Solanum elaeagnifolium Invasiveness under Semi-Arid Environmental Conditions in Tunisia
Abstract
1. Introduction
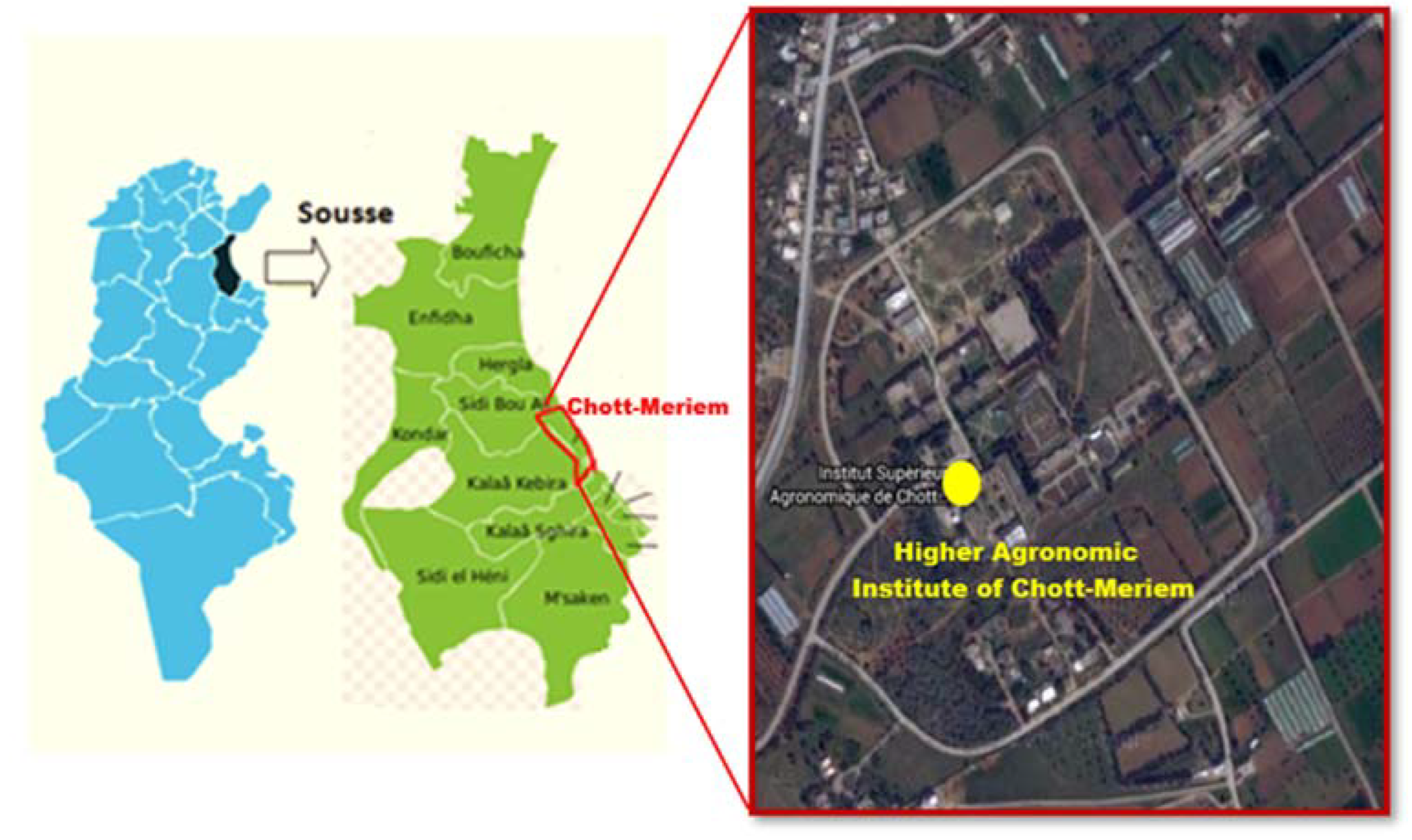
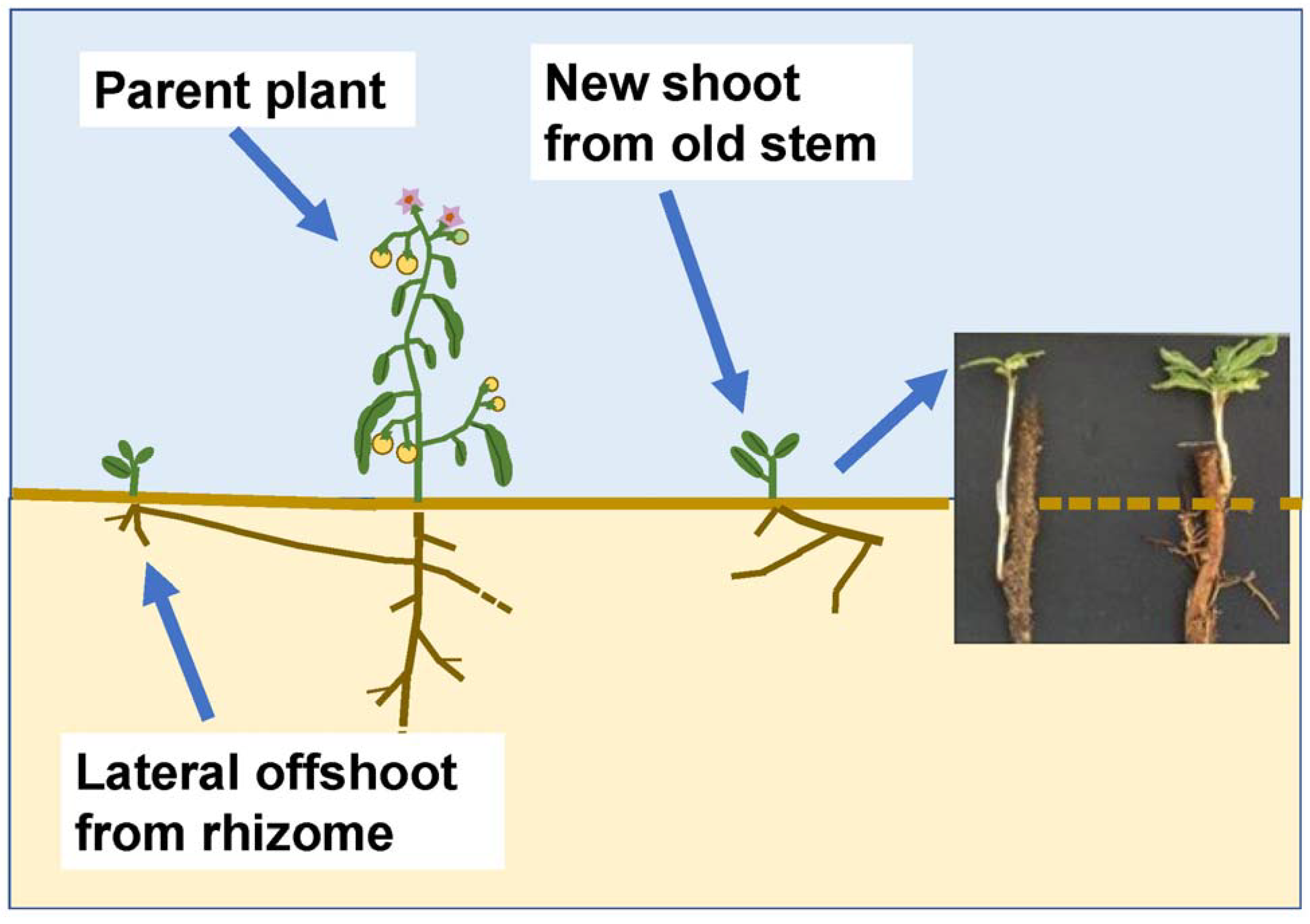
2. Materials and Methods
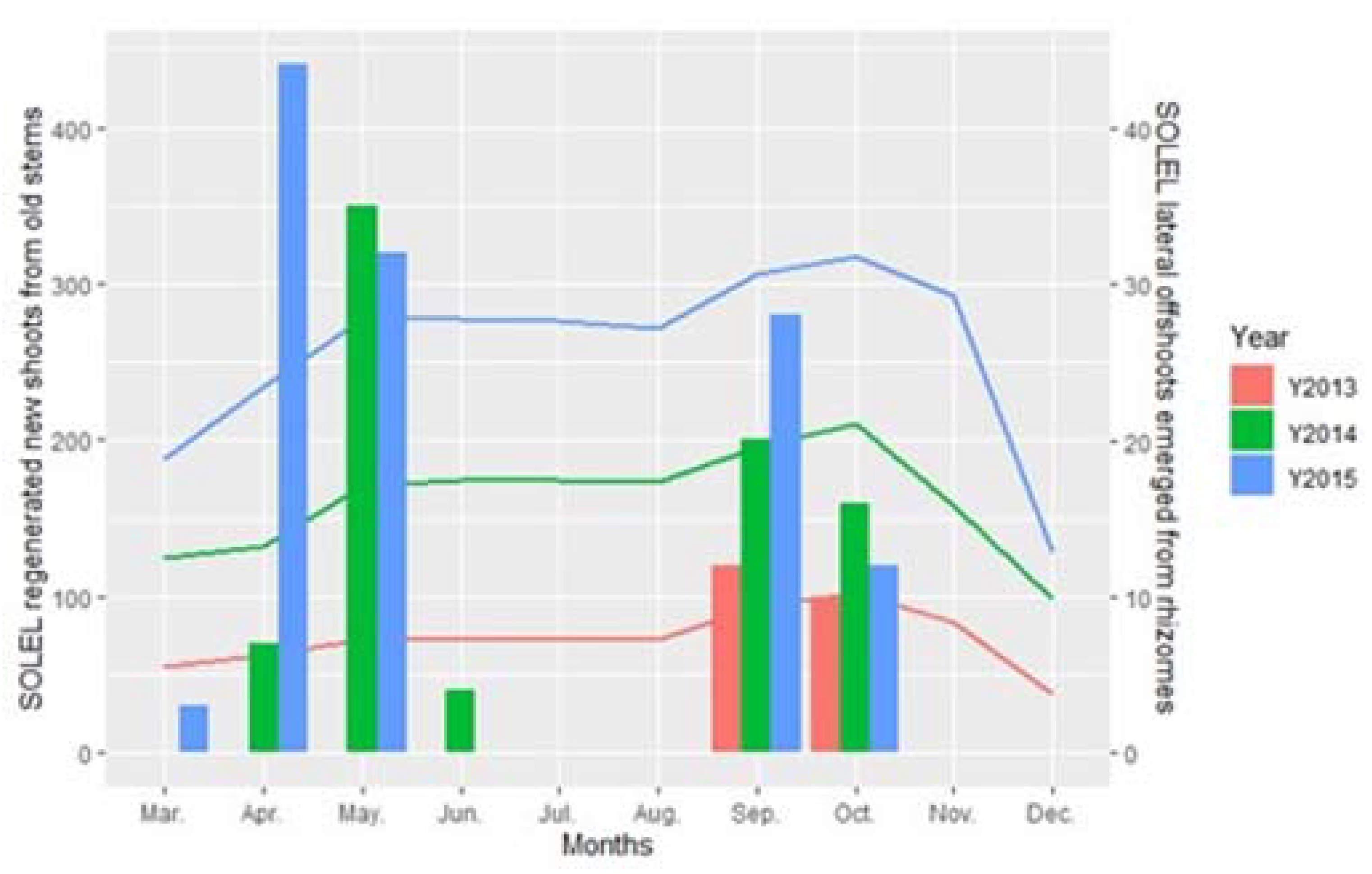
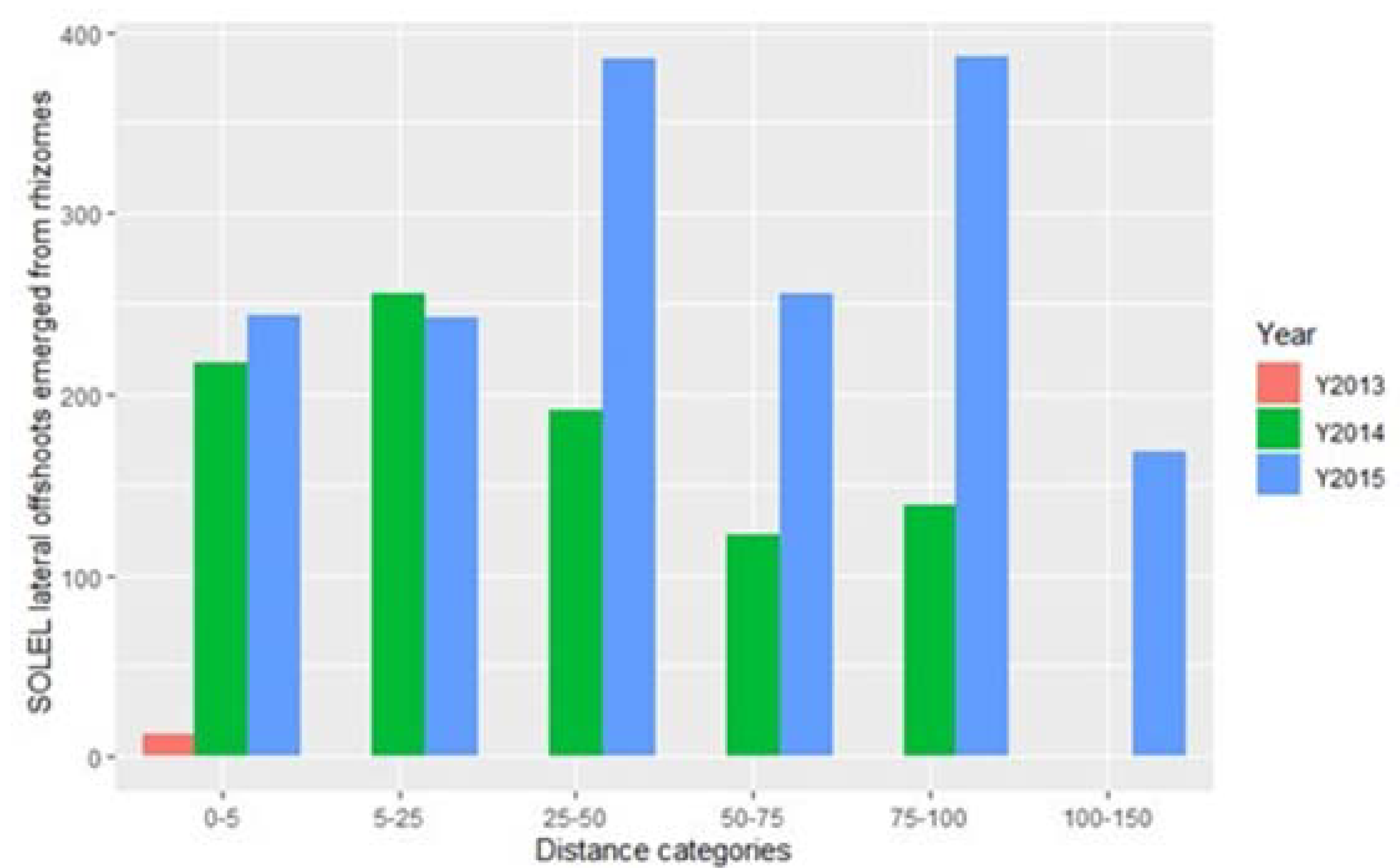
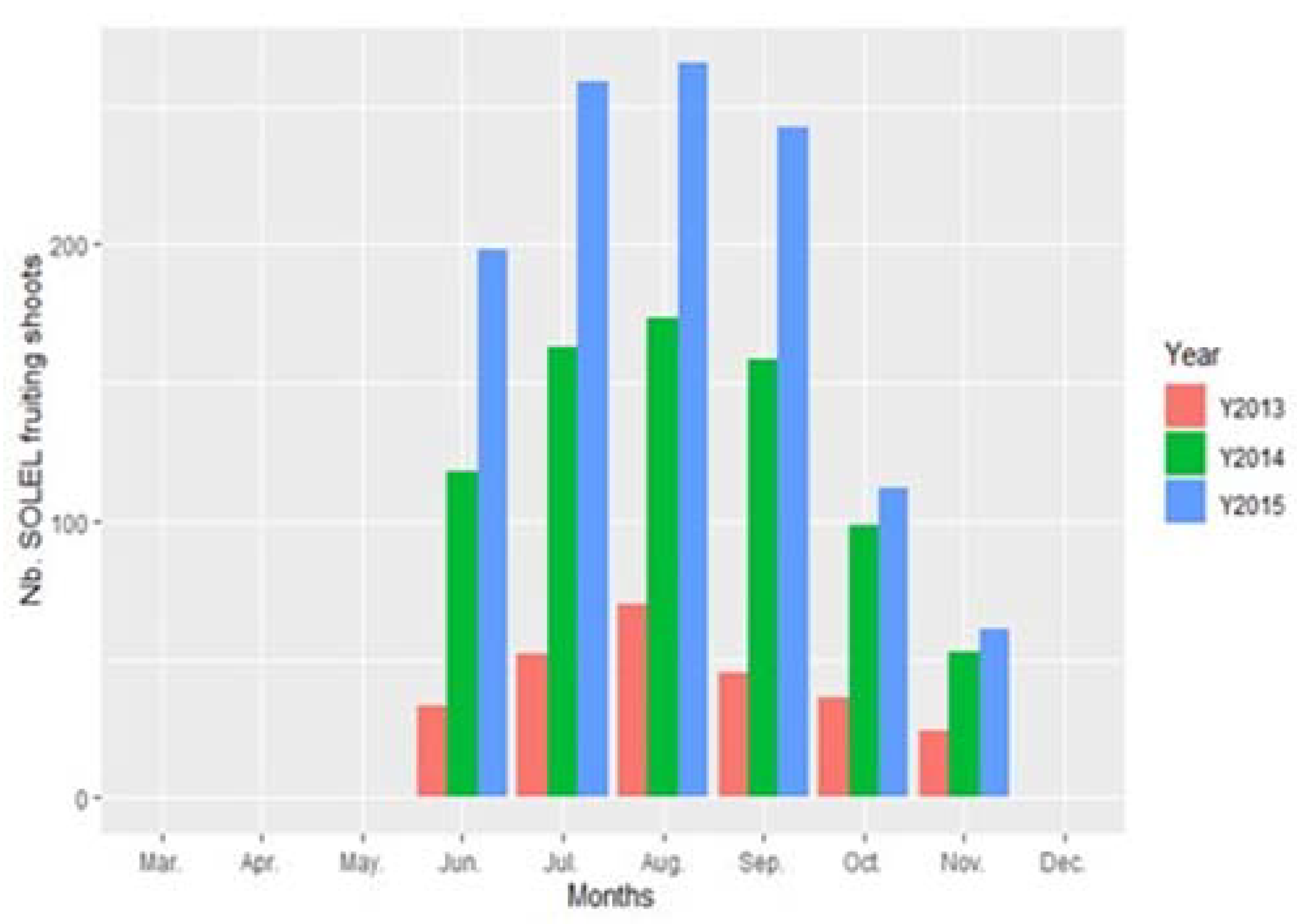
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gallardo, B.; Bacher, S.; Bradley, B.; Comín, F.A.; Gallien, L.; Jeschke, J.M.; Sorte, C.J.B.; Vilà, M. InvasiBES: Understanding and Managing the Impacts of Invasive Alien Species on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services. NeoBiota 2019, 50, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilà, M.; Hulme, P.E. Invading Nature–Springer Series in Invasion Ecology. In Impact of Biological Invasions on Ecosystem Services; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; Volume 12. [Google Scholar]
- Haubrock, P.J.; Turbelin, A.J.; Cuthbert, R.N.; Novoa, A.; Taylor, N.G.; Angulo, E.; Ballesteros-Mejia, L.; Bodey, T.W.; Capinha, C.; Diagne, C.; et al. Economic Costs of Invasive Alien Species across Europe. NeoBiota 2021, 67, 153–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, G.; Chauvel, B.; Reynaud, P.; Sache, I. Decreases in Crop Production by Non-Native Weeds, Pests, and Pathogens. In Impact of Biological Invasions on Ecosystem Services; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 83–101. [Google Scholar]
- Lososová, Z.; Chytrý, M.; Tichý, L.; Danihelka, J.; Fajmon, K.; Hájek, O.; Kintrová, K.; Láníková, D.; Otýpková, Z.; Řehořek, V. Biotic Homogenization of Central European Urban Floras Depends on Residence Time of Alien Species and Habitat Types. Biol. Conserv. 2012, 145, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilà, M.; Espinar, J.L.; Hejda, M.; Hulme, P.E.; Jarošík, V.; Maron, J.L.; Pergl, J.; Schaffner, U.; Sun, Y.; Pyšek, P. Ecological Impacts of Invasive Alien Plants: A Meta-Analysis of Their Effects on Species, Communities and Ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2011, 14, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartz, R.; Kowarik, I. Assessing the Environmental Impacts of Invasive Alien Plants: A Review of Assessment Approaches. NeoBiota 2019, 43, 69–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, S.; Sagona, E.; Carbonell, A.K.Z.; Chiarini, F. A Revision of the Solanum elaeagnifolium Clade (Elaeagnifolium Clade; Subgenus leptostemonum, Solanaceae). PhytoKeys 2017, 84, 1–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaldaferro, M. Geographical Pattern and Ploidy Levels of the Weed Solanum elaeagnifolium (Solanaceae) from Argentina. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2012, 59, 1833–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, J.W.; Murray, D.S.; Tyrl, R.J. Silverleaf nightshade, Solarium elaeagnifolium, Origin, Distribution, and Relation to Man. Econ. Bot. 1984, 38, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krigas, N.; Tsiafouli, M.A.; Katsoulis, G.; Votsi, N.-E.; van Kleunen, M. Investigating the Invasion Pattern of the Alien Plant Solanum elaeagnifolium Cav. (Silverleaf nightshade): Environmental and Human-Induced Drivers. Plants 2021, 10, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EPPO. Solanum elaeagnifolium. EPPO Bull. 2007, 37, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunel, S. Pest Risk Analysis for Solanum elaeagnifolium and International Management Measures Proposed. EPPO Bull. 2011, 41, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formozis, G.; Tsakaldimi, M.; Ganatsas, P. Are Mediterranean Forest Ecosystems under the Threat of Invasive Species Solanum elaeagnifolium? iForest Biogeosci. For. 2021, 14, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.C.; Wu, H.W.; Stanton, R.; Burrows, G.E.; Lemerle, D.; Raman, H. Morphological Variation of Solanum elaeagnifolium in South-Eastern Australia. Weed Res. 2013, 53, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uludag, A.; Gbehounou, G.; Kashefi, J.; Bouhache, M.; Bon, M.-C.; Bell, C.; Lagopodi, A.L. Review of the Current Situation for Solanum elaeagnifolium in the Mediterranean Basin. EPPO Bull. 2016, 46, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasem, J.R.; Al Abdallat, A.M.; Hasan, S.M. Genetic Diversity of Solanum elaeagnifolium, an Invasive Problematic Weed in Jordan. Weed Res. 2019, 59, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tataridas, A.; Oliveira, R.S.; Frazão, L.; Moreira, M.; Travlos, I.; Freitas, H. Solanum elaeagnifolium Cav. (Solanales: Solanaceae) Presence Confirmed in Portugal. EPPO Bull. 2022, 52, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gmira, N.; Douira, A.; Bouhache, M. Ecological Grouping of Solanum elaeagnifolium: A Principal Weed in the Irrigated Tadla Plain (Central Morocco). Weed Res. 1998, 38, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanton, R.; Heap, J.; Carter, R.; Wu, H. Solanum elaeagnifolium Cav. In The Biology of Australian Weeds. Volume 3; R.G. and F.J. Richardson: Melbourne, Australia, 2009; pp. 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Vladimirov, V.; Bancheva, S.; Delcheva, M. Solanum elaeagnifolium (Solanaceae), a New Alien Species for the Bulgarian Flora. Fl. Medit 2015, 25, 121–125. [Google Scholar]
- Tscheulin, T.; Petanidou, T.; Potts, S.G.; Settele, J. The Impact of Solanum elaeagnifolium, an Invasive Plant in the Mediterranean, on the Flower Visitation and Seed Set of the Native Co-Flowering Species Glaucium Flavum. Plant Ecol. 2009, 205, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmezi, M.; Krigas, N.; Argyropoulou, M.D. The Invasion and Long Naturalization of Solanum elaeagnifolium Affects the Soil Nematode Community: Evidence from a Comparative Study. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjim, Z.; Tani, C.K. L’infestation Par Solanum elaeagnifolium Menace l’Algérie. Rev. D’ecologie Terre Vie 2018, 73, 569–581. [Google Scholar]
- Chalghaf, E.; Aissa, M.; Mellassi, H.; Mekki, M. Maîtrise de La Propagation de La Morelle Jaune (Solanum elaeagnifolium Cav.) Dans Le Gouvernorat de Kairouan (Tunisie)*. EPPO Bull. 2007, 37, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekki, M. Potential Threat of Solanum elaeagnifolium Cav. To the Tunisian Fields. In Invasive Plants in Mediterranean Type Regions of the World. Mèze, France, 2005; Brunel, S., Ed.; Council of Europe Publishing: Strasbourg, France, 2006; pp. 170–175. [Google Scholar]
- Mekki, M. Biology, Distribution and Impacts of Silverleaf nightshade (Solanum elaeagnifolium Cav.)*. EPPO Bull. 2007, 37, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayari, N.; Brundu, G.; Mekki, M. Mapping and Monitoring an Invasive Alien Plant in Tunisia: Silverleaf nightshade (Solanum elaeagnifolium) a Noxious Weed of Agricultural Areas. Tunis. J. Plant Prot. 2016, 11, 219–227. [Google Scholar]
- Wassermann, V.D.; Zimmermann, H.G.; Neser, S. The Weed Silverleaf Bitter Apple (“Satansbos”) (Solanum elaeagnifolium Cav.) with Special Reference to Its Status in South Africa. South Afr. Dep. Agric. Water Supply Tech. Commun. 1988. Available online: https://eurekamag.com/research/007/945/007945510.php (accessed on 1 July 2022).
- Kidston, J.; Thompson, R.; Johnson, A. Silverleaf nightshade. New South Wales: Primefact 237. 2007. Available online: http://www.dpi.nsw.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0008/90890/silverleaf-nightshade.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2022).
- Douh, B.; Mguidiche, A.; Jar Allah al-Marri, M.; Moussa, M.; Rjeb, H. Assessment of Deficit Irrigation Impact on Agronomic Parameters and Water Use Efficiency of Six Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) Cultivars under Mediterranean Semi-Arid Climate. Ital. J. Agrometeorol. 2021, 2, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venables, W.N.; Ripley, B.D. Modern Applied Statistics with S-PLUS; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H.; Chang, W.; Wickham, M.H. Package ‘Ggplot2.’ Create elegant data visualisations using the grammar of graphics. Version 2016, 2, 1–189. [Google Scholar]
- Stanton, R.; Wu, H.; Lemerle, D. Root Regenerative Ability of Silverleaf nightshade (‘Solanum elaeagnifolium’ Cav.) in the Glasshouse. Plant Protection Quarterly 2011, 26, 54–56. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández, O.; Brevedan, R. Regeneracion de Solanum elaeagnifolium Cav. a Partir de Fragmentos de Sus Raices. Darwiniana 1972, 433–442. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.-J.; Müller-Schärer, H.; van Kleunen, M.; Cai, A.-M.; Zhang, P.; Yan, R.; Dong, B.-C.; Yu, F.-H. Invasive Alien Plants Benefit More from Clonal Integration in Heterogeneous Environments than Natives. New Phytol. 2017, 216, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Dong, M.; Miao, S.L.; Li, Z.Y.; Song, M.H.; Wang, R.Q. Invasive Alien Plants in China: Role of Clonality and Geographical Origin. Biol. Invasions 2006, 8, 1461–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, V.; Ede, F.J.; Sunnucks, P. Unravelling the Paradox of Loss of Genetic Variation during Invasion: Superclones May Explain the Success of a Clonal Invader. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Heap, J.; Carter, R. The Biology of Australian Weeds: 35. Solanum elaeagnifolium Cav. Plant Prot. Q. 1999, 14, 2–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ghabrit, S.B.; Bouhache, M.; Birouk, A.; BON, C. Variation Intraspécifique Du Potentiel Invasif de La Morelle Jaune (Solanum elaeagnifolium Cav.) Au Maroc: Influence Des Conditions Écologiques. Rev. Maroc. Prot. Plantes 2020, 14, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Baye, Y.; Ameur, A.; Bouhache, M.; Taleb, A. Strategie de Lutte Chimique Contre La Morelle Jaune (Solanum elaeagnifolium Cav.) Au Maroc*. EPPO Bull. 2007, 37, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baye, Y. Influence de Certains Facteurs Sur l’efficacité Du Glyphosate et de l’aminotriazole Contre Solanum elaeagnifolium Cav.*. EPPO Bull. 2007, 37, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Stanton, R.; Lemerle, D. Herbicidal Control of Solanum elaeagnifolium Cav. in Australia. Crop Prot. 2016, 88, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhache, M.; Boulet, C.; El Karakhi, F. Evolution Des Hydrates de Carbone Non Structuraux Chez La Morelle Jaune (Solatium elaeagnifolium Cav.). Weed Res. 1993, 33, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavana, J.; Singh, S.; Vazquez, A.; Christoffersen, B.; Racelis, A.; Kariyat, R.R. Local Adaptation to Continuous Mowing Makes the Noxious Weed Solanum elaeagnifolium a Superweed Candidate by Improving Fitness and Defense Traits. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulme, P.E.; Liu, W. Species Prevalence and Plant Traits Discriminate between Herbicide Resistant and Susceptible Weeds. Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Year | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Ago | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Tot |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 | 32.5 | 35.7 | 40.5 | 32.4 | 60.0 | 31.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 135.5 | 67.0 | 20.5 | 455.6 |
| 2012 | 32.0 | 55.2 | 80.1 | 15.0 | 7.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 6.5 | 81.5 | 8.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 285.5 |
| 2013 | 14.0 | 19.0 | 44.5 | 8.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 8.0 | 23.5 | 29.5 | 27.0 | 94.7 | 268.2 |
| 2014 | 6.3 | 5.4 | 9.7 | 2.7 | 2.7 | 3.9 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 18.7 | 3.5 | 13.4 | 41.7 | 108.1 |
| 2015 | 0.0 | 40.0 | 39.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 3.0 | 79.0 | 33.0 | 39.0 | 40.0 | 22.3 | 295.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sayari, N.; Brundu, G.; Soilhi, Z.; Mekki, M. Solanum elaeagnifolium Invasiveness under Semi-Arid Environmental Conditions in Tunisia. Earth 2022, 3, 1076-1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth3040062
Sayari N, Brundu G, Soilhi Z, Mekki M. Solanum elaeagnifolium Invasiveness under Semi-Arid Environmental Conditions in Tunisia. Earth. 2022; 3(4):1076-1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth3040062
Chicago/Turabian StyleSayari, Najla, Giuseppe Brundu, Zayneb Soilhi, and Mounir Mekki. 2022. "Solanum elaeagnifolium Invasiveness under Semi-Arid Environmental Conditions in Tunisia" Earth 3, no. 4: 1076-1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth3040062
APA StyleSayari, N., Brundu, G., Soilhi, Z., & Mekki, M. (2022). Solanum elaeagnifolium Invasiveness under Semi-Arid Environmental Conditions in Tunisia. Earth, 3(4), 1076-1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth3040062






