Abstract
In this current work, we assume the mathematical modelling of non-Newtonian time-dependent hybrid nanoparticles via a cylindrical stenosis artery. In this work, blood is used as a base fluid, and the nanoparticles (copper and aluminum oxide) of cylindrical shape are inserted inside the artery to combine with blood to form hybrid nanofluid (HNF). The homotopy analysis method (HAM) is deployed for the solution of nonlinear resulting equations. For the validation of this current work, the results of the existing work have been compared with our proposed model results. A comparison of key profiles like velocity, temperature, wall shear stress, and flow rate is also performed at a specific critical height of the stenosis. It is also observed that the thermal conductance of hybrid nanofluids is greater than that of nanofluids. Including the hybrid nanoparticles (copper and aluminum oxide) inside the blood enhances the blood axial velocity. These simulations are applicable to the magnetic targeting treatment of stenosed artery disorders and the diffusion of nanodrugs.
1. Introduction
In the field of biomedical engineering, nanofluids have gained significant attention in recent decades. The application of nanoparticles in addressing various biomedical challenges has gained significant attraction and recognition in both theoretical and practical studies. This emerging area of research has greatly influenced the current literature in the field of bioscience. Nanoscale processes are used to produce nanomaterials. They exhibit a wide range of shapes including rods, shells, films, wires, tubes, fibers, spherical particles, cylinders, blades, polymeric structures, and other forms. By incorporating these nanoparticles into conventional base fluids with inferior thermophysical properties, a distinct class of fluids has been developed which is known as “nanofluids”. The term “nanofluid”, coined by Choi and Eastman [1], refers to the suspension of nanoparticles with base fluid that enhances thermal properties as a whole. These nanoparticles, which are typically composed of carbides, metals, or oxides having much thermal conductivities, are mixed with base fluids such as oil, water, or plasma. They hold immense potential in various applications, including drug carriers, which allow researchers to explore molecular-level interventions for significant advancements in healthcare. This opens up new avenues for improving drug delivery and personalized medicine. Tripathi et al. [2] led a comprehensive review focusing on the latest advancements in blood flow for delivery systems of nanodrugs. Vasu et al. [3] performed a detailed finite element analysis using FREEFEM++ software to examine non-Newtonian blood flow inside a stenosed coronary artery. The influence of slip conditions over blood flow via a tapering stenosed artery in the existence of nanoparticles was firstly investigated by Nadeem and Ijaz [4]. Bashaga and Shaw [5] studied the dispersion of nanoparticles while administering a nanodrug within blood flow via a microvessel. Maiti et al. [6], Roy and Shaw [7] studied the drug delivery of nanoparticles, emphasizing several sides of this field and its applications.
The formation of a hybrid nanofluid arises from the dispersion of two or more types of nanoparticles within a single base fluid. This combination results in improved thermophysical properties, including convective heat transfer coefficient, viscosity, thermal conductivity, and thermal diffusivity. These hybrid nanofluids have proven effective in various heat transfer applications. Numerous applications in biomedical engineering make use of hybrid nanoparticles, such as gene therapy, MRI, tracking agents, drug delivery, tissue regeneration, wound healing, and biomagnetic nanopharmacodynamics. Dinarvandb et al. [8] investigated the influence of induced and external magnetic fields on the continuous flow of a hybrid nanofluid (CuO-Cu/blood) over a stretched sheet. A mathematical model for drug delivery utilizing Au-Al2O3/blood hybrid nanoparticles in a bell-shaped stenosed artery was developed by Gandhi et al. [9]. Poonam et al. [10] assessed the impact of hybrid nanoparticles on hemodynamic parameters in a curved artery with aneurysm and stenosis, considering blood viscosity to be dependent on hematocrit levels. The joint effects of radiation and generated magnetic fields on the flow of hybrid nanofluids in an artery were studied by Dolui et al. [11] and Gandhi and Sharma [12].
In this current work, we select copper () and aluminum oxide () as they have some special thermal characteristics like robust thermal conductivity, high aspect ratio, etc. A new model is used to investigate the hybrid nanofluid time-dependent unhealthy arterial hemodynamics. By considering these factors and incorporating the relevant equations and models, the study aims to gain insights into the complex dynamics of hybrid nanofluid blood flow in diseased arteries. The homotopy analysis method (HAM) is used in order to solve the nonlinear nondimensional conservation equations. Furthermore, visualizations and simulations are performed to analyze and interpret the obtained results.
2. Geometry of the Flow
Bi-directional and unsteady blood flow through a cylindrical stenotic artery is investigated in this suggested model. The cylindrical coordinate system is utilized. The flow is assumed to be axisymmetric; therefore, all the variables are independent of . The magnetic field is applied normally to the blood flow. The temperature field and velocity field of the nanoparticles are provided by:
3. Mathematical Formulation
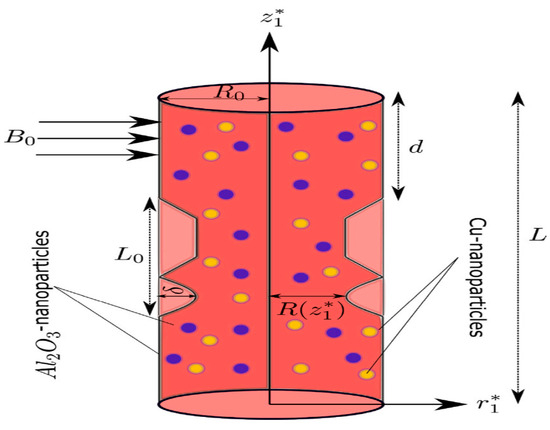
Figure 1.
Fluid flow configuration.
Here, denotes the radial coordinate, is the axial velocity, is the radial velocity component, is the axial coordinate, is used for time, denotes the pressure, and is the blood temperature. is the fluid density, represents the coefficient of thermal expansion, denotes the concentration expansion coefficient, is used for fluid electrical conductivity, denotes the thermal conductivity, is the specific heat, and is used for the reference temperature.
4. Nondimensionalization of the Model
The proposed model can be made dimensionless by using the following scaling parameters (Zaman et al. [13]).
5. Discussions
Table 1 presents the thermophysical characteristics of copper (Cu), aluminium oxide () and the base fluid blood. The comparison between our suggested model and Ijaz and Nadeem [11] is shown in Table 2. The results show that there is a very excellent and satisfying agreement. Figure 1 explains the influence of the magnetic parameter M on the velocity profile w(x). Applications of magnetic fields that regulate blood flow for medical purposes heavily depend on the magnetic coefficient M. It has been noted that as the value M rises, blood flow falls. The effect of the Brownian motion parameter on the velocity profile w(x) is seen in Figure 2. This image illustrates how velocity rises as increases, meaning that when nanoparticle size is tiny, blood flow increases.

Table 1.
Thermophysical characteristics of nanoparticles and blood [14].

Table 2.
Comparison with Ijaz and Nadeem [11] of stenosis artery for axial velocity at z = 1.5 and t = 1.2.
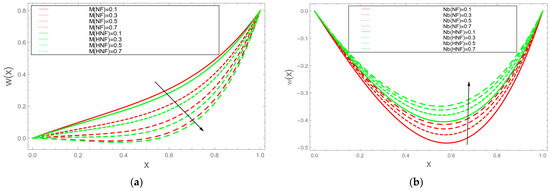
Figure 2.
(a) Velocity decreases with . (b) Velocity increases with .
As a result of setting x = r/(R(z)) in the governing equations mentioned above, Equations (1)–(4) undergo a contraction and can be expressed in the following condensed form:
where , , , , , .
Moreover, the corresponding boundary and initial conditions in their dimensionless form are expressed as follows:
6. Conclusions
The mathematical modelling of non-Newtonian time-dependent hybrid nanofluid flow via a cylindrical stenosis artery is considered in this proposed model. In this work, blood is used as a base fluid, and the nanoparticles (copper and aluminum oxide) of cylindrical shape are inserted inside the artery to combine with blood to form a hybrid nanofluid (HNF). Furthermore, the HAM technique is used to solve the governing equations. The axial velocity of blood increases by injecting the hybrid nanoparticles (copper and aluminum oxide) inside the blood. Moreover, the temperature profile increases while concentration decreases as the volume fraction of the nanoparticle increases.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.Z. and Z.S.; methodology, M.R.; software, T.Z.; validation, H.U., Z.S. and M.R.; formal analysis, Z.S.; investigation, T.Z.; resources, Z.S.; data curation, M.R.; writing—original draft preparation, T.Z.; writing—review and editing, Z.S.; visualization, M.R.; supervision, Z.S.; project administration, M.R.; funding acquisition, Z.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study available from the corresponding author (Z.S.) on reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Choi, S.U.S.; Eastman, J.A. Enhancing Thermal Conductivity of Fluids with Nanoparticles; Argonne National Lab. (ANL): Argonne, IL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi, J.; Vasu, B.; Bég, O.A.; Gorla, R.S.R. Unsteady hybrid nanoparticle-mediated magneto-hemodynamics and heat transfer through an overlapped stenotic artery: Biomedical drug delivery simulation. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 2021, 235, 1175–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasu, B.; Dubey, A.; Bég, O.A. Finite element analysis of non-Newtonian magnetohemodynamic flow conveying nanoparticles through a stenosed coronary artery. Heat Transf. Res. 2020, 49, 33–66. [Google Scholar]
- Nadeem, S.; Ijaz, S.; Sadiq, M.A. Inspiration of induced magnetic field on a blood flow of Prandtl nanofluid model with stenosis. Curr. Nanosci. 2014, 10, 753–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashaga, G.; Shaw, S. Shear-augmented solute dispersion during drug delivery for three-layer flow through microvessel under stress jump and momentum slip-Darcy model. Appl. Math. Mech. 2021, 42, 901–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, S.; Shaw, S.; Shit, G.C. Caputo–Fabrizio fractional order model on MHD blood flow with heat and mass transfer through a porous vessel in the presence of thermal radiation. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2020, 540, 123149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.K.; Shaw, S. Shear augmented microvascular solute transport with a two-phase model: Application in nanoparticle assisted drug delivery. Phys. Fluids 2021, 33, 31904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarvand, S.; Rostami, M.N.; Dinarvand, R.; Pop, I. Improvement of drug delivery micro-circulatory system with a novel pattern of CuO-Cu/blood hybrid nanofluid flow towards a porous stretching sheet. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 2019, 29, 4408–4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, R.; Sharma, B.K.; Kumawat, C.; Beg, O.A. Modeling and analysis of magnetic hybrid nanoparticle (au-al 2 o 3/blood) based drug delivery through a bell-shaped occluded artery with joule heating, viscous dissipation and variable viscosity effects. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part E J. Process Mech. Eng. 2022, 236, 2024–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, V.P.; Vishnoi, R.; Mishra, S.; Sinha, P. Blood flow through a composite stenosis in catheterized arteries. E-J. Sci. Technol. 2015, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolui, S.; Bhaumik, B.; De, S. Combined effect of induced magnetic field and thermal radiation on ternary hybrid nanofluid flow through an inclined catheterized artery with multiple stenosis. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2023, 811, 140209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, R.; Sharma, B.K.; Mishra, N.K.; Al-Mdallal, Q.M. Computer Simulations of EMHD Casson Nanofluid Flow of Blood through an Irregular Stenotic Permeable Artery: Application of Koo-Kleinstreuer-Li Correlations. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaman, A.; Sajid, M.; Kousar, N. Biomedical study of effects nanoparticles on unsteady blood (non-Newtonian) flow through a catheterized stenotic vessel. Can. J. Phys. 2019, 97, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, J.; Vasu, B.; Dubey, A.; Gorla, R.S.; Murthy, P.V.S.N.; Bég, O.A.; Prasad, V.R.; Saikrishnan, P. A review on recent advancements in the hemodynamics of nano-drug delivery systems. Nanosci. Technol. An Int. J. 2020, 11, 73–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijaz, S.; Nadeem, S. Slip examination on the wall of tapered stenosed artery with emerging application of nanoparticles. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2016, 109, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
