Abstract
Wastewater contamination of freshwater ecosystems is a major driver of the spread of antibiotic resistance (AR). This preliminary study investigated the impact of wastewater pollution on the AR profiles of bacterial communities in the Oued–Zénati waterway, Algeria, across a pollution gradient. From September 2017 to May 2018, water samples were collected from an upstream reference site (P1), a site downstream of urban and hospital discharges (P2), and a downstream recovery site (P3). Physicochemical and microbiological analyses revealed a critical pollution hotspot at P2, with fecal coliform concentrations reaching 9.5 × 105 MPN/100 mL, nearly 40 times higher than at P1. From a representative subset of 33 bacterial isolates characterized in this study, susceptibility testing showed a high prevalence of resistance, with observed trends matching the pollution gradient. Specifically, 100% of isolates from the polluted sites (P2 and P3) were resistant to ampicillin, and 60% of isolates from the hotspot (P2) were resistant to amoxicillin/clavulanic acid. Conversely, all isolates remained susceptible to gentamicin. These initial findings suggest that direct wastewater discharge is creating a significant reservoir for AR, highlighting potential risks to public and environmental health and underscoring the urgent need for improved wastewater management infrastructure.
1. Introduction
Freshwater, an indispensable resource for life and socioeconomic development, is increasingly threatened by pollution from anthropogenic activities [1,2,3]. The discharge of untreated or inadequately treated wastewater, industrial effluents, and agricultural runoff has led to a widespread degradation of water body quality, posing significant risks to both human health and ecological integrity [2,4,5,6,7,8]. This situation is often aggravated by a lack of rigorous planning and continuous monitoring, which compromises effective decision-making for resource protection [9,10]. The impact of these human activities on the microbiome and “resistome”—the collection of all antibiotic resistance genes in a given environment—has been demonstrated globally, transforming rivers into vectors for contaminant dissemination [11,12,13,14].
Among the emerging threats, the rise and spread of antibiotic resistance (AR) within aquatic bacterial communities is a major global public health concern [15,16,17]. Wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs), while crucial, are recognized as imperfect barriers and key nodes in this cycle, receiving a high load of antibiotic-resistant bacteria (ARB) and ARGs but failing to eliminate them completely [18,19,20,21,22]. In fact, WWTPs are often considered hotspots for the proliferation and horizontal gene transfer of ARGs, as conventional treatments are not efficient in removing them [23]. Hospital effluents are considered particularly critical “hotspots” due to their high concentration of multidrug-resistant pathogens and antibiotic residues, which can induce toxic effects on aquatic organisms, even at low concentrations [24,25,26]. The recent COVID-19 pandemic, for example, has exacerbated this issue by increasing the load of antibiotics like azithromycin and ciprofloxacin in hospital wastewaters, leading to heightened ecological risks in receiving rivers [27]. Even wastewater from pharmaceutical production facilities can drastically enrich for ARGs in the environment [28]. This critical role of hospitals as reservoirs of resistance is confirmed by numerous systematic reviews and meta-analyses showing a significantly higher prevalence and diversity of ARGs in hospital wastewater compared to community wastewater [15,17,29,30,31]. Specific tracking studies have followed high-risk clones from patient rooms directly into the environment [32,33], highlighting the unique and dangerous resistance profiles originating from clinical settings.
To properly contextualize our research, it is important to note that recent studies show the global scale of the problem. Numerous articles confirm the major role of wastewater in the spread of antibiotic resistance. They emphasize that conventional wastewater treatment plants are often unable to eliminate antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) and can even act as contamination “hotspots” [34,35,36,37].
Hospital wastewater is particularly highlighted. For example, a comprehensive analysis by Hassoun-Kheir et al. [29] concluded that it is richer in multi-resistant bacteria. More recently, advanced genetic analyses, such as those by Shafiq et al. [38], have refined this finding by identifying genes conferring resistance to last-resort treatments (like blaNDM) in hospital discharges.
This situation is confirmed worldwide. In Pakistan, Rahim et al. [39] observed high resistance in E. coli bacteria in the Sutlej River. In Switzerland, Lee et al. [40] proved that discharges from treatment plants strongly alter the presence of resistance genes in rivers, with some genes like sul1 even serving as indicators of this pollution.
Furthermore, resistance can survive treatment. Siri et al. [41] observed that the removal of highly problematic genes like mcr-1 is inefficient in hospital wastewater treatment plants. The impact also affects the agricultural sector: research by Soufi et al. [42] in Mexico demonstrated that irrigation with wastewater contaminates agricultural soils with these resistance genes. Faced with the ineffectiveness of standard methods, research is therefore turning to alternatives such as constructed wetlands [43].
The widespread use of antibiotics like amoxicillin, often combined with clavulanic acid, contributes significantly to this environmental pressure [44]. Its incomplete removal in WWTPs [45] and its demonstrated capacity to increase the prevalence of resistant E. coli in both clinical and veterinary contexts [46,47,48] make it a key molecule in the environmental dissemination of AR. The dissemination of AR is a complex process mediated by mobile genetic elements (MGEs) such as plasmids, transposons, and integrons, which facilitate horizontal gene transfer between different bacterial species [49,50]. This “mobilome” is a key driver in the evolution of the environmental resistome [51]. Furthermore, the selection pressure is not exerted by antibiotics alone. The co-occurrence of heavy metals, often found in mixed industrial–urban effluents, can co-select for antibiotic resistance, further complicating the issue [52,53]. The final environmental impact depends on a delicate balance between treatment efficiency and the background quality of the receiving water body [54].
In Algeria, water resources are under severe pressure from a combination of factors, including demographic growth and industrial development [3,6]. Waterways like the Oued–Zénati, receiving multiple untreated discharges, constitute a relevant case study to assess these dynamics in a North African context where data remains scarce. In fact, to our knowledge, the number of published studies specifically assessing antibiotic resistance in Algerian waterways is so limited that they can be counted on one hand, highlighting a critical data gap. Although previous work in the region has highlighted related challenges, such as the contamination of sanitation by-products like sewage sludge [55], a direct assessment of the impact of wastewater on AR in this specific watercourse is lacking. Consequently, there is a clear need for foundational data to understand the local scale of this problem and to guide future, more extensive research.
Therefore, this preliminary study was designed to characterize the impact of wastewater pollution on the antibiotic resistance of bacteria isolated from the Oued–Zénati. Using a gradient approach, we aimed to generate baseline data and test the hypothesis that the site directly impacted by urban and hospital effluents (P2) would act as a hotspot for antibiotic resistance. Specifically, we hypothesized that (1) the site directly impacted by urban and hospital effluents (P2) would exhibit significantly greater physicochemical and microbiological degradation compared to the upstream reference site (P1) and (2) that this increased pollution would be directly correlated with a higher prevalence and a broader spectrum of antibiotic resistance profiles among the isolated bacteria. This work serves as a foundational step to justify and design larger-scale monitoring programs in the region.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites and Sampling Strategy
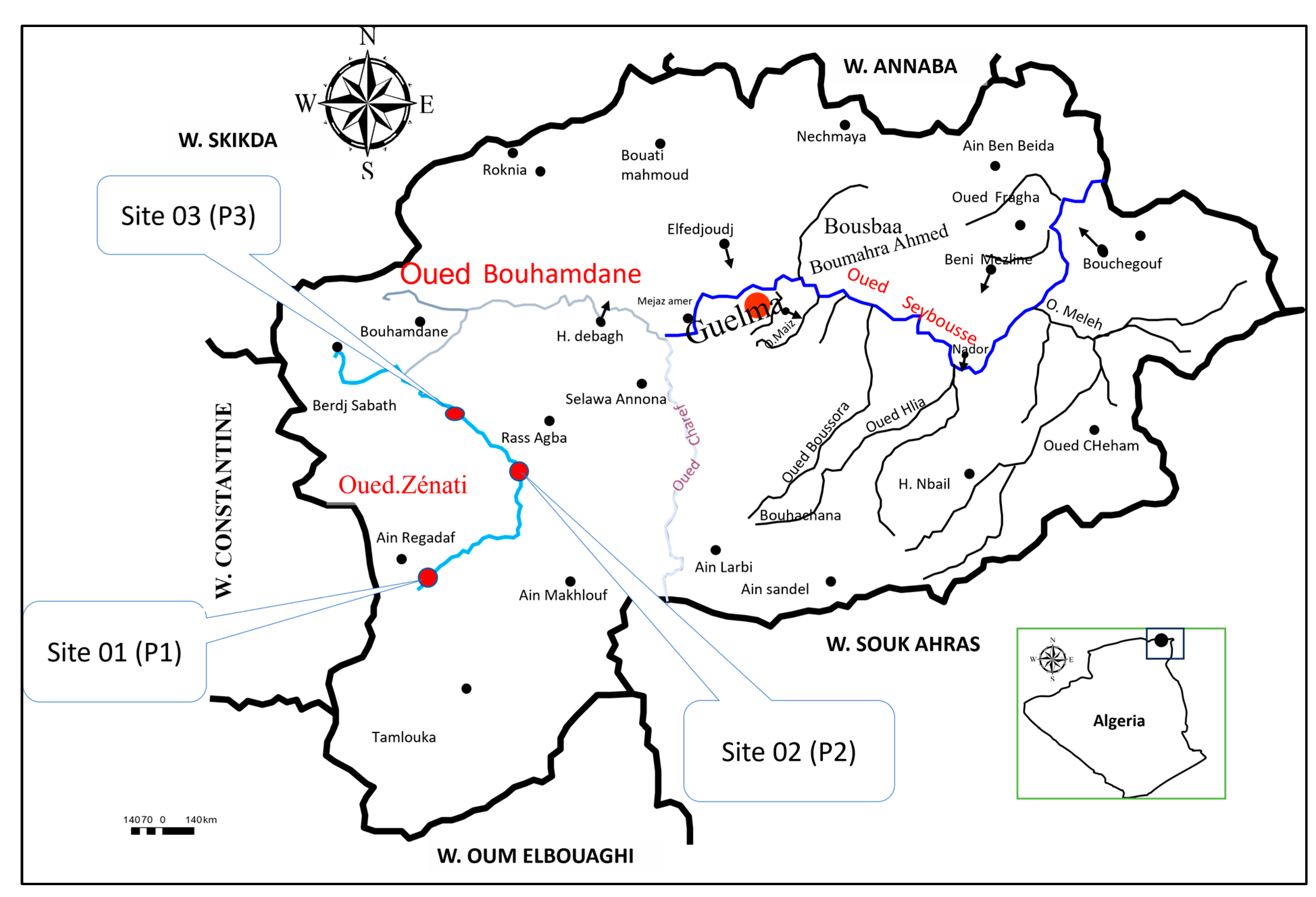
The watercourse “Oued-Zénati” represents the most important stream in the hydrographic network of the municipality, which also bears its name. It is located at the following geographical coordinates (36°18′37″ N, 7°19′56″ E). It also includes several smaller Chaâbats that act as tributaries within the municipality (Figure 1) [56]. It originates in the west and flows across the entire municipality of Oued–Zénati over a distance of more than 2 km. Its sources arise to the west of Ain Regada, near the Ain-Abid region, from the confluence of the Oued El M’leh—originating in Djebel Oum Settas (1326 m)—and Chaâbet Touifsa, which has its source at Kef Eddeb (1142 m) [9]. Its valley stretches from Constantine to Guelma (Figure 1). On its left bank, it receives the tributaries Oued Bou Skoum, Berneb, Kalech, Chaâbet Errassoul, and Snoussi; on its right bank, it is fed by Chaâbet Guelt and Terba, Oued El Gloub, and Chaâbet Mrassel. Beyond the town of Oued–Zénati, the stream passes through Bordj Sabbat, where it receives Oued El-Meridj, which originates from the Constantine plateaus [57]. All these tributaries feed into Oued Bou Hamdane and eventually flow into Oued Seybouse.
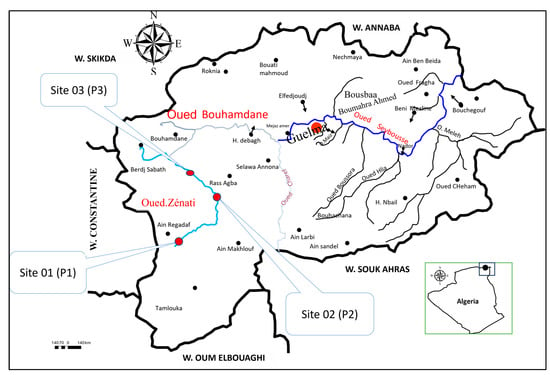
Figure 1.
Map of the study area showing the location of the three sampling sites (P1, P2, and P3) along the Oued–Zénati waterway.
The physical and morphometric characteristics of the watercourse, according to a study by the Hydraulic Directorate of the Guelma Wilaya [9], indicate that the Oued–Zénati basin covers an area of 592.15 km2, with the main stream flowing for a length of 41.30 km.
The major issue with Oued–Zénati is that it serves as an open-air sewer. Due to its location, it is the only outlet for all discharges from the municipality and the hospital. It is also used as an open public dumping ground by nearby residents. Its waters are extensively used for irrigation along the entire valley. As such, it is considered a source of pollution and waterborne diseases (bacterial and parasitic) and therefore represents a public health concern that needs urgent attention.
The entire Oued–Zénati basin is subject to a semi-arid climate, with a noticeable seasonal coefficient. Precipitation is more abundant in winter and lower in summer. These seasonal variations in rainfall affect the flow of Oued–Zénati, with higher monthly flow rates observed during the winter season [9,57,58].
To provide a preliminary assessment of the impact of wastewater pollution on antibiotic resistance, three sampling sites were selected along the Oued–Zénati waterway in Algeria (Figure 1). The key characteristics of these sites are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Description of the Sampling Sites along the Oued–Zénati Waterway.
The selection of these sites, whose physicochemical characteristics were studied in greater detail in our previous work [45], allows for a comparative assessment of the impact of discharges on AR dynamics.
2.2. Sample Collection and Preservation
Water samples were collected monthly from September 2017 to May 2018 from the three sampling sites. During each monthly sampling event, three replicate samples were collected at each site, at a depth of 30 cm in sterile glass bottles. They were transported to the Laboratory of Biology, Water and Environment (LBEE) at 8 May 1945 University, Guelma, and the Biotechnology Research Center (CRBt), in a cooler at 4 °C, and analyzed within 24 h, in accordance with standard recommendations for water analysis [59].
2.3. Microbiological Analyses
2.3.1. Enumeration of Fecal Contamination Indicators
Total coliforms (TC), fecal coliforms (FC), and fecal streptococci (FS) were enu-merated from each replicate sample using the Most Probable Number (MPN) method, following standardized protocols. The results presented are the average of these triplicates for each sampling event.
The following culture media and incubation conditions were used:
- Total coliforms and Escherichia coli: Bromocresol Purple Lactose Broth (BCPL), incubated at 37 °C for 24–48 h, in accordance with the principles of the ISO 9308-2:2012 standard [60].
- Fecal coliforms: Brilliant Green Bile Broth (BGBB) and peptone water, incubated at 44 °C for 24 h, following the miniaturized method described in the ISO 9308-3:1998 standard [61].
- Intestinal enterococci (Fecal streptococci): Litsky Broth (EVA), incubated at 37 °C for 24–48 h, in accordance with the ISO 7899:2000 standard [62].
2.3.2. Bacterial Isolation and Identification
Water samples were inoculated on non-selective (Nutrient Agar) and selective (MacConkey) culture media for the isolation of Gram-negative bacilli. After incubation, colonies exhibiting distinct morphologies were purified, creating a pool of over 200 isolates collected throughout the nine-month study period. From this pool, a representative subset of 33 isolates was selected for in-depth characterization. The selection strategy was a non-random, purposive sampling designed to ensure spatial and morphological representativeness: specifically, we aimed to select at least one isolate of each distinct morphotype (based on colony size, shape, and color) from each of the three sampling sites. When multiple isolates of the same species were identified at a given site, three were chosen to assess potential intra-species variability. This approach was chosen over random selection to capture the broadest possible spectrum of cultivable diversity within the practical limits of this preliminary investigation. The objective was thus to maximize the observable taxonomic diversity, rather than to reflect the relative abundance of dominant species. The identification of these 33 isolates was performed using the API 20E biochemical test system (bioMérieux, Marcy-l′Étoile, France), following the manufacturer’s instructions.
2.3.3. Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing (Antibiogram)
The susceptibility of the 33 isolates was assessed using the disk diffusion method on Mueller-Hinton agar, in accordance with the guidelines of the Antibiogram Committee of the French Society for Microbiology (CA-SFM) [63]. The antibiotic panel was selected to represent several major classes of clinical and environmental importance: Amikacin (AK, 30 µg), Tetracycline (TE, 30 µg), Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole (SXT, 1.25/23.75 µg), Amoxicillin/Clavulanic acid (AX, 20/10 µg), Gentamicin (CN, 10 µg), Ampicillin (AM, 10 µg), and Cefazolin (CZ, 30 µg). This panel provides an initial profile of resistance to β-lactams, aminoglycosides, tetracyclines, and sulfonamides.
To ensure the reliability of the results, each antibiogram test was performed in triplicate. Inhibition zone diameters were measured after 18–24 h of incubation at 37 °C. The interpretation of results (Susceptible, Intermediate, Resistant) was carried out according to CA-SFM guidelines. Due to evolving standards, the CA-SFM/EUCAST 2019 recommendations were applied for most antibiotics.
The selection of these antibiotics for susceptibility testing was guided by several criteria, including their prevalence in wastewater from the study area, their accessibility, and their representation of different therapeutic classes. According to information obtained from local hospitals and pharmaceutical sales representatives, ampicillin, tetracycline, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, gentamicin, colistin, nalidixic acid, amoxicillin/clavulanic acid, and cefazolin were among the most commonly prescribed and used antibiotics in the region during the study period.
2.4. Physicochemical Analyses
Temperature, pH, electrical conductivity, and dissolved oxygen were measured in situ using a multiparameter probe (Inolab 750 WTW, Weilheim, Germany). Suspended solids (SS), nitrates (NO3−), nitrites (NO2−), ammonium (NH4+), and orthophosphates (PO43−) were quantified in the laboratory using spectrophotometric methods with a HACH Lange DR3900 spectrophotometer (Loveland, CO, USA) and cuvette test kits, following the manufacturer’s protocols.
For each site, three samples were analyzed for physicochemical parameters throughout the study, and the average value was systematically considered.
2.5. Statistical Analyses
Statistical analyses were performed using XLSTAT (v. 2016) and JASP (v. 0.19.3). Differences in mean values between sites were assessed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. Due to the low counts of isolates in some categories, differences in species distribution between sites were evaluated descriptively rather than by formal statistical tests like the Chi-square (χ2), which would be inappropriate. Pearson’s correlation coefficient was calculated in an exploratory manner to investigate potential trends between water quality parameters and antibiotic resistance patterns. Due to the small number of sampling sites (n = 3), the results of the correlation analysis should be interpreted with extreme caution, as they do not allow for causal inference. A significance threshold of p < 0.05 was applied to all statistical tests.
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical and Microbiological Water Characterization
Physicochemical parameters showed significant variations between the three sampling sites, as detailed in Table 2. Site P2, which is impacted by effluent discharges, exhibited significantly higher temperature, electrical conductivity, and salinity compared to the reference site P1 (ANOVA, p < 0.05). Conversely, the dissolved oxygen concentration was significantly lower at site P2 (5.7 ± 5.26 mg/L) compared to sites P1 (12.2 ± 5.26 mg/L) and P3 (12.5 ± 5.26 mg/L). Nutrient concentrations followed a similar pattern: nitrites (NO2−) and orthophosphates (PO43−) were significantly higher at site P2, while nitrates (NO3−) were lower, a trend that may suggest active nitrification processes or varying dilution effects. No significant difference in ammonium concentration was observed between the sites.

Table 2.
Mean values and standard deviations of physicochemical parameters measured at the three sampling sites.
Microbiological analyses revealed significant fecal contamination with marked spatial variations (Table 3). The concentrations of total coliforms (TC), fecal coliforms (FC), and fecal streptococci (FS) were markedly higher at site P2 compared to sites P1 and P3, a trend supported by ANOVA (p < 0.05). For instance, the mean concentration of FC at site P2 (9.5 × 105 MPN/100 mL) was nearly 38 times higher than that of the reference site P1 (2.5 × 104 MPN/100 mL).

Table 3.
Mean values (± standard deviation) and [Min–Max] ranges of fecal contamination indicators (MPN/100 mL) at the three sampling sites.
3.2. Bacterial Community Composition
From the representative subset of 33 bacterial isolates, belonging to seven distinct genera, some were identified and selected for in-depth resistance characterization. The distribution of these isolates (Table 4) revealed notable differences in the composition of the cultivable bacterial community between sites, providing a preliminary snapshot of the impact of pollution. Site P2, directly affected by effluent discharges, exhibited the greatest species diversity, within our collection of isolates, including isolates of Escherichia coli and Serratia odorifera, which were not detected at the other sites. Conversely, Plesiomonas shigelloides was specifically isolated from the reference site P1. Some species appeared to be more ubiquitous, such as Aeromonas hydrophila and Chryseobacterium miningosepticum, which were found both upstream (P1) and at the impacted site (P2). Klebsiella pneumoniae proved to be the most persistent species, having been isolated from all three sites along the pollution gradient.

Table 4.
Distribution of bacterial species isolated from the three sampling sites.
3.3. Antibiotic Resistance Profiles
Antibiotic susceptibility was determined for all 33 isolates. To ensure data reliability, each test was performed in triplicate. Table 5 presents the mean diameters of inhibition zones (± standard deviation) for each strain.

Table 5.
Inhibition zone diameters (mm) for selected bacterial species against tested antibiotics. Values are presented as mean ± standard deviation of three technical replicates. (AK: Amikacin, TE: Tetracycline, SXT: Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole, AX: Amoxicillin/Clavulanic acid, CN: Gentamicin, AM: Ampicillin, CZ: Cefazolin).
A notable variability in susceptibility was observed between different species and sites (Table 5). For instance, Aeromonas hydrophila isolates from both P1 and P2 showed large inhibition zones for amikacin (40 mm) and gentamicin (46 mm), indicating high susceptibility. In contrast, Klebsiella pneumoniae from the polluted site P2 exhibited very small inhibition zones for multiple antibiotics, including tetracycline (7 mm) and ampicillin (8 mm), suggesting a multidrug-resistant profile. It is also noteworthy that all tested isolates showed some level of inhibition zone for gentamicin, whereas for ampicillin, several isolates, including E. coli from P2, showed diameters close to zero, indicating complete resistance.
The interpretation of these data, based on the breakpoints defined by the Antibiogram Committee of the French Society for Microbiology [63], allowed for the calculation of resistance prevalence at each sampling site (Table 6). Overall, the results indicate a clear trend between the degree of pollution and the increase in antibiotic resistance rates.

Table 6.
Percentage of bacterial isolates exhibiting a resistant phenotype to antibiotics, by sampling site.
Firstly, a nearly universal resistance to ampicillin (AM) was observed, with a rate of 75% at the reference site P1, reaching 100% at sites P2 and P3, located downstream of discharge points. Secondly, a noticeable emergence of resistance was found for tetracycline (TE) and cefazolin (CZ). While no resistance was detected at site P1 (0%), it appeared significantly at site P2 (20%) and further increased at site P3 (33.3%).
Furthermore, site P2 stands out as a potential hotspot for multidrug resistance among the studied isolates, displaying the highest resistance rates for both amoxicillin/clavulanic acid (AX) and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (SXT), each reaching 60%. Finally, it is worth noting a particularly remarkable finding: complete susceptibility to gentamicin (CN) was observed across all 33 isolates, regardless of their site of origin.
3.4. Correlations Between Environmental Parameters and Antibiotic Resistance
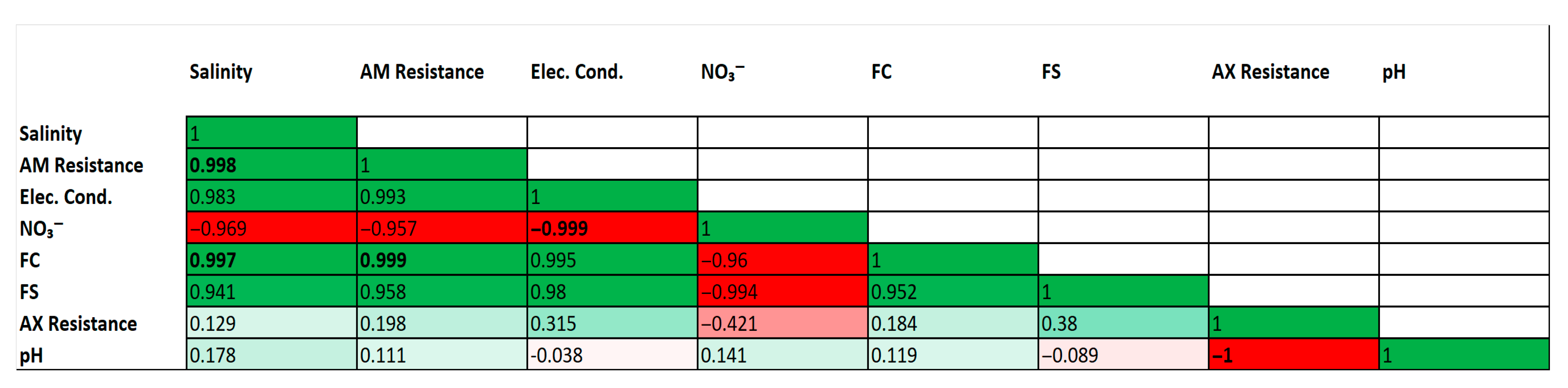
An exploratory correlation analysis was conducted to investigate potential trends between environmental parameters and antibiotic resistance patterns (Figure 2). Several strong and statistically significant correlations were observed. For instance, a very strong positive correlation was found between fecal coliforms (FC) and ampicillin (AM) resistance (r = 0.999, p < 0.05). Strong positive correlations were also identified between physical indicators of wastewater pollution, such as salinity and electrical conductivity, and the abundance of fecal coliforms.
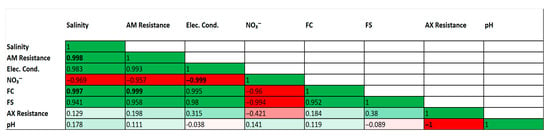
Figure 2.
Correlation matrix of environmental parameters and antibiotic resistance patterns. Heatmap of Pearson correlation coefficients (r) between selected environmental parameters and antibiotic resistance patterns. The color scale indicates the strength and direction of the correlation (green for positive, red for negative). Correlation coefficients in bold are statistically significant (p < 0.05). Analysis is based on mean values for each of the three sampling sites (n = 3).
Conversely, strong negative correlations were identified, notably a perfect negative correlation between pH and amoxicillin/clavulanic acid (AX) resistance (r = −1.000, p < 0.05), and between electrical conductivity and nitrate concentrations (r = −0.999, p < 0.05). Consistent with the exploratory nature of this analysis (based on n = 3 sites), these high correlation coefficients are interpreted with extreme caution and are not considered evidence of a direct causal relationship.
4. Discussion
The results of this preliminary study strongly suggest that the Oued–Zénati is an aquatic ecosystem under intense anthropogenic pressure, serving as both a receptacle and a potential vector for the dissemination of antibiotic resistance. This work demonstrates that a pollution gradient approach is a highly effective methodology for assessing the impact of wastewater discharge on the environmental resistome, even with a limited number of sites. This discussion aims to interpret these initial findings, contextualize them with respect to the scientific literature, and highlight their potential implications for public health and environmental management in the region.
The analysis of physicochemical and microbiological parameters reveals a textbook case of severe water degradation at site P2. The significant increase in temperature is a direct consequence of the discharge of domestic and hospital wastewater, which is typically warmer than the receiving river water. The elevated salinity and electrical conductivity at P2 are also clear markers of sewage, reflecting a higher load of dissolved salts and ions compared to the natural background levels observed at P1. The most critical indicator, however, is the sharp drop in dissolved oxygen. The mean value of 5.7 mg/L indicates hypoxic conditions, a direct result of the high load of biodegradable organic matter from the wastewater [64]. The decomposition of this matter by heterotrophic microorganisms is a highly oxygen-consuming process that depletes the stream’s oxygen reserves. This oxygen deficit has cascading consequences on biogeochemical cycles, such as promoting denitrification, which explains the lower nitrate concentrations observed at P2 despite high nitrogen inputs. Simultaneously, the peaks of nitrites and orthophosphates at P2 are direct chemical markers of recent and untreated fecal pollution, a finding consistent with studies in other polluted urban water systems [65,66]. The slight, non-significant increase in salinity at P3 compared to P2 could be attributed to evaporation between the two sites, which would concentrate dissolved salts, and potential diffuse inputs from agricultural soil runoff.
Microbiological contamination confirms this diagnosis. The surge in total coliforms, fecal coliforms, and fecal streptococci at P2, with a fecal load nearly 40 times higher than upstream, demonstrates that the watercourse receives a continuous influx of human and potentially animal fecal matter. This corroborates observations made in other urban contexts where sanitation systems are deficient or absent [67]. The presence of these bacteria is not just an indicator; it is the primary vehicle by which resistant bacteria and their genes—originating from the human gut microbiota and clinical pathogens—are introduced into the environment.
The core of our findings lies in the apparent trend linking this pollution gradient to the prevalence of antibiotic resistance among the isolates we analyzed. Based on our data, site P2 emerged as a potential “hotspot” of resistance, supporting our main hypothesis. The significantly higher prevalence of resistance to multiple antibiotics at P2 compared to P1 suggests that wastewater discharges act as the primary driver for the selection and dissemination of antibiotic resistance (AR) in this ecosystem. This conclusion is strongly supported by a growing body of literature; numerous reviews and meta-analyses have established that hospital and urban wastewaters are major contributors to AMR in aquatic environments [34,37]. This phenomenon is widely documented globally, where urban and especially hospital effluents are identified as major sources of environmental contamination by multidrug-resistant bacteria (MDRB) and antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) [29,30,68].
Our limited set of isolates nonetheless revealed concerning resistance profiles. It is crucial to interpret these findings with caution; the resistance percentages are based on a small number of isolates (e.g., n = 15 at site P2), meaning these estimates are associated with large confidence intervals (e.g., 60% ± approx. 25% for n = 15). Therefore, these rates should be considered as preliminary observations of trends rather than robust prevalence measures. The high resistance to ampicillin (75% at P1, 100% at P2 and P3) could suggests either long-standing background contamination by low-level penicillinase-producing strains or an intense and diffuse selection pressure such that even the reference site is already heavily impacted. This high prevalence of resistance to older antibiotics like ampicillin and tetracycline is a common feature of polluted waterways, as reported by Rahim et al. [39] in Pakistan, who also found high resistance rates for these agents in E. coli. More concerning is the 60% resistance rate to the amoxicillin/clavulanic acid combination at P2. Resistance to this combination could imply the presence of more complex mechanisms, perhaps involving extended-spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs) or AmpC-type cephalosporinases [44,69]. The search for new strategies to circumvent these resistances, such as encapsulating the inhibitor in nanocarriers, underscores the clinical challenge posed by such profiles [70].
The contrast with gentamicin, for which complete susceptibility was observed, is both striking and informative. This result, similar to that found by Saciuk et al. [47], who used gentamicin as a negative control, suggests several non-exclusive hypotheses. Gentamicin and other aminoglycosides may be less frequently used in outpatient medicine in the region, thus reducing specific selection pressure. Alternatively, the most prevalent mobile genetic elements (plasmids, integrons) in this environment may not commonly carry aminoglycoside resistance genes. While many metagenomic studies report the presence of aminoglycoside resistance genes in wastewater (e.g., aadA, as shown by Lee et al. [40], our phenotypic results suggest that either these genes are not highly expressed in the cultivable bacteria we isolated, or that the specific strains prevalent in our study area do not carry them, highlighting a unique local characteristic that warrants further investigation. Whatever the case, this result provides a valuable baseline and shows that the “resistome” sampled in Oued–Zénati, while concerning, may not yet be uniformly resistant to all antibiotic classes. This contrasts with findings from some highly impacted environments, such as those receiving wastewater from pharmaceutical production, where a much broader enrichment of ARGs has been observed [28], suggesting that the pollution load in our study site, while severe, may not yet have selected for resistance across all antibiotic classes.
The exploratory correlation analysis, although to be interpreted with extreme caution due to the small number of sites, revealed some interesting trends. The near-perfect correlation between salinity/conductivity and resistance to ampicillin (r > 0.99) likely does not mean that salt causes resistance. Rather, these parameters are more plausibly co-tracers of the same source: wastewater. Urban discharges simultaneously increase the ionic load of the water and the proportion of ampicillin-resistant bacteria. Likewise, the perfect negative correlation (r = −1.000) between pH and resistance to amoxicillin/clavulanic acid is a clear statistical artifact. Site P2 combines a slightly lower pH with the highest resistance prevalence, creating this mathematical correlation. The biological cause is not the pH, but the overall pollution signature of site P2.
The dissemination of resistant bacteria in a watercourse actively used for agricultural irrigation could create a vicious cycle and a potential threat to public health from a “One Health” perspective. Resistant pathogens could contaminate crops, be ingested by livestock, and thus enter the human food chain [69]. The risk of community-acquired infections by resistant strains—whose treatment will be more complex and costly—is therefore likely increased [15,71]. Furthermore, direct contact with water during recreational or agricultural activities represents another significant route of exposure, especially given that hospital wastewater is a confirmed reservoir of antibiotic resistance genes, posing a direct public health risk [30].
Beyond the bacteria themselves, the main danger likely lies in the reservoir of mobile resistance genes (the “mobilome”) that is created [49,50,51]. Under the nutrient- and bacteria-rich conditions at site P2, the opportunities for horizontal gene transfer between non-pathogenic environmental bacteria and opportunistic or strict pathogens are multiplied. The potential presence of co-pollutants such as heavy metals from industrial or artisanal discharges may act as strong co-selective agents, maintaining antibiotic resistance genes in the microbial community even in the absence of the antibiotic itself [8,52,53]. By highlighting the presence of this potential resistance hotspot, our study raises the alarm about the possible risk of emergent multidrug-resistant strains arising directly in the local environment.
A discussion of these findings would be incomplete without addressing the regulatory context. In Algeria, the Water Law (Law No. 05-12) and its associated executive decrees establish standards for wastewater discharge. However, the situation observed in the Oued–Zénati suggests a significant gap between legislation and enforcement. This gap is a common challenge in many regions and can be attributed to several factors, including insufficient wastewater treatment infrastructure for small and medium-sized municipalities, limited resources for monitoring, and challenges in applying penalties effectively. This context is crucial for understanding why such direct pollution persists despite existing regulations.
It is essential to thoroughly acknowledge the limitations inherent in this preliminary approach. The primary limitation is the small number of isolates (N = 33) characterized for antibiotic susceptibility. While our selection aimed to maximize diversity, this small sample size means that the calculated resistance percentages (e.g., 60% resistance to AX at P2) should be interpreted not as definitive prevalence rates for the entire ecosystem, but as indicative trends that require confirmation through larger-scale studies. These findings, therefore, represent a lower-bound estimate of the resistance problem. Furthermore, our non-random selection strategy, designed to maximize taxonomic diversity, may have introduced a selection bias. The resulting resistance profiles might therefore not be representative of the most dominant bacterial populations in the environment but rather reflect a broader spectrum of resistance found across various, including potentially rarer, species. An additional limitation is the disconnect between the enumeration of fecal indicator bacteria (e.g., coliforms) and the isolates selected for susceptibility testing. While we observed high levels of both fecal contamination and antibiotic resistance at site P2, our study did not determine whether the dominant indicator organisms were themselves the primary carriers of the observed resistance profiles. Future work should aim to bridge this gap by performing susceptibility testing directly on a larger number of isolates from these dominant indicator groups (e.g., E. coli) to better assess the public health risks. Furthermore, culture-based methods only allow visualization of the “tip of the iceberg” of the microbial community, as cultivable bacteria often represent only a small fraction of total diversity. Thus, the “resistome” of non-cultivable bacteria, which may be vast, remains entirely inaccessible. Moreover, our phenotypic analysis, though essential, provides no insight into the underlying genetic mechanisms. We do not know whether the observed resistances are due to chromosomal mutations or, more worryingly, carried by easily transferable conjugative plasmids.
These limitations nonetheless open up clear and necessary research avenues. This study serves as a crucial proof of concept, justifying the need for a logical continuation towards molecular approaches. A full metagenomic analysis, as performed by Shafiq et al. [38] on hospital wastewater, would be the ideal next step to characterize the full spectrum of ARGs, including last-resort resistance genes like blaNDM, and to identify their bacterial hosts. A metagenomic analysis of DNA extracted from water and sediments would allow for a comprehensive inventory of ARGs and MGEs, quantifying their abundance and identifying their potential bacterial hosts, including non-cultivable ones [52]. This would provide a much more accurate view of the actual dissemination risk. Quantitative PCR (qPCR) monitoring of specific genes (e.g., β-lactamase genes, class 1 integron genes) could also serve as a faster and more targeted surveillance tool.
From a management perspective, our findings, while preliminary, call for consideration of immediate and concrete actions. The situation of Oued–Zénati illustrates the potential failure of a wastewater management strategy based on “dilution.” As numerous reviews have pointed out, conventional wastewater treatment is often insufficient for removing ARGs, making source control and advanced treatment essential [35,36]. In light of the enforcement challenges discussed, our results call not only for a strengthening of monitoring capacities and the application of existing laws but also for the urgent implementation of effective wastewater treatment systems. This is especially critical for hospital effluents, which should ideally be treated at the source before being mixed with municipal wastewater [31,32]. Technologies such as membrane bioreactors (MBRs) have shown some effectiveness in reducing antibiotic residues such as amoxicillin, although degradation products may persist [45]. The establishment of a regular water quality monitoring program, including resistance indicators, is non-negotiable to protect both ecosystem health and the health of populations that depend on it.
5. Conclusions
This preliminary investigation provides strong evidence that the direct discharge of untreated wastewater, including domestic, hospital, and industrial effluents, into the Oued–Zénati leads to severe and statistically significant degradation of its water quality. This pollution likely acts as a primary driver for the proliferation and dissemination of antibiotic resistance. The pollution hotspot (site P2) exhibited a fecal contamination load up to 40 times higher than the reference site, but also hypoxic conditions with dissolved oxygen levels dropping to 5.7 mg/L. A markedly higher prevalence of resistance to key antibiotics among the tested isolates, including 100% resistance to ampicillin and 60% to amoxicillin/clavulanic acid, in stark contrast to the complete susceptibility to gentamicin observed across all sites.
While based on a limited dataset, these findings represent critical first assessment for local authorities, highlighting the potential public health risks associated with the current situation, particularly the use of this water for irrigation. It is imperative to move beyond existing regulations towards concrete action. This includes implementing effective wastewater management strategies, such as the source-directed treatment of high-risk effluents, and strengthening the enforcement of environmental laws. This work underscores the urgent need for and provides the foundational data to design future, larger-scale research, notably using metagenomic approaches for a comprehensive characterization of the aquatic resistome in this understudied region.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.B., A.A., N.G. and M.H.; methodology, L.B., F.Z.M., A.A., N.G. and M.H.; software, L.B., F.Z.M. and M.H.; validation, L.B., N.G. and M.H.; formal analysis, L.B., F.Z.M., A.A. and M.H.; investigation, L.B., F.Z.M., A.A. and N.G.; resources, L.B., F.Z.M., A.A., N.G. and M.H.; data curation, L.B., F.Z.M. and M.H.; writing—original draft preparation, L.B., F.Z.M., A.A., N.G. and M.H.; writing—review and editing, L.B., F.Z.M., A.A., N.G. and M.H.; visualization, L.B., F.Z.M., A.A., N.G. and M.H.; supervision, L.B., F.Z.M., A.A., N.G. and M.H.; project administration, L.B., F.Z.M., A.A., N.G. and M.H.; funding acquisition, L.B., F.Z.M., A.A., N.G. and M.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no specific funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated in this study are presented in this paper.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the encouragement provided by the General Directorate of Scientific Research and Technological Development (DGRSDT), Algeria. We also wish to extend our thanks to the technical staff and colleagues at the Environmental Research Center (CRE) and the University 8 May 1945 Guelma for their support and assistance during this project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Du Plessis, A. Persistent degradation: Global water quality challenges and required actions. One Earth 2022, 5, 129–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettab, A. Les ressources en eau en Algérie: Stratégies, enjeux et vision. Desalination 2001, 136, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debieche, T.H. Evolution de la Qualité des Eaux (Salinité, Pollution) Sous L’effet de la Pollution Urbaine, Industrielle et Agricole. Cas de la Basse Plaine de la Seybouse (Nord-Est Algérien). Ph.D. Thesis, University of Constantine, Constantine, Algeria, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Agence Européenne de l’Environnement. State and Pressure of the Marine and Coastal Mediterranean Environment; Environmental Assessment Series No. 7; Agence Européenne de l’Environnement: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Salah, D.; Laffite, A.; Sivalingam, P.; Poté, J.W. Occurrence of toxic metals and their selective pressure for antibiotic-resistant clinically relevant bacteria in hospital wastewater and their receiving urban river in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 29, 20530–20541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guergazi, S.; Achour, S. Caractéristiques physico-chimiques des eaux d’alimentation de la ville de Biskra. Larhyss J. 2005, 4, 119–127. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, B.J.; Chakraborty, A.; Sehgal, R. A systematic review of industrial wastewater management: Evaluating challenges and enablers. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 348, 119230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, Z.; Manik, M.C.; Rahman, A.; Mondal, M.I.H.; Ullah, A.K.M.A.; Munna, M.S.; Sha-Alm, M.; Asaduzzaman, M.; Rubayet-Ul-Alam, A.S.M.; Rahman, M.Z.; et al. Impact of untreated tannery wastewater in the evolution of multidrug-resistant bacteria in Bangladesh. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 7147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benchaiba, L. Condition D’écoulement et Impact sur la Mobilisation des Ressources en eau: Bassin Versant de L’oued Bouhamdene (W. de Guelma, Est Algérien). Master’s Thesis, El Hadj Lakhder University, Batna, Algeria, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kafi-Benyahia, M. Variabilité Spatiale des Caractéristiques et des Origines des Polluants de Temps de Pluie Dans le Réseau D’assainissement Unitaire Parisien. Ph.D. Thesis, Ecole Nationale des Ponts et Chaussées, Paris, France, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Muurinen, J.; Muziasari, W.I.; Hultman, J.; Pärnänen, K.; Narita, V.; Lyra, C.; Fadlillah, L.N.; Rizki, L.P.; Nurmi, W.; Tiedje, J.M.; et al. Antibiotic Resistomes and Microbiomes in the Surface Water along the Code River in Indonesia Reflect Drainage Basin Anthropogenic Activities. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 14994–15006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; He, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, T.; Chen, Z.; Su, J.; Zhu, Y.-G.; Li, L.-G. Integrating global microbiome data into antibiotic resistance assessment in large rivers. Water Res. 2023, 250, 121030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joakim Larsson, D.G.; Flach, F. Antibiotic resistance in the environment. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 20, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodhi, K.; Kumar, M.; Singh, D. Insight into the amoxicillin resistance, ecotoxicity, and remediation strategies. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 39, 101858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmanuel, E. Evaluation des Risques Sanitaires et Ecotoxicologiques Liés aux Effluents Hospitaliers. Ph.D. Thesis, INSA de Lyon, Lyon, France, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.-B.; Kim, D.-W.; Lee, D.-H.; Kim, M.; Kim, M.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Cha, C.-J. Mobile resistome of human gut and pathogen drives anthropogenic bloom of antibiotic resistance. Microbiome 2020, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagra, K.; Singh, H.; Klümper, U.; Singh, G. Drivers of antibiotic resistance in two monsoon-impacted Indian urban rivers receiving untreated wastewater. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, X.; Fan, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Z. Wastewater treatment plants as reservoirs and sources for antibiotic resistance genes: A review on occurrence, transmission and removal. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 45, 102539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marathe, N.P.; Berglund, F.; Razavi, M.; Johnning, A.; Fick, J.; Flach, C.-F.; Larsson, D.G.J. Sewage effluent from an Indian hospital harbors novel carbapenemases and integron-borne antibiotic resistance genes. Microbiome 2019, 7, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, H.; Wu, D.; Luo, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y. Deciphering the antibiotic resistome and microbial community in municipal wastewater treatment plants at different elevations in eastern and western China. Water Res. 2022, 229, 119461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leroy-Freitas, D.; Machado, E.A.S.; Presa, P.I.; Alves, B.C.R.; O’Dwyer, D.B.; Lira, N.; de Oliveira, J.C.F.; Paulo, A.C.; Santos, C.E.I.; de Oliveira, R.R.R.; et al. Exploring the microbiome, antibiotic resistance genes and potential human pathogens in municipal wastewater treatment plants in Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 844, 156773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ping, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Huang, Y. The prevalence and removal of antibiotic resistance genes in full-scale wastewater treatment plants and their contributing factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 823, 154154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pazda, M.; Kumirska, J.; Stepnowski, P.; Mulkiewicz, E. Antibiotic resistance genes identified in wastewater treatment plant systems—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 134023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ory, J.; Bricheux, G.; Togola, A.; Bonnet, J.L.; Donnadieu-Bernard, F.; Nakusi, L.; Forestier, C.; Traoré, O. Ciprofloxacin residue and antibiotic-resistant biofilm bacteria in hospital effluent. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 214, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Alvarez, I.; Islas-Flores, H.; Gómez-Oliván, L.M.; Mejía-García, M.S.; SanJuan-Reyes, M.G.; Galar-Martínez, N. Determination of metals and pharmaceutical compounds released in hospital wastewater from Toluca, Mexico, and evaluation of their toxic impact. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 240, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzitelli, J.; Budzinski, H.; Cachot, J.; Geffard, O.; Marty, P.; Chiffre, A.; François, A.; Bonnafé, E.; Geret, F. Evaluation of psychiatric hospital wastewater toxicity: What is its impact on aquatic organisms? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 26090–26102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Bin, L.; Guo, P.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, C.; Chen, Z.; Tang, B. Ecological risk assessment of the typical anti-epidemic drugs in the Pearl River Delta by tracing their source and residual characteristics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 463, 132914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Milakovic, M.; Švecová, H.; Ganjto, M.; Jonsson, V.; Grabic, R.; Udiković-Kolić, N. Industrial wastewater treatment plant enriches antibiotic resistance genes and alters the structure of microbial communities. Water Res. 2019, 162, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassoun-Kheir, N.; Stabholz, Y.; Kreft, J.-U.; de la Cruz, Z.C.; Cytryn, E.; Kolodny, I.; Béjà, O.; Halpern, M. Comparison of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and antibiotic resistance genes abundance in hospital and community wastewater: A systematic review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 743, 140804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Huang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Cao, Y.; Li, B. Hospital Wastewater as a Reservoir for Antibiotic Resistance Genes: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 574968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandja, W.; Onanga, R.; Nguema, P.; Lekana-Douki, J.B.; Nguema-Amvane, P.; Ondo, J.P.; Mv-Meyo, F. Emergence of Antibiotic Residues and Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria in Hospital Wastewater: A Potential Route of Spread to African Streams and Rivers, a Review. Water 2024, 16, 3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehl, K.; Schallenberg, A.; Szekat, C.; Albert, C.; Sib, E.; Exner, M.; Zacharias, N.; Schreiber, C.; Parčina, M.; Bierbaum, G. Dissemination of carbapenem resistant bacteria from hospital wastewater into the environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 800, 151339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dávidová-Geržová, L.; Lausova, J.; Sukkar, I.; Růžička, F.; Látal, J.; Woznicová, V.; Holý, O.; Dolejská, M. Hospital and community wastewater as a source of multidrug-resistant ESBL-producing Escherichia coli. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1184081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambaza, S.S.; Naicker, N. Contribution of wastewater to antimicrobial resistance: A review article. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2023, 34, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uluseker, C.; Kaster, K.M.; Thorsen, K.; Gözderliler, E.; Özkök, E.; Uçar, F.B.; Gali, H.E.; Yesiladali, S.K.; Gredičak, M.; Pozo, C.; et al. A Review on Occurrence and Spread of Antibiotic Resistance in Wastewaters and in Wastewater Treatment Plants: Mechanisms and Perspectives. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 717809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Chen, L.; Wen, D. Impact of wastewater treatment plant effluent discharge on the antibiotic resistome in downstream aquatic environments: A mini review. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2024, 18, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Rosa, M.C.; Maugeri, A.; Favara, G.; Mastra, C.L.; San Lio, R.M.; Barchitta, M.; Agodi, A. The Impact of Wastewater on Antimicrobial Resistance: A Scoping Review of Transmission Pathways and Contributing Factors. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafiq, M.; Guo, X.; Wang, M.; Bilal, H.; Xin, L.; Yuan, Y.; Yao, F.; Sheikh, T.M.M.; Khan, M.N.; Jiao, X. Integrative metagenomic dissection of last-resort antibiotic resistance genes and mobile genetic elements in hospital wastewaters. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 949, 174930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahim, K.; Nawaz, M.N.; Almehmadi, M.; Alsuwat, M.A.; Liu, L.; Yu, C.; Khan, S.S. Public health implications of antibiotic resistance in sewage water: An epidemiological perspective. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2024, 11, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Ju, F.; Beck, K.; Bürgmann, H. Differential effects of wastewater treatment plant effluents on the antibiotic resistomes of diverse river habitats. ISME J. 2023, 17, 1993–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siri, Y.; Sresung, M.; Paisantham, P.; Mongkolsuk, S.; Sirikanchana, K.; Honda, R.; Precha, N.; Makkaew, P. Antibiotic resistance genes and crAssphage in hospital wastewater and a canal receiving the treatment effluent. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 361, 124771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soufi, L.; Kampouris, I.D.; Lüneberg, K.; Heyde, B.J.; Pulami, D.; Glaeser, S.P.; Siebe, C.; Siemens, J.; Smalla, K.; Grohmann, E.; et al. Wastewater-borne pollutants influenced antibiotic resistance genes and mobile genetic elements in the soil without affecting the bacterial community composition in a changing wastewater irrigation system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 494, 138680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazra, M.; Joshi, H.; Williams, J.B.; Watts, J.E.M. Antibiotics and antibiotic resistant bacteria/genes in urban wastewater: A comparison of their fate in conventional treatment systems and constructed wetlands. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 135148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahni, R.; Veeraraghavan, B.; Bakthavatchalam, Y. Orally Administered Amoxicillin/Clavulanate: Current Role in Outpatient Therapy. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2020, 10, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, M.E.; Helwig, K.; Hunter, C.; Roberts, J.; Subtil, E.L.; Coelho, L.H.G. Amoxicillin removal by pre-denitrification membrane bioreactor (A/O-MBR): Performance evaluation, degradation by-products, and antibiotic resistant bacteria. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 192, 110258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straubinger, R.K.; Lidbury, J.A.; Hartmann, K.; Leutenegger, C.M.; Unterer, S.; da Costa, R.C.; Hartmann, A.; de Godoy, K.; Suchodolski, J.S. Effect of amoxicillin-clavulanic acid on clinical scores, intestinal microbiome, and amoxicillin-resistant Escherichia coli in dogs with uncomplicated acute diarrhea. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2020, 34, 1166–1176. [Google Scholar]
- Saciuk, Y.; Nevo, D.; Chowers, M.; Obolski, U. Penicillin allergy as an instrumental variable for estimating antibiotic effects on resistance. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velho, P.; Lopes, C.; Macedo, E. Water Purification Using Choline-Amino Acid Ionic Liquids: Removal of Amoxicillin. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2024, 63, 10427–10435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miguel, A.G.S.; Jetten, M.S.M.; Welte, C.U. The role of mobile genetic elements in organic micropollutant degradation during biological wastewater treatment. Water Res. X 2020, 9, 100065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón-Franco, D.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Abeel, T.; Weissbrodt, D.G. Free-floating extracellular DNA: Systematic profiling of mobile genetic elements and antibiotic resistance from wastewater. Water Res. 2020, 189, 116592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Nies, L.; Busi, S.B.; Kunath, B.J.; May, P.; Wilmes, P. Mobilome-driven segregation of the resistome in biological wastewater treatment. eLife 2021, 11, e81196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Zeng, X.; Cao, Y.; Yang, Q.; Riaz, L.; Wang, Q. Distribution of antibiotic resistance genes from human and animal origins to their receiving environments: A regional scale survey of urban settings. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 290, 118512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Li, G.; Su, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, J.; Huang, G. Environmental drivers and interaction mechanisms of heavy metal and antibiotic resistome exposed to amoxicillin during aerobic composting. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1079114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C.; Abreu-Silva, J.; Manaia, C.M. The balance between treatment efficiency and receptor quality determines wastewater impacts on the dissemination of antibiotic resistance. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 434, 128933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchaala, L.; Grara, N.; Charchar, N.; Nourine, H.; Dahdah, K.; Driouche, Y.; Amrane, A.; Alsaeedi, H.; Cornu, D.; Bechelany, M.; et al. Microbiological Characterization and Pathogen Control in Drying Bed-Processed Sewage Sludge. Water 2024, 16, 3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchaala, L.; Charchar, N.; Grara, N.; Amor, I.B.; Zeghoud, S.; Hemmami, H.; Houhamdi, M.; Szparaga, A.; Murariu, O.C.; Caruso, G.; et al. Assessing the Efficiency of Phragmites australis in Wastewater Treatment as a Natural Approach to Water Quality Improvement. Sustainability 2025, 17, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niox, J. Algérie et Tunisie, 2nd ed.; Région de L’est (Province de Constantine); Géographie Militaire, 2005; 47p, Available online: http://aj.garcia.free.fr/geographie_alg/pdf/chap6.pdf (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- Gueroui, Y. Caractérisation Hydrochimique et Bactériologique des Eaux Souterraines de L’aquifère Superficiel de la Plaine de Tamlouka (Nord-Est Algérien). Ph.D. Thesis, Université 8 Mai 1945-Guelma, Guelma, Algérie, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Rodier, J.; Legube, B.; Merlet, N. L’analyse de L’eau, 9th ed.; Dunod: Malakoff, France, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 9308-2:2012; Water Quality—Enumeration of Escherichia coli and Coliform Bacteria—Part 2: Most Probable Number Method. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012.
- ISO 9308-3:1998; Water Quality—Detection and Enumeration of Escherichia coli and Coliform Bacteria—Part 3: Miniaturized Method (Most Probable Number). ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998.
- ISO 7899:2000; Water Quality—Detection and Enumeration of Intestinal Enterococci. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000.
- Comité de l’Antibiogramme de la Société Française de Microbiologie. Recommandations; SFM: Paris, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yilmaz, G.; Kaya, Y.; Vergili, I.; Beril Gönder, Z.; Özhan, G.; Ozbek Celik, B.; Altinkum, S.M.; Bagdatli, Y.; Boergers, A.; Tuerk, J. Characterization and toxicity of hospital wastewaters in Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboulkacem, A.; Chahlaoui, A.; Soulaymani, A.; Rhazi-Filali, F.; Et Bena, D. Etude Comparative de la Qualité Bactériologique des Eaux des Oueds Boufekrane et Ouislane à la Traversée de la Ville de Meknès (Maroc). Rev. Microbiol. Ind. San. Environ. 2007, 1, 10–22. [Google Scholar]
- Degbey, C.; Makoutode, M.; Ouendo, E.-M.; Fayomi, B. La qualité de l’eau de puits dans la commune d’Abomey-Calavi au Bénin. Environ. Risques Santé 2008, 4, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-López, M.; Miranda-Falcón, M.; Correa-Ramírez, M.; Loredo-Treviño, A. Effect of Two Types of Wastewater Treatment Plants on Antibiotic Resistance of Fecal Coliform. Water 2024, 16, 2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Salah, D.M.M.; Ngweme, G.N.; Laffite, A.; Otamonga, J.P.; Mulaji, C.; Poté, J. Hospital wastewaters: A reservoir and source of clinically relevant bacteria and antibiotic resistant genes dissemination in urban river under tropical conditions. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 200, 110767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerzsele, Á.; Szabó, Á; Barnácz, F.; Csirmaz, B.; Kovács, L.; Kerek, Á. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Profiles of Escherichia coli Isolates from Clinical Cases of Turkeys in Hungary (2022–2023). Antibiotics 2025, 14, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filby, B.; Weldrick, P.; Paunov, V. Overcoming Beta-Lactamase-Based Antimicrobial Resistance by Nanocarrier-Loaded Clavulanic Acid and Antibiotic Cotreatments. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2022, 8, 3826–3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathur, R. Community-acquired resistance and health impact. J. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2022, 10, 15–22. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).