The Development of an Affordable Graphite-Based Conductive Ink for Printed Electronics †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
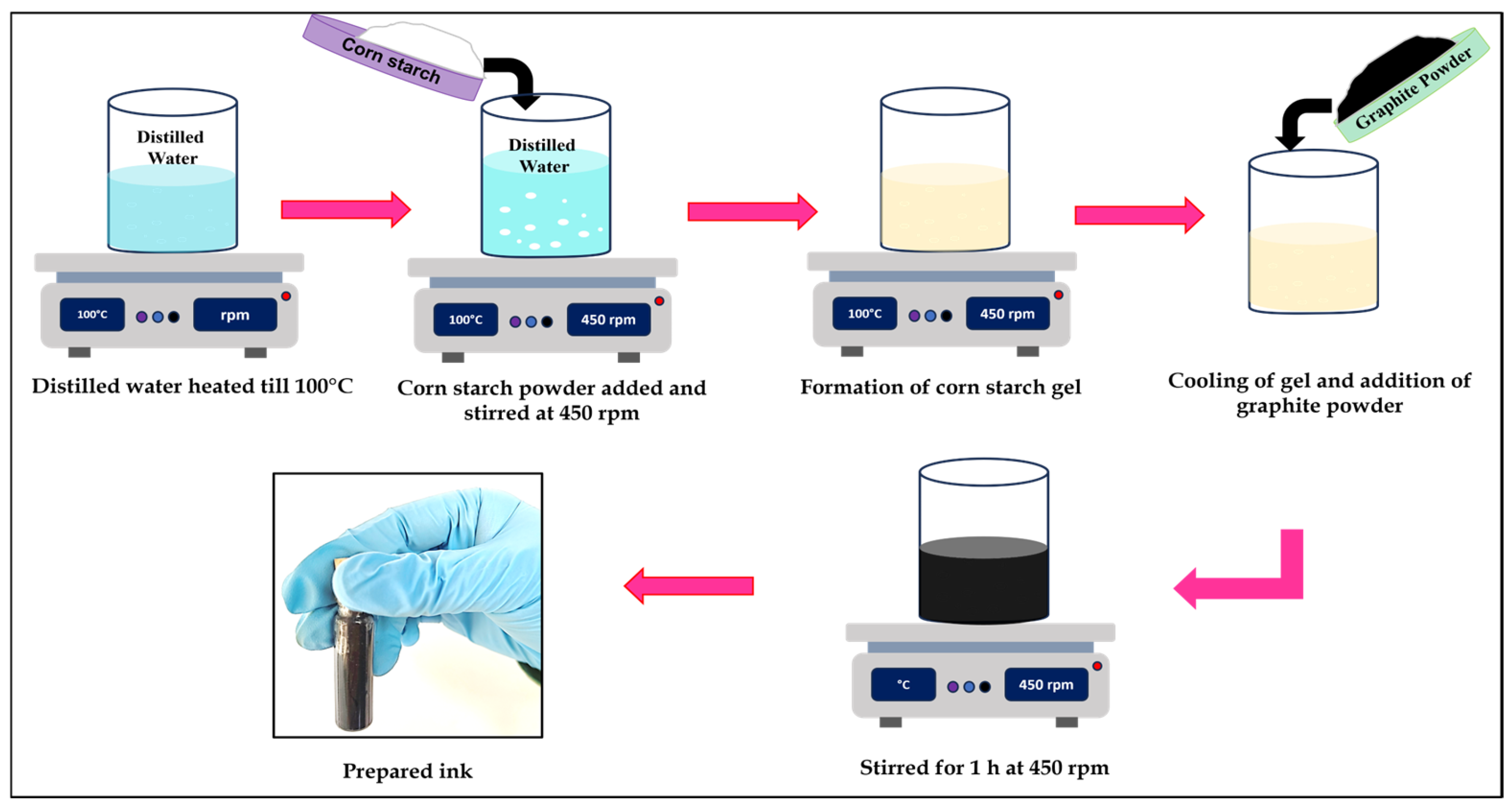
2.2. Preparation of Graphite-Based Conductive Ink
2.3. Characterization Techniques
3. Results and Discussions
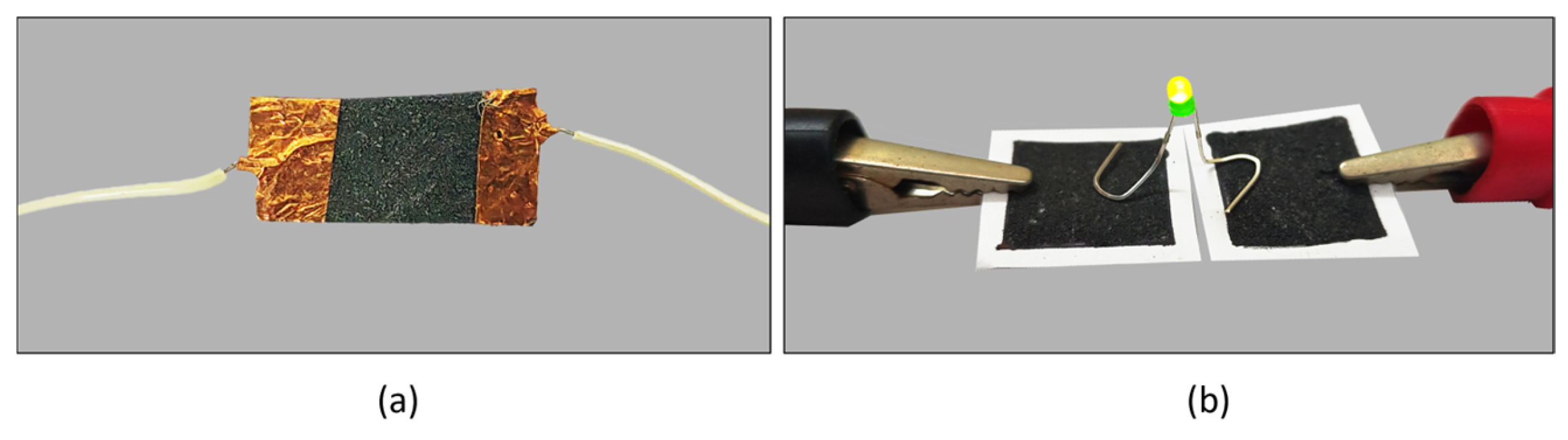
3.1. Conductivity Test
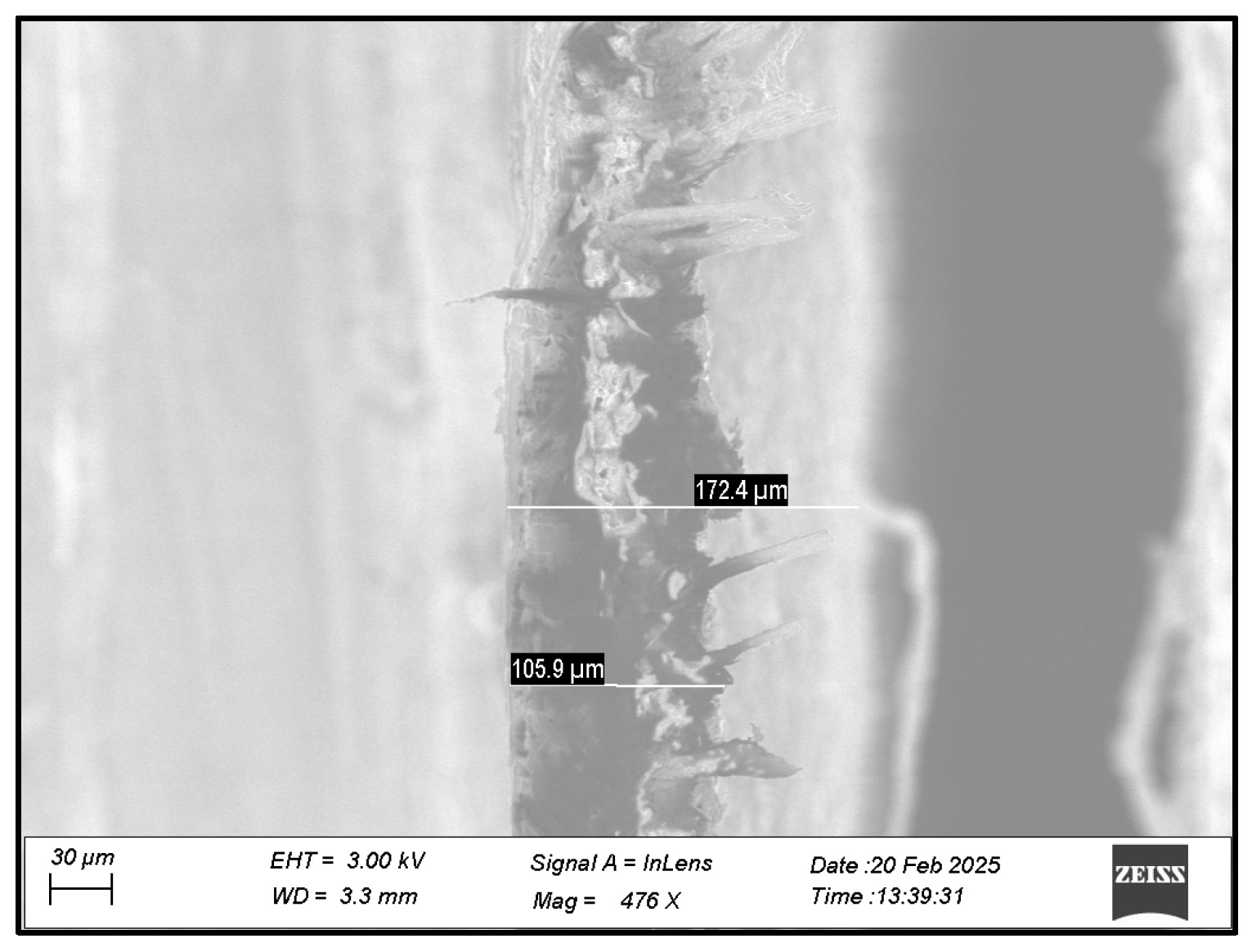
3.2. Characterization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, Y.; Thielens, A.; Muin, S.; Ting, J.; Baumbauer, C.; Arias, A.C. A new frontier of printed electronics: Flexible hybrid electronics. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1905279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, J.R.; Orzari, L.O.; Araujo DA, G.; de Oliveira, P.R.; Kalinke, C.; Rocha, D.P.; dos Santos, A.L.; Takeuchi, R.M.; Munoz, R.A.A.; Bonacin, J.A.; et al. Development of conductive inks for electrochemical sensors and biosensors. Microchem. J. 2021, 164, 105998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, R.; Khair, N.; Ahmed, D.M.; Shahariar, H. Fabrication of low cost and scalable carbon-based conductive ink for E-textile applications. Mater. Today Commun. 2019, 19, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.Y.; Xu, B.; Tan, D.; Yang, Q.; Li, Z.; Fu, H. Naturally Crosslinked Biocompatible Carbonaceous Liquid Metal Aqueous Ink Printing Wearable Electronics for Multi-Sensing and Energy Harvesting. Nano-Micro Lett. 2024, 16, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisales, C.; Herrera, N.; Fajardo, F. Preparation of graphite conductive paint and its application to the construction of RC circuits on paper. Phys. Educ. 2016, 51, 055011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Ouyang, X.; Lv, Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, Q.; Wang, S. A review of carbon-based conductive inks and their printing technologies for integrated circuits. Coatings 2023, 13, 1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradela-Filho, L.A.; Andreotti, I.A.; Carvalho, J.H.; Araujo, D.A.; Orzari, L.O.; Gatti, A.; Takeuchi, R.M.; Santos, A.L.; Janegitz, B.C. Glass varnish-based carbon conductive ink: A new way to produce disposable electrochemical sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 305, 127433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, J.R.; Silva, T.A.; Rivas, G.A.; Janegitz, B.C. Novel eco-friendly water-based conductive ink for the preparation of disposable screen-printed electrodes for sensing and biosensing applications. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 409, 139968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidina, D.S.; Eawwiboonthanakit, N.; Mariatti, M.; Fontana, S.; Hérold, C. Recent development of graphene-based ink and other conductive material-based inks for flexible electronics. J. Electron. Mater. 2019, 48, 3428–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira AE, F.; Pereira, A.C. Development of a simple and cheap conductive graphite ink. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2021, 168, 087508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Cândido, T.C.; Pereira, A.C.; da Silva, D.N. Development and characterization of conductive ink composed of graphite and carbon black for application in printed electrodes. Analytica 2023, 4, 513–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Freitas, R.C.; Fonseca, W.T.; Azzi, D.C.; Raymundo-Pereira, P.A.; Oliveira, O.N., Jr.; Janegitz, B.C. Flexible electrochemical sensor printed with conductive ink made with craft glue and graphite to detect drug and neurotransmitter. Microchem. J. 2023, 191, 108823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchianò, V.; Tricase, A.; Caputo, M.; Farinini, E.; Leardi, R.; Imbriano, A.; Leech, D.; Kidayaveettil, R.; Gentile, L.; Torsi, L.; et al. Tailoring water-based graphite conductive ink formulation for enzyme stencil-printing: Experimental design to enhance wearable biosensor performance. Chem. Mater. 2023, 36, 358–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaghela, N.R.; Nath, K. Reduced graphene oxide coated graphite electrodes for treating Reactive Turquoise Blue 21 rinse water using an indirect electro-oxidation process. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoumaki, M.; Tzetzis, D.; Mansour, G. Development and characterization of starch-based nanocomposite materials. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 564, 012037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibar, E.A.A.; Gönenç, I.; Us, F. Gelatinization of waxy, normal and high amylose corn starches. GIDA-J. Food 2010, 35, 237–244. [Google Scholar]

| Sample | Mean (Ω) | Variance (Ω2) | Standard Deviation (Ω) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 558.8 | 313.36 | 17.70 |
| B | 658.6 | 581.84 | 24.12 |
| C | 614.6 | 885.84 | 29.76 |
| Reference | Ink Composition | Solvent | Substrate | Measured Resistance | Application | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [10] | Graphite and nail polish | Acetone | Paper | 2.17 KΩ | Electrochemical sensors | Easy preparation and cheap |
| [11] | Graphite, carbon black, and nail polish | Acetone | Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) sheets | Low | Electrochemical sensors | Easy to prepare, low cost, and adequate homogeneity |
| [12] | Graphite and craft glue | Acetone, ethyl acetate, and glycerin | Ecoflex™ | - | Electrochemical sensors | Inexpensive and easy to prepare |
| [13] | Graphite, chitosan, and glycerol | Acetic acid and water | Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) sheets | Resistance to the charge transfer (RCT) = 9.6 ± 0.6 kΩ | Wearable biosensors | Enzyme-based biocompatible water-based ink |
| [5] | Graphite and gum arabic | Water | Paper | Range of ~kΩ | Printed electronics | Simple, low cost, and environment friendly |
| [This work] | Graphite and corn starch | Water | Paper | ~560 Ω | Printed electronics | Easy to prepare, affordable, and biocompatible |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dey, A.; Kalita, A.J.; Khatun, H.; Sarma, U. The Development of an Affordable Graphite-Based Conductive Ink for Printed Electronics. Eng. Proc. 2025, 87, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025087017
Dey A, Kalita AJ, Khatun H, Sarma U. The Development of an Affordable Graphite-Based Conductive Ink for Printed Electronics. Engineering Proceedings. 2025; 87(1):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025087017
Chicago/Turabian StyleDey, Anandita, Ankur Jyoti Kalita, Hiramoni Khatun, and Utpal Sarma. 2025. "The Development of an Affordable Graphite-Based Conductive Ink for Printed Electronics" Engineering Proceedings 87, no. 1: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025087017
APA StyleDey, A., Kalita, A. J., Khatun, H., & Sarma, U. (2025). The Development of an Affordable Graphite-Based Conductive Ink for Printed Electronics. Engineering Proceedings, 87(1), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025087017






