Integrating Internet-of-Things (IoT) into a Cultural Game Authoring Tool: An Innovative Approach in Maker Education †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hofstede, G.; McCrae, R.R. Personality and Culture Revisited: Linking Traits and Dimensions of Culture. Cross Cult. Res. 2004, 38, 52–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, M. Interacting with heritage: On the use and potential of IoT within the cultural heritage sector. In Proceedings of the 2018 Fifth International Conference on Internet of Things: Systems, Management and Security, Valencia, Spain, 15–18 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ćosović, M.; Brkić, B.R. Game-Based Learning in Museums—Cultural Heritage Applications. Inf. Int. Interdiscip. J. 2019, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulrazic, M.O.M.; Sanzana, M.R.; Ng, K.H.; Maul, T.; Wong, J.Y. Maker Education for Cultural Awareness With a Serious 3D Game Authoring Tool: Design Considerations. SSRN Electron. J. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Lo, W.H.; Ng, K.H.; Brailsford, T.; O’Malley, C. Enhancing reflective learning experiences in museums through interactive installations. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference of the Learning Sciences (ICLS’18), London, UK, 23–27 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Ng, K.H. Designing for cultural learning and reflection using IoT serious game approach. Pers. Ubiquitous Comput. 2021, 25, 509–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

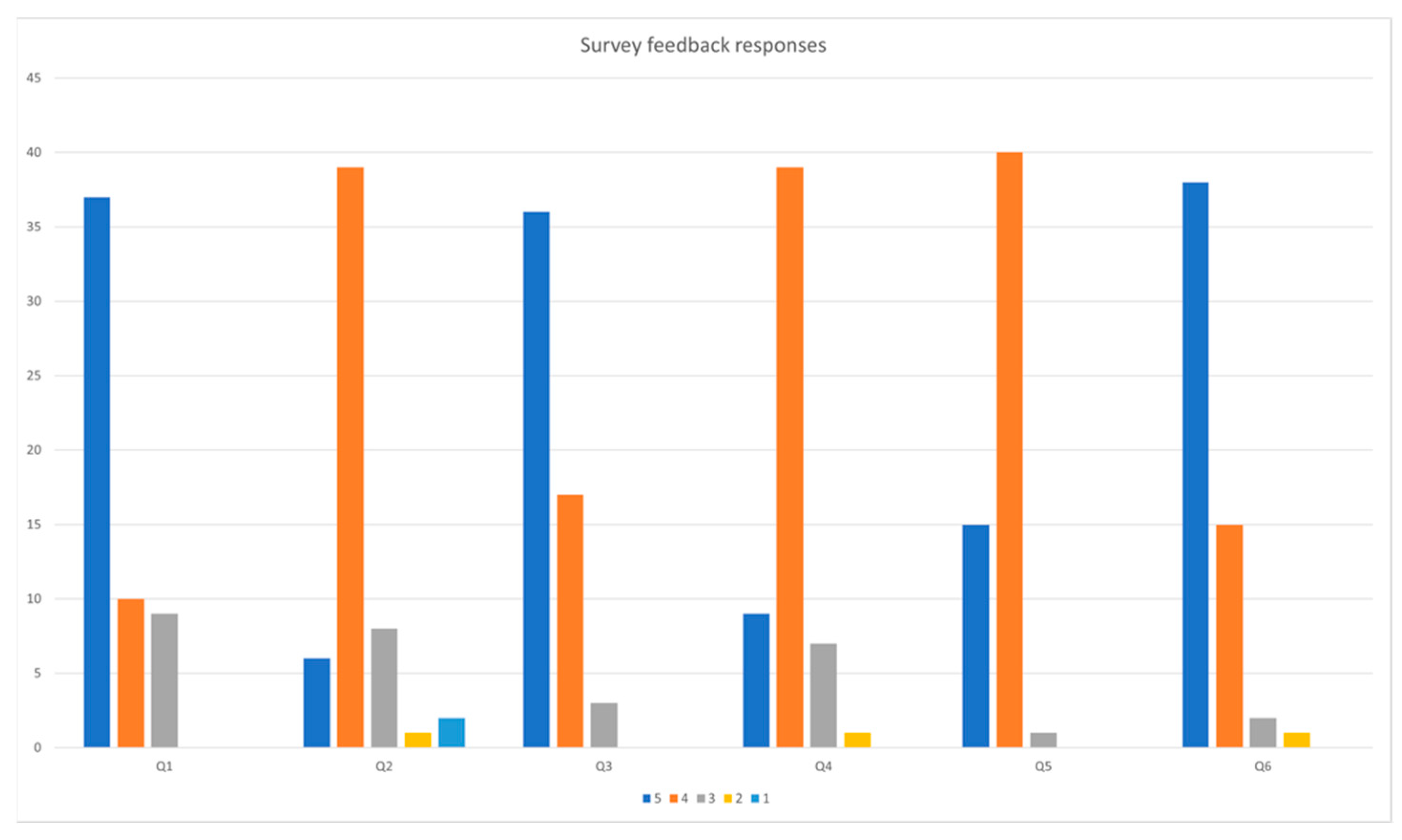
| No. | Question Description |
|---|---|
| Q1 | Do you think cultural game authoring tool will help people share cultural heritage in an immersive way? |
| Q2 | Do you think integrating IoT in the form of RFID cards in this cultural game authoring tool would be engaging? |
| Q3 | Did you enjoy making a short game scene with the game authoring tool? |
| Q4 | Would you like to use RFID cards as a form of IoT integration in your cultural game? |
| Q5 | Would you want to use the RFID cards for performing actions in the game? |
| Q6 | While designing your own game scene, did you find the game authoring tool hard to use? |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdulrazic, M.O.M.; Sanzana, M.R.; Ng, K.H. Integrating Internet-of-Things (IoT) into a Cultural Game Authoring Tool: An Innovative Approach in Maker Education. Eng. Proc. 2022, 27, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsa-9-13371
Abdulrazic MOM, Sanzana MR, Ng KH. Integrating Internet-of-Things (IoT) into a Cultural Game Authoring Tool: An Innovative Approach in Maker Education. Engineering Proceedings. 2022; 27(1):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsa-9-13371
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdulrazic, Mostafa Osama Mostafa, Mirza Rayana Sanzana, and Kher Hui Ng. 2022. "Integrating Internet-of-Things (IoT) into a Cultural Game Authoring Tool: An Innovative Approach in Maker Education" Engineering Proceedings 27, no. 1: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsa-9-13371
APA StyleAbdulrazic, M. O. M., Sanzana, M. R., & Ng, K. H. (2022). Integrating Internet-of-Things (IoT) into a Cultural Game Authoring Tool: An Innovative Approach in Maker Education. Engineering Proceedings, 27(1), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsa-9-13371






