Clinical Imaging and Dosimetry of a Pan-Cancer Targeting Alkylphosphocholine Analog, [124I]I-NM404
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.2. Patients
2.3. Synthesis of Radioiodinated NM404
2.4. PET/CT Imaging Protocols
2.5. Semiquantitative and Qualitative Image Analysis
2.6. Biodistribution and Dosimetry
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Safety of [124I]I-NM404 Administration
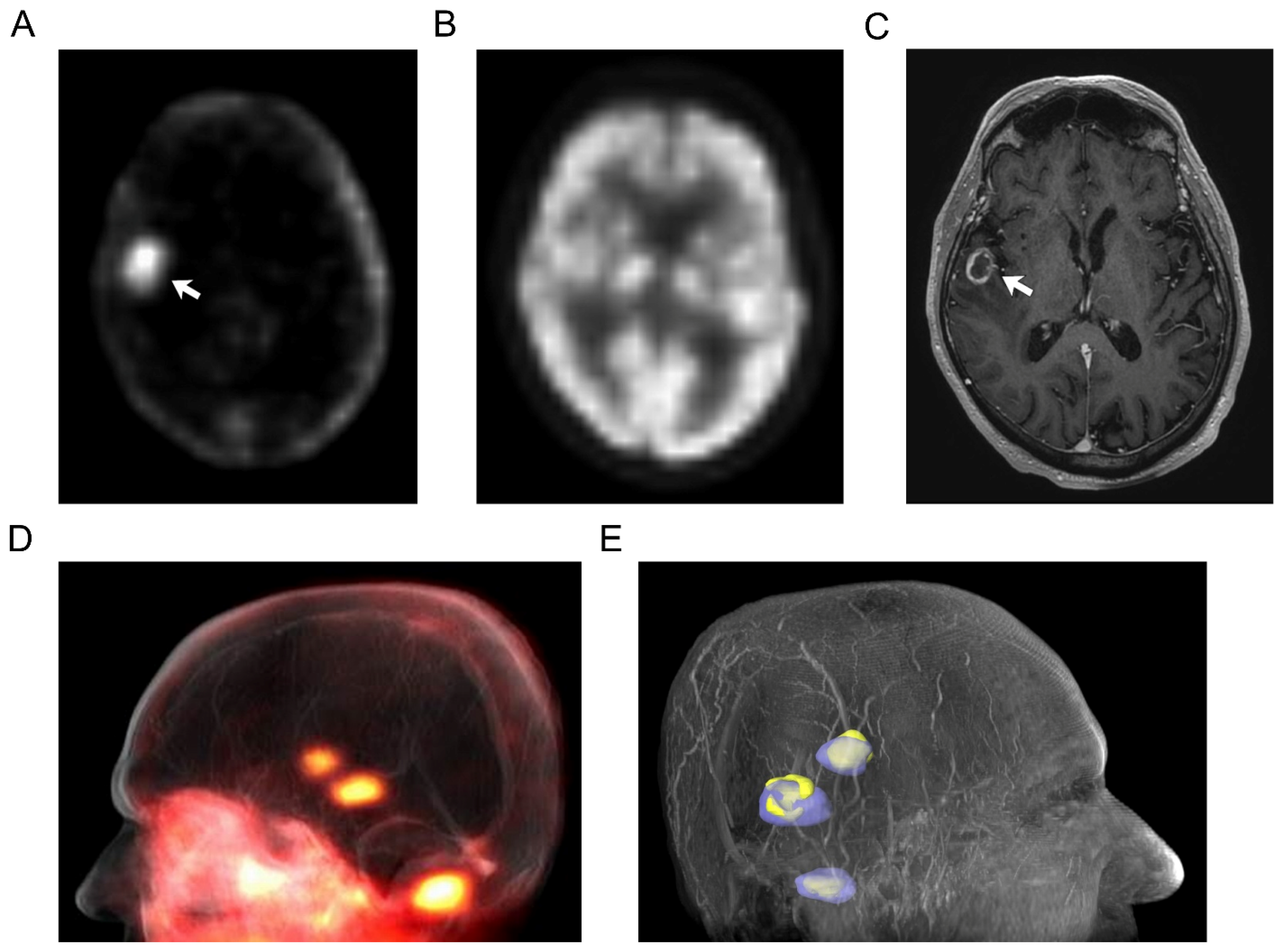
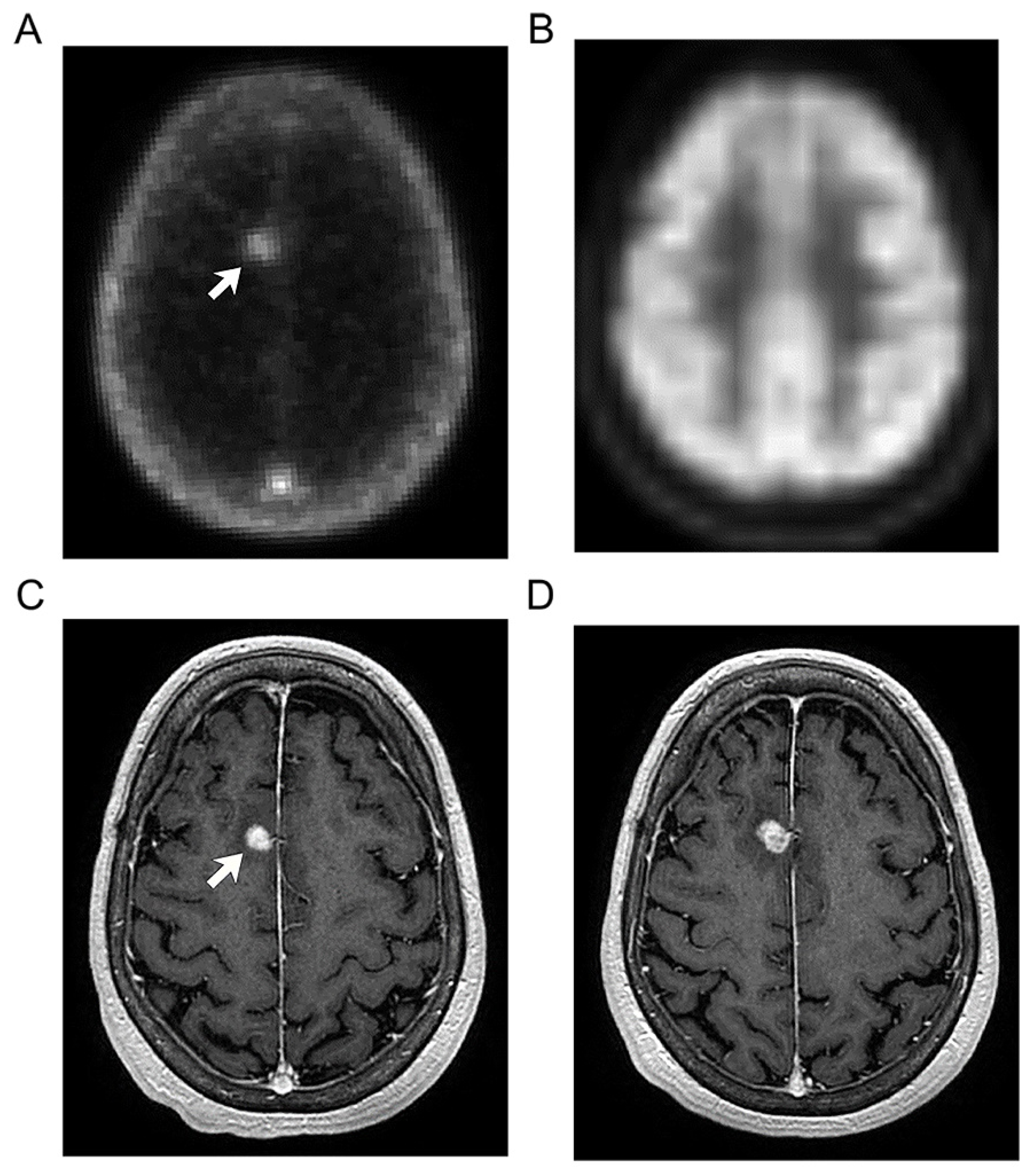
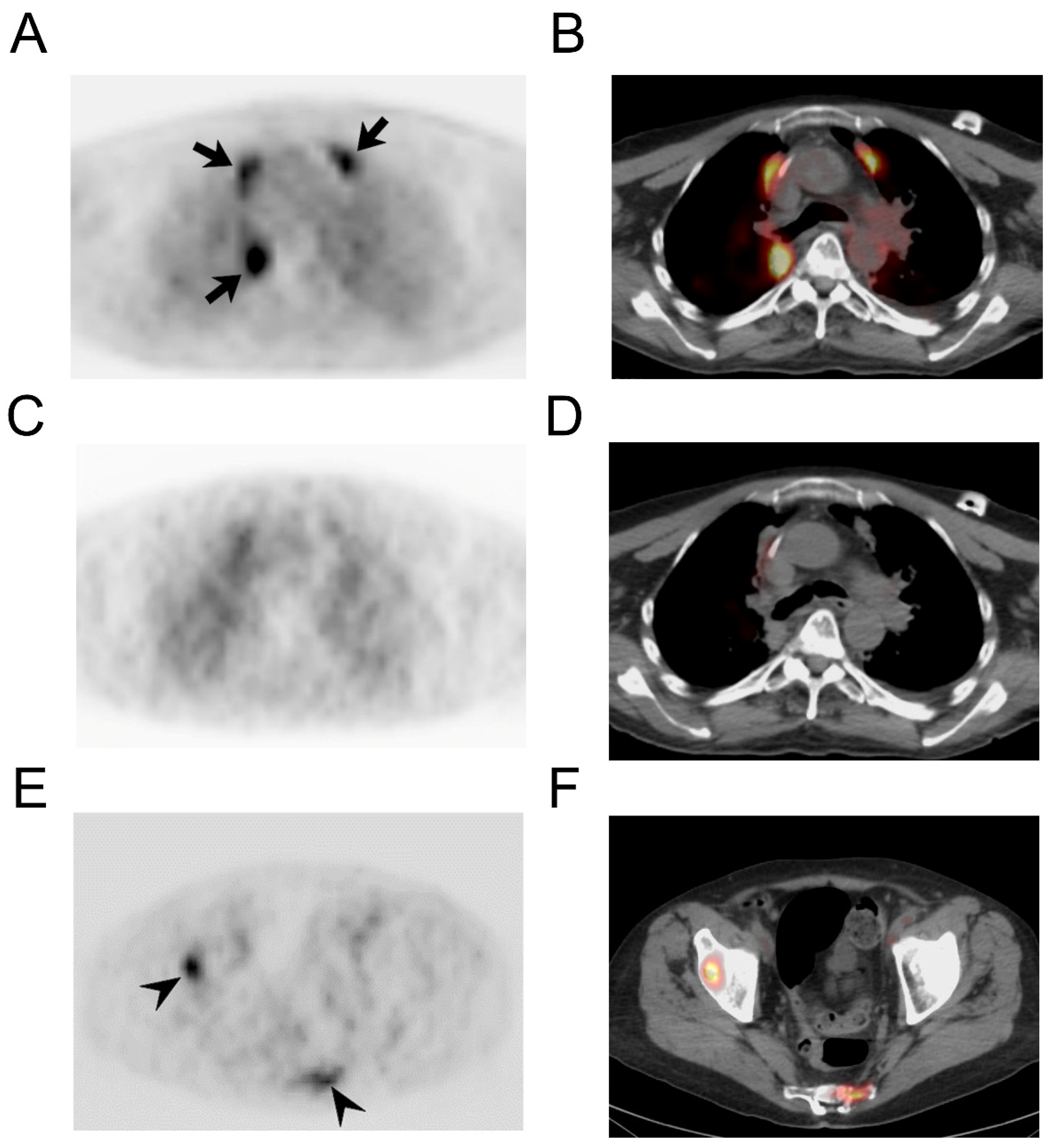
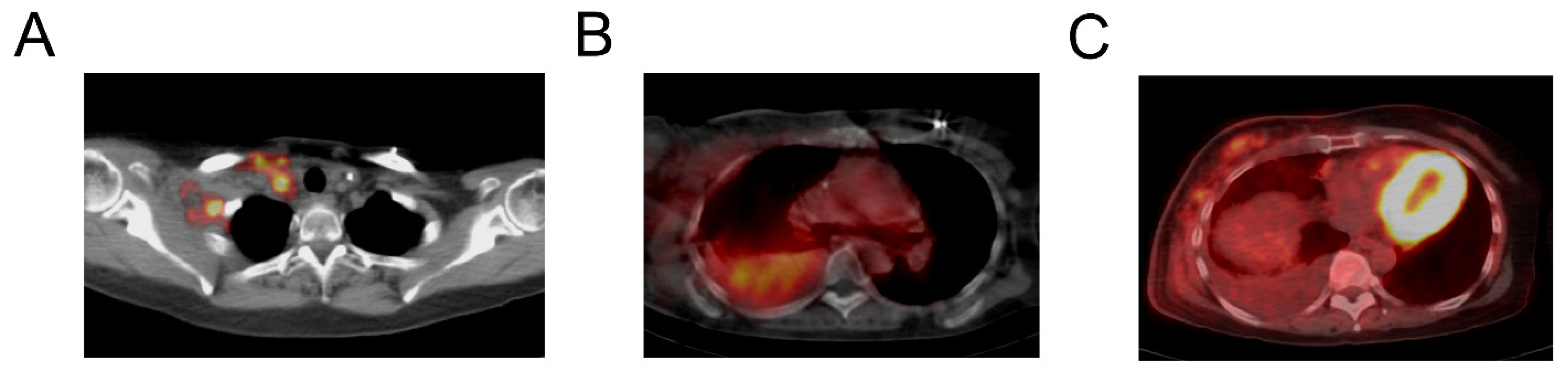
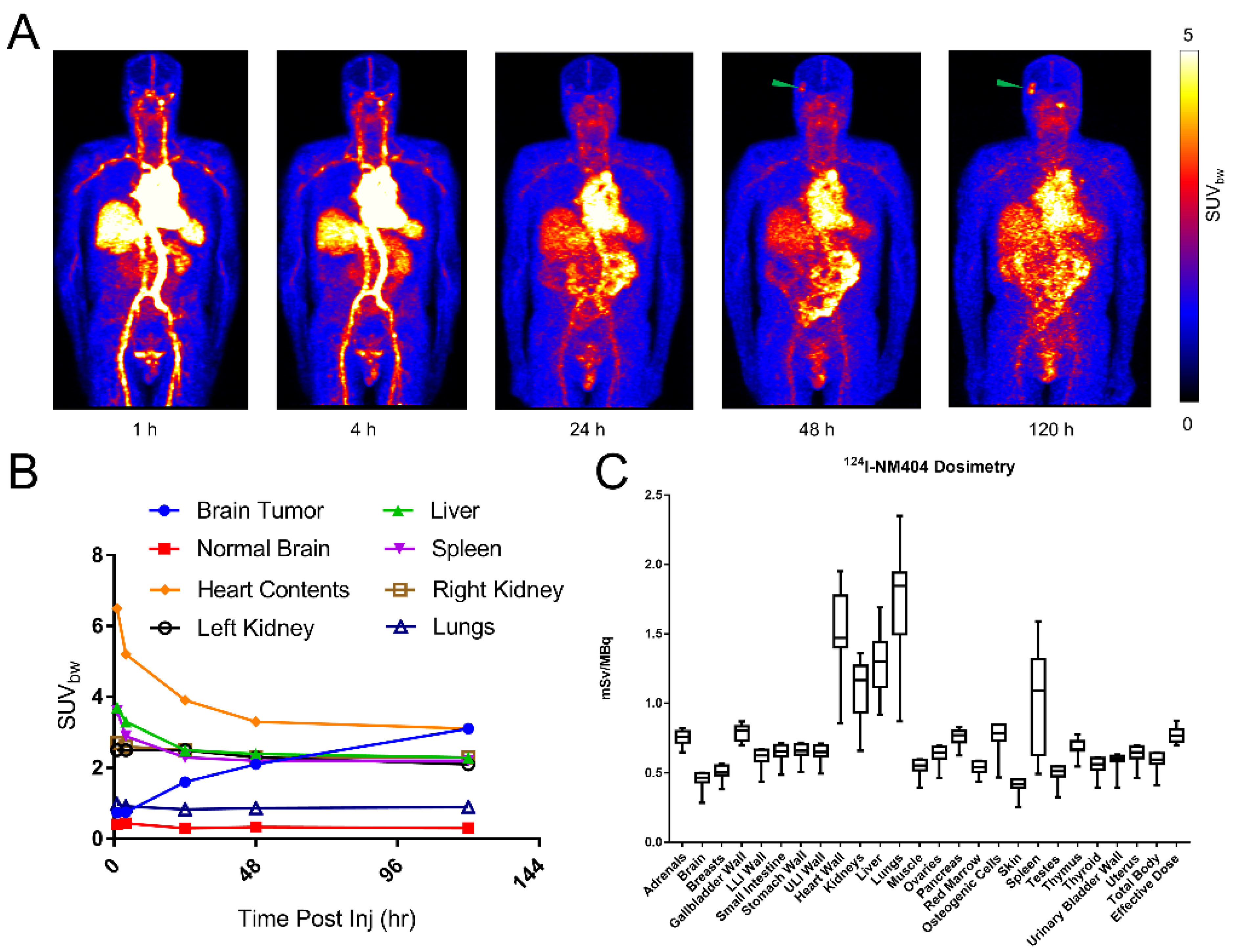
3.2. Imaging Findings
3.3. [124I]I-NM404 Biodistribution and Dosimetry Estimation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Herrmann, K.; Schwaiger, M.; Lewis, J.S.; Solomon, S.B.; McNeil, B.J.; Baumann, M.; Gambhir, S.S.; Hricak, H.; Weissleder, R. Radiotheranostics: A roadmap for future development. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, e146–e156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinchuk, A.N.; Rampy, M.A.; Longino, M.A.; Skinner, R.W.; Gross, M.D.; Weichert, J.P.; Counsell, R.E. Synthesis and structure-activity relationship effects on the tumor avidity of radioiodinated phospholipid ether analogues. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 2155–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weichert, J.P.; Clark, P.A.; Kandela, I.K.; Vaccaro, A.M.; Clarke, W.; Longino, M.A.; Pinchuk, A.N.; Farhoud, M.; Swanson, K.I.; Floberg, J.M.; et al. Alkylphosphocholine Analogs for Broad-Spectrum Cancer Imaging and Therapy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 240ra75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kirschner, A.S.; Ice, R.D.; Beierwaltes, W.H. Radiation dosimetry of 131I-19-Iodocholesterol. J. Nucl. Med. 1973, 14, 713–717. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carrasco, M.P.; Jiménez-López, J.M.; Ríos-Marco, P.; Segovia, J.L.; Marco, C. Disruption of cellular cholesterol transport and homeostasis as a novel mechanism of action of membrane-targeted alkylphospholipid analogues. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 160, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gajate, C. The antitumor ether lipid ET-18-OCH3 induces apoptosis through translocation and capping of Fas/CD95 into membrane rafts in human leukemic cells. Blood 2001, 98, 3860–3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reis-Sobreiro, M.; Roué, G.; Moros, A.; Gajate, C.; de la Iglesia-Vicente, J.; Colomer, D.; Mollinedo, F. Lipid raft-mediated Akt signaling as a therapeutic target in mantle cell lymphoma. Blood Cancer J. 2013, 3, e118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van der Luit, A.H.; Budde, M.; Ruurs, P.; Verheij, M.; Van Blitterswijk, W.J. Alkyl-lysophospholipid accumulates in lipid rafts and induces apoptosis via raft-dependent endocytosis and inhibition of phosphatidylcholine synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 39541–39547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lasserre, R.; Guo, X.-J.; Conchonaud, F.; Hamon, Y.; Hawchar, O.; Bernard, A.-M.; Soudja, S.M.; Lenne, P.-F.; Rigneault, H.; Olive, D.; et al. Raft nanodomains contribute to Akt/PKB plasma membrane recruitment and activation. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2008, 4, 538–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.C.; Park, M.J.; Ye, S.-K.; Kim, C.-W.; Kim, Y.-N. Elevated levels of cholesterol-rich lipid rafts in cancer cells are correlated with apoptosis sensitivity induced by cholesterol-depleting agents. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 168, 1107–1118; quiz 1404–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mollinedo, F.; Gajate, C. Lipid rafts and clusters of apoptotic signaling molecule-enriched rafts in cancer therapy. Future Oncol. 2010, 6, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, L.T.; Fourzali, Y.; Hernan, H.; Weichert, J.P.; Traynor, A.M. First in human use of 124I-NM404 PET/CT in primary and metastatic brain tumors. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2012, 14, S1644. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, L.T.; Titz, B.; Robins, H.I.; Bednarz, B.P.; Perlman, S.B.; Weichert, J.P.; Kuo, J.S. I-CLR1404 in high and low-grade brain tumors. Am. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2017, 7, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grudzinski, J.J.; Titz, B.; Kozak, K.; Clarke, W.; Allen, E.; Trembath, L.; Stabin, M.; Marshall, J.; Cho, S.Y.; Wong, T.Z.; et al. A Phase 1 Study of 131I-CLR1404 in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Advanced Solid Tumors: Dosimetry, Biodistribution, Pharmacokinetics, and Safety. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubner, S.J.; Mullvain, J.; Perlman, S.; Pishvaian, M.; Mortimer, J.; Oliver, K.; Heideman, J.; Hall, L.; Liu, G.; Joseph, S.; et al. A Phase 1, Multi-Center, Open-Label, Dose- Escalation Study of I-CLR1404 in Subjects with Relapsed or Refractory Advanced Solid Malignancies I-CLR1404 in Subjects with Relapsed or Refractory Advanced Solid Malignancies. Cancer Investig. 2015, 33, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAuliffe, M.J.; Lalonde, F.M.; McGarry, D.; Gandler, W.; Csaky, K.; Trus, B.L. Medical image processing, analysis & visualization in clinical research. In Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems, CBMS, Bethesda, MD, USA, 26–27 July 2001; Volume 2001, pp. 381–386. [Google Scholar]
- Barrett, P.H.; Bell, B.M.; Cobelli, C.; Golde, H.; Schumitzky, A.; Vicini, P.; Foster, D.M. SAAM II: Simulation, Analysis, and Modeling Software for Tracer and Pharmacokinetic Studies. Metabolism 1998, 47, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stabin, M.G.; Siegel, J.A. Physical Models and Dose Factors for Use in Internal Dose Assessment. Health Phys. 2003, 85, 294–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stabin, M.G.; Sparks, R.B.; Crowe, E. OLINDA/EXM: The second-generation personal computer software for internal dose assessment in nuclear medicine. J. Nucl. Med. 2005, 46, 1023–1027. [Google Scholar]
- Pickhardt, P.J.; Hall, L.T.; Lee, M.; Longino, M.; Pinchuk, A.; Banash, M.; Grudzinski, J.; Titz, B.; Jaskowiak, C.; Kuo, J.S.; et al. A novel “diapeutic” molecular imaging agent for combined oncologic diagnosis and therapy in a broad spectrum of human cancers: Preliminary clinical experience with CLR1404. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 11000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, L.T.; Titz, B.; Baidya, N.; van der Kolk, A.G.; Robins, H.I.; Otto, M.; Perlman, S.B.; Weichert, J.P.; Kuo, J.S. [124I]CLR1404 PET/CT in High-Grade Primary and Metastatic Brain Tumors. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2020, 22, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, K.I.; Clark, P.A.; Zhang, R.R.; Kandela, I.K.; Farhoud, M.; Weichert, J.P.; Kuo, J.S. Fluorescent Cancer-Selective Alkylphosphocholine Analogs for Intraoperative Glioma Detection. Neurosurgery 2014, 90, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lingwood, D.; Simons, K. Lipid rafts as a membrane-organizing principle. Science 2010, 327, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shreve, P.D.; Anzai, Y.; Wahl, R.L. Pitfalls in oncologic diagnosis with FDG PET imaging: Physiologic and benign variants. Radiographics 1999, 19, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.S.; Ahn, S.H.; Moon, B.S.; Chun, K.S.; Kang, J.H.; Cheon, G.J.; Choi, C.W.; Lim, S.M. Comparison of 18F-FDG, 18F-FET and 18F-FLT for differentiation between tumor and inflammation in rats. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2009, 36, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, S.T.; Suh, J.H.; Raja, S.; Lee, S.Y.; Barnett, G. The sensitivity and specificity of FDG PET in distinguishing recurrent brain tumor from radionecrosis in patients treated with stereotactic radiosurgery. Int. J. Cancer 2001, 96, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zechmann, C.M.; Afshar-Oromieh, A.; Armor, T.; Stubbs, J.B.; Mier, W.; Hadaschik, B.; Joyal, J.; Kopka, K.; Debus, J.; Babich, J.W.; et al. Radiation dosimetry and first therapy results with a (124)I/(131)I-labeled small molecule (MIP-1095) targeting PSMA for prostate cancer therapy. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2014, 41, 1280–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Patient | Age (Dx) | Age (Im) | Gender | Weight (kg) | Primary Tumor | Dose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 63 | 64 | F | 57 | Pancreas | 185 MBq |
| 2 | 51 | 53 | F | 65 | Breast, triple-negative | 185 MBq |
| 3 | 46 | 46 | M | 93 | SCC tongue base | 185 MBq |
| 4 | 56 | 61 | M | 131 | Colorectal | 185 MBq |
| 5 | 66 | 75 | M | 98 | Prostate | 185 MBq |
| 6 | 61 | 61 | M | 132 | SCC tonsil | 185 MBq |
| 7 | 55 | 60 | F | 83 | Melanoma | 185 MBq |
| 8 | 60 | 62 | M | 75 | Bronchogenic | 185 MBq |
| 9 | 56 | 61 | F | 74 | Bronchogenic | 185 MBq |
| 10 | 68 | 70 | M | 77 | Bronchogenic | 185 MBq |
| 11 | 62 | 63 | F | 88 | Bronchogenic | 111 MBq |
| 12 | 63 | 63 | F | 93 | Bronchogenic | 111 MBq |
| 13 | 64 | 65 | M | 88 | Bronchogenic | 277.5 MBq |
| 14 | 80 | 80 | F | 71 | Bronchogenic | 277.5 MBq |
| Patient | Index Lesion | Maximum TBR | Mean TBR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | No active focal index lesion | n/a | n/a | |
| 2 | Right axillary lymph node | 1.95 | 1.63 | |
| 3 | Right cervical node | 6.39 | 4.21 | |
| 4 | No active focal index lesion | n/a | n/a | |
| 5 | Right iliac lymph node | 4.31 | 2.39 | |
| 6 | Left cervical lymph node | 3.95 | 2.63 | |
| 7 | Right frontal lobe brain lesion | 5.73 | 4.07 | |
| 8 | No active focal index lesion | n/a | n/a | |
| 9 | Left upper lobe lung lesion | 3.32 | 2.31 | |
| 10 | Right temporal lobe brain lesion | 15.36 | 6.63 | |
| 11 | No active focal index lesion | n/a | n/a | |
| 12 | T2 vertebral bone lesion | 6.22 | 3.55 | |
| 13 | Right scapular lesion | 8.40 | 3.36 | |
| 14 | Right lung lesion | 4.64 | 2.97 | |
| 6.03 | 3.38 | Mean | ||
| 3.74 | 1.40 | SD |
| mSv/MBq | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | COV (%) | |
| Adrenals | 7.55 × 10−1 | 5.06 × 10−2 | 6.70 |
| Brain | 4.50 × 10−1 | 5.79 × 10−2 | 12.86 |
| Breasts | 5.11 × 10−1 | 4.93 × 10−2 | 9.65 |
| Gallbladder Wall | 7.86 × 10−1 | 5.57 × 10−2 | 7.09 |
| LLI Wall | 6.08 × 10−1 | 6.52 × 10−2 | 10.72 |
| Small Intestine | 6.47 × 10−1 | 6.29 × 10−2 | 9.73 |
| Stomach Wall | 6.56 × 10−1 | 5.71 × 10−2 | 8.70 |
| ULI Wall | 6.47 × 10−1 | 6.07 × 10−2 | 9.38 |
| Heart Wall | 1.52 × 100 | 2.88 × 10−1 | 19.00 |
| Kidneys | 1.09 × 100 | 2.04 × 10−1 | 18.71 |
| Liver | 1.28 × 100 | 2.12 × 10−1 | 16.56 |
| Lungs | 1.74 × 100 | 3.88 × 10−1 | 22.29 |
| Muscle | 5.43 × 10−1 | 5.57 × 10−2 | 10.24 |
| Ovaries | 6.31 × 10−1 | 6.55 × 10−2 | 10.37 |
| Pancreas | 7.60 × 10−1 | 5.50 × 10−2 | 7.24 |
| Red Marrow | 5.37 × 10−1 | 4.45 × 10−2 | 8.29 |
| Osteogenic Cells | 7.63 × 10−1 | 1.00 × 10−1 | 13.11 |
| Skin | 4.09 × 10−1 | 5.22 × 10−2 | 12.77 |
| Spleen | 1.05 × 100 | 3.55 × 10−1 | 33.70 |
| Testes | 4.95 × 10−1 | 6.03 × 10−2 | 12.19 |
| Thymus | 6.87 × 10−1 | 6.00 × 10−2 | 8.74 |
| Thyroid | 5.52 × 10−1 | 5.96 × 10−2 | 10.81 |
| Urinary Bladder Wall | 5.86 × 10−1 | 6.08 × 10−2 | 10.37 |
| Uterus | 6.33 × 10−1 | 6.55 × 10−2 | 10.35 |
| Total Body | 5.89 × 10−1 | 6.16 × 10−2 | 10.45 |
| Effective Dose | 7.72 × 10−1 | 5.49 × 10−2 | 7.11 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grudzinski, J.J.; Hall, L.T.; Cho, S.; Liu, G.; Traynor, A.; Lee, M.H.; Longino, M.; Pinchuk, A.; Jaskowiak, C.; Bednarz, B.; et al. Clinical Imaging and Dosimetry of a Pan-Cancer Targeting Alkylphosphocholine Analog, [124I]I-NM404. Radiation 2022, 2, 215-227. https://doi.org/10.3390/radiation2020015
Grudzinski JJ, Hall LT, Cho S, Liu G, Traynor A, Lee MH, Longino M, Pinchuk A, Jaskowiak C, Bednarz B, et al. Clinical Imaging and Dosimetry of a Pan-Cancer Targeting Alkylphosphocholine Analog, [124I]I-NM404. Radiation. 2022; 2(2):215-227. https://doi.org/10.3390/radiation2020015
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrudzinski, Joseph J., Lance T. Hall, Steve Cho, Glenn Liu, Anne Traynor, Matthew H. Lee, Marc Longino, Anatoly Pinchuk, Christine Jaskowiak, Bryan Bednarz, and et al. 2022. "Clinical Imaging and Dosimetry of a Pan-Cancer Targeting Alkylphosphocholine Analog, [124I]I-NM404" Radiation 2, no. 2: 215-227. https://doi.org/10.3390/radiation2020015
APA StyleGrudzinski, J. J., Hall, L. T., Cho, S., Liu, G., Traynor, A., Lee, M. H., Longino, M., Pinchuk, A., Jaskowiak, C., Bednarz, B., Weichert, J., & Kuo, J. S. (2022). Clinical Imaging and Dosimetry of a Pan-Cancer Targeting Alkylphosphocholine Analog, [124I]I-NM404. Radiation, 2(2), 215-227. https://doi.org/10.3390/radiation2020015






