Evaluation of Seismic Effects on Atmospheric Pressure Liquid Storage Tanks †
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Seismic Stress Modeling
1.2. Seismic Damage Characteristics
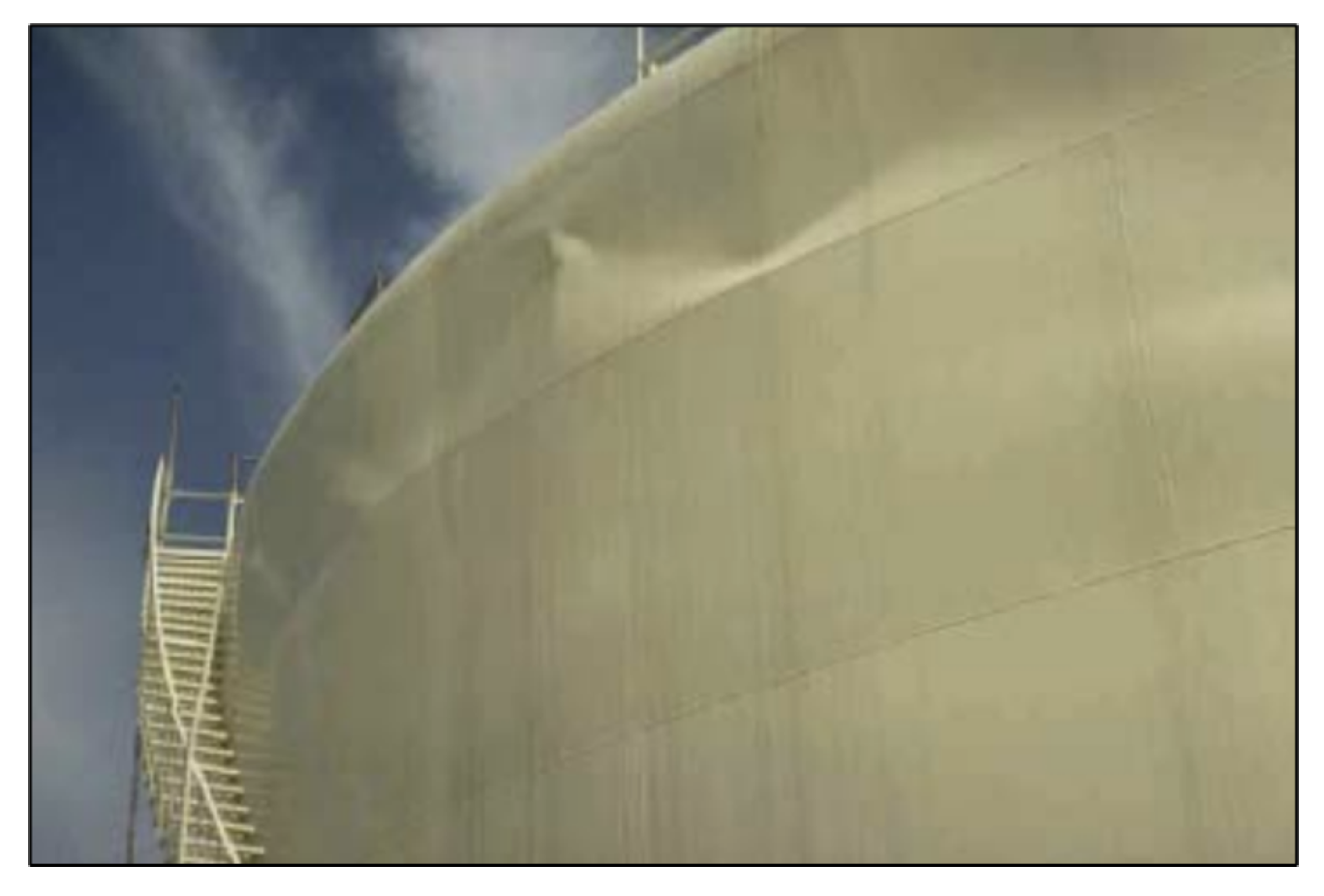
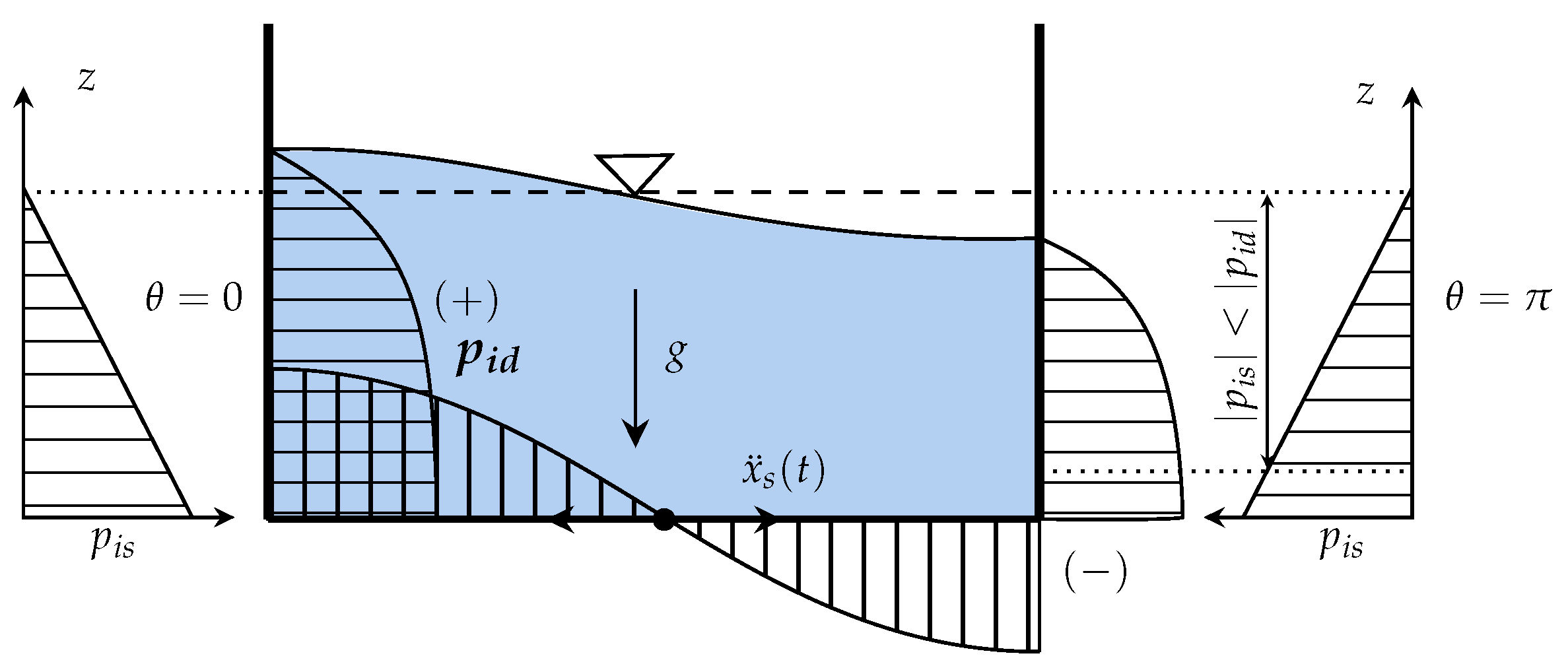
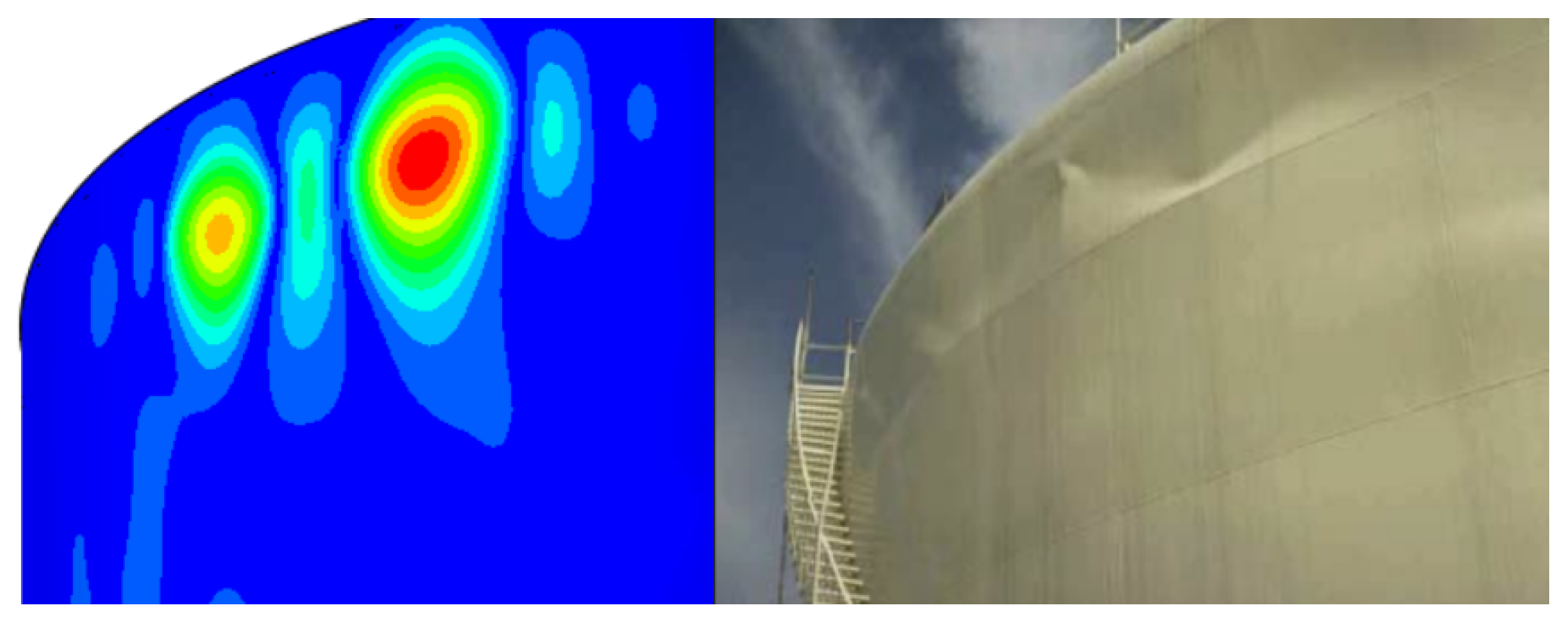
- Buckling in the upper portion of the shell (top buckling): if the depression due to the hydrodynamic effect is excessive, the tank may collapse inwards (Figure 3).
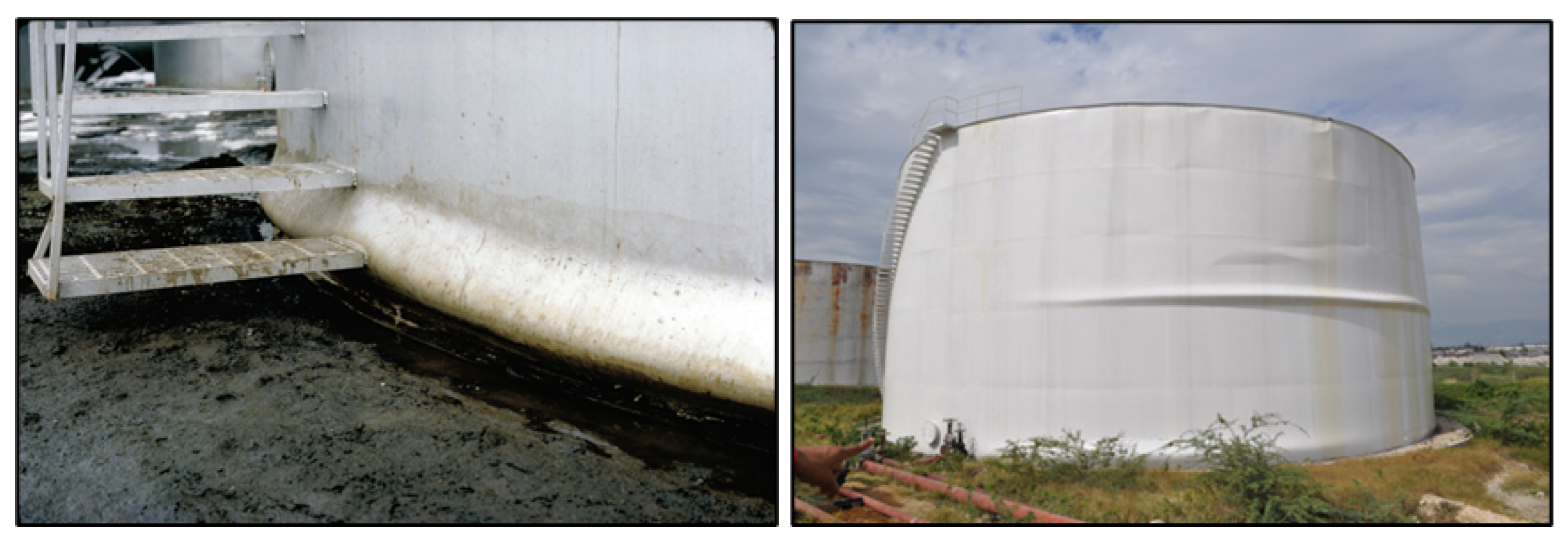
- Instability in the lower portion of the tank: if the overpressure due to hydrostatic loading and the hydrodynamic effect exceeds the yield strength of the material, even if the course is mainly stressed still in the plane (as a membrane), there is excessive deformation due to plasticization, which, with the effect of axial stress, can lead to instability. This damage is usually called elephant foot (Figure 4).
1.3. Reference Norms
2. Eurocode 8 Theoretical Bases—Part 4
2.1. Seismic Analysis Procedures for Tanks (Annex A)
- the impulsive contribution;
- the convective contribution.
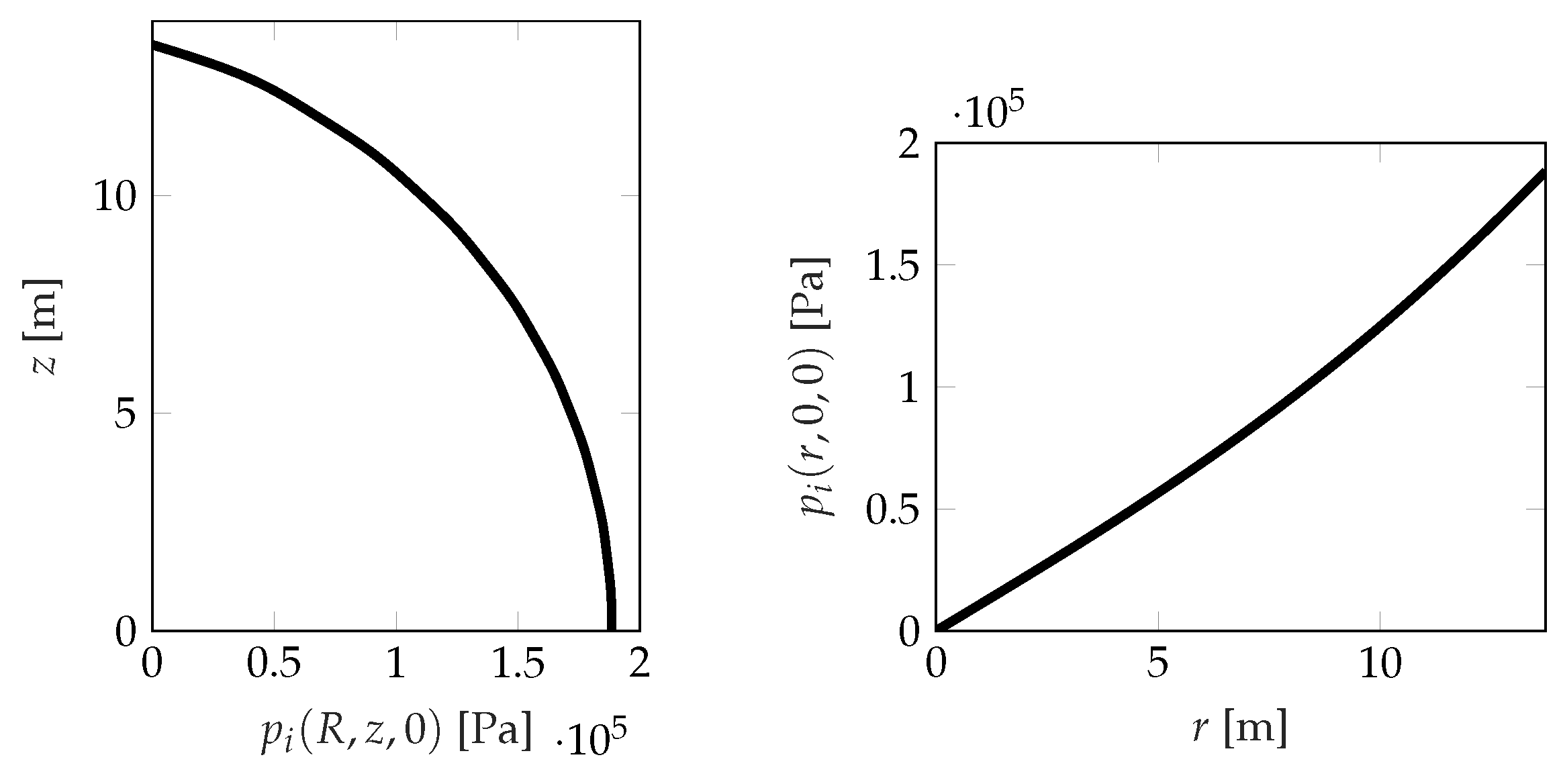
2.2. Rigid Impulsive Component
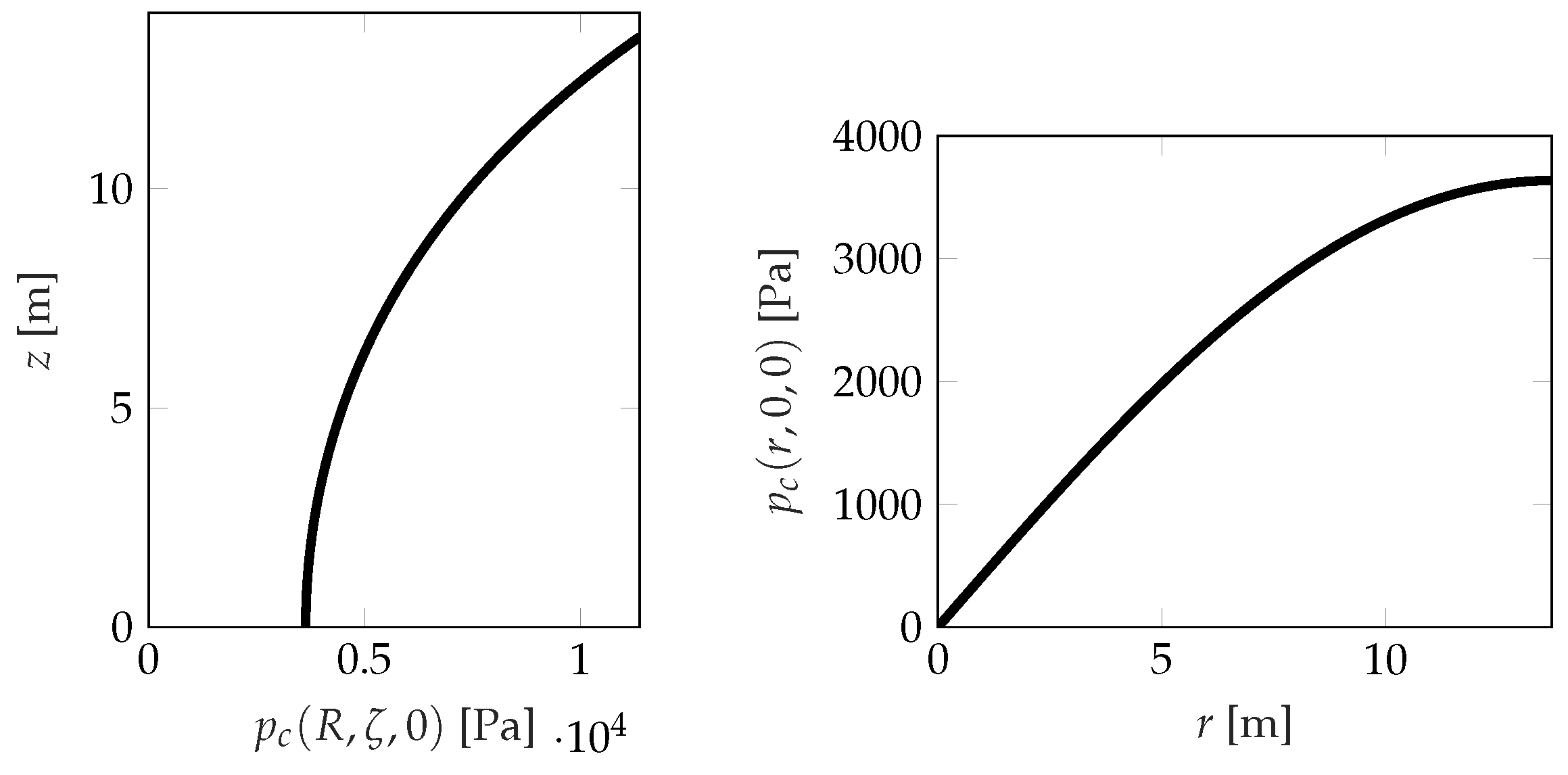
2.3. Convective Contribution
2.4. Solution Method Considerations
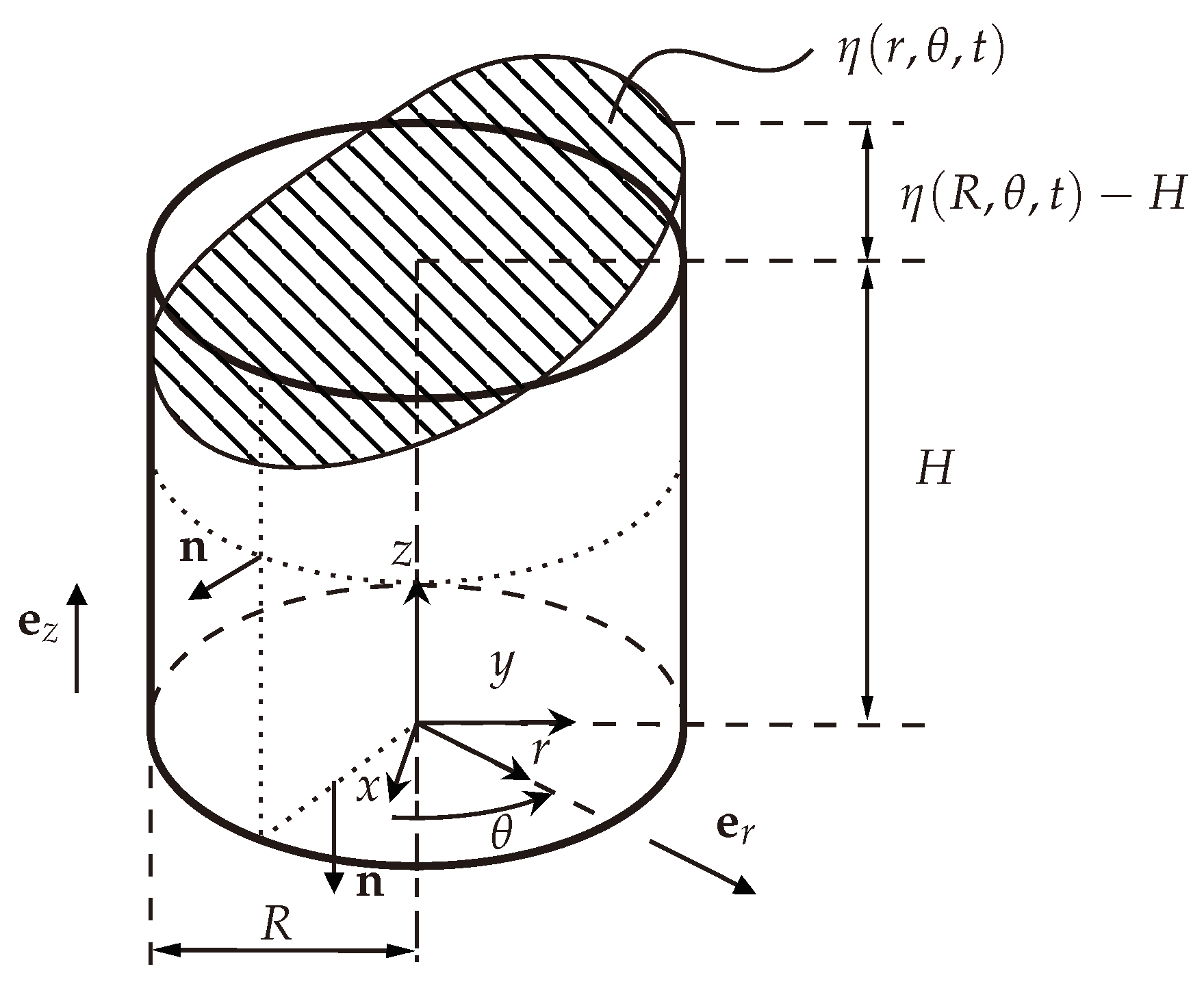
3. Deformable Tanks
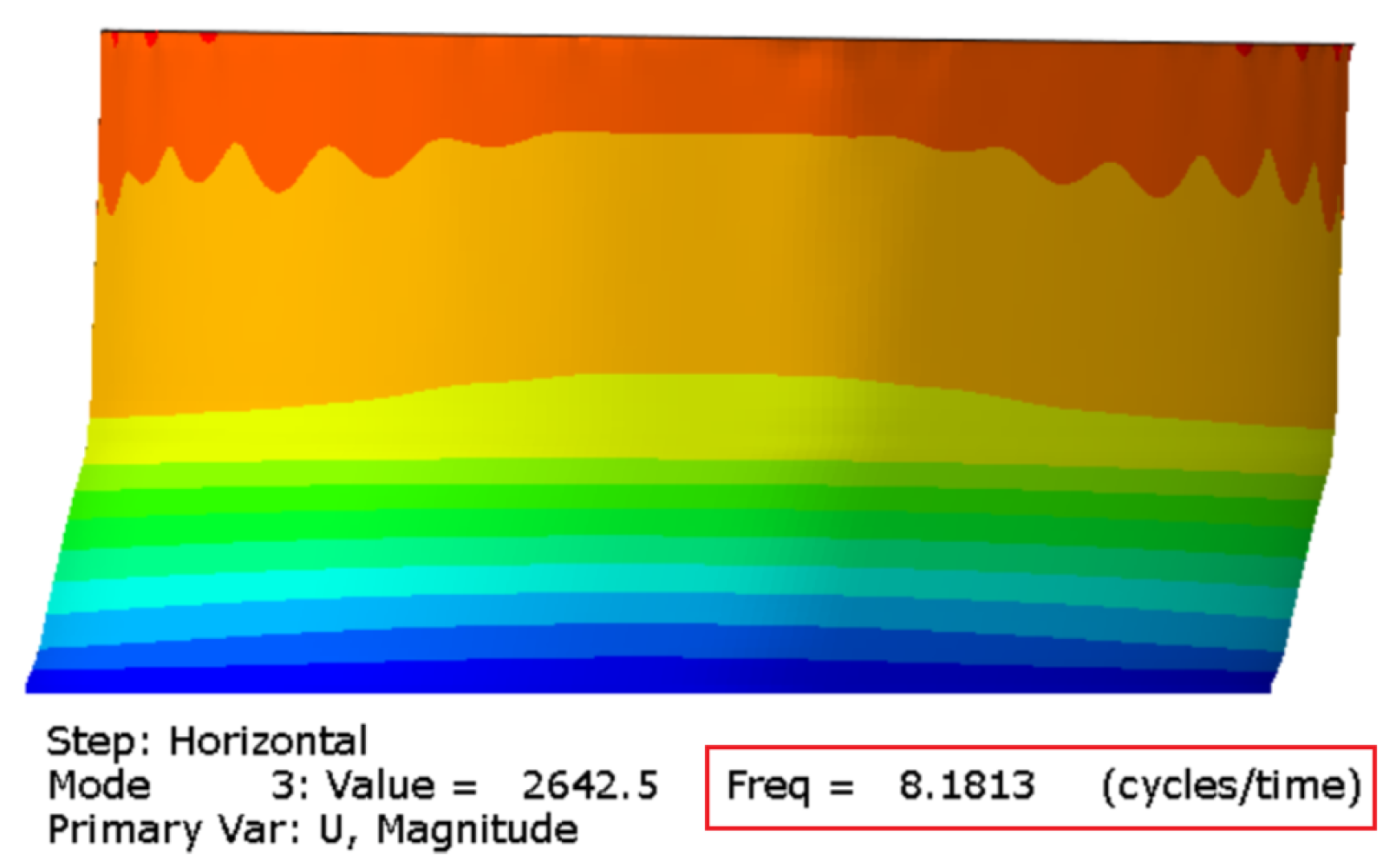
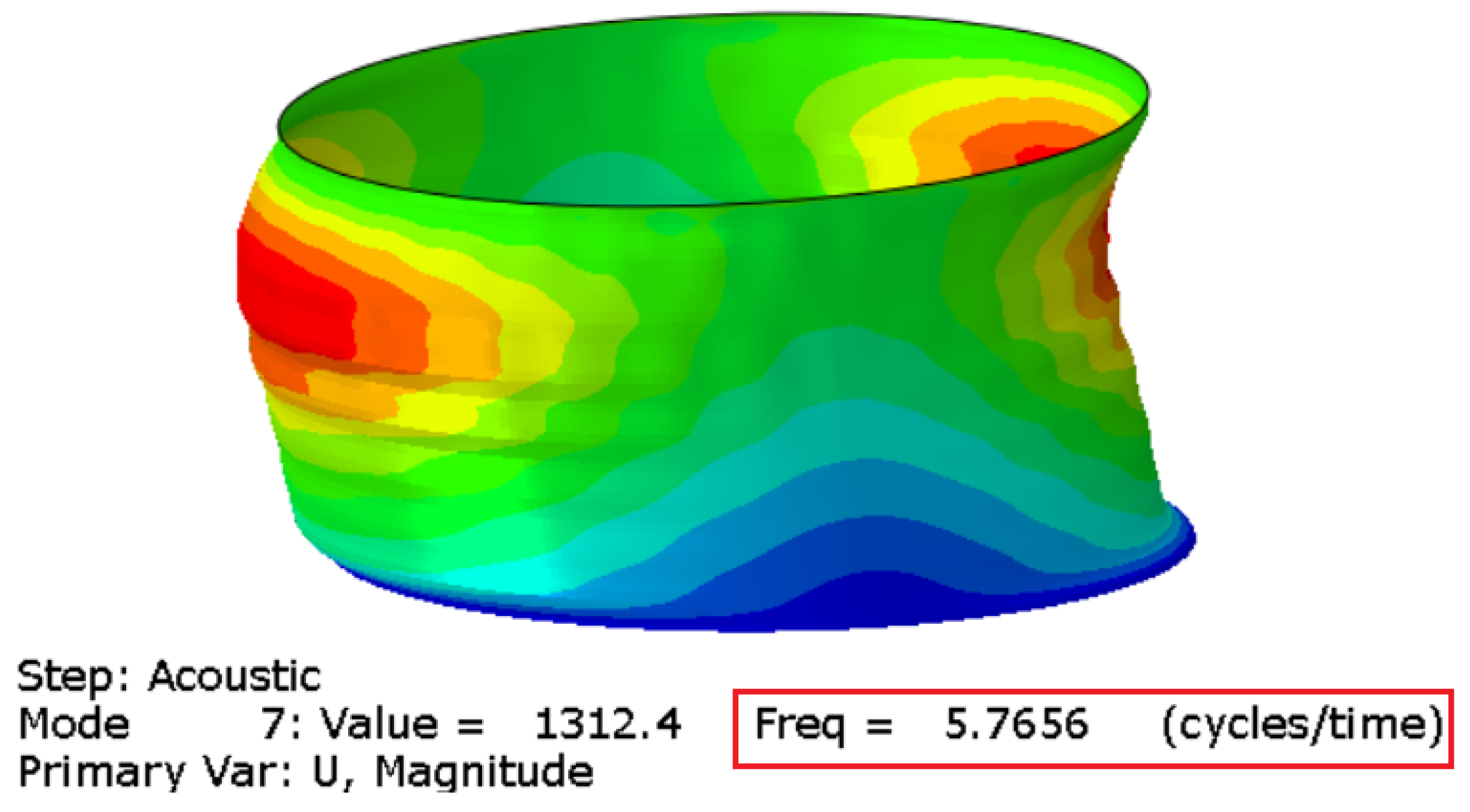
3.1. Fluid–Structural Modal Analysis
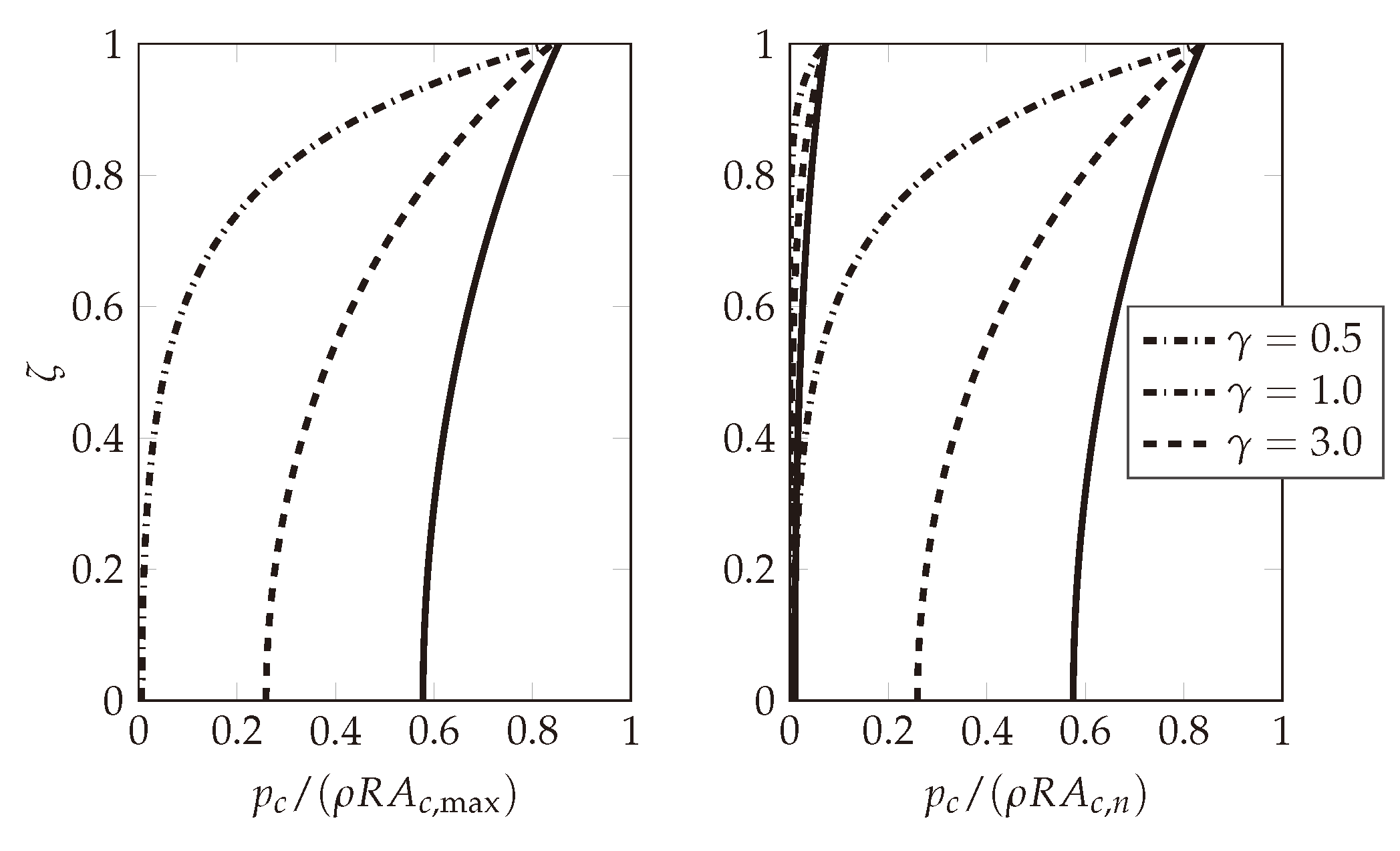
3.2. Acoustic Modal Analysis
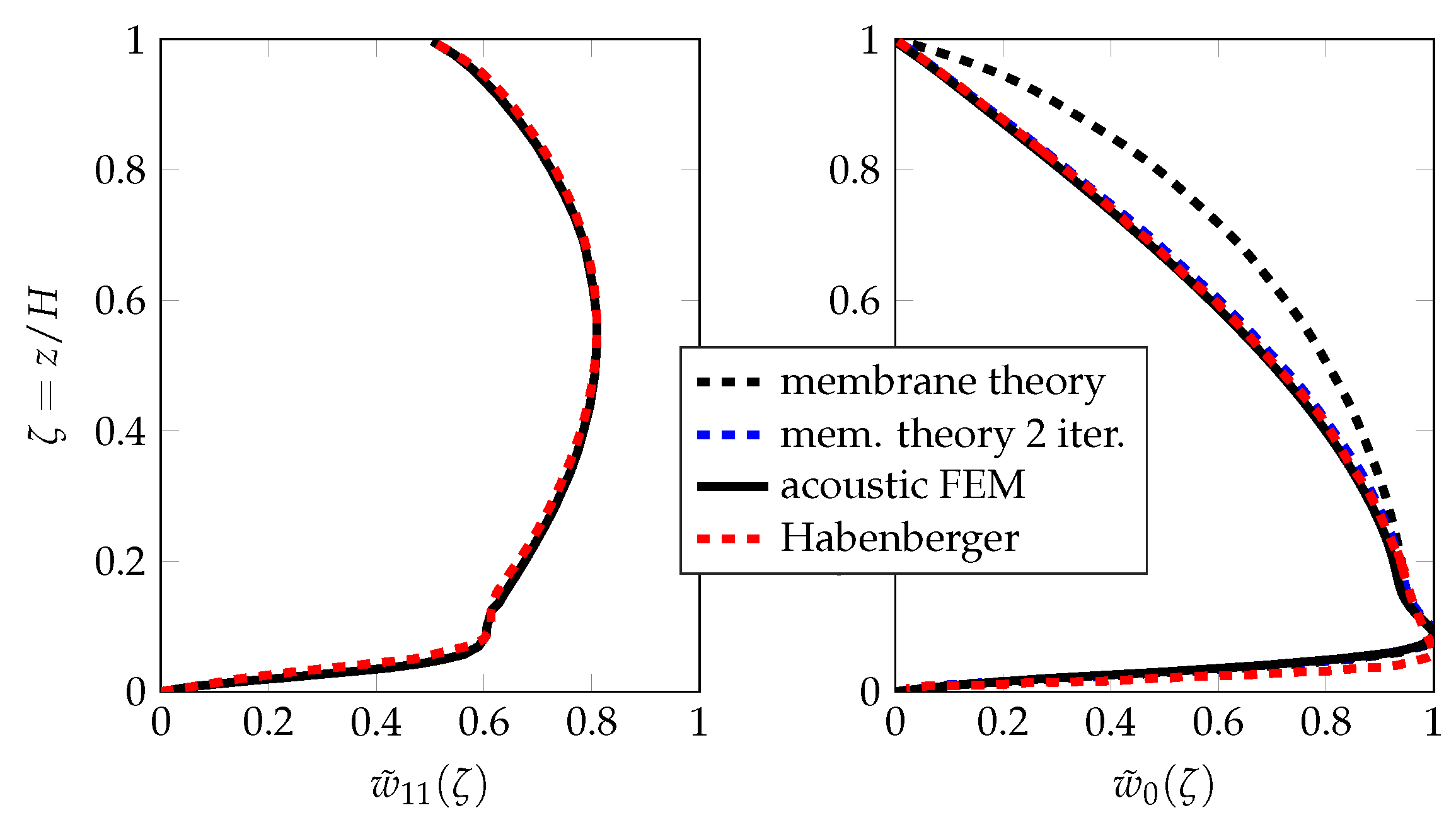
3.3. Comparative Verification
- Radius m;
- Wetted height m coincident with the height of the freeboard;
- Liquid content: water kg/m3, GPa;
- Steel shell, GPa, , kg/m3;
- Constant thickness, m.
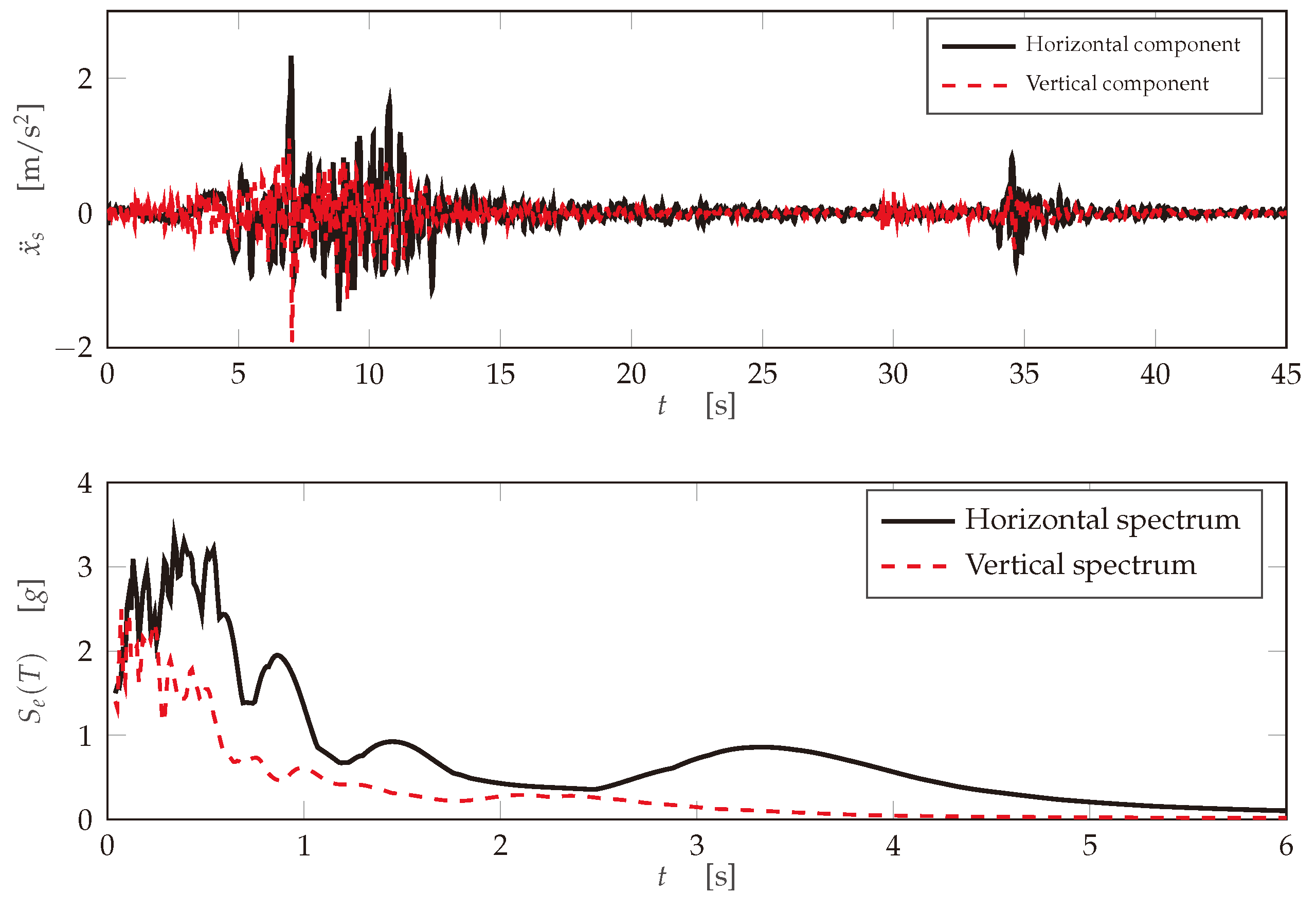
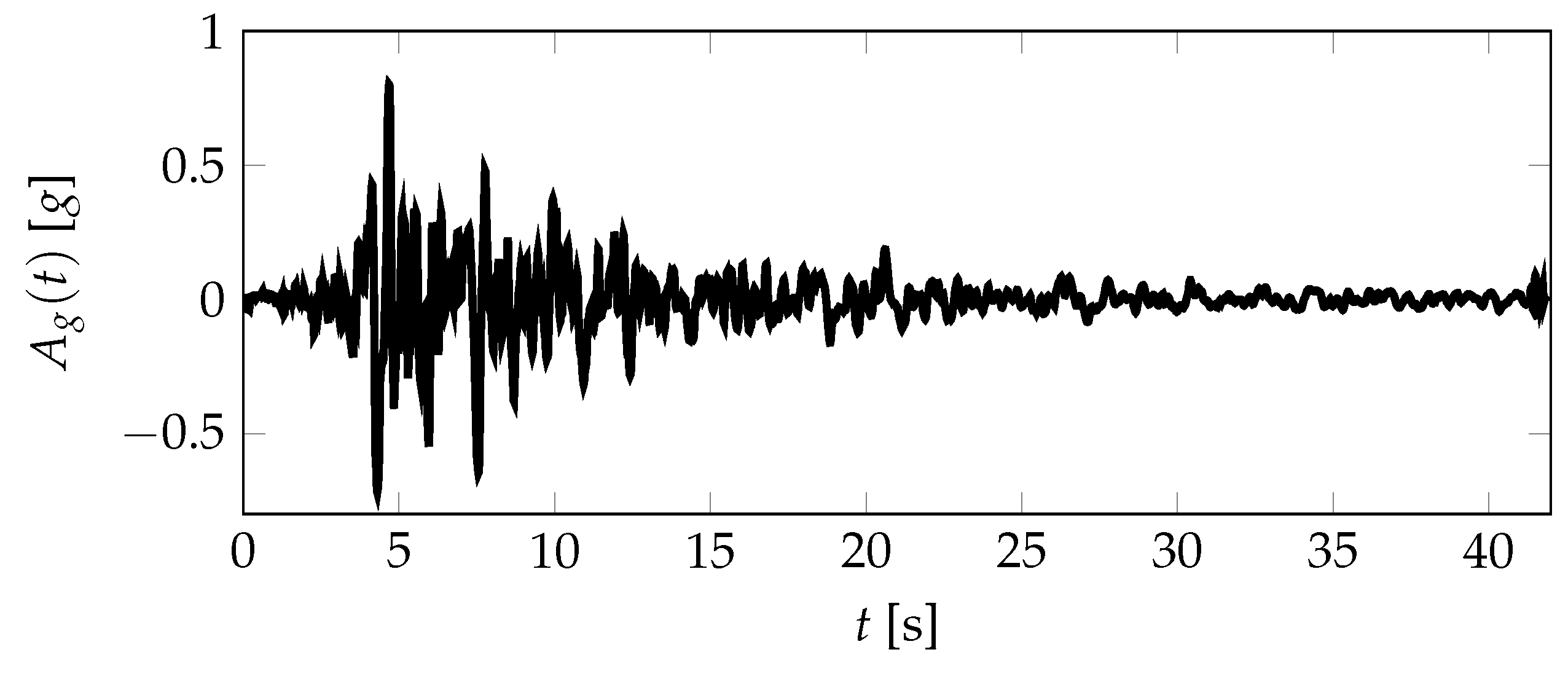
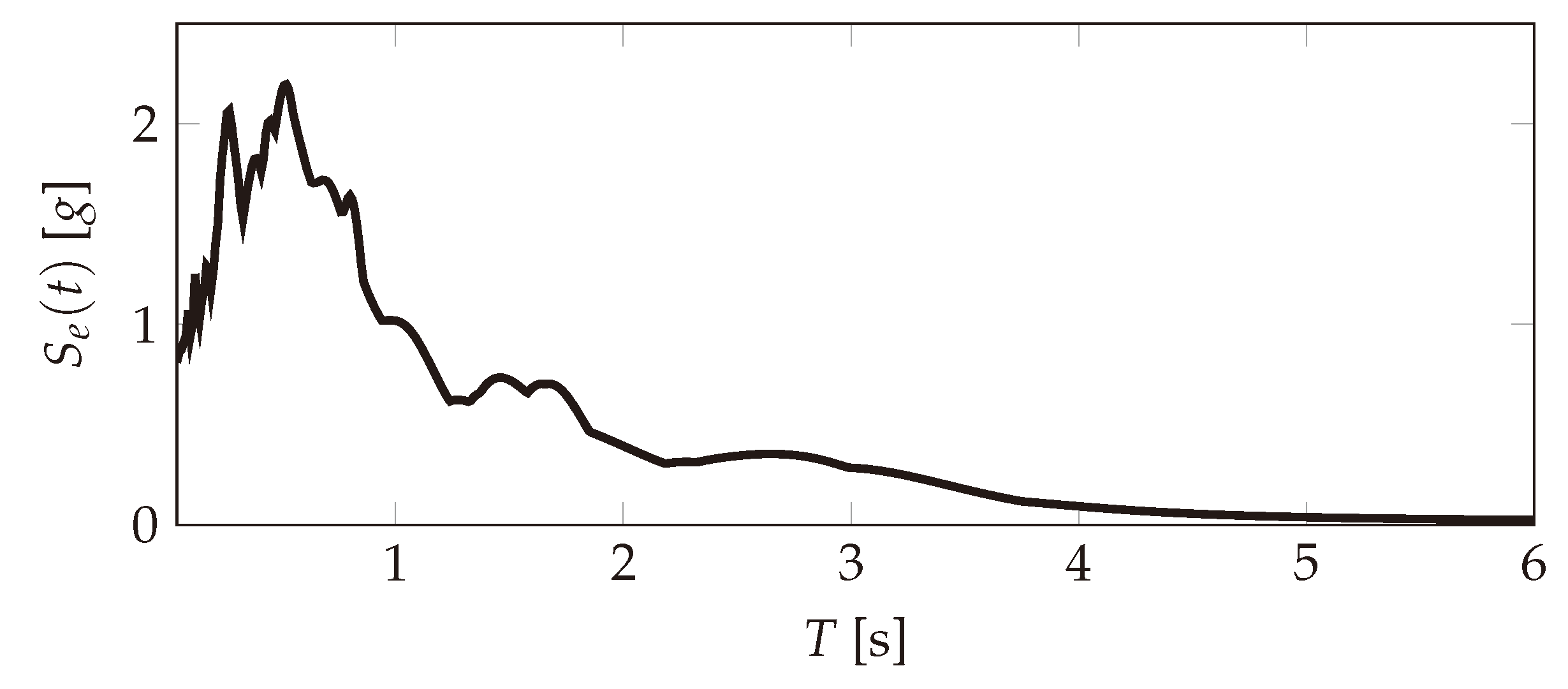
4. Case Study
- Earthquake Ground Motion Level 1 (DD-1): characterizes a very rare seismic event where the corresponding return period is 2475 years.
- Earthquake Ground Motion Level 2 (DD-2): characterizes a rare seismic event where the corresponding return period is 475 years.
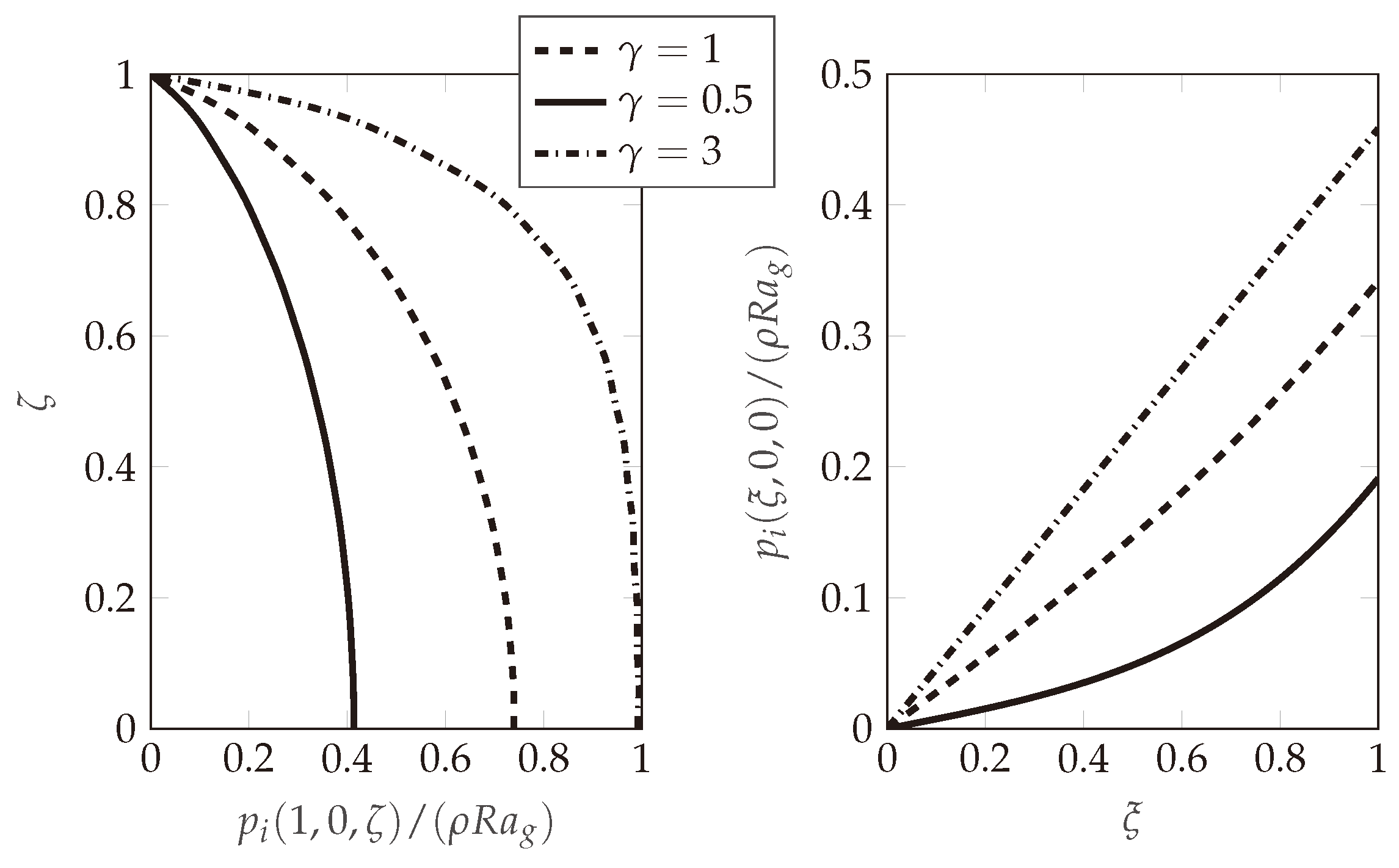
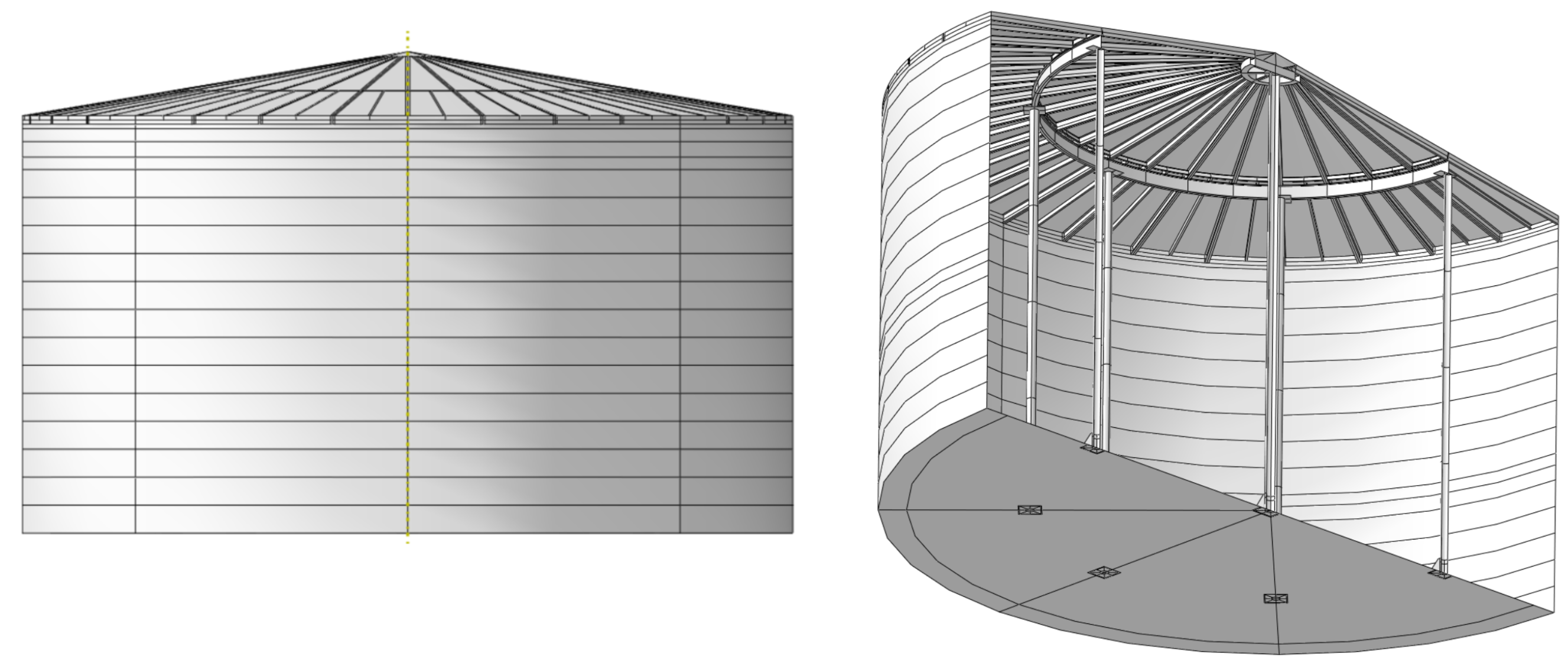
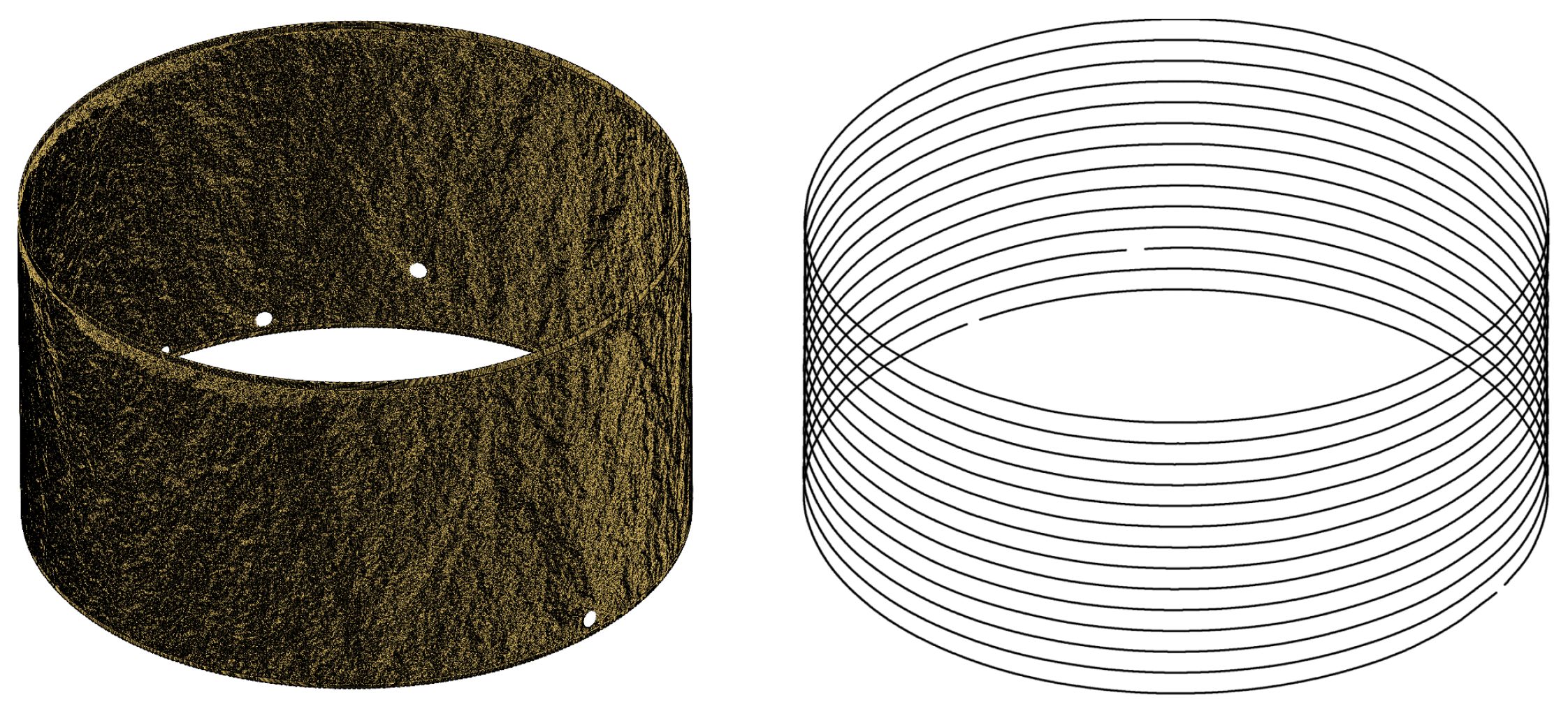
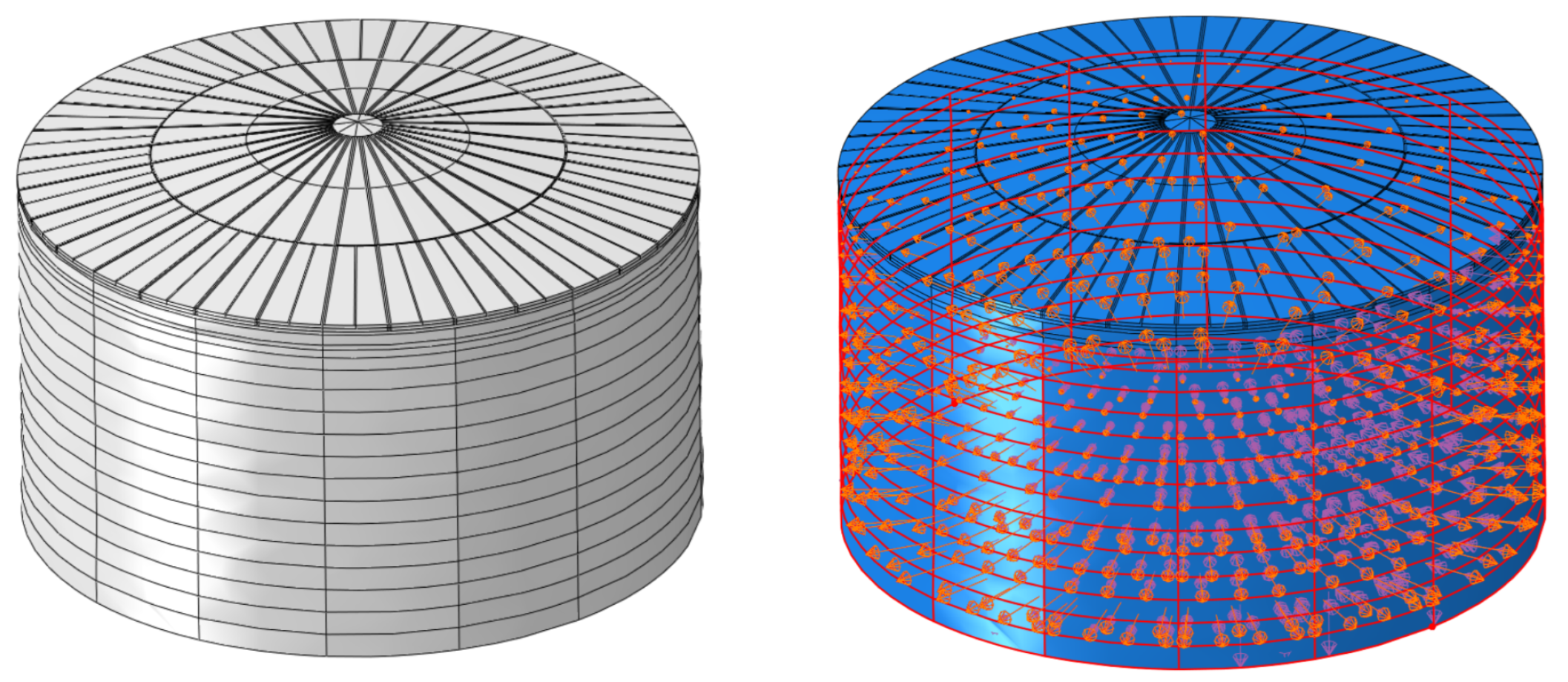
4.1. Ideal Model
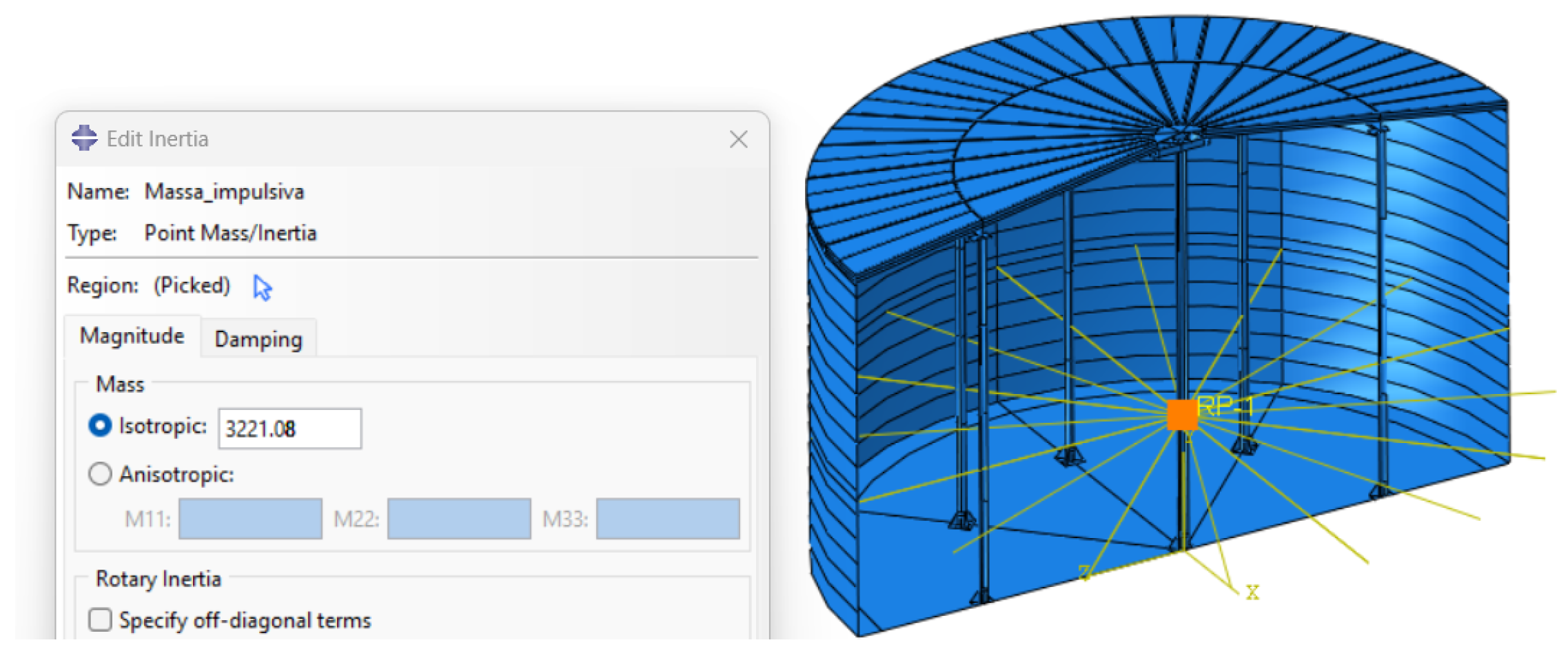
4.2. Impulsive Rigid Contribution
4.3. Convective Contribution
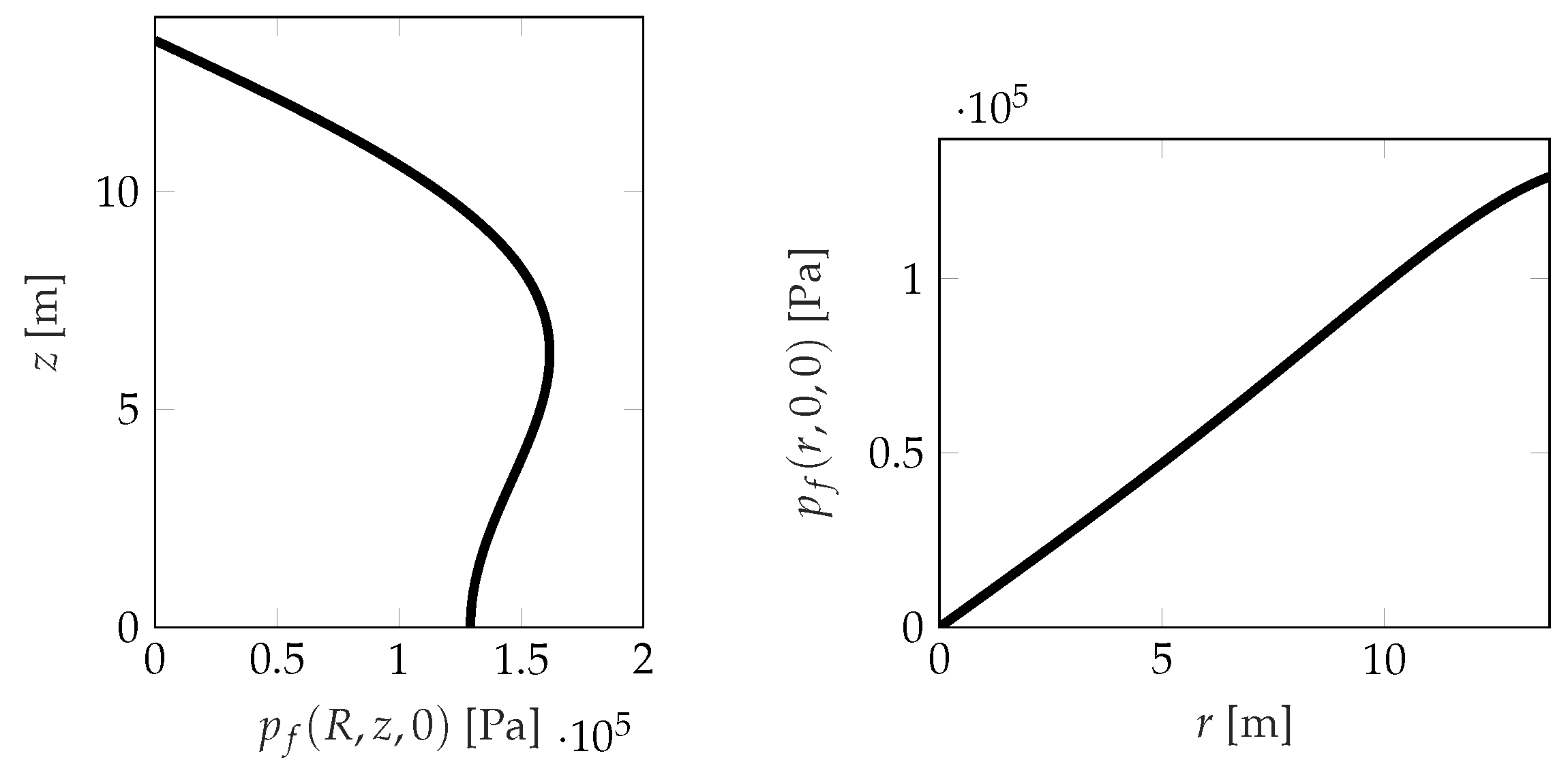
4.4. Deformability Contribution
4.5. Deformed Model
4.6. Setting Up Analyses
- Generic static step: in this step, the hydrostatic load and the force of gravity are applied with linear progression; in this step, it is required to update the stiffness matrix by including the geometric non-linearities, a calculation necessary in the regime of large displacements.
- Incremental non-linear static step: in this step, the hydrodynamic loads are applied and the analysis is carried out using the modified Riks method.
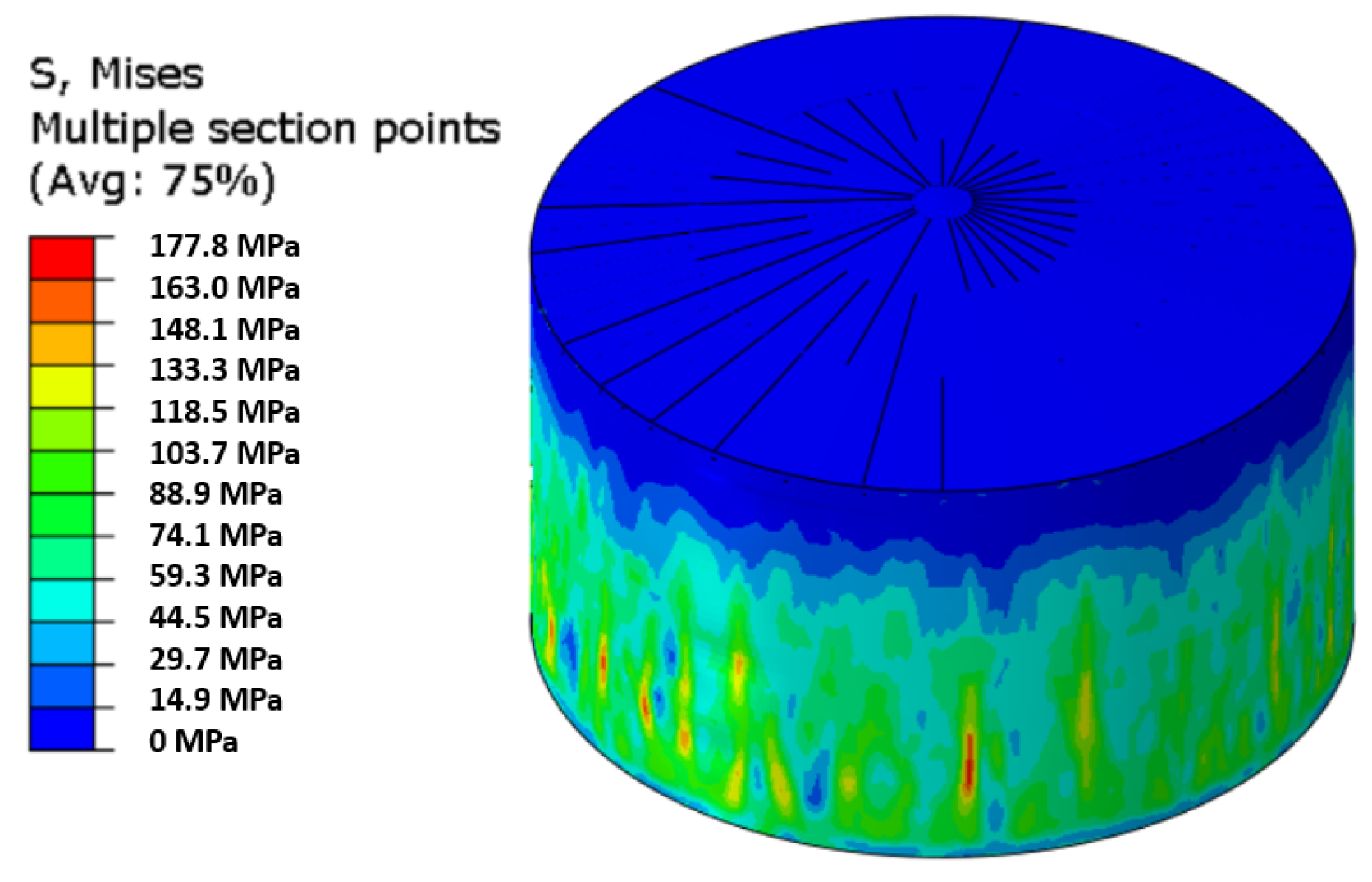
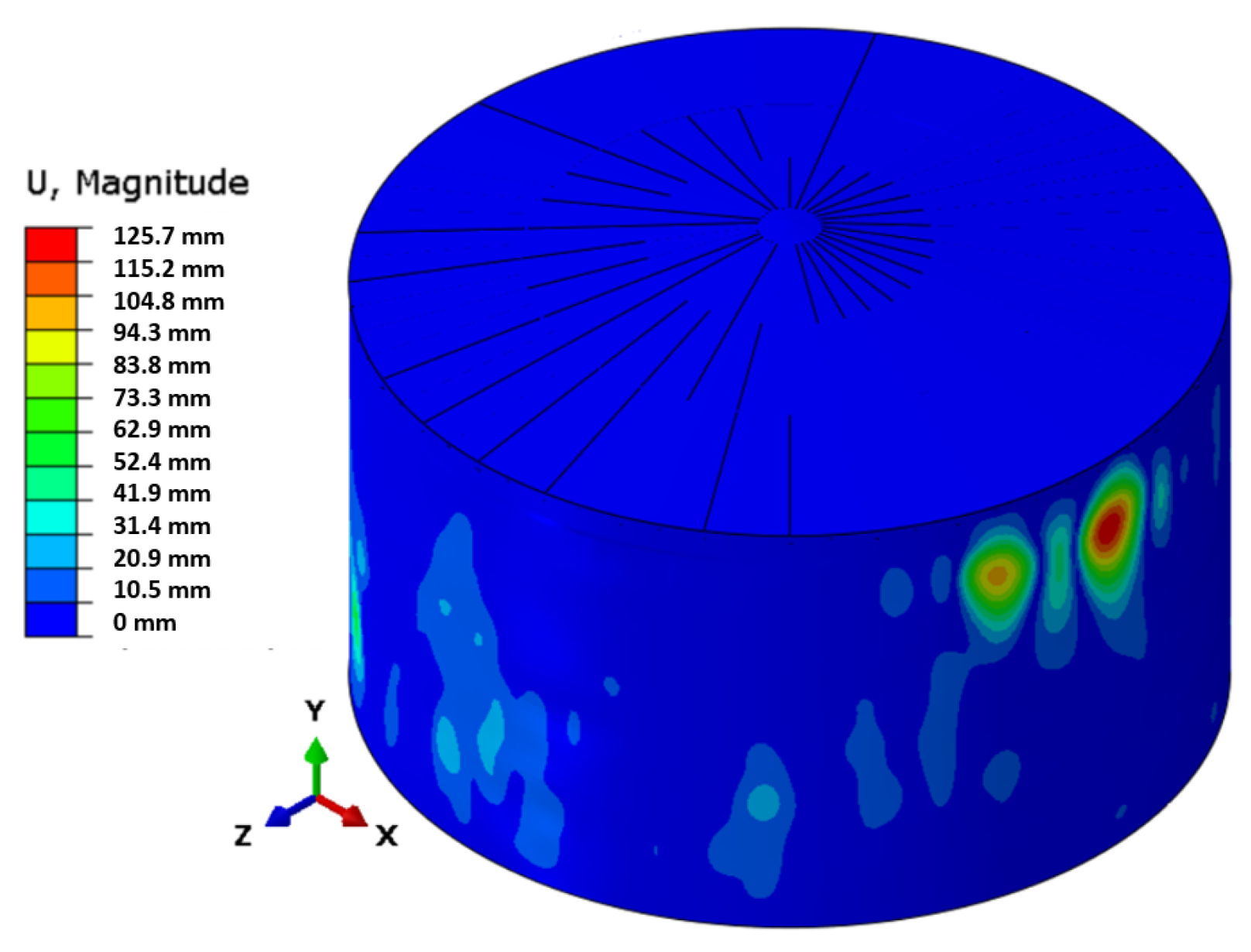
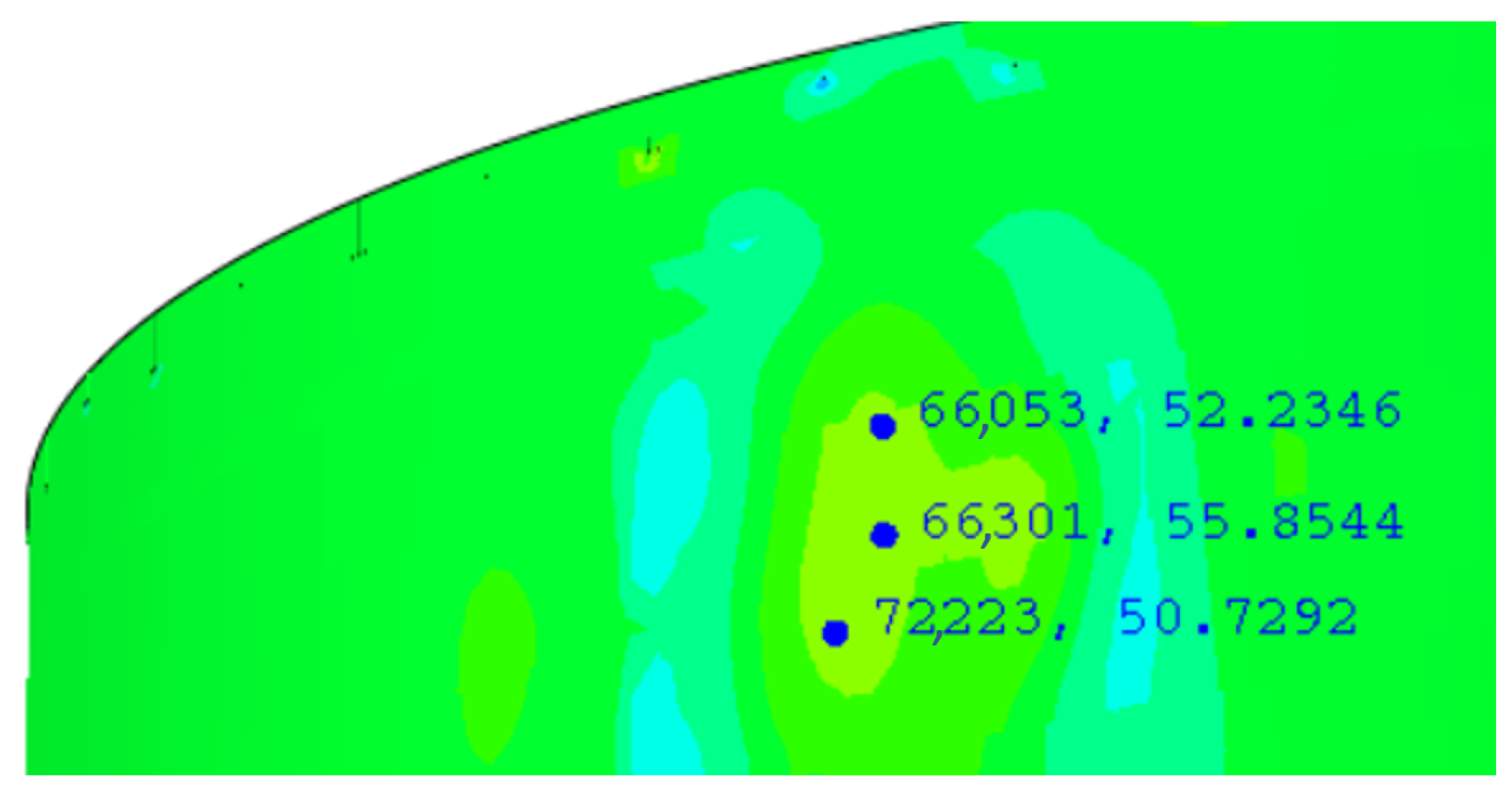
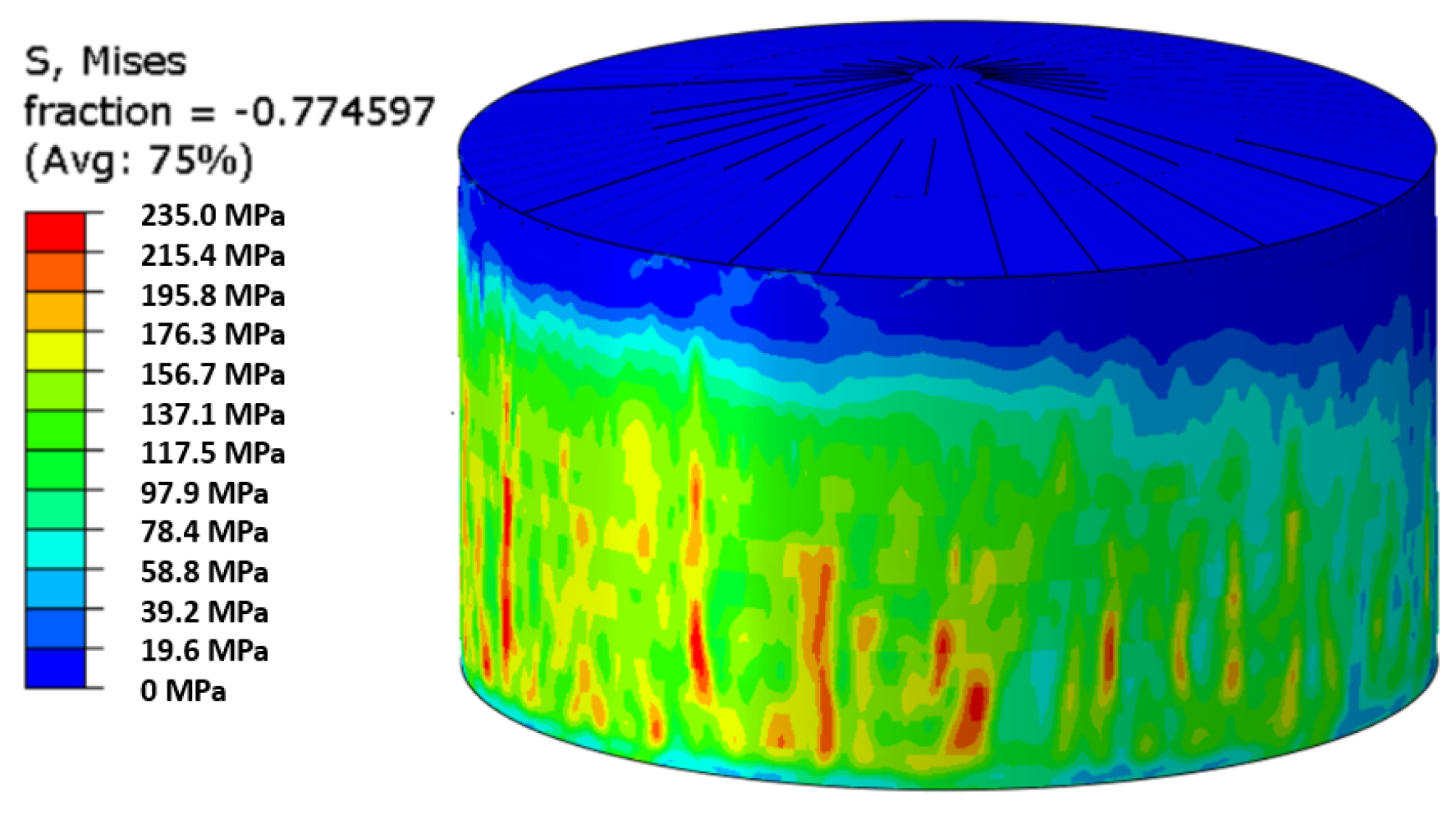
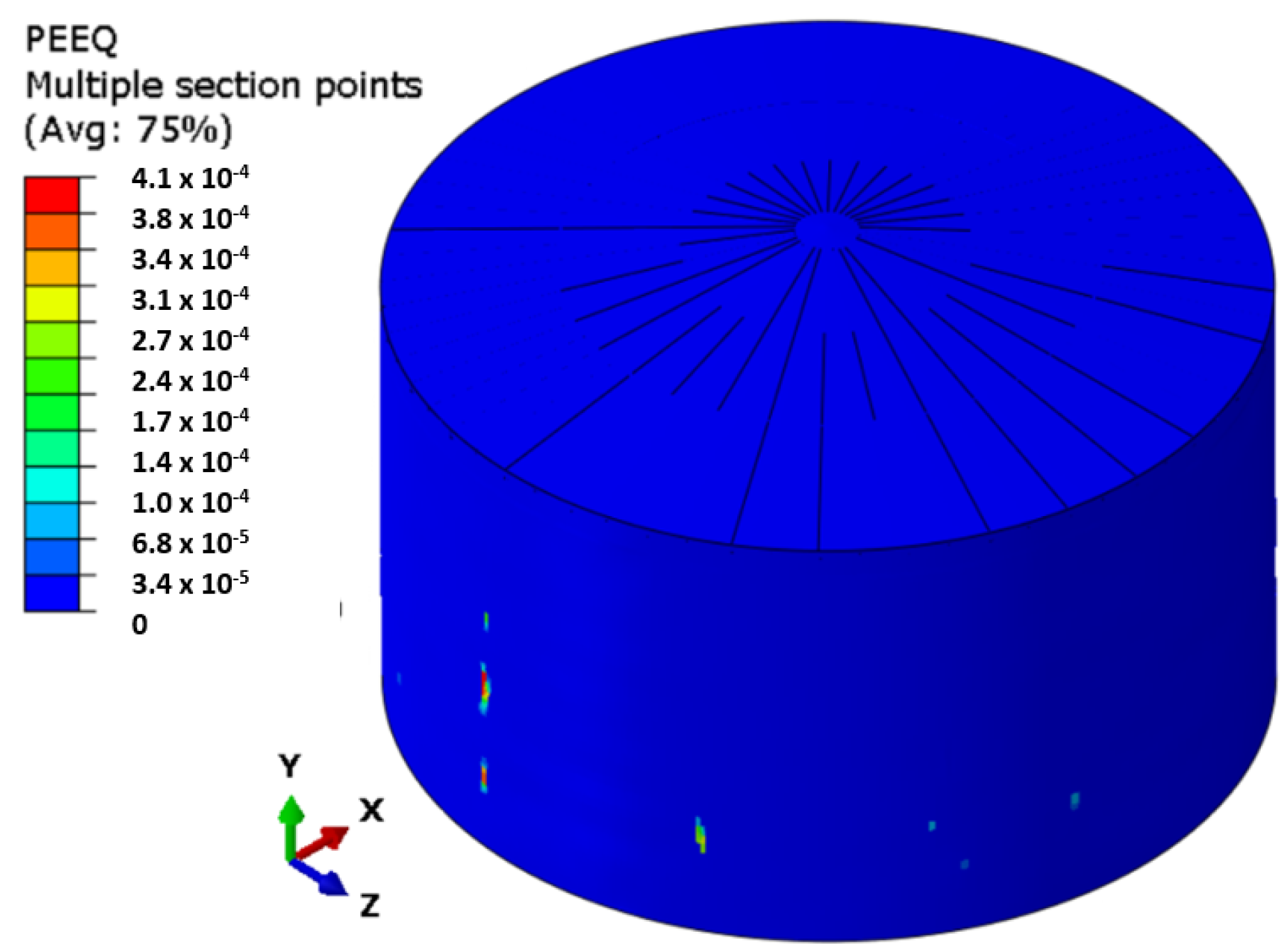
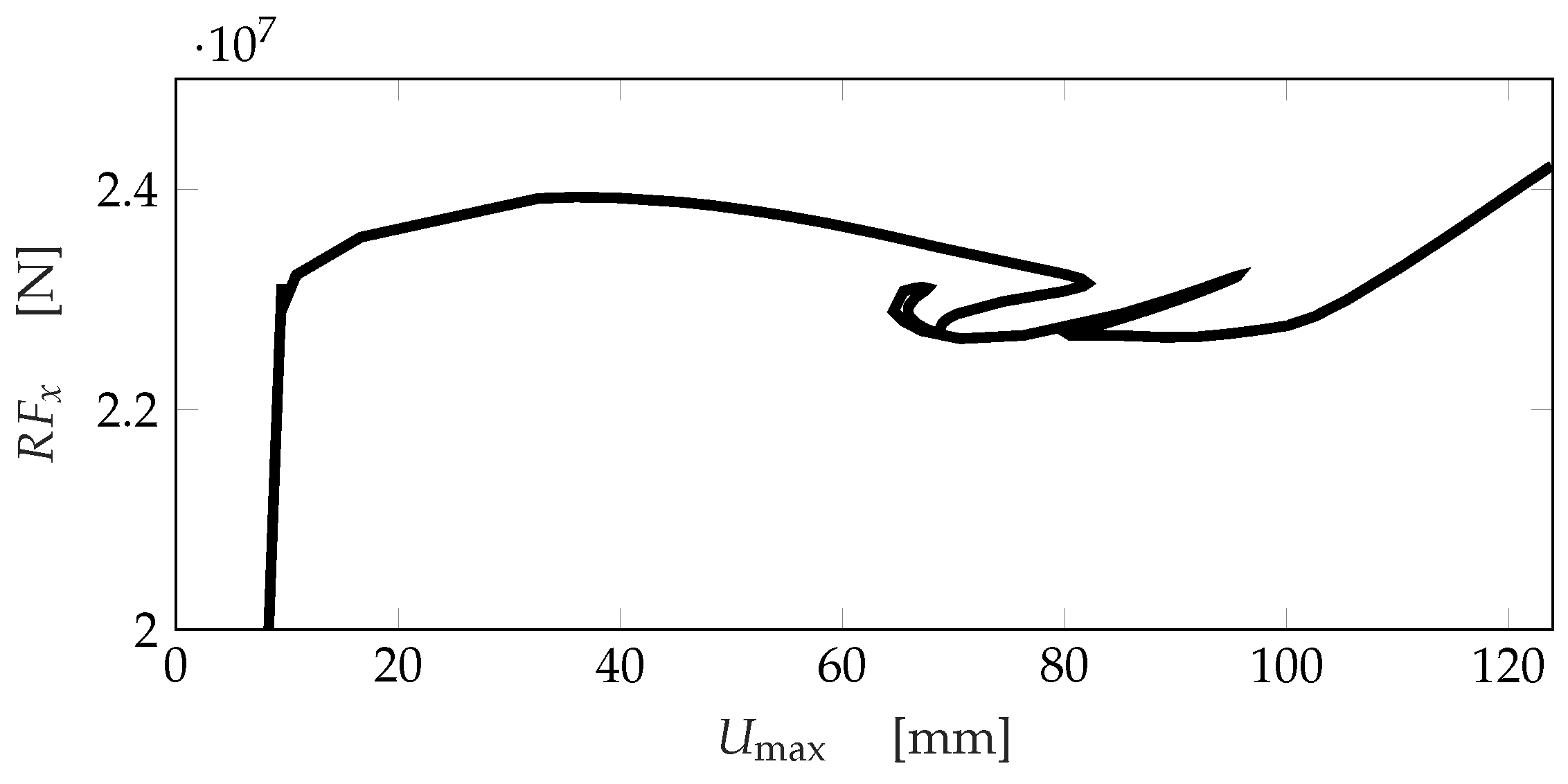
5. Results
- Load proportionality factor ;
- Constraining reaction of the central node of the base along the direction of the load;
- Moment modulus reaction of the central node of the base;
- Displacement of the node that exhibits the greatest displacement at the beginning of the non-linear step;
- Displacement of the node that exhibits the greatest displacement in the non-linear step.
5.1. Static Step
5.2. Non-Linear Step, Seismic Case DD1
5.3. Non-Linear Step, Seismic Case DD2
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Turkish Ministry of Construction and Settlement. Design Code for Buildings in Seismic Regions; Turkish Ministry of Construction and Settlement: Ankara, Türkiye, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen, L.S. Impulsive hydrodynamics of fluid inside a cylindrical tank and of fluid surrounding a cylindrical pier. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1949, 39, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Housner, G.W. Dynamic pressures on accelerated fluid containers. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1957, 47, 15–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Housner, G.W. The dynamic behavior of water tanks. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1963, 53, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, F.D.; Rammerstorferf, F.G.; Scharf, K. Earthquake Resistant Design of Anchored and Unanchored Liquid Storage Tanks Under Three-Dimensional Earthquake Excitation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1991; pp. 317–371. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, F.D.; Rammerstorfer, F.G. A refined analysis of sloshing effects in seismically excited tanks. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 1999, 76, 693–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Topa, A.; Djukic, L.P.; Herath, M.T.; Pearce, G.M. Evaluation of rigid body force in liquid sloshing problems of a partially filled tank: Traditional CFD/SPH/ALE comparative study. Ocean. Eng. 2021, 236, 109556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caprinozzi, S.; Paolacci, F.; Dolšek, M. Seismic risk assessment of liquid overtopping in a steel storage tank equipped with a single deck floating roof. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2020, 67, 104269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souli, M.; Kultsep, A.V.; Al-Bahkali, E.; Pain, C.C.; Moatamedi, M. Arbitrary Lagrangian Eulerian formulation for sloshing tank analysis in nuclear engineering. Nucl. Sci. Eng. 2016, 183, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, Z.; Souli, M.; Fahjan, Y.M. FSI methods for seismic analysis of sloshing tank problems. Mech. Ind. 2010, 11, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, T.W.; Yang, H.I.; Jeon, J.S. Earthquake-induced sloshing effects on the hydrodynamic pressure response of rigid cylindrical liquid storage tanks using CFD simulation. Eng. Struct. 2019, 197, 109376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, P.; Cruchaga, M.; Larreteguy, A. Study of 3D sloshing in a vertical cylindrical tank. Phys. Fluids 2018, 30, 082112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Ming, F.; Zhang, A. Sloshing in a rectangular tank based on SPH simulation. Appl. Ocean. Res. 2014, 47, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiee, A.; Pistani, F.; Thiagarajan, K. Study of liquid sloshing: Numerical and experimental approach. Comput. Mech. 2011, 47, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiśniewski, A.; Kucharski, R. Eigencharacteristics of fluid filled tanks: An extended symmetrical coupled approach. TASK Q. 2006, 10, 455–468. [Google Scholar]
- Phan, H.N.; Paolacci, F. Fluid-structure interaction problems: An application to anchored and unanchored steel storage tanks subjected to seismic loadings. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.00679. [Google Scholar]
- Rawat, A.; Matsagar, V.; Nagpal, A.K. Seismic Analysis of Steel Cylindrical Liquid Storage Tank Using Coupled Acoustic-Structural Finite Element Method For Fluid-Structure Interaction. Int. J. Acoust. Vib. 2020, 25, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhulipala, S.L.N.; Bolisetti, C.; Munday, L.B.; Hoffman, W.M.; Yu, C.C.; Mir, F.U.H.; Kong, F.; Lindsay, A.D.; Whittaker, A.S. Development, verification, and validation of comprehensive acoustic fluid-structure interaction capabilities in an open-source computational platform. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 51, 2188–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veletsos, A.S. Seismic effects in flexible liquid storage tanks. In Proceedings of the 5th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering, Rome, Italy, 25–29 June 1973; Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America: McLean, VA, USA, 1974; Volume 1, pp. 630–639. [Google Scholar]
- Balendra, T.; Ang, K.K.; Paramasivam, P.; Lee, S.L. Free vibration analysis of cylindrical liquid storage tanks. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 1982, 24, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flügge, W. Stresses in Shells; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Habenberger, J. Beitrag zur Berechnung von nachgiebig gelagerten Behältertragwerken unter seismischen Einwirkungen. Ph.D. Thesis, Bauhaus-Universität Weimar, Weimar, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Chiappelloni, L.; Belardi, V.; Serraino, F.; Trupiano, S.; Gaetani, L.; Vivio, F. Structural behaviour of single-deck floating roof tanks subject to seismic loading. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2024, 1306, 012002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudarzi, M.A. Seismic behavior of a single deck floating roof due to second sloshing mode. J. Press. Vessel. Technol. 2013, 135, 011801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotter, J. Buckling of ground-supported cylindrical steel bins under vertical compressive wall loads. In Proceedings of the Metal Structures Conference, Melbourne, Australia, 23–24 May 1985; p. 16. [Google Scholar]
- Causevic, M.; Mitrovic, S. Comparison between non-linear dynamic and static seismic analysis of structures according to European and US provisions. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2011, 9, 467–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosco, M.; Ghersi, A.; Marino, E.M. On the evaluation of seismic response of structures by nonlinear static methods. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2009, 38, 1465–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakalis, K.; Kazantzi, A.K.; Vamvatsikos, D.; Fragiadakis, M. Seismic performance evaluation of liquid storage tanks using nonlinear static procedures. J. Press. Vessel. Technol. 2019, 141, 010902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bal, I.E.; Smyrou, E. Implementation of Emerging Technologies in Seismic Risk Estimation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Earthquake Engineering and Seismology, Bucharest, Romania, 4–9 September 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 279–294. [Google Scholar]


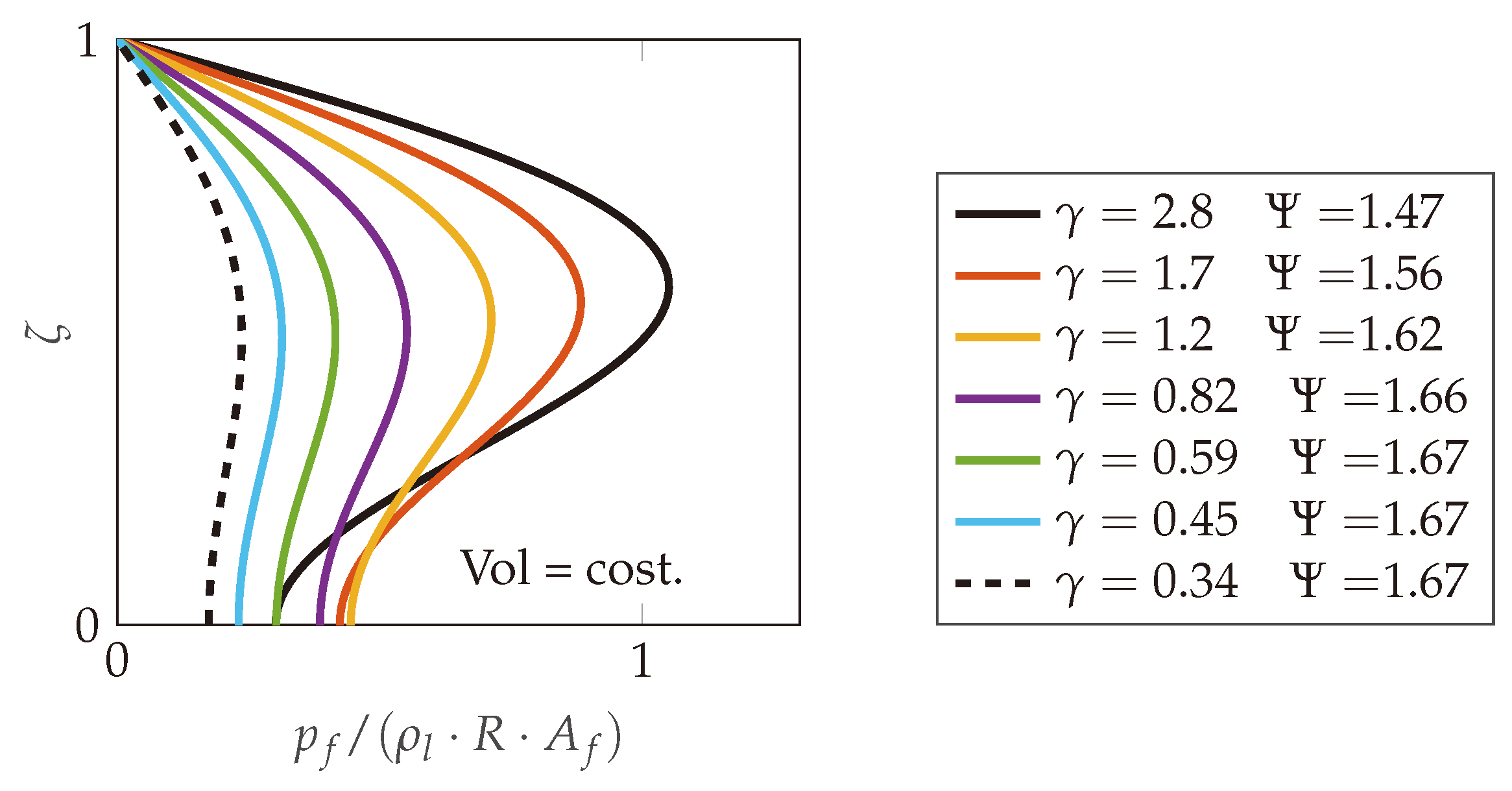






| Tank Design Data | |
|---|---|
| Tank diameter [m] | 27.50 |
| Tank height (filling) [m] | 13.50 |
| Tank height (geometric) [m] | 15.00 |
| Design density of content [kg/m3] | 750.00 |
| Assigned Materials | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material | [MPa] | [MPa] | [GPa] | [kg/m3] | ||
| A283-gr. C | 235 | 0.11 | 236 | 210 | 8000 | 0.3 |
| R-ST-37-2 | 235 | 0.11 | 236 | 210 | 8000 | 0.3 |
| SA106-gr. B | 241 | 0.11 | 242 | 210 | 8000 | 0.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chiappelloni, L.; Serraino, F.; Belardi, V.; Trupiano, S.; Gaetani, L.; Vivio, F. Evaluation of Seismic Effects on Atmospheric Pressure Liquid Storage Tanks. Eng. Proc. 2025, 85, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025085054
Chiappelloni L, Serraino F, Belardi V, Trupiano S, Gaetani L, Vivio F. Evaluation of Seismic Effects on Atmospheric Pressure Liquid Storage Tanks. Engineering Proceedings. 2025; 85(1):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025085054
Chicago/Turabian StyleChiappelloni, Luca, Francesco Serraino, Valerio Belardi, Simone Trupiano, Luca Gaetani, and Francesco Vivio. 2025. "Evaluation of Seismic Effects on Atmospheric Pressure Liquid Storage Tanks" Engineering Proceedings 85, no. 1: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025085054
APA StyleChiappelloni, L., Serraino, F., Belardi, V., Trupiano, S., Gaetani, L., & Vivio, F. (2025). Evaluation of Seismic Effects on Atmospheric Pressure Liquid Storage Tanks. Engineering Proceedings, 85(1), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025085054







