Denoising and Voxelization for Finite Element Analysis: A Review †
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Denoising
1.2. Voxel
1.3. Finite Element Analysis (FEA)
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Exploratory Survey for Keywords Detection
2.2. Screening and Inclusion Phases
- Type of applications out of topic such as medical or additive manufacturing research.
- Type of applications regarding built environment but not inherent with cultural heritage (both movable and immovable), such as aqueducts, viaducts, bridges and/or very modern structures (built environment <20 years).
- Papers particularly focused on the effectiveness of these techniques separately, without exploring their joint or simultaneous use for monitoring the condition of historical structures or heritage objects.
2.3. State-of-the-Art in the Integration of Denoising Algorithms and Voxels
3. Results
3.1. Denoising
3.2. Voxelization
- Imposition of voxel size to downsample;
- Definition of the resolution of the voxel grid;
- Creation of the voxel grid (Figure 4);
- Creation of a binary occupancy grid;
- Activation of a corresponding index in the binary grid for each voxel;
- Application of the Marching Cubes algorithm to extract the mesh surface;
- STL file is then saved.
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pedersoli, J.L., Jr.; Antomarchi, C.; Michalski, S. A Guide to Risk Management of Cultural Heritage; ICCROM ATHAR Regional Conservation Centre: Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, A.; Cipriani, L.; Cabezos-Bernal, P.M. 3D Digital Models. Accessibility and Inclusive Fruition. DISEGNARECON 2024, 17, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonizzi Barsanti, S.; Guagliano, M.; Rossi, A. 3D Reality-Based Survey and Retopology for Structural Analysis of Cultural Heritage. Sensors 2022, 22, 9593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fratino, M.; Rossi, A. Re-construction of the small Xanten dart launcher. In Discovering Pompeii: From Effects to Causes. From Surveying to the Reconstructions of Ballistae and Scorpiones; Real Casa dell’Annunziata, Department of Engineering Vanvitelli University; MDPI: Basel, Switzerland, 2025; under process of publication. [Google Scholar]
- Tomasi, C.; Manduchi, R. Bilateral filtering for gray and color images. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Computer Vision, Bombay, India, 7 January 1998; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1998; pp. 839–846. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Shen, J. Denoising of point cloud data for computer-aided design, engineering, and manufacturing. Eng. Comput. 2018, 34, 523–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Digne, J.; Franchis, C.D. The bilateral filter for point clouds. Image Process. Online 2017, 7, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Sun, J.; Tang, X. Guided image filtering. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 35, 1397–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Jin, J.S.; Wang, M.; Jiang, W. Guided 3D point cloud filtering. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2018, 77, 17397–17411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.A.; Magli, E. Exploiting color for graph-based 3d point cloud denoising. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2021, 75, 103027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinesh, C.; Cheung, G.; Bajić, I.V. Point cloud denoising via feature graph Laplacian regularization. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 4143–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Foi, A. Anisotropic denoising of 3D point clouds by aggregation of multiple surface-adaptive estimates. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2021, 27, 2851–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakotosaona, M.J.; La Barbera, V.; Guerrero, P.; Mitra, N.J.; Ovsjanikov, M. Pointcleannet: Learning to denoise and remove outliers from dense point clouds. Comput. Graph. Forum 2021, 39, 185–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Ji, Y.M.; Wu, F.; Zhang, C.; Sun, Y. Semantic-aware 3D-voxel CenterNet for point cloud object detection. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2022, 98, 107677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Li, R.; Li, S.; Zhang, L. Voxel set transformer: A set-to-set approach to 3D object detection from point clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 8417–8427. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud, A.; Hu, J.S.; Waslander, S.L. Dense voxel fusion for 3D object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 663–672. [Google Scholar]
- Shrout, O.; Ben-Shabat, Y.; Tal, A. GraVoS: Voxel Selection for 3D Point-Cloud Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 21684–21693. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Shi, S.; Li, P.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H. Voxel r-cnn: Towards high performance voxel-based 3D object detection. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2021, 35, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Zeng, H.; Huang, J.; Hua, X.S.; Zhang, L. Structure Aware Single-Stage 3D Object Detection from Point Cloud. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11870–11879. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, C.; Lin, W.; Zhao, B. Voxel Structure-Based Mesh Reconstruction From a 3D Point Cloud. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2022, 24, 1815–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sas, A.; Ohs, N.; Tanck, E.; van Lenthe, G.H. Nonlinear voxel-based finite element model for strength assessment of healthy and metastatic proximal femurs. Bone Rep. 2020, 12, 100263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.Y.; Weng, T.L.; Lin, C.H.; Sun, Y.N. Interactive voxel surface rendering in medical applications. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 1999, 23, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y. A comparison of voxel- and surface-based cone-beam computed tomography mandibular superimposition in adult orthodontic patients. J. Int. Med. Res. 2021, 49, 0300060520982708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, M.; Abe, O.; Hagiwara, A.; Fujita, S.; Kamagata, K.; Hori, M.; Aoki, S.; Osada, T.; Konishi, S.; Masutani, Y.; et al. Advantages of Using Both Voxel- and Surface-based Morphometry in Cortical Morphology Analysis: A Review of Various Applications, Magnetic Resonance. Med. Sci. 2022, 21, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babich, M.; Kublanov, V. Voxel Based Finite Element Method Modelling Framework for Electrical Stimulation Applications Using Open-Source Software. In Proceedings of the Ural Symposium on Biomedical Engineering, Radioelectronics and Information Technology (USBEREIT), Yekaterinburg, Russia, 25–26 April 2019; pp. 127–130. [Google Scholar]
- Sapozhnikov, S.B.; Shchurova, E.I. Voxel and Finite Element Analysis Models for Ballistic Impact on Ceramic-polymer Composite Panels. Procedia Eng. 2017, 206, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doğan, S.; Güllü, H. Multiple methods for voxel modeling and finite element analysis for man-made caves in soft rock of Gaziantep. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2022, 81, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Iijima, Y.; Kawano, K.; Igarashi, H. Voxel Based Finite Element Method Using Homogenization. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonizzi Barsanti, S.; Marini, M.R.; Malatesta, S.G.; Rossi, A. Evaluation of Denoising and Voxelization Algorithms on 3D Point Clouds. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zienkiewicz, O.C.; Taylor, R.L. The Finite Element Method; McGraw Hill: London, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muzahid, A.A.M.; Han, H.; Zhang, Y.; Dawei, L.; Zhang, Y.; Jamshid, J. Ferdous Sohel, Deep learning for 3D object recognition: A survey. Neurocomputing 2024, 608, 128436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, F.; Lu, W.; Webster, C.J.; Chen, K. A derivative-free optimization-based approach for detecting architectural symmetries from 3D point clouds. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 148, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahab, S.S.; Himeur, Y.; Kheddar, H.; Amira, A.; Fadli, F.; Atalla, S.; Copiaco, A.; Mansoor, W. Advancing 3D point cloud understanding through deep transfer learning: A comprehensive survey. Inf. Fusion 2025, 113, 102601. [Google Scholar]
- Di Angelo, L.; Di Stefano, P.; Guardiani, E. A review of computer-based methods for classification and reconstruction of 3D high-density scanned archaeological pottery. J. Cult. Herit. 2022, 56, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Tong, X.; Stilla, U. Voxel-based representation of 3D point clouds: Methods, applications, and its potential use in the construction industry. Autom. Constr. 2021, 126, 103675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, X.; Gao, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Hou, R.; Wang, Y. Machine intelligence for interpretation and preservation of built heritage. Autom. Constr. 2025, 172, 106055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Cao, K.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Meng, X.; Ao, T.; Zhang, H. Study on weathering corrosion characteristics of red sandstone of ancient buildings under the perspective of non-destructive testing. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 85, 108520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bi, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y. Overcoming single-technology limitations in digital heritage preservation: A study of the LiPhoScan 3D reconstruction model. Alex. Eng. J. 2025, 119, 518–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, H.; Fu, W.; Chai, C.; Su, T. Damage volumetric assessment and digital twin synchronization based on LiDAR point clouds. Autom. Constr. 2024, 157, 105168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yao, W.; Li, Y.; Zhou, W.; Chen, X. Topology optimization via implicit neural representations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2023, 411, 116052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Z. Statistical learning prediction of fatigue crack growth via path slicing and re-weighting. Theor. Appl. Mech. Lett. 2023, 13, 100477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourian, P.; Azadi, S. Voxel graph operators: Topological voxelization, graph generation, and derivation of discrete differential operators from voxel complexes. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2024, 196, 103722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakir, F.; Kucuk, S. A case study on the restoration of a three-story historical structure based on field tests, laboratory tests and finite element analyses. Structures 2022, 44, 1356–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shitong, L.; Hu, W. Score-based point cloud denoising. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 4563–4572. [Google Scholar]
- Baert, J. Cuda Voxelizer: A Gpu-Accelerated Mesh Voxelizer. 2017. 4. Available online: https://github.com/Forceflow/cuda_voxelizer (accessed on 5 February 2025).
- Zhou, Q.Y.; Park, J.; Koltun, V. Open3D: A modern library for 3D data processing. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.09847. [Google Scholar]
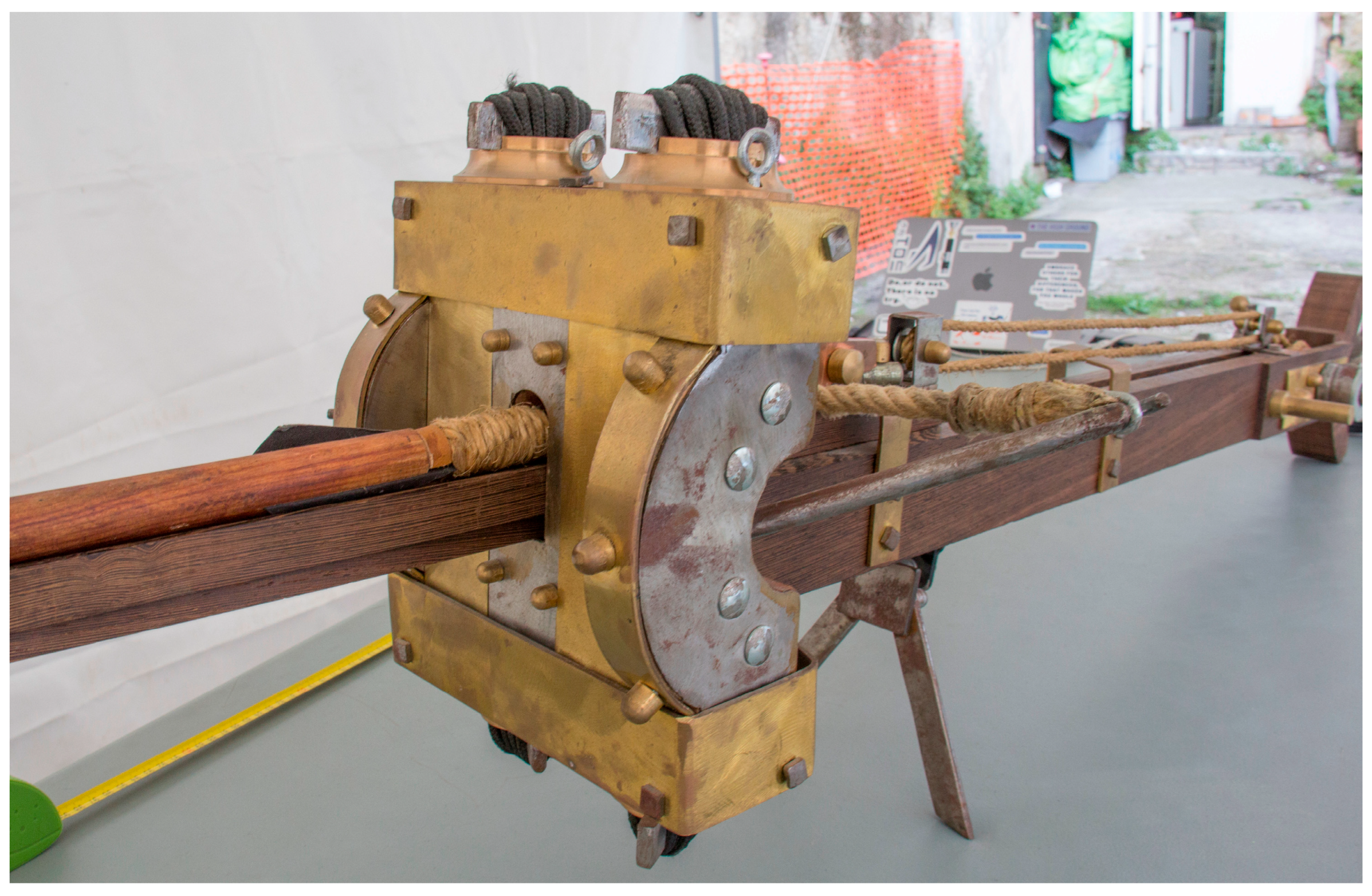
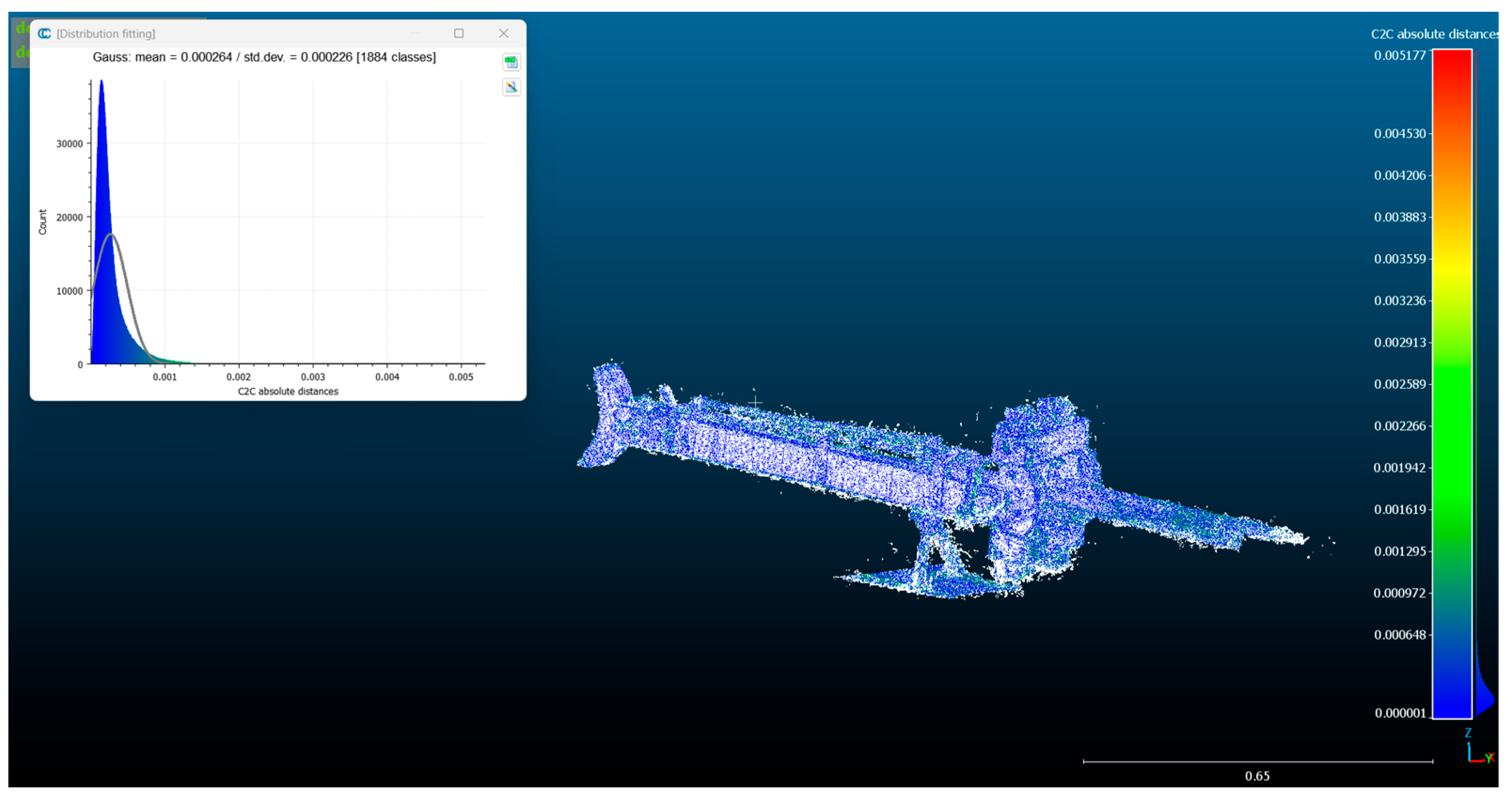
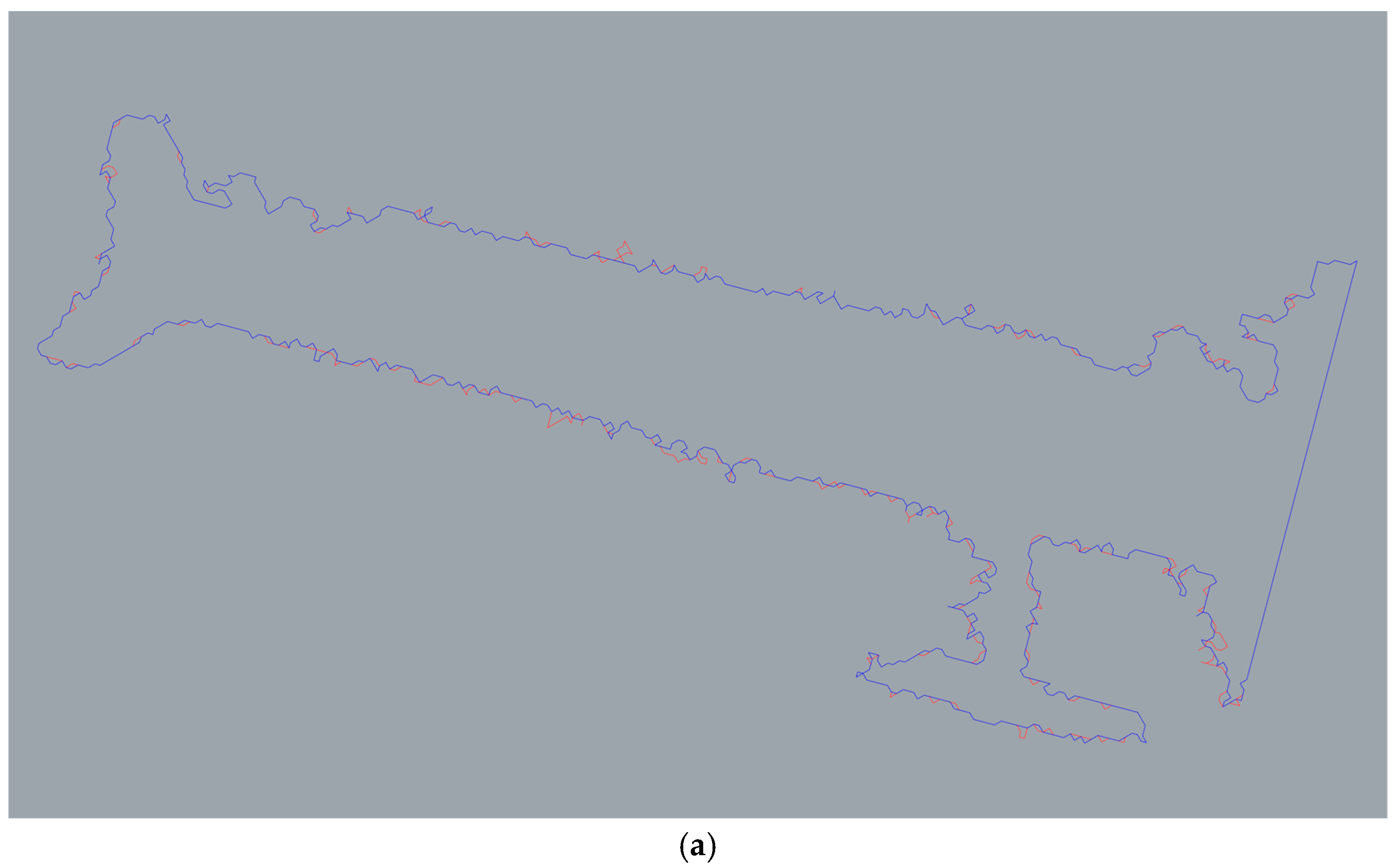
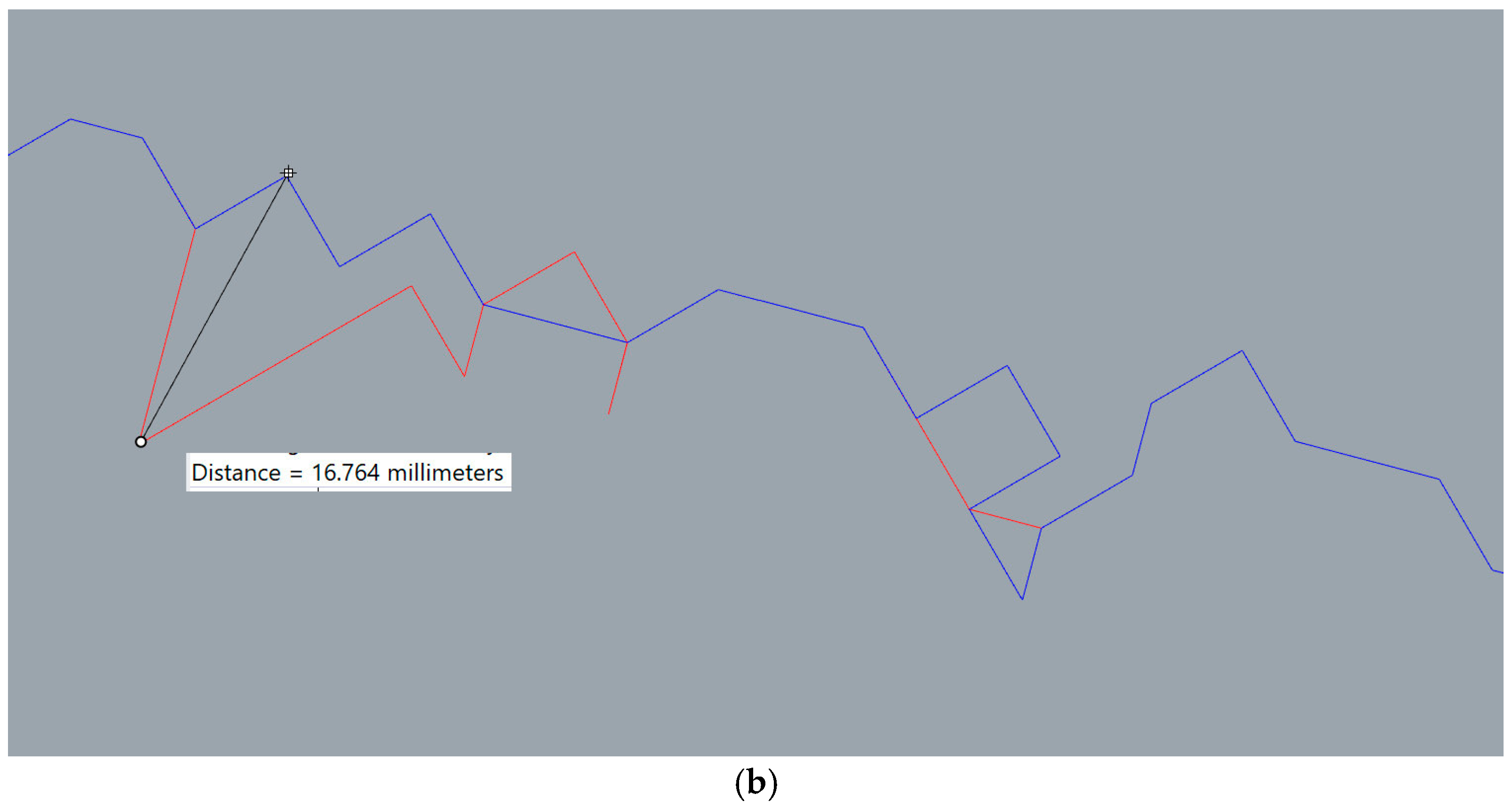
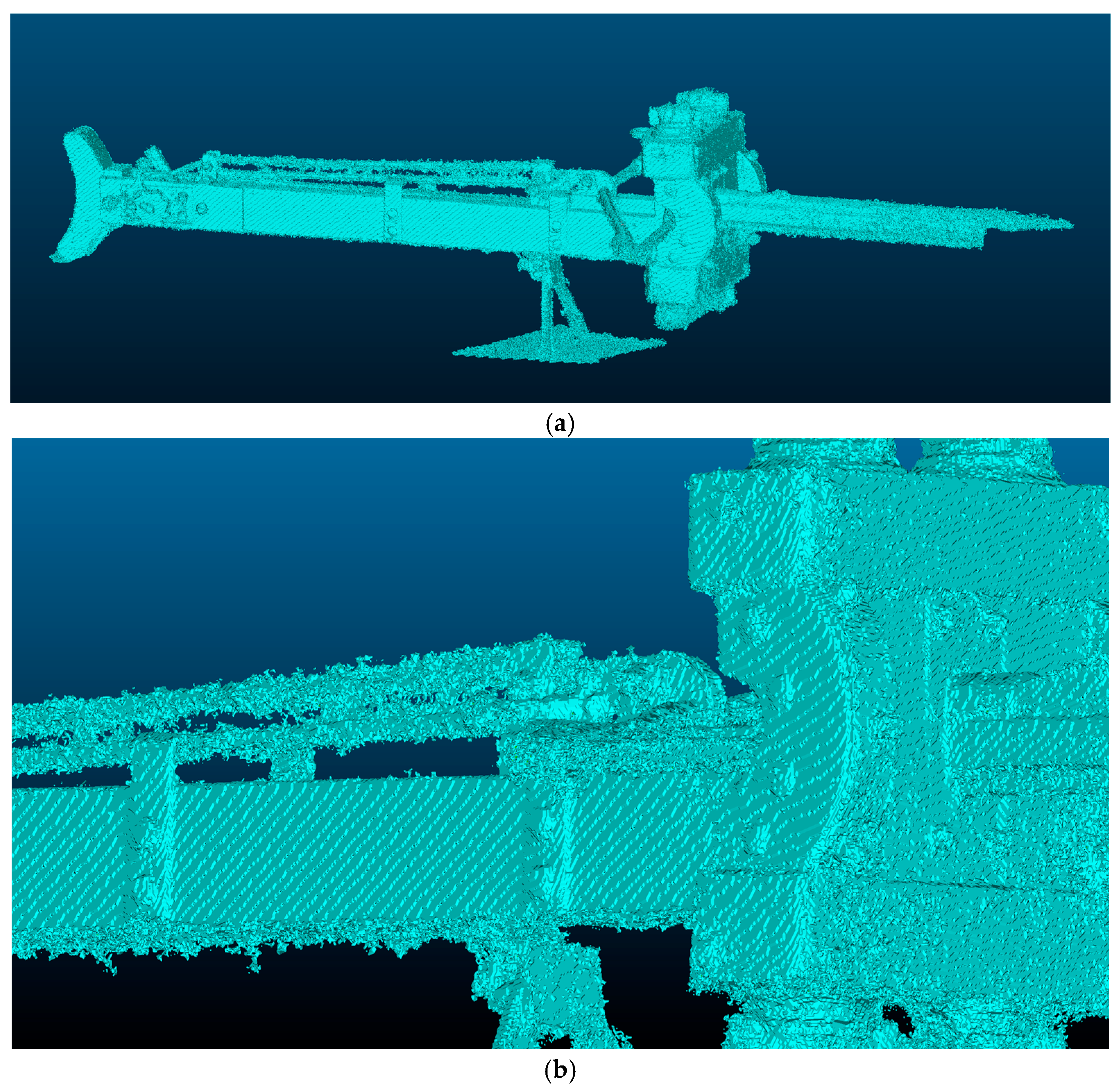
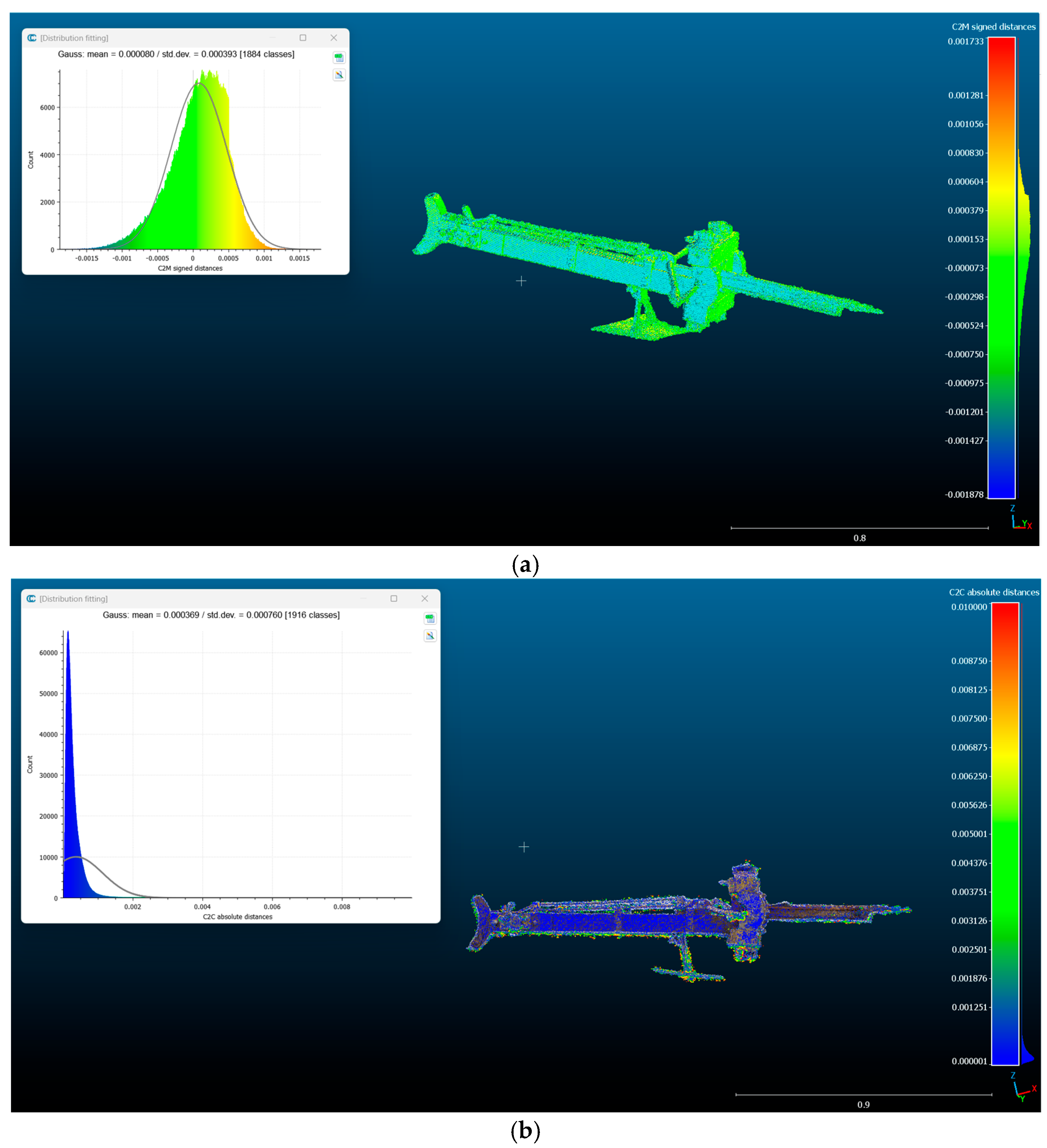
| Object | Mean (mm) | Standard Deviation (mm) | Profiles Max Distance (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scorpionide | 0.000264 | 0.000226 | 16,764 |
| Mean (mm) | Standard Deviation (mm) | |
|---|---|---|
| Cfr denoised/voxel (mm) | 0.00008 | 0.000393 |
| Cfr voxel/mesh | 0.000369 | 0.000760 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barsanti, S.G. Denoising and Voxelization for Finite Element Analysis: A Review. Eng. Proc. 2025, 96, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025096006
Barsanti SG. Denoising and Voxelization for Finite Element Analysis: A Review. Engineering Proceedings. 2025; 96(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025096006
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarsanti, Sara Gonizzi. 2025. "Denoising and Voxelization for Finite Element Analysis: A Review" Engineering Proceedings 96, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025096006
APA StyleBarsanti, S. G. (2025). Denoising and Voxelization for Finite Element Analysis: A Review. Engineering Proceedings, 96(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025096006






