Abstract
In recent years, LiDAR Odometry (LO) and LiDAR Inertial Odometry (LIO) algorithms for robot localization have considerably improved, with significant advancements demonstrated in various benchmarks. However, their performance in agricultural environments remains underexplored. This study addresses this gap by evaluating five state-of-the-art LO and LIO algorithms—LeGO-LOAM, DLO, DLIO, FAST-LIO2, and Point-LIO—in a blueberry farm setting. Using an Ouster OS1-32 LiDAR mounted on a four-wheeled mobile robot, the algorithms were evaluated using the translational error metric across four distinct sequences. DLIO showed the highest accuracy across all sequences, with a minimal error of 0.126 m over a 230 m path, while FAST-LIO2 achieved its lowest translational error of 0.606 m on a U-shaped path. LeGO-LOAM, however, struggled due to the environment’s lack of linear and planar features. The results underscore the effectiveness and potential limitations of these algorithms in agricultural environments, offering insights into future improvements and adaptations.
1. Introduction
LiDAR Odometry (LO) and LiDAR Inertial Odometry (LIO) algorithms enable robot localization by leveraging LiDAR and Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) data to compute odometry. The last decade has witnessed considerable advancements in these algorithms’ performance, evident in benchmarking datasets such as the KITTI Dataset and the Hilti SLAM Challenge. Despite these achievements, challenges persist in specific scenarios, notably in agricultural environments. Addressing this problem does not necessarily entail developing new algorithms as it may be possible to adapt existing ones to function effectively in such environments.
Ref. [1] illustrates the application of various localization algorithms in agriculture by different studies, emphasizing adaptations for these environments. Many of the approaches integrate additional sensors besides LiDAR, including cameras and high-precision GPS, as seen in [2,3,4]. However, such multi-sensor integrations often incur higher costs, sometimes beyond individual project budgets.
In this context, this paper focuses on the performance of LO and LIO algorithms with the aim of avoiding escalating system costs. Conventional LO and LIO algorithms frequently underperform in agricultural settings, yet their specific limitations remain underexplored. This paper conducts a comparative analysis of LO and LIO algorithms in the context of navigating blueberry crops, assessing five state-of-the-art algorithms: LeGO-LOAM [5], DLO [6], DLIO [7], FAST-LIO2 [8], and Point-LIO [9].
The study aims to (1) provide an in-depth analysis of LiDAR inertial odometry algorithms in a blueberry farm setting, and (2) identify potential areas for improvement in algorithm design and implementation. The rest of this article is structured as follows: Section 2 details the materials and methods, including descriptions of the tuning of the algorithms’ parameters. Section 3 discusses comparative results, focusing on translational error as the evaluation metric. Section 4 and Section 5 conclude with a discussion and conclusions, respectively.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Blueberry Crop Dataset and Experimental Setup
The dataset employed for the experiments consists of four distinct sequences of point cloud and Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) data, obtained using an Ouster OS1-32 LiDAR system mounted on a four-wheeled mobile robot. These data were methodically collected at a blueberry farm in Trujillo, Peru.
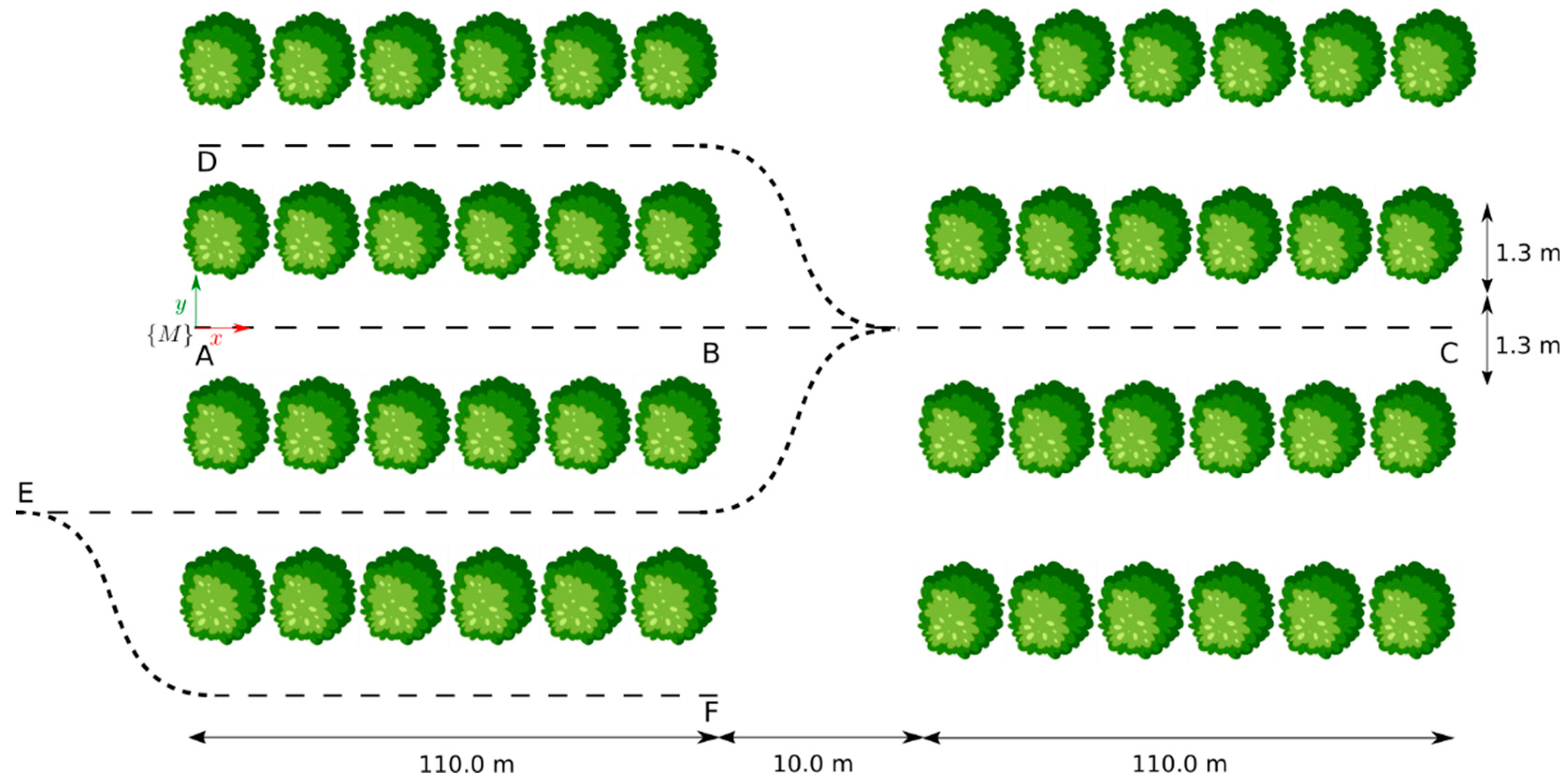
For each sequence, the robot was manually teleoperated starting from the map reference frame, {M}, to emulate navigation patterns that are pertinent to tasks in precision agriculture. The specific trajectories were as follows: (AB) a straight 110 m path along the inter-row space of blueberry crops, (AC) a 230 m linear route starting at the inter-row space, traversing a transit zone between crop blocks, and continuing for another 110 m to the end of a second crop row, (AD) a U-shaped trajectory encompassing sequence AB and the adjacent inter-row space, and (AF) an S-shaped path covering three adjacent inter-row spaces. Figure 1 provides a bird’s eye view of these trajectories within the farm setting. Both farm personnel and in situ measurements contributed to this diagram.
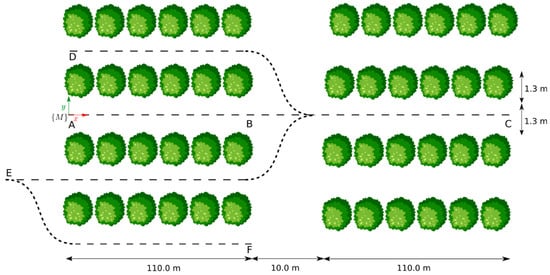
Figure 1.
Designated paths for each sequence followed by the robot at the blueberry farm, where each letter represents a waypoint along the trajectories.
A summary of the details for each sequence of the dataset is presented in Table 1, including the duration of the sequence and average speed the robot sustained during its trajectory, as determined by the robot’s onboard encoders.

Table 1.
Details for all the Sequences of the Blueberry Crop Dataset.
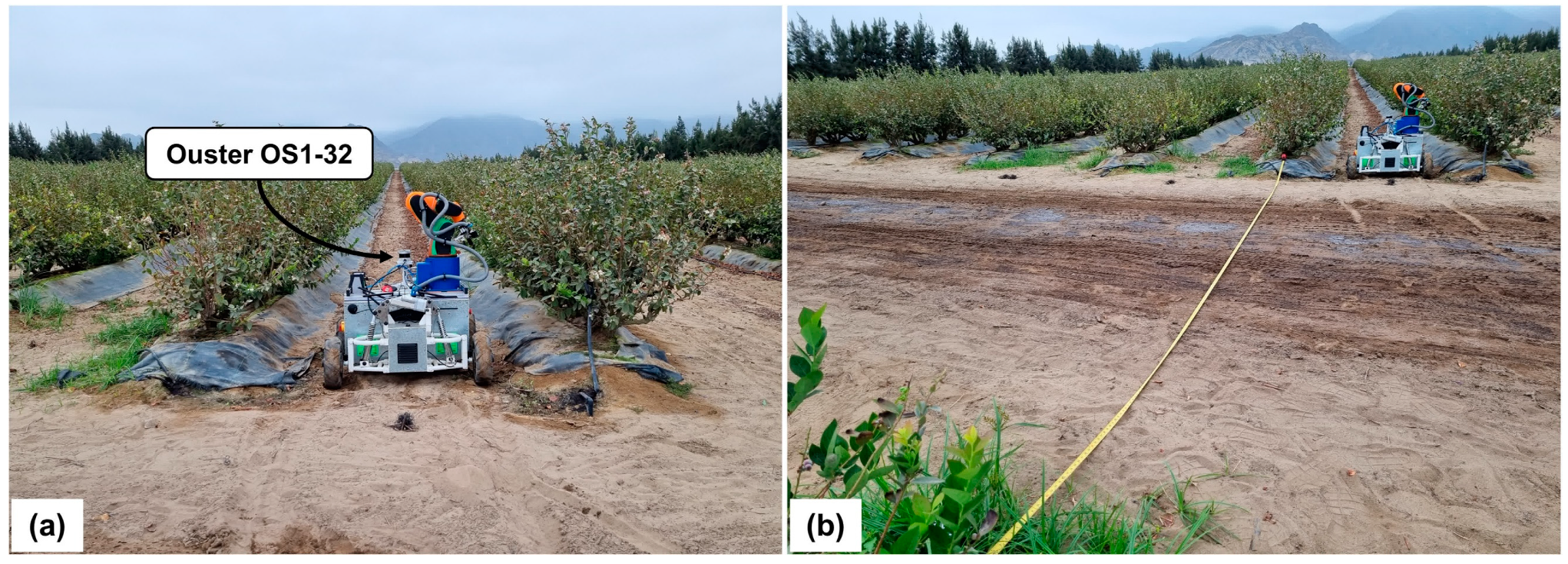
Figure 2 provides a visual representation of the robot’s navigation within the blueberry farm, illustrating the environmental conditions pertinent to the data collection process. Specifically, Figure 2a presents the robot at the onset of its trajectory, corresponding to sequence AB, where the robot’s pose predominantly varies in the x-axis, with minimal deviations in the y-axis. Conversely, Figure 2b captures the robot as it transitions into a different crop block, traversing the transit zone described in sequence AC. This zone is marked and measured using a measuring tape.

Figure 2.
Wheeled mobile robot at the blueberry farm. (a) The robot in its initial position within an inter-row space. (b) The robot transitioning between blocks of crops and the separation between these marked with a yellow measuring tape.
To evaluate the performance of the selected LiDAR Odometry (LO) and LiDAR-Inertial Odometry (LIO) algorithms, the translational error metric was employed. This metric serves as a proxy for assessing accuracy in scenarios where ground truth data for computing absolute trajectory error is unavailable. Specifically, the translational error was calculated using the Euclidean distance between the designated endpoint of each sequence with the corresponding endpoint estimated by each algorithm. This approach enables a quantitative assessment of the positional accuracy of the LO and LIO algorithms within the given experimental context.
2.2. Parameters of the LiDAR Odometry and LiDAR Inertial Odometry Algorithms
The algorithms evaluated in this work each have a different number of parameters. The initialization of these parameters was conducted in accordance with their official repositories, and they were later tuned through iterative testing. The primary aim of this tuning process was the minimization of the translational error. The parameters mentioned in this section were those that produced meaningful variations in the algorithm’s localization performance. The non-mentioned parameters retained their default values.
2.2.1. LeGO-LOAM
In the case of the LeGO-LOAM algorithm, modifications were confined solely to those parameters associated with the hardware configuration of the LiDAR system. Specifically, adjustments were made to align with the specifications of the Ouster OS1-32 LiDAR utilized in the study.
2.2.2. DLO
In the calibration of the DLO algorithm, several parameters were changed from their default values. Both s2s and s2m maxCorrespondenceDistance were set to 0.15, establishing a uniform maximum correspondence for both scan-to-scan and scan-to-map processes. The s2s maxIterations and s2m maxIterations were also set to 4, optimizing the number of iterations for efficient convergence in both stages. Regarding the number of correspondences, s2s kCorrespondences was set to 8, while s2m kCorrespondences was adjusted to 16.
2.2.3. DLIO
The DLIO algorithm was configured to better conform to the environmental geometry and the requirements for the Generalized Iterative Closest Point (GICP) algorithm. Two parameters were specifically adjusted from their default values: the maxCorrespondenceDistance parameter was established at 0.25, and the maxIterations parameter was set to 4. These modifications were implemented to optimize alignment and aid convergence within the given context.
2.2.4. FAST-LIO2
In the optimization of the FAST-LIO2 algorithm, adjustments were made to three parameters. The filter_size_surf parameter was set to 0.75, enhancing its response to the specific characteristics of the terrain and crop structure. The max_iteration parameter was limited to 8, reflecting the need to maintain computational efficiency and accuracy within the complex farm environment. Finally, the point_filter_num was configured to 2.
2.2.5. Point-LIO
For the Point-LIO algorithm, the use_imu_as_input was set to 1, enabling the use of this IMU configuration for improved pose estimation according to the original paper. The point_filter_num was adjusted to 2, to balance processing with data detail retention. Lastly, the filter_size_surf parameter was set to 0.7, aiding in effective pose estimation.
3. Results
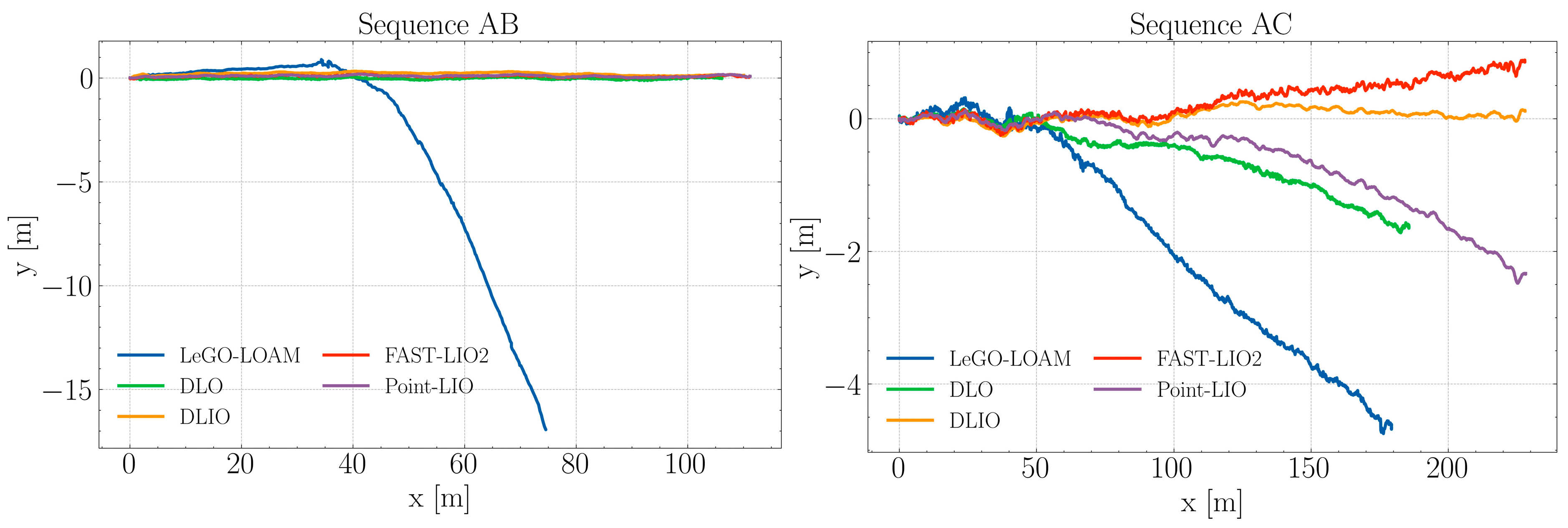
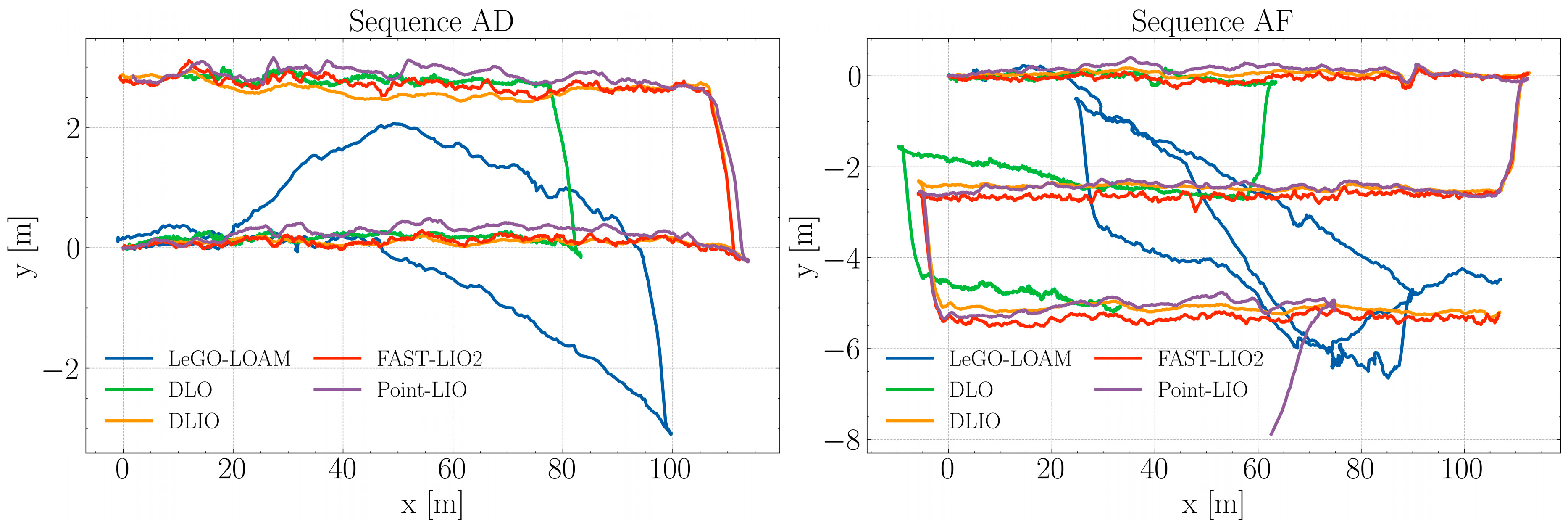
The algorithms were evaluated using the four sequences from the self-collected Blueberry Crop Dataset, each employing distinct approaches for LiDAR odometry and point cloud deskewing, thereby creating a meaningful comparison of the current state-of-the-art algorithms. To ensure consistency in the starting section of the trajectories, a rotation alignment was applied. This involved calculating the offset angle for the estimated trajectories and then applying a rotation matrix to align them with the x-axis, a measure adopted to mitigate potential offset errors from the data collection phase. These tests were conducted on a laptop equipped with an Intel i7-8650U CPU. The resulting trajectories, post-alignment, are depicted in Figure 3 and Figure 4.
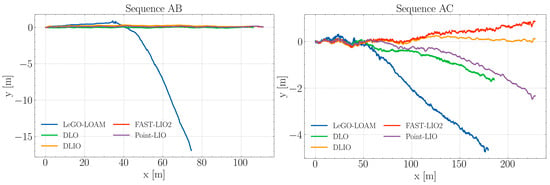
Figure 3.
Estimated trajectories by each algorithm during sequences AB and AC.
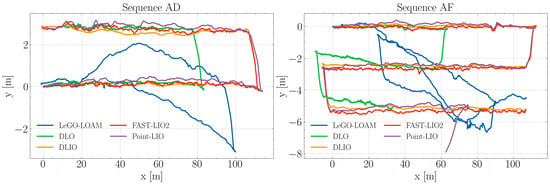
Figure 4.
Estimated trajectories by each algorithm during sequences AD and AF.
Figure 3 illustrates the trajectory estimation for sequence AB amidst blueberry crops. In this sequence, four algorithms exhibit closely grouped trajectories, maintaining linear path consistency. Conversely, LeGO-LOAM initially aligns with these trajectories but begins to diverge noticeably beyond the 40 m mark. This divergence is marked by a sharp deviation from the collective path of the other algorithms. LeGO-LOAM’s estimated path fails to extend beyond 80 m along the x-axis, highlighting a significant discrepancy in its trajectory estimation compared to the other evaluated algorithms.
It can be noted that in sequence AC, DLIO, FAST-LIO2, and Point-LIO show consistency with each other regarding the path length, although they start to separate from each other as distance increases. DLO’s estimation resembles that of Point-LIO but is unable to complete the route. LeGO-LOAM exhibits the most significant divergence from the intended path early on and continues this trend throughout the sequence. This may reflect limitations in the algorithm’s ability to handle the challenges in the present context, such as feature-poor areas within the crops for feature matching, only managing to get past 175 m due to the presence of windbreak nets at the middle and end regions of the sequence.
In Figure 4, sequence AD shows that the DLIO, FAST-LIO2, and Point-LIO algorithms exhibit a high degree of overlap, indicating similar performance in trajectory estimation. These paths closely adhere to the intended sideways U-shaped path, reflecting robustness in these algorithms’ ability to handle the environmental conditions during this experiment. The DLO algorithm while in alignment with the aforementioned three, incorrectly estimates the horizontal displacement of the robot, stopping at around 83 m for the first linear section. Conversely, LeGO-LOAM maintains a linear path until the 40 m mark, where it starts failing to compute the ego-motion of the platform. Nonetheless, when approaching the end of the first linear section, it managed to retrieve features from the windbreak net dividing the blueberry crop blocks, which allowed it to closely estimate the turn to the left and the beginning of the returning path.
During sequence AF, the DLIO and FAST-LIO2 algorithms both again show a significant level of similarity in their estimated paths, closely approximating the intended S-shape. This consistent performance underscores these algorithms’ robustness to aggressive motion, as well as the effective integration of data from the IMU, which is critical in maintaining trajectory estimation accuracy through the varying dynamics of agricultural settings. Point-LIO also showed a comparable performance up until the last section of the trajectory when it incorrectly estimated a turn to the right. In the case of DLO, both transitions to the contiguous inter-row spaces were correctly captured; however, the horizontal sections did not match the actual length of the blueberry bush rows. Finally, LeGO-LOAM initially adheres closely to the path but deviates noticeably around the middle and end sections. The erratic shape of this path, particularly in the turns of the S-curve, points to deficiencies in the algorithm’s feature extraction and matching, possibly exacerbated by the nature of the agricultural environment.
Table 2 summarizes the results for the translational error. From the data, it can be noted that DLIO achieved a superior performance across all test sequences. With translational errors of 0.142 m, 0.126 m, 0.548 m, and 3.129 m in sequences AB, AC, AD, and AF, respectively. DLIO demonstrates a consistently high level of accuracy. In contrast, LeGO-LOAM, an LO algorithm, shows a marked discrepancy in performance. Notably, in sequences AD and AF, the lower translational errors (2.655 m and 3.141 m, respectively) are misleading. The asterisks indicating sub-optimal paths reveal significant divergence from the intended trajectories. This consistent under-performance across varied sequences highlights inherent limitations in LeGO-LOAM’s approach to LiDAR-based odometry for agricultural settings.

Table 2.
Comparison with Blueberry Crop Dataset.
DLO, another LO algorithm, exhibits a varying performance profile. It achieves a relatively low error in sequence AB (3.882 m) but records a substantial error in sequence AF (76.712 m). This inconsistency may point to limitations in the algorithm’s handling of diverse environmental conditions typical of agricultural settings. The other LIO algorithms, FAST-LIO2 and Point-LIO, show moderate performance levels. However, Point-LIO encounters significant challenges in sequence AF, with an error of 47.514 m, indicating potential issues with reliability in this environment.
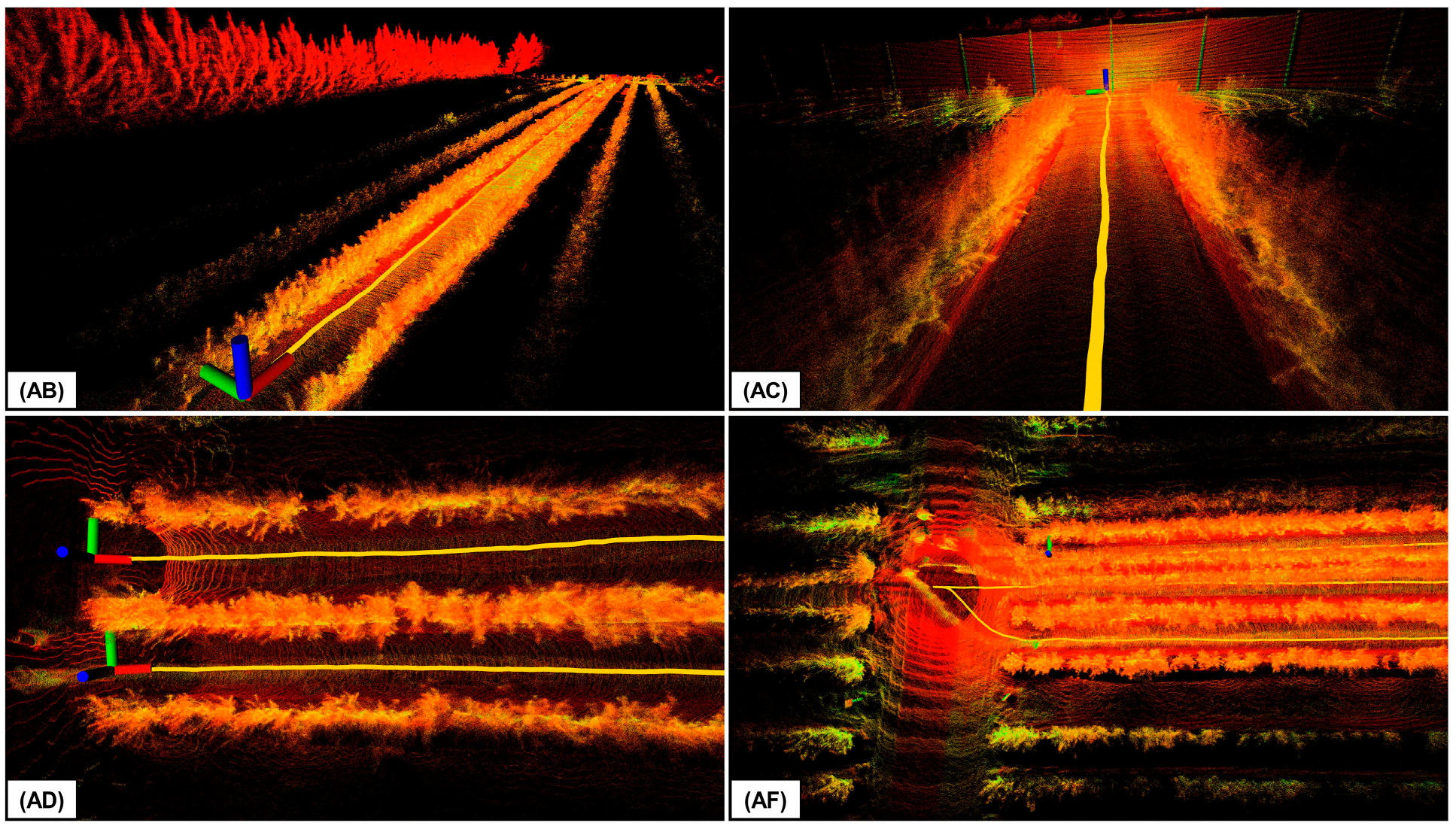
Figure 5 illustrates the 3D point cloud maps generated by DLIO in each of the sequences, highlighting DLIO’s capability to capture detailed environmental features. These maps are essential for autonomous mobile robots, providing data for terrain traversability assessment and supporting applications such as crop monitoring.
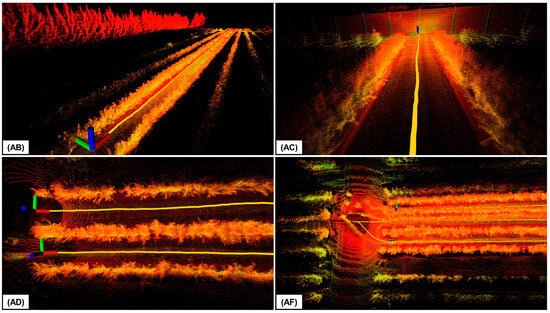
Figure 5.
Close-up views of the 3D maps generated using DLIO, with each label designating the corresponding sequence from the Blueberry Crop Dataset. The path taken to create these maps is shown in yellow. The point cloud color indicates the intensity of the point return.
4. Discussion
The LiDAR Inertial Odometry (LIO) algorithms, particularly DLIO and Fast-LIO, effectively manage cumulative errors and deskew point cloud data in agricultural settings as evidenced in the experiments. This effectiveness is attributed to the precise compensation for sensor drift and environmental factors, as opposed to LiDAR-only-based methods. The integration of a six-axis Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) with LiDAR point cloud data, without necessitating high-grade sensors, significantly enhances state estimation, which is essential for long-distance navigation. While DLIO is robust against aggressive motion, it is necessary to consider adequate parameter values to prevent convergence issues that may negatively influence pose estimation and make autonomous navigation unreliable.
5. Conclusions
This study assessed the localization capabilities of five LiDAR odometry and LiDAR Inertial odometry algorithms, namely LeGO-LOAM, DLO, DLIO, FAST-LIO2, and Point-LIO. Experiments were conducted at a blueberry farm, utilizing an Ouster OS1-32 LiDAR mounted on a four-wheeled robot to record four distinct sequences. DLIO emerged as the most accurate, achieving a minimal error of 0.126 m in a 230 m linear path through the blueberry crops. FAST-LIO2 also exhibited robust performance across all sequences with its lowest translational error being 0.606 m. In contrast, LeGO-LOAM’s path estimation was notably inaccurate, primarily due to the absence of linear and planar features, with the existing windbreak nets proving insufficient. In future work, we plan to test algorithms such as those presented in [10,11], which were used in the DARPA Subterranean Challenge. Finally, this research offered valuable insights into the efficacy of various LO/LIO algorithms within agricultural environments and may aid in guiding future research in robot localization and mapping, particularly for applications beyond urban landscapes where certain algorithms are prone to face challenges.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.H. and C.G.; methodology and software, R.H. and C.G.; formal analysis, R.H.; writing—original draft preparation, R.H.; writing—review and editing, R.H., C.G. and S.P.; supervision, S.P.; project administration, S.P.; funding acquisition, S.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Fondo Nacional de Desarrollo Científico, Tecnológico y de Innovación Tecnológica (171-2020-FONDECYT).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available on request from the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ding, H.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, J.; Yan, Y.; Tian, G.; Gu, B. Recent Developments and Applications of Simultaneous Localization and Mapping in Agriculture. J. Field Robot. 2022, 39, 956–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Kang, H.; Chen, C. ORB-Livox: A Real-Time Dynamic System for Fruit Detection and Localization. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 209, 107834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohi, N.; Lassak, K.; Watson, R.; Strader, J.; Du, Y.; Yang, C.; Hedrick, G.; Nguyen, J.; Harper, S.; Reynolds, D.; et al. Design of an Autonomous Precision Pollination Robot. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Madrid, Spain, 1–5 October 2018; pp. 7711–7718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpyshev, P.; Ilin, V.; Kalinov, I.; Petrovsky, A.; Tsetserukou, D. Autonomous Mobile Robot for Apple Plant Disease Detection Based on CNN and Multi-Spectral Vision System. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (SII), Iwaki, Japan, 11–14 January 2021; pp. 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, T.; Englot, B. LeGO-LOAM: Lightweight and Ground-Optimized Lidar Odometry and Mapping on Variable Terrain. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Madrid, Spain, 1–5 October 2018; pp. 4758–4765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Lopez, B.T.; Agha-mohammadi, A.a.; Mehta, A. Direct LiDAR Odometry: Fast Localization with Dense Point Clouds. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2110.00605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Nemiroff, R.; Lopez, B.T. Direct LiDAR-Inertial Odometry: Lightweight LIO with Continuous-Time Motion Correction. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2203.03749. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Cai, Y.; He, D.; Lin, J.; Zhang, F. FAST-LIO2: Fast Direct LiDAR-inertial Odometry. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.06829. [Google Scholar]
- He, D.; Xu, W.; Chen, N.; Kong, F.; Yuan, C.; Zhang, F. Point-LIO: Robust High-Bandwidth Light Detection and Ranging Inertial Odometry. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2023, 5, 2200459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, P.; Nogueira, L.; Scherer, S. Super odometry: Imu-centric lidar-visual-inertial estimator for challenging environments. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Prague, Czech Republic, 27 September–1 October 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 8729–8736. [Google Scholar]
- Nubert, J.; Khattak, S.; Hutter, M. Graph-based Multi-sensor Fusion for Consistent Localization of Autonomous Construction Robots. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 23–27 May 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).