Wireless Soil Health Beacons: An Intelligent Sensor-Based System for Real-Time Monitoring in Precision Agriculture †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Wireless Soil Health Beacons
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khanna, A.; Kaur, S. Evolution of Internet of Things (IoT) and its significant impact in the field of Precision Agriculture. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 157, 218–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, M. ISPA Forms Official Definition of ‘Precision Agriculture’, Global Ag Tech Initiative. 2021. Available online: https://www.globalagtechinitiative.com/market-watch/ispa-forms-official-definition-of-precision-agriculture/ (accessed on 30 November 2025).
- PsiBorg Technologies Pvt. Ltd. Soil Health Monitoring System for Better Crop Yield. 27 February 2025. Available online: https://psiborg.in/iot-case-studies/soil-health-monitoring-system-for-better-crop-yield/ (accessed on 30 November 2025).
- DeFord, L.; Yoon, J.Y. Soil microbiome characterization and its future directions with biosensing. J. Biol. Eng. 2024, 18, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DADB. 10 Applications of IoT in Agriculture: Transforming Farming Practices. DADB India. 20 February 2025. Available online: https://dadb.com/in/blog/10-applications-of-iot-in-agriculture-transforming-farming-practices/ (accessed on 30 November 2025).
- Singh, R.K.; Aernouts, M.; De Meyer, M.; Weyn, M.; Berkvens, R. Leveraging LoRaWAN Technology for Precision Agriculture in Greenhouses. Sensors 2020, 20, 1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, T.; Mikiciuk, G.; Durlik, I.; Mikiciuk, M.; Łobodzińska, A.; Śnieg, M. The IoT and AI in Agriculture: The Time Is Now—A Systematic Review of Smart Sensing Technologies. Sensors 2025, 25, 3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, R.; Baggard, J. Wireless sensor network for monitoring soil moisture and weather conditions. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2015, 31, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, E.; Costa, N.; Pereira, A. A Systematic Review of IoT Solutions for Smart Farming. Sensors 2020, 20, 4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahab, H.; Naeem, M.; Iqbal, M.; Aqeel, M.; Ullah, S.S. IoT-driven smart agricultural technology for real-time soil and crop optimization. Smart Agric. Technol. 2025, 10, 100847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Chabla, R.; Real-Avilés, K.; Morán, C.; Grijalva, P.; Recalde, T. IoT applications in agriculture: A systematic literature review. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on ICTs in Agronomy and Environment, Guayaquil, Ecuador, 22–25 January 2019; pp. 68–76. [Google Scholar]
- Faqir, Y.; Qayoom, A.; Erasmus, E.; Schutte-Smith, M.; Visser, H.G. A review on the application of advanced soil and plant sensors in the agriculture sector. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 226, 109385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Oliullah, K.; Kabir, M.M.; Alom, M.; Mridha, M.F. Machine learning enabled IoT system for soil nutrients monitoring and crop recommendation. J. Agric. Food Res. 2023, 14, 100880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, D.; Kumar, Y.; Kumar, A.; Singh, P.K. Applicability of wireless sensor networks in precision agriculture: A review. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2019, 107, 471–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Shen, M.; Zhou, L.; Ma, F.; Lin, X.; Xiong, Y. Design of a wireless sensor network for farmland monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2010 Fifth International Conference on Frontier of Computer Science and Technology, Changchun, China, 18–22 August 2010; pp. 370–375. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A.; Sharma, D.K.; Sahai, D.N. A High QoS Cluster Routing Scheme for Wireless Sensor Networks in Smart Agriculture Application. In International Conference on Information Technology; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2024; pp. 83–95. [Google Scholar]
- Bhosale, T.; Patil, M.; Wadhai, V. A smart farming alternative for small Pomegranate farms of India. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Communications and Signal Processing (ICCSP), Melmaruvathur, India, 2–4 April 2015; pp. 0540–0544. [Google Scholar]
- Le, T.D.; Tan, D.H. Design and deploy a wireless sensor network for precision agriculture. In Proceedings of the 2015 2nd National Foundation for Science and Technology Development Conference on Information and Computer Science (NICS), Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 16–18 September 2015; pp. 294–299. [Google Scholar]
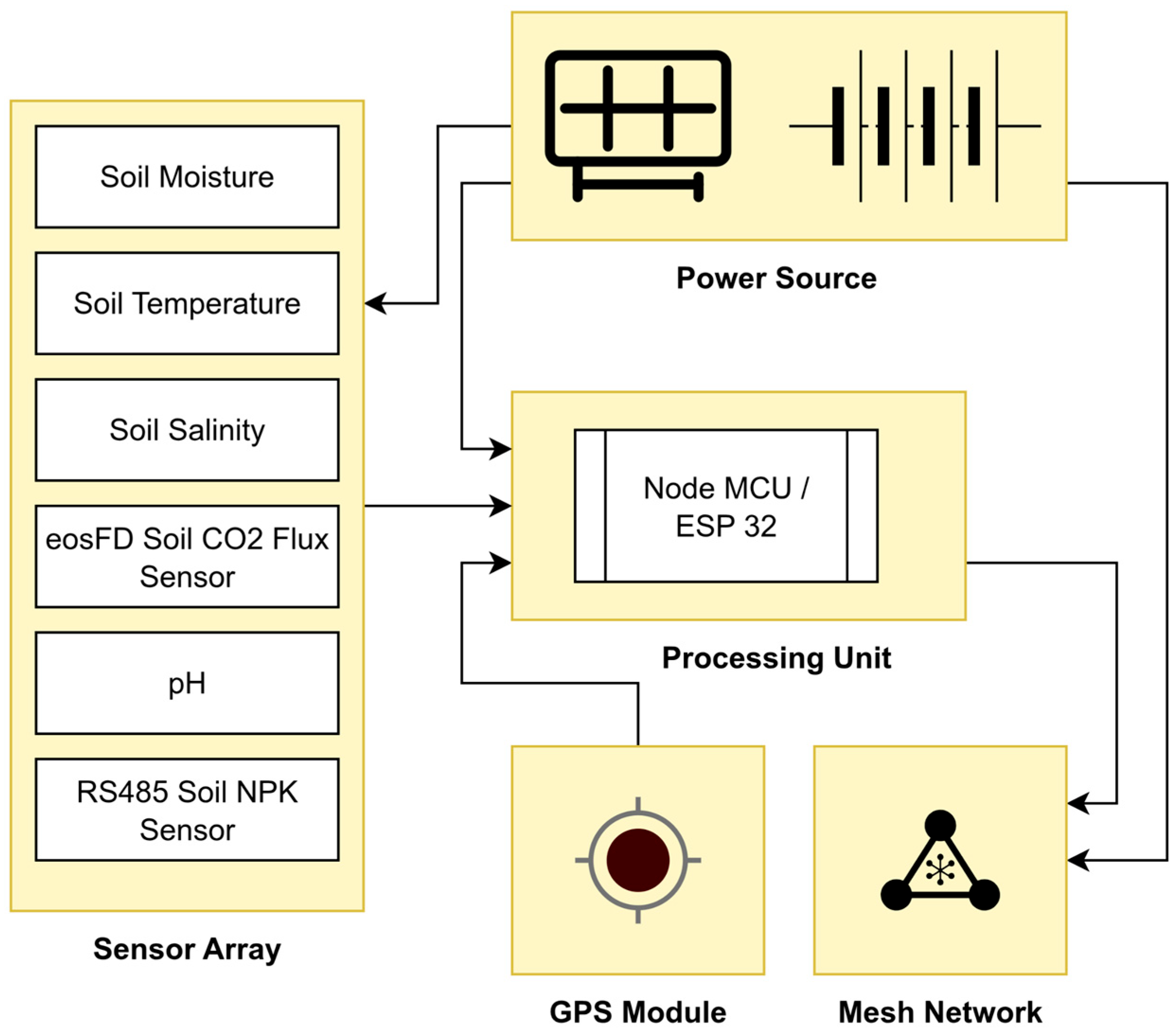
| Parameter | Sensor | Manufacturer | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soil Moisture | 31076 Capacitive Soil Moisture | Physiz Agtech Private Limited, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India | Measures the volumetric water content in the soil. Triggering alerts and optimising irrigation schedules to prevent plant stress. |
| Soil Temperature | DS18B20 Waterproof Temperature | Analog Devices, Bangalore, Karnataka, India | Monitors soil temperature, which has a direct influence on the microbial activity, nutrient availability, and seed germination. |
| Soil Salinity | PHYFARM Electrical Conductivity (EC) | Physiz Agtech Private Limited, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India | Measures the concentration of soluble salts in the soil by testing its electrical conductivity (EC), as high salinity limits plant water uptake. |
| General Microbial Activity | eosFD Soil CO2 Flux Sensor | Eosense, Dartmouth, Nova Scotia, Canada | Soil respiration strongly indicates the overall microbial population and metabolic activity. Shifts in CO2 levels can indicate changes in soil fertility and health. |
| pH | Soil Sensor JXBS-3001-PH-I20 | JXCT, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India | Measures the pH value of the soil that controls nutrient availability and microbial health |
| NPK Availability | RS-485 Soil NPK Sensor | REES52, Delhi, India | It measures nitrate concentration (NO3−), the primary form of nitrogen absorbed by plants, which is used for fertiliser optimisation and understanding nutrient availability. |
| Processing Unit | ESP32 | Espressif Systems, Pune, Maharashtra, India | A microcontroller with integrated Wi-Fi and Bluetooth for data aggregation, local processing, and communication with the cloud platform. |
| Power Source | solar panel, LiPo/Li-ion battery, charge controller | Provides a self-sustaining power source, enabling long-term, unattended deployment of the beacons in the field. | |
| GPS | GPS/GNSS Receiver Module (M20050-1) | Antenova, Hatfield, Hertfordshire, UK | GPS Location for geotagging |
| Mesh Network | HopeRF RFM95 | REES52, Delhi, India | Mesh network configuration for long-range, low-power data transmission between beacons and the central gateway, ensuring robust connectivity across a large field. |
| { “beacon_id”: “WSHB-03”, “timestamp”: “2025-08-10T14:30:00+05:30”, “soil”: { “moisture_vwc_pct”: 21.8, “temperature_c”: 25.7, “ec_ds_m”: 1.82, “ph”: 6.7, “co2_flux_umol_m2_s”: 3.2, “nitrate_mg_kg”: 35, “phosphate_mg_kg”: 18, “potassium_mg_kg”: 152 }, “device”: { “battery_v”: 3.93, “fw”: “1.0.0”, “seq”: 1248 } } |
| Condition Detected | Evidence | Rule/Trigger (Generic) | Recommendation/Action | Priority | Action Window |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Irrigation watch (near-dry) | VWC 21.8% (midday) | If VWC < 22% and falling over 2 readings | Monitor next 2–3 h; if still ↓, irrigate overnight (light cycle) to avoid stress and minimise evap. | Medium | Check again |
| Salinity caution | EC 1.82 dS/m | If EC ≥ 1.5 dS/m (sensitive crops) | Avoid saline fertigation today; after irrigation, consider leaching if EC stays ≥1.8; use low-EC water if available. | Medium | Check again |
| pH acceptable | pH 6.7 | Target 6.0–7.5 | No liming/sulfur needed. Keep as-is. | Low | |
| Temperature optimal | 25.7 °C | Crop-optimal 20–30 °C for roots | Good for root activity; keep moisture steady to avoid heat and salt stress. | Low | |
| Microbial activity normal | CO2 flux 3.2 | Within the local baseline band | No action; use as bio health reference. If it drops with drying, prioritise irrigation. | Low | |
| Nitrogen status adequate | NO3− 35 mg/kg | If 25–40 mg/kg = OK | Hold N today; consider light top-dress next irrigation only if crop demand is rising. | Low | Next irrigation |
| Phosphorus adequate | P 18 mg/kg | If >10–15 mg/kg = adequate (Olsen-P equiv.) | No P this cycle; reassess pre-flowering/critical growth stage. | Low | Next check in 2–3 weeks |
| Potassium adequate | K 152 mg/kg | If >120 mg/kg = adequate (crop/soil dependent) | No K this cycle; monitor leaf symptoms and soil trend. | Low | Next check in 2–3 weeks |
| Data quality check | EC high + VWC near threshold | If EC ≥ 1.8 and VWC < 25% | Rinse EC probe at service visit; ensure temp compensation enabled; verify soil-specific moisture calibration. | Medium | Within 1–2 days |
| Device health | Battery 3.93 V | If >3.6 V = OK | No action. Log RSSI/SNR on the next uplink for link QA. | Low |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Subramanian, V.; Joseph, A.; Paramasivam, D.; Tamilselvan, A.; Thangavel, M.K. Wireless Soil Health Beacons: An Intelligent Sensor-Based System for Real-Time Monitoring in Precision Agriculture. Eng. Proc. 2025, 118, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECSA-12-26539
Subramanian V, Joseph A, Paramasivam D, Tamilselvan A, Thangavel MK. Wireless Soil Health Beacons: An Intelligent Sensor-Based System for Real-Time Monitoring in Precision Agriculture. Engineering Proceedings. 2025; 118(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECSA-12-26539
Chicago/Turabian StyleSubramanian, Vijayalakshmi, Alwin Joseph, Durgadevi Paramasivam, Akilan Tamilselvan, and Mahesh Kumar Thangavel. 2025. "Wireless Soil Health Beacons: An Intelligent Sensor-Based System for Real-Time Monitoring in Precision Agriculture" Engineering Proceedings 118, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECSA-12-26539
APA StyleSubramanian, V., Joseph, A., Paramasivam, D., Tamilselvan, A., & Thangavel, M. K. (2025). Wireless Soil Health Beacons: An Intelligent Sensor-Based System for Real-Time Monitoring in Precision Agriculture. Engineering Proceedings, 118(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECSA-12-26539






