Abstract
This study proposes a bi-objective optimization model for the inventory routing problem with pickup and delivery (IRP–PD) in a closed-loop supply chain, addressing the growing demand for sustainable logistics solutions. The model simultaneously minimizes transportation costs and inventory costs and enhances driver well-being by incorporating regular rest breaks. The network operates within a circular economy framework, where pallets are both delivered and returned for reuse, contributing to waste reduction. A normalized weighted-sum method is initially used to balance the conflicting objectives. However, since the model cannot efficiently solve large-scale instances, we adopt the NSGA-II metaheuristic to generate a Pareto front, enabling decision-makers to explore trade-offs between objectives. The model is tested on a single instance, and the results demonstrate a promising compromise between economic and social goals.
1. Introduction
In recent years, the transition toward sustainable supply chains has emphasized the importance of circular economy principles and reverse logistics, where resource efficiency, waste reduction, and product recovery are key goals. Closed-loop supply chains, which integrate forward logistics (product delivery) with reverse flows (returns, reuse, and recycling), have emerged as vital frameworks for achieving environmental, social, and economic sustainability. A central challenge within these systems is the inventory routing problem with pickup and delivery (IRP–PD), which simultaneously coordinates transportation routes and inventory levels across multiple time periods. Solving the IRP-PD problem efficiently allows companies to reduce operational costs while promoting environmental goals through the reuse of materials and packaging. Early studies have shown that integrating inventory and routing decisions can yield significant cost benefits. A branch-and-cut algorithm was used to reduce overall logistics costs by jointly optimizing pickups and deliveries [1]. The classical Inventory Routing Problem (IRP), as discussed in [2], considers deterministic demand over a finite planning horizon and integrates inventory control with vehicle routing. A branch-and-cut algorithm is proposed to minimize combined routing and inventory holding costs. A green inventory routing problem with split delivery and pickup to minimize emissions in food logistics was presented [3]. The Closed-loop Inventory Routing Problem (CIRP) optimizes delivery and return routes for reusable transport items while managing customer inventory. It accounts for bidirectional logistics flows, demand uncertainty, fuel consumption, and multiple products to minimize total costs and environmental impact. This contribution was examined by [4]. Advanced models now integrate production, inventory, and reverse logistics elements. Remanufacturing and disassembly in a closed-loop supply network were modeled, emphasizing strategic trade-offs [5]. In a related study, carbon tax constraints were incorporated into a location-inventory-routing model to support sustainable network design [6]. Despite these developments, few studies have explicitly addressed the bi-objective optimization of both economic and social dimensions in IRP–PD contexts. This study proposes a model that minimizes total costs while enhancing driver well-being through regulated rest breaks. By balancing operational efficiency with human-centered design, the model supports the evolution of sustainable, inclusive logistics systems aligned with circular economy goals.
2. Literature Review
The inventory routing problem with pickup and delivery (IRP–PD) has received increasing attention in recent years due to its ability to integrate inventory management with transportation planning in a single framework. From an economic perspective, the integration of deliveries and pickups offers significant potential for cost reduction. A parameterized heuristic combined with optimal learning techniques is developed for dynamic waste collection from sensor-equipped underground containers by [7], demonstrating through a real-world Dutch case study that cost savings up to 40% are possible by optimizing collection parameters. A bi-objective stochastic inventory routing problem is developed for infectious medical waste collection, balancing social objectives (satisfaction, public health) against economic costs using three heuristic approaches tested on French real-world data. A multi-objective stochastic inventory routing problem model is developed for perishable products, integrating economic performance (profit), service level (delivery delays and stockouts), and environmental footprint under demand and transportation cost uncertainty [8].
In addition to cost optimization, the recent literature also highlights the social dimension of the IRP–PD, especially in the context of collaborative logistics and urban service equity. A multi-depot, multi-period IRP–PD with collaborative vehicle routing and resource sharing was investigated [9]. Their findings showed that coordination among logistics service providers reduces the total number of required vehicles and travel distances, leading not only to cost savings but also to a more equitable and accessible service network. Furthermore, circular logistics practices—such as those studied in the context of perishable goods—demonstrate how pickup operations can serve socially beneficial functions by recovering unsold or expired products, thus contributing to waste reduction and social responsibility [10]. While these contributions offer valuable insights into the economic and social benefits of IRP–PD models, few studies have proposed integrated approaches that explicitly optimize both aspects in a balanced manner. This research aims to address this gap by developing a sustainable IRP–PD model that jointly considers cost minimization and social equity objectives, with the goal of supporting the development of inclusive and economically efficient transportation systems.
3. Problem Description
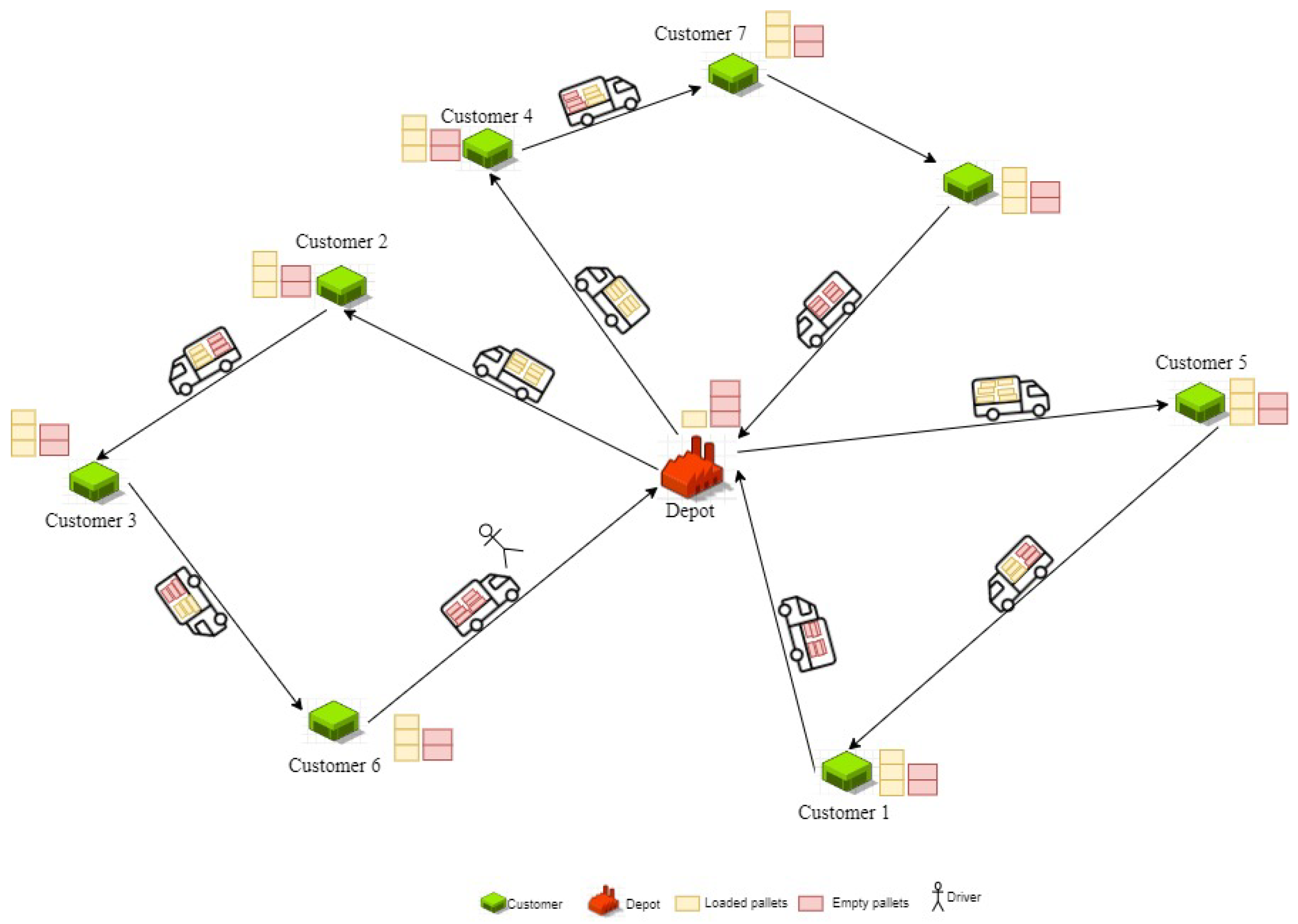
This research investigates a multi-period inventory routing problem with pickup and delivery (IRP–PD), where multiple vehicles are responsible for distributing filled pallets to customers while simultaneously collecting empty pallets for reuse. The main objective is to determine the optimal set of delivery routes and inventory decisions over a finite time horizon in order to minimize the total operational costs while also addressing social considerations related to driver welfare, as shown in Figure 1. Each customer has a known demand in each period. After delivering filled pallets to each customer, the vehicle collects the empty ones, which are transported back to the depot for future use. This closed-loop flow supports a circular logistics strategy and reduces waste by enabling pallet reuse. The total transportation cost consists of two components: a fixed cost and a variable cost that depends on the quantity transported along that arc. Additionally, inventory holding costs are incurred at both the depot and customer locations depending on the stock levels. Thus, the problem aims to minimize the sum of fixed transportation costs, quantity-dependent transportation costs, and inventory holding costs. From a social perspective, the well-being of drivers is explicitly considered by incorporating mandatory rest breaks into the route planning. This ensures compliance with labor regulations and promotes sustainable human resource practices. The complexity of the problem lies in balancing multiple, often conflicting objectives: minimizing costs, satisfying customer demands, maintaining appropriate inventory levels, and respecting social criteria such as driver rest times. This study proposes a solution approach that integrates these dimensions into a unified decision-making framework for sustainable logistics network design.
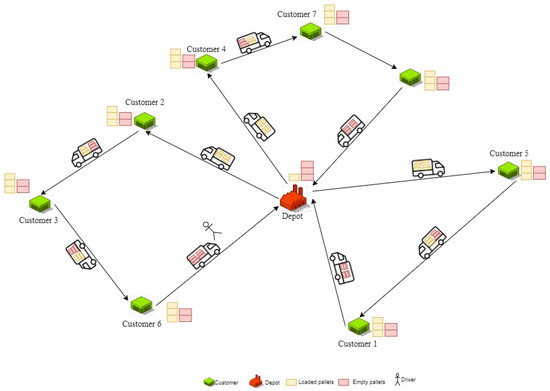
Figure 1.
Illustration of the inventory routing problem with pickup and delivery.
4. Mathematical Formulation
We define the problem on a directed graph , where . N is the set of nodes, including the depot (node 0) and customers , and A is the set of arcs. The planning horizon is divided into T discrete time periods.
4.1. Parameters
The model uses the following parameters:
- : Fixed transportation cost of traveling arc ;
- : Variable transportation cost per unit transported on arc ;
- : Inventory holding cost of loaded pallets at node i;
- : Inventory holding cost of empty pallets at node i;
- : Inventory capacity of loaded pallets at node i;
- : Inventory capacity of empty pallets at node i;
- : Demand of customer i in period t;
- : Vehicle capacity;
- : Weight of a loaded pallet;
- : Weight of an empty pallet;
- : Limit on driving time before a break;
- G: The necessary time at the customer’s gate;
- : Maximum driving time per day.
4.2. Decision Variables
The following decision variables define the model’s decisions:
- : Equals 1 if arc is used along vehicle itinerary v during time period t;
- : The quantity of loaded pallets available at node i by the end of period t;
- : The quantity of empty pallets available at node i by the end of period t;
- : The quantity of loaded pallets delivered to node i in period t;
- : The quantity of empty pallets returned to node i in period t;
- : The quantity of loaded pallets carried from node i to node j during period t;
- : The quantity of empty pallets carried from node i to node j during period t;
- : The time length of the itinerary;
- : The time at which vehicle v arrives at customer i during period t;
- : The number of breaks per vehicle v;
- : Customer’s relative position in the tour sequence during period t;
- : Equals 1 if a vehicle is resting at a node.
4.3. Objective Function: Normalized Weighted Sum
The model features two objective functions: the first minimizes total costs, while the second focuses on social considerations related to the logistics process. Since the objectives have different units ( for monetary costs and for social impact), normalization is necessary. To achieve this, the Nadir and ideal points are employed, as proposed by [11]. The ideal point () represents the best possible values for both and . The Nadir point () is defined such that is the optimal value of corresponding to the best value of , while is the optimal value of corresponding to the best value of . The resulting normalized formulation is expressed in Equation (1):
where
4.4. Constraints
The model is subject to the following constraints:
The first objective function (1) is to minimize various costs. The first term is the transportation cost, and the second is the inventory cost. The second objective function (2) is aimed at minimizing duration. The model is characterized by a comprehensive set of constraints. Specifically, constraint (3) guarantees that vehicle capacity is never exceeded. Constraint (4) expresses the loaded pallet inventory in period t as the inventory from period plus the quantity of loaded pallets delivered, minus the demand. Finally, constraint (5) defines the empty pallet inventory in period t as the inventory from period minus the returned empty pallets plus the demand. Constraint (6) ensures that the inventory in period t is the inventory held in period plus the pallet quantity filled from the producer, minus the quantity of loaded pallets delivered to customers. Constraint (7) ensures that the inventory in period t is the inventory held in period minus the quantity of pallets filled from the supplier, plus newly bought pallets and empty pallets returned from customers. Constraint (8) establishes the inventory limits for loaded pallets for each customer during every period. Constraint (9) sets the inventory limits for empty pallets for each customer in each period. Constraint (10) ensures that the quantities of loaded pallets are delivered. Constraint (11) ensures that empty pallets are returned. Constraints (12), (13), and (14) ensure proper routing, stipulating that if a vehicle visits a customer in period t, it must leave the customer in the same period and that a vehicle can visit at most one customer per period. These constraints also ensure that vehicles leave the depot only once per period. Constraint (15) is the sub-tour elimination. Constraint (16) calculates the travel time. Constraint (17) ensures that the arrival time at one customer is greater than the arrival time at a previous customer on the same route unless the vehicle does not travel between the two nodes in the period. Constraint (18) ensures that the total route time is within the maximum allowed arrival time. Constraint (19) ensures that the vehicle returns directly to the depot once it has served the last customer. Constraint (20) represents rest only at client nodes. Constraint (21) ensures that the vehicle takes enough breaks if its travel time exceeds the allowed limit without a pause. Constraint (22) limits the travel time to what is reasonable based on the number of breaks scheduled. Constraint (23) directly links the binary pause decisions to the break counter. Constraint (24) states that a break can only be taken at a node if the vehicle has driven at least T_limit minutes. This prevents taking breaks too early, enforcing the minimum drive time before a pause. Constraints (25) and (26) define the non-negativity and binary conditions on the variables.
5. Experiments and Results
To demonstrate the trade-off between the two objectives ( and ), the proposed mathematical model (MO-MIP) is evaluated on an instance from [12]. The model is solved on a professional-grade computer (13th Gen Intel® Core™i7-13800H) using Gurobi Optimizer (version 11.0.3). Table 1 provides a summary of the parameter values used in these instances.

Table 1.
Values of parameters in the instance.
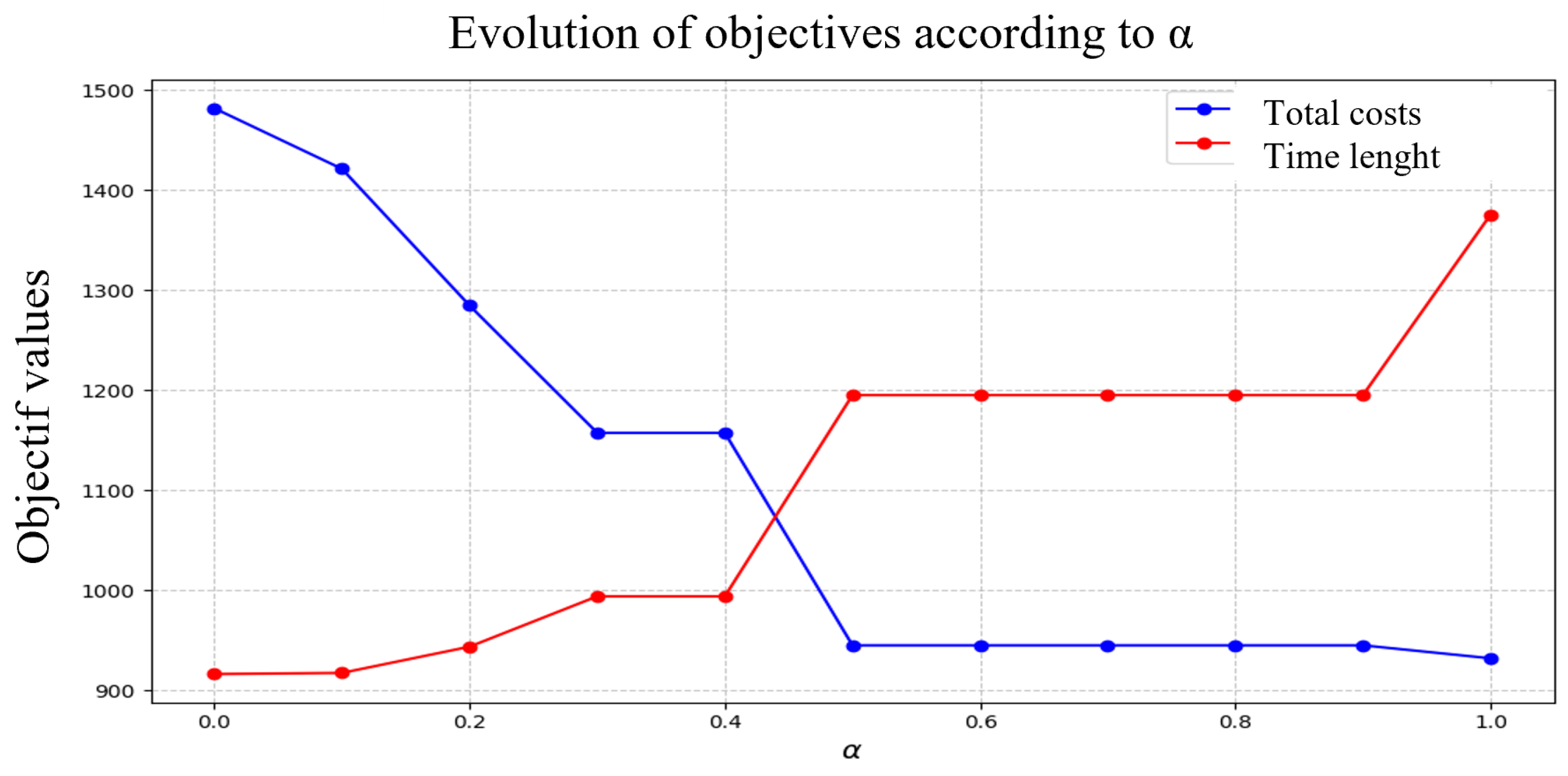
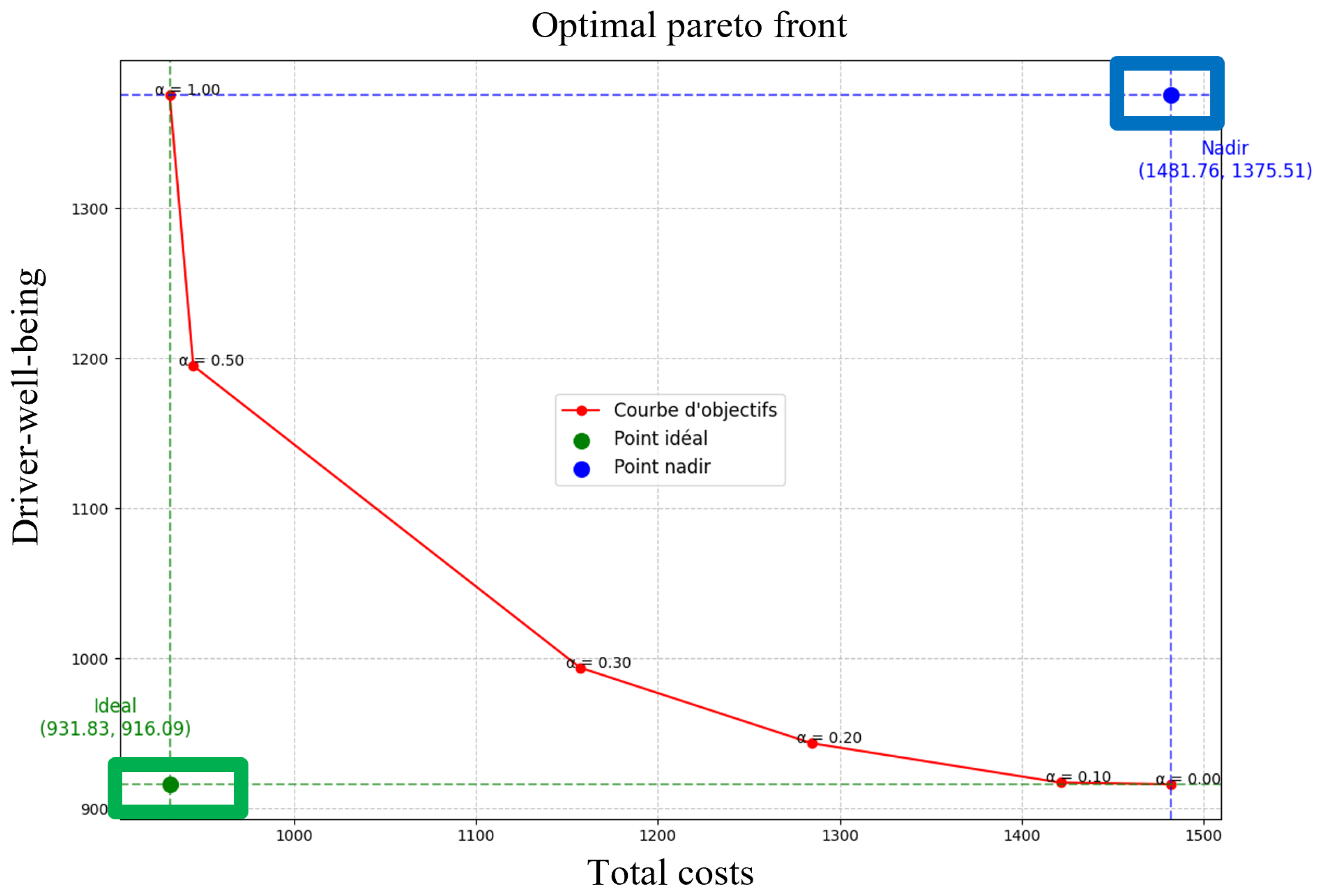
The results obtained are presented in Table 2. The first column shows the value of that varies from 0.0 to 1.0 in steps of 0.1. The second and third columns present the total costs and duration, respectively. These results are illustrated in Figure 2. The two objective functions evolve as varies. When the total costs () decrease, driver well-being () increases significantly, indicating a clear trade-off between the two objectives. Figure 3 highlights the optimal Pareto front for the two objectives, showing the ideal points and possible trade-off solutions. The parameter plays a crucial role as a tuning coefficient, allowing the decision-maker to balance these priorities based on routes and inventory levels.

Table 2.
Detailed results for .
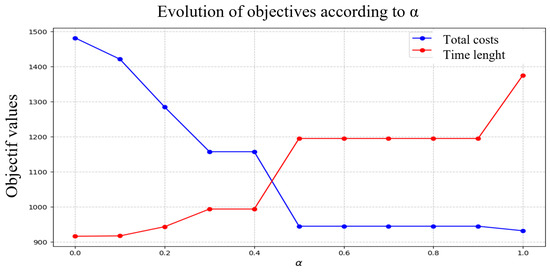
Figure 2.
Objective functions (F1 and F2) for .
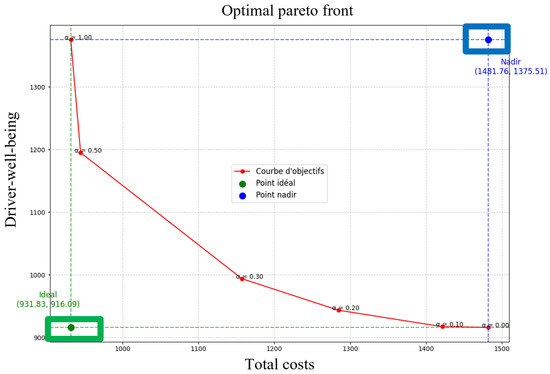
Figure 3.
The optimal Pareto front for F1 and F2.
6. Non-Dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm II
This study uses NSGA-II (Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm II) to solve the multi-objective IRP–PD–TW. NSGA-II efficiently handles multi-objective optimization by combining non-dominated sorting, a crowding distance mechanism to ensure solution diversity, and elitism to retain the best solutions. Its robustness makes it suitable for addressing the conflicting economic and social objectives of the IRP. Table 3 summarizes the performance of solutions obtained using the NSGA-II algorithm with respect to two objective functions, F1 and F2.

Table 3.
NSGA-II results.
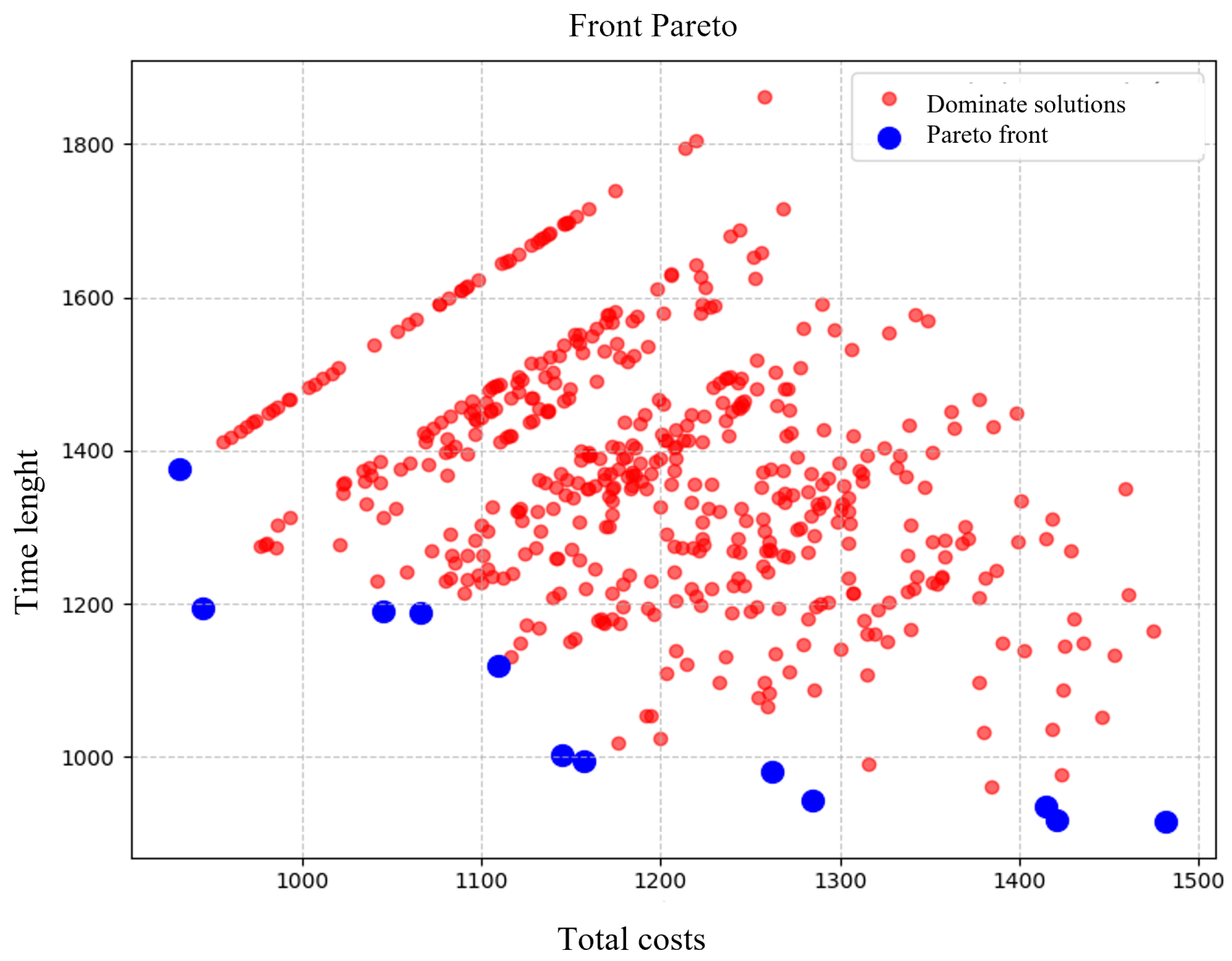
For each solution, both raw and normalized values are provided, along with a distance metric indicating the proximity to an ideal point (typically (0,0)). This normalization enables fair comparison across solutions, and the distance values help identify those closest to the Pareto-optimal front by evaluating the trade-offs between the two objectives. Figure 4 illustrates the distinction between the non-dominated (Pareto front) and dominated solutions. The blue points represent the non-dominated solutions, which balance minimizing total costs with maximizing driver well-being, while the red points correspond to the dominated solutions, which are outperformed by at least one other solution in both objectives. This visualization highlights the trade-offs and emphasizes the importance of non-dominated solutions for decision-makers. The graph illustrates a scatter plot in which the horizontal axis represents the total costs and the vertical axis represents the social impact. The blue points denote the solutions on the Pareto front, meaning they are non-dominated alternatives that provide an optimal trade-off between minimizing costs and maximizing social impact. The set of non-dominated solutions includes, for example, Solution 1, with a total cost of and a social impact of , and extends to Solution 9, with a total cost of and a social impact of . To select the optimal solution, we first define an ideal reference point by taking the minimum cost and the minimum duration from the Pareto front. In this case, the reference point is (, ) = (931.83, 916.09). We then calculate the Euclidean distance for each solution i using the formula , where and are the cost and social impact of the i-th solution, respectively. Since Solution 6 is identical to the reference point, its distance is , indicating that it is the closest to the ideal and thus represents the best compromise according to our criterion.
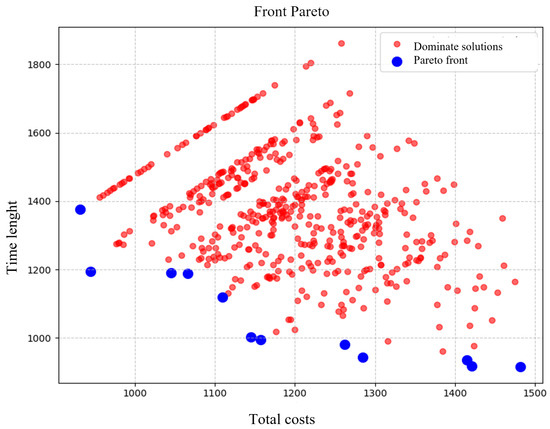
Figure 4.
Pareto front.
7. Discussion
The comparative analysis presented highlights essential considerations for decision-makers when selecting optimization methods for IRP–PD–TW problems. The exact MO-MIP approach provides rigorous, optimal solutions essential in scenarios where precision and accuracy outweigh computational cost concerns. Such exactness is particularly relevant in critical logistics contexts, where economic implications or regulatory compliance related to driver welfare may demand exact quantification and optimization.
Conversely, the NSGA-II method demonstrates significant advantages regarding computational efficiency and scalability, making it particularly appealing for real-world applications involving large-scale, complex logistics networks. Despite not guaranteeing absolute optimality, its ability to generate high-quality solutions with reasonable computational effort positions NSGA-II as a practical approach in dynamic operational contexts where rapid decision-making and flexibility are crucial.
However, the inherent approximation characteristic of NSGA-II solutions introduces uncertainty into decision-making processes, potentially critical in scenarios demanding high precision. Moreover, the quality of NSGA-II results heavily depends on parameter tuning and computational settings, necessitating careful calibration. The choice between these methodologies depends on the specific objectives, constraints, and available computational resources.
8. Conclusions
This paper presents a bi-objective optimization model for the inventory routing problem with pickup and delivery (IRP–PD) within a closed-loop logistics framework, incorporating both cost efficiency and social sustainability. By integrating forward and reverse logistics with time windows and driver rest constraints, the model supports circular economy practices such as pallet reuse while ensuring compliance with labor standards. The results demonstrate that optimizing both economic and social objectives simultaneously leads to a clear trade-off between total operational costs and driver well-being. Decision-makers can adjust the weighting parameter to prioritize different aspects based on specific operational goals. The use of the normalized weighted-sum method and Pareto analysis provides flexible, data-driven support for sustainable logistics planning. Overall, this study contributes to the growing body of research on sustainable supply chains by offering a comprehensive, scalable, and practical tool for the design of inclusive and resource-efficient logistics networks. Future work may include extending the model to multi-vehicle fleets, stochastic demand, or carbon-emission minimization for broader real-world applications.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.Z.; methodology, C.Z.; software, C.Z.; validation, T.C., A.B. and A.A.-E.-C.; formal analysis, C.Z.; investigation, C.Z.; resources, C.Z.; data curation, C.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, C.Z.; writing—review and editing, C.Z., A.B., A.A.-E.-C. and T.C.; visualization, C.Z.; supervision, A.B., A.A.-E.-C. and T.C.; project administration, A.A.-E.-C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Archetti, C.; Speranza, M.G.; Boccia, M.; Sforza, A.; Sterle, C. A branch-and-cut algorithm for the inventory routing problem with pickups and deliveries. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2020, 282, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Alcoba, A.; Rossi, R.; Martin-Barragan, B.; Embley, T. The stochastic inventory routing problem on electric roads. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2023, 310, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahjoob, M.; Fazeli, S.S.; Tavassoli, L.S.; Mirmozaffari, M.; Milanlouei, S. A green multi-period inventory routing problem with pickup and split delivery: A case study in flour industry. Sustain. Oper. Comput. 2021, 2, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soysal, M. Closed-loop Inventory Routing Problem for returnable transport items. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2016, 48, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, M.K.; Hammami, R.; Battaia, O.; Dolgui, A. Simultaneous Pickup-and-Delivery Production-Routing Problem in closed-loop supply chain with remanufacturing and disassembly consideration. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2024, 273, 109290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindan, K.; Salehian, F.; Kian, H.; Hosseini, S.T.; Mina, H. A location-inventory-routing problem to design a circular closed-loop supply chain network with carbon tax policy for achieving circular economy: An augmented epsilon-constraint approach. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2023, 257, 108771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mes, M.; Schutten, M.; Pérez Rivera, A. Inventory routing for dynamic waste collection. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 1564–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimi, M.; Baboli, A.; Rekik, Y. Multi-objective inventory routing problem: A stochastic model to consider profit, service level and green criteria. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2017, 101, 59–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Guan, X.; Fan, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H. Collaboration and Resource Sharing in the Multidepot Multiperiod Vehicle Routing Problem with Pickups and Deliveries. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navazi, F.; Sazvar, Z.; Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, R. A sustainable closed-loop location-routing-inventory problem for perishable products. Sci. Iran. 2021, 30, 757–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, E.; Bektas, T.; Laporte, G. The bi-objective Pollution-Routing Problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2014, 232, 464–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iassinovskaia, G.; Limbourg, S.; Riane, F. The inventory-routing problem of returnable transport items with time windows and simultaneous pickup and delivery in closed-loop supply chains. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2017, 183, 570–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).