Abstract
Urban flood risk mitigation requires fine-scale near-real-time precipitation observations that are challenging to obtain from traditional monitoring networks. Novel data and computational techniques offer a valuable potential source of information. This study explores an unprecedented, device-independent, artificial intelligence-based system for opportunistic rainfall monitoring through deep learning models that detect rainfall presence and estimate quasi-instantaneous intensity from single pictures. Preliminary results demonstrate the models’ ability to detect a significant meteorological state corroborating the potential of non-dedicated sensors for hydrometeorological monitoring in urban areas and data-scarce regions. Future research will involve further experiments and crowdsourcing, to improve accuracy and promote public resilience.
1. Introduction
In the last 50 years, flooding has been the most common and widespread natural disaster [1]. Climate changes can exacerbate extreme precipitation events [2], heightening the flood risk, especially in urban areas where impervious surfaces alter natural hydrological response [3]. Fine-scaled and near real-time rain observations are essential to assess the rainfall-runoff response in urban areas [4] and therefore the risk scenarios and alerts for exposed population [5]. The dedicated monitoring networks—from in situ devices (rain gauges, disdrometers) and remote sensors (radars, satellites)—differ in spatio-temporal representativeness and availability both regionally and temporally, thus require additional information to fill gaps [4].
In this context, newly available data sources and computational techniques offer enormous potential in risk understanding, analysis, forecasting, and warning [5]. Repurposing data that are continuously being produced can yield useful information so that non-dedicated devices can serve as low-cost “opportunistic” hydrological sensors [4].
This study explores the potential and limitations of hydrometeorological monitoring using generic consumer cameras as smart, non-traditional, opportunistic sensors.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Rainfall and Computer Vision
Digital pictures and videos are affected by weather conditions, in particular by precipitation. In fact, the rainfall produces local variations in the pixel’s intensity value of raster images depending on the following: raindrops characteristics (shape, size, velocity, density), camera parameters (exposure time, F-number, depth of field, etc.), and environment settings (scene brightness, background, etc.) [6]. Rain-induced artifacts reduce the performance of computer vision (CV) systems, thus several rain detection and removal techniques were developed to improve algorithms robustness in adverse weather conditions. Publications that concentrate on video-frame sequences adopt both classical CV and deep learning (DL) techniques—whereas studies that use single images adopt mainly DL-based methods. Instead, a smaller body of literature is concerned with meteo-hydrological purposes. Machine earning (ML) and DL methods have become the standard for classifying weather conditions from single outdoor images (e.g., sunny, cloudy, snowy, rainy, and foggy [7]). Rain measurement methods are based on classical image processing algorithms and exploit temporal information derived from video-frame sequences thus presenting stringent acquisition requirements (time step, device settings, resolution, etc.). For an overview of existing techniques, the reader is directed to [8].
All studies support the notion that cameras can function as rainfall sensors. However, such methods remain narrow in focus using only one of the following specific image sources at one time: vehicle-mounted cameras; surveillance cameras; outdoor scenes; and adjustable cameras [8].
An effective monitoring network must maximize sensors redundancy to improve accuracy and reliability and, at the same time, must minimize processed data amount to reduce computational resources and time. Thus, our research approach hinges on the following: application simplicity and readiness; adherence to the perceptual reality; cost-effectiveness.
As opposed to existing works, our methodology exploits general-purpose cameras (e.g., smartphones, surveillance cameras, dashcams, etc.) without requiring parameter setting, timeline shots, or videos. Using DL models based on transfer learning (TL) with convolutional neural networks (CNNs), our method can be seen as a two-stage process:
- Detection task: the CNN descries rainfall presence through a binary classification;
- Estimation task: the CNN estimates the quasi-instantaneous rainfall intensity through a multi-class classification;
A CNN-based approach was chosen since it is the state-of-art among other image recognition methods [9]. Contrary to traditional CV techniques, CNNs avoid the problem of manually engineered feature descriptors since such algorithms recognize visual patterns directly in images, learning automatically the most salient features [9,10].
Rain-induced visual effects are complex and often inconspicuous [6]. Furthermore, public big datasets are lacking and data creation is challenging. The non-triviality of the task and the size of available data drove the choice to exploit the common visual semantics of images by TL strategies combining fine-tuning and freezing layers [9].
2.2. Dataset and Model Setup
Datasets for training, validation, and test (ratio of 60:20:20) mimic real-world scenarios. Different sources have been combined following the criteria of availability, weather conditions representativeness, location, and lightning conditions diversity. Each input image was paired with exactly one output label describing the rain class.
For the binary classification [8], the dataset included 4788 images—crowdsourced images from Image2Weather set [7]; images from dashcams moving around Tokyo metropolitan area from 19 August 2017 for 48 h (©NIED) coupled with rainfall rates retrieved from XRAIN multiparameter radar (©NIED) [11] by capture time and GPS location (threshold 4 mm/h); pictures taken during experiments in the NIED Large-scale Rainfall Simulator located in Tsukuba (Japan) with different devices (Canon XC10, Sony DSC-RX10M3, Olympus TG-2, XiaoYI YDXJ 2, XiaoMi MI8) coupled with the nominal values of produced intensity ranging from 20 mm/h to 150 mm/h.
For the multiclass classification, the dataset included 55,600 images from: dashcams moving around Tokyo metropolitan area from 19 August 2017 for 48 h and in several Japanese prefectures from 8 July 2017 to 19 June 2018 (©NIED), coupled with XRAIN rainfall rates (©NIED) [11] by time and location; experiments in the NIED Simulator coupled with the nominal produced intensity (from 20 mm/h to 150 mm/h). Rain rates were binned into 6 non-overlapping classes.
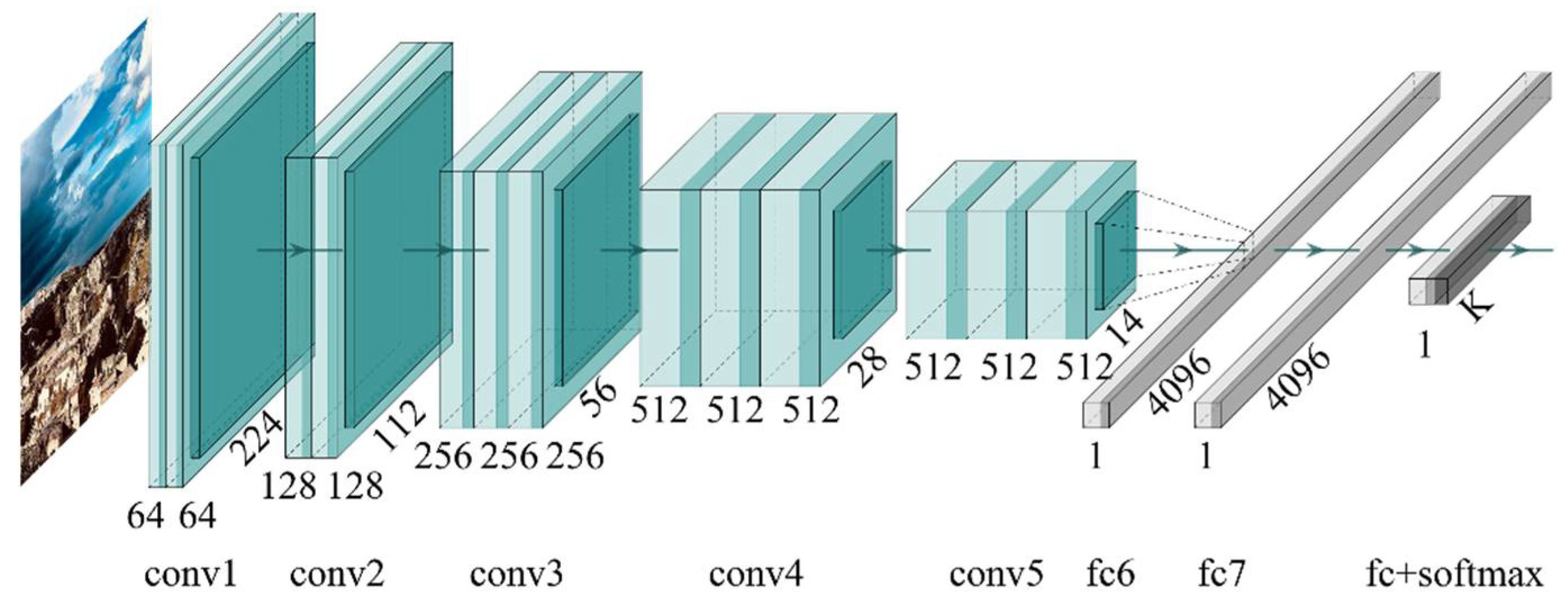
Using a TL approach, the VGG16 network [12] (Figure 1)—pre-trained on the large-scale dataset ImageNet—was employed as convolutional base because of its generality and the portability of learned features [9].
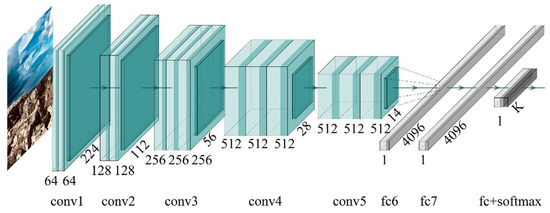
Figure 1.
VGG16 model architecture.
To mitigate overfitting, different regularization techniques were adopted during training and validation phases, such as holdout train-valid-test data split; training data augmentation; dropout; adaptive learning rate; small batch training; early stopping; etc.
The models were entirely implemented with open-source tools, namely R language with RStudio using Keras framework and Tensorflow engine backend [9].
3. Results
To evaluate unbiasedly the predictive skills, the test sets were exposed to the models trained as described. Each test set (holdout set) was locked away completely during the training and evaluation steps [9]. The binary prototype was deployed in a real-world environment in Matera (Italy) in [8], showing great robustness and portability, contrary to the other algorithms [8]. The rainfall estimator presented the best performances with no-rain and heavy rainfall (the most critical condition for urban flood risk). Table 1 shows the overall metrics; the obtained classifications are significantly better than random predictions in both models. The non-informative accuracy values correspond to 50% for a binary classification and 16, 67% for a balanced 6-way classification. F1 score and Cohen’s kappa shows consistency, such metrics considers the balance of recall and precision and compare observed accuracy with an expected accuracy (random chance), respectively.

Table 1.
Performance metrics.
4. Discussion—Conclusions
This study presented a prototyping method for smart opportunistic near real-time rainfall monitoring in urban areas. Starting from the authors’ previous work [8], it represents an update of an Artificial Intelligence-based approach to gather rainfall observations from single images shot in very heterogeneous conditions.
The results achieved by the models test and deployment [8] proved that our system can provide approximated but robust near-real-time precipitation observations. In comparison with algorithms based on frame sequences or video, our single-image classification algorithms process less data volume and are more robust in urban scenarios where the background contains non-static elements, such as moving pedestrians or vehicles, as they don’t depend on background subtraction techniques.
The major limitation concerns the approximations inherent in the following output types: rainfall presence and intensity ranges. Another limitation can stem from visual ambiguities in scenes that are also misleading for human perception. However, redundant observations from a dense network with many inaccurate nodes can enhance overall performances.
Our methodology offers an expeditious operative opportunistic sensors system intending not to substitute, but instead to support traditional measurement methods. The readiness level, cost-effectiveness, and limited operational requirements allow an easy implementation by exploiting pre-existent devices. Hence, observations retrieved from camera-based opportunistic sensors can effectively complement dedicated rainfall observational methods especially in areas where the traditional monitoring networks is sparse, such as urban areas but also low- or lower-middle-income countries.
Future research will involve further experiments and crowdsourcing, to improve accuracy and at the same time promote public resilience through a smart city perspective.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.A. and A.S.; methodology, N.M.N.; software, N.M.N.; validation, N.M.N., A.S. and R.A.; formal analysis, N.M.N.; investigation, N.M.N. and K.H.; resources, K.H.; data curation, N.M.N. and K.H.; writing—original draft preparation, N.M.N.; writing—review and editing, N.M.N., R.A., K.H. and A.S.; supervision, A.S.; project administration, A.S.; and funding acquisition, A.S. and R.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the “Casa delle Tecnologie Emergenti di Matera” project.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the National Research Institute for Earth Science and Disaster Resilience (NIED). Restrictions apply to the availability of these data, which were used under license for this study.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the staff at the NIED, the Storm, Flood and Landslide Research Division and the Large-scale Rainfall Simulator for the assistance with data and experiments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- EM-DAT|OFDA/CRED International Disaster Database. Available online: www.emdat.be (accessed on 15 April 2022).
- Myhre, G.; Alterskjær, K.; Stjern, C.W.; Hodnebrog, Ø.; Marelle, L.; Samset, B.H.; Sillmann, J.; Schaller, N.; Fischer, E.; Schulz, M.; et al. Frequency of Extreme Precipitation Increases Extensively with Event Rareness under Global Warming. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, T.D.; Andrieu, H.; Hamel, P. Understanding, Management and Modelling of Urban Hydrology and Its Consequences for Receiving Waters: A State of the Art. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 51, 261–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, M.F.; Rodell, M.; Alsdorf, D.E.; Miralles, D.G.; Uijlenhoet, R.; Wagner, W.; Lucieer, A.; Houborg, R.; Verhoest, N.E.C.; Franz, T.E.; et al. The Future of Earth Observation in Hydrology. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 3879–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albano, R.; Sole, A. Geospatial Methods and Tools for Natural Risk Management and Communications. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, K.; Nayar, S.K. Vision and Rain. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2007, 75, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, W.-T.; Zheng, X.-Y.; Ding, D.-S. Camera as Weather Sensor: Estimating Weather Information from Single Images. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2017, 46, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notarangelo, N.M.; Hirano, K.; Albano, R.; Sole, A. Transfer Learning with Convolutional Neural Networks for Rainfall Detection in Single Images. Water 2021, 13, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahony, N.O.; Campbell, S.; Carvalho, A.; Harapanahalli, S.; Velasco-Hernandez, G.; Krpalkova, L.; Riordan, D.; Walsh, J. Deep Learning vs. Traditional Computer Vision. In Science and Information Conference; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 943, pp. 128–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollet, F.; Allaire, J.J. Deep Learning with R, 1st ed.; Manning Publications Co.: Greenwich, CT, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hirano, K.; Maki, M.; Maesaka, T.; Misumi, R.; Iwanami, K.; Tsuchiya, S. Composite Rainfall Map from C-Band Conventional and X-Band Dual-Polarimetric Radars for the Whole of Japan. In Proceedings of the ERAD 2014—8th European Conference on Radar in Meteorology and Hydrology, Garmisch-Partenkirchen, Germany, 5–7 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).