Analysis of the Multimedia, Crossmedia and Transmedia Elements in Spanish Journalistic Media Projects During the Period 2020–2022
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Approach to Authorship and Information Architecture Within the Hybrid Media, News Life Logics
- (a)
- Authenticity, credibility and transparency;
- (b)
- Creativity, innovation and originality;
- (c)
- Plausibility, quality and trust;
- (d)
- The importance of belonging to a community or society and feeling like part of the solution (journalism);
- (e)
- Cultivating collaboration among professionals, projects, and users; moving from hyperlocal and local issues, scopes, and perspectives to those that are global;
- (f)
- Enhanced user experience;
- (g)
- 360° augmented-extended-virtual-mixed reality, internet of things, artificial intelligence, and big data;
- (h)
- Interface design and information architecture—SEO;
- (i)
- Media integration or combination (critical selection) and media literacy.
- Study and understand the audience (both for the story as well as the audience segmented across different media);
- Put together a team of truly diverse talents and skills, all with a passion for transmedia storytelling;
- Invest in understanding the unique affordances of each medium used in the transmedia experience;
- Always test elements of the story compared to the overall idea(l) of the storyworld;
- Be ambitious regarding the overall concept (the ‘heart’ of the story), but start small and build the storyworld outwards gradually, organically—and keep testing whether (parts of) the story still resonate with the audience.
3. Methodology
3.1. Journalistic Media and Projects Selected for the Sample
- (a)
- Selection of Spanish national and regional journalistic media whose qualitative study exceeds 4 case studies (6 journalistic media are analyzed).
- (b)
- Journalistic projects that contain multimedia, crossmedia or transmedia development of their contents.
- (c)
- Projects developed during the period 2020–2022.
- (d)
- The projects were selected based on criteria of appropriateness, quality and innovation. We define below each category criteria:
- (d.1)
- Appropriateness: journalism-based projects produced by Spanish newspapers during the period 2020–2022 (which fall within the scope of reporting on the COVID-19 pandemic).
- (d.2)
- Quality: projects that demonstrate rigorous selection and presentation of information and the sources from which it was obtained.
- (d.3)
- Innovation: projects that innovate in terms of the content and form of traditional journalism, using digital media, interactivity and transmedia storytelling as forms of narrative expression.
- (e)
- Priority on current issues of the international agenda that will be developed over a substantial period of time (COVID-19 pandemic, Ukraine war, etc.).
3.2. In-Depth Interviews
3.3. Analysis Sheet Proposal
3.3.1. Justification of the Analysis Sheet
Authorship (D)
Information Architecture (F)
4. Project Analysis
4.1. elDiario.es
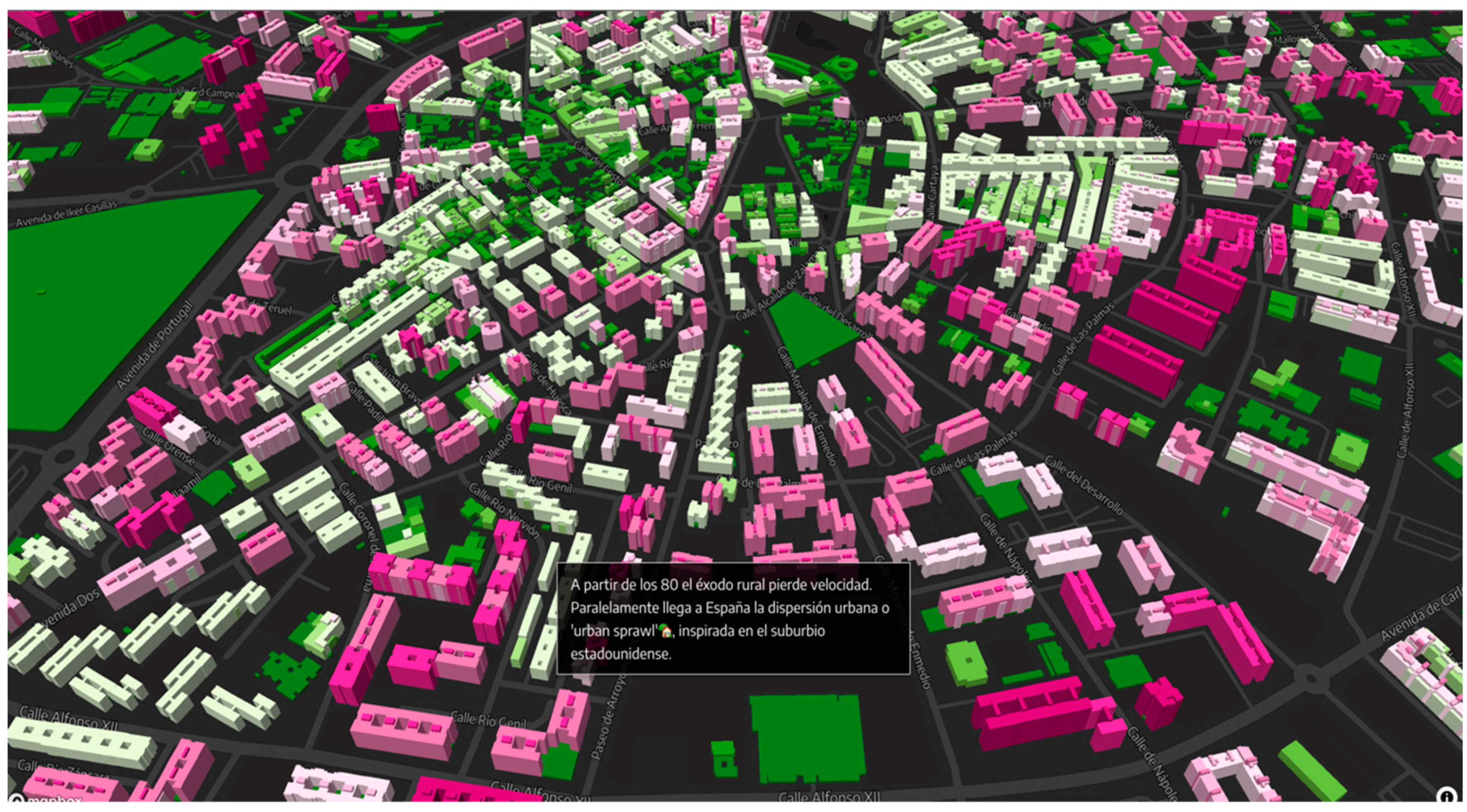
‘España Vive en Pisos: Por Qué Hemos Construido Nuestras Ciudades en Vertical’ (‘Spain Lives in Apartments: Why We Have Built Our Cities Vertically’)1
4.2. ABC
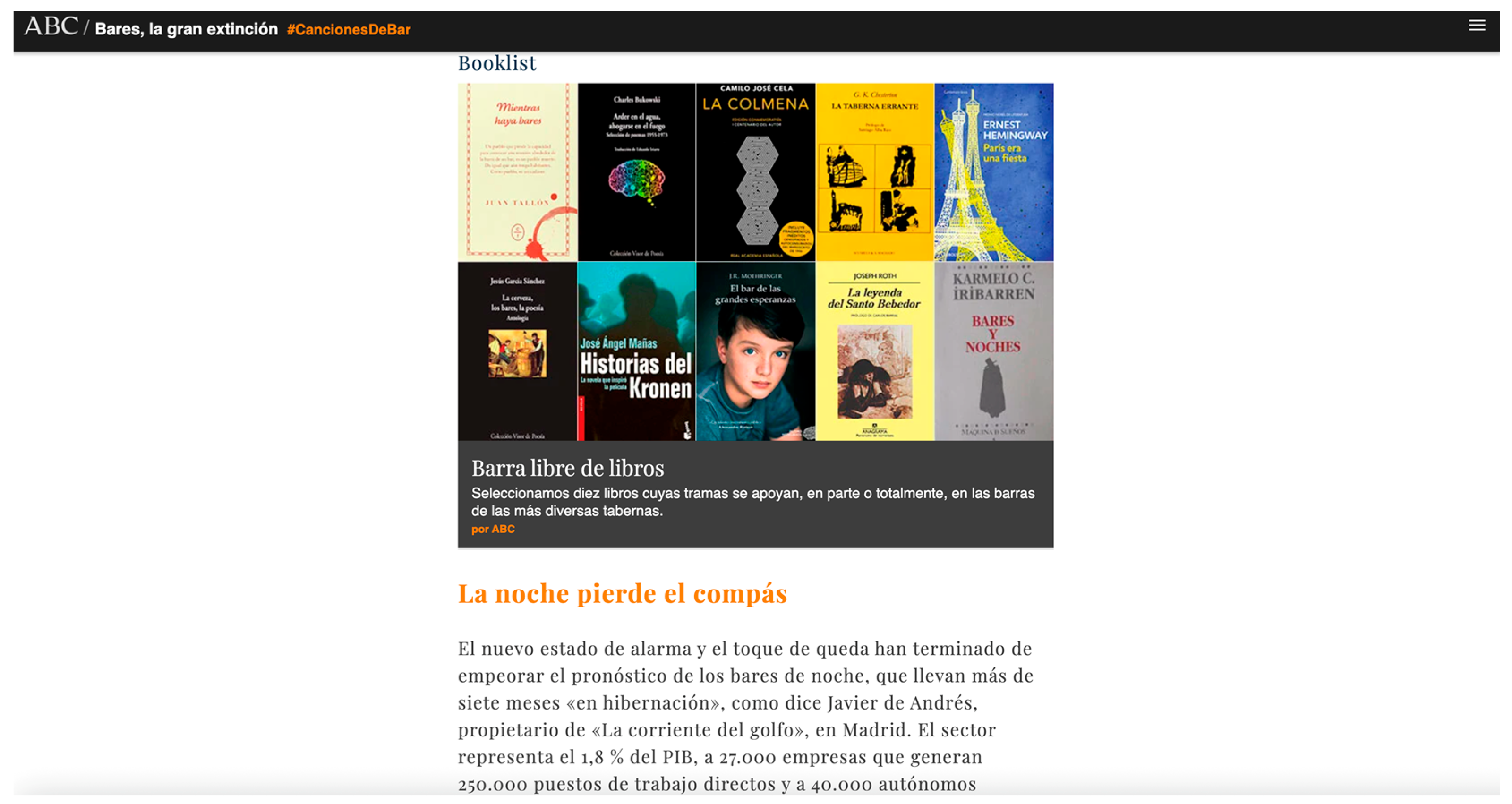
‘Bares, la Gran Extinción’ (‘Bars, the Great Extinction’)2
4.3. IDEAL
4.4. El Correo
4.5. ElConfidencial.com
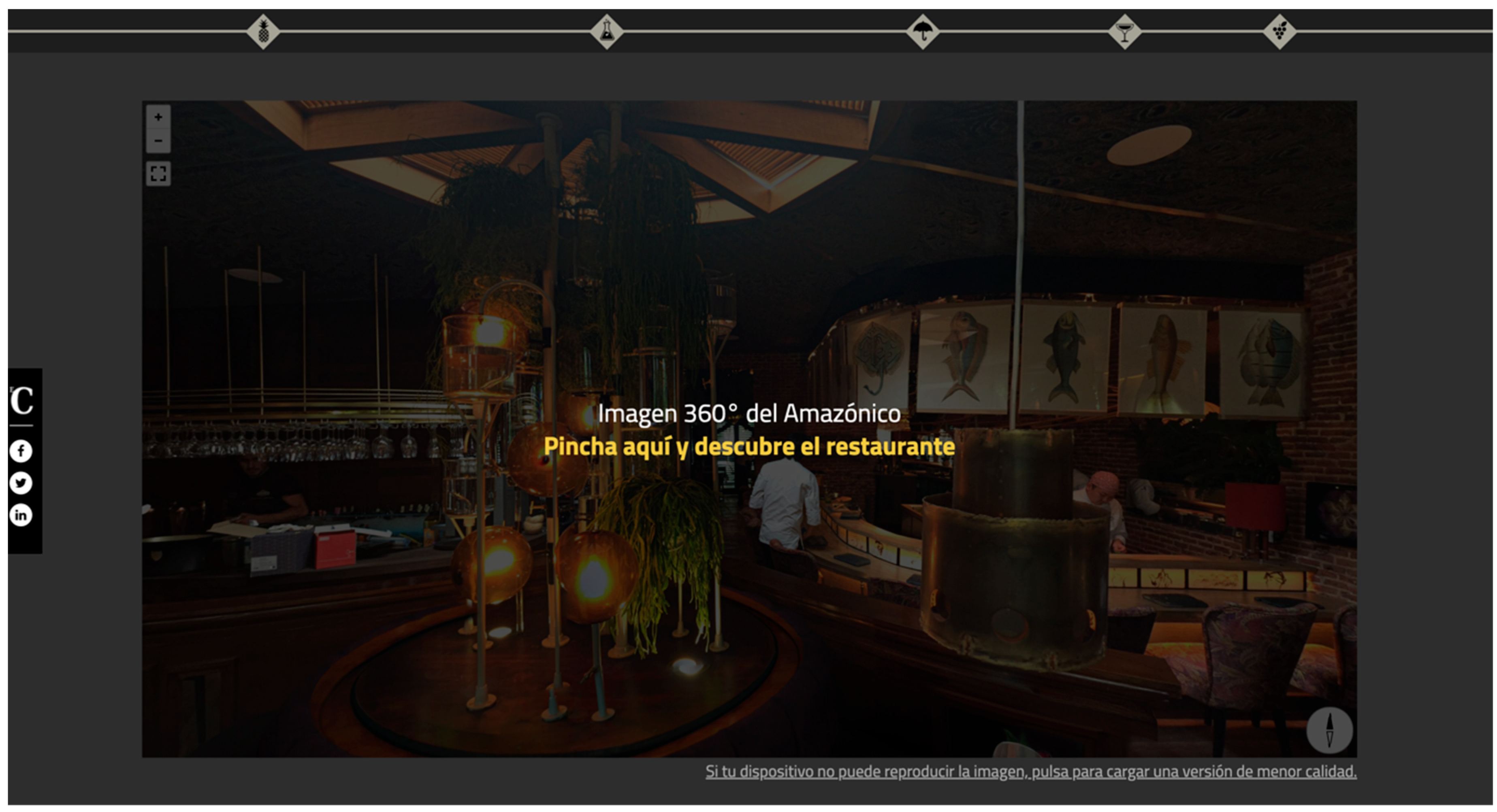
‘Marta y Sandro, el Triunfo sin Estrellas Michelin’ (‘Marta and Sandro, the Triumph Without Michelin Stars’)5
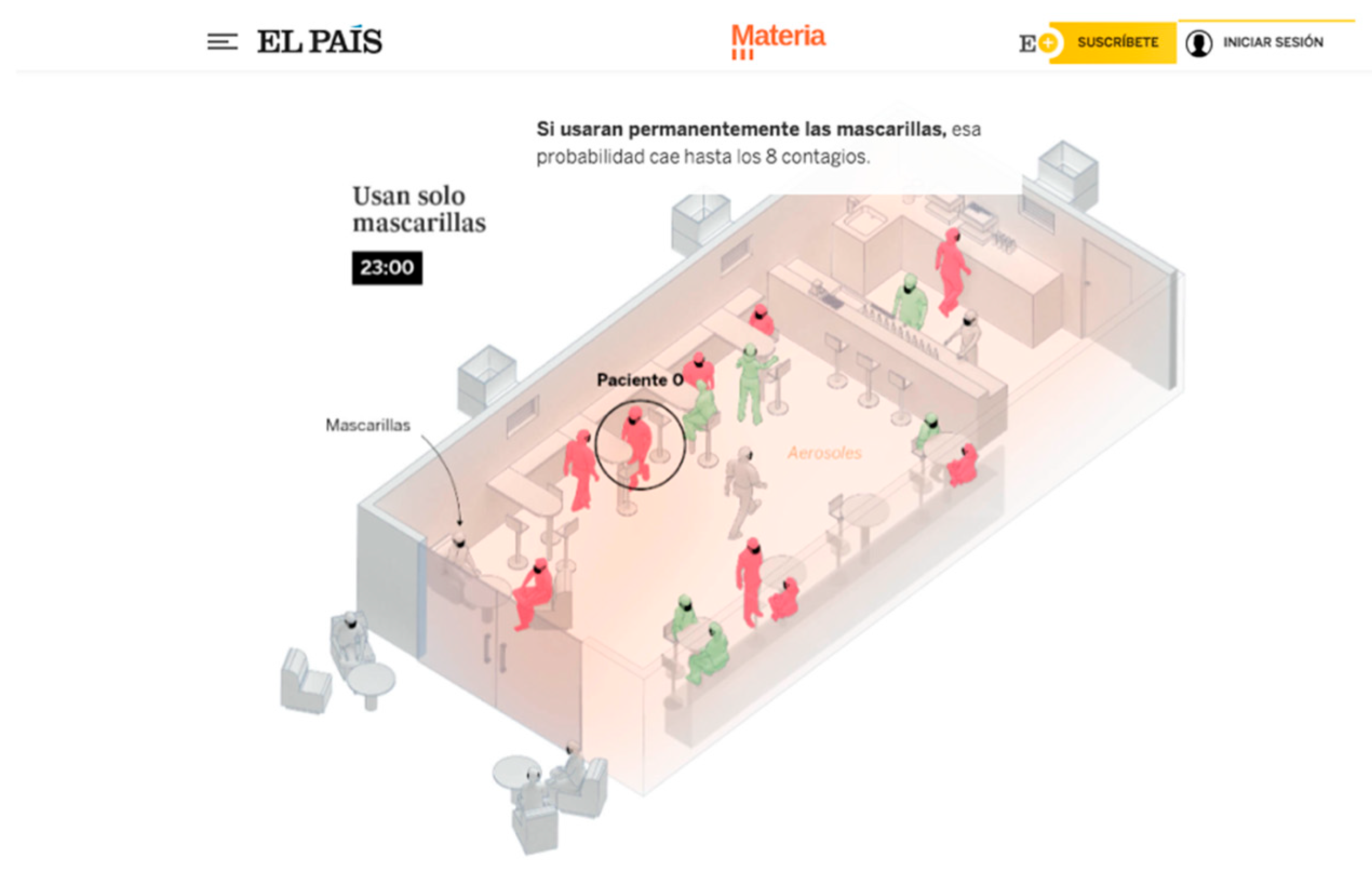
4.6. El País
4.7. Key Categories of Comparative Analysis
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
| 1 | |
| 2 | URL [https://www.abc.es/cultura/bares-la-gran-extincion/] (accessed on 23 August 2025). |
| 3 | For reasons of length, we do not analyze in this paper any of the projects of this medium in depth. |
| 4 | See Note 3 |
| 5 | URL [https://www.vanitatis.elconfidencial.com/gastronomia/2016-07-01/amazonico-paraguas-tenconten-restaurante-madrid_1226328/] (accessed on 23 August 2025). |
| 6 | URL [https://elpais.com/especiales/coronavirus-covid-19/un-salon-un-bar-y-una-clase-asi-contagia-el-coronavirus-en-el-aire/] (accessed on 23 August 2025). |
References
- ABC.es. (2022). Cien años. Available online: https://www.abc.es/informacion/centenario/cien_historia/cien.htm (accessed on 6 December 2022).
- Chadwick, A. (2013). The hybrid media system: Politics and power. Oxford University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Costera Meijer, I., Rogers, R., Westlund, O., & Witschge, T. (2021). Researching the news in the hybrid media system: An expert panel report (J. Díaz-Noci, Ed.). Universitat Pompeu Fabra. Departament de Comunicació. Serie Editorial DigiDoc. DigiDoc Reports. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10230/47055 (accessed on 6 December 2022).
- Deuze, M. (2012). Media life. Polity Press. [Google Scholar]
- ElConfidencial.com. (2022). Quienes somos. Available online: https://www.elconfidencial.com/espana/2020-12-14/quienes-somos_2876379/ (accessed on 6 December 2022).
- elDiario.es. (2022). ¿Qué es elDiario.es? Available online: https://www.eldiario.es/que-es-eldiario-es/ (accessed on 6 December 2022).
- Eldridge, S., II, & Franklin, B. (2018). The Routledge handbook of developments in digital journalism studies. Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- El País. (2022). Communication Team. Grupo Prisa. Available online: https://www.prisa.com/en/info/el-pais-1 (accessed on 8 December 2022).
- Franklin, B., & Eldridge, S., II. (2017). The Routledge companion to digital journalism studies. Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, M. (2017). Historicising transmedia storytelling. Early twentieth-century transmedia story worlds. Routledge, Taylor & Francis. ISBN 9780367884710. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, M., & Rampazzo Gambarato, R. (2020). The Routledge companion to transmedia studies. Routledge, Taylor & Francis. [Google Scholar]
- Grupo Prisa. (2022). El País. Available online: https://elpais.com/noticias/prisa/ (accessed on 6 December 2022).
- Grupo Vocento. (2022a). IDEAL. Available online: https://www.ideal.es/ (accessed on 6 December 2022).
- Grupo Vocento. (2022b). El Correo. Available online: https://www.elcorreo.com/ (accessed on 6 December 2022).
- Klein, N. (2020, May 13). How big tech plans to profit from the pandemic. The Guardian. Available online: https://www.theguardian.com/news/2020/may/13/naomi-klein-how-big-tech-plans-to-profit-from-coronavirus-pandemic (accessed on 6 December 2022).
- Nieborg, D., & Poell, T. (2019). The platformization of making media. In M. Deuze, & M. Prenger (Eds.), Making media. Production, practices and professions. Amsterdam University Press Academic. [Google Scholar]
- Radsch, C. C. (2023). Platformization and media capture: A framework for regulatory analysis of media-related platform regulations. UCLA Journal of Law & Technology, Platforms and the Press, 28(no. 2, Winter 2023), 175–223. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4397263 (accessed on 6 December 2022).
- Rampazzo-Gambarato, R., & Carvalho-Alzamora, G. (2018). Exploring transmedia journalism in the digital age. IGI Global. [Google Scholar]
- Rampazzo-Gambarato, R., Carvalho-Alzamora, G., & Tarcia, L. (2020). Theory, development, and strategy in transmedia storytelling. Routledge, Taylor & Francis. [Google Scholar]
- Reuters Institute for the Study of Journalism. (2023). Digital news report 2023. University of Oxford. Available online: https://reutersinstitute.politics.ox.ac.uk/digital-news-report/2023 (accessed on 6 December 2022).
- Scolari, C. A. (2013). Narrativas transmedia. Cuando todos los medios cuentan. Deusto. [Google Scholar]
- Serrano-Tellería, A. (Ed.). (2017). Between the public and private in mobile communication. In Routledge studies in new media and cyberculture. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-138-22555-8 (hbk) ISBN: 978-1-315-39930-0 (ebk). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Tellería, A. (2023). News life cycle and the hybrid media system. Anàlisi, 68, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Tellería, A., & Prenger, M. (2019). Transmedia production: Key steps in creating a storyworld. In M. Deuze, & M. Prenger (Eds.), Making media. Production, practices and professions. Amsterdam University Press Academic. [Google Scholar]
- Steensen, & Westlund. (2020). What is digital journalism studies? Routledge Focus. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dijk, J., Poell, T., & de Waal, M. (2018). The platform society. Public values in a connective world. Oxford University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Vázquez-Herrero, J., & Gifreu-Castells. (2019). Interactive and transmedia documentary: Production, interface, content and representation. In M. Túñez-López, V. A. Martínez-Fernández, X. López-García, X. Rúas-Araújo, & F. Campos-Freire (Eds.), Communication: Innovation & quality. Studies in systems, decision and control (Vol. 154). Springer. [Google Scholar]
- Witschge, T., Anderson, C. W., Domingo, D., & Hermida, A. (2017). The SAGE handbook of digital journalism. SAGE. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W. (2021). The logic of platformization and news [Ph.D. disstertation, Universidad Autónoma de Barcelona]. Available online: https://ddd.uab.cat/record/244189 (accessed on 6 December 2022).



| NEWS MEDIA | INTERVIEWEE | POSITION | INTREVIEW DATE |
|---|---|---|---|
| elDiario.es | Ignacio Escolar Ander Oliden | Director Deputy director | Interview conducted on 25 January 2022 Interview conducted on 9 February 2022 |
| ABC | Elena de Miguel | Deputy director | Interview conducted on 8 February 2022 |
| ElConfidencial.com | Marcos Lamelas | Economics Editor | Interview conducted on 3 February 2022 |
| El País | Borja Echevarría | Deputy and Innovation Director | Interviews conducted on 31 January and 4 February 2022 |
| La Vanguardia | Josep Corbella | Journalist responsible for science and health information | Interview conducted on 18 January 2022 |
| CATEGORIES | INDICATORS | DESCRIPTORS |
|---|---|---|
| A JOURNALISTIC GENRE | A.1. Type | A.1.1. News |
| A.1.2. Chronicle | ||
| A.1.3. Editorial | ||
| A.1.4. Report | ||
| A.1.5. Special | ||
| A.2. Hybridization | ||
| A.3. Elements of the title | A.3.1. Headline | |
| A.3.2. Subtitle | ||
| A.3.3. Entry | ||
| A.4. Highlighted | ||
| A.5. Ladillo | ||
| B FORMATTING | B.1. Audiovisual B.2. Interactive B.3. Multi/Cross/Transmedia B.4. Immersive B.5. Hybrid B.6. Gamified | |
| C NARRATIVE | C.1. Idea C.2. Theme/Story C.3. Title and subtitle | |
| D AUTHORSHIP | D.1. Author/s D.2. Sources D.3. Tags D.4. Mentions D.5. Hashtags D.6. Social profile | |
| E LIFE CYCLE | E.1. Date of publication (Launch) E.2. Update (Evolution of the news) | |
| F INFORMATION ARCHITECTURE | F.1. Type of hierarchy | F.1.1. Element selection menu |
| F.1.2. Vertical/Horizontal scrolling | ||
| F.2. Layers of information | F.2.1. Menu option selection | |
| F.2.2. Access to new page | ||
| F.2.3. Link to an anchor | ||
| F.2.4. Access to a section | ||
| F.2.5. Image pin | ||
| F.2.6. Set | ||
| F.2.7. Audio listening | ||
| F.2.8. Video viewing | ||
| F.3. Elements | F.3.1. Textual | |
| F.3.2. Visuals | ||
| F.3.3. Auditory | ||
| F.3.4. Interactive | ||
| F.3.5. Immersive | ||
| F.4. Type of structure | F.4.1. Hierarchical | |
| F.4.2. Linear | ||
| F.4.3. Circular | ||
| F.4.4. Spiral | ||
| F.4.5. Networked | ||
| F.4.6. Faceted | ||
| F.4.7. Semantic | ||
| G DESIGN | G.1. Hierarchy | G.1.1. Size |
| G.1.2. Color | ||
| G.1.3. Font/typography | ||
| G.2. Information layers | G.2.1. Option selection menu | |
| G.2.2. Access to new page | ||
| G.2.3. Link to an anchor | ||
| G.2.4. Access to a section | ||
| G.2.5. Image pin | ||
| G.2.6. Game | ||
| G.2.7. Audio listening | ||
| G.2.8. Video display | ||
| G.3. Elements | G.3.1. Textual | |
| G.3.2. Visual | ||
| G.3.3. Auditory | ||
| G.3.4. Interactive | ||
| G.3.5. Immersive | ||
| G.4. Layout type | G.4.1. Fixed design | |
| G.4.2. Elastic design | ||
| G.4.3. Liquid/fluid design | ||
| G.4.4. Responsive/adaptive design | ||
| G.4.5. Flexible design | ||
| G.5. Usability | G.5.1. Intuitive | |
| G.5.2. Accessible | ||
| G.5.3. Simple | ||
| G.5.4. Optimal/Deficient Usability | ||
| H EXPANSION AND DISTRIBUTION CHANNELS | H.1. Channels/Platforms | H.1.1. Website/web platform |
| H.1.2. Written press | ||
| H.1.3. Social networks | ||
| H.1.4. News aggregators/distributors | ||
| H.1.5. Television | ||
| H.1.6. Radio | ||
| H.2. Other | ||
| I AUDIENCE AND PARTICIPATION CHANNELS | I.1. Channel | I.1.1. Forum |
| I.1.2. Chat | ||
| I.1.3. Social network | ||
| I.1.4. Content contribution | ||
| I.1.5. Participation | ||
| I.1.6. Gamification | ||
| I.2. Social media strategy | I.2.1. Yes—Which one(s)? | |
| I.2.1. No | ||
| I.3. Type of participation | I.3.1. Passive | |
| I.3.2. Collaborative | ||
| I.3.3. Co-creative | ||
| I.4. Strategies to attract and consolidate audiences | I.4.1. Yes—Which one(s)? | |
| I.4.2. No | ||
| I.5 Other | ||
| J IMPACT MEASURES | J.1. Visits | J.1.1. Days |
| J.1.2. Weeks | ||
| J.1.3. Months | ||
| J.2. Likes (and other social network indicators) | J.2.1. Facebook | |
| J.2.2. Instagram | ||
| J.2.3. TikTok | ||
| J.2.4. Twitter | ||
| J.3. Search engine indexing | J.3.1. Google | |
| J.3.2. Bing | ||
| J.4. Analytics (similar tracking programs) | J.4.1. Google Analytics | |
| J.4.2. YouTube Study | ||
| J.4.3. Facebook Business | ||
| J.5. Time spent | J.5.1. Hours | |
| J.5.2. Minutes | ||
| J.5.3. Seconds |
| España vive en pisos: por qué hemos construido nuestras ciudades en vertical (elDiario.es) | Bares, la gran extinción (ABC) | Marta y Sandro, el triunfo sin estrellas Michelin (ElConfidencial.com) | Un salón, un bar y una clase: así contagia el coronavirus en el aire (El País) | |
| D.1. Author/s | Mentioned on the cover: Yes Cover author info: By Raúl Sánchez and Analía Plaza A project by elDiario.es with data from the Cadastre No credits at the end of the text | Mentioned on the cover: Yes Cover author info: Guillermo Navarro Text: Juan Francisco Alonso Contributors: Andrés Calamaro, Érika Montañés, Julián de Velasco, Bruno Pardo, Carlos Maribona, Emma Sueiro, Fernando Muñoz, Lucía M. Cabanelas y Federico Marín Bellón Videos: David Conde and Andrea Carrasco Section: ‘Marchando una de firmas de ABC’: Various authors Video: David Conde and Carolina Mínguez Special collaboration: Nacho Serrano and Julio Bravo End of text credits: ABC news special courtesy of ABC Premium Coordination and script: Jesús García Calero Design: Lucía R. de Lillo and Ángel Ruiz | Mentioned on the cover: Yes Cover author info: A report by Ana Sánchez Juárez End of text credits: A project of EC Brands Pablo Lopez, Brenda Valverde, Julio Cerezo, Antonio Esquembre, Luis Rodriguez, Antonio Comesaña, Sofia Fernandez and Carmen Castellón | Mentioned on the cover: Yes Cover author info: Mariano Zafra & Javier Salas End of text credits: Videos by Luis Almodóvar |
| D.2. Sources | Description: To produce this information, elDiario.es has compiled, processed and analyzed the cartographic data of more than 12 million buildings constructed throughout Spain published by the website of the General Directorate of the property register. To elaborate this special edition we have consulted different experts in urban planning and architecture: Oriol Nel-lo, doctor in Geography, former director of the Institute of Metropolitan Studies of Barcelona and former secretary of Territorial Planning of the Generalitat; Javier Martínez, president of the Union of Urbanist Architects Groupings; Joan Romero, professor of Human Geography at the University of Valencia; Laura Gil, architect by the School of Architecture of A Coruña; Álvaro Ardura, architect at the Escuela Técnica Superior de Arquitectura de Madrid; Isabelle Anguelovski, PhD in Urban Planning from MIT and director of the Barcelona Lab for Urban Environmental Justice and Sustainability; Antonio López Gay, researcher at the Centro de Estudios Demográficos, and Adrián Fernández, public works engineer and head of mobility at Greenpeace | Description: All multimedia contents have their source and author. INE—National Statistics Institute | Description: Not specified | Description: Methodology: The risk of COVID-19 infection was calculated using a tool developed by José Luis Jiménez, an expert in airborne particle chemistry and dynamics at the University of Colorado. |
| D.3. Tags | No | No | No | No |
| D.4. Mentions | No | No | No | No |
| D.5. Hashtags | No | No | No | No |
| D.6. Social profile | No | No | No | Twitter profiles of the authors |
| Other | Facebook and Twitter recommendation | Facebook and Twitter recommendation | Facebook, Twitter and Linkedin recommendation | Facebook, Twitter Linkedin and Pinterest recommendation |
| España vive en pisos: por qué hemos construido nuestras ciudades en vertical (elDiario.es) | Bares, la gran extinción (ABC) | Marta y Sandro, el triunfo sin estrellas Michelin (ElConfidencial.com) | Un salón, un bar y una clase: así contagia el coronavirus en el aire (El País) | |
| F.1. Type of hierarchy | Text and image animation in this order through different maps of Spanish cities | Vertical displacement (Parallax technique—Scrollytelling) | Vertical displacement (Parallax technique—Scrollytelling) | Vertical displacement (Parallax technique—Scrollytelling) |
| F.2. Layers of information | Immersive map with graphics, vertical scroll | Text blocks, interspersed with photos, video and music playlists | Text blocks interspersed with photos, 360 photos and videos | Text blocks interspersed with animations and infographics |
| F.3. Elements | Text Image Infographics | Text Photographs Audiovisual reports Podcast Music playlist Booklist—Selection of 10 books centered on the bars of different taverns. Other short stories (Ex: “It’s the same construction disaster of a decade ago”—ABC.es by Érika Montañés) | Text Photographic slides Immersive—360º image | Text Infographics Animations Links |
| F.4. Type of structure | Linear Hierarchical | Linear | Linear Colors contribute to create the structure divided in sections | Linear The animations fulfill the rhetorical function of separators between the different scenarios—proposed spaces. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Serrano-Tellería, A.; Gifreu-Castells, A. Analysis of the Multimedia, Crossmedia and Transmedia Elements in Spanish Journalistic Media Projects During the Period 2020–2022. Journal. Media 2025, 6, 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/journalmedia6040169
Serrano-Tellería A, Gifreu-Castells A. Analysis of the Multimedia, Crossmedia and Transmedia Elements in Spanish Journalistic Media Projects During the Period 2020–2022. Journalism and Media. 2025; 6(4):169. https://doi.org/10.3390/journalmedia6040169
Chicago/Turabian StyleSerrano-Tellería, Ana, and Arnau Gifreu-Castells. 2025. "Analysis of the Multimedia, Crossmedia and Transmedia Elements in Spanish Journalistic Media Projects During the Period 2020–2022" Journalism and Media 6, no. 4: 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/journalmedia6040169
APA StyleSerrano-Tellería, A., & Gifreu-Castells, A. (2025). Analysis of the Multimedia, Crossmedia and Transmedia Elements in Spanish Journalistic Media Projects During the Period 2020–2022. Journalism and Media, 6(4), 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/journalmedia6040169







