1. Introduction
Air pollution is a serious issue that has been recognized as a global threat, with its contribution to premature deaths reaching 7 million annually [
1]. Research has demonstrated a direct link between elevated pollution levels and adverse health outcomes within the world population. Several factors contribute to this concerning situation such as rapid urbanization, industrial expansion, and population growth, which have led to increased emissions coming from vehicles. Heavy traffic has emerged as one of the primary challenges in urban environments [
2]. A study indicated that, during identical trips, vehicles produced greater pollution due to increased fuel consumption in congested traffic conditions compared to less congested scenarios [
3]. Additional challenges stem from outdated and inadequately maintained public transportation systems, as well as industrial emissions from factories and power plants, which release high levels of harmful pollutants including sulfate, ammonium, nitrate, and black carbon [
4]. Moreover, the burning of waste, emissions from household stoves and generators, and dust generated from construction activities and unpaved roads further deteriorate air quality in a more localized fashion [
5]. Considering this, there is a need to effectively monitor the air quality in a more localized fashion, particularly along roadsides with heavy traffic.
Monitoring air quality is particularly challenging in urban and semi-urban areas where localized emissions from vehicles and industries vary dramatically. The advent of the Internet of Things (IoT) has enabled the development of low-cost sensor-based air quality monitoring systems (AQMSs). The data collected through IoT systems is typically stored in cloud platforms for monitoring, visualization, and analysis [
6]. However, existing systems generally rely on Wi-Fi-based connectivity, which limits the usage of AQMSs to indoors or at a fixed location [
7,
8,
9,
10]. Therefore, a large number of AQMSs are needed to monitor a wider geographical area.
In this work, we have proposed and developed an AQMS that uses existing cellular infrastructure instead of conventional Wi-Fi to collect AQMS data. The proposed cellular IoT (C-IoT)-based AQMS is useful for monitoring the air quality while moving around the city and is able to record air quality parameters for a wide area, thereby providing an opportunity to prepare a pollution map of a region.
In this paper, we report the design and development of C-IoT-based portable AQMS for the pollution mapping of an area. The developed system uses specialized sensors to measure temperature, humidity, Particulate Matter (PM) concentration and Carbon Dioxide (CO2) concentration. The sensors are integrated with an ESP32 microcontroller which collects the sensor data and periodically transmits to a central gateway through SMS messages by using GSM modules. In order to identify the correct location of the sensor node, we used a Global Positioning System (GPS) module to simultaneously collect the location information and send it to a central gateway along with the air quality data. The node is powered through a portable battery to ensure complete mobility of the system.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows.
Section 2 presents a system model for the development of the AQMS system.
Section 3 describes the hardware configuration for the developed system.
Section 4 provides a brief overview of the data collection and visualization at the cloud storage stage. We present the samples of data collected during a drive test of the developed system in
Section 5.
Section 6 concludes the paper.
2. System Model
Our proposed C-IoT-based AQMS comprises two segments, as illustrated in
Figure 1. The first segment is the outdoor portable sensor node which is controlled by an ESP32 microcontroller [
11] and powered by a portable battery bank to ensure mobility. The microcontroller provides an interface between the air quality sensors and the GPS module [
12] with the GSM modules. The location data collected through the GPS modules and the air quality data collected through the sensors are aggregated by the microcontroller and communicated to the GSM module [
13]. The GSM module transmits the collected data to the central gateway [
14] as a SMS using the existing cellular infrastructure. This node also offers live data visualization of the sensed parameters through an OLED display.
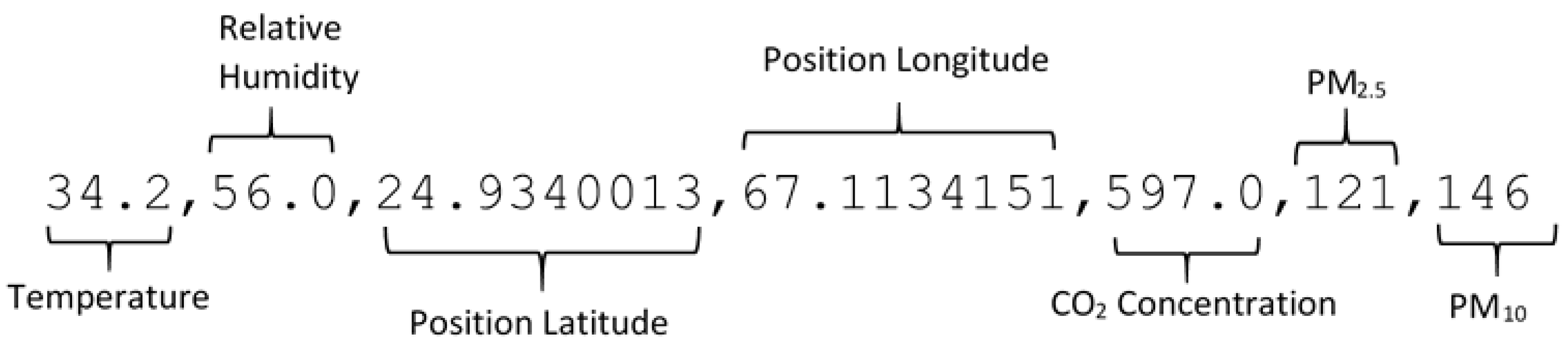
The second segment of the system is the central gateway which is placed at a fixed location and provides an interface to route the collected data to the cloud storage. The central gateway is also equipped with a GSM module to receive the data SMS. The GSM module in the gateway is connected to the ESP32 microcontroller which can transmit data to the cloud using Wi-Fi in addition to using a USB connection with a dedicated computer. The comma-separated data in the SMS, as shown in
Figure 2, is transmitted to a cloud for storage and analysis. A web-based dashboard is also developed for the live visualization of the collected data.
3. Hardware Development
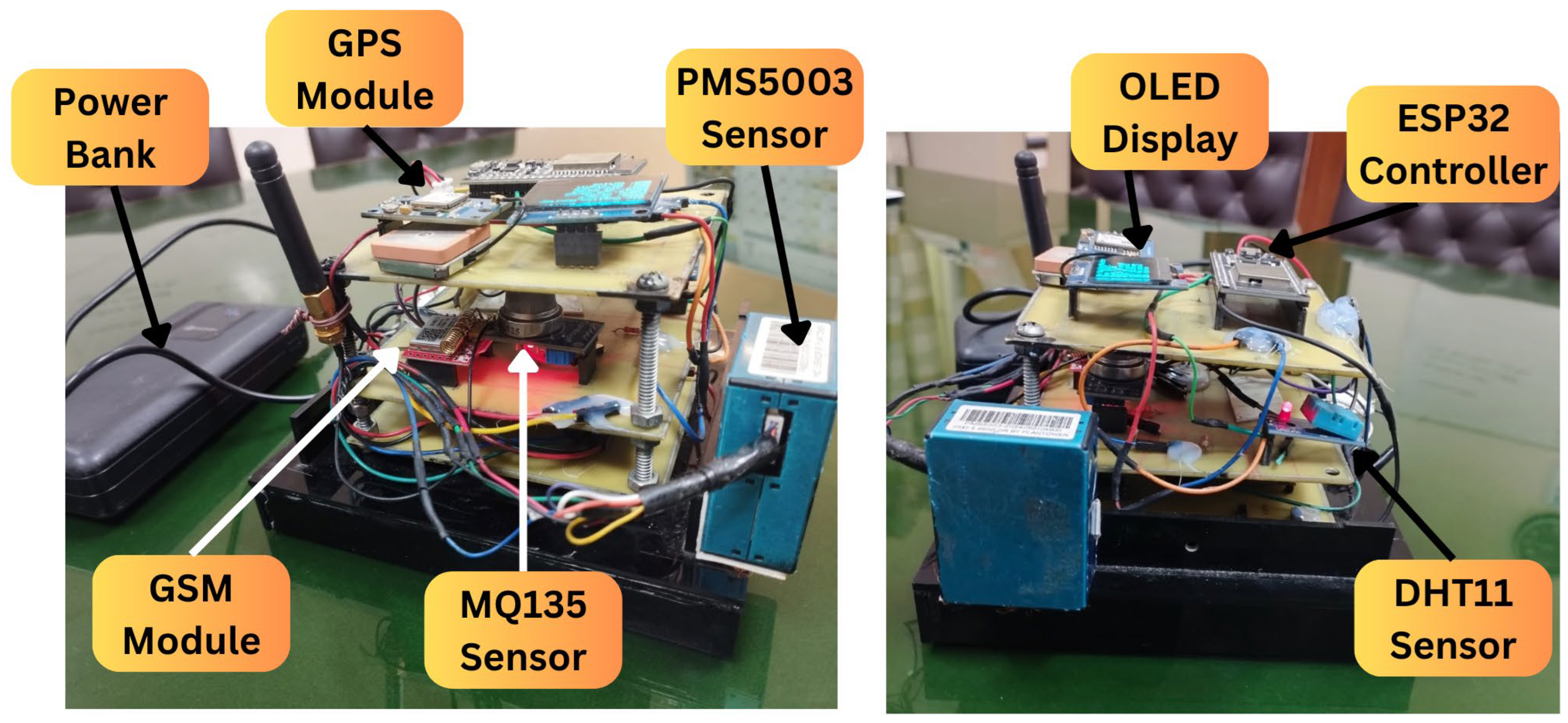
The hardware development started with the selection of the appropriate components for system development. In this work, we used the ESP32 microcontroller [
11] as the main processing unit for the mobile sensor node. From the sensor side, we used a DHT-11 sensor by ASAIR [
15] to sense relative humidity and temperature, an MQ-135 sensor [
16] calibrated to measure CO
2 concentration, and a PMS-5003 plantower sensor [
17] to measure PM concentrations. Although PMS-5003 is capable of recoding different PM concentrations based on the size of the dust particles, we only used PM
2.5 and PM
10 to measure the concentrations of dust particles of diameters up to 2.5 µm and 10 µm, respectively. To collect location information, the GPS Neo6m Module [
12] was used. The SIM800L GSM module [
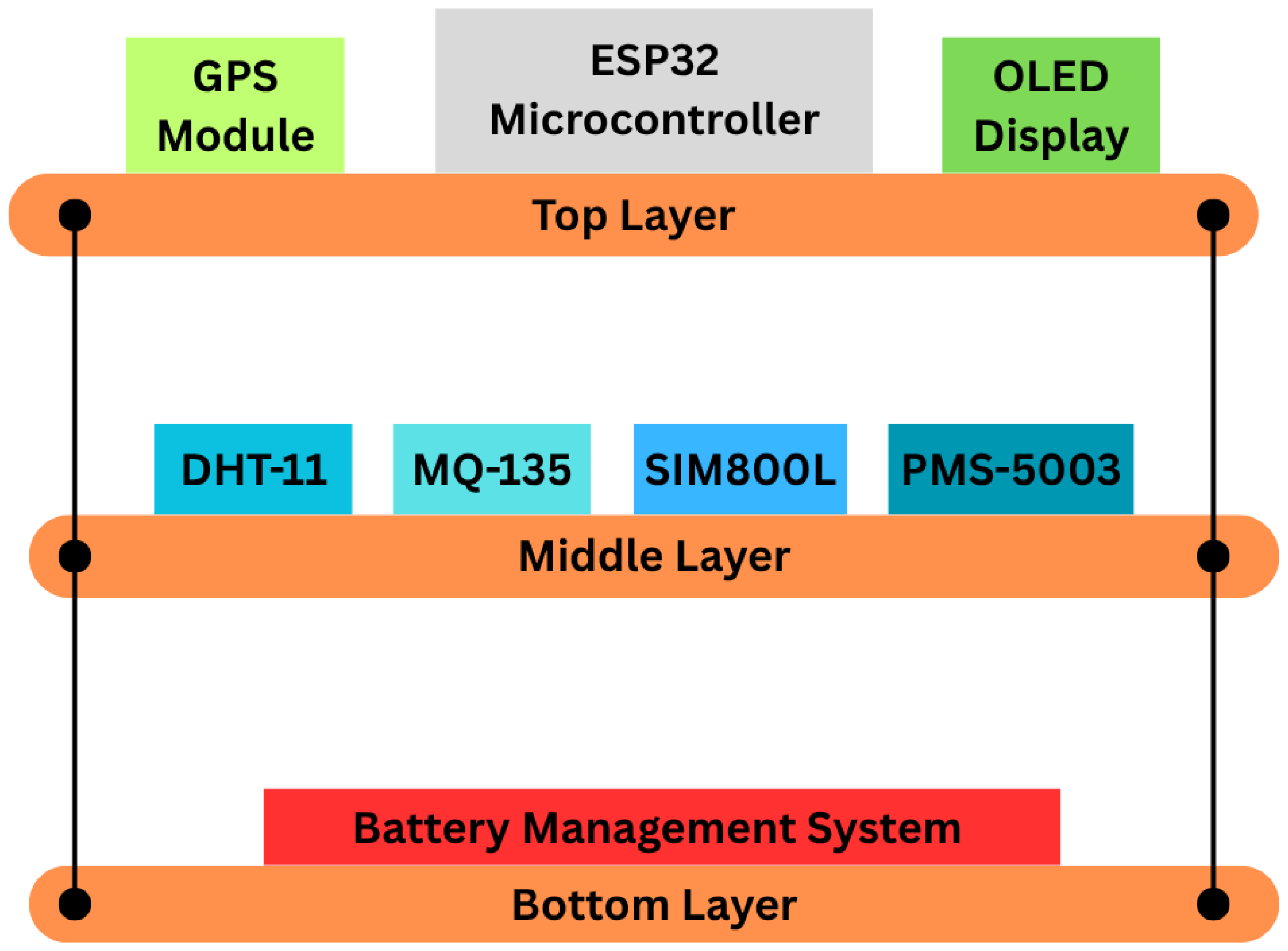
13] was used at the portable node to transmit the data SMS from the sensor node. To ensure that the hardware was portable and robust, a three-layer PCB design was conceived and fabricated as illustrated in
Figure 3.
The top-layer serves as the main control and monitoring layer as it hosts the microcontroller, GPS module, and OLED display module. The mounting of these components on the top layer supports reliable GPS positioning, easy visualization, effective heat dissipation, and easy microcontroller access for programming and debugging.
The middle layer serves as the sensor core of the system, which hosts the sensors and GSM module. Though the interface was provided through the middle layer of the system, all the air quality sensors were positioned in such a way that they were fully exposed to air for accurate measurement. The bottom layer of the system holds a battery management system to ensure all components obtain the required voltage and power for proper functioning. Each layer was designed on a 4 × 4 inch board. For the PCB design, we used the EasyEDA tool [
18] and then fabricated the design using conventional ironing and etching methods. Additionally, standoffs were used to ensure a consistent separation between the three vertically stacked PCB layers. The separation was approximately 4 cm in measurement. This enables a clear path for the air to flow between the layers to overcome the risk of heating up, improving the performance of the sensors, controller, and power regulation circuits. The structure was then made rigid using some screws as spacers between the PCBs to prevent electrical shorts and ensure structural integrity under harsh outdoor conditions; additionally, it also attached an acrylic base to the hardware for easier handling and portability.
Figure 4 depicts the developed sensor node.
The gateway design was very simple as it only required the interfacing of the GSM module with the microcontroller. For the gateway, we used an ESP32 D1 Mini microcontroller and the SIM900A GSM module [
14].
4. AQMS Data Visualization
In this section, we present the real-time, interactive dashboard developed to provide a data visualization platform for our developed AQMS. We used Google Firebase Firestore for this purpose [
19]. Firestore is a flexible, scalable database for mobile, web, and server development from Firebase and Google Cloud, allowing data to sync across client apps in real-time. Using Firebase, we have developed a custom real-time web dashboard to display the parameters used in monitoring, which include CO
2, PM
2.5, PM
10, temperature, and humidity. Moreover, using the dashboard, historical data of the mentioned parameters can also be seen, allowing users to understand the trends of sensor readings. The system also utilizes the location provided using the GPS module to map the location of the sensor node on the map. The dashboard is also customized for a mobile-friendly view to facilitate monitoring for users on-the-go.
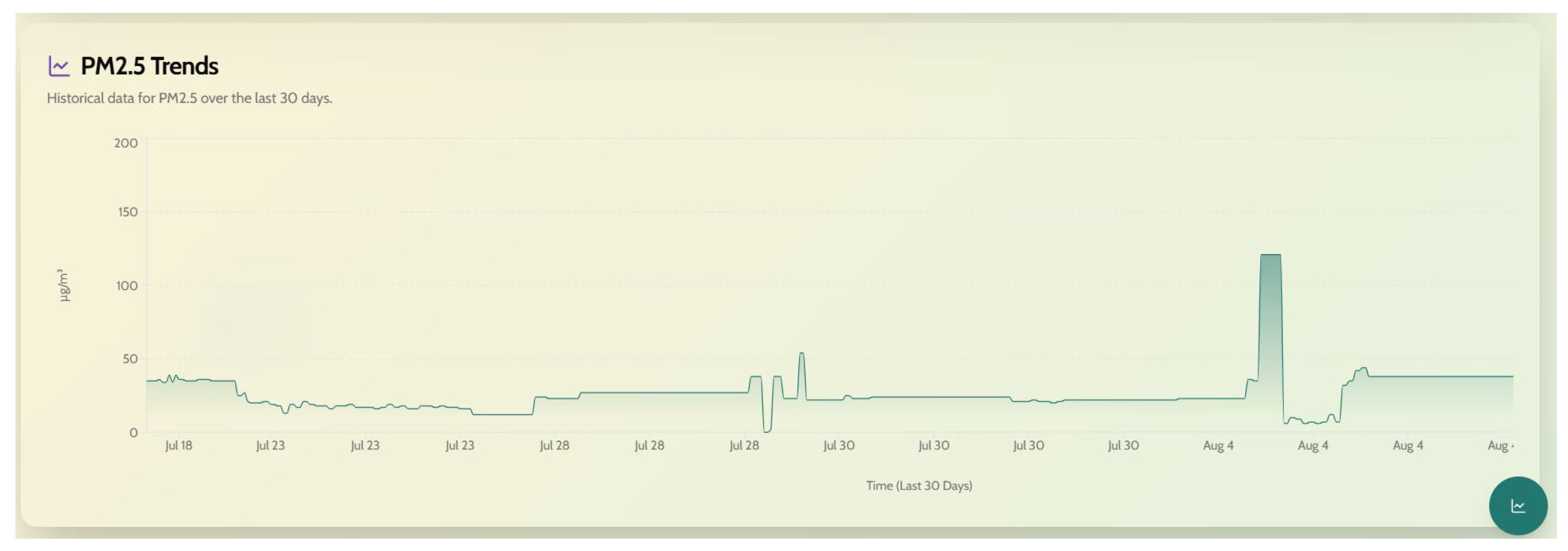
Figure 5 shows the dashboard GUI developed using Firebase for AQMS data visualization. Each air quality parameter can also visualized as a trend curve, displaying current and historical data.
Figure 6 depicts an example of such a plot, displaying PM
2.5 levels recorded over an extended period of time. Similar graphs can be obtained for other parameters as well. Using the live map option, the GPS location of the node can be visualized in real-time, as depicted in
Figure 7.
5. Results and Discussion
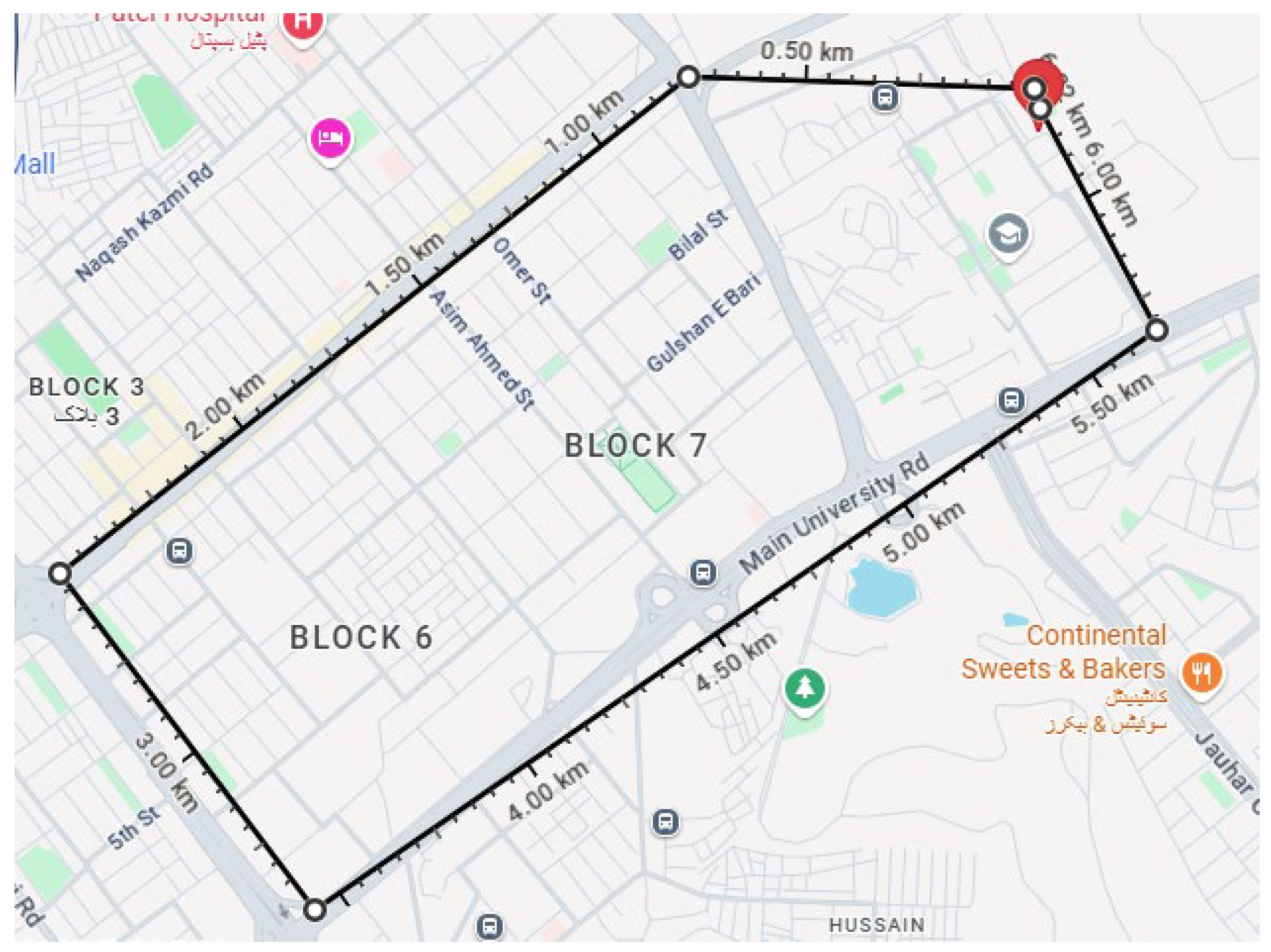
In this section, we present the details of the results obtained through a sample drive test conducted over a travel distance of 6.18 km and a covered area of 1.936 km
2. The region covered through this drive test is a part of Gulshan-e-Iqbal town (East district) of Karachi, Pakistan, a heavily populated, urban region with a population density of 33,776/km
2 [
20]. Moreover, this region houses schools, colleges, universities, and several commercial buildings, attracting hundreds of thousands of vehicles (bikes, buses, cars, and rickshaws) every day.
For effective visualization, we have integrated the firebase with the Google My Maps tool [
21]. Using this tool, we have established a visualization system for the air quality data collected using the mobile AQMS sensor node.
Figure 8 shows the visualization of the distance and route covered during the sample drive test generated via Google Maps. During the drive test, we measured several air quality parameters on 10 critical locations on the defined route. These locations were shortlisted because of the nature of vehicular and passenger traffic experienced on these locations.
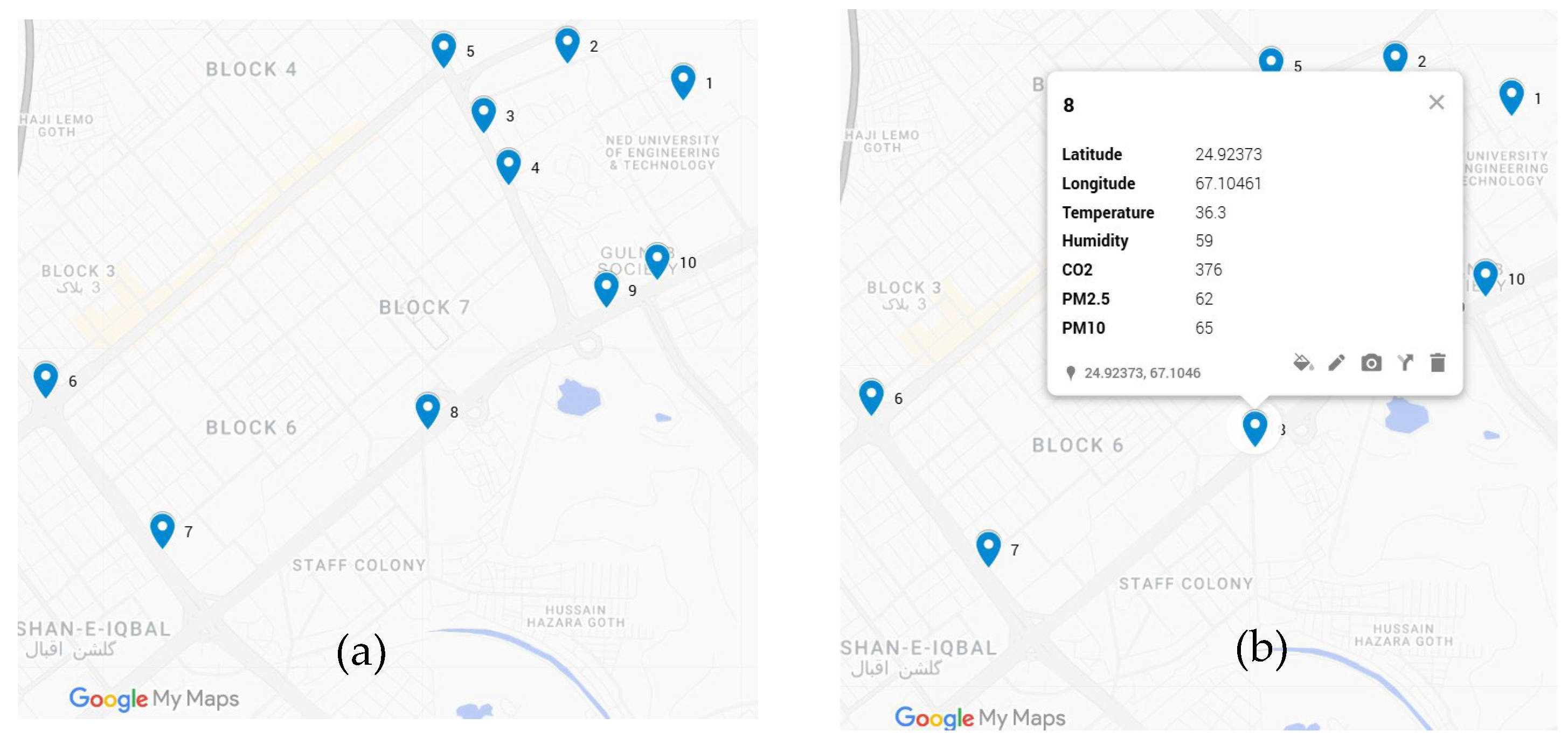
Figure 9a depicts the sequence of air quality data collection where point 1 represents the first data collection point at the beginning of the drive test and point 10 represents the last data collection point where the drive test concluded. As evident from the figure, we have targeted data collection over intersections and locations where vehicular traffic aggregates (choke points).
Figure 9b shows a sample of air quality data being visualized using the My Maps application. Users of this platform can observe latitude, longitude position, temperature, humidity, CO
2, PM
2.5, and PM
10 concentrations.
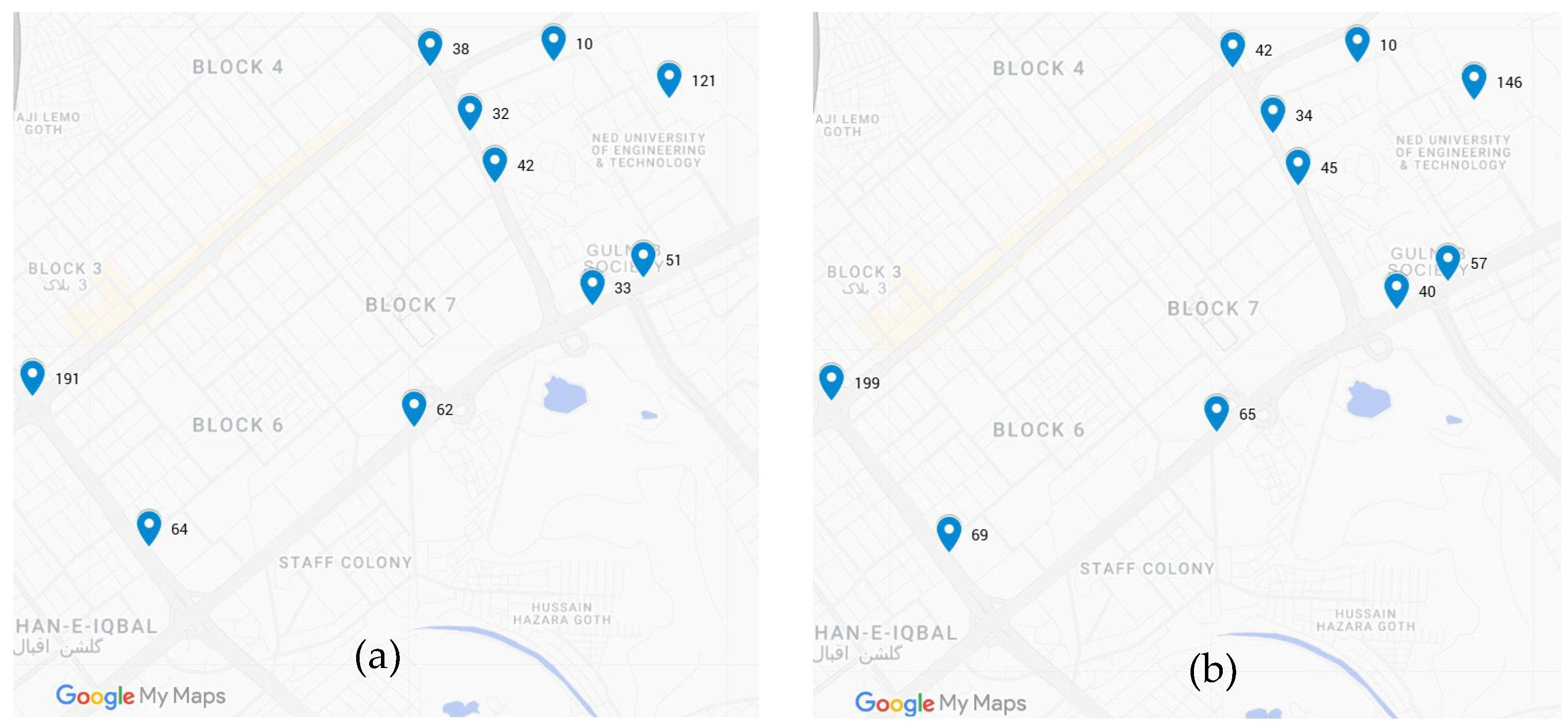
Figure 10a depicts temperature levels measured in degree centigrade observed at the selected data collection points over the route. An interesting observation is that only in a region of 1.936 km
2 is there a significant variation in temperature observed, with the highest temperature recorded being 36.3 degrees and the minimum temperature recorded being 26.7 degrees (a difference of 9 degrees). Overall average temperature recorded was 31.5 degrees.
Figure 10b presents humidity levels, measured in percentage and recorded at selected locations on the route. Unlike temperature, the humidity levels recorded over the route show consistency, with most of the data points showing the same humidity levels.
Figure 11a,b shows the PM
2.5 and PM
10 levels in ppm, respectively, as recorded at selected locations on the route. Both figures depict consistent trends in PM levels as well as variation in said levels. Higher PM levels were observed around Block 6 of Gulshan-e-Iqbal.
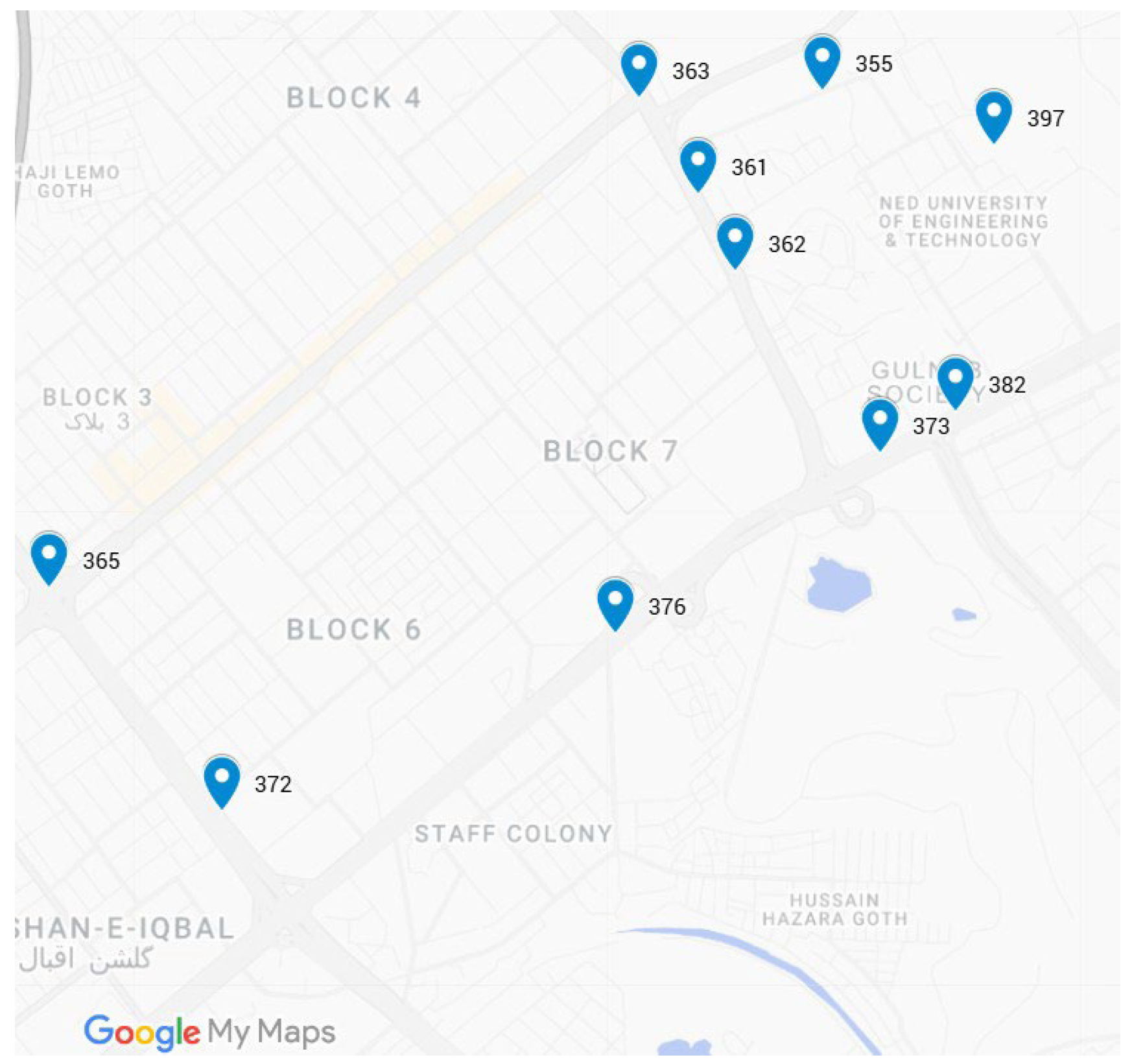
Figure 12 depicts CO
2 levels measured in ppm recorded at selected locations on the route. The levels recorded over the route are at acceptable levels (between 300 and 400 ppm). The variation in the CO
2 concentrations can be observed in the figure, with minimum and maximum levels of 355 and 397, respectively.
6. Conclusions
In this paper, we have presented the three-layer design and development of the C-IoT-based AQMS system. The system is designed to ensure complete mobility and collection of air quality parameters while moving around roads. Unlike conventional Wi-Fi-based IoT systems, the developed system utilizes existing cellular infrastructure to transmit collected data using an SMS service. The developed AQMS is capable of collecting temperature, relative humidity, CO2 concentration, and PM2.5 and PM10 values. Furthermore, the system also records the position of these levels in terms of the latitude and longitude of the sensor node using GPS. A live dashboard is also developed for visualization of the recorded data. We have also presented the results of a test drive using the developed system by recording air quality parameters in an area.