Abstract
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is a neurodegenerative disorder that has a complex differential diagnosis that has not been elucidated due to the variety of clinical manifestations or specific biological markers. This review aims at studying the application of ensemble machine learning classifiers for enhancing the classification of ALS based on several models such as RandomForest, ExtraTrees, XGBoost, LightGBM, CatBoost, AdaBoost, Voting, and Stacking classifiers. Ensemble models offer enhanced performance in diagnosing ALS by utilizing diverse classification techniques with appropriate feature selection method. This study finds that while the Voting classifier produces comparatively inferior results, the ExtraTrees and CatBoost models perform better with adequate precision and recall and specificity. These studies on improvements in ensemble learning methods have the potential to greatly improve disease diagnosis and early identification, which will support individualized care plans for patient with ALS.
1. Introduction
Neurological disorders such as sporadic ALS and familial ALS are two main categories of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Sporadic ALS is more frequent, and it occurs in roughly 90–95% of patients, meaning they cannot trace the disease back to a genetic source in their families. Changes in vocal characteristics in patients first appear at the age of 55–65 years on average. It develops by attacking the motor neurons, which leads to muscle wastage and weakness in the muscles used for speech and swallowing, leading to muscle paralysis. One gene can develop the symptoms of ALS and it can also be caused by mutations. Familial ALS is responsible for 5–10% of cases and the pattern of inheritance is autosomal dominant. Familial ALS generally progresses more rapidly than the sporadic type, and is usually seen in a younger population.
Clinical examination together with the elimination of other possible diseases forms part of the diagnostic procedure in ALS. Assessing the muscle and nerve involvement and the characteristics of denervation and reinnervation that are particular to ALS electroneuromyography and nerve conduction studies are obligatory. For instance, a blood and spinal fluid test will help eliminate other cause of neurological issues while magnetic resonance imaging curtails structural issues of the brain and spine. Genetic testing is essential when diagnosing Familial ALS since, in most of the cases, the patient will have previously seen other family members suffering from the same disease. There are not many biomarkers detectable in ALS patients, therefore early detection of the disease is challenging given the symptoms of the disease mentioned above. By examining patient histories, genetic profiles, and EMG results to find patterns for an early diagnosis, machine learning applied to clinical data has improved the detection and management of ALS in recent years. Additionally, wearable technology, voice, and movement data can be used by ML models to follow the evolution of diseases, enabling individualized care. This methodology improves early identification, forecasts results, and could provide fresh perspectives on ALS and potential therapeutic options.
2. Literature Review
ALS is a type of neurological disorder that usually leads to muscle atrophy, muscle weakness, and eventual paralysis. Most other conditions may pose challenges to the physician attempting to make a diagnosis at early stages when muscular strength is slightly affected. Previously, patients were diagnosed based on clinical examinations, electrodiagnostic techniques, and imaging studies using magnetic resonance. Studies are being performed that implement deep learning and machine learning in relation to diagnosis and prognosis of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. We developed a Deep Ensemble Forward Neural Network aimed at measuring cognitive performance of patients suffering from ALS. The network simulated has a target accuracy rate of 95%. There is one neural network that demonstrates the potential power of machine learning to enhance diagnostic capability by integrating imaging and clinical parameters. This network consists of multiple types. Erdaş et al. [1] focused on improving the diagnosis of neurodegenerative diseases using 3-D CNN and Convolutional LSTM models. These include Huntington’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
These models demonstrate some approaches that the deep learning and machine learning employed may operate on different sorts of motor function deficits. In the course of their research, Iadanza et al. [2] employed gene expression data for their model training. Leão et al. [3] described a vision transformer model as an efficient means in the diagnosis proven in the analysis of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. This model analyses MRI images and carries out the extraction of spatial as well as frequency information. These snapshots illustrate the likely integration of various patient data into deep learning approaches that could assist in the more challenging aspect of developing and implementing diagnostic and treatment options for ALS. Longitudinal studies are necessary for the assessment of ALS regarding the patients’ further potentialities. In their paper, Migliorelli et al. [4] developed a CNN named “DDK-AID” for assessment of ALS language functions. This CNN was created based on studies of neurological audio recordings. The recent developments in technology have made it easy to keep track of a disease in real time with more focus on early detection of language-related problems. Studies have been performed on sEMG as a method among the accessible non-invasive approaches to diagnostics. Zhang et al. [5] devised three diagnostic criteria designed to differentiate between healthy individuals and patients with ALS, including the clustering index, the kurtosis of the EMG amplitude histogram, and the kurtosis of the EMG crossing rate expansion. At the same time, Behler et al. [6] studied whether it is plausible to obtain the biological markers of ALS using machine learning and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI). Without going into too much detail, it was found that with the help of machine learning algorithms, abnormalities in large DTI datasets caused by degenerative processes of white matter motor neurons in ALS could be detected. This could help in the development of concepts in new diagnostic as well as predictive interventions for ALS. Ahangaran et al. [7] utilized causal graph analysis to examine the connection between genetics and the progression of ALS. There is also a huge potential in this domain for applying machine learning and deep learning techniques. The model examined three levels and rates of progression in those affected by ALS: slow, moderate, and rapid progression. The AALSFRS-R score was fed into the program. In the end, comparing their approaches to more traditional methods, such as linear regression or support vector machine regression, they came to the conclusion that the causal graph approach brought the best results concerning the development of the disease. To some extent, and more recently, the genetic components are being integrated into the medical diagnosis. In research involving 99 caregivers and individuals with sclerosis (ALS), it was discovered that the burden on caregivers was greatly influenced by their emotional well-being and overall quality of life, highlighting the importance of utilizing technology to identify the need for tailored therapy solutions for caregivers facing challenges in caregiving situations for ALS patients. Burgh et al. [8] examined how clinical information and MRI scans could help predict the life expectancy of patients with ALS using learning techniques. The combination of data and MRI images advanced the development of deep learning algorithms. The results demonstrated an 84% improvement in accuracy when utilizing this approach, suggesting that MRI data could play a role in predicting the survival outlook for ALS patients. Bean et al. [9], on the other hand, utilized machine learning to discover genes associated with ALS. This was achieved by an independent study. An ontology-driven system for mining gene annotations and protein–protein interaction data discovered ALS and other significant biological processes.
This study is about how machine learning can be applied to help discover new genetic targets for ALS research and treatment. Despite great advancements, ALS pathogenesis and diagnosis are still vague. The unpredictable nature of ALS throws a barrier toward the development of effective diagnostic and prognostic tools. Onset of ALS cannot be predicted due to the inherent unpredictability of the disease in such a manner that diagnostic tests would only work at the time individuals develop symptoms. A large dataset spanning genomic, biomarker, and clinical information is needed for a more detailed mapping of the genetic basis of ALS.
Forecasting of the disease might be facilitated by an ALS-Net, the deep learning architecture designed by Yin et al. [10]. While increasing detection rates could be an objective, benefits of such strategies have not been ruled out. Deep learning and machine learning studies have significantly expanded our understanding of ALS and the diagnosis mechanisms related to it. Thus, diagnostics have greatly improved due to the integration of the imaging, genetic, and clinical data. In addition, recent strategies for offering treatment for ALS are emerging based on machine learning–based computational algorithms used to decide on the stress factors of caregivers and survival prospects. The intrinsic diversity of ALS and the need for bigger, more comprehensive datasets are two ongoing problems. More research is needed to develop expandable and non-invasive monitoring technologies, improve genetic testing procedures, and create personalized diagnostic models. If these barriers can be removed, the quality of life for those suffering from ALS and their caregivers might improve dramatically. It is equally important to promote early diagnosis and individualized treatment. Table 1 offers a brief review on existing works for ALS classification.

Table 1.
Reviews on existing works for ALS classification.
3. Methodology
Several ensemble learning models are used in this work to improve prediction robustness and accuracy for ALS classification. Developed from numerous decision trees, the RandomForestClassifier is a basic model that reduces overfitting and enhances generalization. In a comparable way, the ExtraTreesClassifier expands on this idea by employing random splits, which frequently produce different trees with quicker training periods. Using a distinct methodology, the GradientBoostingClassifier builds models one after the other, correcting the mistakes of the earlier models to produce higher accuracy. XGBoost is an optimized version of gradient boosting which is prominent for its efficiency making it suitable for large datasets due to its ability to handle missing values and implement regularization techniques.
LightGBM, another important model examined in this paper, has been optimized to be highly efficient and has the ability to process categorical information directly, which minimizes the need for preprocessing. With its unique ordered boosting technique, the CatBoost model reduces overfitting and performs exceptionally well with categorical data. While the BaggingClassifier trains models on various subsets of the data to efficiently minimize variance and prevent overfitting, AdaBoost combines many weak classifiers to boost accuracy by modifying the weights of instances based on prior misclassifications. Together with these models, this work constructs a StackingClassifier, which takes advantage of the capabilities of each model by leveraging the information from many base classifiers to inform a higher-level meta-classifier. To improve accuracy, the VotingClassifier integrates predictions from multiple models using both hard and soft voting techniques. Last but not least, an ensemble neural network that leverages neural networks’ capacity to identify intricate patterns in data combines two Multilayer Perceptron classifiers through soft voting. In medical contexts, where precise diagnoses can have a substantial impact on patient outcomes, it is imperative that ensemble approaches such as this one work together to improve the prediction performance in ALS classification.
4. Experiments and Results
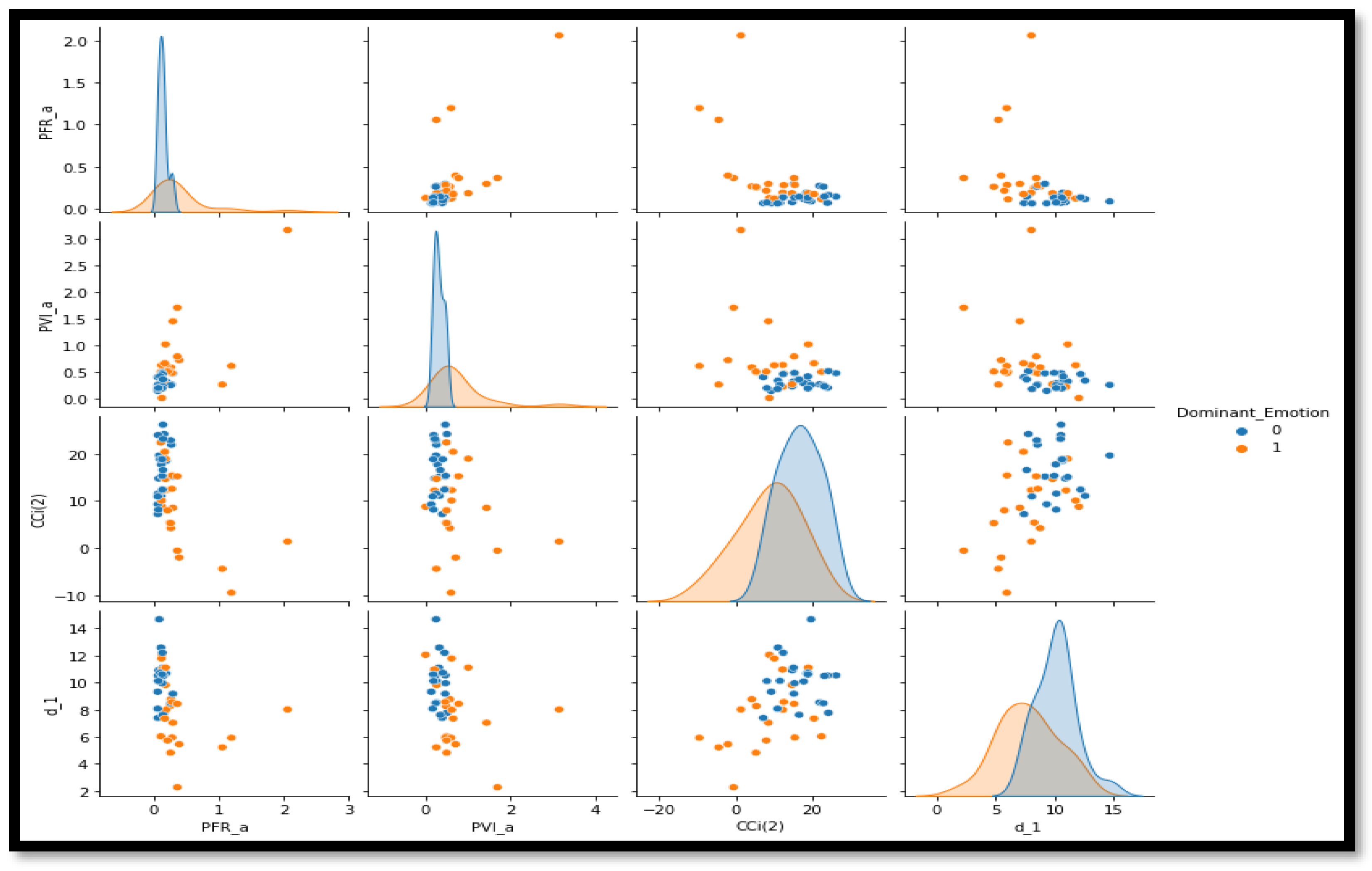
In order to improve model performance for the categorization of ALS, feature selection is essential similar to any domain where classification involved features. To prepare for model training, the dataset first goes through preprocessing, which involves encoding categorical features and standardizing numerical values. To systematically select and maintain the most significant features, the RandomForestClassifier is used as the base estimator in the Recursive Feature Elimination approach. By using an incremental approach that eliminates the features with the lowest significance each time, the final four features are determined to have incredible potential of enhancing the predictive value of the models. The pair plot of these features is provided in Figure 1. Due to these extracted features, the subsequent ensemble models are able to work more effectively and be computationally more explosive by eliminating dimensionality. The experiments carried out include setting up and assessing multiple kinds of ensemble classifiers, such as RandomForest, XGBoost, LightGBM, and Voting and Stacking techniques. Through each model, various methods of performance analysis are examined and include accuracy, recall, specificity, F1 score, and AUC-ROC for a comprehensive understanding of how well each model predicts data. This systematic approach to feature selection and model experimentation ensures that the classification framework is both robust and interpretable, which ultimately facilitates more accurate predictions in ALS diagnosis. Figure 2 provides performance of classification of ALS using different ensemble machine leaning classifiers.
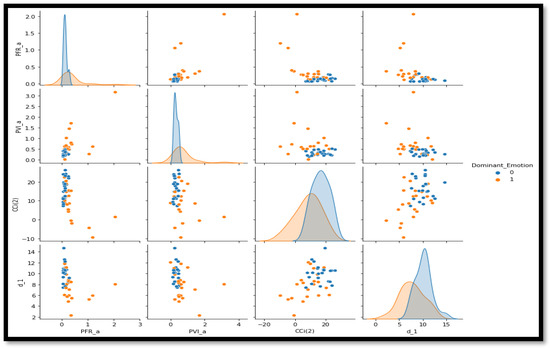
Figure 1.
Pair plot for prominent features selected through the RFE method.
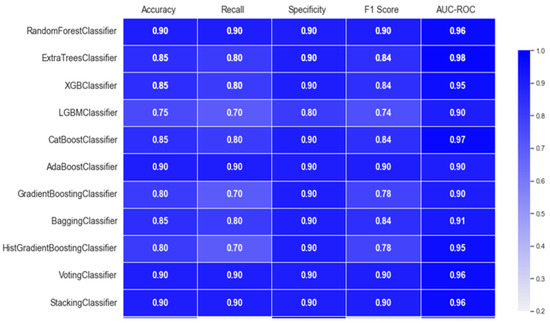
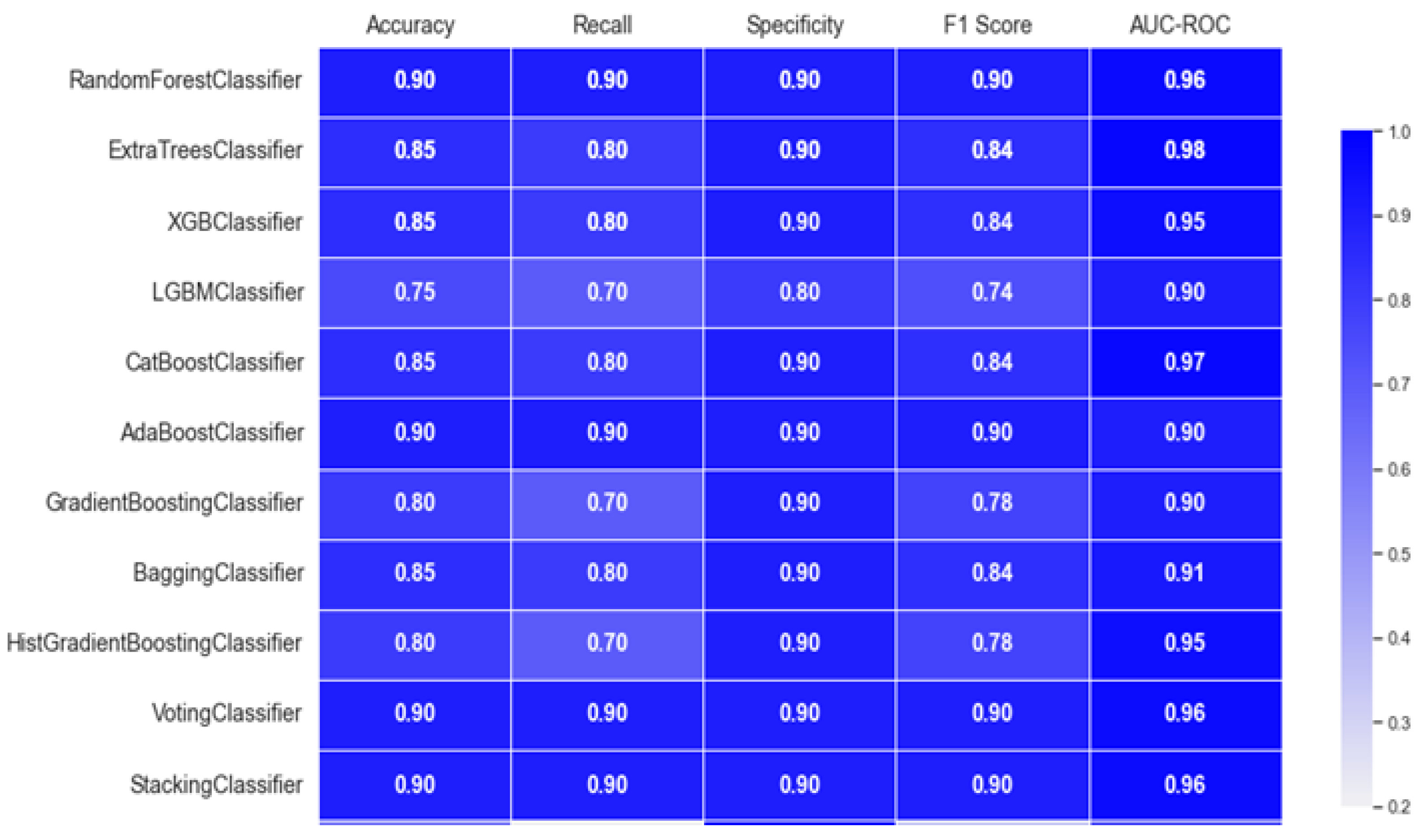
Figure 2.
Performance of classification of ALS using different ensemble machine leaning classifiers.
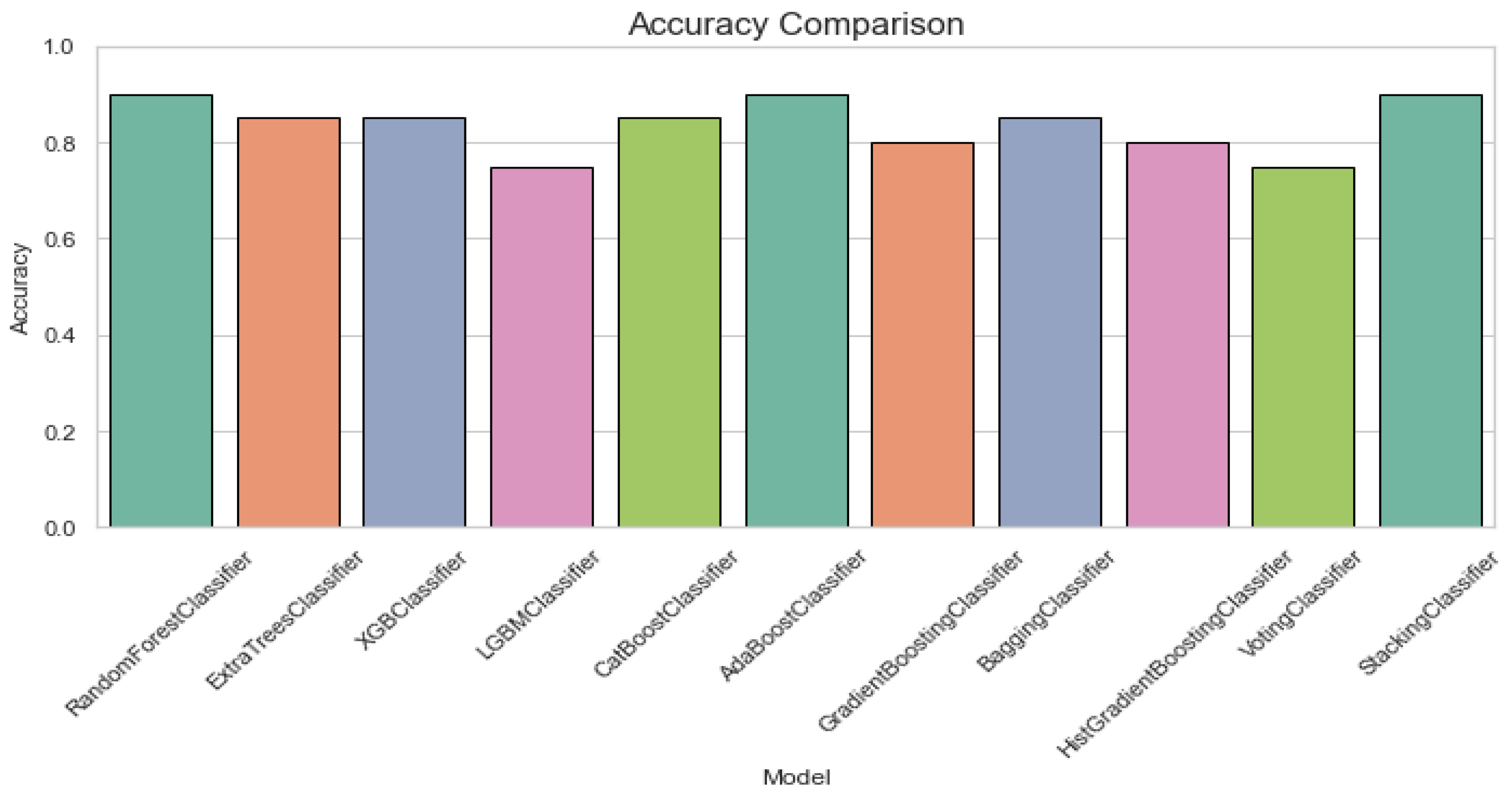
The RandomForestClassifier and AdaBoostClassifier show strong performance across all metrics, with 0.90 for accuracy, recall, specificity, and F1 score, and AUC-ROC values above 0.95. ExtraTrees, XGBoost, and CatBoost also perform well with slight differences in recall and specificity. The LGBMClassifier lags slightly, especially in recall and F1 score. Figure 3 offers an accuracy comparison plot for classification of ALS using different ensemble machine leaning classifiers. The Accuracy Comparison chart shows that the AdaBoostClassifier and StackingClassifier have the highest accuracy slightly above 0.9. LGBMClassifier has the lowest accuracy, around 0.75, while the other models, including RandomForest, XGBoost, and ExtraTrees perform a similar score close to 0.85.
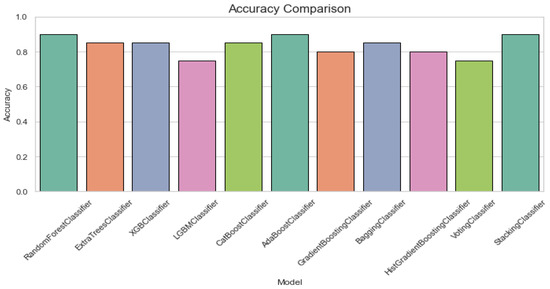
Figure 3.
Accuracy comparison plot for classification of ALS using different ensemble machine leaning classifiers.
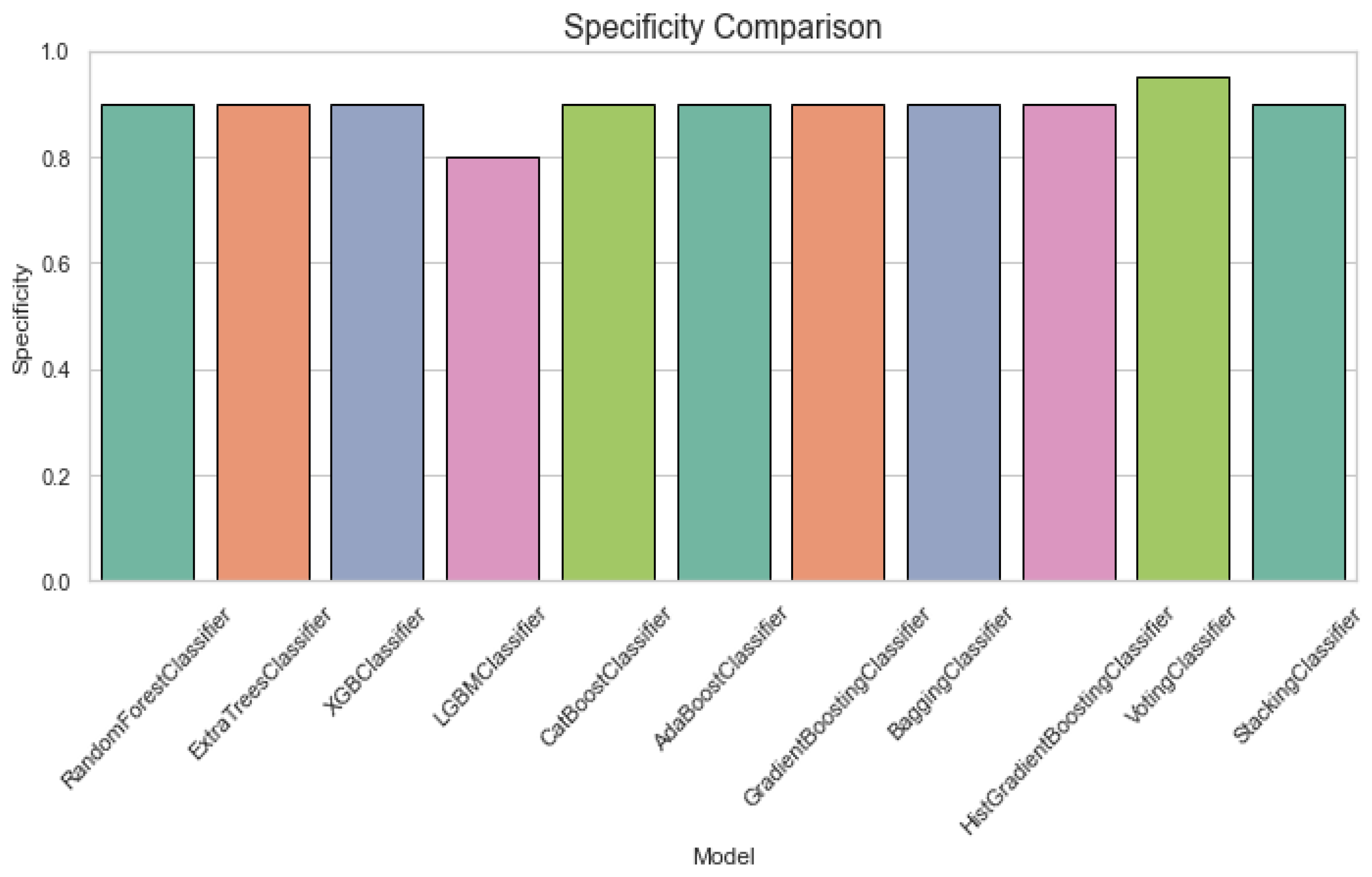
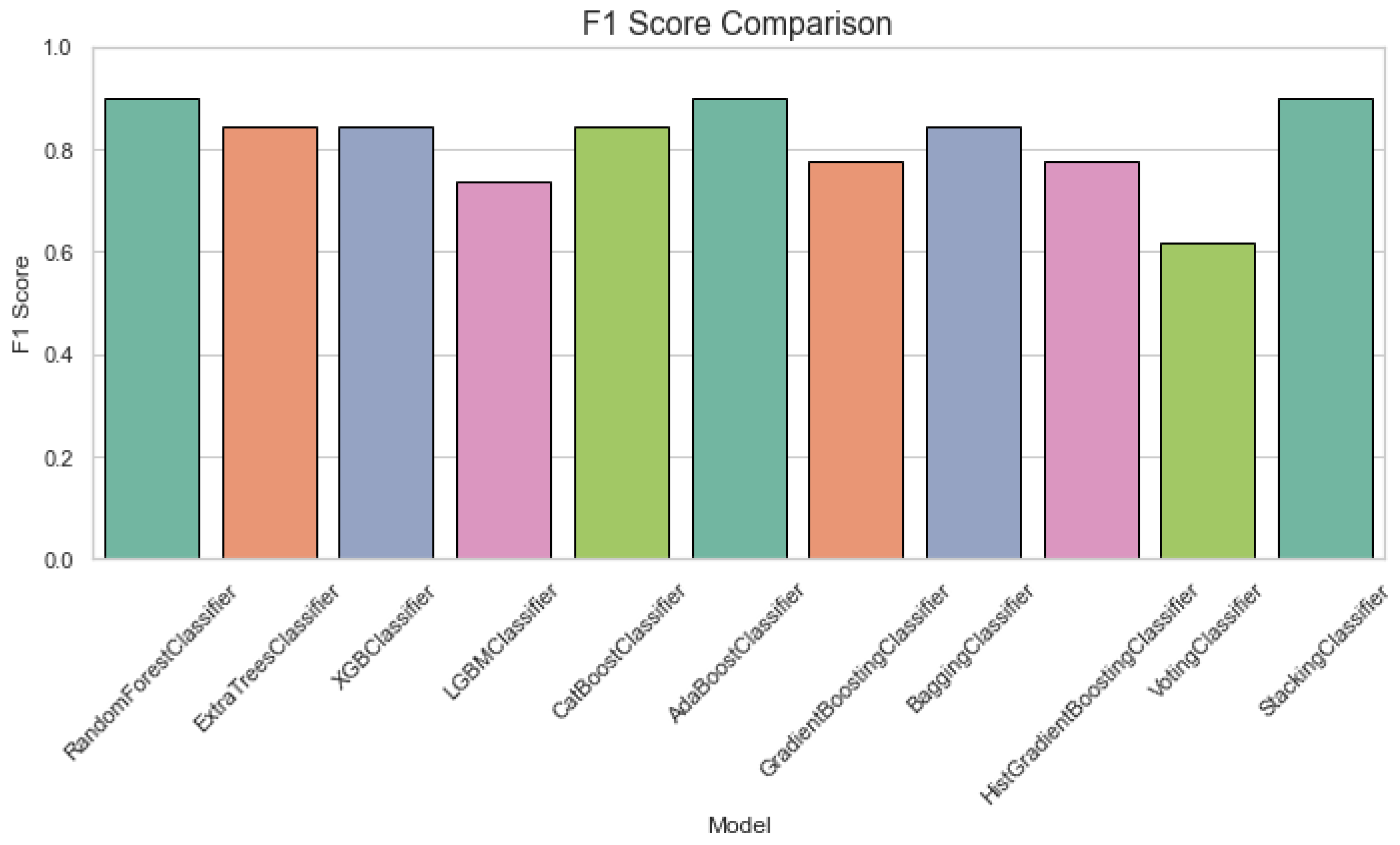
Figure 4 displays a specificity comparison plot for classification of ALS using different ensemble machine leaning classifiers. The Specificity Comparison chart indicates that all classifiers perform well, with most achieving scores above 0.8. The VotingClassifier stands out with a perfect specificity of 1.0, while the other models, including RandomForest and ExtraTrees, maintain strong performance with scores close to 0.9. Figure 5 provides an F1 score comparison plot for ALS classification using different ensemble machine leaning classifiers. The chart shows that most models achieve F1 scores above 0.8, with StackingClassifier performing the best followed by the GradientBoostingClassifier and AdaBoostClassifier. The VotingClassifier has the lowest F1 score, suggesting that it underperforms compared to the other ensemble methods.
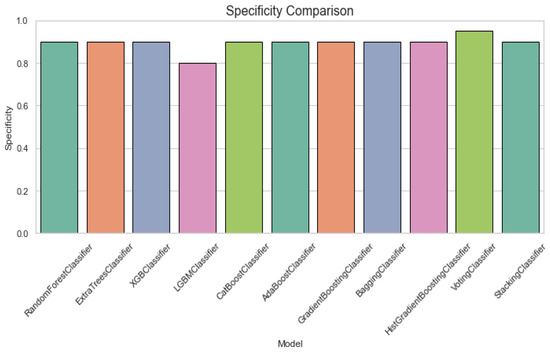
Figure 4.
Specificity comparison plot for classification of ALS using different ensemble machine leaning classifiers.
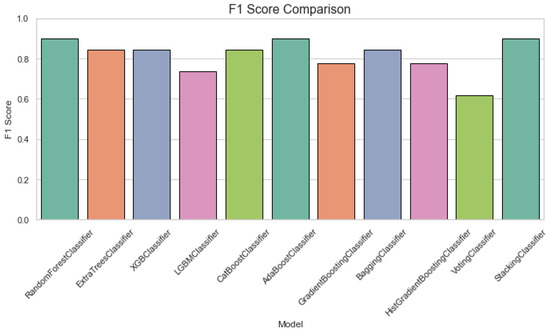
Figure 5.
F1 score comparision plot for classification of using different ensemble machine leaning classifiers.
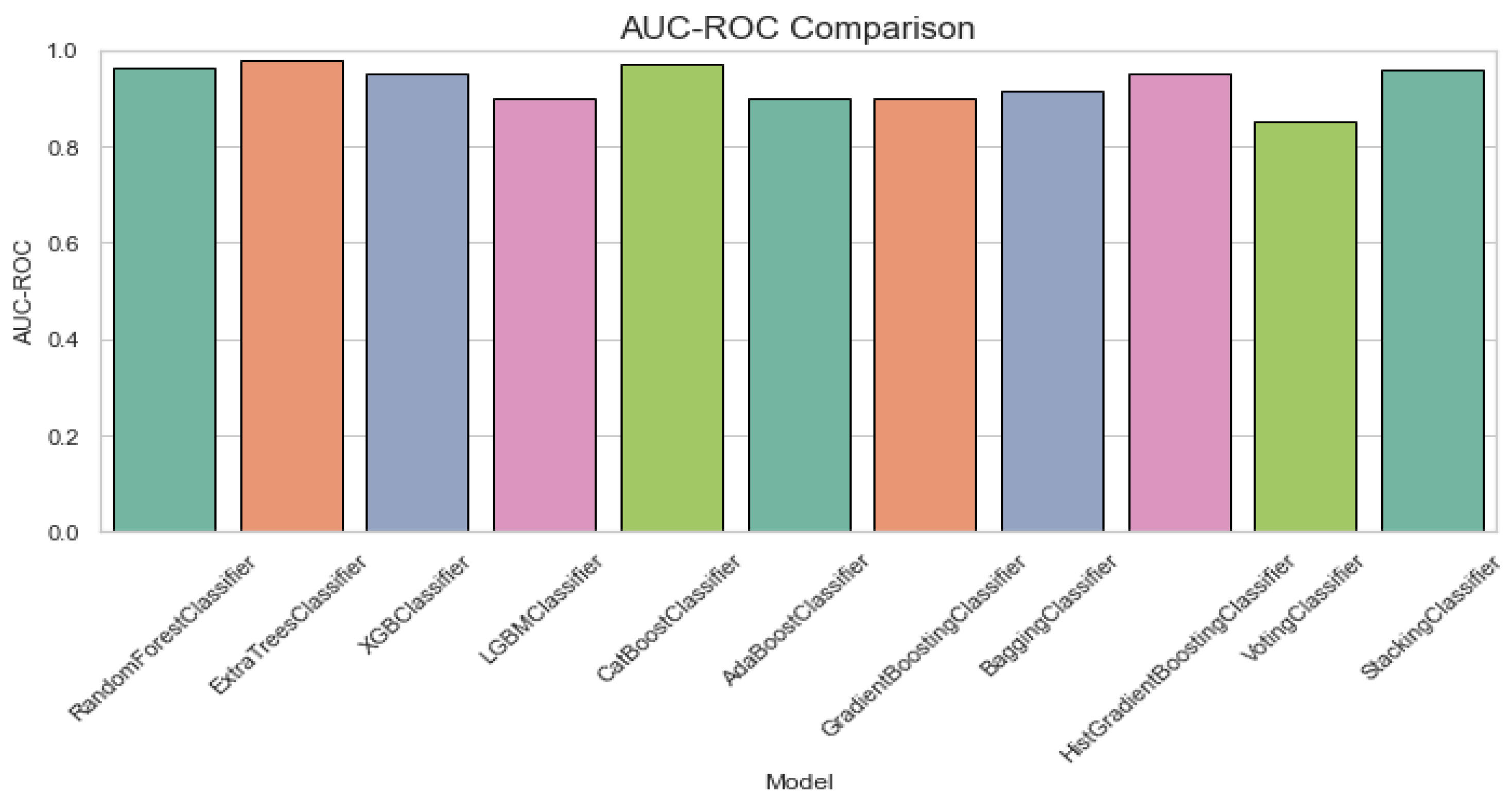
Figure 6 displays AUC-ROC comparison plot for ALS classification. The AUC-ROC comparison chart shows that most models perform well with AUC-ROC values close to 0.9. StackingClassifier and RandomForestClassifier achieve the highest AUC-ROC, while VotingClassifier performs the worst, slightly below the others.
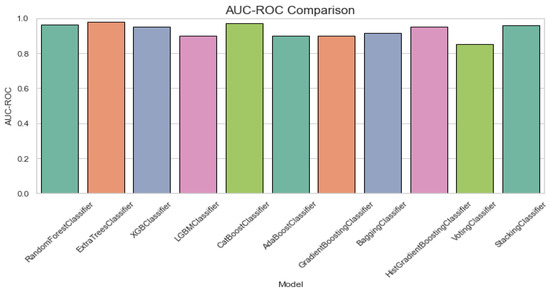
Figure 6.
AUC-ROC comparison plot for classification of ALS using different ensemble machine leaning classifiers.
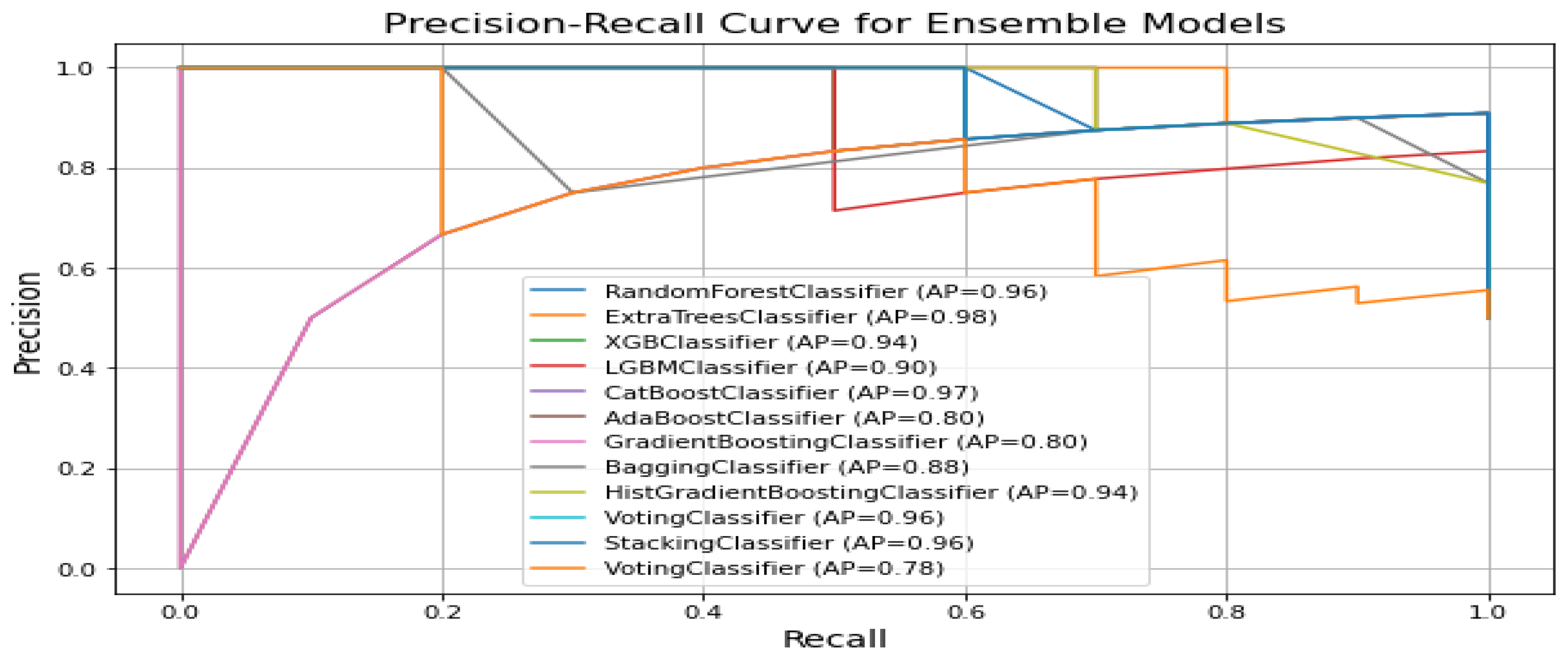
Figure 7 displays the precision recall curves for classification of ALS using different ensemble machine leaning classifiers. The precision–recall curve shows that ExtraTreesClassifier and CatBoostClassifier have the highest average precision (i.e., 0.98 and 0.97, respectively). This indicates superior precision and recall performance. The VotingClassifier performs the worst (i.e., 0.78), suggesting weaker precision–recall trade-offs compared to other ensemble models like the RandomForestClassifier and StackingClassifier with a 0.96 score.
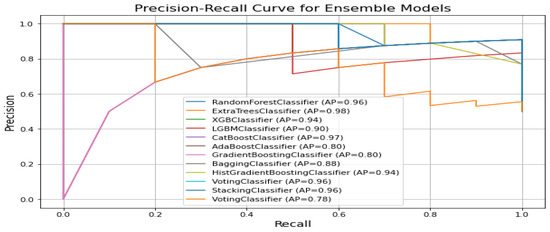
Figure 7.
Specificity comparision plot for classification of ALS using different ensemble machine leaning classifiers.
5. Conclusions
The predicted accuracy and resilience of ALS classification models are greatly improved by the application of ensemble machine learning classifiers. The models with the highest precision and recall are the ExtraTreesClassifier and CatBoostClassifier, whereas the VotingClassifier performs poorly. Through the reduction of dimensionality and enhancement of computing efficiency, feature selection techniques such as RFE aid in the optimization of model performance. Despite these advancements, few challenges remain unsolved such as including the need for larger datasets and more comprehensive diagnostic biomarkers. Continued refinement of machine learning models and the integration of novel data sources hold great promise for improving early diagnosis, treatment outcomes, and the overall quality of life for ALS patients.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.T. and A.S.; methodology, A.S.; coding, S.T.; validation, A.S.; formal analysis, S.T.; investigation, S.T.; resources, A.S.; data curation, A.S.; writing—original draft preparation, S.T.; writing—review and editing, A.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Erdaş, Ç.B.; Sümer, E.; Kibaroğlu, S. Neurodegenerative disease detection and severity prediction using deep learning ap-proaches. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2021, 70, 103069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iadanza, E.; Fabbri, R.; Goretti, F.; Nardo, G.; Niccolai, E.; Bendotti, C.; Amedei, A. Machine learning for analysis of gene expression data in fast- and slow-progressing amyotrophic lateral sclerosis murine models. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 42, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leão, T.; Madeira, S.C.; Gromicho, M.; de Carvalho, M.; Carvalho, A.M. Learning dynamic Bayesian networks from time-dependent and time-independent data: Unraveling disease progression in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. J. Biomed. Informatics 2021, 117, 103730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migliorelli, L.; Massini, L.S.; Coccia, M.; Villani, L.; Frontoni, E.; Squartini, S. A deep learning-based telemonitoring application to automatically assess oral diadochokinesis in patients with bulbar amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2023, 242, 107840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Barkhaus, P.E.; Rymer, W.Z.; Zhou, P. Machine Learning for Supporting Diagnosis of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Using Surface Electromyogram. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2014, 22, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behler, A.; Müller, H.-P.; Ludolph, A.C.; Kassubek, J. Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Machine Learning for Biomarker Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahangaran, M.; Chiò, A.; D’Ovidio, F.; Manera, U.; Vasta, R.; Canosa, A.; Moglia, C.; Calvo, A.; Minaei-Bidgoli, B.; Jahed-Motlagh, M.-R. Causal associations of genetic factors with clinical progression in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2022, 216, 106681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Burgh, H.K.; Schmidt, R.; Westeneng, H.-J.; de Reus, M.A.; Berg, L.H.v.D.; Heuvel, M.P.v.D. Deep learning predictions of survival based on MRI in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. NeuroImage Clin. 2017, 13, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bean, D.M.; Al-Chalabi, A.; Dobson, R.J.B.; Iacoangeli, A. A Knowledge-Based Machine Learning Approach to Gene Prioritisation in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Genes 2020, 11, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, B.; Balvert, M.; van der Spek, R.A.A.; Dutilh, B.E.; Bohté, S.; Veldink, J.; Schönhuth, A. Using the structure of genome data in the design of deep neural networks for predicting amyotrophic lateral sclerosis from genotype. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, i538–i547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, A.; Alsubai, S.; Sha, M.; Dutta, A.K.; Zhang, Y.-D. Intellectual Assessment of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Using Deep Resemble Forward Neural Network. Neural Netw. 2024, 178, 106478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelik, M.H.; Gagneur, J.; Lim, R.G.; Wu, J.; Thompson, L.M.; Xie, X. Identifying dysregulated regions in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis through chromatin accessibility outliers. Hum. Genet. Genom. Adv. 2024, 5, 100318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, J.; Lerner, B. Insights into Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis from a Machine Learning Perspective. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kew, S.Y.N.; Mok, S.-Y.; Goh, C.-H. Machine Learning and Brain-Computer Interface Approaches in Prognosis and Individualized Care Strategies for Individuals with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Systematic Review. MethodsX 2024, 13, 102765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzahrani, A.K.; Alsheikhy, A.A.; Shawly, T.; Azzahrani, A.S.; AbuEid, A.I. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis prediction framework using a multi-level encoders-decoders-based ensemble architecture technology. J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2024, 36, 101960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemasov, N.A.; Timofeev, V.S.; Ivanisenko, N.V.; Kolchanov, N.A.; Ivanisenko, V.A. Computer analysis of the relation between hydrogen bond stability in SOD1 mutants and the survival time of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2022, 110, 108026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pancotti, C.; Birolo, G.; Rollo, C.; Sanavia, T.; Di Camillo, B.; Manera, U.; Chiò, A.; Fariselli, P. Deep learning methods to predict amyotrophic lateral sclerosis disease progression. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoniadi, A.M.; Galvin, M.; Heverin, M.; Hardiman, O.; Mooney, C. Prediction of caregiver burden in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A machine learning approach using random forests applied to a cohort study. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e033109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).