Pesticides, Drinking Water and Cancer Risk: A Portrait of Paraná Southwest, Brazil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Panis, C.; Kawassaki, A.C.B.; Crestani, A.P.J.; Pascotto, C.R.; Bortoloti, D.S.; Vicentini, G.E.; Lucio, L.C.; Ferreira, M.O.; Prates, R.T.C.; Vieira, V.K.; et al. Evidence on Human Exposure to Pesticides and the Occurrence of Health Hazards in the Brazilian Population: A Systematic Review. Front. Public Health 2022, 9, 787438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydinalp, C.; Porca, M.M. The effects of pesticides in water resources. J. Cent. Eur. Agric. 2004, 5, 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Panis, C.; Gaboardi, S.C.; Kawassaki, A.C.B.; Dias, E.C.M.; Teixeira, G.T.; Silva, D.R.P.; Rech, D.; Candiotto, L.Z.P. Characterization of occupational exposure to pesticides and its impact on the health of rural women. Rev. Ciênc. Farm. Básica Apl. 2022, 43, e748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panis, C.; Candiotto, L.Z.P.; Gaboardi, S.C.; Gurzenda, S.; Cruz, J.; Castro, M.; Lemos, B. Widespread pesticide contamination of drinking water and impact on cancer risk in Brazil. Environ. Int. 2022, 165, 107321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, Á.G.P.; López, M.I.R.; Casillas, T.Á.D.; León, J.A.A.; Mahjoub, O.; Prusty, A.K. Monitoring of organochlorine pesticides in blood of women with uterine cervix cancer. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, J.N.; Freeman, L.E.B.; Murata, K.; Andreotti, G.; Shearer, J.J.; Thoren, K.; Ramanathan, L.; Parks, C.G.; Koutros, S.; Lerro, C.C.; et al. Lifetime Pesticide Use and Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance in a Prospective Cohort of Male Farmers. Environ. Health Perspect. 2021, 129, 17003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, S.; Parks, C.G.; Goldner, W.S.; Kamel, F.; Umbach, D.M.; Ward, M.H.; Lerro, C.C.; Koutros, S.; Hoffmann, J.N.; Freeman, L.E.B.; et al. Pesticide use and incident hypothyroidism in pesticide applicators in the Agricultural Health Study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2018, 126, 97008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerro, C.C.; Freeman, L.E.B.; Dellavalle, C.T.; Andreotti, G.; Hoffmann, J.N.; Koutros, S.; Parks, C.G.; Shrestha, S.; Alavanja, M.C.R.; Blair, A.; et al. Pesticide exposure and incident thyroid cancer among male pesticide applicators in agricultural health study. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreotti, G.; Freeman, L.E.B.; Shearer, J.J.; Lerro, C.C.; Koutros, S.; Parks, C.G.; Blair, A.; Lynch, C.F.; Lubin, J.H.; Sandler, D.P.; et al. Occupational Pesticide Use and Risk of Renal Cell Carcinoma in the Agricultural Health Study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2020, 128, 67011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearer, J.J.; Sandler, D.P.; Andreotti, G.; Murata, K.; Shrestha, S.; Parks, C.G.; Liu, D.; Alavanja, M.C.; Landgren, O.; Freeman, L.E.B.; et al. Pesticide Use and Kidney Function among Farmers in the Biomarkers of Exposure and Effect in Agriculture Study. Environ. Res. 2021, 199, 111276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Zhou, T.; Tao, Y.; Feng, Y.; Shen, X.; Mei, S. Exposure to organochlorine pesticides and non-Hodgkin lymphoma: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabarwal, A.; Kumar, K.; Singh, R.P. Hazardous effects of chemical pesticides on human health-cancer and other associated disorders. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 63, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, S.; Parks, C.G.; Umbach, D.M.; Richards-Barber, M.; Hoffmann, J.N.; Chen, H.; Blair, A.; Freeman, L.E.B.; Sandler, D.P. Pesticide use and incident Parkinson’s disease in a cohort of farmers and their spouses. Environ. Res. 2020, 191, 110186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farr, S.L.; Cooper, G.S.; Cai, J.; Savitz, D.A.; Sandler, D.P. Pesticide use and menstrual cycle characteristics among premenopausal women in the Agricultural Health Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2004, 160, 1194–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, C.G.; Santos, A.d.S.E.; Lerro, C.C.; Dellavalle, C.T.; Ward, M.H.; Alavanja, M.C.; Berndt, S.I.; Freeman, L.E.B.; Sandler, D.P.; Hoffmann, J.N. Lifetime Pesticide Use and Antinuclear Antibodies in Male Farmers from the Agricultural Health Study. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thongprakaisang, S.; Thiantanawat, A.; Rangkadilok, N.; Suriyo, T.; Satayavivad, J. Glyphosate induces human breast cancer cells growth via estrogen receptors. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 59, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, C. EPA halts dieldrin production. Nature 1974, 250, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musicco, M.; Sant, M.; Molinari, S.; Filippini, G.; Gatta, G.; Berrino, F. A case-control study of brain gliomas and occupational exposure to chemical carcinogens: The risk to farmers. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1988, 128, 778–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Instituto Brasileiro do Meio Ambiente e dos Recursos Naturais Renováveis. Relatório de Comercialização de Agrotóxicos. Available online: https://www.gov.br/ibama/pt-br/assuntos/quimicos-e-biologicos/agrotoxicos/relatorios-de-comercializacao-de-agrotoxicos (accessed on 29 March 2024).
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Pesticides Use Datasheet. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/%23data/RP/visualize (accessed on 18 March 2024).
- Associação Brasileira de Saúde Coletiva. Afinal, o Brasil é o Maior Consumidor de Agrotóxico do Mundo? Available online: https://abrasco.org.br/afinal-o-brasil-e-o-maior-consumidor-de-agrotoxico-do-mundo/ (accessed on 18 March 2024).
- Swaminathan, M.S. Politics of pesticides. Nature 1982, 296, 521–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sistema de Informações de Vigilância da Qualidade da Água. Quantitativo das Análises. 2021. Available online: https://dados.gov.br/dataset?tags=AN%25C3%2581LISE%2bDA%2b%25C3%2581GUA (accessed on 18 March 2024).
- Agência Ambiental dos Estados Unidos. Human Health Benchmarks for Pesticides: Updated 2017 Technical Document. 2017. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-10/documents/hh-benchmarks-techdoc.pdf (accessed on 18 March 2024).
- International Agency for Cancer Research. Standard IARC Classification. 2021. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/health/scientific_committees/opinions_layman/en/electromagnetic-fields/glossary/ghi/iarc-classification.htm (accessed on 18 March 2024).
- Bombardi, L.M. A Geography of Agrotoxins Use in Brazil and Relations to the European Union; em; FFLCH/US: São Paulo, Brazil, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaimala, P.; Khunlert, P.; Chuntib, P.; Pundee, R.; Kallayanatham, N.; Nankongnab, N.; Kongtip, P.; Woskie, S. Pesticide residues on children’s hands, home indoor surfaces, and drinking water among conventional and organic farmers in Thailand. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonen, S.; Argaw, R.; Simanesew, A.; Houbraken, M.; Senaeve, D.; Ambelu, A.; Spanoghe, P. Pesticides residues in drinking water and associated risk to consumers in Ethiopia. Chemosphere 2016, 162, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Swartz, M.D.; Langlois, P.H.; Romitti, P.A.; Weyer, P.; Mitchell, L.E.; Luben, T.J.; Ramakrishnan, A.; Malik, S.; Lupo, P.J.; et al. Estimated Maternal Pesticide Exposure from Drinking Water and Heart Defects in Offspring. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syafrudin, M.; Kristanti, R.A.; Yuniarto, A.; Hadibarata, T.; Rhee, J.; Al-Onazi, W.A.; Algarni, T.S.; Almarri, A.H.; Al-Mohaimeed, A.M. Pesticides in Drinking Water—A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamata, M.; Matsiu, Y.; Asami, M. National trends in pesticides in drinking water and water sources in Japan. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 744, 140930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjerps, R.M.A.; Kooij, P.J.F.; Van Loon, A.; Van Wezel, A.P. Occurrence of pesticides in Dutch drinking water sources. Chemosphere 2019, 235, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Instituto Nacional do Câncer. Estimativa De Novos Casos. 2020. Available online: https://www.inca.gov.br/estimativa/estado-capital/parana-curitiba (accessed on 18 March 2024).
- Rech, D. Perfil do Câncer de Mama em Mulheres do Sudoeste do Paraná: Identificação de Possíveis Fatores de Risco Regionais e Correlação Clínico-Patológica. 2018. Master’s Thesis, (Mestrado em Ciências Aplicadas à Saúde). Faculdade de Medicina, Universidade Estadual do Oeste do Paraná, Francisco Beltrão, Brazil, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gaboardi, S.C. O Uso de Agrotóxicos no Sudoeste do Paraná a Partir de Uma Perspectiva Geográfica Multiescalar. Ph.D. Thesis, (Doutorado em Geografia). Faculdade de Geografia, Universidade Estadual do Oeste do Paraná, Francisco Beltrão, Brazil, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística. Censo. 2022. Available online: https://censo2022.ibge.gov.br/panorama/ (accessed on 18 March 2024).
- Office in Environmental Health Hazard Assessment. California Environmental Protection Agency. Technical Support Document for Cancer Potency Factors: Methodologies for Derivation, Listing of Available Values, and Adjustments to Allow for Early Life Stage Exposures. 2009. Available online: https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/document?repid=rep1&type=pdf&doi=89b4a869a8fb001661c411bd4a62d4167179caf6 (accessed on 18 March 2024).
- Instituto Nacional do Câncer. Informações do Registro Hospitalar de Câncer—Tabulador Hospitalar Base do Estado: PR. 2022. Available online: https://irhc.inca.gov.br/RHCNet/selecionaTabulador.action?initial=1%26local=uf%26unidFed=PR (accessed on 18 March 2024).
- Instituto Nacional do Câncer. Atlas Online da Mortalidade. Available online: https://mortalidade.inca.gov.br/MortalidadeWeb/ (accessed on 18 March 2024).
- Pawlak, F.; Koziol, K.; Polkowska, Z. Chemical hazard in glacial melt? The glacial system as a secondary source of POPs (in the Northern Hemisphere). A systematic review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 145244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, M.A.; Slimak, M.W.; Gabel, N.W. Water-Related Environmental Fate of 129 Priority Pollutants; Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1979.
- Kucka, M.; Pogrmic-Majkic, K.; FA, S.; Stojilkovic, S.S.; Kovacevic, R. Atrazine acts as an endocrine disrupter by inhibiting cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase-4. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 265, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axelstad, M.; Boberg, J.; Nellemann, C.; Kiersgaard, M.; Jacobsen, P.R.; Christiansen, S.; Hougaard, K.S.; Hass, U. Exposure to the Widely Used Fungicide Mancozeb Causes Thyroid Hormone Disruption in Rat Dams but No Behavioral Effects in the Offspring. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 120, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesseur, C.; Pirrotte, P.; Pathak, K.V.; Manservisi, F.; Mandrioli, D.; Belpoggi, S.; Li, Q.; Barrett, E.S.; Nguyen, R.H.N.; Sathyanarayana, S.; et al. Maternal urinary levels of glyphosate during pregnancy and anogenital distance in newborns in a US multicenter pregnancy cohort. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 280, 117002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Sarma, D.K.; Shubham, S.; Kumawat, M.; Verma, V.; Prakash, A.; Tiwari, R. Environmental Endocrine-Disrupting Chemical Exposure: Role in Non-Communicable Diseases. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 553850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odewale, G.O.; Sosan, M.B.; Oyekunle, J.A.O.; Adeleye, A.O. Human health risk assessment of dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) and hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables in Nigeria. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 33133–33145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woldetsadik, D.; Simon, M.P.; Knuth, D.; Hailu, H.; Gebresilassie, A.; Dejen, A.; Düring, R.A. Exposure to DDT and HCH congeners and associated potential health risks through khat (Catha edulis) consumption among adults in South Wollo, Ethiopia. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 3597–3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steenland, K.; Cedillo, L.; Tucker, J.; Hines, C.; Sorensen, K.; Deddens, J.; Cruz, V. Thyroid hormones and cytogenetic outcomes in backpack sprayers using ethylenebis(dithiocarbamate) (EBDC) fungicides in Mexico. Environ. Health Perspect. 1997, 105, 1126–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Panganiban, L.; Cortes-Maramba, N.; Dioquino, C.; Suplido, M.L.; Ho, H.; Francisco-Rivera, A.; Manglicmot-Yabes, A. Correlation between blood ethylenethiourea and thyroid gland disorders among banana plantation workers in the Philippines. Environ. Health Perspect. 2004, 112, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kaur, N.; Swain, S.K.; Banerjee, B.D.; Sharma, T.; Krishnalata, T. Organochlorine pesticide exposure as a risk factor for breast cancer in young Indian women: A case-control study. South Asian J. Cancer 2019, 8, 212–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Louis, L.M.; Lerro, C.C.; Friesen, M.C.; Andreotti, G.; Koutros, S.; Sandler, D.P.; Blair, A.; Robson, M.G.; Freeman, L.E.B. A prospective study of cancer risk among Agricultural Health Study farm spouses associated with personal use of organochlorine insecticides. Environ. Health 2017, 16, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kass, L.; Gomez, A.L.; Altamirano, G.A. Relationship between agrochemical compounds and mammary gland development and breast cancer. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2020, 508, 110789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, R.H.; Gottlieb, M.; Clute, E.; Pongsiri, M.J.; Sherman, J.; Obrams, G.I. Breast cancer and pesticides in Hawaii: The need for further study. Environ. Health Perspect. 1997, 105 (Suppl. 3), 679–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Panis, C.; Lemos, B. Pesticide exposure and increased breast cancer risk in women population studies. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 933, 172988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Serra, F.M.; Parizi, J.L.S.; Odorizzi, G.A.S.M.; Sato, G.M.R.H.; Patrão, I.B.; Chagas, P.H.N.; Mello, F.d.A.; Nai, G.A. Subchronic exposure to a glyphosate-based herbicide causes dysplasia in the digestive tract of Wistar rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 61477–61496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, J.Y.; Jiang, T.; Huang, X.J. Glyphosate-induced Delayed Pyloric Obstruction, Ulcer and Scar Changes. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak. 2020, 30, 868–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jyoti, W.; Thabah, M.M.; Rajagopalan, S.; Hamide, A. Esophageal perforation and death following glyphosate poisoning. J. Postgrad Med. 2014, 60, 346–347, Erratum in: J. Postgrad Med. 2020, 66, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, M.I.G.; Moreno, M.; De Sá, C.A.; Rizzi, C.A.; Ribeiro, E.A.W.; Ripke, M.O.; Corralo, V.d.S. Mortality from breast cancer and use of pesticides in the western mesoregion of Santa Catarina—Brazil. Rev. Bras. Ciências Ambient. (RBCIAMB) 2024, 59, e1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, A.P.d.S.; Figueiredo, E.R.L.; Melo, G.S.; Souza, J.d.S.e.; Gonçalves, N.V.; Gomes, F.d.C.; Neto, J.S.d.M. Predictors of Testicular Cancer Mortality in Brazil: A 20-Year Ecological Study. Cancers 2023, 15, 4149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Untalan, M.; Ivic-Pavlicic, T.; Taioli, E. Urinary glyphosate levels and association with mortality in the 2013-16 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Carcinogenesis 2024, 45, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alif, S.M.; Benke, G.P.; Kromhout, H.; Vermeulen, R.; Tran, C.; Ronaldson, K.; Walker-Bone, K.; Woods, R.; Beilin, L.; Tonkin, A.; et al. Long-term occupational exposures on disability-free survival and mortality in older adults. Occup. Med. 2023, 73, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alehashem, M.; Peters, R.; Fajana, H.O.; Eslamizad, S.; Hogan, N.; Hecker, M.; Siciliano, S.D. Herbicides and pesticides synergistically interact at low concentrations in complex mixtures. Chemosphere 2024, 353, 141431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Roque, A.A.; Da Luz, J.Z.; Santurio, M.T.K.; Neto, F.F.; Ribeiro, C.A.d.O. Complex mixtures of pesticides and metabolites modulate the malignant phenotype of murine melanoma B16-F1 cells. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 47366–47380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Pesticide | Benchmark Cancer Risk of 1 Case/106 People (EPA/OEHAA) | Classification | Cancer Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|
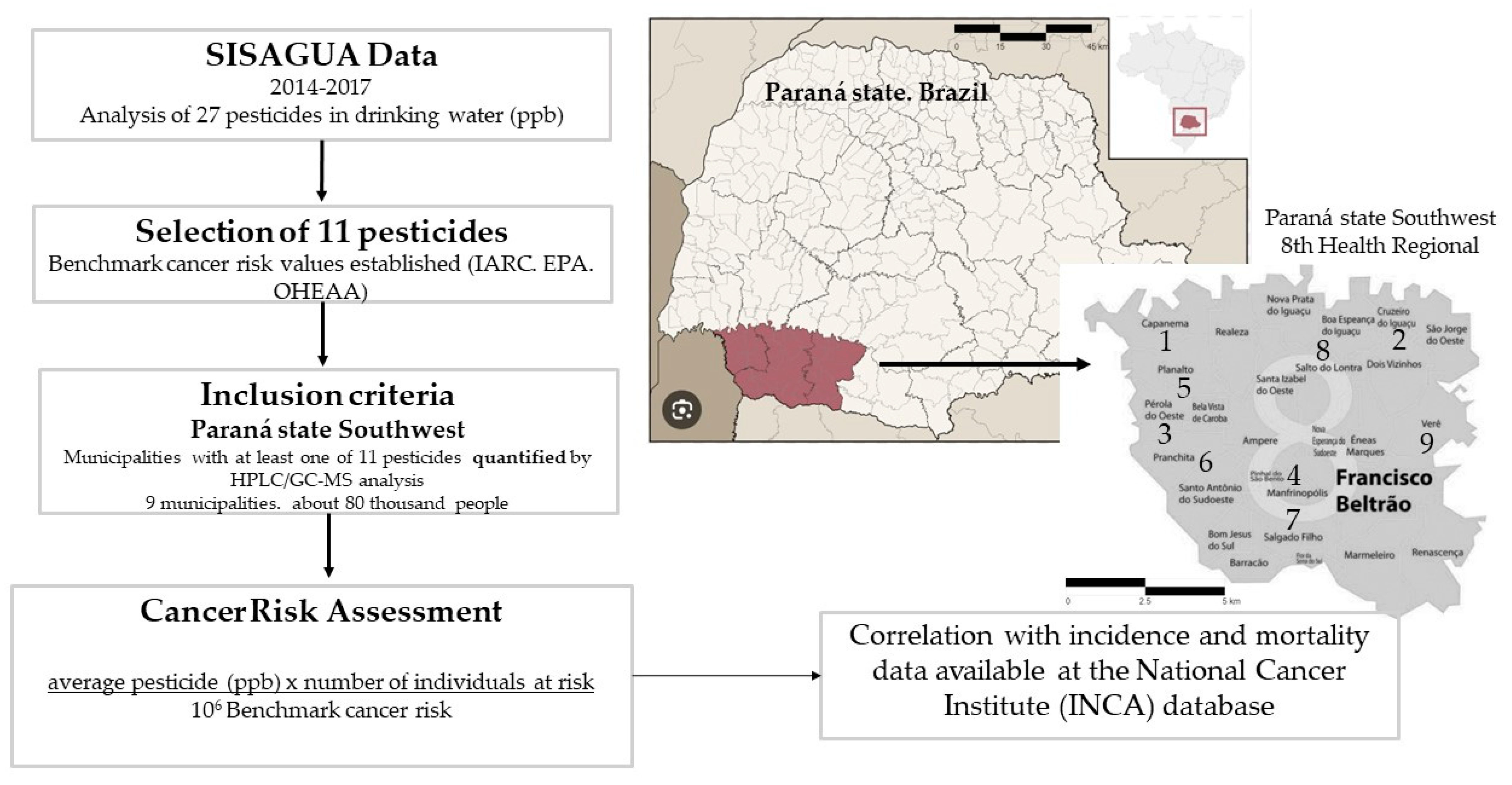
 Alachlor Alachlor | 0.4 | Probably carcinogenic to humans (IARC. EPA) | Laryngeal cancer. lymphohematopoietic (IARC) Urinary tract (EPA) |
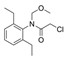
 Aldrin-dieldrin Aldrin-dieldrin | 0.002 | Probably carcinogenic to humans (IARC. EPA) | Breast (IARC) Liver (EPA) |
 Atrazine Atrazine | 0.15 | Not classifiable as to human carcinogenicity (IARC) | Thyroid (OEHAA) |
 Chlordane Chlordane | 0.1 | Possibly carcinogenic (IARC. EPA) | Liver (IARC and EPA) Thyroid (OEHAA) |
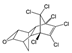
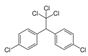 DDT-DDD-DDE DDT-DDD-DDE | 0.1 | Possibly carcinogenic (IARC. EPA) | Testis. liver and lymphoma (IARC) Liver (EPA) |
 Diuron Diuron | 2 | Probably carcinogenic to humans (IARC. EPA) | Kidney. lung (IARC) Urinary tract (EPA) |
 Glyphosate-AMPA Glyphosate-AMPA | 56.45 | Probably carcinogenic to humans(IARC) Not Classifiable as to Human Carcinogenicity (EPA) | Lymphoma (IARC. OEHAA) |
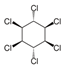 Lindane Lindane | 0.032 | Carcinogenic to humans (IARC. EPA) | Lymphoma (IARC) Liver (EPA and OEHAA) |
 Mancozeb-ETU Mancozeb-ETU | 0.06 (ETU) | No data (IARC) Probably carcinogenic (EPA for ETU) | Thyroid (IARC) |
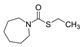 Molinate Molinate | 1 | Not classifiable as to human carcinogenicity (IARC) | Urinary tract (OEHAA) |
 Trifluralin Trifluralin | 4 | Not classifiable as to human carcinogenicity (IARC) Possibly carcinogenic (EPA) | Lymphoma. thyroid. stomach. liver (IARC) Urinary tract (EPA) |
| Alachlor | Aldrin-diheldrin | Atrazine | Chlordane | DDT-DDD-DDE | Diuron | Glyphosate-AMPA | Lindane | Mancozeb-ETU | Molinate | Trifluraline | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capanema (#1) | 0.2 | 0.004 | 0.01 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 90 | 65 | 0.002 | 180 | 0.5 | 0.02 |
| Cruzeiro do Iguaçu (#2) | 0.2 | 0.004 | 0.198 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 90 | 65 | 0.002 | 180 | 0.5 | 0.02 |
| Pérola D’Oeste (#3) | 0.2 | 0.004 | 0.01 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 90 | 65 | 0.002 | 180 | 0.3 | 0.02 |
| Pinhal de São Bento (#4) | 0.01 | 0.001 | 0.01 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.0007 | 65 | 0.002 | 0.027 | 0.1 | 0.02 |
| Planalto (#5) | 0.2 | 0.004 | 0.01 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 90 | 65 | 180 | 180 | 0.5 | 0.02 |
| Pranchita (#6) | 0.3 | 0.03 | 1 | 0.05 | 0.3 | 10 | 200 | 0.3 | 100 | 3 | 0.3 |
| Salgado Filho (#7) | 0.2 | 0.008 | 0.01 | 15 | 0.002 | 90 | 65 | 0.002 | 180 | 0.5 | 0.02 |
| Salto do Lontra (#8) | 0.01 | 0.001 | 0.01 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.0007 | 65 | 0.002 | 0.027 | 0.1 | 0.02 |
| Verê (#9) | 0.2 | 0.004 | 0.01 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 90 | 45 | 0.002 | 180 | 0.5 | 0.02 |
| Maximum allowed in Brazil | 20 | 0.03 | 2 | 0.2 | 1 | 90 | 500 | 2 | 180 | 6 | 20 |
| Maximum allowed in the European Union | 0.1 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 |
| Alachlor | Aldrin-diheldrin | Atrazine | Chlordane | DDT-DDD-DDE | Diuron | Glyphosate-AMPA | Lindane | Mancozebe-ETU | Molinate | Trifluraline | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capanema (#1) | 0.009562 | 0.038248 | 0.001275 | 0.000382 | 0.000382 | 0.86058 | 0.001381 | 0.001195 | 5.7372 | 0.009562 | 0.0000956 |
| Cruzeiro do Iguaçu (#2) | 0.002126 | 0.0000068 | 0.005613 | 0.000000068 | 0.00008504 | 0.19134 | 0.000307 | 0.000266 | 0.09567 | 0.002126 | 0.00002126 |
| Pérola D’Oeste (#3) | 0.003174 | 0.012694 | 0.000423 | 0.000127 | 0.000127 | 0.285615 | 0.000458 | 0.000397 | 0.142808 | 0.001904 | 0.0000317 |
| Pinhal de São Bento (#4) | 0.0000683 | 0.001366 | 0.000182 | 0.0000273 | 0.0000546 | 0.000000956 | 0.000197 | 0.000171 | 0.00000922 | 0.000273 | 0.0000137 |
| Planalto (#5) | 0.00674 | 0.026958 | 0.000899 | 0.00027 | 0.00027 | 0.606555 | 0.000973 | 0.000842 | 0.303278 | 0.00674 | 0.0000674 |
| Pranchita (#6) | 0.002579 | 0.010314 | 0.000344 | 0.000103 | 0.000103 | 0.232065 | 0.000372 | 29.00813 | 0.116033 | 0.002579 | 0.0000258 |
| Salgado Filho (#7) | 0.00179 | 0.01432 | 0.000239 | 0.537 | 0.0000716 | 0.1611 | 0.000259 | 0.000224 | 0.08055 | 0.00179 | 0.0000179 |
| Salto do Lontra (#8) | 0.00037 | 0.007393 | 0.000986 | 0.000148 | 0.000296 | 0.00000517 | 0.001068 | 0.000924 | 0.0000499 | 0.001479 | 0.0000739 |
| Verê (#9) | 0.003939 | 0.015756 | 0.000525 | 0.000158 | 0.000158 | 0.35451 | 0.000394 | 0.000492 | 0.177255 | 0.003939 | 0.0000394 |
| SUM | 0.030348 | 0.1270558 | 0.010486 | 0.538215 | 0.00154724 | 2.691771 | 0.005409 | 29.01264 | 6.65285312 | 0.030392 | 0.0003867 |
| Total estimated cancer cases: 39 | |||||||||||
| Alachlor | Aldrin-diheldrin | Atrazine | Chlordane | DDT-DDD-DDE | Diuron | Glyphosate-AMPA | Lindane | Mancozeb-ETU | Molinate | Trifluraline | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spearman R (BREAST CANCER) | 0.6169 | 0.7396 * | 0.6786 * | 0.7525 * | 0.6228 | 0.3701 | 0.4549 | 0.5145 | 0.3701 | 0.7006* | 0.6228 |
| Spearman R (PROSTATE CANCER) | 0.5209 | 0.5968 | 0.6487 * | 0.6228 | 0.4671 | 0.4661 | 0.2759 | 0.1715 | 0.4661 | 0.5060 | 0.4671 |
| Spearman R (COLON CANCER) | 0.3907 | 0.4671 | 0.2162 | 0.5709 | 0.07785 | 0.8431 ** | −0.02237 | 0.1715 | 0.8431 ** | 0.4671 | 0.07785 |
| Spearman R (LUNG CANCER) | 0.6037 | 0.4138 | 0.7473 * | 0.3218 | 0.5517 | 0.3539 | 0.5058 | 0.6114 | 0.3539 | 0.5320 | 0.5517 |
| Spearman R (UTERINE CANCER) | −0.01388 | −0.1839 | −0.02265 | −0.1839 | 0.000 | 0.3469 | −0.09813 | −0.03774 | 0.3469 | −0.1576 | 0.000 |
| Spearman R (STOMACH CANCER) | 0.6360* | 0.6670* | 0.2319 | 0.7191 * | 0.2733 | 0.8285 ** | 0.000 | 0.09723 | 0.8285 ** | 0.5759 | 0.2733 |
| Spearman R (THYROID CANCER) | 0.1316 | 0.2699 | −0.1989 | 0.3668 | 0.000 | 0.4387 | −0.1193 | 0.2784 | 0.4387 | 0.2699 | 0.000 |
| Spearman R (ORAL CANCER) | 0.4899 | 0.3668 | 0.3579 | 0.2699 | 0.5813 | 0.08043 | 0.6443 | 0.6443 | 0.08043 | 0.3114 | 0.5813 |
| Spearman R (ESOPHAGUS CANCER) | 0.2706 | 0.1379 | 0.5058 | 0.04597 | 0.5517 | −0.06245 | 0.6869* | 0.5360 | −0.06245 | 0.2561 | 0.5517 |
| Spearman R (BLADDER CANCER) | −0.3677 | −0.4552 | −0.2308 | −0.4552 | 0.000 | −0.1414 | −0.1077 | −0.03847 | −0.1414 | −0.3815 | 0.000 |
| Alachlor | Aldrin-diheldrin | Atrazine | Chlordane | DDT-DDD-DDE | Diuron | Glyphosate-AMPA | Lindane | Mancozeb-ETU | Molinate | Trifluraline | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spearman R (BREAST CANCER) | 0.1891 | 0.06507 | 0.4862 | −0.04555 | 0.6637 * | −0.2716 | 0.5385 | 0.6208 | −0.2716 | 0.2343 | 0.6637 * |
| Spearman R (PROSTATE CANCER) | 0.2810 | 0.2790 | 0.4549 | 0.2141 | 0.7006 * | −0.1576 | 0.5742 | 0.7233 * | −0.1576 | 0.2919 | 0.7006 * |
| Spearman R (COLON CANCER) | 0.2193 | 0.2206 | −0.007457 | 0.2725 | 0.1557 | 0.5209 | 0.03728 | 0.4549 | 0.5209 | 0.1168 | 0.1557 |
| Spearman R (LUNG CANCER) | 0.4524 | 0.4476 | 0.3206 | 0.4087 | 0.6228 | 0.1645 | 0.6935 * | 0.5891 | 0.1645 | 0.2530 | 0.6228 |
| Spearman R (UTERINE CANCER) | 0.1901 | 0.02768 | 0.1829 | 0.02768 | 0.000 | 0.5118 | −0.05568 | 0.1989 | 0.5118 | 0.04152 | 0.000 |
| Spearman R (STOMACH CANCER) | 0.3261 | 0.2627 | 0.2642 | 0.1970 | 0.5517 | 0.006939 | 0.2038 | 0.4605 | 0.006939 | 0.4335 | 0.5517 |
| Spearman R (THYROID CANCER) | Not calculated | Not calculated | Not calculated | Not calculated | Not calculated | Not calculated | Not calculated | Not calculated | Not calculated | Not calculated | Not calculated |
| Spearman R (ORAL CANCER) | −0.2348 | −0.2639 | −0.1064 | −0.2639 | 0.000 | −0.1467 | −0.2767 | −0.1064 | −0.1467 | −0.1806 | 0.000 |
| Spearman R (ESOPHAGUS CANCER) | 0.3128 | 0.2408 | 0.5161 | 0.1887 | 0.5076 | 0.09969 | 0.6881* | 0.6507* | 0.09969 | 0.2733 | 0.5076 |
| Spearman R (BLADDER CANCER) | −0.1414 | −0.08702 | −0.2308 | −0.02677 | 0.000 | 0.1414 | −0.1077 | 0.2693 | 0.1414 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Machado, M.G.; Orrutéa, J.F.G.; Panis, C. Pesticides, Drinking Water and Cancer Risk: A Portrait of Paraná Southwest, Brazil. Pollutants 2024, 4, 302-315. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants4030020
Machado MG, Orrutéa JFG, Panis C. Pesticides, Drinking Water and Cancer Risk: A Portrait of Paraná Southwest, Brazil. Pollutants. 2024; 4(3):302-315. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants4030020
Chicago/Turabian StyleMachado, Murilo G., Julia F. G. Orrutéa, and Carolina Panis. 2024. "Pesticides, Drinking Water and Cancer Risk: A Portrait of Paraná Southwest, Brazil" Pollutants 4, no. 3: 302-315. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants4030020
APA StyleMachado, M. G., Orrutéa, J. F. G., & Panis, C. (2024). Pesticides, Drinking Water and Cancer Risk: A Portrait of Paraná Southwest, Brazil. Pollutants, 4(3), 302-315. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants4030020






