Physiological Effects of Low Salinity Exposure on Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Sample Collection and Processing
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Blood Analysis Results
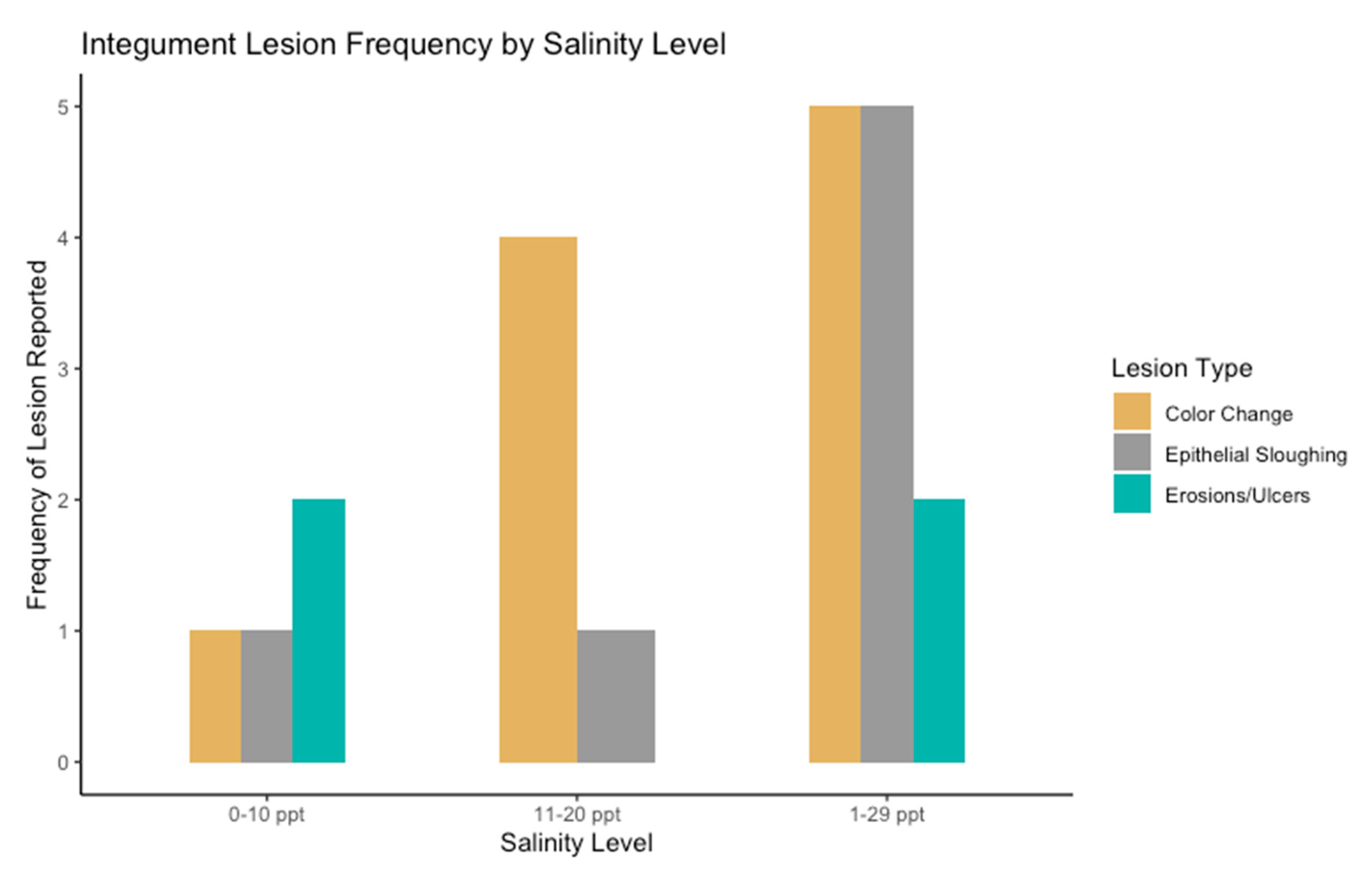
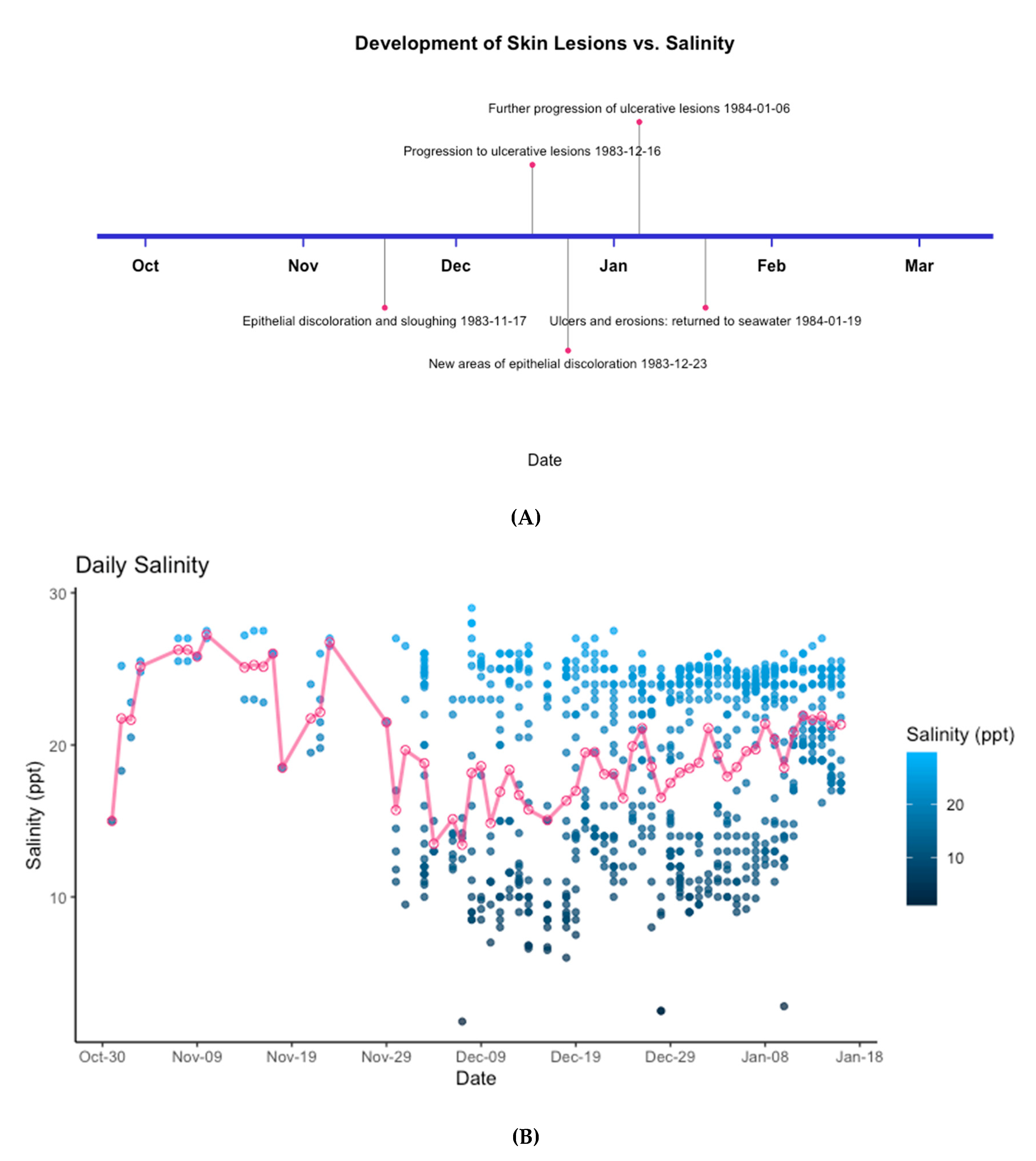
3.2. Epidermal Assessment
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sowa, S. Sighting Aggregations for Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) in the Lower St. Johns River Basin N. Florida, USA. Master’s Thesis, Jacksonville University, Jacksonville, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- McDonald, T.L.; Hornsby, F.E.; Speakman, T.R.; Zolman, E.S.; Mullin, K.D.; Sinclair, C.; Rosel, P.E.; Thomas, L.; Schwake, L.H. Survival, density, and abundance of common bottlenose dolphins in Barataria Bay (USA) following the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Endanger. Species Res. 2017, 33, 193–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deming, A.C.; Wingers, N.L.; Moore, D.P.; Rotstein, D.; Wells, R.S.; Ewing, R.; Hodanbosi, M.R.; Carmichael, R.H. Health impacts and recovery from prolonged freshwater exposure in a Common bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus). Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, F.G. Marine Mammals and Man: The Navy’s porpoises and Sea Lions. R.B.; Luce: New York, NY, USA, 1973; p. 50. [Google Scholar]
- Hornsby, F.E.; McDonald, T.L.; Balmer, B.C.; Speakman, T.R.; Mullin, K.D.; Rosel, P.E.; Wells, R.S.; Telander, A.C.; Marcy, P.W.; Klaphake, K.C.; et al. Using salinity to identify common bottlenose dolphin habitat in Barataria Bay, Louisiana, USA. Endanger. Species Res. 2017, 33, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewing, R.Y.; Mase-Guthrie, B.; McFee, W.; Townsend, F.; Manire, C.A.; Walsh, M.; Borkowski, R.; Bossart, G.D.; Schaefer, A.M. Evaluation of Serum for Pathophysiological Effects of Prolonged Low Salinity Water Exposure in Displaced Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncates). Front Vet Sci 2017, 4, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridgway, S.H. The bottlenosed dolphin in biomedical research. In Methods of animal experimentation; Gay, W.I., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1968; Volume III, pp. 387–440. [Google Scholar]
- Ridgway, S.H. Homeostasis in the aquatic environment. In Mammals of the Sea: Biology and Medicine; Ridgway, S.H., Ed.; Charles C Thomas: Springfield, IL, USA, 1972; pp. 611–612. [Google Scholar]
- Rash, R.; Lillywhite, H.B. Drinking behaviors and water balance in marine vertebrates. Mar. Biol. 2019, 166, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, R.M.; Worthy, G.A.J.; MacKenzie, D.S. Osmoregulation in Wild and Captive West Indian Manatees (Trichechus manatus). Physiol. Zool. 1998, 71, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telfer, N.; Cornell, L.H.; Prescott, J.H. Do dolphins drink water? JAVMA 1970, 157, 555–558. [Google Scholar]
- Malvin, R.L.; Ridgway, S.H.; Cornell, L. Renin and aldosterone levels in dolphins and sea lions. Exp. Biol. Med. 1978, 157, 665–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, S.; Crocker, D.; Houser, D.; Mashburn, K. Stress physiology in marine mammals: How well do they fit the terrestrial model? J. Comp. Physiol. B 2015, 185, 463–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridgway, S.; Venn-Watson, S. Effects of fresh and seawater ingestion on osmoregulation in Atlantic bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus). J. Comp. Physiol. B 2010, 180, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahay, M.; Sahay, R. Hyponatremia: A practical approach. Indian J. Endocr. Metab. 2014, 18, 760–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adrogue, H.J.; Madias, N.E. Hyponatremia. Prim. Care 2000, 342, 1581–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruce, R.C.; Kliegman, R.M. Hyponatremic seizures secondary to oral water intoxication in infancy: Association with commercial bottled drinking water. Pediatrics 1997, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, J.G.; Gardner, M.B. Comparative microscopic anatomy of selected marine mammals. In Mammals of the Sea: Biology and Medicine; Ridgway, S.H., Ed.; Thomas: Springfield, IL, USA, 1972; pp. 298–418. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, P.M.; Hammond, P.S. The Use of Photography to Monitor Dermal Disease in Wild Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus). AMBIO 1992, 21, 135–137. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, B.; Arnold, H.; Bearzi, G.; Fortuna, C.M.; Gaspar, R.; Ingram, S.; Liret, C.; Pribanic, S.; Read, A.J.; Ridoux, V.; et al. Epidermal diseases in bottlenose dolphins: Impacts of natural and anthropogenic factors. P. Roy. Soc. B 1999, 266, 1077–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, F.I., Jr. Prolonged Freshwater Exposure. In Atlas of Skin Diseases of Small Cetaceans; Townsend, F.I., Jr., Staggs, L., Eds.; Forrest I. Townsend: Fort Walton Beach, FL, USA, 2020; pp. 94–97. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, R.J.; Thurley, K.W. Structure of the epidermis in Tursiops, Delphinus, Orcinus and Phocoena in Functional Anatomy of Marine Mammals; Harrison, R.J., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1974; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Colbert, A.A.; Scott, G.I.; Fulton, M.H.; Wirth, E.F.; Daugomah, J.W.; Key, P.B.; Strozier, E.D.; Galloway, S.B. Investigation of Unusual Mortalities of Bottlenose Dolphins along the Mid-Texas Coastal Bay Ecosystem during 1992; NOAA Technical Report NMFS 147; U.S. Department of Commerce: Seattle, WA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Fazioli, K.; Mintzer, V. Short-term effects of Hurricane Harvey on bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) in Upper Galveston Bay, TX. Estuaries Coasts 2017, 43, 1013–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyronnin, N.S.; Caffey, R.H.; Cowan, J.H., Jr.; Justic, D.; Kolker, A.S.; Laska, S.B.; McCorquodale, A.; Meancon, E., Jr.; Nyman, J.A.; Twilley, R.R. Optimizing sediment diversion operations: Working group recommendations for integrating complex ecological and social landscape interactions. Water 2017, 9, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cable, J.E.; Swenson, E.M.; Snedden, A.G.; Swarzzenski, C.M. Surface Water Hydrology in Upper Breton Sound Basin, Louisiana: Effects of the Caernarvon Freshwater Diversion and Hydrologic Characterization and Monitoring of Flow Dynamics in Breton Sound: Numan; Coastal Restoration Division Louisiana Department of Natural Resources Technical Report 2503-03-45; Louisiana Department of Natural Resources: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 5 March 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Mullin, K.D.; Barry, K.; Sinclair, C.; Litz, J.; Maze-Foley, K.; Fougeres, E.; Mase-Guthrie, B.; Ewing, R.; Gorgone, A.; Adams, J.; et al. Common Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) in Lake Pontchartrain, Louisiana: 2007 to Mid-2014; NOAA Technical Memorandum NMFS-SEFSC-673; National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration National Marine Fisheries Service: Pascagoula, MS, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ridgway, S.H.; Simpson, J.G.; Patton, G.S.; Gilmartin, G. Hematologic findings in certain small cetaceans. JAVMA 1970, 157, 566–575. [Google Scholar]
- Worthley, L.I.; Guerin, M.; Pain, R.W. For calculating osmolality, the simplest formula is the best. Anaesth. Intens. Care 1987, 15, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 20 March 2020).
- RStudio Team. Rstudio: Integrated Development for R, version 1.2.5019, “Elderflower”; RStudio, Inc.: Boston, MS, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, D.; Maechler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, A.; Brockhoff, P.B.; Christensen, R.H.B. lmerTest package: Tests in linear mixed effects models. J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 82, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.H.; Dunn, R.J. Physiology, Aldosterone. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470339/ (accessed on 20 March 2020).
- McClain, A.M.; Daniels, R.; Gomez, F.M.; Ridgway, S.; Schwacke, L.; Jensen, E.D.; Smith, C.R. The Effects of Low Salinity Environmental Exposures on Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) (NIWC Technical Report); Naval Information Warfare Center: San Diego, CA, USA, 2020; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Houser, D.S.; Yeates, L.C.; Crocker, D.E. Cold stress induces an adrenocortical response in bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus). J. Zoo Wildlife Med. 2011, 42, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Champagne, C.D.; Kellar, N.M.; Trego, M.L.; Delehanty, B.; Boonstra, R.; Wasser, S.K.; Booth, R.K.; Crocker, D.E.; Houser, D.S. Comprehensive endocrine response to acute stress in the bottlenose dolphin from serum, blubber, and feces. Gen. Comp. Endocr. 2018, 266, 178–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwacke, L.H.; Smith, C.R.; Townsend, F.I.; Wells, R.S.; Hart, L.B.; Balmer, B.C.; Collier, T.K.; De Guise, S.; Fry, M.M.; Guillette, L.J., Jr.; et al. Health of Common Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) in Barataria Bay, Louisiana, Following the Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill. Environ. Sci. Tech. 2013, 48, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venn-Watson, S.; Colegrove, K.M.; Litz, J.; Kinsel, M.; Terio, K.; Saliki, J.; Fire, S.; Carmichael, R.; Chevis, C.; Hatchett, W.; et al. Adrenal Gland and Lung Lesions in Gulf of Mexico Common Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) Found Dead Following the Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venn-Watson, S.; Jensen, E.D.; Ridgway, S.H. Effects of age and sex on clinicopathologic reference ranges in a healthy managed Atlantic bottlenose dolphin population. JAVMA 2007, 231, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, C. Urea and the Clinical Value of Measuring Blood Urea Concentration. Available online: https://acutecaretesting.org/en/articles/urea-and-the-clinical-value-of-measuring-blood-urea-concentration (accessed on 26 March 2020).
- Seifter, J.L.; Chang, H.Y. Disorders of Acid-Base Balance: New Perspectives. Kidney Dis. 2017, 2, 170–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
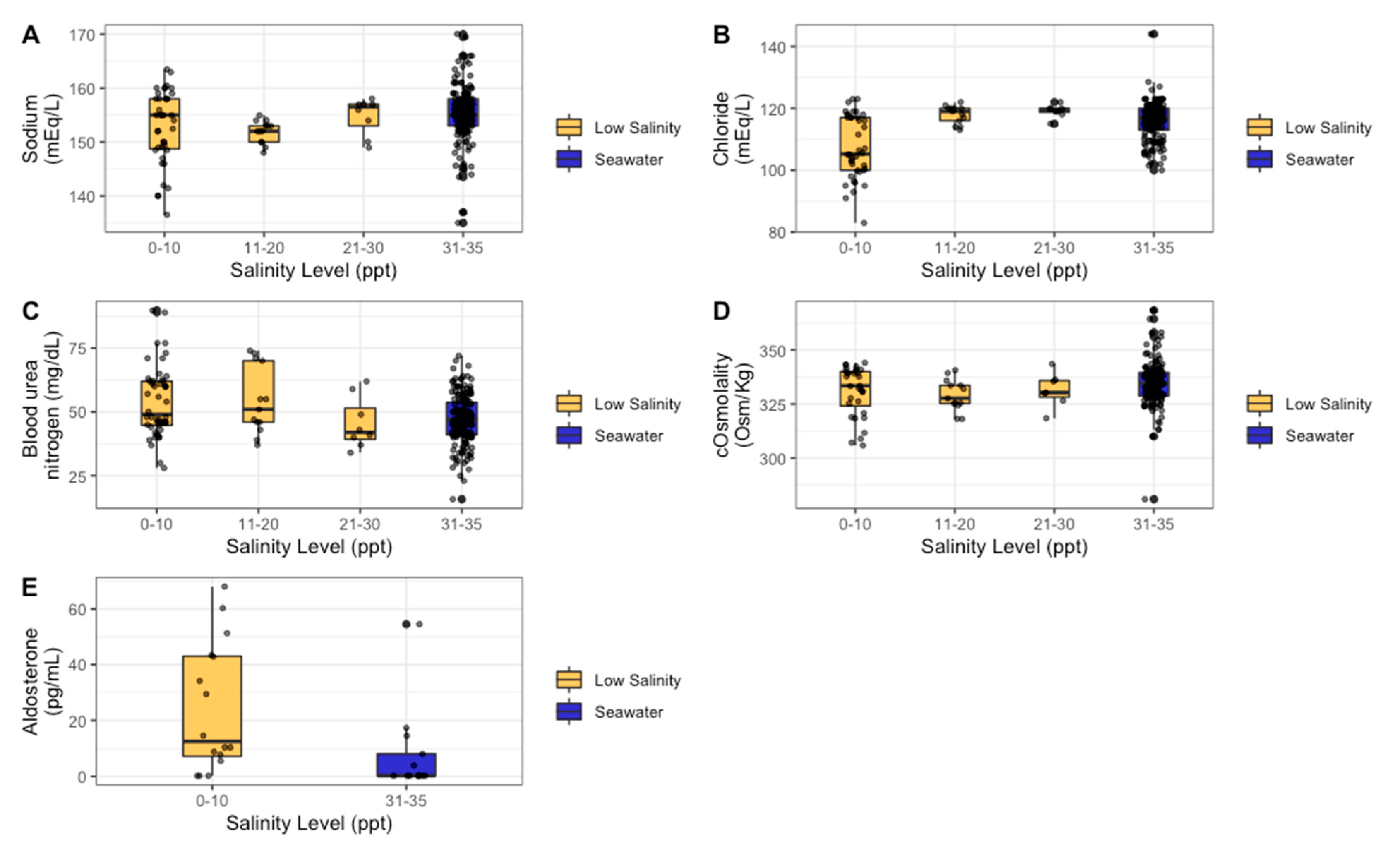
| Analyte | Salinity | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| p-Value | p-Value | |
| Sodium | 0.001 * | 0.719 |
| Chloride | <0.001 * | 0.501 |
| Blood Urea Nitrogen | <0.001 * | 0.683 |
| Aldosterone | 0.018 * | 0.891 |
| Calculated osmolality | 0.043 * | 0.941 |
| Potassium | 0.130 | 0.570 |
| Phosphorus | 0.175 | 0.139 |
| Glucose | 0.927 | 0.109 |
| Creatinine | 0.081 | 0.901 |
| Cortisol | 0.263 | 0.075 |
| Analyte | Units | Category | Salinity Range | Average Change in Analyte Compared to Controls | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium | mEq/L | 1 | 0–10 ppt | −3.85 | <0.001 * |
| 2 | 11–20 ppt | −3.34 | 0.018 * | ||
| 3 | 21–30 ppt | −0.79 | 0.674 | ||
| Chloride | mEq/L | 1 | 0–10 ppt | −8.43 | <0.001 * |
| 2 | 11–20 ppt | −0.33 | 0.830 | ||
| 3 | 21–30 ppt | −1.54 | 0.495 | ||
| Potassium | mEq/L | 1 | 0–10 ppt | −0.04 | 0.484 |
| 2 | 11–20 ppt | 0.09 | 0.388 | ||
| 3 | 21–30 ppt | 0.27 | 0.041* | ||
| Blood Urea Nitrogen | mg/dL | 1 | 0–10 ppt | 8.69 | <0.001 * |
| 2 | 11–20 ppt | 7.31 | 0.007 * | ||
| 3 | 21–30 ppt | 2.33 | 0.591 | ||
| Calculated osmolality | cOsm/Kg | 1 | 0–10 ppt | −7.26 | 0.012 * |
| 2 | 11–20 ppt | −4.33 | 0.142 | ||
| 3 | 21–30 ppt | −2.64 | 0.537 | ||
| Glucose | mg/dL | 1 | 0–10 ppt | 2.47 | 0.599 |
| 2 | 11–20 ppt | −0.07 | 0.735 | ||
| 3 | 21–30 ppt | 1.91 | 0.900 | ||
| Phosphorus | mg/dL | 1 | 0–10 ppt | 0.27 | 0.145 |
| 2 | 11–20 ppt | −0.58 | 0.106 | ||
| 3 | 21-30 ppt | −0.08 | 0.661 | ||
| Creatinine | mg/dL | 1 | 0–10 ppt | −0.02 | 0.959 |
| 2 | 11–20 ppt | −0.08 | 0.047 * | ||
| 3 | 21–30 ppt | −0.16 | 0.010 * | ||
| Aldosterone | pg/mL | 1 | 0–10 ppt | 3.1 times greater than seawater values | 0.018 * |
| Cortisol | mcg/dL | 1 | 0–10 ppt | 1.27 times greater than seawater values | 0.263 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
McClain, A.M.; Daniels, R.; Gomez, F.M.; Ridgway, S.H.; Takeshita, R.; Jensen, E.D.; Smith, C.R. Physiological Effects of Low Salinity Exposure on Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus). J. Zool. Bot. Gard. 2020, 1, 61-75. https://doi.org/10.3390/jzbg1010005
McClain AM, Daniels R, Gomez FM, Ridgway SH, Takeshita R, Jensen ED, Smith CR. Physiological Effects of Low Salinity Exposure on Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus). Journal of Zoological and Botanical Gardens. 2020; 1(1):61-75. https://doi.org/10.3390/jzbg1010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcClain, Abby M., Risa Daniels, Forrest M. Gomez, Sam H. Ridgway, Ryan Takeshita, Eric D. Jensen, and Cynthia R. Smith. 2020. "Physiological Effects of Low Salinity Exposure on Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus)" Journal of Zoological and Botanical Gardens 1, no. 1: 61-75. https://doi.org/10.3390/jzbg1010005
APA StyleMcClain, A. M., Daniels, R., Gomez, F. M., Ridgway, S. H., Takeshita, R., Jensen, E. D., & Smith, C. R. (2020). Physiological Effects of Low Salinity Exposure on Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus). Journal of Zoological and Botanical Gardens, 1(1), 61-75. https://doi.org/10.3390/jzbg1010005





