Effects of Vegetation Density on Sediment Transport in Lateral Cavities †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Model Equations
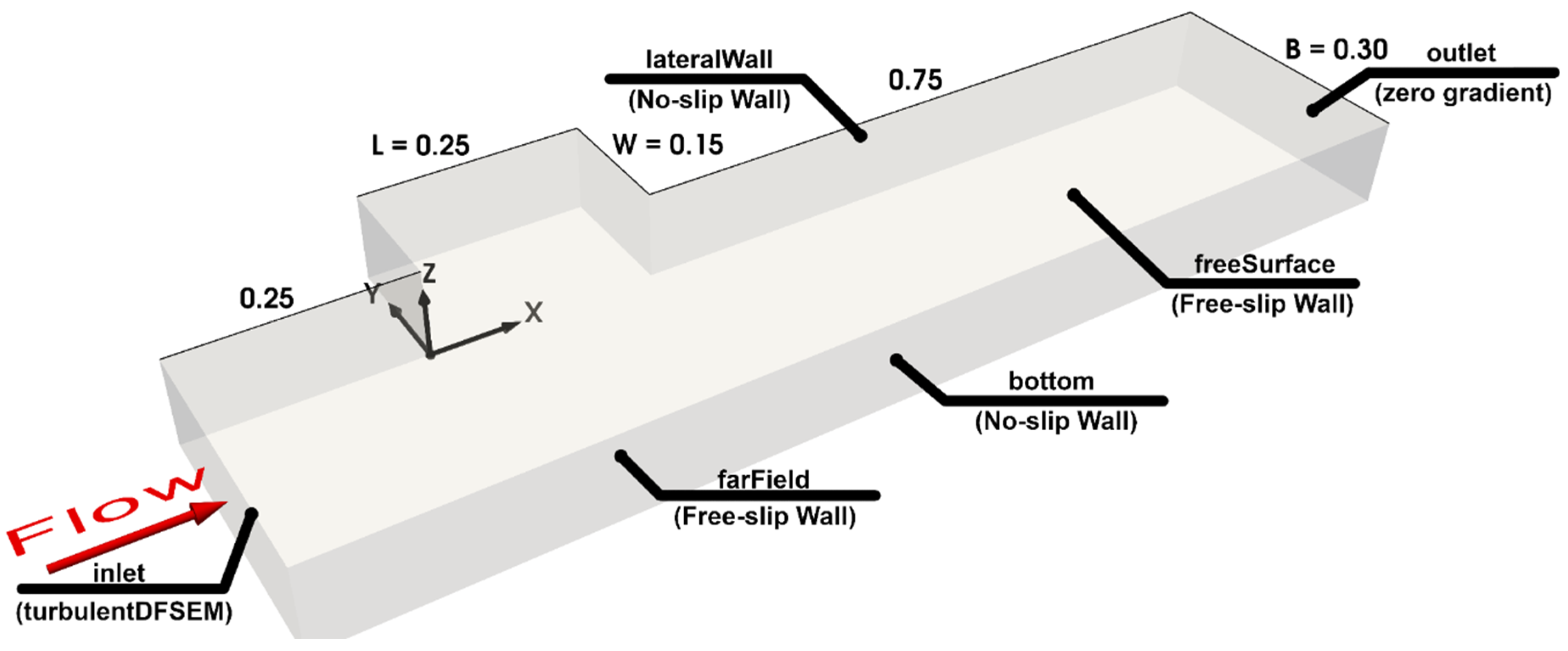
2.2. Numerical Model and Boundary Conditions
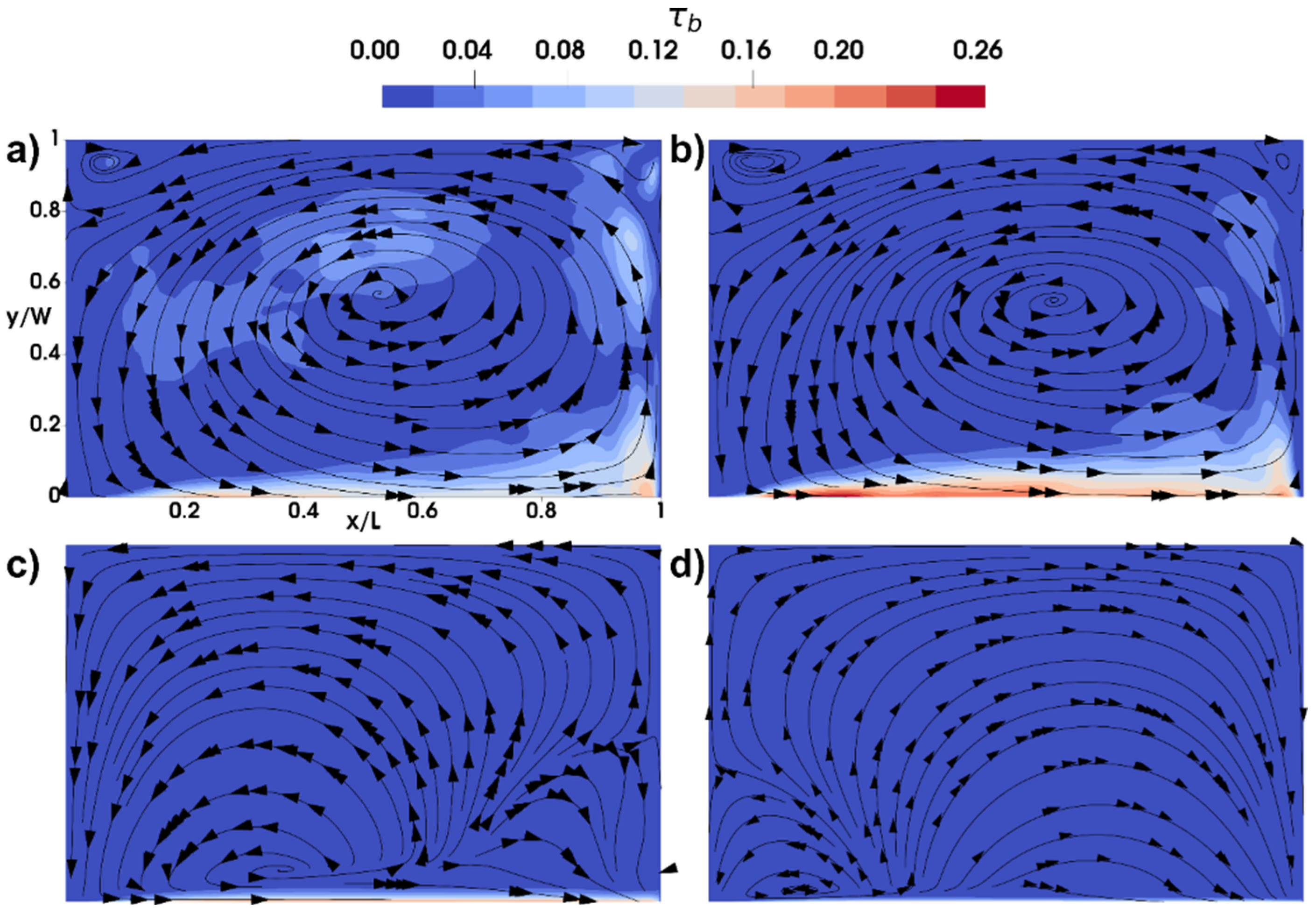
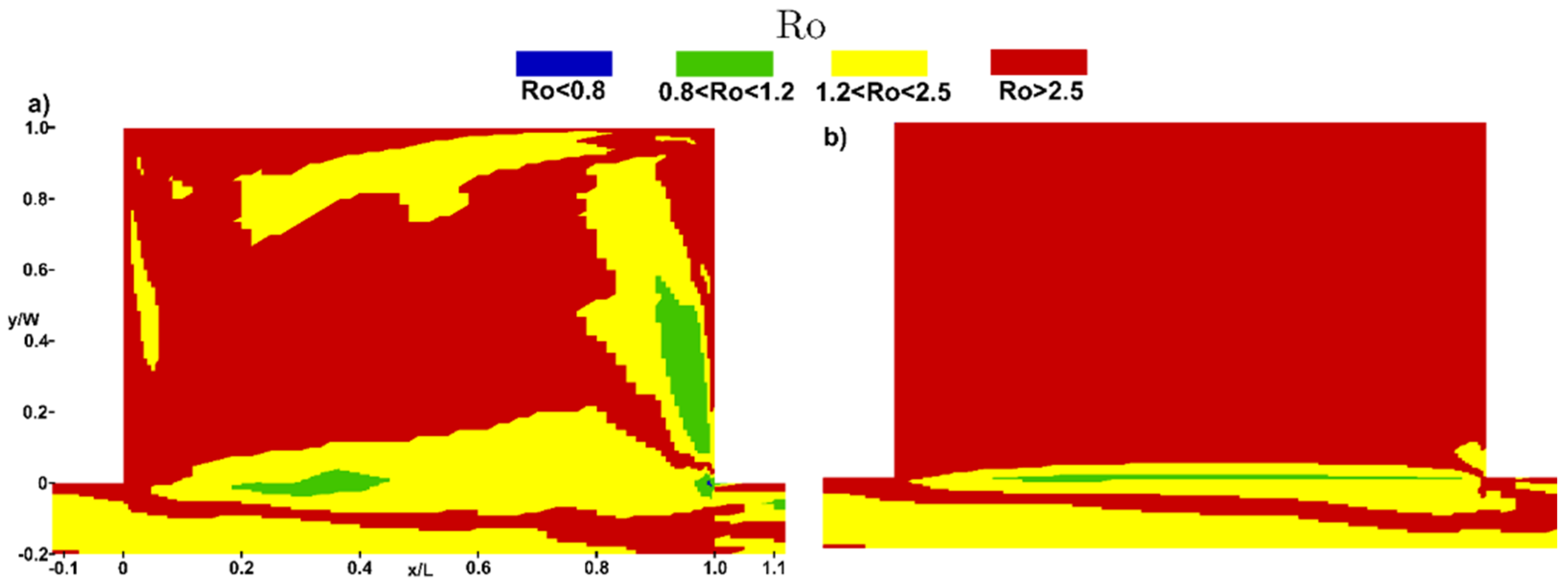
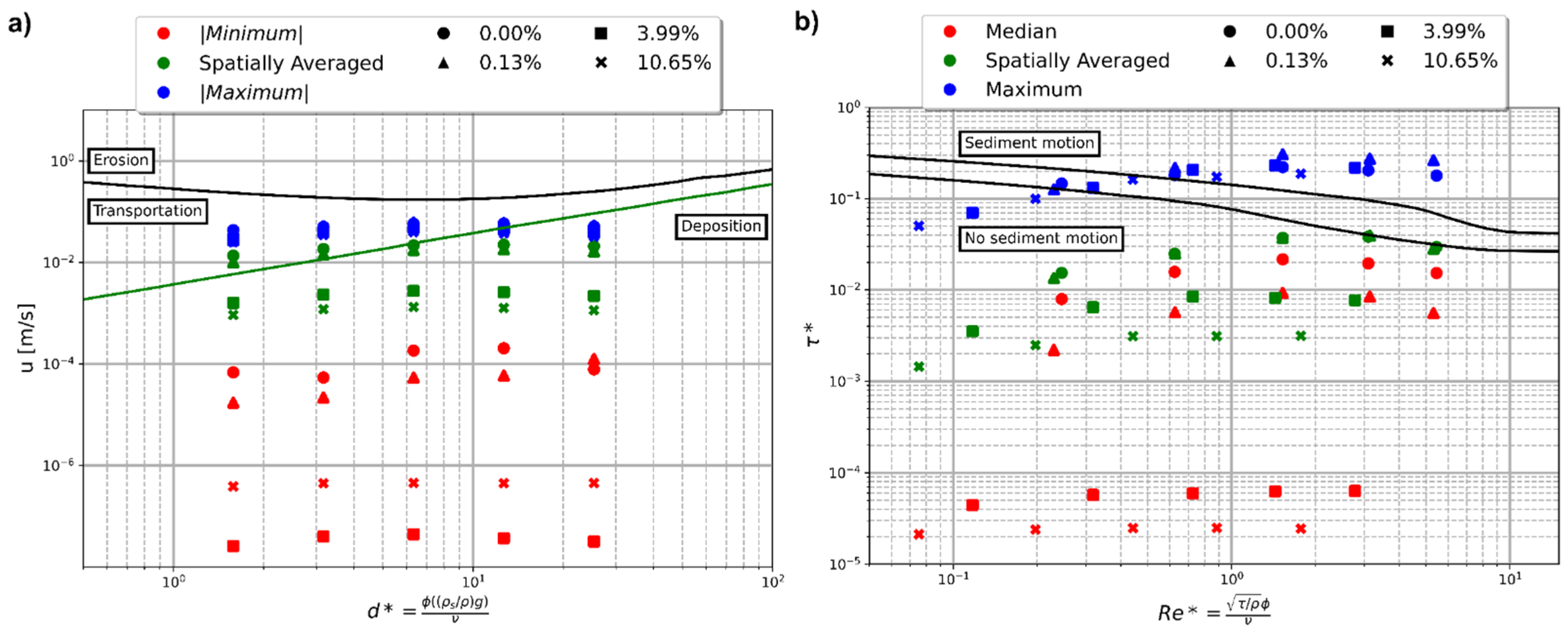
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Juez, C.; Bühlmann, I.; Maechler, G.; Schleiss, A.J.; Franca, M.J. Transport of suspended sediments under the influence of bank macro-roughness. Earth Surf. Process. Landforms 2018, 43, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignot, E.; Cai, W.; Launay, G.; Riviere, N.; Escauriaza, C. Coherent turbulent structures at the mixing-interface of a square open-channel lateral cavity. Phys. Fluids 2016, 28, 045104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouro, P.; Juez, C.; Franca, M. Drivers for mass and momentum exchange between the main channel and river bank lateral cavities. Adv. Water Resour. 2020, 137, 103511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelen, L.; Perrot-Minot, C.; Mignot, E.; Rivière, N.; De Mulder, T. Lagrangian study of the particle transport past a lateral, open-channel cavity. Phys. Fluids 2021, 33, 013303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualtieri, C. Numerical simulation of flow patterns and mass exchange processes in dead zones. In Proceedings of the 4th International Congress on Environmental Modelling and Software (iEMSs 2008), Barcelona, Spain, 6–10 July 2008; Volume 1, pp. 150–161. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, T.R.; Haggerty, R.; Apte, S.V. A fluid-mechanics based classification scheme for surface transient storage in riverine environments: Quantitatively separating surface from hyporheic transient storage. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 2747–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, T.R.; Apte, S.V.; Haggerty, R.; Budwig, R. Flow structure and mean residence times of lateral cavities in open channel flows: Influence of bed roughness and shape. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2015, 15, 1069–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, J.W. Hydrologic Exchange Flows and Their Ecological Consequences in River Corridors. In Stream Ecosystems in a Changing Environment; Jones, J.B., Stanley, E.H., Eds.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 1–83. Available online: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780124058903000014 (accessed on 18 March 2022)ISBN 9780124058903.
- Ribi, J.-M.; Boillat, J.-L.; Peter, A.; Schleiss, A.J. Attractiveness of a lateral shelter in a channel as a refuge for juvenile brown trout during hydropeaking. Aquat. Sci. 2014, 76, 527–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, R.J.; Johnson, M.S. Estuaries, lagoons and enclosed embayments: Habitats that enhance population subdivision of inshore fishes. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2004, 55, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.E.D. Mass Exchange in Dead Zones: A Numerical Approach. Fundação Universidade Federal de Mato Grosso do Sul, Campo Grande, Brazil, 2021. Master’s Thesis. Available online: https://repositorio.ufms.br/handle/123456789/3633 (accessed on 18 March 2022).
- Nepf, H.M. Flow and Transport in Regions with Aquatic Vegetation. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2012, 44, 123–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.C. Recovery of a Tidal Freshwater Embayment from Eutrophication: A Multidecadal Study. Estuaries Coasts 2020, 43, 1318–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, K.; Yang, Z.; Huai, W.; Ding, R. Large eddy simulation of turbulent flow structure in a rectangular embayment zone with different population densities of vegetation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 14583–14597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraus, R.T.; Jones, R.C. Fish abundances in shoreline habitats and submerged aquatic vegetation in a tidal freshwater embayment of the Potomac River. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 3341–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arend, K.K.; Bain, M.B. Fish communities in coastal freshwater ecosystems: The role of the physical and chemical setting. BMC Ecol. 2008, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maceina, M.J.; Slipke, J.W.; Grizzle, J.M. Effectiveness of Three Barrier Types for Confining Grass Carp in Embayments of Lake Seminole, Georgia. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 1999, 19, 968–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, L.G.; Michael Kemp, W.; Boynton, W.R. The influence of waves and seagrass communities on suspended particulates in an estuarine embayment. Mar. Geol. 1984, 59, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duró, G.; Crosato, A.; Kleinhans, M.G.; Roelvink, D.; Uijttewaal, W.S.J. Bank Erosion Processes in Regulated Navigable Rivers. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2020, 125, e2019JF005441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodi, W.; Constantinescu, G.; Stoesser, T. Large-Eddy Simulation in Hydraulics, 1st ed.; Davies, P.A., Ed.; CRC Press/Balkema: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 1, ISBN 9781138000247. [Google Scholar]
- Nicoud, F.; Ducros, F. Subgrid-scale stress modelling based on the square of the velocity gradient tensor. Flow Turbul. Combust. 1999, 62, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, T.N.; de Lima, P.H.S.; Silva, D.F.; Preza, C.G.d.A.; Janzen, J.G.; Nepf, H.M. From patch to channel scale: The evolution of emergent vegetation in a channel. Adv. Water Resour. 2019, 129, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, T.N.; Janzen, J.G. Estimating the resistance of a porous media that numerically represents a floating treatment wetland. In Proceedings of the 1st IAHR Young Professionals Congress; Carrillo, J.M., Fenrich, E., Ferràs, D., Wieprecht, S., Eds.; International Association for Hydro-Environment Engineering and Research-IAHR: Madrid, Spain, 2020; pp. 199–200. [Google Scholar]
- Khosronejad, A.; Arabi, M.G.; Angelidis, D.; Bagherizadeh, E.; Flora, K.; Farhadzadeh, A. A comparative study of rigid-lid and level-set methods for LES of open-channel flows: Morphodynamics. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2020, 20, 145–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brevis, W.; García-Villalba, M.; Niño, Y. Experimental and large eddy simulation study of the flow developed by a sequence of lateral obstacles. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2014, 14, 873–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poletto, R.; Craft, T.; Revell, A. A new divergence free synthetic eddy method for the reproduction of inlet flow conditions for les. Flow Turbul. Combust. 2013, 91, 519–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Ortiz, A.; Zong, L.; Nepf, H. The wake structure behind a porous obstruction and its implications for deposition near a finite patch of emergent vegetation. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, R.; Xing, T. Five-equation and robust three-equation methods for solution verification of large eddy simulation. J. Hydrodyn. 2018, 30, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignot, E.; Cai, W.; Riviere, N. Analysis of the transitions between flow patterns in open-channel lateral cavities with increasing aspect ratio. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2019, 19, 231–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julien, P.Y. Erosion and Sedimentation, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010; Volume 52, ISBN 9780511806049. Available online: http://ebooks.cambridge.org/ref/id/CBO9780511806049 (accessed on 18 March 2022).
- Whipple, K. 12.163 Surface Processes and Landscape Evolution. 2004. Available online: https://ocw.mit.edu/courses/earth-atmospheric-and-planetary-sciences/12-163-surface-processes-and-landscape-evolution-fall-2004/lecture-notes/4_sediment_transport_edited.pdf (accessed on 18 March 2022).

| Case | a (%) | Horizontal Direction (x- and y-axis) | Vertical Direction (z-axis) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d (1/m2) | f (1/m) | dh (m) | d (1/m2) | f (1/m) | ||
| 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 1 | 0.13 | 116.53 | 3.09 | 0.7624 | 0.0004 | 0.006 |
| 2 | 3.99 | 120,314.00 | 105.38 | 0.0210 | 613.12 | 7.52 |
| 3 | 10.65 | 1,061,150.94 | 348.58 | 0.0041 | 140,829.09 | 126.99 |
| Sand Granulometry | Φ [m] | ws [m/s] |
|---|---|---|
| Very Fine | 0.0000625 | 0.112 |
| Fine | 0.000125 | 0.0703 |
| Medium | 0.00025 | 0.036 |
| Coarse | 0.0005 | 0.0128 |
| Very Coarse | 0.001 | 0.00347 |
| Sediment | Max (102) | Mean | Median |
|---|---|---|---|
| Very Fine | 2.00/10.31/38.45/55.20 | 4.26/8.02/63.04/84.82 | 2.45/3.10/20.08/31.17 |
| Fine | 7.63/63.03/134.87/255.42 | 10.91/20.69/200.28/294.80 | 7.02/8.63/68.57/111.48 |
| Medium | 15.61/46.07/379.28/411.36 | 24.61/39.43/559.63/820.10 | 17.59/21.15/188.95/311.26 |
| Coarse | 54.77/68.02/814.16/1467.31 | 48.54/78.04/1092.73/1616.80 | 33.09/40.67/373.46/612.30 |
| Very Coarse | 95.00/129.07/1562.37/1316.96 | 78.11/125.22/1762.61/2570.15 | 52.80/71.68/608.14/954.70 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Oliveira, L.E.D.; da Costa, F.R.; Gualtieri, C.; Janzen, J.G. Effects of Vegetation Density on Sediment Transport in Lateral Cavities. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2022, 21, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2022021016
de Oliveira LED, da Costa FR, Gualtieri C, Janzen JG. Effects of Vegetation Density on Sediment Transport in Lateral Cavities. Environmental Sciences Proceedings. 2022; 21(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2022021016
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Oliveira, Luiz Eduardo Domingos, Felipe Rezende da Costa, Carlo Gualtieri, and Johannes Gérson Janzen. 2022. "Effects of Vegetation Density on Sediment Transport in Lateral Cavities" Environmental Sciences Proceedings 21, no. 1: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2022021016
APA Stylede Oliveira, L. E. D., da Costa, F. R., Gualtieri, C., & Janzen, J. G. (2022). Effects of Vegetation Density on Sediment Transport in Lateral Cavities. Environmental Sciences Proceedings, 21(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2022021016







