Influence of LPBF Process Parameters on the Surface Quality of Stainless Steel on the Adhesion Properties with Thermoplastics †
Abstract
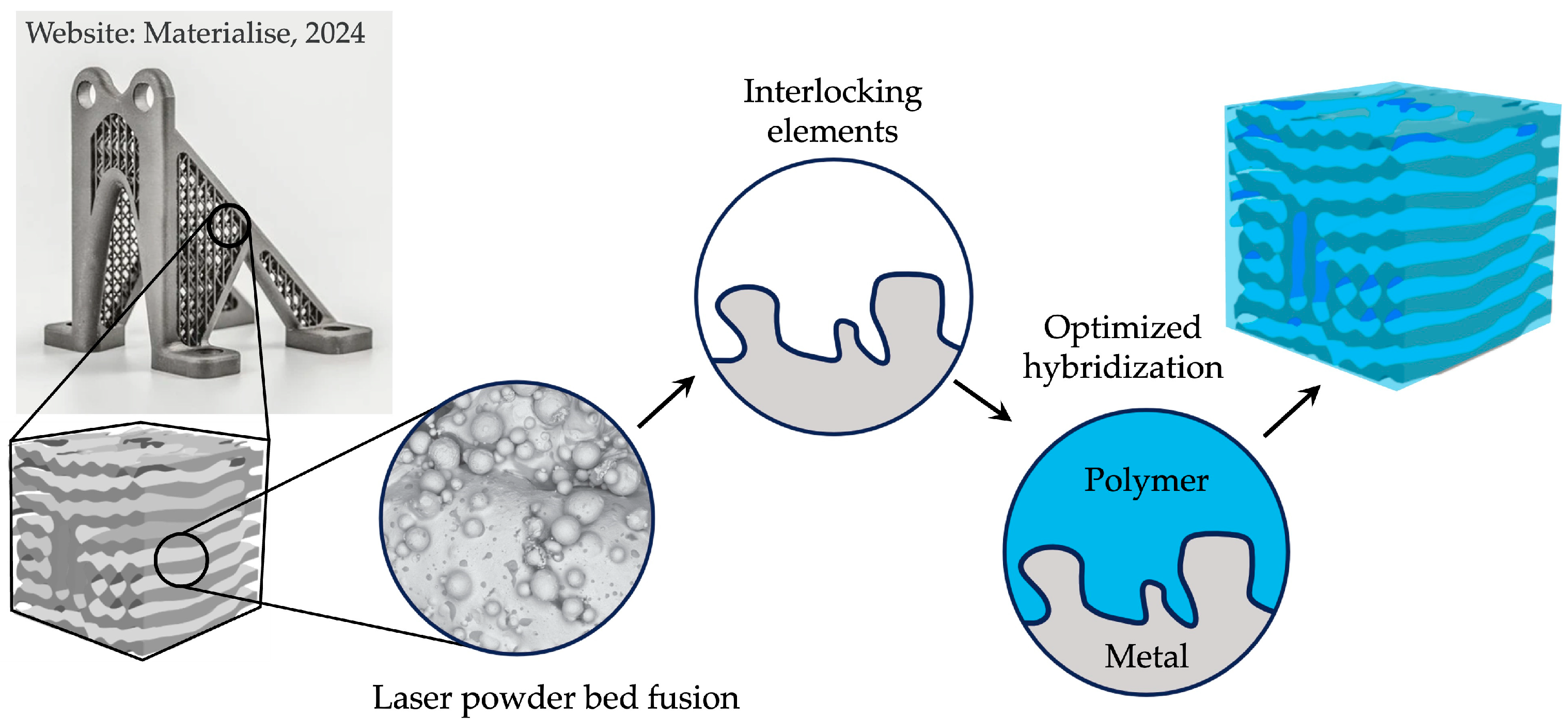
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Production (Laser–Powder–Bed–Fusion)
2.2. SEM Analysis
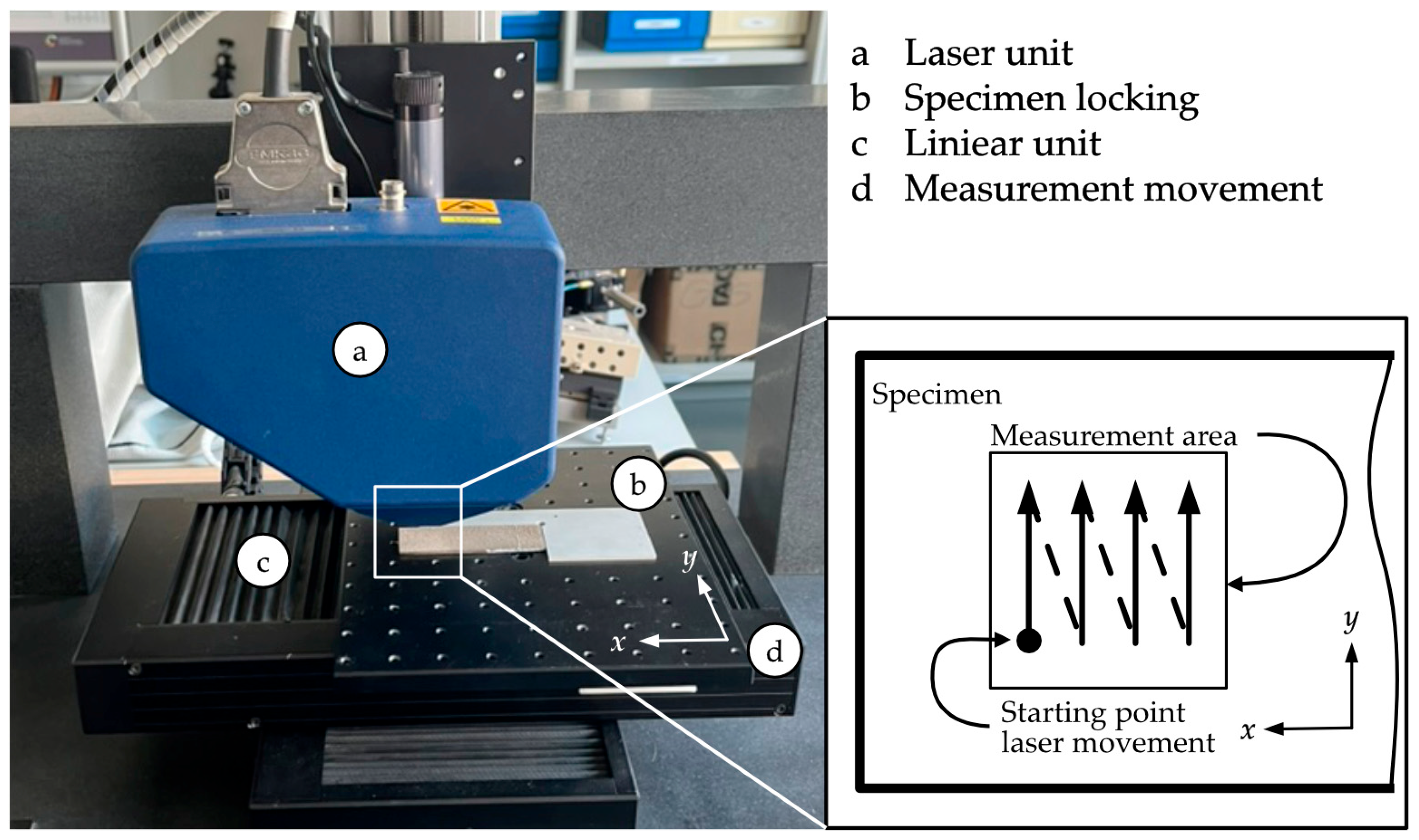
2.3. Laser Profilometry
3. Results
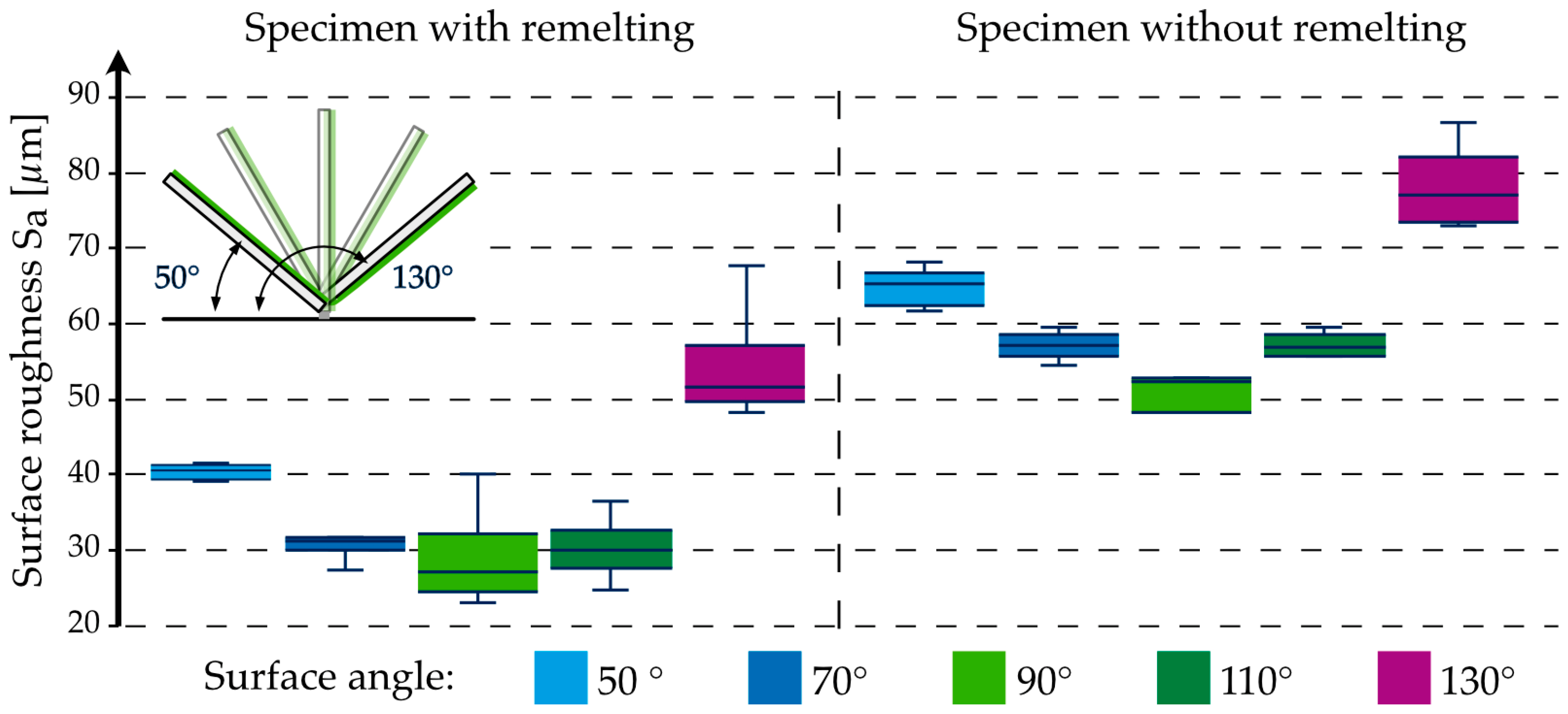
3.1. Roughness Measurements
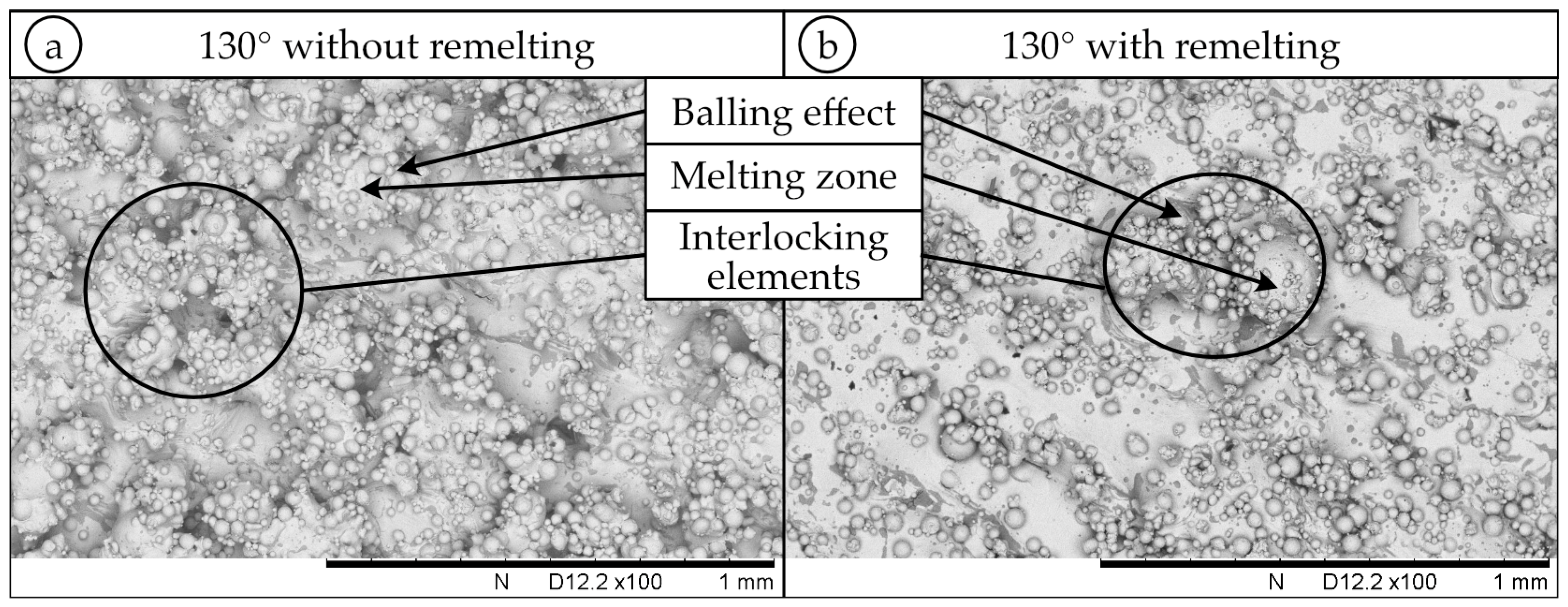
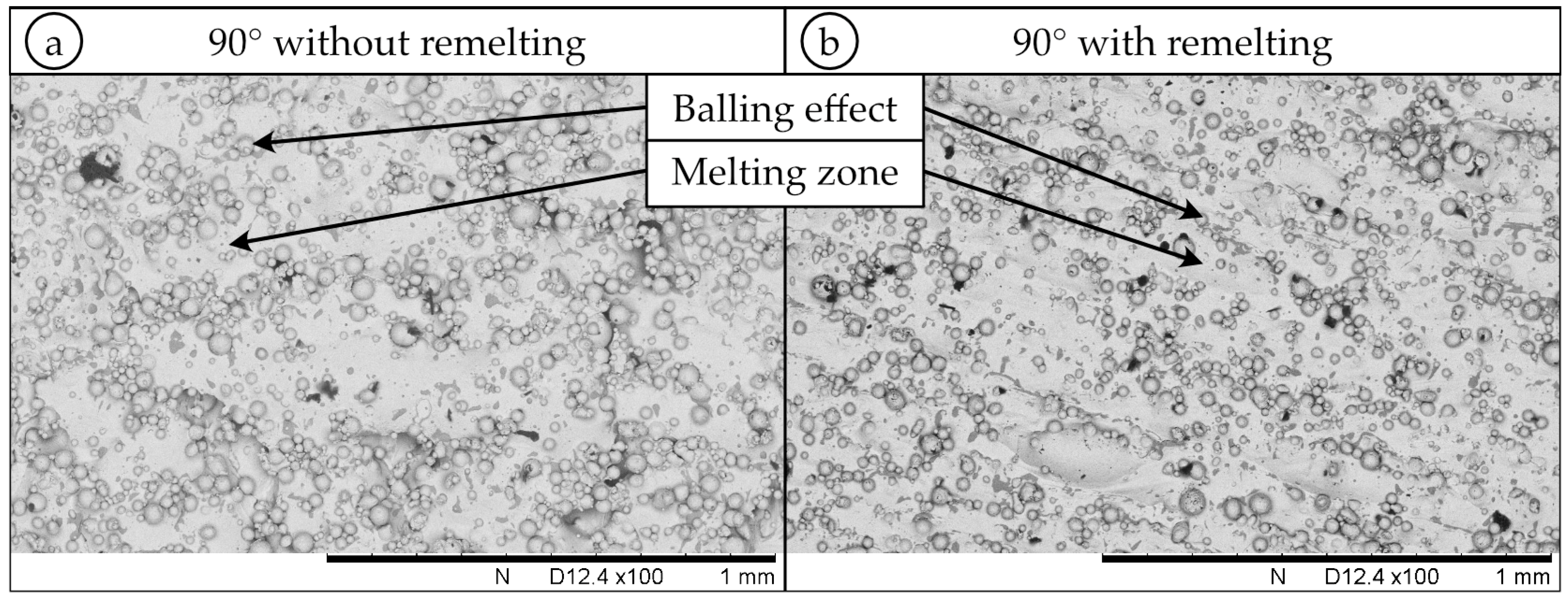
3.2. SEM Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Outlook
- The surface roughness ranges from 27.14 µm (at an overhang angle of 90° with remelting) to 77.07 µm (at an overhang angle of 130° without remelting);
- Extreme overhang angles show the highest roughness, independent of remelting;
- Overhang angles of 90° exhibit the lowest roughness in the test series with and without remelting;
- Remelting increases roughness by an average of 20–25 µm;
- SEM images of the 50° and 130° samples without remelting show the most possibilities for interlocking elements;
- Remelting leads to a homogeneous surface property with fewer balling effects;
- In the case of a 50° to 110° overhang angle, only minor changes in surface topology as a result of remelting are observed.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kadic, M.; Milton, G.W.; van Hecke, M.; Wegener, M. 3D metamaterials. Nat. Rev. Phys. 2019, 1, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenz, F.; Schmidt, I.; Leichner, A.; Lichti, T.; Baumann, S.; Andrae, H.; Eberl, C. Designing Shape Morphing Behavior through Local Programming of Mechanical Metamaterials. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2008617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florijn, B.; Coulais, C.; van Hecke, M. Programmable Mechanical Metamaterials. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 113, 175503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soroka, M.; Kang, J.H.; Gordon, K.; Thibeault, S. Aerospace Applications and Relaxation Prediction of Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK) Composites. In Proceedings of the 2021 Summer Student Research Symposium, Hampton, VA, USA, 10 August 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Amend, P. Laserbasiertes Schmelzkleben von Thermoplasten Mit Metallen. Ph.D. Thesis, Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg, Erlangen, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barfuss, D.; Grützner, R.; Hirsch, F.; Gude, M.; Müller, R.; Kästner, M. Multi-scale structuring for thermoplastic-metal contour joints of hollow profiles. Prod. Eng. Res. Dev. 2018, 12, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grothe, R.; Pohl, M.; Troschitz, J.; Weidemann, C.; Weiss, K.-P.; Gude, M. Characterization of intrinsic interfaces between fibre-reinforced composites and additively manufactured metal for designing hybrid structures. J. Adv. Join. Process. 2024, 9, 100209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novák, L.; Fojtl, L.; Kadlečková, M.; Maňas, L.; Smolková, I.; Musilová, L.; Minařík, A.; Mráček, A.; Sedláček, T.; Smolka, P. Surface Modification of Metallic Inserts for Enhancing Adhesion at the Metal–Polymer Interface. Polymers 2021, 13, 4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strano, G.; Hao, L.; Everson, R.M.; Evans, K.E. Surface roughness analysis, modelling and prediction in selective laser melting. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2013, 213, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viale, V.; Stravridis, J.; Salmi, A.; Bondioli, F.; Saboori, A. Optimisation of downskin parameters to produce metallic parts via laser powder bed fusion process: An overview. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 123, 2159–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherry, J.A.; Davies, H.M.; Mehmood, S.; Lavery, N.P. Investigation into the effect of process parameters on microstructural and physical properties of 316L stainless steel parts by selective laser melting. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 76, 869–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneyder, J.C.; Thole, K.A. Understanding Laser Powder Bed Fusion Surface Roughness. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2020, 142, 071003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasa, E.; Kruth, J.P. Microstructural investigation of selective laser melting 316L stainless steel parts exposed to laser re-melting. Process Eng. 2011, 19, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Sing, S.L.; Chua, C.K.; Tian, X. Influence of re-melting on surface roughness and porosity of AlSi10Mg parts fabricated by selective laser melting. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 792, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaithilingam, J.; Goodridge, R.D.; Hague, R.J.M.; Christie, S.D.R.; Edmondson, S. The effect of laser remelting on the surface chemistry of Ti6al4V components fabricated by selective laser melting. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2016, 232, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Shen, Y. Balling phenomena in direct laser sintering of stainless steel powder: Metallurgical mechanisms and control methods. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 2903–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Liu, J.; Shi, Y.; Wang, L. Balling behavior of stainless steel and nickel powder during selective laser melting process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2012, 59, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ein 63% Leichteres Luft- und Raumfahrtteil Aus Titan. Available online: https://www.materialise.com/de/inspiration/fallstudien/ein-63-leichteres-luft-und-raumfahrtteil-aus-titan (accessed on 27 October 2024).
- ISO 4587:2003; Adhesives—Determination of Tensile Lap-Shear Strength of Rigid-to-Rigid Bonded Assemblies. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2003.
- DIN EN ISO 25178:2023-09; Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS)—Surface Texture: Areal—Part 2: Terms, Definitions and Surface Texture Parameters. Beuth Verlag, DIN e.V.: Berlin, Germany, 2023.





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lehmann, F.; Troschitz, J.; Gude, M. Influence of LPBF Process Parameters on the Surface Quality of Stainless Steel on the Adhesion Properties with Thermoplastics. Eng. Proc. 2025, 90, 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025090113
Lehmann F, Troschitz J, Gude M. Influence of LPBF Process Parameters on the Surface Quality of Stainless Steel on the Adhesion Properties with Thermoplastics. Engineering Proceedings. 2025; 90(1):113. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025090113
Chicago/Turabian StyleLehmann, Florian, Juliane Troschitz, and Maik Gude. 2025. "Influence of LPBF Process Parameters on the Surface Quality of Stainless Steel on the Adhesion Properties with Thermoplastics" Engineering Proceedings 90, no. 1: 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025090113
APA StyleLehmann, F., Troschitz, J., & Gude, M. (2025). Influence of LPBF Process Parameters on the Surface Quality of Stainless Steel on the Adhesion Properties with Thermoplastics. Engineering Proceedings, 90(1), 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025090113






