Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Factors of Surface Temperature Changes Before and After Ecological Restoration of Mines in the Plateau Alpine Permafrost Regions Based on Landsat Images
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
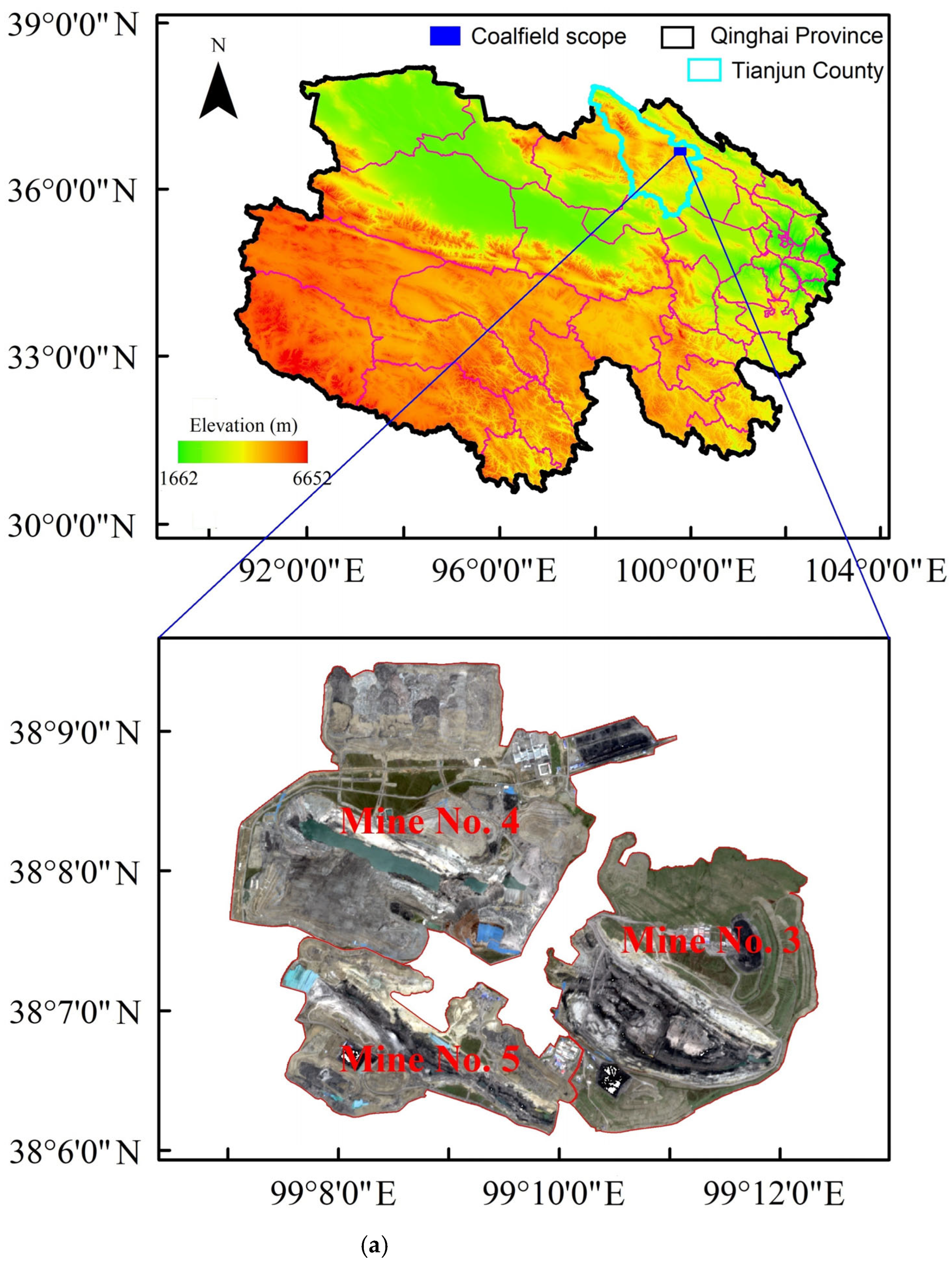
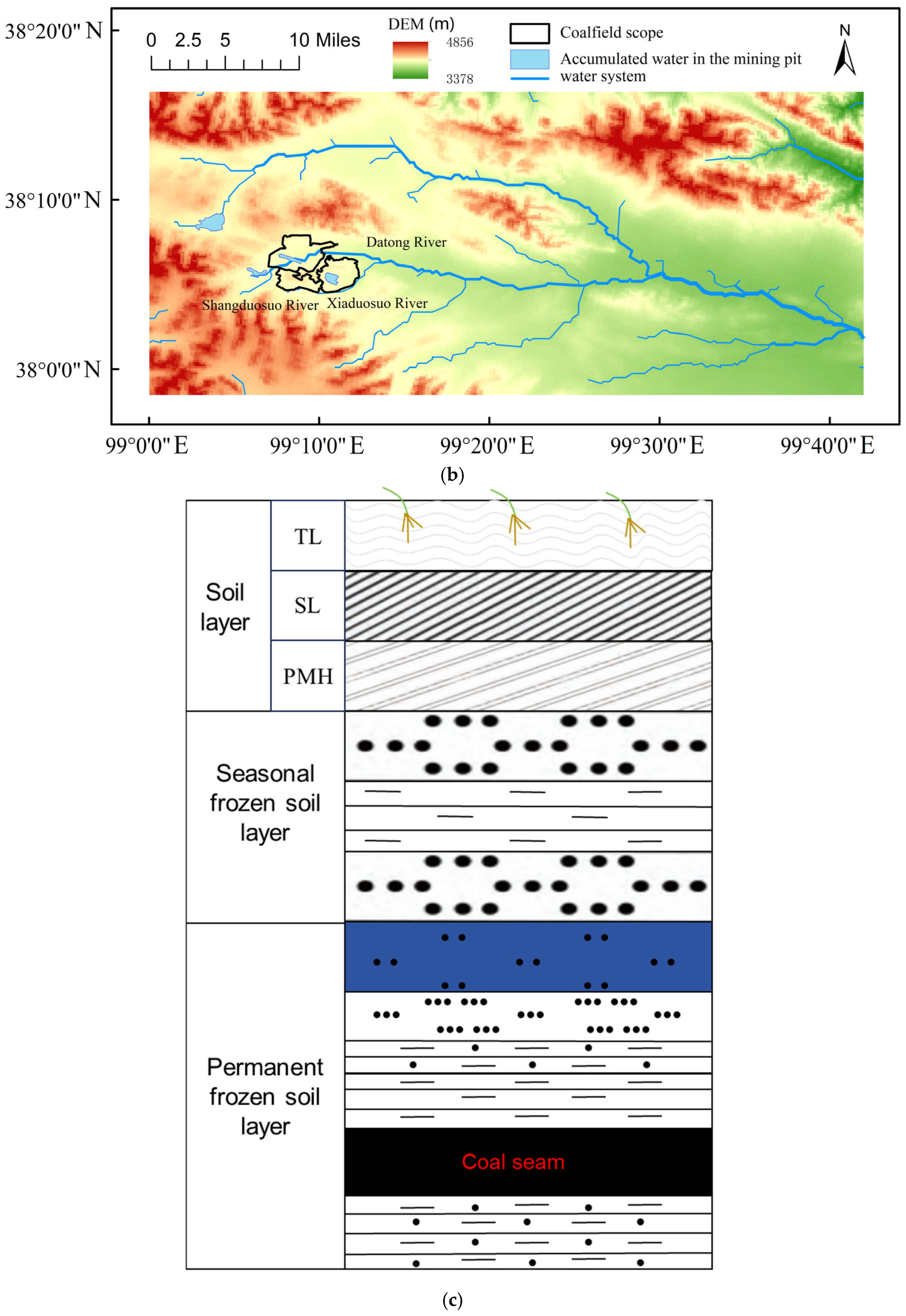
2.1. Study Area
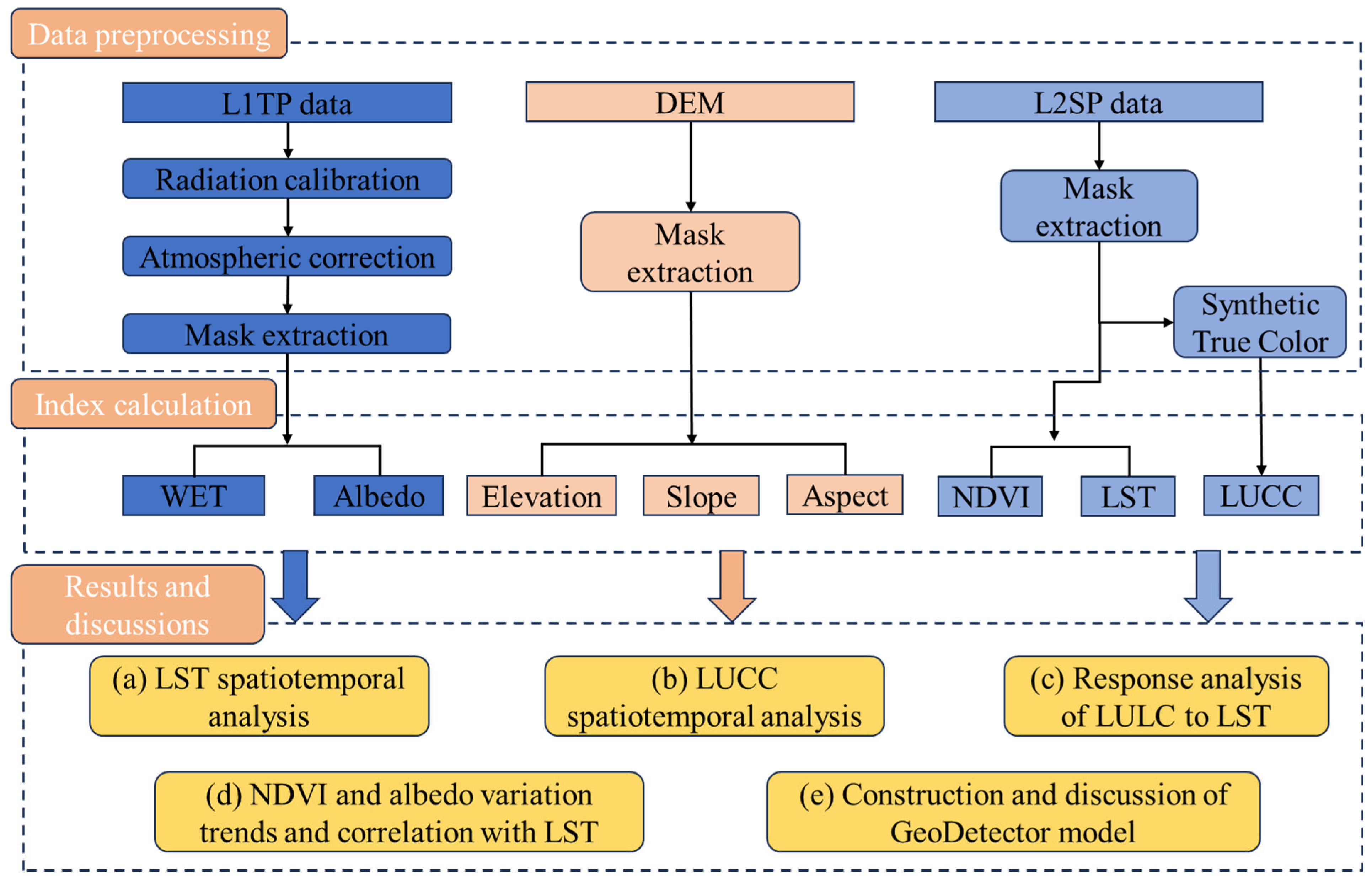
2.2. Data Source
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Land Surface Temperature
2.3.2. Albedo
2.3.3. Normalized Difference Vegetation Index
2.3.4. Soil Wetness
2.3.5. Variation Trend
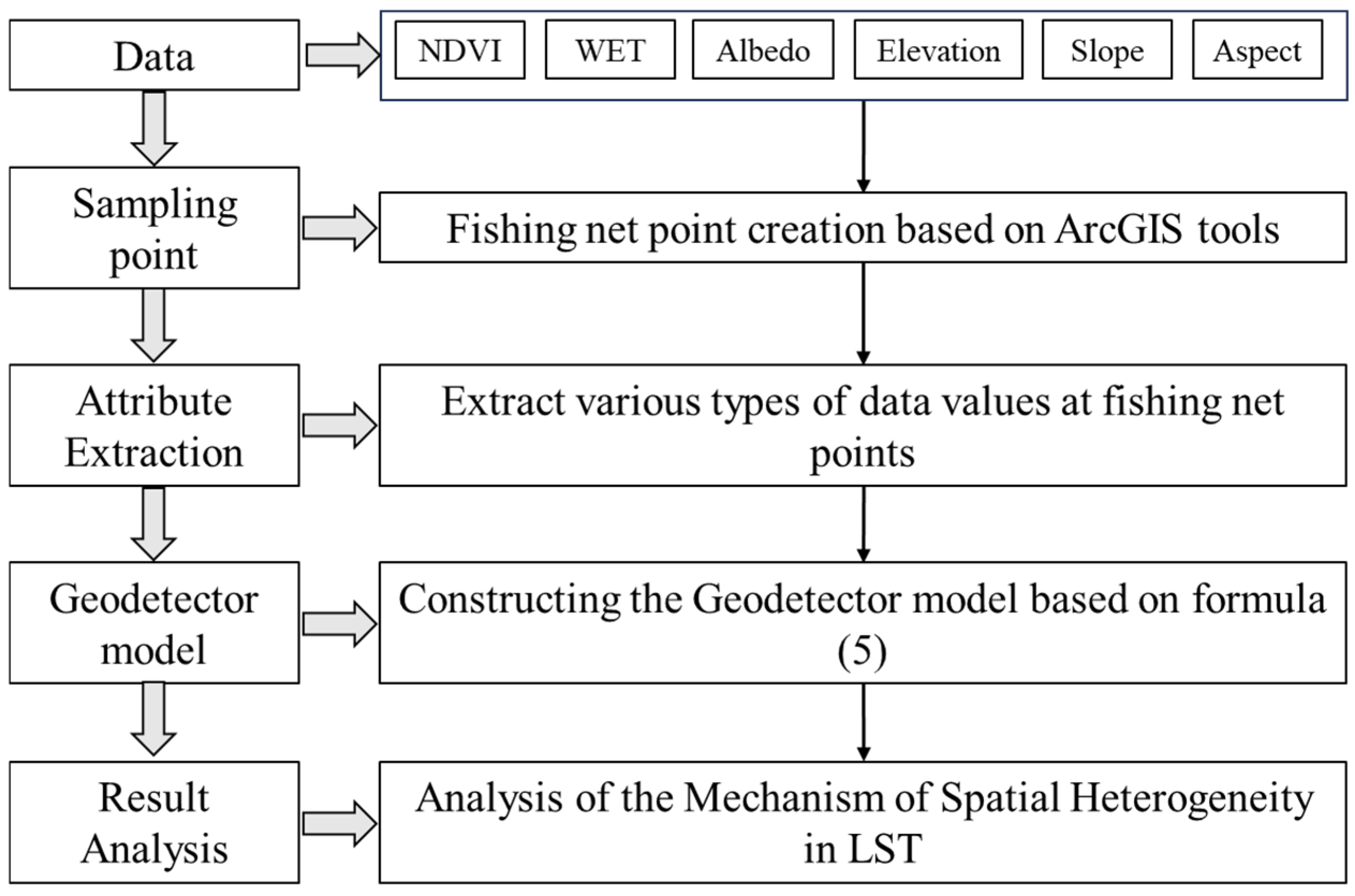
2.3.6. Geodetector
3. Results
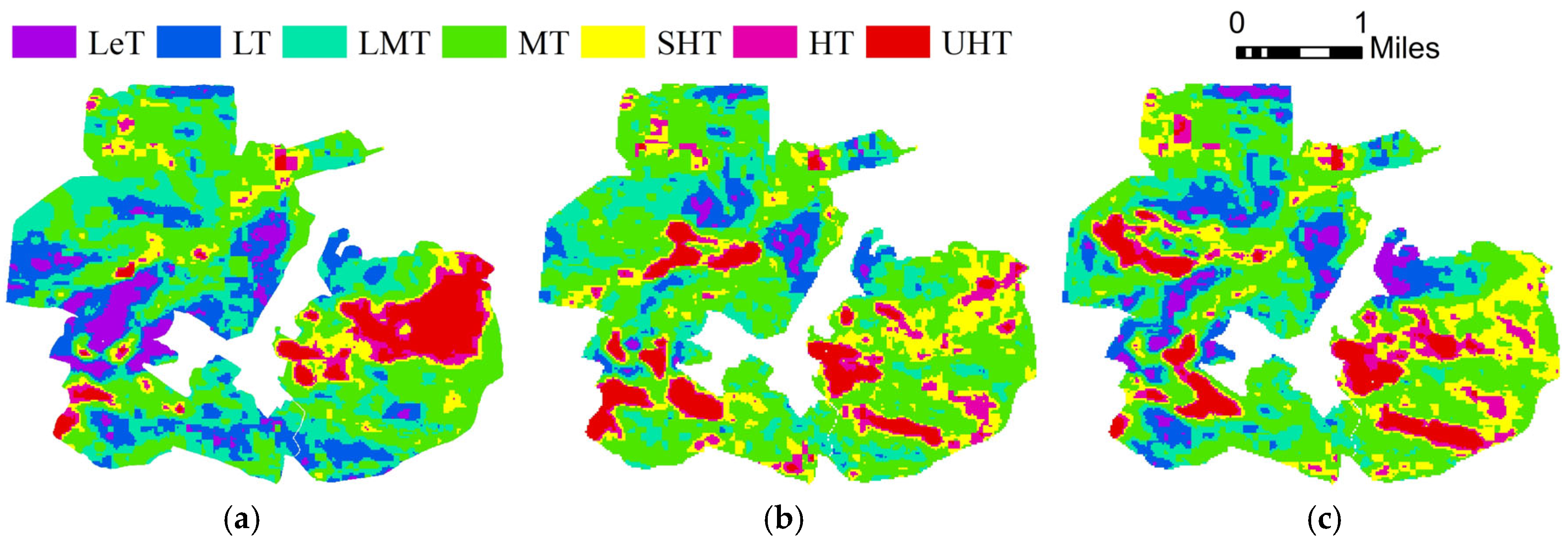
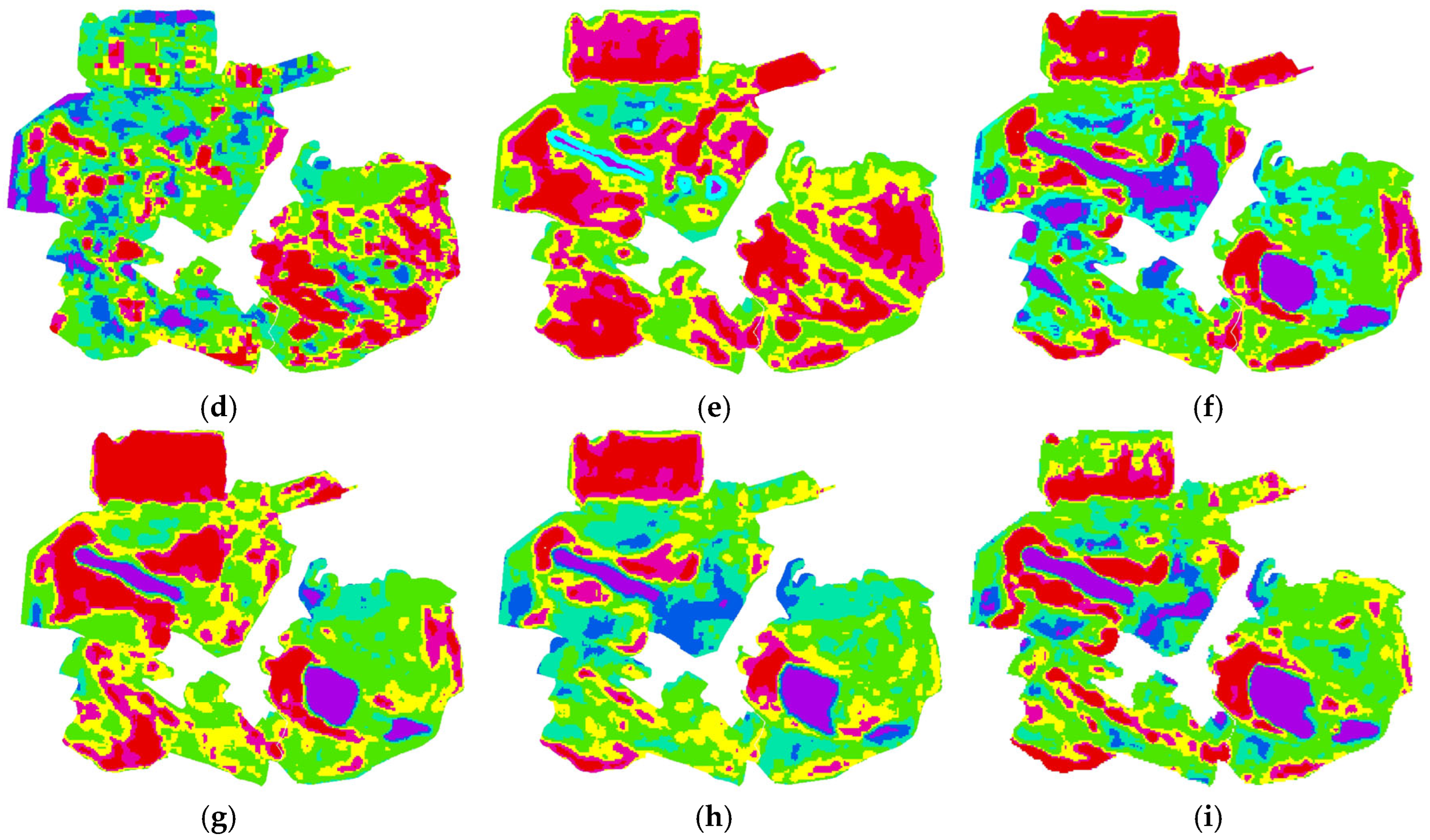
3.1. Spatiotemporal Variations of LST in the Mining Area Before and After Ecological Restoration
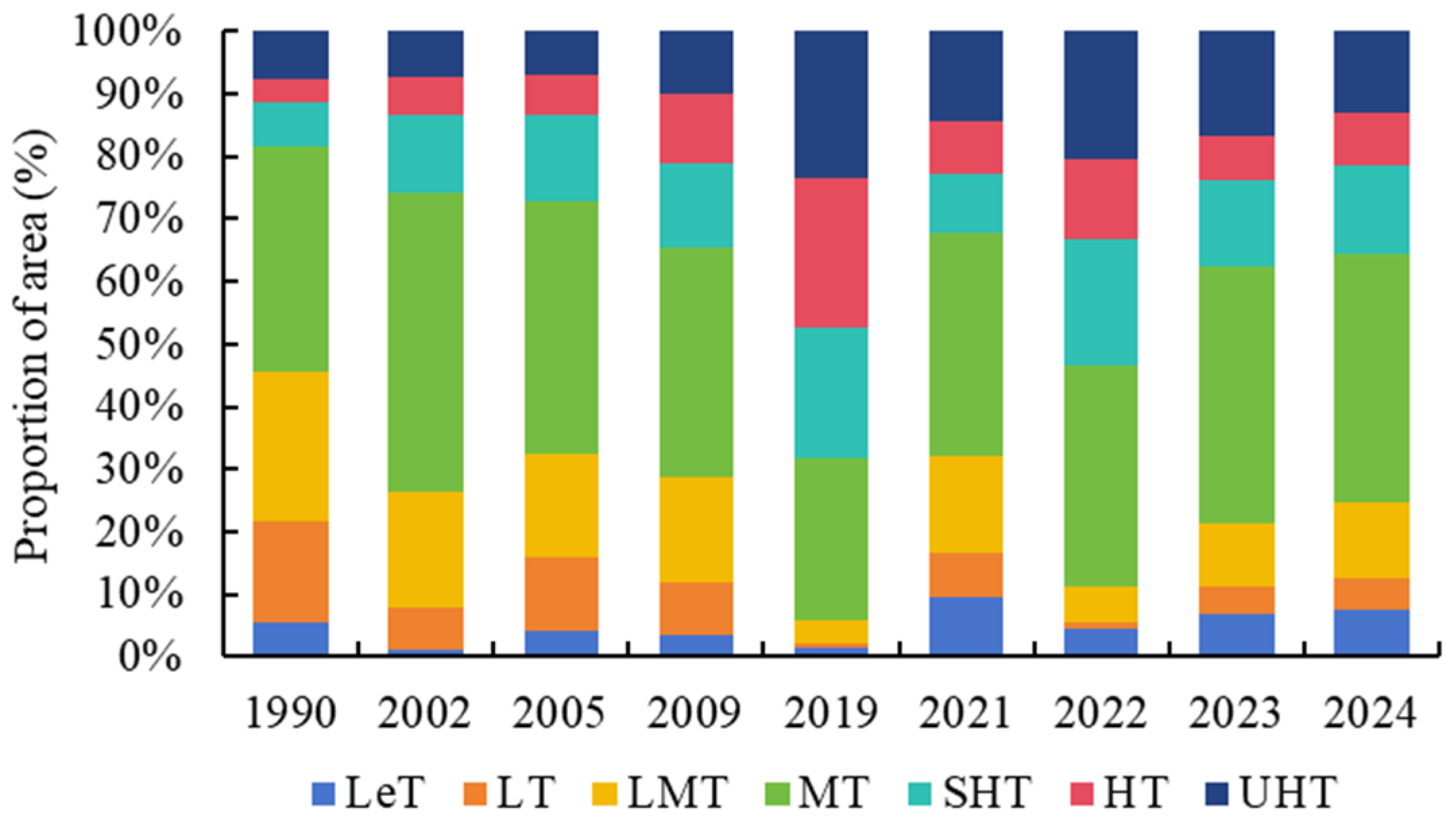
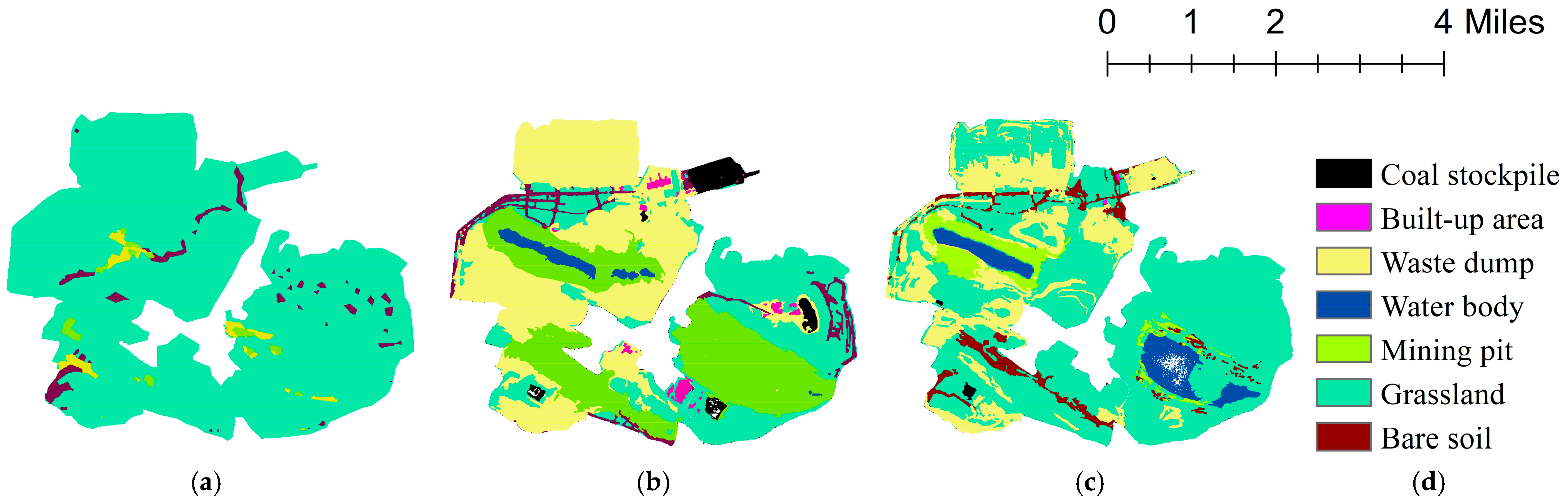
3.2. Spatiotemporal Variations of LUCC
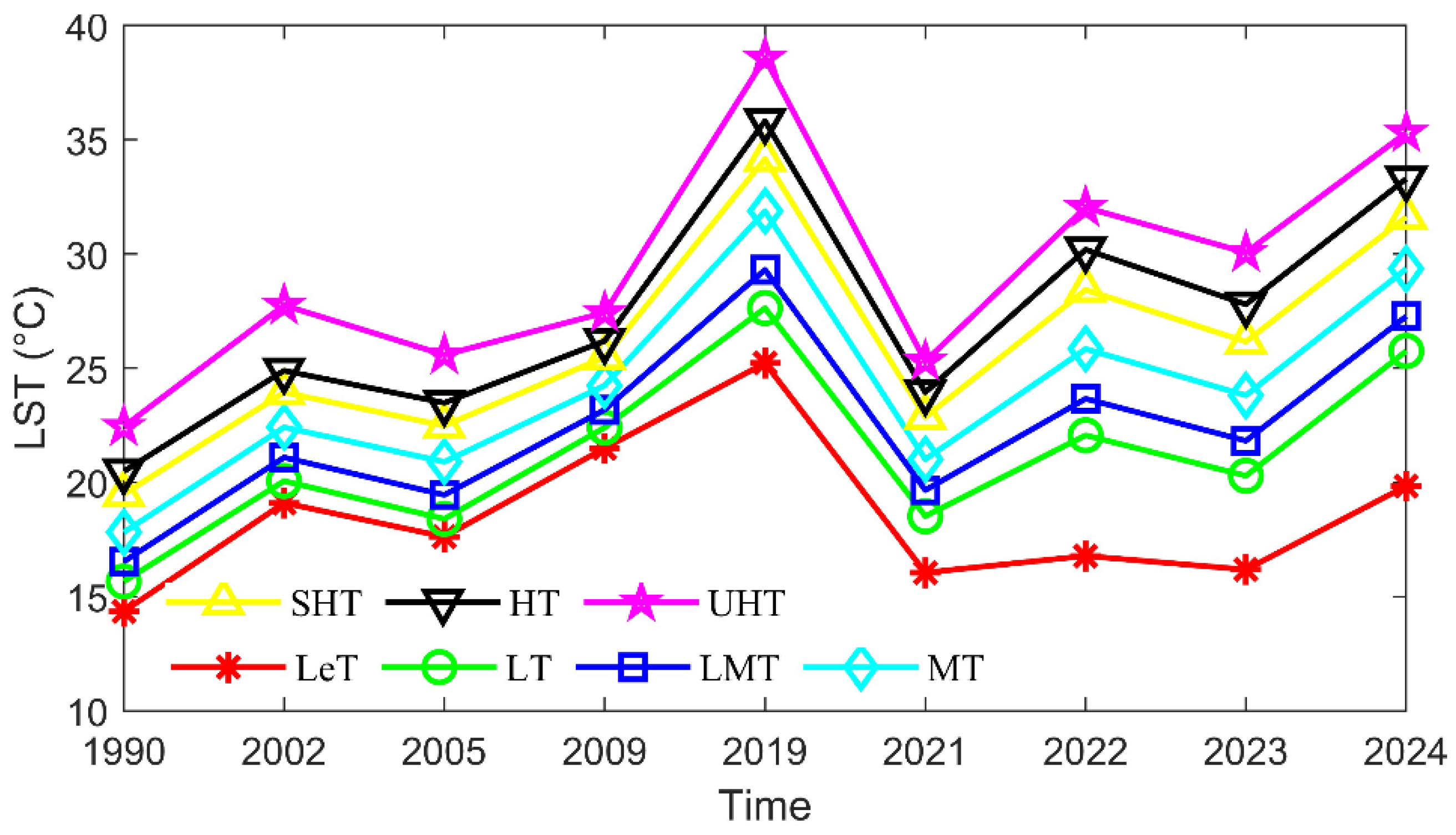
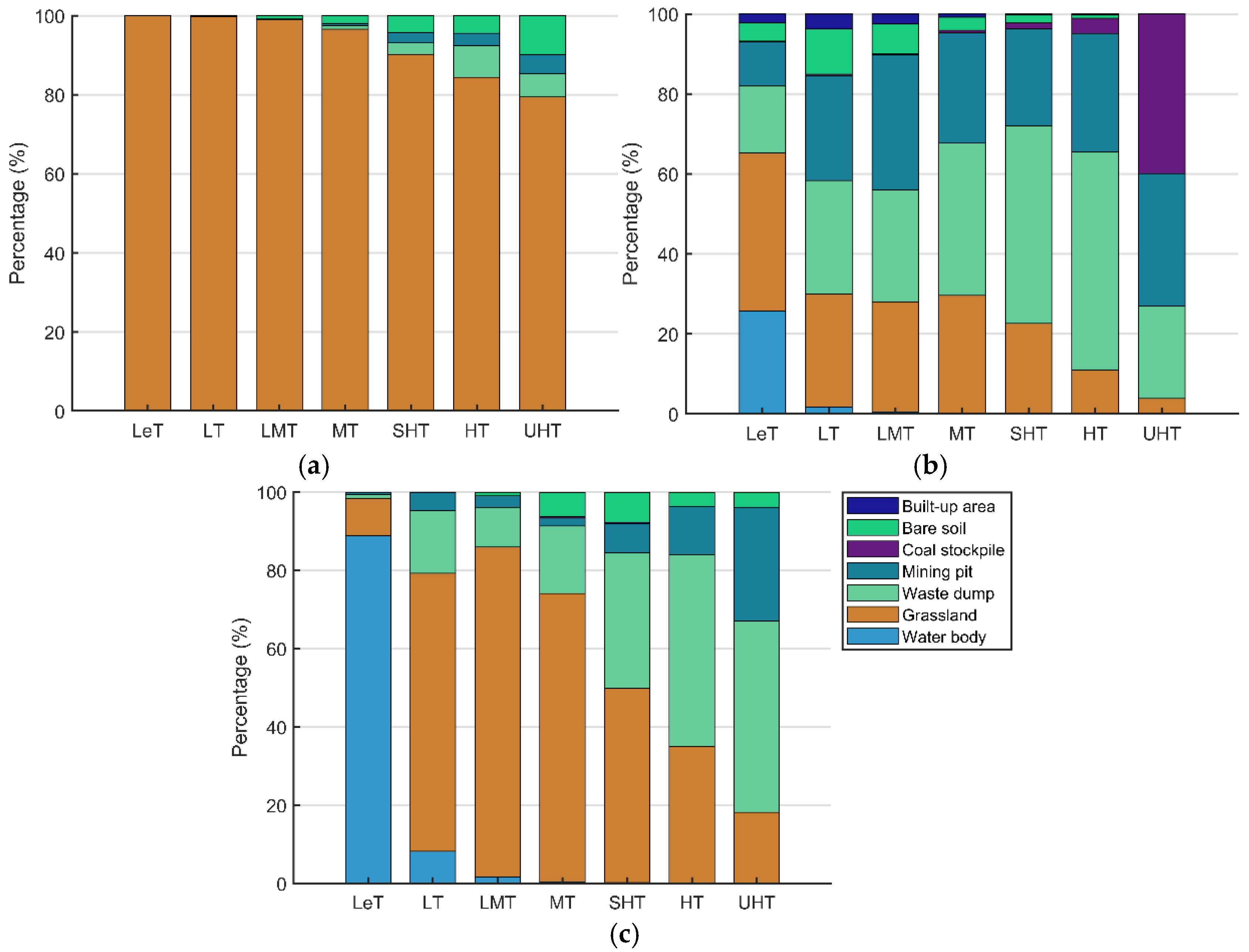
3.3. Response of Spatiotemporal Variations of LULC to LST
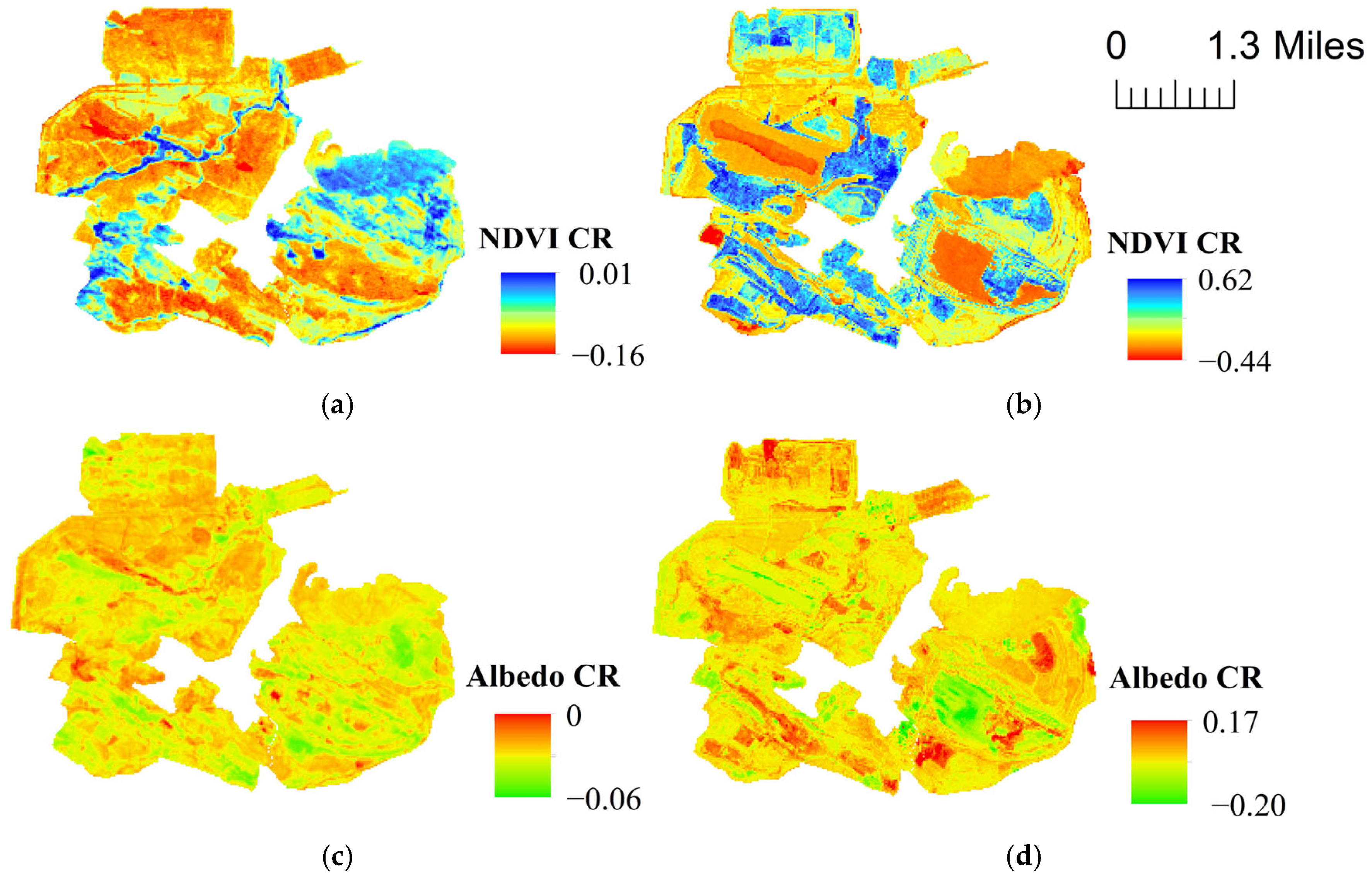
3.4. NDVI and Albedo Variation Trends and Their Correlation with LST
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, S.; Li, X. Several basic issues of ecological restoration of coal mines under background of carbon neutrality. Coal Sci. Technol. 2022, 50, 286–292. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kang, S.; Niu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Han, Y.; Dong, J.; Zhang, J. Impacts of mining on landscape pattern and primary productivity in the grassland of Inner Mongolia: A case study of Heidaigou open pit coal mining. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 2855–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ma, C.; Ma, Y.; Li, T. Monitoring and evaluation of ecological restoration in open-pit coal mine using remote sensing data based on a OM-RSEI model. Int. J. Min. Reclam. Environ. 2025, 600–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phengsaart, T.; Srichonphaisan, P.; Kertbundit, C.; Soonthornwiphat, N.; Sinthugoot, S.; Phumkokrux, N.; Juntarasakula, O.; Maneeintra, K.; Numprasanthaia, A.; Parkb, I.; et al. Conventional and recent advances in gravity separation technologies for coal cleaning: A systematic and critical review. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Ouyang, J.; Zheng, S.; Tian, Y.; Sun, R.; Bao, R.; Li, T.; Yu, T.; Li, S.; Wu, D.; et al. Research on Ecological Effect Assessment Method of Ecological Restoration of Open-Pit Coal Mines in Alpine Regions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2022, 19, 7682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.; Song, W.; Gu, H.; Li, F. Progress in the remote sensing monitoring of the ecological environment in mining areas. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Shi, Y.; Fu, Y. Identifying vegetation restoration effectiveness and driving factors on different micro-topographic types of hilly Loess Plateau: From the perspective of ecological resilience. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 289, 112562–112576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Ye, B.; Bai, Z.; Feng, Y. Remote sensing monitoring of vegetation reclamation in the Antaibao open-pit mine. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Huang, J.; Lei, S.; Cao, Z. Study on vegetation coverage change of Xilinhot’s Shengli mining area in recent 30 years. J. Henan Polytech. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2019, 38, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zahidi, I.; Liang, D. Spatiotemporal variation of vegetation cover in mining areas of Dexing City, China. Environ. Res. 2023, 225, 115634–115643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karan, S.; Samadder, S.; Maiti, S. Assessment of the capability of remote sensing and GIS techniques for monitoring reclamation success in coal mine degraded lands. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 182, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yan, X.; Cao, Z.; Yang, Z.; Liang, J.; Ma, T.; Liu, Q. Identification of successional trajectory over 30 years and evaluation of reclamation effect in coal waste dumps of surface coal mine. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 269, 122161–122174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, X.; Jiao, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhang, H. Investigating the spatio-temporal pattern evolution characteristics of vegetation change in Shendong coal mining area based on kNDVI and intensity analysis. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 11, 1344664–1344684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y. Response of net primary productivity of vegetation to land cover change in six coal fields of Shanxi province. China Min. Mag. 2021, 30, 107–114. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Ma, G. Soil erosion changes in Jiangxi Province from 2001 to 2015 based on USLE model. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 38, 8–11. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guha, S.; Govil, H.; Gill, N.; Dey, A. A long-term seasonal analysis on the relationship between LST and NDBI using Landsat data. Quatern Int. 2020, 575–576, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagat, S.; Prasad, P. Assessing the Impact of Spatio-Temporal Land Use and Land Cover Changes on Land Surface Temperature, with a Major Emphasis on Mining Activities in the State of Chhattisgarh, India. Spat. Inf. Res. 2024, 32, 339–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, T.; Jhariya, D.; Kishore, N. The Effects of Coal Mining on Land Use and Land Surface Temperature: A Case Study of Korba District, Chhattisgarh. J. Environ. Inform. Lett. 2023, 10, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Guo, J.; Wang, F.; Song, Z. Monitoring the Characteristics of Ecological Cumulative Effect Due to Mining Disturbance Utilizing Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaddad, F.; Mello, F.; Tayebi, M.; Safanelli, J.; Campos, L.; Amorim, M.; de Sousa, G.; Ferreira, T.; Ruiz, F.; Perlatti, F. Impact of Mining-Induced Deforestation on Soil Surface Temperature and Carbon Stocks: A Case Study Using Remote Sensing in the Amazon Rainforest. J. South Am. Earth Sci. 2022, 119, 103983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimish, G.; Bharath, H.; Lalitha, A. Exploring Temperature Indices by Deriving Relationship Between Land Surface Temperature and Urban Landscape. Remote Sens. Appl. 2020, 18, 100299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Li, C.; Liu, X.; Zhao, X. Assessing Ecological Restoration in Arid Mining Regions: A Progressive Evaluation System. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, M.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, Q.; Yu, W.; Liang, S. Determining the scale of coal mining in an ecologically fragile mining area under the constraint of water resources carrying capacity. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 279, 111621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siqi, J.; Yuhong, W. Effects of Land Use and Land Cover Pattern on Urban Temperature Variations: A Case Study in Hong Kong. Urban Clim. 2020, 34, 100693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Gupta, K. Urban Heat Island Formation in Relation to Land Transformation: A Study on a Mining Industrial Region of West Bengal. In Regional Development Planning and Practice: Contemporary Issues in South Asia; Mishra, M., Singh, R.B., Lucena, A.J., de Chatterjee, S., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 297–323. ISBN 978-981-16-5681-1. [Google Scholar]
- Kandulna, W.; Jain, M.; Chugh, Y.; Agarwal, S. Spatial Variability of Land Surface Temperature of a Coal Mining Region Using a Geographically Weighted Regression Model: A Case Study. Land 2025, 14, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudriki Semlali, B.E.; Molina, C.; Park, H.; Camps, A. Fengyun-2F/VISSR Land Surface Temperature Anomalies Between 2014 and 2022 and Their Potential Correlation with Earthquakes. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2023-2023 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Pasadena, CA, USA, 16–21 July 2023; pp. 2560–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudriki Semlali, B.E.; Molina, C.; Park, H.; Camps, A. Association of land surface temperature anomalies from GOES/ABI, MSG/SEVIRI, and Himawari-8/AHI with land earthquakes between 2010 and 2021. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2024, 15, 2324982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Li, X.; Sun, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y. Effects of Restoration Years on Vegetation and Soil Characteristics under Different Artificial Measures in Alpine Mining Areas, West China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, F.; He, G.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Peng, Y. Monitoring of Land Cover and Vegetation Changes in Juhugeng Coal Mining Area Based on Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Hu, Z.; Yang, K.; Guo, J.; Li, P.; Li, G. Assessment of the Ecological Impacts of Coal Mining and Restoration in Alpine Areas: A Case Study of the Muli Coalfield on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 162919–162934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Guo, J.; He, T.; Lei, K.; Deng, X. Assessing the ecological impacts of opencast coal mining in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau-a case study in Muli coal field, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 153, 110454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Guo, H.; Ouyang, X.; Gunasekera, D.; Sun, Z. Land surface temperature retrieval from SDGSAT-1: Assessment of different retrieval algorithms with different atmospheric reanalysis data. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2025, 18, 2492314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Dozier, J. A Generalized Split-window Algorithm for Retrieving Land-surface Temperature from Space. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1996, 34, 892–905. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, S.; Shuey, C.; Russ, A.; Fang, H.; Chen, M.; Walthall, C.; Daughtry, C.; Hunt, R. Narrowband to broadband conversions of land surface albedo: II. validation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 84, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valor, E. Mapping Land Surface Emissivity from NDVI: Application to European, African, and South American Areas. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 57, 167–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdun, I.; Bechtold, M.; Sagris, V.; Mander, U. Satellite Determination of Peatland Water Table Temporal Dynamics by Localizing Representative Pixels of A SWIR-Based Moisture Index. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, C. Geodetector: Principle and prospective. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Qi, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Yang, R.; Cao, Y. Variation of land surface temperature and its influencing factors in Muli Coalfield, Qinghai Province. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2023, 45, 980–992. [Google Scholar]
- Firozjaei, M.; Sedighi, A.; Firozjaei, H.; Kiavarz, M.; Panah, S. A historical and future impact assessment of mining activities on surface biophysical characteristics change: A remote sensing-based approach. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 107264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owolabi, A.; Amujo, K.; Olorunfemi, I. Spatiotemporal changes on land surface temperature, land and water resources of host communities due to artisanal mining. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 36375–36398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Chatterjee, R.; Kumar, D.; Panigrahi, D. Spatio-temporal variation and propagation direction of coal fire in Jharia Coalfield, India by satellite-based multi-temporal night-time land surface temperature imaging. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2021, 31, 765–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, H.; Xu, F. Spatiotemporal changes in desertified land in rare earth mining areas under different disturbance conditions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 30323–30334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, X.; Hu, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Ruan, M. Research on Temporal and Spatial Resolution and the Driving Forces of Ecological Environment Quality in Coal Mining Areas Considering Topographic Correction. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Deng, Y.; Wang, J.; Luo, M. Fine identification of vegetation types in open pit mining regions using combined UAV RGB imagery and LiDAR point cloud data. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2025, 18, 2515269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Operation Steps | Detailed Description of LST Inversion |
|---|---|
| (1) Remote sensing image collection | L2SP image collection from 1990 to 2024 (https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov (accessed on 10 May 2025)) |
| (2) LST inversion | Scale and data type conversion of LST: ① (LST_K = DN × 0.00341802 + 149); LST_K is the scale factor corrected LST (unit: Kelvin). ② (LST = LST_K − 273.15); LST is the surface temperature in Celsius units. |
| (3) LST extraction in the research area | Extraction of LST masks for each phase in the research area |
| (4) Application and analysis | Long time scale spatiotemporal analysis and visualization |
| Classification Criteria of LST | Temperature Range |
|---|---|
| Lower temperature | Ti < Ta − 1.5S |
| Low temperature | Ta − 1.5S ≤ Ti < Ta − S |
| Low-medium temperature | Ta − S ≤ Ti < Ta − 0.5S |
| Medium temperature | Ta − 0.5S ≤ Ti < Ta + 0.5S |
| Sub-high temperature | Ta + 0.5S ≤ Ti < Ta + S |
| High temperature | Ta + S ≤ Ti < Ta + 1.5S |
| Ultra-high temperature | Ti ≥ Ta + 1.5S |
| Year | LULC | Albedo | Soil Wetness | Slope | Aspect | Elevation | NDVI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1990 | Grassland | 0.218 | 0.315 | 0.028 | 0.093 | 0.027 | 0.112 |
| 2019 | Grassland | 0.092 | 0.013 | 0.016 | 0.064 | 0.051 | 0.043 |
| Mining pit | 0.096 | 0.087 | 0.031 | 0.119 | 0.093 | 0.065 | |
| Waste Dump | 0.105 | 0.041 | 0.019 | 0.174 | 0.073 | 0.073 | |
| 2024 | Grassland | 0.052 | 0.070 | 0.015 | 0.037 | 0.041 | 0.057 |
| Mining pit | 0.121 | 0.067 | 0.110 | 0.189 | 0.172 | 0.010 | |
| Waste Dump | 0.058 | 0.088 | 0.069 | 0.185 | 0.089 | 0.144 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, L.; Ju, L.; Liu, J.; Jiao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, X.; Yue, C. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Factors of Surface Temperature Changes Before and After Ecological Restoration of Mines in the Plateau Alpine Permafrost Regions Based on Landsat Images. Earth 2025, 6, 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth6040141
Chen L, Ju L, Liu J, Jiao S, Zhang Y, Yin X, Yue C. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Factors of Surface Temperature Changes Before and After Ecological Restoration of Mines in the Plateau Alpine Permafrost Regions Based on Landsat Images. Earth. 2025; 6(4):141. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth6040141
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Lei, Linxue Ju, Junxing Liu, Sen Jiao, Yi Zhang, Xianyang Yin, and Caiya Yue. 2025. "Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Factors of Surface Temperature Changes Before and After Ecological Restoration of Mines in the Plateau Alpine Permafrost Regions Based on Landsat Images" Earth 6, no. 4: 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth6040141
APA StyleChen, L., Ju, L., Liu, J., Jiao, S., Zhang, Y., Yin, X., & Yue, C. (2025). Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Factors of Surface Temperature Changes Before and After Ecological Restoration of Mines in the Plateau Alpine Permafrost Regions Based on Landsat Images. Earth, 6(4), 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth6040141







