Impact of Climate Change on the Spatio-Temporal Groundwater Recharge Using WetSpass-M Model in the Weyib Watershed, Ethiopia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
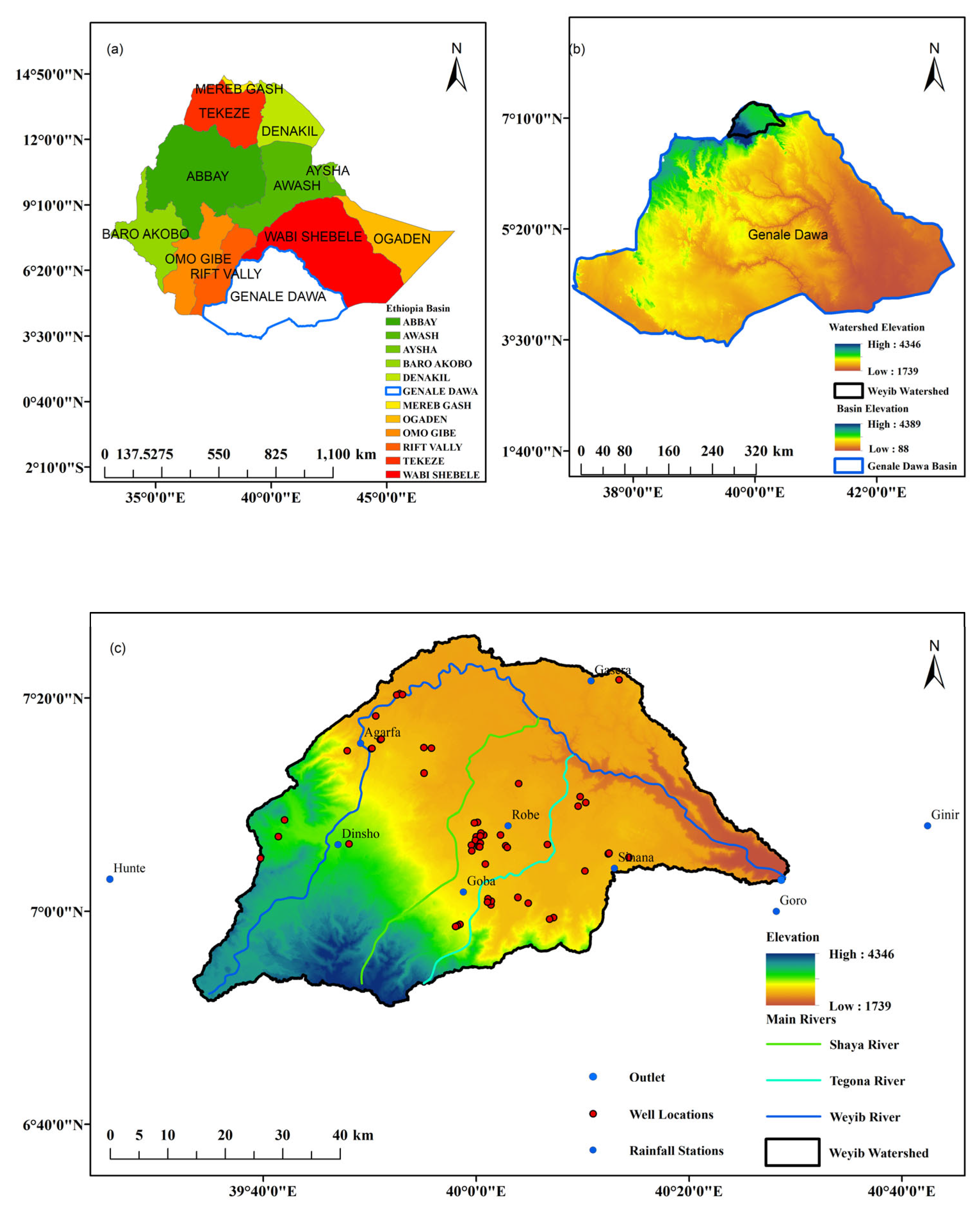
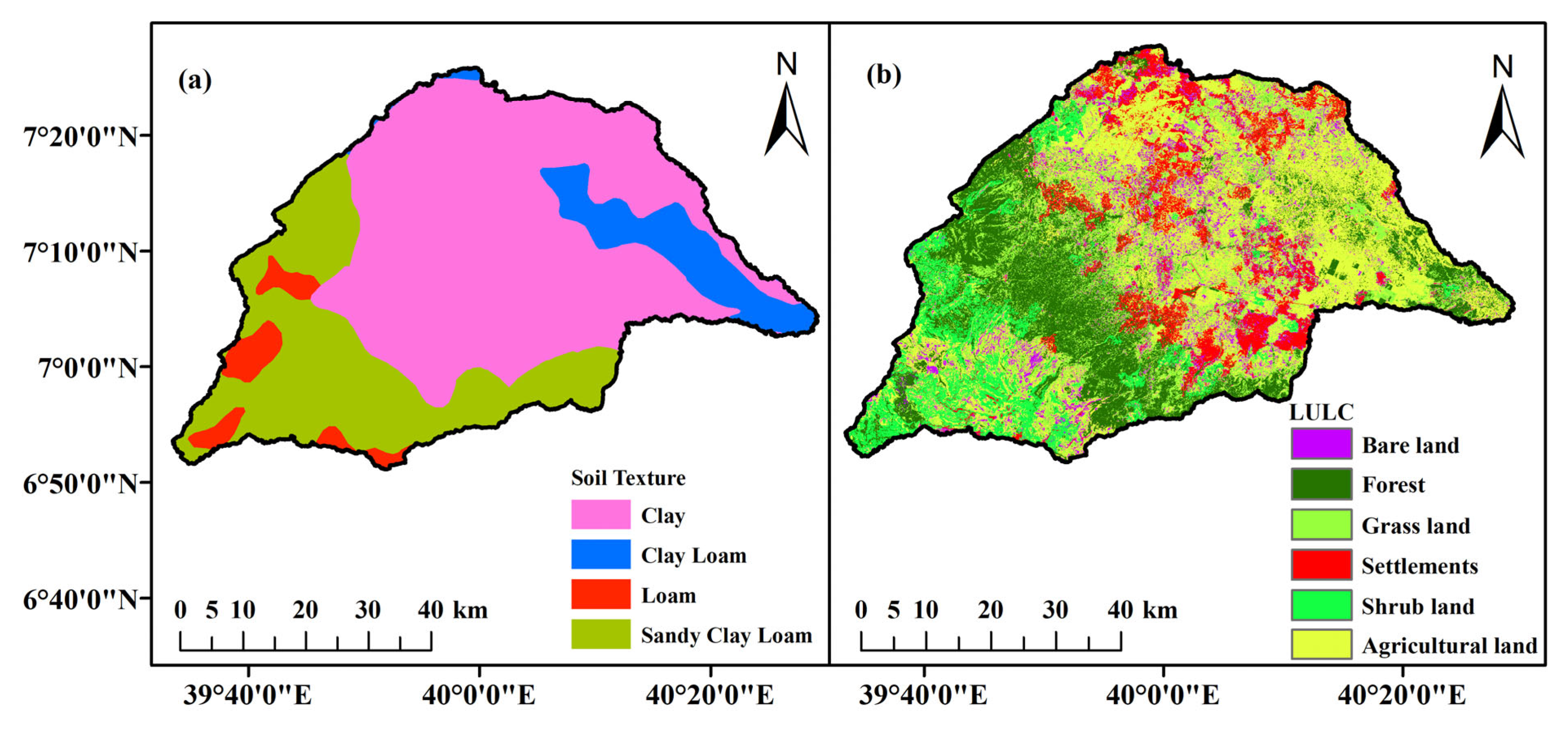
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Model Description
2.3. Data Used and Analysis
2.4. Climate Model Selection and Analysis
2.5. WetSpass-M Model Input Data
2.6. Model Performance Evaluation
2.7. Baseflow Separation
2.8. Methodological Flowchart
3. Results
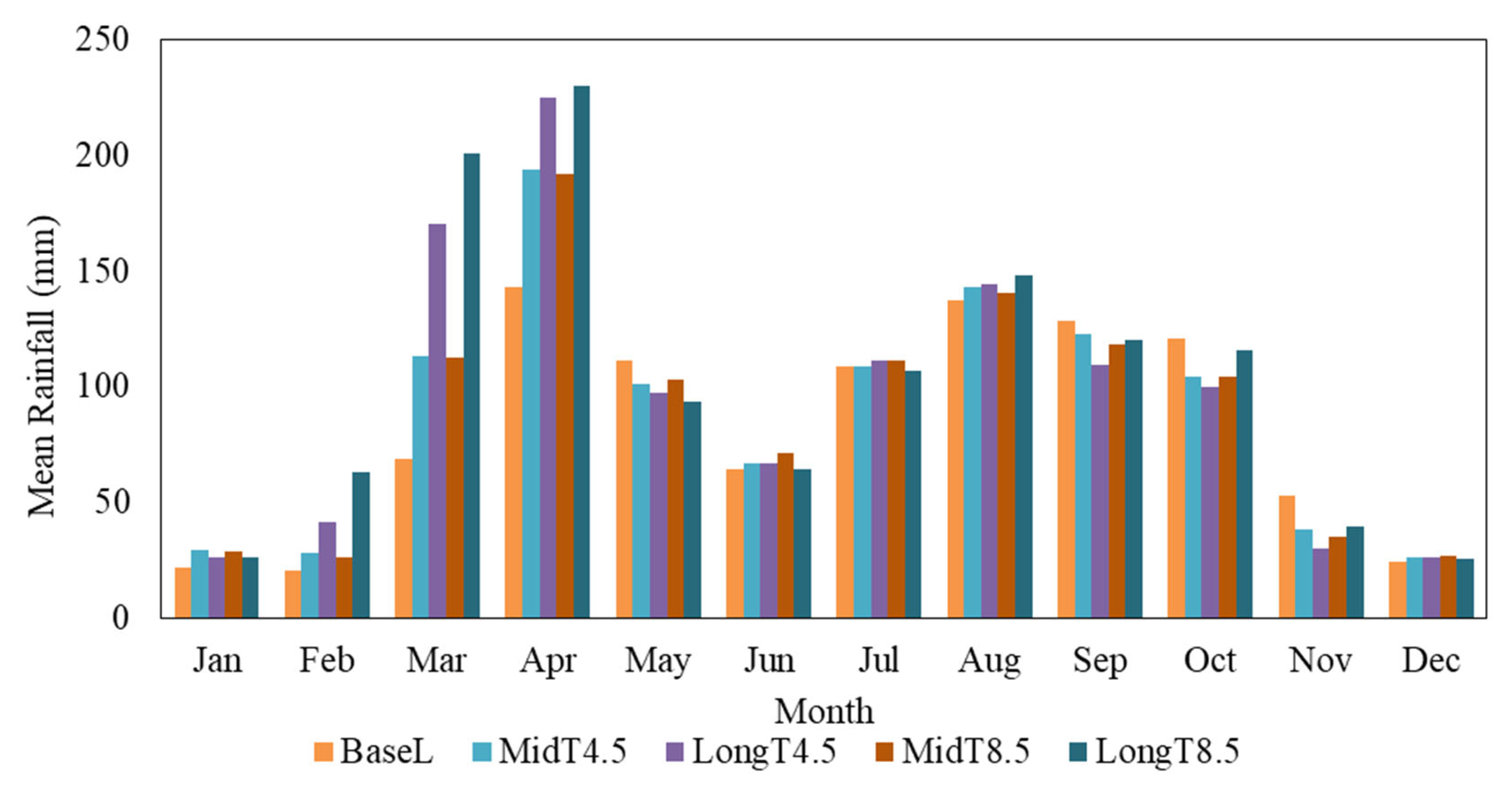
3.1. Analysis of Projected Climate
3.2. WetSpass-M Model Evaluation
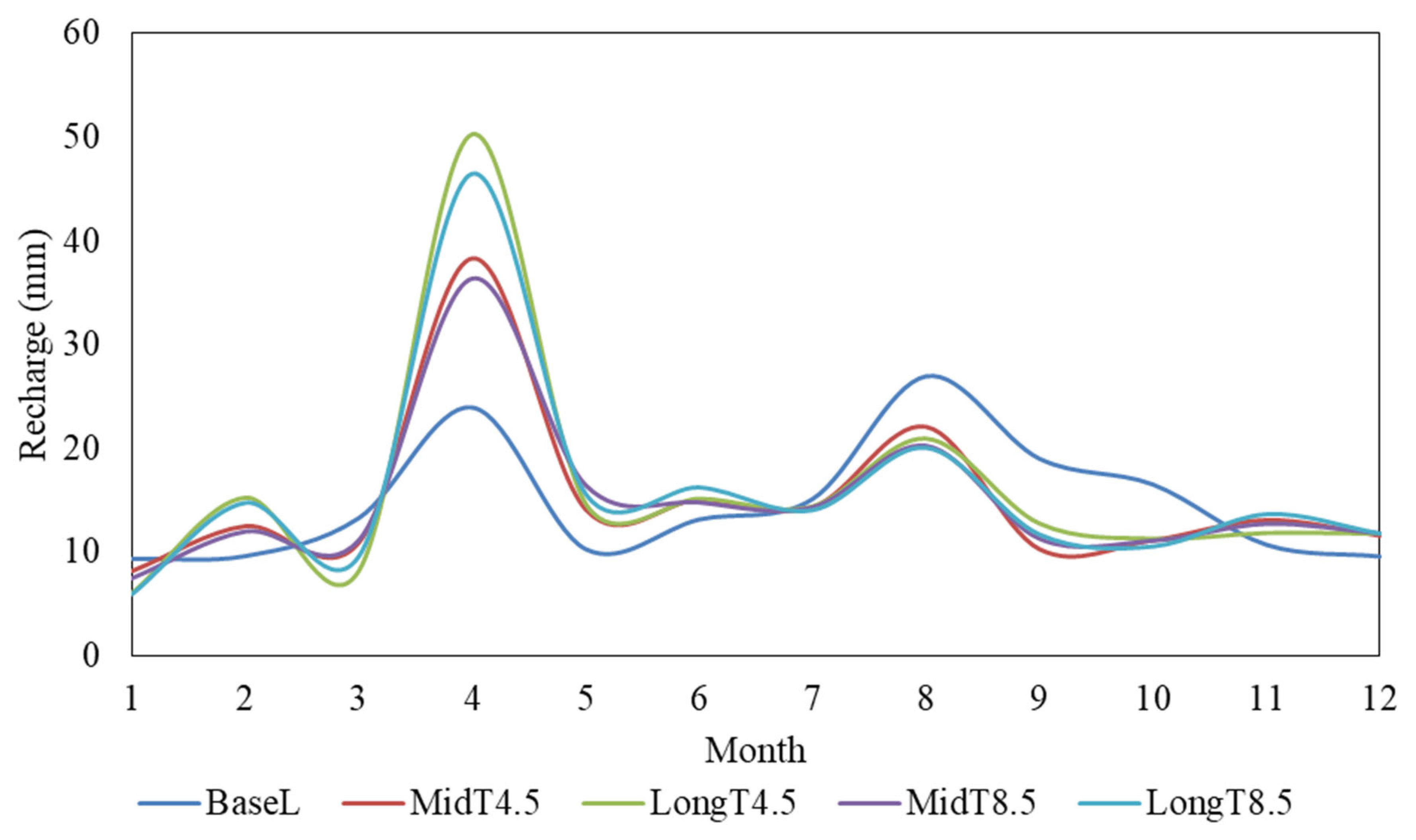
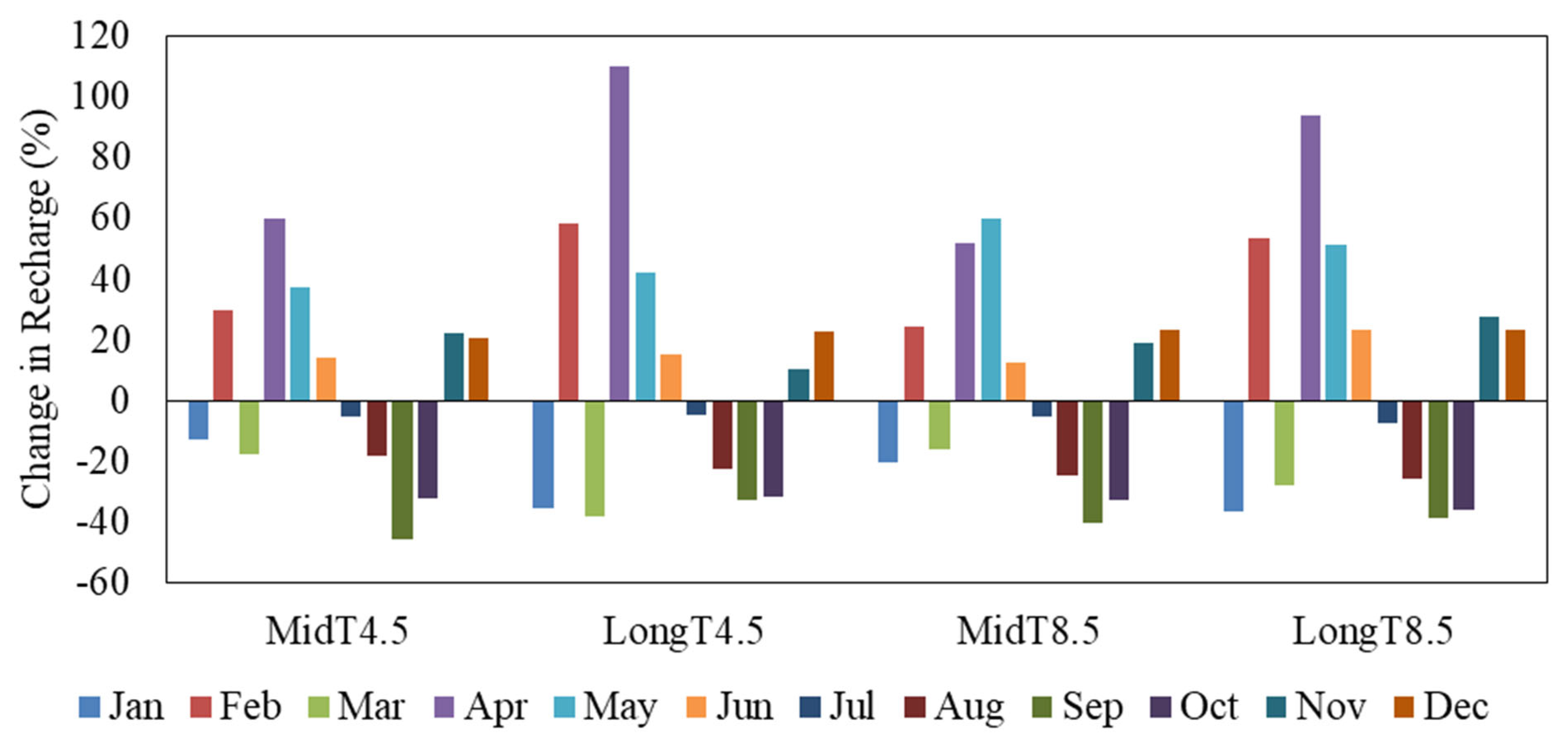
3.3. Mean Monthly Recharge Variability
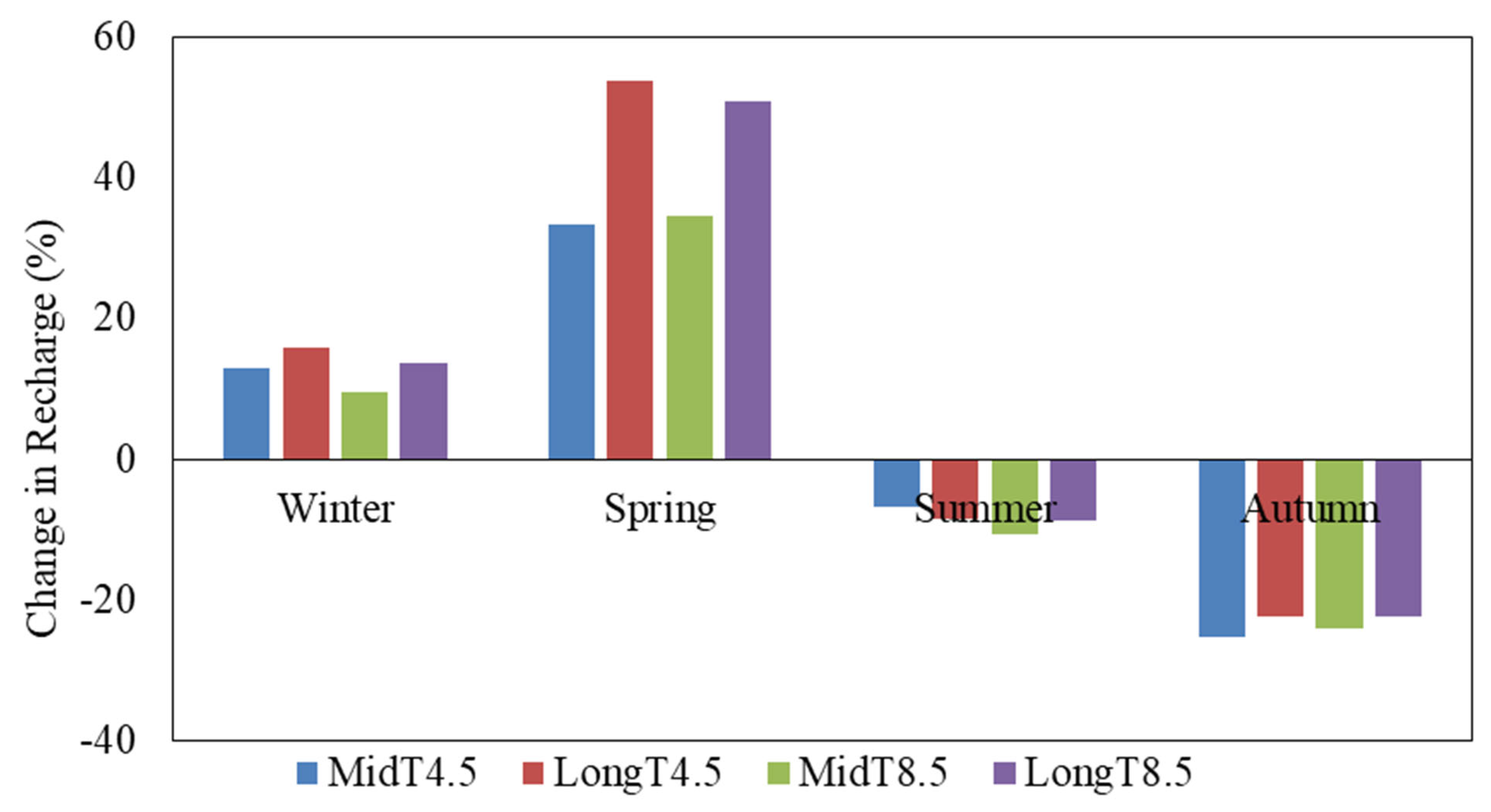
3.4. Seasonal Recharge Variability
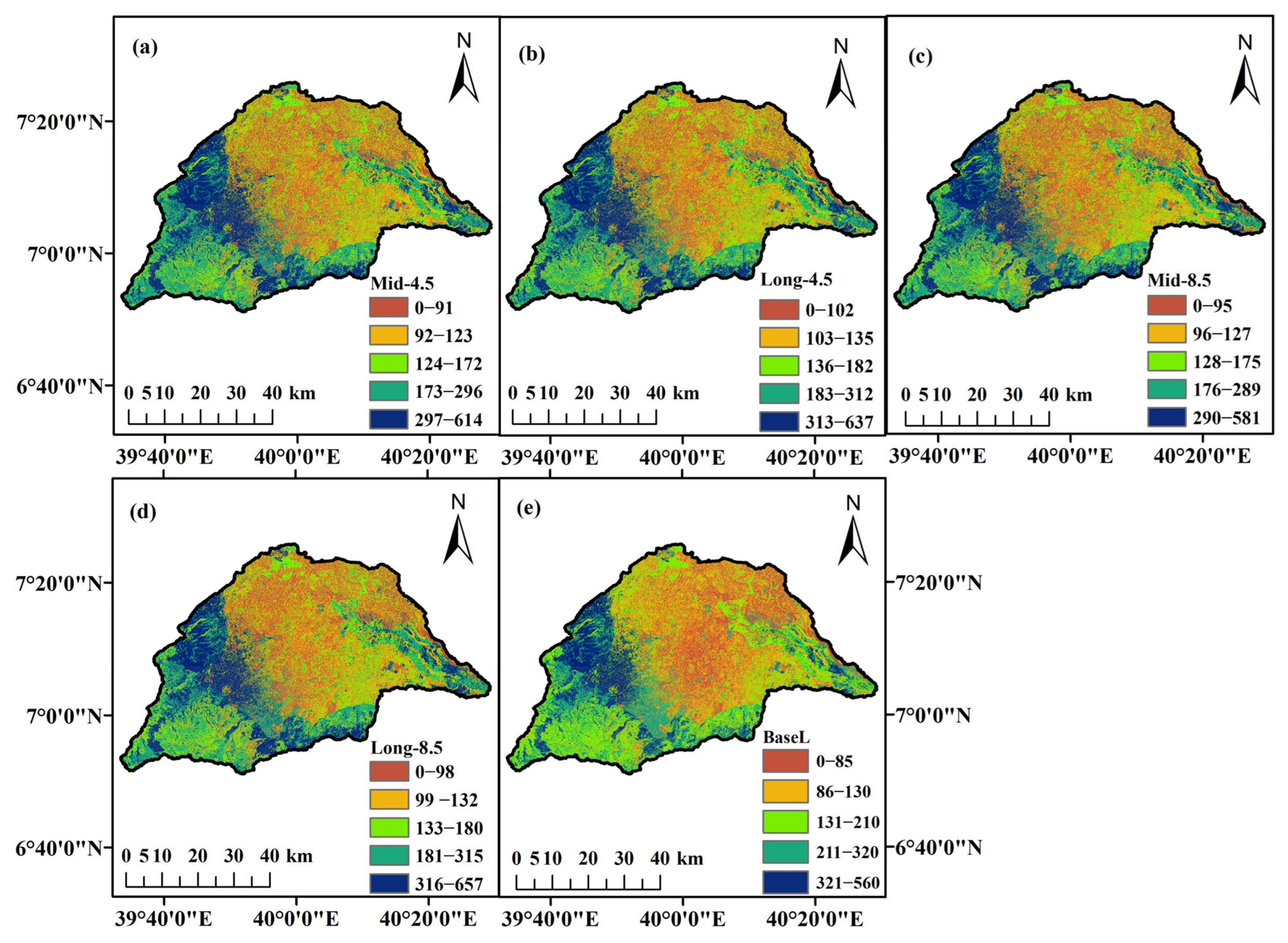
3.5. Estimated Annual Recharge
4. Discussion
4.1. Climate Variability Analysis
4.2. Spatio-Temporal Recharge
4.3. Climate Model Uncertainties
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nannawo, A.S.; Lohani, T.K.; Eshete, A.A. Envisaging the actual evapotranspiration and elucidating its effects under climate change scenarios on agrarian lands of bilate river basin in Ethiopia. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nannawo, A.S.; Lohani, T.K.; Eshete, A.A. Groundwater recharge evaluation due to climate change using WetSpass-M distributed hydrological model in Bilate river basin of Ethiopia. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 19, 100860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aredo, M.R.; Lohani, T.K.; Mohammed, A.K. Groundwater recharge estimation using WetSpass-M and MTBS leveraging from HydroOffice and WHAT tools for baseflow in Weyib watershed, Ethiopia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aredo, M.R.; Lohani, T.K.; Mohammed, A.K. Revisiting the global weights of the integrated watershed health assessment framework and Weyib watershed health analysis: Ethiopia’s policy prospects. World Water Policy 2024, 10, 940–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demissie, E.S.; Gashaw, D.Y.; Altaye, A.A.; Demissie, S.S.; Ayele, G.T. Groundwater Recharge Estimation in Upper Gelana Watershed, South-Western Main Ethiopian Rift Valley. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meresa, E.; Taye, G. Estimation of groundwater recharge using GIS-based WetSpass model for Birki watershed, the eastern zone of Tigray, Northern Ethiopia. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 5, 1555–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremichael, M.; Mechal, A. Groundwater potential mapping using WetSpass-M and GIS-based multi-criteria decision analysis (MCDA) models in the Chamo Lake basin, Ethiopian rift. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2025, 11, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahsay, G.H.; Gebreyohannes, T.; Gebremedhin, M.A.; Gebrekirstos, A.; Birhane, E.; Gebrewahid, H.; Welegebriel, L. Spatial groundwater recharge estimation in Raya basin, Northern Ethiopia: An approach using GIS based water balance model. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 5, 961–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechal, A.; Karuppannan, S.; Bayisa, A. Groundwater recharge estimation in the Ziway Lake Watershed, Ethiopian Rift: An approach using SWAT and CMB techniques. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2024, 10, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran-Gurgul, K.; Rutkowska, A. Water Resource Management: Hydrological Modelling, Hydrological Cycles, and Hydrological Prediction. Water 2024, 16, 3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, D.; Ayenew, T.; Fletcher, C.G.; Duraisamy, R.; Jothimani, M. Numerical groundwater flow modelling under changing climate in Abaya–Chamo lakes basin, Rift Valley, Southern Ethiopia. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2022, 8, 3985–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadim, F.K.; Dokou, Z.; Lazin, R.; Bagtzoglou, A.C.; Anagnostou, E. Groundwater Modeling to Assess Climate Change Impacts and Sustainability in the Tana Basin, Upper Blue Nile, Ethiopia. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merga, D.D.; Adeba, D.; Regasa, M.S.; Leta, M.K. Evaluation of Surface Water Resource Availability under the Impact of Climate Change in the Dhidhessa Sub-Basin, Ethiopia. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcha, S.K.; Awass, A.A.; Hulluka, T.A.; Bantider, A.; Ayele, G.T. Assessment of future climate change impact on water balance components in Central Rift Valley Lakes Basin, Ethiopia. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2023, 14, 175–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alehu, B.A.; Bitana, S.G. Assessment of Climate Change Impact on Water Balance of Lake Hawassa Catchment. Environ. Process. 2023, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mummed, B.A.; Seleshi, Y. Assessment of the effects of climate change on water balance components in the upper Erer subbasin, Ethiopia. Heliyon 2024, 10, e30297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; Available online: www.ipcc.ch/site/assets/uploads/2018/03/WGI_TAR_full_report.pdf (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Ayalew, D.W.; Asefa, T.; Moges, M.A.; Leyew, S.M. Evaluating the potential impact of climate change on the hydrology of Ribb catchment, Lake Tana Basin, Ethiopia. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2022, 13, 190–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daba, M.H.; You, S. Assessment of Climate Change Impacts on River Flow Regimes in the Upstream of Awash Basin, Ethiopia: Based on IPCC Fifth Assessment Report (AR5) Climate Change Scenarios. Hydrology 2020, 7, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyembo, L.O.; Larbi, I.; Mwabumba, M.; Selemani, J.R.; Dotse, S.Q.; Limantol, A.M.; Bessah, E. Impact of climate change on groundwater recharge in the lake Manyara catchment, Tanzania. Sci. Afr. 2022, 15, e01072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengistu, A.G.; Tesfuhuney, W.A.; Woyessa, Y.E.; Ejigu, A.A.; Alemu, M.D. Contrasting hydro-climatic trends and drought dynamics in Ethiopia and South Africa under climate change. Clim. Dyn. 2025, 63, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsano, Y.; Tamrat, I. Ethiopia and the Eastern Nile Basin. Aquat. Sci. 2005, 67, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aredo, M.R.; Lohani, T.K.; Mohammed, A.K. Assessment of river response to water abstractions in the Weyib Watershed, Ethiopia. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2023, 23, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aredo, M.R.; Lohani, T.K.; Mohammed, A.K. Numerical groundwater modelling under changing water abstraction in Weyib watershed, Ethiopia. Cogent Eng. 2023, 10, 2283297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremeskel, G.; Kebede, A. Estimating the effect of climate change on water resources: Integrated use of climate and hydrological models in the Werii watershed of the Tekeze river basin, Northern Ethiopia. Agric. Nat. Resour. 2018, 52, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molla, D.D.; Tegaye, T.A.; Fletcher, C.G. Simulated surface and shallow groundwater resources in the Abaya-Chamo Lake basin, Ethiopia using a spatially-distributed water balance model. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2019, 24, 100615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dile, Y.T.; Ayana, E.K.; Worqlul, A.W.; Xie, H.; Srinivasan, R.; Lefore, N.; You, L.; Clarke, N. Evaluating satellite-based evapotranspiration estimates for hydrological applications in data-scarce regions: A case in Ethiopia. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 743, 140702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Hu, H.; Wei, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xu, H.; Yan, H. Estimating the Actual Evapotranspiration of Different Vegetation Types Based on Root Distribution Functions. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 893388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hordofa, A.T.; Leta, O.T.; Alamirew, T.; Chukalla, A.D. Climate Change Impacts on Blue and Green Water of Meki River Sub-Basin. Water Resour. Manag. 2023, 37, 2835–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiferaw, H.; Gebremedhin, A.; Gebretsadkan, T.; Zenebe, A. Modelling hydrological response under climate change scenarios using SWAT model: The case of Ilala watershed, Northern Ethiopia. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2018, 4, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serur, A.B.; Sarma, A.K. Climate change impacts analysis on hydrological processes in the Weyib River basin in Ethiopia. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 134, 1301–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awulachew, S.B.; Yilma, A.D.; Loulseged, M.; Loiskandl, W.; Ayana, M.; Alamirew, T. Water Resources and Irrigation Development in Ethiopia; IWMI Working Paper 123; International Water Management Institute (IWMI): Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2007; 66p, Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/10568/39349 (accessed on 20 August 2020).
- NDRMC. Flood Alert #2, 04 June 2020; National Disaster Risk Management Commission (NDRMC): Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2020. Available online: https://reliefweb.int/report/ethiopia/ndrmc-flood-alert-2-04-june-2020 (accessed on 20 August 2020).
- Aredo, M.R.; Hatiye, S.D.; Pingale, S.M. Impact of land use/land cover change on stream flow in the Shaya catchment of Ethiopia using the MIKE SHE model. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengistu, T.D.; Feyissa, T.A.; Chung, I.M.; Chang, S.W.; Yesuf, M.B.; Alemayehu, E. Regional Flood Frequency Analysis for Sustainable Water Resources Management of Genale–Dawa River Basin, Ethiopia. Water 2022, 14, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessema, Y.M.; Jasińska, J.; Yadeta, L.T.; Świtoniak, M.; Puchałka, R.; Gebregeorgis, E.G. Soil loss estimation for conservation planning in the welmel watershed of the Genale Dawa Basin, Ethiopia. Agronomy 2020, 10, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebe, B.W.; Mana, T.T.; Hatiye, S.D. Assessment of meteorological drought and its association with global climate drivers in Genale Dawa River Basin, South-East of Ethiopia. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2024, 10, 5027–5042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serur, A.B. Modeling blue and green water resources availability at the basin and sub-basin level under changing climate in the Weyb River basin in Ethiopia. Sci. Afr. 2020, 7, e00299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulti, A.; Abegaz, F. Impacts of Climate Change on Temperature and Rainfall on Dawa Sub-watershed, Genale Dawa River Basin, Southern Ethiopia. Int. J. Atmos. Ocean Sci. 2024, 8, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdule, A.M.; Muluneh, A.; Woldemichael, A. Impact of Climate and Land Use/Cover Changes on Streamflow in Yadot Watershed, Genale Dawa Basin, Ethiopia. Air Soil Water Res. 2023, 16, 11786221231200106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gashaw, T.; Worqlul, A.W.; Lakew, H.; Taye, M.T.; Seid, A.; Haileslassie, A. Evaluations of satellite/reanalysis rainfall and temperature products in the Bale Eco-Region (Southern Ethiopia) to enhance the quality of input data for hydro-climate studies. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2023, 31, 100994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustefa, A.; Muluneh, A. Modeling climate change projection and its impact on the streamflow in the Yadot watershed, Genale Dawa basin, Ethiopia. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2024, 15, 3487–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassahun, N.; Mohamed, M. Groundwater Potential Assessment and Characterization of Genale-Dawa River Basin. Open J. Mod. Hydrol. 2018, 8, 126–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yenehun, A.; Dessie, M.; Nigate, F.; Belay, A.S.; Azeze, M.; Camp, M.V.; Taye, D.F.; Kidane, D.; Adgo, E.; Nyssen, J.; et al. Spatial and temporal simulation of groundwater recharge and cross-validation with point estimations in volcanic aquifers with variable topography. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 42, 101142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, K.; Bashir, I.; Verbeiren, B.; Harouna, M.R.; Van Griensven, A.; Huysmans, M.; Batelaan, O. A distributed monthly water balance model: Formulation and application on Black Volta Basin. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelebo, A.H.; Kasiviswanathan, K.S.; Khare, D. Assessment of the spatial–temporal distribution of groundwater recharge in data-scarce large-scale African river basin. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woldu, T.T.; Ayenew, T.; Baychken, B.; Birhanu, B. Spatiotemporal recharge estimation in the upper Awash sub-basin, central Ethiopia. Hydrol. Res. 2024, 55, 711–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batelaan, O.; De Smedt, F. GIS-based recharge estimation by coupling surface–subsurface water balances. J. Hydrol. 2007, 337, 337–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeabraha, A.; G/yohannes, T.; W/Mariyam, F.; Mulugeta, A.; Gebreyesus, Z. Application of a spatially distributed water balance model for assessing surface and groundwater resources: A case study of Adigrat area, Northern Ethiopia. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2020, 6, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, S.J.; Tombul, M. Comparison of Spatial Interpolation Methods of Precipitation and Temperature Using Multiple Integration Periods. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2018, 46, 1187–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirani, F.J.; Modarres, R. Geostatistical and deterministic methods for rainfall interpolation in the Zayandeh Rud basin, Iran. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2020, 65, 2678–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-H.; Hung, M.-C. Comparison of Spatial Interpolation Techniques Using Visualization and Quantitative Assessment. In Applications of Spatial Statistics; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016; Volume 11, pp. 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worku, G.; Teferi, E.; Bantider, A.; Dile, Y.T. Modelling hydrological processes under climate change scenarios in the Jemma sub-basin of upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Clim. Risk Manag. 2021, 31, 100272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengistu, A.G.; Woldesenbet, T.A.; Dile, Y.T.; Bayabil, H.K. Modeling the impacts of climate change on hydrological processes in the Baro–Akobo River basin, Ethiopia. Acta Geophys. 2023, 71, 1915–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigute, M.; Alamirew, T.; Abebe, A.; Ndehedehe, C.E.; Kassahun, H.T. Assessing the impacts of climate change on hydrological processes in the upper Genale River basin, Ethiopia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2024, 83, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoben, W.J.M.; Freer, J.E.; Woods, R.A. Technical note: Inherent benchmark or not? Comparing Nash-Sutcliffe and Kling-Gupta efficiency scores. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 4323–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashaolu, E.D.; Olorunfemi, J.F.; PaulIfabiy, I.; Abdollahi, K.; Batelaan, O. Spatial and temporal recharge estimation of the basement complex in Nigeria, West Africa. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2020, 27, 100658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negewo, T.F.; Sarma, A.K. Estimation of Water Yield under Baseline and Future Climate Change Scenarios in Genale Watershed, Genale Dawa River Basin, Ethiopia, Using SWAT Model. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2021, 26, 05020051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getachew, B.; Manjunatha, B.R. Potential climate change impact assessment on the hydrology of the Lake Tana Basin, Upper Blue Nile River Basin, Ethiopia. Phys. Chem. Earth 2022, 127, 103162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asrade, T. Application of coupled WetSpass-M and MODFLOW models to estimate spatial–temporal water balance components in the Chemoga watershed, Ethiopia. Water Pract. Technol. 2024, 19, 3833–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadesse, G.; Jothimani, M. Assessing Groundwater Recharge in the Wabe River Catchment, Central Ethiopia, Through a GIS-Based Distributed Water Balance Model. Earth 2024, 5, 20–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, T.M.L.; Wang, S.J.; Chen, P.Y. Assessment of future climate change impacts on groundwater recharge using hydrological modeling in the Choushui River Alluvial Fan, Taiwan. Water 2024, 16, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, S.-K.; Hense, A. A Bayesian approach to climate model evaluation and multi-model averaging with an application to global mean surface temperatures from IPCC AR4 coupled climate models. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L08708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buontempo, C.; Mathison, C.; Jones, R.; Williams, K.; Wang, C.; McSweeney, C. An ensemble climate projection for Africa. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 44, 2097–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Ivanov, V.Y.; Fatichi, S. Climate change and uncertainty assessment over a hydroclimatic transect of Michigan. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2016, 30, 923–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, D.; Pepin, N.; Kang, S. Simulation of temperature extremes in the Tibetan Plateau from CMIP5 models and comparison with gridded observations. Clim. Dyn. 2018, 51, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.; Sachindra, D.A.; Shahid, S.; Demirel, M.C.; Chung, E.S. Selection of multi-model ensemble of general circulation models for the simulation of precipitation and maximum and minimum temperature based on spatial assessment metrics. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 4803–4824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| No | Data Type | Resolution | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Historical climate data | 1986 to 2015 | National Meteorology Agency, Ethiopia https://www.ethiomet.gov.et/ (accessed on 20 August 2020) |
| 2 | Stream flow | 1986 to 2015 | Ministry of Water and Energy, Ethiopia https://www.mowe.gov.et (accessed on 20 August 2020) |
| 3 | LULC | 30 × 30 m | Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 20 August 2020) |
| 4 | Groundwater levels | 53 wells | Field measurement |
| 5 | Soil texture | 30 × 30 m | Ethiopian Ministry of Agriculture (https://www.moa.gov.et) (accessed on 20 August 2020) and FAO (https://www.fao.org) (accessed on 20 August 2020) |
| 6 | DEM | 30 × 30 m | USGS Earth Explorer https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 20 August 2020) |
| Scenarios | Temperature (°C) | Rainfall (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| Baseline Period | 14.05 ± 0.74 | 83.57 ± 46.75 |
| MidT4.5 | 14.95 ± 0.84 | 89.77 ± 52.78 |
| LongT4.5 | 15.70 ± 0.78 | 95.64 ± 62.52 |
| MidT8.5 | 15.52 ± 0.86 | 89.18 ± 52.46 |
| LongT8.5 | 17.63 ± 0.82 | 102.86 ± 65.54 |
| Scenarios | Mean ± Standard Deviation |
|---|---|
| Baseline Period | 177.7 ± 105.5 |
| MidT4.5 | 181.9 ± 108.1 |
| LongT4.5 | 192.9 ± 109.7 |
| MidT8.5 | 180.0 ± 101.6 |
| LongT8.5 | 190.8 ± 113.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aredo, M.R.; Dinka, M.O. Impact of Climate Change on the Spatio-Temporal Groundwater Recharge Using WetSpass-M Model in the Weyib Watershed, Ethiopia. Earth 2025, 6, 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth6040118
Aredo MR, Dinka MO. Impact of Climate Change on the Spatio-Temporal Groundwater Recharge Using WetSpass-M Model in the Weyib Watershed, Ethiopia. Earth. 2025; 6(4):118. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth6040118
Chicago/Turabian StyleAredo, Mesfin Reta, and Megersa Olumana Dinka. 2025. "Impact of Climate Change on the Spatio-Temporal Groundwater Recharge Using WetSpass-M Model in the Weyib Watershed, Ethiopia" Earth 6, no. 4: 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth6040118
APA StyleAredo, M. R., & Dinka, M. O. (2025). Impact of Climate Change on the Spatio-Temporal Groundwater Recharge Using WetSpass-M Model in the Weyib Watershed, Ethiopia. Earth, 6(4), 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth6040118






