Programmed Cell Death in SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Short Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Apoptosis
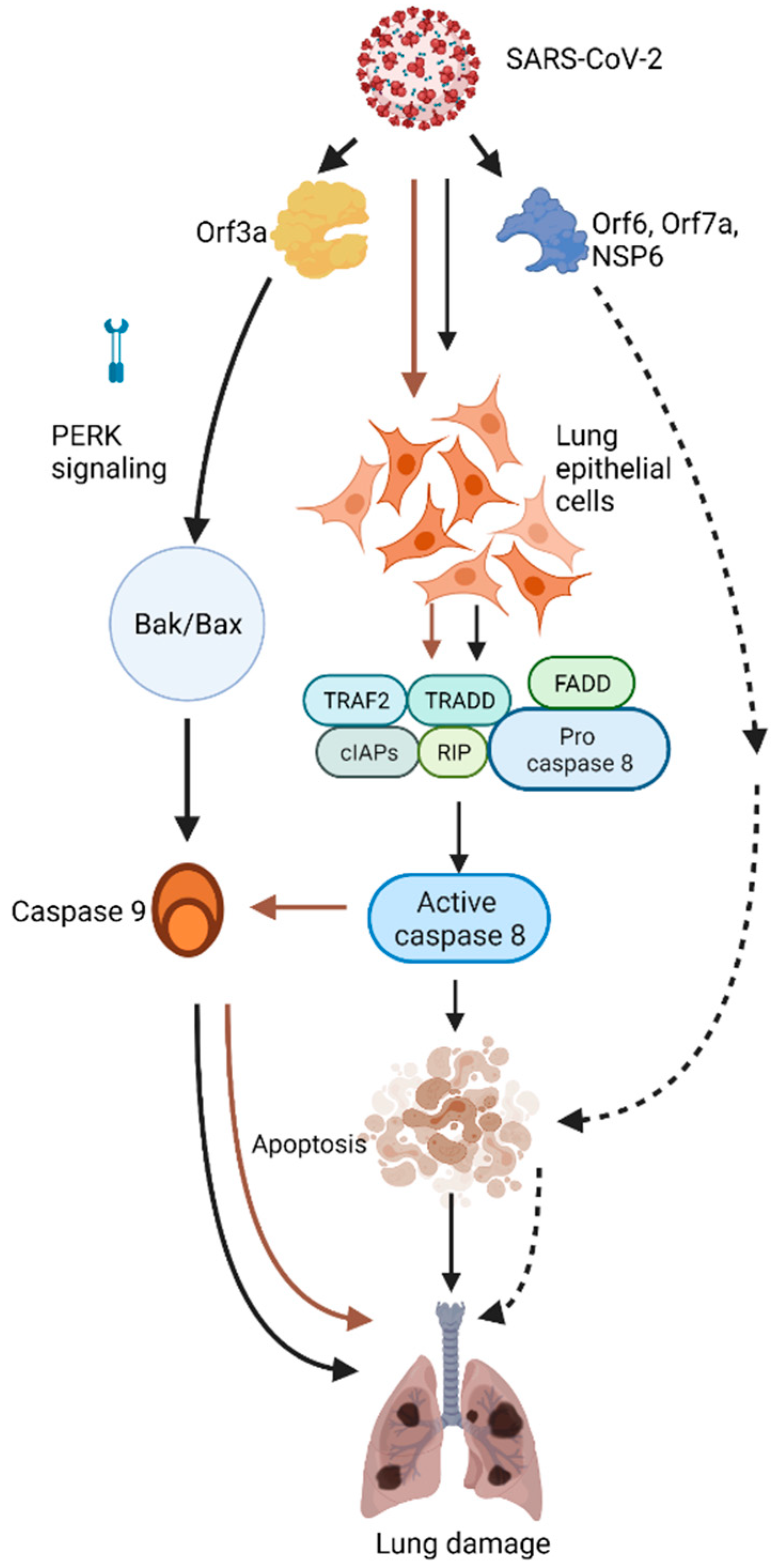
3. SARS-CoV-2 Induces Lung Epithelial Cell Apoptosis
4. The Role of Individual SARS-CoV-2 Proteins in Apoptosis
5. ORF3a
6. ORF6, NSP6, and ORF7A
7. ORF8
8. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pal, M.; Berhanu, G.; Desalegn, C.; Kandi, V. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2): An Update. Cureus 2020, 12, e7423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.X.; Liang, J.Q.; Fung, T.S. Human Coronavirus-229E, -OC43, -NL63, and -HKU1 (Coronaviridae). Encycl. Virol. 2021, 2, 428–440. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Z.W.; Yuan, S.; Yuen, K.S.; Fung, S.Y.; Chan, C.P.; Jin, D.Y. Zoonotic origins of human coronaviruses. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 1686–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshimoto, F.K. The Proteins of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 (SARS CoV-2 or n-COV19), the Cause of COVID-19. Protein J. 2020, 39, 198–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galluzzi, L.; Vitale, I.; Aaronson, S.A.; Abrams, J.M.; Adam, D.; Agostinis, P.; Alnemri, E.S.; Altucci, L.; Amelio, I.; Andrews, D.W.; et al. Molecular mechanisms of cell death: Recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2018. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 486–541. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, P.G. Viruses, apoptosis, and neuroinflammation—A double-edged sword. J. Neurovirol. 2015, 21, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, G. Host defense, viruses and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2001, 8, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fleisher, T.A. Apoptosis. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1997, 78, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Jiang, W.; Liu, Z.; Liu, S.; Liang, X. Virus Infection and Death Receptor-Mediated Apoptosis. Viruses 2017, 9, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hengartner, M.O. The biochemistry of apoptosis. Nature 2000, 407, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashkenazi, A.; Dixit, V.M. Death receptors: Signaling and modulation. Science 1998, 281, 1305–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pereira, W.O.; Amarante-Mendes, G.P. Apoptosis: A programme of cell death or cell disposal? Scand. J. Immunol. 2011, 73, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Troiano, L.; Ferraresi, R.; Lugli, E.; Nemes, E.; Roat, E.; Nasi, M.; Pinti, M.; Cossarizza, A. Multiparametric analysis of cells with different mitochondrial membrane potential during apoptosis by polychromatic flow cytometry. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 2719–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, Z.; Li, H.; Ye, M.; Chen, X.; Shen, J.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, Z.-L.; Zhou, P.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 triggers inflammatory responses and cell death through caspase-8 activation. Sig. Transduct. Target Ther. 2020, 5, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Garron, T.M.; Chang, Q.; Su, Z.; Zhou, C.; Qiu, Y.; Gong, E.C.; Zheng, J.; Yin, Y.W.; Ksiazek, T.; et al. Cell-Type Apoptosis in Lung during SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Pathogens 2021, 10, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Shuai, H.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wen, L.; Huang, X.; Hu, B.; Yang, D.; Wang, Y.; Yoon, C.; et al. Targeting highly pathogenic coronavirus-induced apoptosis reduces viral pathogenesis and disease severity. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabf8577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Shu, T.; Wu, D.; Mu, J.; Wang, C.; Huang, M.; Han, Y.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Zhou, W.; Qiu, Y.; et al. The ORF3a protein of SARS-CoV-2 induces apoptosis in cells. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 881–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, P.T.W.; Wong, C.H.; Au, T.C.C.; Chuck, C.-P.; Kong, S.-K.; Chan, P.; To, K.-F.; Lo, A.; Chan, J.; Suen, Y.-K.; et al. The 3a protein of severe acute respiratory syndrome-associated coronavirus induces apoptosis in Vero E6 cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 1921–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-G.; Huang, W.; Lee, H.; van de Leemput, J.; Kane, M.A.; Han, Z. Characterization of SARS-CoV-2 proteins reveals Orf6 pathogenicity, subcellular localization, host interactions and attenuation by Selinexor. Cell Biosci. 2021, 11, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Lee, J.; van de Leemput, J.; Lee, H.; Han, Z. Functional analysis of SARS-CoV-2 proteins in Drosophila identifies Orf6-induced pathogenic effects with Selinexor as an effective treatment. Cell Biosci. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-Y.; Ping, Y.-H.; Lee, H.-C.; Chen, K.-H.; Lee, Y.-M.; Chan, Y.-J.; Lien, T.-C.; Jap, T.-S.; Lin, C.-H.; Kao, L.-S.; et al. Open reading frame 8a of the human severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus not only promotes viral replication but also induces apoptosis. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 196, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, F.; Dzakah, E.E.; Wang, H.; Tang, S. The ORF8 protein of SARS-CoV-2 induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and mediated immune evasion by antagonizing production of interferon beta. Virus Res. 2021, 296, 198350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceraolo, C.; Giorgi, F.M. Genomic variance of the 2019-nCoV coronavirus. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deshpande, R.; Zou, C. Programmed Cell Death in SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Short Review. J. Respir. 2021, 1, 223-228. https://doi.org/10.3390/jor1040021
Deshpande R, Zou C. Programmed Cell Death in SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Short Review. Journal of Respiration. 2021; 1(4):223-228. https://doi.org/10.3390/jor1040021
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeshpande, Rushikesh, and Chunbin Zou. 2021. "Programmed Cell Death in SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Short Review" Journal of Respiration 1, no. 4: 223-228. https://doi.org/10.3390/jor1040021
APA StyleDeshpande, R., & Zou, C. (2021). Programmed Cell Death in SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Short Review. Journal of Respiration, 1(4), 223-228. https://doi.org/10.3390/jor1040021






