A Clean and Efficient Energy Solution for Climate Change Mitigation and Energy Crises in Pakistan: The Atmospheric Vortex Engine †
Abstract
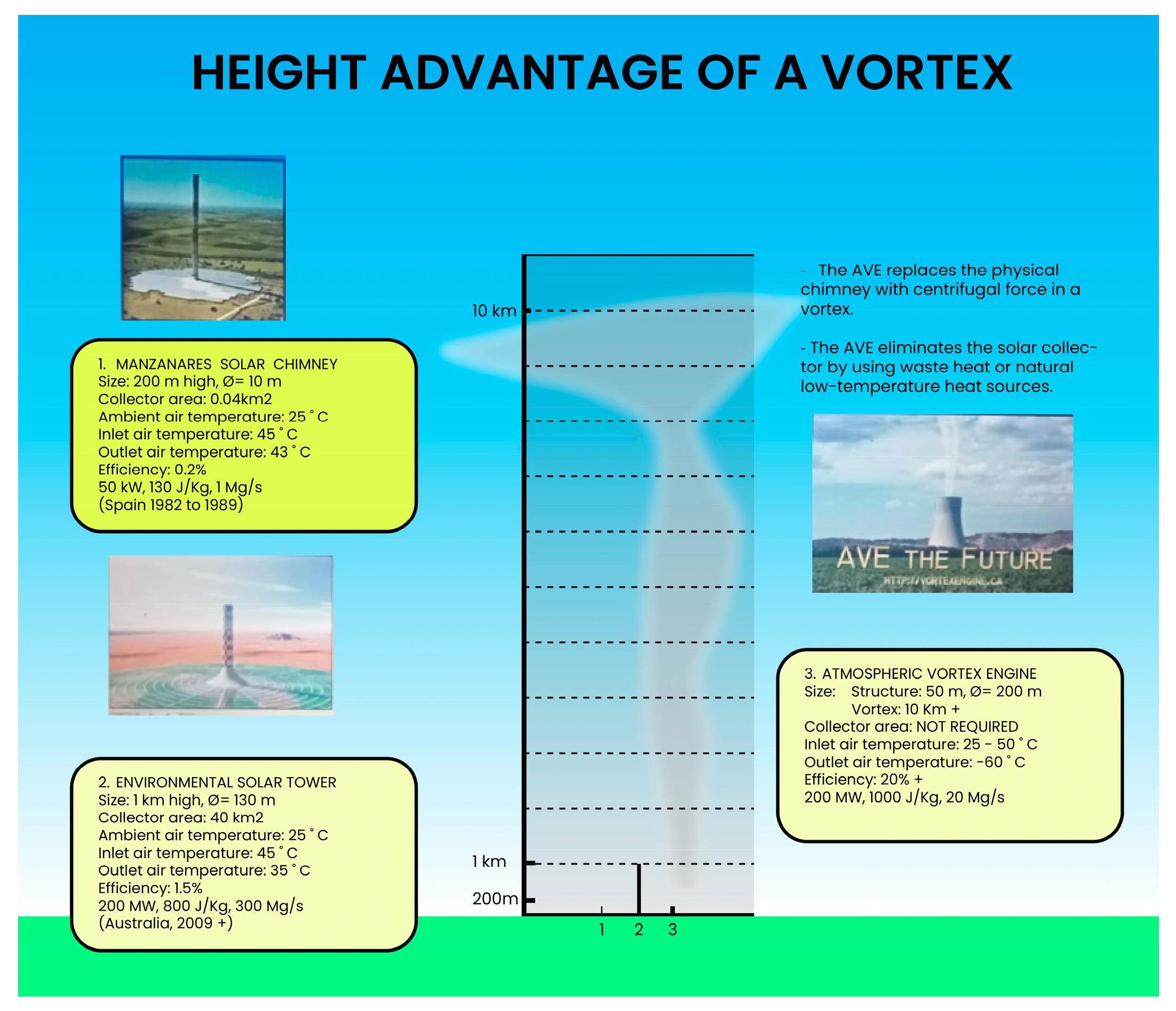
1. Introduction
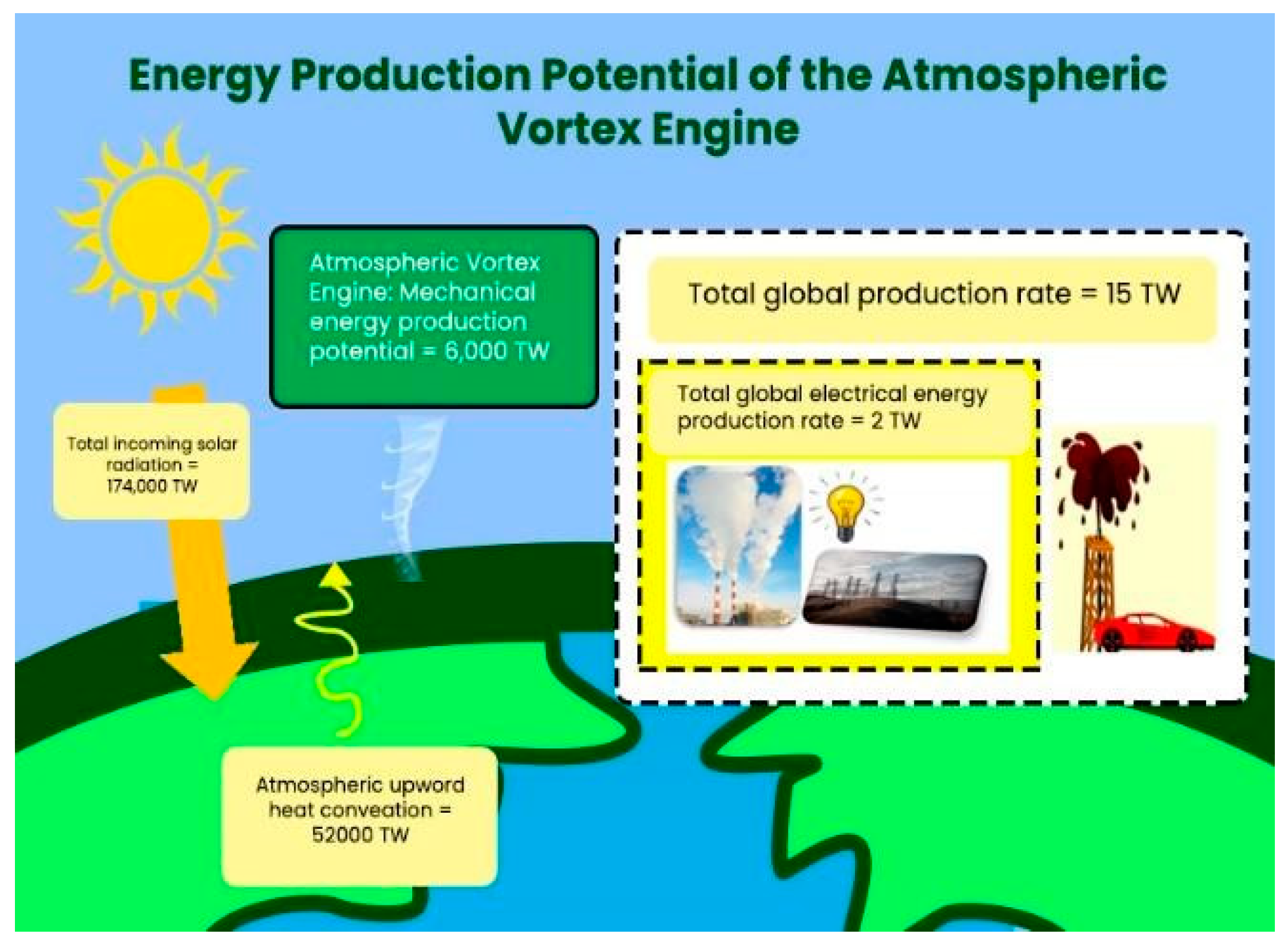
2. Methodology
3. Analysis
4. Conclusions and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- MKhan, T.; Yu, M.; Waseem, M. Review On Recent Optimization Strategies for Hybrid Renewable Energy System with Hydrogen Technologies: State of the Art, Trends and Future Directions. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 25155–25201. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, Z.; Cheng, L.; Xue, W.; Yu, J. A Study of the Twisted Strength of the Whirled Airflow in Murata Vortex Spinning. Text. Res. J. 2008, 78, 682–687. [Google Scholar]
- Michaud, L.M. Atmospheric Vortex Engine. U.S. Patent 7,086,823, 8 August 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Cheridi, A.D.; Bouam, A.; Dadda, A.; Attari, K.; Koudiah, N.; Hadjam, A.; Dahia, A.; Messen, N.; Aguedal, I.; Kerris, A. Numerical investigation of a novel cooling vortex tower using Relap5 computer code. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2022, 391, 111730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud, L.M. The AVE. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Toronto International Conference Science and Technology for Humanity (TIC-STH), Toronto, ON, Canada, 26–27 September 2009; pp. 971–975. [Google Scholar]
- Natarajan, D. Numerical Simulation of Tornado-Like Vortices. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Western Ontario, London, ON, Canada.
- Grasso, L.D.; Cotton, W.R. Numerical Simulation of a Tornado Vortex. J. Atmos. Sci. 1995, 52, 1192–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ali, A.; Muqeet, H.A.; Khan, T.; Hussain, A.; Waseem, M.; Niazi, K.A.K. IoT-Enabled Campus Prosumer Microgrid Energy Management, Architecture, Storage Technologies, and Simulation Tools: A Comprehensive Study. Energies 2023, 16, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud, L. Proposal for the use of a controlled tornado-like vortex to capture the mechanical energy produced in the atmosphere from 42 solar energy. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 1975, 56, 530–534. [Google Scholar]
- Amirthalingam, M. A Novel Technology utilizing Renewable energies to mitigate air pollution, global warming & climate change. In Proceedings of the 2009 1st International Conference on the Developments in Renewable Energy Technology (ICDRET), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 17–19 December 2009; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Michaud, L. Vortex process for capturing mechanical energy during upward heat-convection in the atmosphere. Appl. Energy 1999, 62, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perivolaris, Y.; Voutsinas, S.G. A CFD Performance Analysis of Vortex Generators Used for Boundary Layer Control on Wind Turbine Blades. In Proceedings of the European Wind Energy Conference 2001, Nice, France, 25–30 March 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Aly, A.M. Atmospheric boundary-layer simulation for the built environment: Past, present and future. Build. Environ. 2014, 75, 206–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouam, A.; Cheridi, A.D.; Attari, K.; Koudiah, N.; Dadda, A.; Kerris, A. Vortex Tower Prototype Realization. In Proceedings of the 2022 2nd International Conference on Advanced Electrical Engineering (ICAEE), Constantine, Algeria, 29–31 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yew, J.W. Experimental and Numerical Investigation of the Top Plate Influence on the Performance of Solar Vortex Engine. Bachelor Thesis, Universiti Teknologi Petronas, Teronoh, Malaysia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Waseem, M.; Lin, Z.; Liu, S.; Sajjad, I.A.; Aziz, T. Optimal GWCSO-based home appliances scheduling for demand response considering end-users comfort. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2020, 187, 106477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, K.; Hussain, A.; Arslan, M.; Tariq, B. Experimental Investigation of Impact of Cool Roof Coating on Bifacial and Monofacial Photovoltaic Modules. Eng. Proc. 2023, 45, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.; Waseem, M.; Muqeet, H.A.; Hussain, M.M.; Yu, M.; Annuk, A. 3E analyses of battery-assisted photovoltaic-fuel cell energy system: Step towards green community. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arslan, M.; Imran, M.A.; Tariq, M.; Afzal, K.H.; Waseem, M. A Clean and Efficient Energy Solution for Climate Change Mitigation and Energy Crises in Pakistan: The Atmospheric Vortex Engine. Mater. Proc. 2024, 17, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2024017011
Arslan M, Imran MA, Tariq M, Afzal KH, Waseem M. A Clean and Efficient Energy Solution for Climate Change Mitigation and Energy Crises in Pakistan: The Atmospheric Vortex Engine. Materials Proceedings. 2024; 17(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2024017011
Chicago/Turabian StyleArslan, Muhammad, Muhammad Ahsan Imran, Muhammad Tariq, Kanwar Haziq Afzal, and Muhammad Waseem. 2024. "A Clean and Efficient Energy Solution for Climate Change Mitigation and Energy Crises in Pakistan: The Atmospheric Vortex Engine" Materials Proceedings 17, no. 1: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2024017011
APA StyleArslan, M., Imran, M. A., Tariq, M., Afzal, K. H., & Waseem, M. (2024). A Clean and Efficient Energy Solution for Climate Change Mitigation and Energy Crises in Pakistan: The Atmospheric Vortex Engine. Materials Proceedings, 17(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2024017011






