IFN-τ Modulates PBMC Cytokine Profile and T Cell Phenotype to Improve Endometrial Immune Composition in the Implantation Window: A Combined In Vitro and In Vivo Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
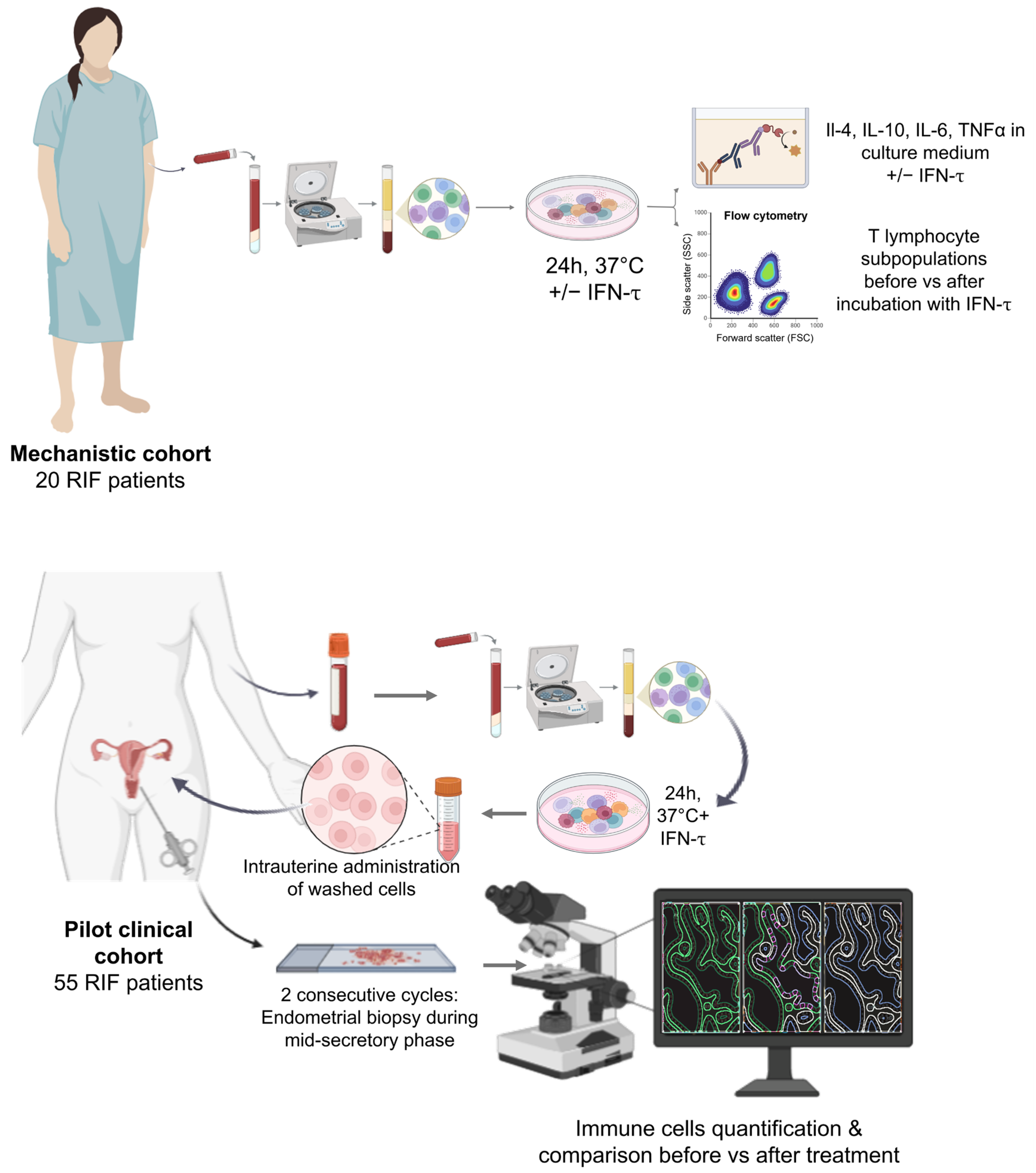
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Autologous Immune Cell Isolation and Modulation
2.3. Cytokine Quantification
2.4. T Subpopulations Phenotyping
2.5. Endometrial Sample Collection and Processing
2.6. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
2.7. Image Acquisition and Quantitative IHC Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. In Vitro Experiments
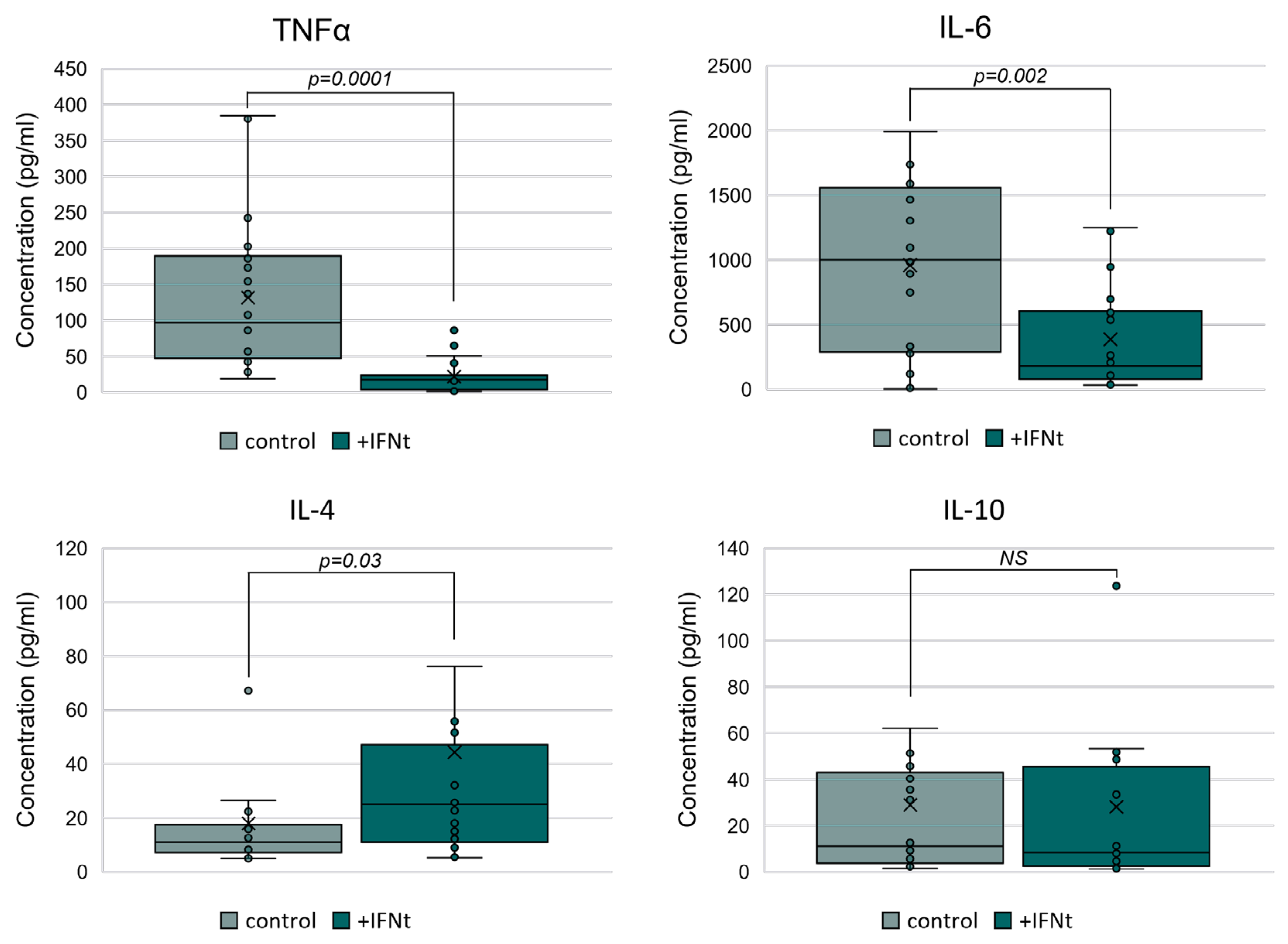
3.2.1. IFN-τ Modulates Cytokine Secretion in PBMCs Toward a Th2 Profile
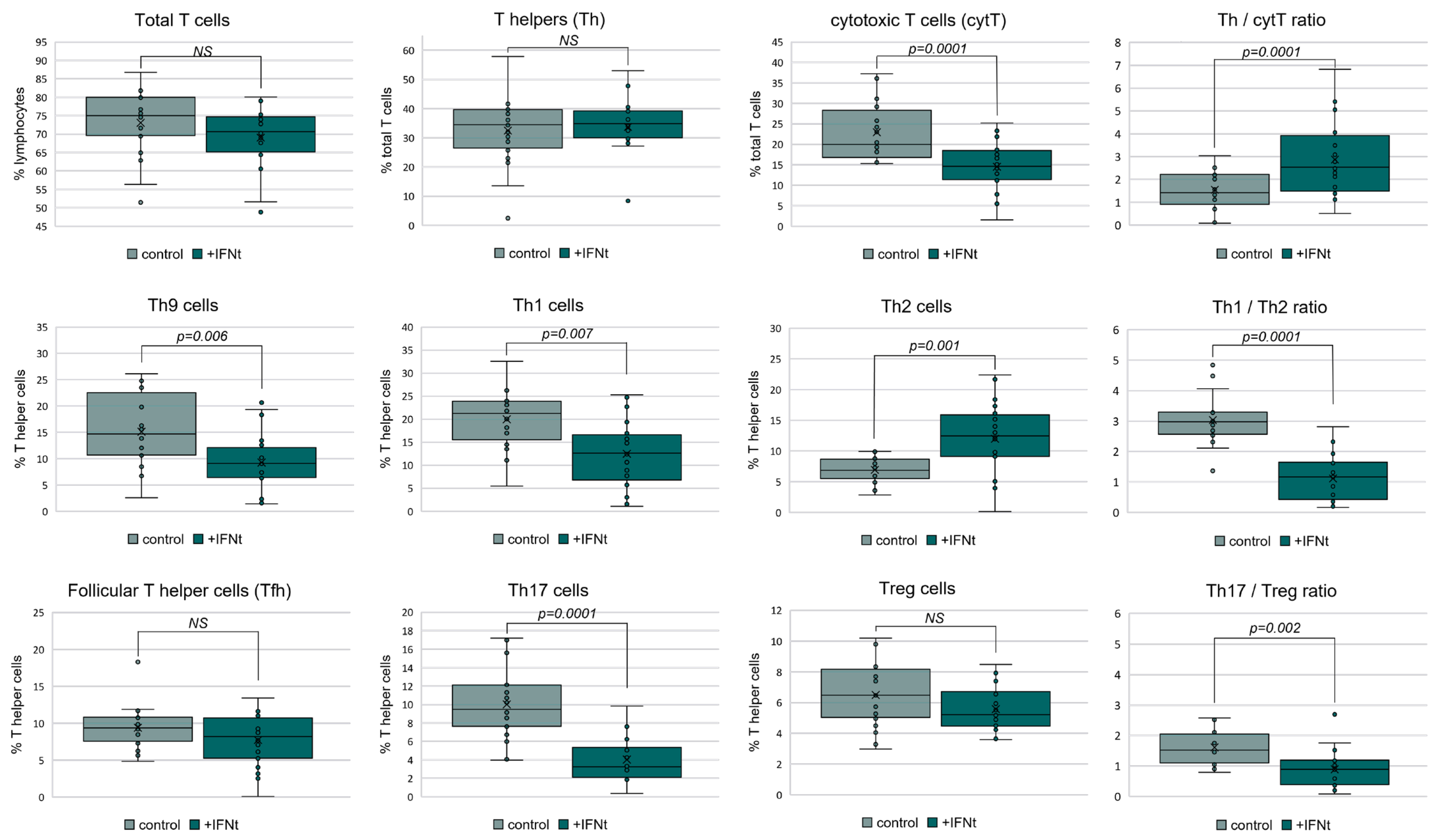
3.2.2. IFN-τ Alters T Cell Subpopulation Profiles in PBMCs
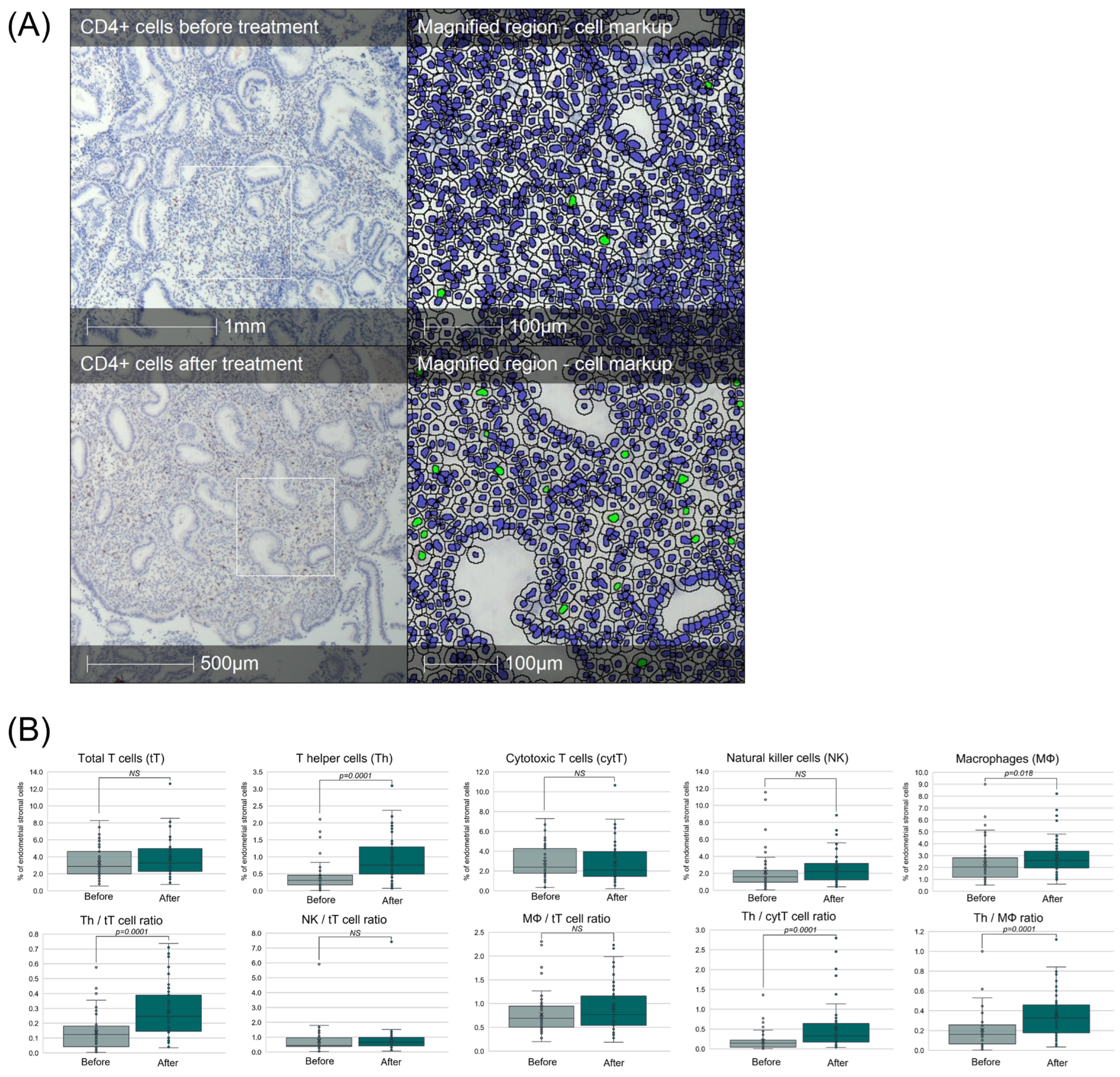
3.3. Intrauterine Administration of IFN-τ-Modulated PBMCs Enhances Endometrial Immune Composition
3.4. Safety and Tolerability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PBMC | Peripheral blood mononuclear cells |
| IFN-τ | Interferon τ |
| hCG | human chorionic gonadotropin |
| RIF | Recurrent implantation failure |
| ART | Assisted reproductive therapy |
| Th | T helper lymphocyte |
| cytT | Cytotoxic T cell |
| Tfh | Follicular T helper |
| Treg | Regulatory T cell |
| IL- | Interleukin- |
| TNFα | Tumor necrosis factor α |
References
- Robertson, S.A.; Moldenhauer, L.M.; Green, E.S.; Care, A.S.; Hull, M.L. Immune determinants of endometrial receptivity: A biological perspective. Fertil. Steril. 2022, 117, 1107–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, S. Role of immune cells in the establishment of implantation and maintenance of pregnancy and immunomodulatory therapies for patients with repeated implantation failure and recurrent pregnancy loss. Reprod. Med. Biol. 2024, 23, e12600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Guo, A.; Yang, F.; Li, L.; Yan, J.; Deng, X.; Dai, C.; Li, Y. Alterations of Cytokine Profiles in Patients With Recurrent Implantation Failure. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 949123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, S.; Nakashima, A.; Shima, T.; Ito, M. Th1/Th2/Th17 and regulatory T-cell paradigm in pregnancy. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2010, 63, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccinni, M.P.; Raghupathy, R.; Saito, S.; Szekeres-Bartho, J. Cytokines, Hormones and Cellular Regulatory Mechanisms Favoring Successful Reproduction. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 717808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccinni, M.P.; Lombardelli, L.; Logiodice, F.; Kullolli, O.; Romagnani, S.; Le Boulteiller, P. T helper cell mediated-tolerance towards fetal allograft in successful pregnancy. Clin. Mol. Allergy 2015, 13, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, S.; Yang, J.; Zhang, K.; Feng, X.; Sun, C.; Feng, Q.; Li, Z. Associations of Th1, Th2, Th17, and Treg cell levels and imbalance with recurrent spontaneous abortion: A meta-analysis. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2025, 51, e16207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleiveland, C.R. Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells. In The Impact of Food Bioactives on Health: In Vitro and Ex Vivo Models; Verhoeckx, K., Cotter, P., López-Expósito, I., Kleiveland, C., Lea, T., Mackie, A., Requena, T., Swiatecka, D., Wichers, H., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Chapter 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Diao, L.; Huang, C.; Li, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Kwak-Kim, J.Y.H. The role of decidual immune cells on human pregnancy. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2017, 124, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.; Zhang, B.; Xu, M.; Wang, S.; Liu, R.; Wu, J.; Yang, J.; Feng, L. Intrauterine administration of autologous peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) activated by HCG improves the implantation and pregnancy rates in patients with repeated implantation failure: A prospective randomized study. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2016, 76, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakin, K.; Oktem, O.; Urman, B. Intrauterine administration of peripheral mononuclear cells in recurrent implantation failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busnelli, A.; Somigliana, E.; Cirillo, F.; Baggiani, A.; Levi-Setti, P.E. Efficacy of therapies and interventions for repeated embryo implantation failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yuan, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Tang, Y.; Sui, X.; Yin, P.; Yang, D. The effectiveness of immunomodulatory therapies for patients with repeated implantation failure: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Wen, L.; Lv, X.; Tang, N.; Yuan, Y. Comparative efficacy of intrauterine infusion treatments for recurrent implantation failure: A network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2025, 42, 1177–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumacher, A.; Zenclussen, A.C. Human Chorionic Gonadotropin-Mediated Immune Responses That Facilitate Embryo Implantation and Placentation. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, N.; Yan, W.; Yin, T.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, D.; Xu, M.; Ding, J.; Yang, J. HCG-Activated Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMC) Promote Trophoblast Cell Invasion. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murira, A.; Lamarre, A. Type-I Interferon Responses: From Friend to Foe in the Battle against Chronic Viral Infection. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graber, J.; Dhib-Jalbut, S. Interferons. In Encyclopedia of the Neurological Sciences, 2nd ed.; Aminoff, M.J., Daroff, R.B., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2014; pp. 718–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazer, F.W.; Thatcher, W.W. Chronicling the discovery of interferon tau. Reproduction 2017, 154, F11–F20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Gong, M.; Zhao, F.; Shao, J.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, H. Type I Interferons: Distinct Biological Activities and Current Applications for Viral Infection. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 51, 2377–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Effects of Intrauterine Administration of Autologous PBMC Modulated With IFNτ on Endometrial Cell Populations, NCT05775211. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05775211 (accessed on 27 July 2025).
- Wang, W.; Sung, N.; Gilman-Sachs, A.; Kwak-Kim, J. T Helper (Th) Cell Profiles in Pregnancy and Recurrent Pregnancy Losses: Th1/Th2/Th9/Th17/Th22/Tfh Cells. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y.; Guo, S.; Zhao, G.; Wu, H.; Deng, G. Protective Effects of Interferon-tau Against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Embryo Implantation Failure in Pregnant Mice. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2018, 38, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soos, J.M.; Stüve, O.; Youssef, S.; Bravo, M.; Johnson, H.M.; Weiner, H.L.; Zamvil, S.S. Cutting edge: Oral type I IFN-tau promotes a Th2 bias and enhances suppression of autoimmune encephalomyelitis by oral glatiramer acetate. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 2231–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, K.; Nakagawa, K.; Horikawa, T.; Moriyama, A.; Ojiro, Y.; Takamizawa, S.; Ochiai, A.; Matsumura, Y.; Ikemoto, Y.; Yamaguchi, K.; et al. Increasing number of implantation failures and pregnancy losses associated with elevated Th1/Th2 cell ratio. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2021, 86, e13429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdiaki, A.; Vergadi, E.; Makrygiannakis, F.; Vrekoussis, T.; Makrigiannakis, A. Repeated implantation failure is associated with increased Th17/Treg cell ratio, during the secretory phase of the human endometrium. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2024, 161, 104170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganeva, R.; Parvanov, D.; Vidolova, N.; Ruseva, M.; Handzhiyska, M.; Arsov, K.; Decheva, I.; Metodiev, D.; Moskova-Doumanova, V.; Stamenov, G. Endometrial immune cell ratios and implantation success in patients with recurrent implantation failure. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2023, 156, 103816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lédée, N.; Petitbarat, M.; Chevrier, L.; Vitoux, D.; Vezmar, K.; Rahmati, M.; Dubanchet, S.; Gahéry, H.; Bensussan, A.; Chaouat, G. The uterine immune profile may help women with repeated unexplained embryo implantation failure after in vitro fertilization. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2016, 75, 388–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Ren, J.; Zhang, T.; Jia, Y.; Han, H.; Shen, H. Immunoregulatory therapy improves live birth in Th17/Treg-cell-elevated women with embryo transfer failure. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. 2023, 161, 1101–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lédée, N.; Petitbarat, M.; Dray, G.; Chevrier, L.; Kazhalawi, A.; Rahmati, M.; Vicaut, E.; Diallo, A.; Cassuto, N.G.; Ruoso, L.; et al. Endometrial immune profiling and precision therapy increase live birth rate after embryo transfer: A randomised controlled trial. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1523871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Tan, X.; He, T. Macrophage polarization disorder in the endometrial immune microenvironment may contribute to recurrent implantation failure. Reprod. Dev. Med. 2024, 8, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Song, M.; Sun, L.; Zou, H.; Yang, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y. Interferon Tau Alleviates Obesity-Induced Adipose Tissue Inflammation and Insulin Resistance by Regulating Macrophage Polarization. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Yang, C.; Wang, T.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, H.; Ma, B.; Xu, M.; Deng, G. IFN-τ Maintains Immune Tolerance by Promoting M2 Macrophage Polarization via Modulation of Bta-miR-30b-5p in Early Uterine Pregnancy in Dairy Cows. Cells 2025, 14, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitawaki, Y.; Horie, A.; Ikeda, A.; Shitanaka, S.; Yanai, A.; Ohara, T.; Nakakita, B.; Sagae, Y.; Okunomiya, A.; Tani, H.; et al. Intrauterine administration of peripheral blood mononuclear cells helps manage recurrent implantation failure by normalizing dysregulated gene expression including estrogen-responsive genes in mice. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaney, H.L.; Grose, L.F.; Charpigny, G.; Behura, S.K.; Sheldon, I.M.; Cronin, J.G.; Lonergan, P.; E Spencer, T.; Mathew, D.J. Conceptus-induced, interferon tau-dependent gene expression in bovine endometrial epithelial and stromal cells. Biol. Reprod. 2021, 104, 669–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casano, A.B.; Barile, V.L.; Menchetti, L.; Guelfi, G.; Brecchia, G.; Agradi, S.; De Matteis, G.; Scatà, M.C.; Grandoni, F.; Barbato, O. Interferon Tau (IFNt) and Interferon-Stimulated Genes (ISGs) Expression in Peripheral Blood Leukocytes and Correlation with Circulating Pregnancy-Associated Glycoproteins (PAGs) during Peri-Implantation and Early Pregnancy in Buffalo Cows. Animals 2022, 12, 3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villarino, A.V.; Gallo, E.; Abbas, A.K. STAT1-activating cytokines limit Th17 responses through both T-bet-dependent and -independent mechanisms. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 6461–6471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, B.; Chang, E.Y.; Cheng, G. The type I IFN induction pathway constrains Th17-mediated autoimmune inflammation in mice. J. Clin. Invest. 2008, 118, 1680–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadreev, I.I.; Chen, M.Z.Q.; Umezawa, Y.; Kajimoto, T.; Li, X.; Okuda, K.; Ishihara, T.; Okamura, H.; O’Shea, J.J.; Koga, T.; et al. The Competitive Nature of Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription Complex Formation Drives Phenotype Switching of T Cells. Immunology 2018, 153, 488–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | In Vitro Cohort (n = 20) | Clinical Cohort (n = 55) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 39.8 ± 5.3 | 38.4 ± 6.2 | NS |
| Type of infertility | NS | ||
| Primary (n, %) | 11 (55%) | 32 (58%) | |
| Secondary (n, %) | 9 (45%) | 23 (42%) | |
| Previous IVF attempts (n) | 3.0 ± 0.9 | 3.1 ± 1.0 | NS |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruseva, M.; Parvanov, D.; Ganeva, R.; Handzhiyska, M.; Safir, J.; Metodiev, D.; Stamenov, G.; Hadjidekova, S. IFN-τ Modulates PBMC Cytokine Profile and T Cell Phenotype to Improve Endometrial Immune Composition in the Implantation Window: A Combined In Vitro and In Vivo Study. Immuno 2025, 5, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5040051
Ruseva M, Parvanov D, Ganeva R, Handzhiyska M, Safir J, Metodiev D, Stamenov G, Hadjidekova S. IFN-τ Modulates PBMC Cytokine Profile and T Cell Phenotype to Improve Endometrial Immune Composition in the Implantation Window: A Combined In Vitro and In Vivo Study. Immuno. 2025; 5(4):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5040051
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuseva, Margarita, Dimitar Parvanov, Rumiana Ganeva, Maria Handzhiyska, Jinahn Safir, Dimitar Metodiev, Georgi Stamenov, and Savina Hadjidekova. 2025. "IFN-τ Modulates PBMC Cytokine Profile and T Cell Phenotype to Improve Endometrial Immune Composition in the Implantation Window: A Combined In Vitro and In Vivo Study" Immuno 5, no. 4: 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5040051
APA StyleRuseva, M., Parvanov, D., Ganeva, R., Handzhiyska, M., Safir, J., Metodiev, D., Stamenov, G., & Hadjidekova, S. (2025). IFN-τ Modulates PBMC Cytokine Profile and T Cell Phenotype to Improve Endometrial Immune Composition in the Implantation Window: A Combined In Vitro and In Vivo Study. Immuno, 5(4), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno5040051






