Health and Lifestyle of Patients with Mesothelioma: Protocol for the Help-Meso Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
Aims and Objectives
- (1)
- To describe the experiences of appetite and physical activity of PwM and attitudes towards lifestyle interventions for PwM, with views sought from patients, their informal carers and health professionals.
- (2)
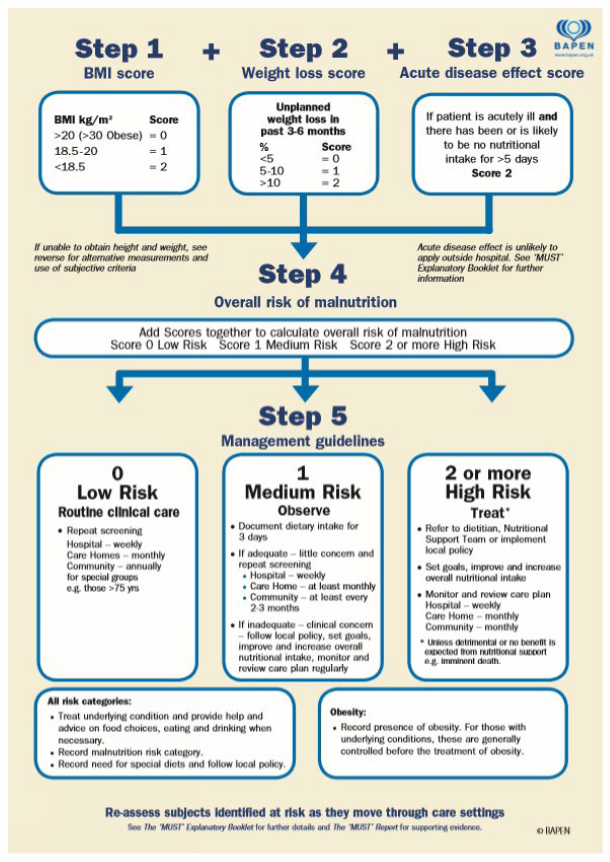
- To assess the feasibility of performing nutritional screening in PwM using the MUST. This data will be used to describe the percent of patients who are at risk of malnutrition and for whom a referral for nutritional intervention and assessment is made.
2.2. Participants
2.2.1. Sampling Technique and Identification of Participants
2.2.2. Consent
2.3. Study Interventions
2.3.1. Qualitative Data: Interviews with Patients with Mesothelioma and Informal Carers
2.3.2. Qualitative Data: Interviews with Health Professionals
2.3.3. Nutritional Screening
2.4. Data Analysis
2.5. Approvals
2.5.1. Ethical Considerations
2.5.2. Adverse Events
2.5.3. Data Handling and Storage
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Interview Schedules |
Title: What are health professionals experiences of weight loss, appetite and physical activity in patients with mesothelioma?
|
Appendix B
References
- Kidd, A.C.; Winter, A.; Miller, L.; Baird, W.; Dick, C.; Pearce, D.; Blyth, K.G. Mesothelioma is associated with ipsilateral thoracic muscle loss. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, A.M.; Power, D.G.; Daly, L.; Cushen, S.J.; Bhuachalla, Ē.N.; Prado, C.M. Cancer-associated malnutrition, cachexia and sarcopenia: The skeleton in the hospital closet 40 years later. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2016, 75, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otten, L.; Stobäus, N.; Franz, K.; Genton, L.; Müller-Werdan, U.; Wirth, R.; Norman, K. Impact of sarcopenia on 1-year mortality in older patients with cancer. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercadante, S.; Degiovanni, D.; Casuccio, A. Symptom burden in mesothelioma patients admitted to home palliative care. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2016, 32, 1985–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, S.L.; Crist, J.D.; Shea, K.; Holland, S.; Cacchione, P.Z. The lived experience of persons with malignant pleural mesothelioma in the United States. Cancer Nurs. 2021, 44, E90–E98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finn, R.S.; Brims, F.J.; Gandhi, A.; Olsen, N.; Musk, A.W.; Maskell, N.A.; Lee, G.Y.C. Postmortem findings of malignant pleural mesothelioma: A two center study of 318 patients. Chest 2012, 142, 1267–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffery, E.; Lee, Y.C.; Newton, R.U.; Lyons-Wall, P.; McVeigh, J.; Nowak, A.K.; Cheah, H.M.; Nguyen, B.; Fitzgerald, D.B.; Creaney, J.; et al. Body composition and nutritional status in malignant pleural mesothelioma: Implications for activity levels and quality of life. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 73, 1412–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, I.; Ahmed Tipu, S.; Ishtiaq, S. Malignant mesothelioma. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 29, 1433–1438. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Woolhouse, I.; Bishop, L.; Darlison, L.; De Fonseka, D.; Edey, A.; Edwards, J.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Fennell, D.A.; Holmes, S.; Kerr, K.M.; et al. British Thoracic Society Guideline for the investigation and management of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Thorax 2018, 73, i1–i30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, P.; Merchant, Z.; Rowlinson-Groves, K.; Taylor, M.; Moore, J.; Evison, M. Feasibility and outcomes of a real-word regional lunch cancer prerehabilitation programme in the UK. Br. J. Anaesth. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faig, J.; Howard, S.; Levine, E.A.; Casselman, G.; Hesdorffer, M.; Ohar, J.A. Changing pattern in malignant mesothelioma survival. Trans. Oncol. 2015, 8, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muruganandan, S.; Jeffery, E.; McIntyre, C.; Lee, Y.G. Nutrition, exercise, and complementary medicine: Potential role in mesothelioma. Curr. Pulmonol. Rep. 2016, 5, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejegi-Memeh, S.; Sherborne, V.; Harrison, M.; Taylor, B.; Senek, M.; Tod, A.; Gardiner, C. Patients’ and informal carers’ experience of living with mesothelioma: A systematic rapid review and synthesis of the literature. Eur. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2022, 58, 102122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, S.; Darlison, L.; Tod, A.M. Living with mesothelioma. A literature review. Eur. J. Cancer Care 2010, 19, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arends, J.; Strasser, F.; Gonella, S.; Solheim, T.S.; Madeddu, C.; Ravasco, P.; Ripamonti, C.I. Cancer cachexia in adult patients: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines. ESMO Open 2021, 6, 100092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takamori, S.; Toyokawa, G.; Taguchi, K.; Edagawa, M.; Shimamatsu, S.; Toyozawa, R.; Nosaki, K.; Seto, T.; Hirai, F.; Yamaguchi, M.; et al. The controlling nutritional status score is a significant independent predictor of poor prognosis in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. Clin. Lung Cancer 2017, 18, e303–e313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The British Association for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (BAPEN). Malnutrition Universal Screening Tool. 2003. Available online: https://www.bapen.org.uk/screening-and-must/must/must-report (accessed on 6 July 2022).
- Elia, M. The ‘MUST’ Report. Nutritional Screening for Adults: A Multidisciplinary Responsibility. Development and Use of the ‘Malnutrition Universal Screening Tool’ (MUST) for Adults. British Association for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (BAPEN). 2003. Available online: https://www.bapen.org.uk/pdfs/must/must-report.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2022).
- Braun, V.; Clarke, V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual. Res. Psychol. 2016, 3, 77–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Inclusion Criteria for Each Participant Group |
|---|
| Patients |
|
| Informal carers |
|
| Health professionals |
|
| Patients | |
| 1 | A semi-structured interview to understand experiences of, and influences on, appetite, including strategies to maintain adequate food intake and attitudes toward health and lifestyle interventions. |
| 2 | A semi-structured interview to understand experiences of, and influences on, physical activity, including strategies to maintain adequate activity levels and attitudes toward lifestyle interventions. |
| 3 | Nutritional screening using the MUST tool (repeated following the guidelines). |
| 4 | A semi-structured interview following identification of change in nutritional status as identified via MUST scores. Semi-structured interviews will explore experiences of, and influences on, appetite and diet. |
| Informal Carers | |
| 1 | A semi-structured interview to understand experiences of, and influences on, appetite, including strategies to maintain adequate food intake and attitudes toward health and lifestyle interventions. |
| 2 | A semi-structured interview to understand experiences of, and influences on, physical activity, including strategies to maintain adequate activity levels and attitudes toward lifestyle interventions. |
| 3 | An optional semi-structured interview following identification of their relative’s change in nutritional status as identified via MUST scores. Semi-structured interviews will explore experiences of, and influences on, appetite and diet. |
| Health Professionals | |
| 1 | A semi-structured interview to understand experiences of nutrition, weight loss and physical activity of PwM. The semi-structured interview aims to understand health professionals’ current practice in assessing nutritional needs of patients and use of appropriate interventions. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Taylor, L.; Swainston, K.; Hurst, C.; Aujayeb, A.; Poulter, H.; Dismore, L. Health and Lifestyle of Patients with Mesothelioma: Protocol for the Help-Meso Study. J. Respir. 2022, 2, 129-138. https://doi.org/10.3390/jor2030011
Taylor L, Swainston K, Hurst C, Aujayeb A, Poulter H, Dismore L. Health and Lifestyle of Patients with Mesothelioma: Protocol for the Help-Meso Study. Journal of Respiration. 2022; 2(3):129-138. https://doi.org/10.3390/jor2030011
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaylor, Leah, Katherine Swainston, Christopher Hurst, Avinash Aujayeb, Hannah Poulter, and Lorelle Dismore. 2022. "Health and Lifestyle of Patients with Mesothelioma: Protocol for the Help-Meso Study" Journal of Respiration 2, no. 3: 129-138. https://doi.org/10.3390/jor2030011
APA StyleTaylor, L., Swainston, K., Hurst, C., Aujayeb, A., Poulter, H., & Dismore, L. (2022). Health and Lifestyle of Patients with Mesothelioma: Protocol for the Help-Meso Study. Journal of Respiration, 2(3), 129-138. https://doi.org/10.3390/jor2030011






