancer. Identifier: NCT06568705. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06568705 (accessed on 17 September 2025).
- ClinicalTrials.gov. SAHARA-04: Adaptive Radiotherapy in Hypersensitive or High Locoregional-Risk Breast Cancer. Identifier: NCT06053086. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06053086 (accessed on 17 September 2025).
- ClinicalTrials.gov. BREAST-ART: Implementation of Online Adaptive Radiotherapy for Breast Cancer on Ethos. Identifier: NCT05727553. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05727553 (accessed on 17 September 2025).
- Qadir, A.; Singh, N.; Dean, J.; Khanduri, S.; Shaikh, F.; Lock, M.; Yartsev, S. Magnetic resonance imaging-guided single-fraction preoperative radiotherapy for early-stage breast cancer (the RICE trial): Feasibility study. Pilot Feasibility Stud. 2024, 10, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civil, Y.A.; Oei, A.L.; Duvivier, K.M.; Bijker, N.; Meijnen, P.; Donkers, L.; Verheijen, S.; van Kesteren, Z.; Palacios, M.A.; Schijf, L.J.; et al. Prediction of pathologic complete response after single-dose MR-guided partial breast irradiation in low-risk breast cancer patients: The ABLATIVE-2 trial—A study protocol. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Real-Time MRI-Guided 3-Fraction Accelerated Partial Breast Irradiation. Identifier: NCT03936478. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03936478 (accessed on 17 September 2025).
- ClinicalTrials.gov. MOMENTUM: Multi-Institutional Registry for MRI-Guided Adaptive Radiotherapy. Identifier: NCT04075305. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04075305 (accessed on 17 September 2025).
- Drost, L.; Yee, C.; Lam, H.; Zhang, L.; Wronski, M.; McCann, C.; Lee, J.; Vesprini, D.; Leung, E.; Chow, E. A systematic review of heart dose in breast radiotherapy. Clin. Breast Cancer 2018, 18, e819–e824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönecker, S.; Angelini, L.; Gaasch, A.; Zinn, A.; Konnerth, D.; Heinz, C.; Xiong, Y.; Unger, K.; Landry, G.; Meattini, I.; et al. Surface-based deep inspiration breath-hold radiotherapy in left-sided breast cancer: Final results from the SAVE-HEART study. ESMO Open 2024, 9, 103993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chenna, S.; Nair, S.S.; Nagesh, J.; Singh, A.; Velu, U.; Mehta, A.; Jayashree, N.P.; Gupta, M.; Krishnan, J.; Kathiresan, K.; et al. Dosimetric comparison of 3D-conformal radiotherapy, volumetric modulated arc therapy, and h-VMAT in left breast radiotherapy under free-breathing and breath-hold conditions. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 33095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruzzaniti, V.; Abate, A.; Pinnarò, P.; D’Andrea, M.; Infusino, E.; Landoni, V.; Soriani, A.; Giordano, C.; Ferraro, A.; Strigari, L. Dosimetric and clinical advantages of deep inspiration breath-hold (DIBH) during radiotherapy of breast cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 32, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Luo, Z.; Hu, H.; Jiang, L.; Wu, J.; Lei, L.; Qu, L.; Wu, Z. SGRT-based DIBH radiotherapy practice for right-sided breast cancer combined with RNI: A retrospective study on dosimetry and setup accuracy. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2023, 24, e13998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).