Potential Bio-Fuel from Refinery Waste through Anaerobic Digestion †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
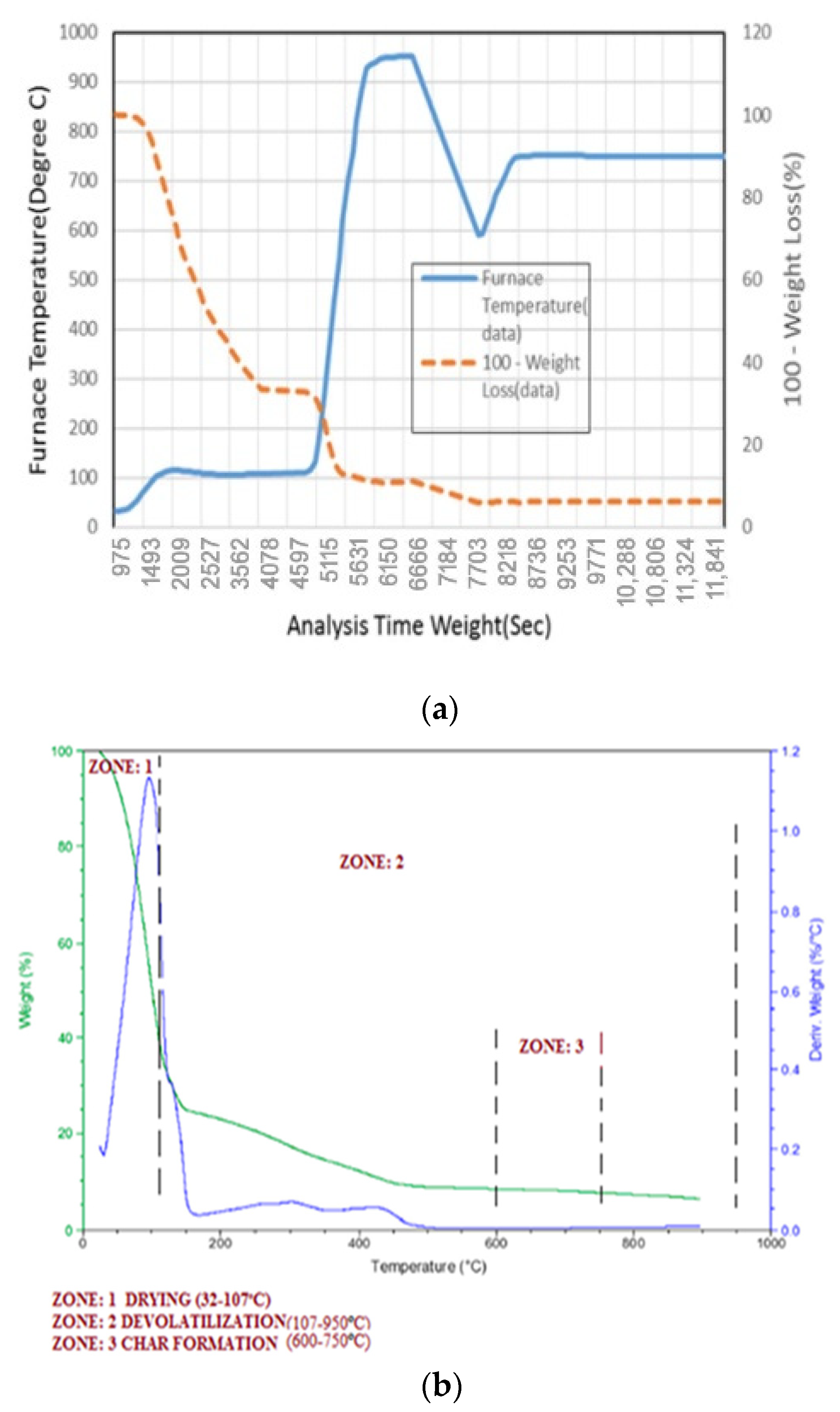
3.1. Proximate and Ultimate Analysis
3.2. Calorific Value of Waste Cake
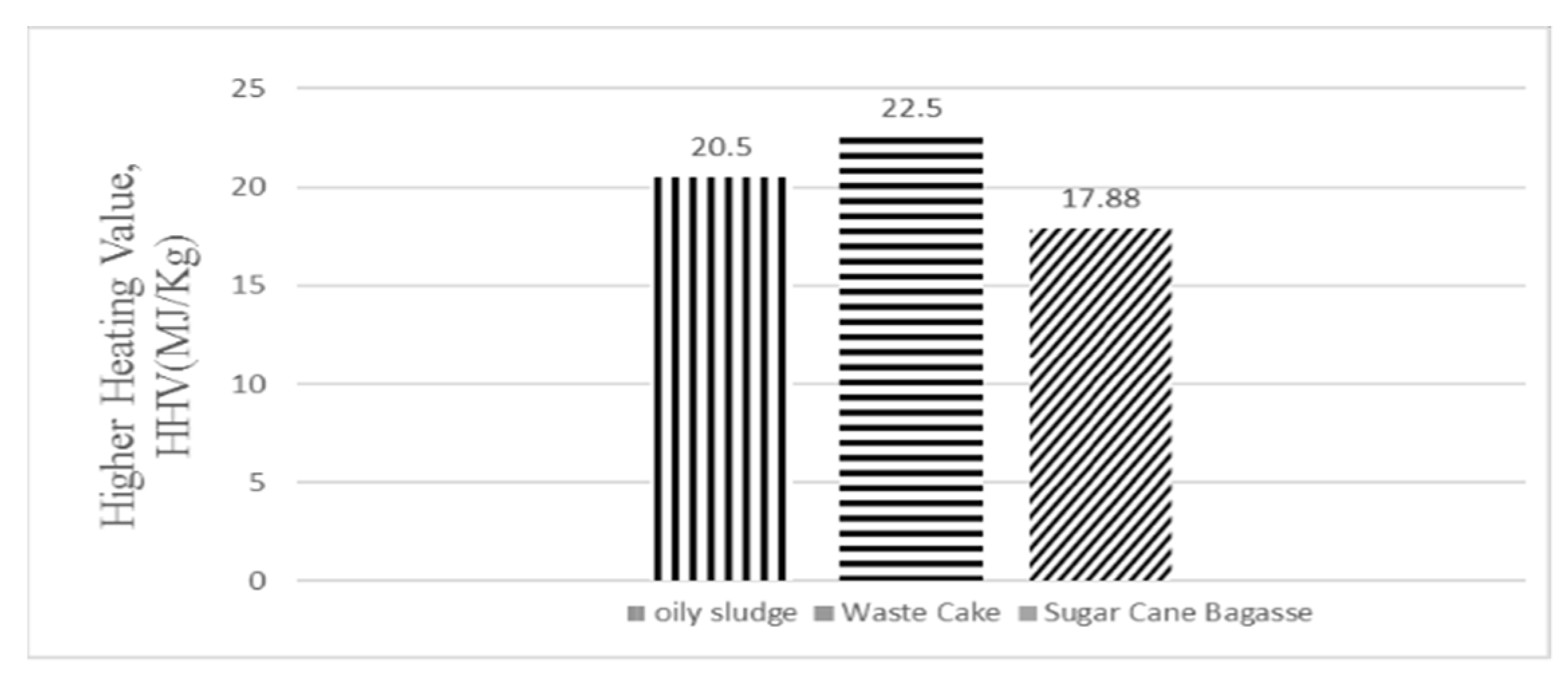
3.3. Comparison of Different Biomasses for Biofuel Potential
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ning, S.K.; Hung, M.C.; Chang, Y.H.; Wan, H.P.; Lee, H.T.; Shih, R.F. Benefit assessment of cost, energy, and environment for biomass pyrolysis oil. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 59, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Zhou, H.; Lin, L. Biodiesel: An Alternative to Conventional Fuel. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Future Energy, Environment, and Materials, Hong Kong, China, 12–13 April 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, S.; Shahzad, K.; Akthar, K.S.; Akhthar, N.A.; Chughtai, A. Investigations of thermal conversion and kinetics of low-grade coal and bagasse using thermogravemetric technique. J. Fac. Eng. Technol. 2014, 21, 105–117. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, A.M.; Abu-Hassan, M.A.; Ibrahim, R.R.; Zaini, M.A.A.; Abdulkarim, B.I.; Hussein, A.S.; Su, S.M.; Mohd Halim, M.A.I. Characterization of Petroleum Sludge from Refinery Industry Biological Wastewater Treatment Unit. Preprints 2017, 2017080033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hou, B.; Xie, S.X.; Chen, M.; Jin, Y.; Hao, D.; Wang, R.S. The Treatment of Refinery Heavy Oil Sludge. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2002, 31, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boateng, A.A.; Daugaard, D.E.; Goldberg, N.M.; Hicks, K.B. Bench-scale fluidized-bed pyrolysis of switchgrass for bio-oil production. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 1891–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullen, C.A.; Boateng, A.A.; Goldberg, N.M.; Lima, I.M.; Laird, D.A.; Hicks, K.B. Bio-oil and bio-char production from corn cobs and stover by fast pyrolysis. Biomass Bioenergy 2010, 34, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ates, F.; Isikday, M.A. Evaluation of the role of pyrolysis temperature in straw biomass samples and characterization of the oils by GC/MS. Energy Fuel 2008, 22, 1936–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Samples | Moisture (%) | Volatile Matter (%) | Fixed Carbon (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wet waste cake | 68.50 | 14.30 | 12.09 |
| Dry waste cake | 40.1 | 30.9 | 11.7 |
| Oily Sludge [3] | 78.9 | 5.5 | 10.1 |
| Sugar cane [4] baggas | 1.03 | 81.33 | 12.28 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gishkori, S.N.; Abbas, G.; Shah, A.A.; Rahman, S.U.; Haider, M.S.; Nisar, F. Potential Bio-Fuel from Refinery Waste through Anaerobic Digestion. Eng. Proc. 2021, 12, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2021012068
Gishkori SN, Abbas G, Shah AA, Rahman SU, Haider MS, Nisar F. Potential Bio-Fuel from Refinery Waste through Anaerobic Digestion. Engineering Proceedings. 2021; 12(1):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2021012068
Chicago/Turabian StyleGishkori, Sophia Nawaz, Ghulam Abbas, Aqeel Ahmad Shah, Sajjad Ur Rahman, Muhammad Salman Haider, and Fahid Nisar. 2021. "Potential Bio-Fuel from Refinery Waste through Anaerobic Digestion" Engineering Proceedings 12, no. 1: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2021012068
APA StyleGishkori, S. N., Abbas, G., Shah, A. A., Rahman, S. U., Haider, M. S., & Nisar, F. (2021). Potential Bio-Fuel from Refinery Waste through Anaerobic Digestion. Engineering Proceedings, 12(1), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2021012068






