A Fuzzy Programming Approach for a Multi-Objective Design of a Sustainable Closed-Loop Supply Chain Network in the Case of End-of-Life Medical Textiles †
Abstract
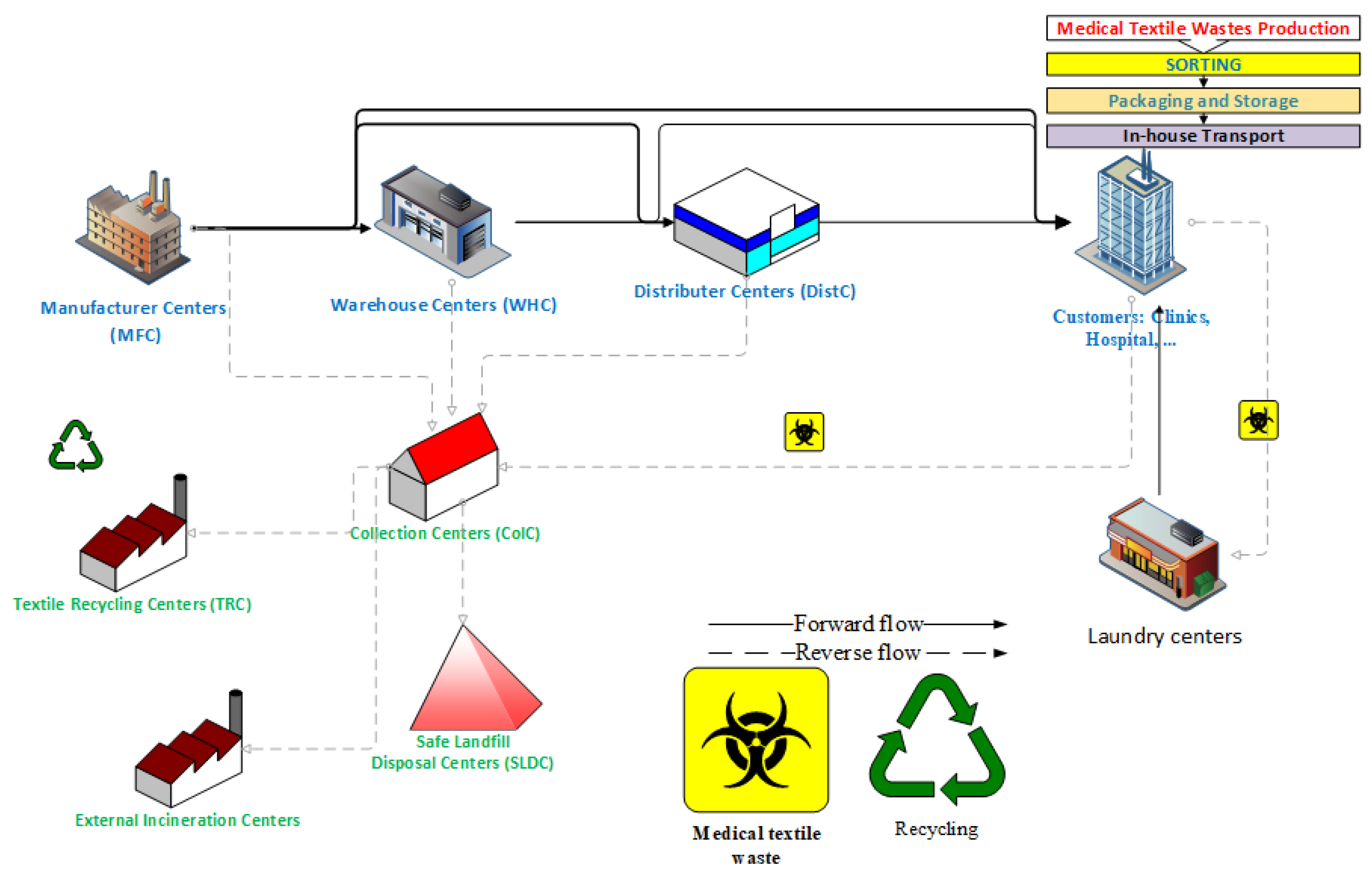
1. Introduction
- A sustainable closed loop supply chain network integrating inventory constraints and location allocation decisions.
- A novel environmental objective function to minimize the risk coming from the transport of used healthcare textiles (Hazmat items).
- A multi-objective model designed to maximize revenue and job creation and minimize transportation risks.
- A three-phase fuzzy mathematical programming approach to optimize the proposed model.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Mathematical Formulation
- Rijpt: Contamination risk on road (i, j) for medical textiles p at time t;
- Lij: Binary variable equals ‘1’ if links is established between facilities ‘i’ and ‘j’;
- C: Set of customers indexed by ‘c’;
- L: Set of collector’s centers indexed by ‘l’;
- S: Set of Safe landfill disposal centers indexed by ‘s’;
- R: Set of textile Recycling centers indexed by ‘r’;
- E: Set of External incinerator centers indexed by ‘e’;
- N: Set of Laundry centers indexed by ‘e’.
- Ja: Number of jobs create with center a, a∈A, with A represent all types of facility;
- Li: binary variable equals ‘1’ if location ‘i’ is open and ‘0’ otherwise.
2.2. Fuzzifying the Model
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahlaqqach, M.; Benhra, J.; Mouatassim, S.; Lamrani, S. Hybridization of game theory and ridesharing to optimize reverse logistics of healthcare textiles. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 827, 012004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, N.; Niaki, S.T.A.; Kashan, A.H.; Seifbarghy, M. An efficient solution method for an agri-fresh food supply chain: Hybridization of Lagrangian relaxation and genetic algorithm. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlevan, S.M.; Hosseini, S.M.S.; Goli, A. Sustainable supply chain network design using products’ life cycle in the aluminum industry. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goli, A.; Tirkolaee, E.B.; Weber, G.-W. A Perishable Product Sustainable Supply Chain Network Design Problem with Lead Time and Customer Satisfaction using a Hybrid Whale-Genetic Algorithm. In Logistics Operations and Management for Recycling and Reuse; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 99–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlaqqach, M.; Benhra, J.; Mouatassim, S.; Lamrani, S. Closed loop location routing supply chain network design in the end of life pharmaceutical products. Supply Chain Forum 2020, 21, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodarzian, F.; Hosseini-Nasab, H.; Fakhrzad, M.B. A Multi-objective Sustainable Medicine Supply Chain Network Design Using a Novel Hybrid Multi-objective Metaheuristic Algorithm. Int. J. Eng. 2020, 33, 1986–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momeni, M.A.; Jain, V.; Bagheri, M. A Multi-Objective Model for Designing a Sustainable Closed-Loop Supply Chain Logistics Network. Logistics 2024, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douaioui, K.; Benmoussa, O.; Ahlaqqach, M. Optimizing Supply Chain Efficiency Using Innovative Goal Programming and Advanced Metaheuristic Techniques. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhrzad, M.B.; Goodarzian, F. A Fuzzy multi-objective programming approach to develop a green closed-loop supply chain network design problem under uncertainty: Modifications of imperialist competitive algorithm. RAIRO-Oper. Res. 2019, 53, 963–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäämaa, L.; Kaipia, R. The first mile problem in the circular economy supply chains—Collecting recyclable textiles from consumers. Waste Manag. 2022, 141, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hole, G.; Hole, A.S. Improving recycling of textiles based on lessons from policies for other recyclable materials: A minireview. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2020, 23, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, M.; Nazam, M.; Zia-ur-Rehman, M.; Abrar, M.; Baig, S.A.; Nazim, M.; Hussain, Z. Modeling Supply Chain Sustainability-Related Risks and Vulnerability: Insights from the Textile Sector of Pakistan. Autex Res. J. 2022, 22, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.H.; Li, Q.; Chen, X.J.; Wang, Y.F. Sustainable Rent-Based Closed-Loop Supply Chain for Fashion Products. Sustainability 2014, 6, 7063–7088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taslimi, M.; Batta, R.; Kwon, C. Medical waste collection considering transportation and storage risk. Comput. Oper. Res. 2020, 120, 104966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamaa, S.B.; Altman, Z.; Picard, J.-M.; Fourestié, B. Optimization of UMTS Radio Access Networks with Genetic Algorithms. In Metaheuristics for Hard Optimization; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 251–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.J.; Hwang, C.L. A new approach to some possibilistic linear programming problems. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1992, 49, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourjavad, E.; Mayorga, R.V. Multi-objective Fuzzy Programming of Closed-Loop Supply Chain Considering Sustainable Measures. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 21, 655–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchis, R.; Díaz-Madroñero, M.; López-Jiménez, P.A.; Pérez-Sánchez, M. Solution Approaches for the Management of the Water Resources in Irrigation Water Systems with Fuzzy Costs. Water 2019, 11, 2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, H.-J. Methods and Applications of Fuzzy Mathematical Programming. In An Introduction to Fuzzy Logic Applications in Intelligent Systems; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1992; pp. 97–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Q.; Zhang, B.; Li, H. Computing efficient solutions to fuzzy multiple objective linear programming problems. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2006, 157, 1328–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werners, B.M. Aggregation Models in Mathematical Programming. In Mathematical Models for Decision Support; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1988; pp. 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, H.; Ozkarahan, I. A supply chain distribution network design model: An interactive fuzzy goal programming-based solution approach. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2006, 36, 401–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torabi, S.A.; Hassini, E. An interactive possibilistic programming approach for multiple objective supply chain master planning. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2008, 159, 193–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Zimmermann max–min Approach | ||||
| MF 1 | MF Value | OF 2 | OF Value | TSD 3 |
| μz1 | 0.496 | Z1 | 3.5 × 106 | 2.518 |
| μz2 | 0.506 | Z2 | 1221 | |
| μz3 | 0.552 | Z3 | 521 | |
| μz4 | 0.439 | Z4 | 402 | |
| μz5 | 0.525 | Z5 | 1233 | |
| LZL Approach | ||||
| MF | MF Value | OF | OF Value | TSD |
| μz1 | 0.777 | Z1 | 6.08 × 106 | 3.362 |
| μz2 | 1.000 | Z2 | 1831 | |
| μz3 | 0.566 | Z3 | 512 | |
| μz4 | 0.440 | Z4 | 403 | |
| μz5 | 0.580 | Z5 | 1165 | |
| TH Approach | ||||
| MF | MF Value | OF | OF Value | TSD |
| μz1 | 0.943 | Z1 | 7.63 × 106 | 3.664 |
| μz2 | 1.000 | Z2 | 1831 | |
| μz3 | 0.521 | Z3 | 542 | |
| μz4 | 0.531 | Z4 | 456 | |
| μz5 | 0.670 | Z5 | 1057 | |
| Selim and Özkarahan Approach | ||||
| MF | MF Value | OF | OF Value | TSD |
| μz1 | 0.433 | Z1 | 2.9 × 106 | 3.001 |
| μz2 | 1.000 | Z2 | 1831 | |
| μz3 | 0.527 | Z3 | 538 | |
| μz4 | 0.483 | Z4 | 429 | |
| μz5 | 0.557 | Z5 | 1194 | |
| Werners Approach | ||||
| MF | MF Value | OF | OF Value | TSD |
| μz1 | 0.433 | Z1 | 2.9 × 106 | 3.001 |
| μz2 | 1.000 | Z2 | 1831 | |
| μz3 | 0.527 | Z3 | 538 | |
| μz4 | 0.483 | Z4 | 429 | |
| μz5 | 0.557 | Z5 | 1194 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahlaqqach, M.; Touil, A.; Benhra, J.; Atwani, M.; Oualidi, M.A.; Lmariouh, J. A Fuzzy Programming Approach for a Multi-Objective Design of a Sustainable Closed-Loop Supply Chain Network in the Case of End-of-Life Medical Textiles. Eng. Proc. 2025, 97, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025097021
Ahlaqqach M, Touil A, Benhra J, Atwani M, Oualidi MA, Lmariouh J. A Fuzzy Programming Approach for a Multi-Objective Design of a Sustainable Closed-Loop Supply Chain Network in the Case of End-of-Life Medical Textiles. Engineering Proceedings. 2025; 97(1):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025097021
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhlaqqach, Mustapha, Achraf Touil, Jamal Benhra, Mariam Atwani, Moulay Ali Oualidi, and Jamal Lmariouh. 2025. "A Fuzzy Programming Approach for a Multi-Objective Design of a Sustainable Closed-Loop Supply Chain Network in the Case of End-of-Life Medical Textiles" Engineering Proceedings 97, no. 1: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025097021
APA StyleAhlaqqach, M., Touil, A., Benhra, J., Atwani, M., Oualidi, M. A., & Lmariouh, J. (2025). A Fuzzy Programming Approach for a Multi-Objective Design of a Sustainable Closed-Loop Supply Chain Network in the Case of End-of-Life Medical Textiles. Engineering Proceedings, 97(1), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025097021






