Bilateral Teleoperation with Force Feedback and Obstacle Detection-Based Navigation for Mobile Robots in Congested Environments †
Abstract
1. Introduction
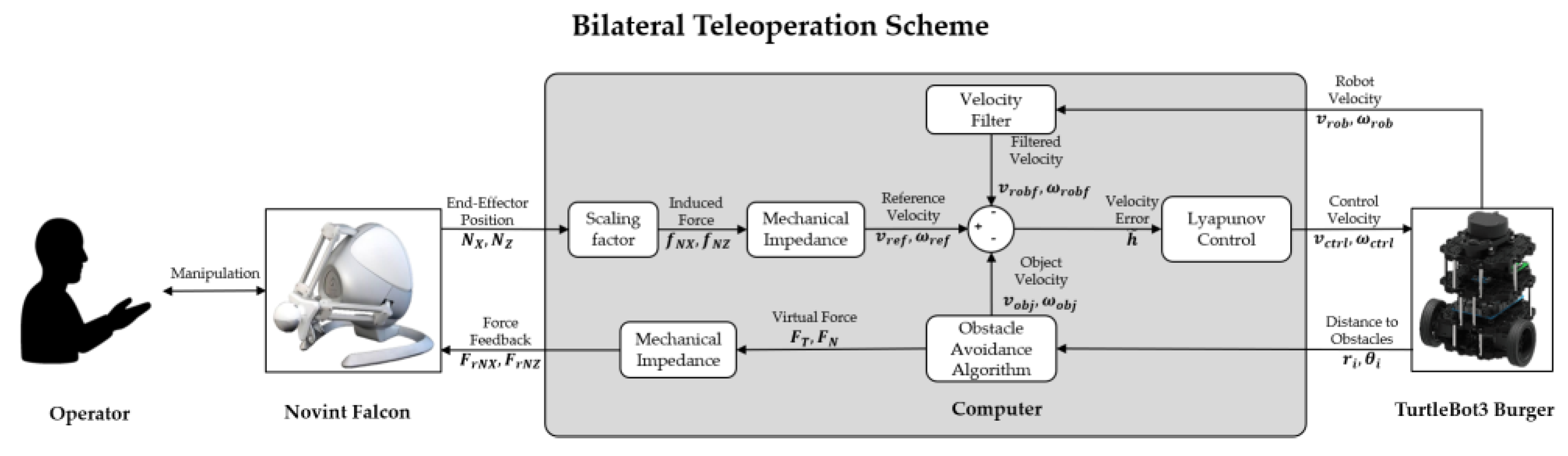
2. Modeling
2.1. TurtleBot3 Mobile Robot
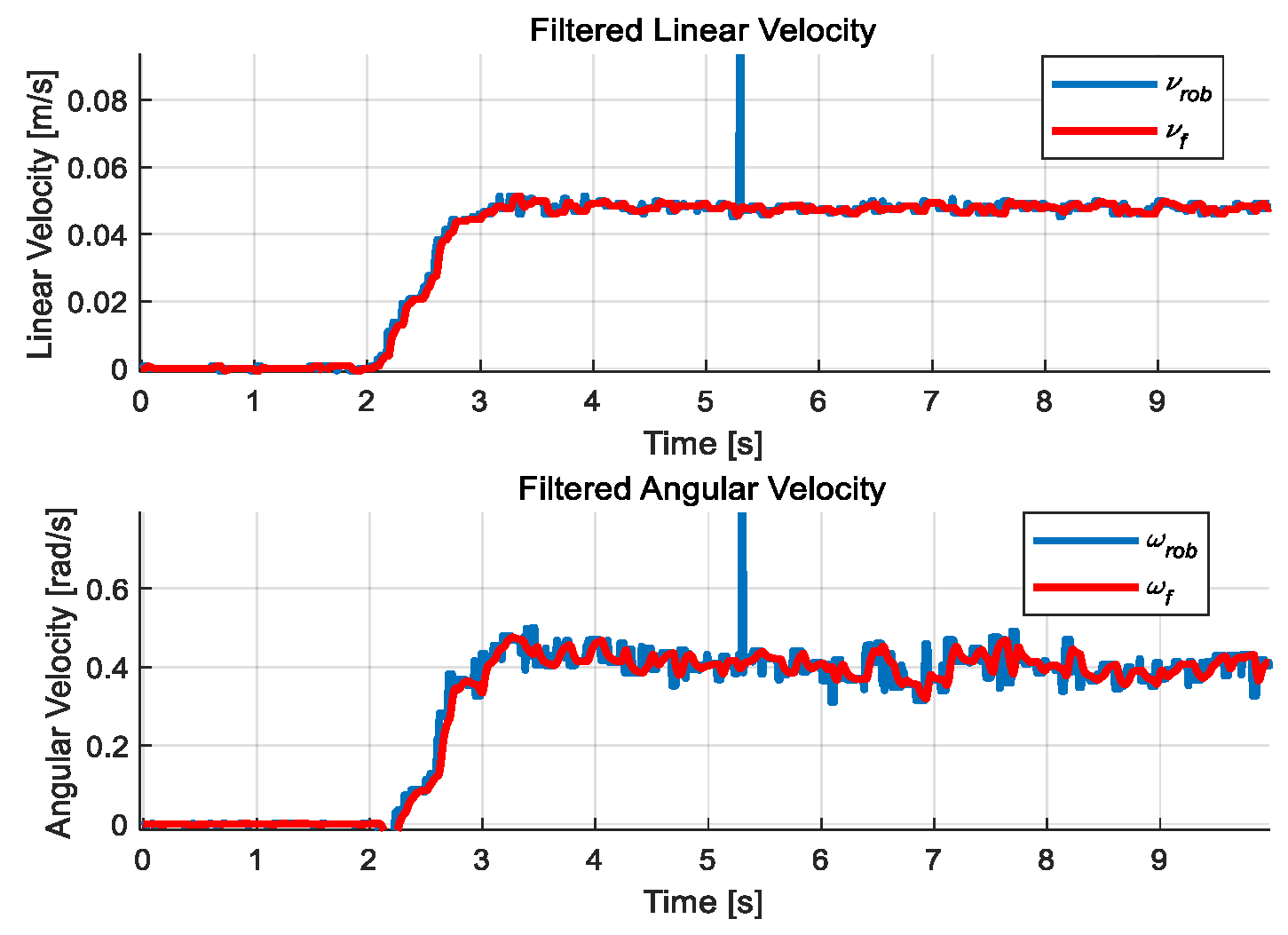
2.2. Velocity Filter
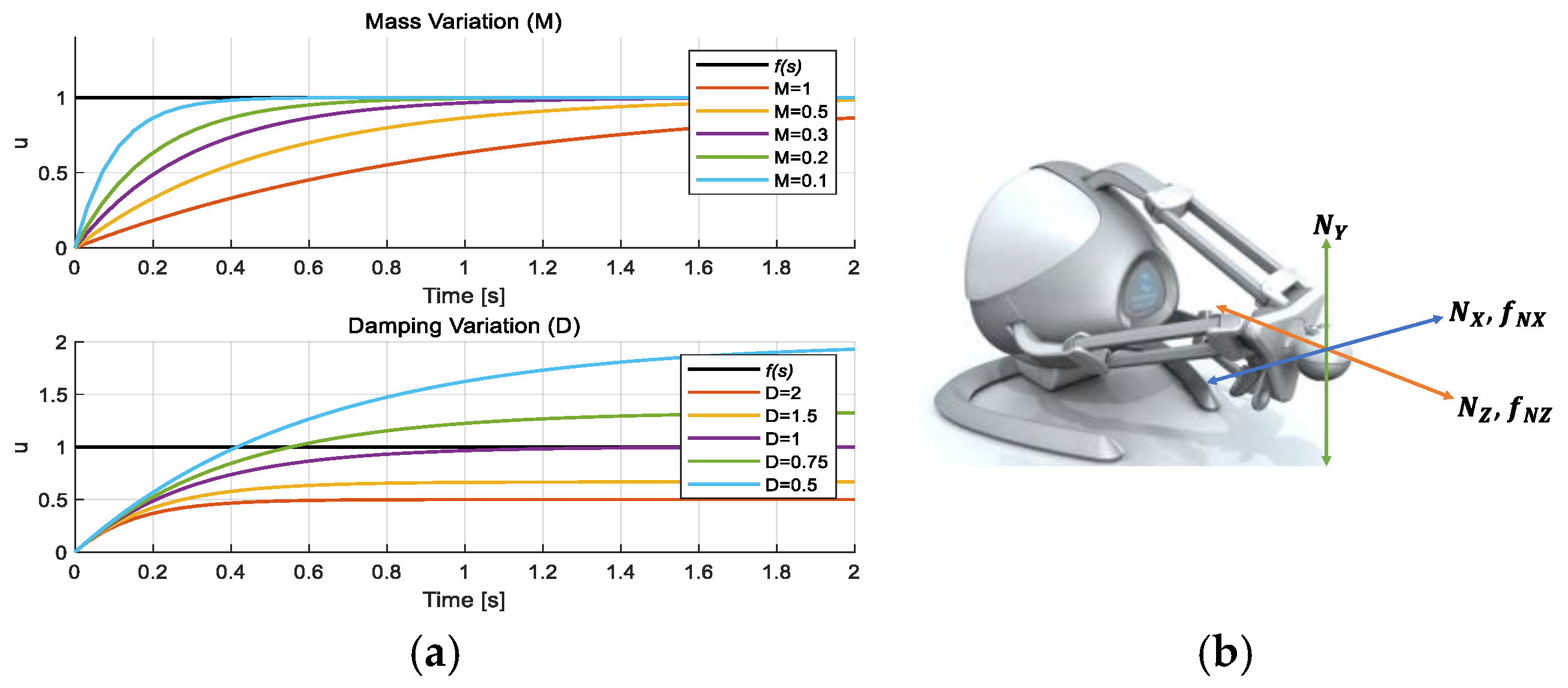
2.3. Mechanical Impedance
2.3.1. Reference Velocity
2.3.2. Feedback Force
3. Controllers
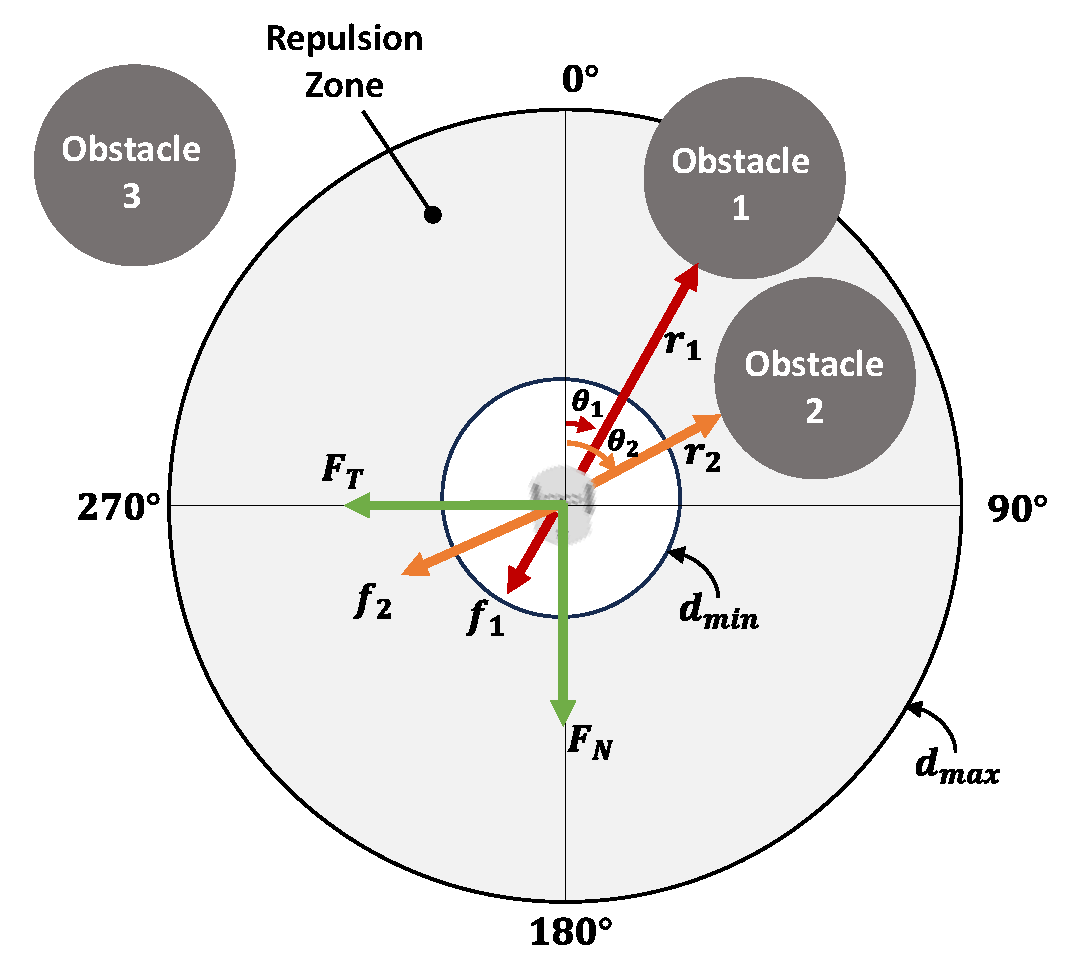
3.1. Obstacle Avoidance Algorithm
3.1.1. Virtual Forces
3.1.2. Object Velocity
3.2. Lyapunov Control
4. Experimental Tests and Results
4.1. Experimental Setup and Parameters
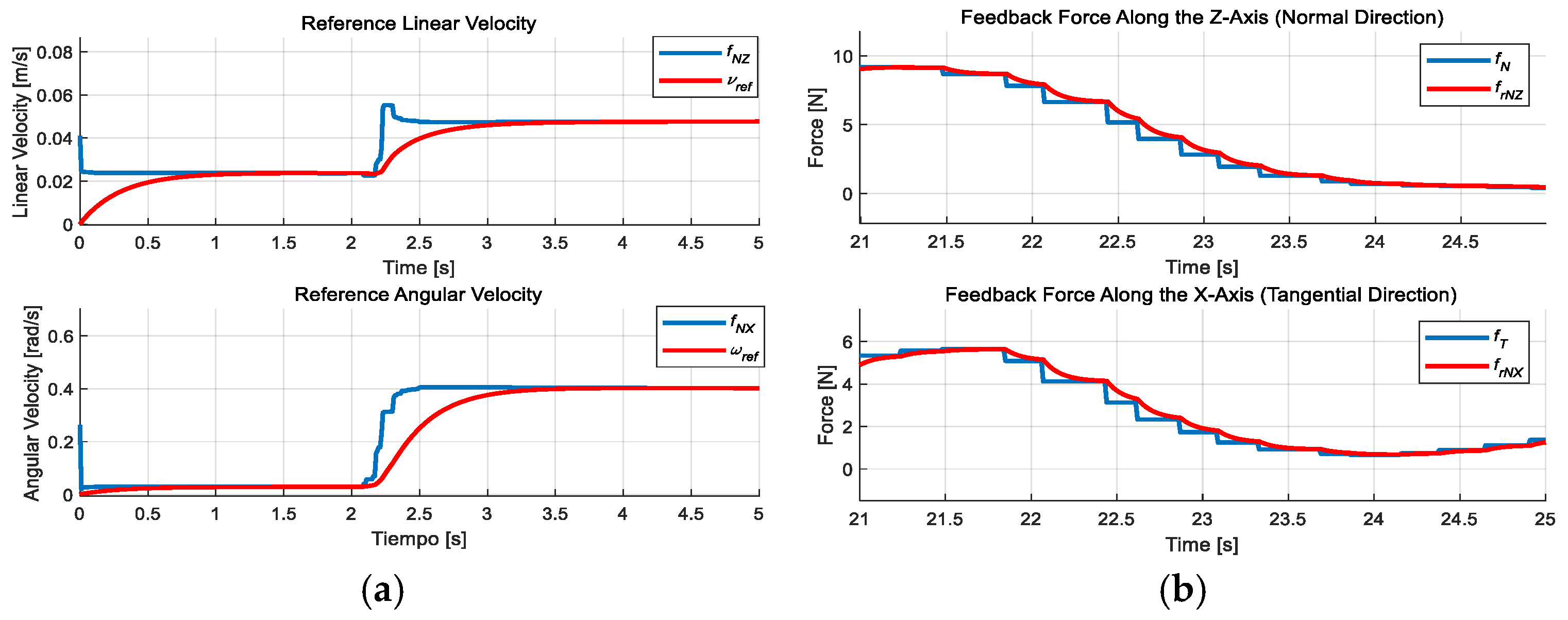
4.2. Test in an Obstacle-Free Environment
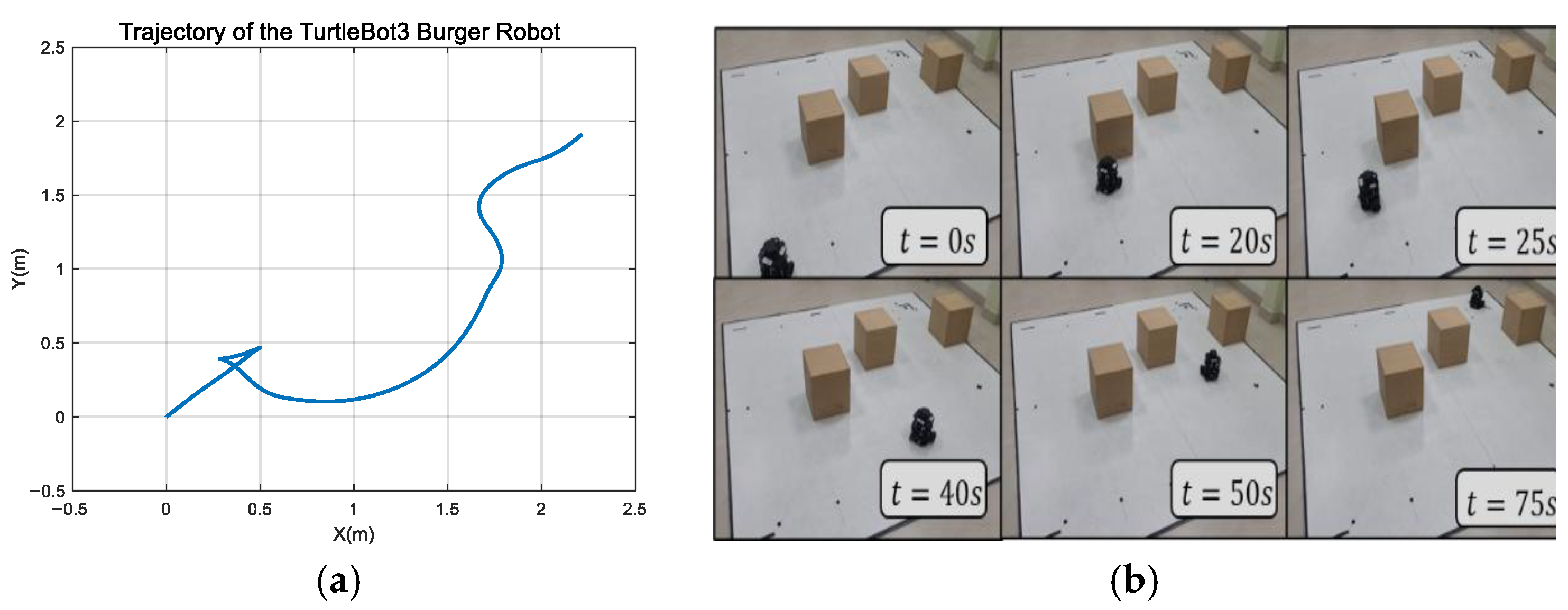
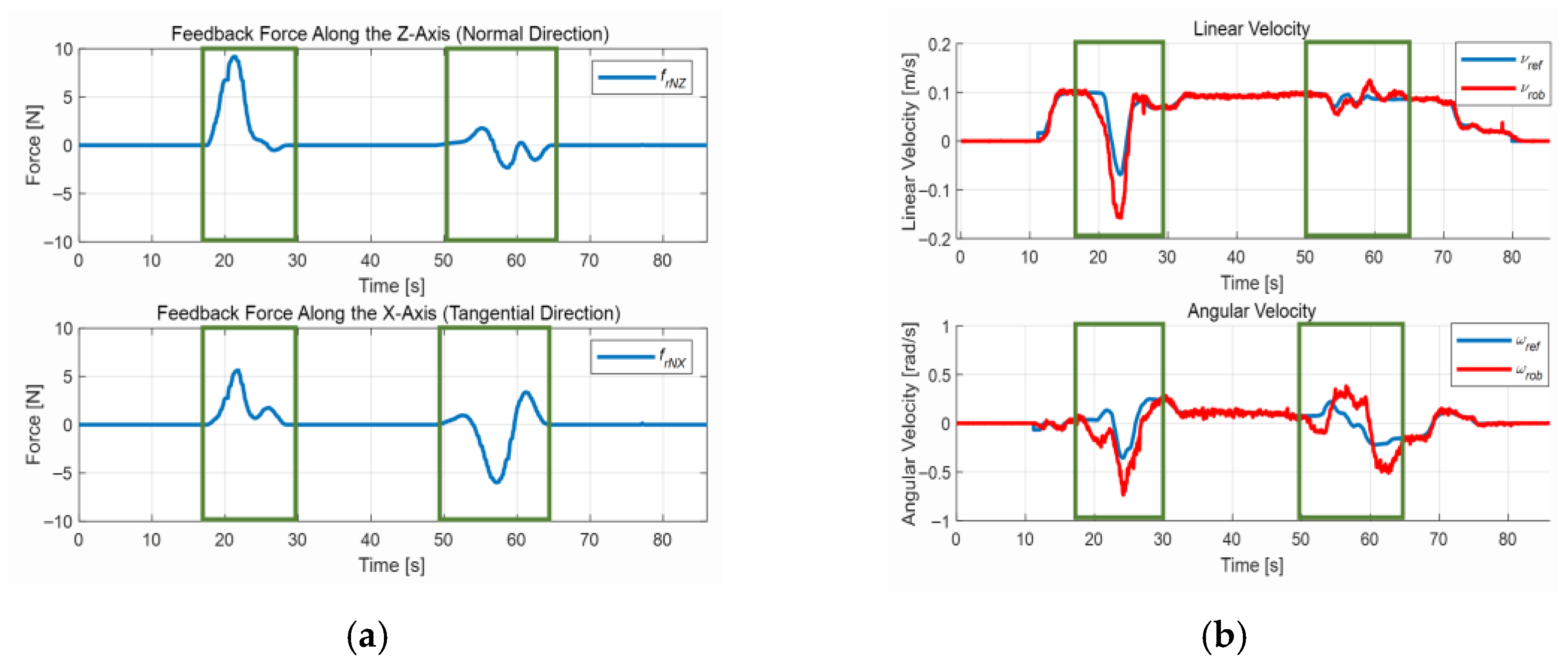
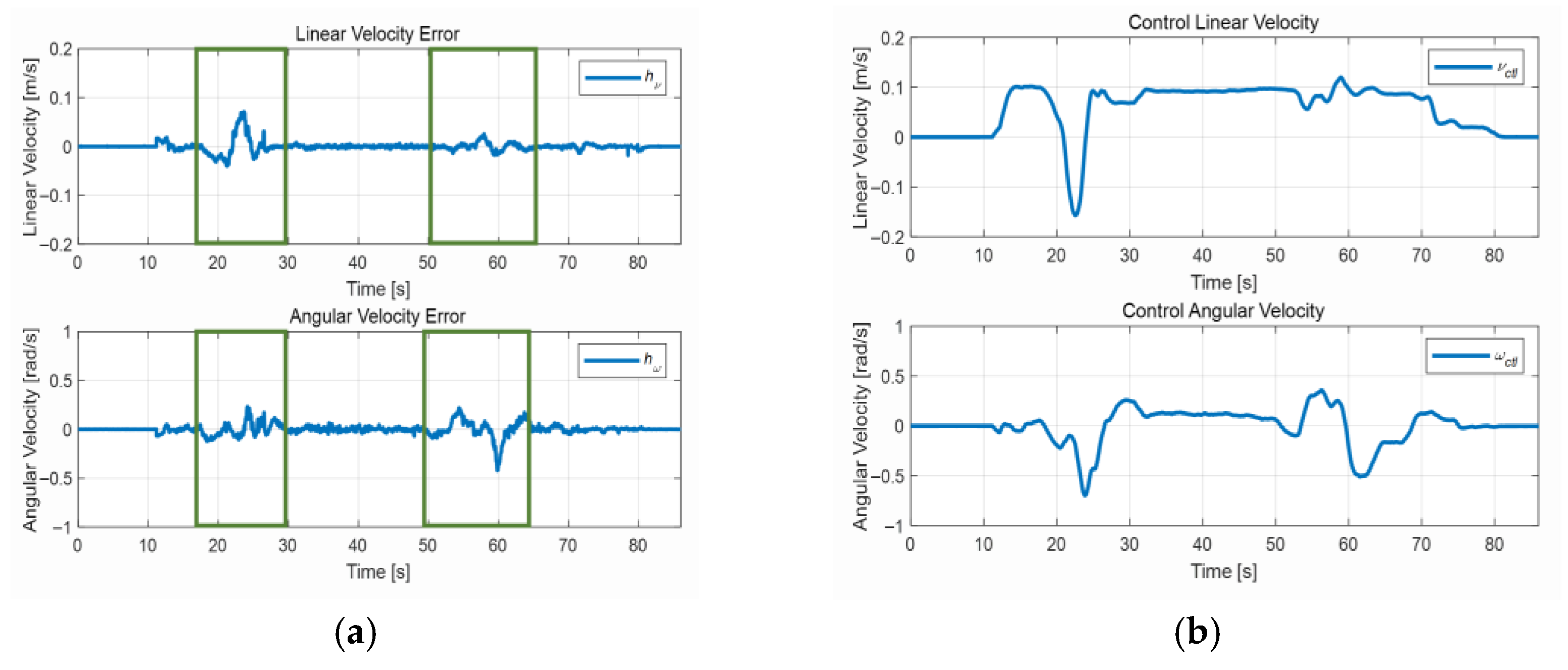
4.3. Test in a Congested Environment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bergholz, M.; Ferle, M.; Weber, B.M. The benefits of haptic feedback in robot assisted surgery and their moderators: A meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 19215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Ni, T.; Zhao, Z.; Ren, C. Unified Human Intention Recognition and Heuristic-Based Trajectory Generation for Haptic Teleoperation of Non-Holonomic Vehicles. Machines 2023, 11, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Ban, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, B.; Liu, S.; Yin, L.; Zheng, W. Adaptive control of time delay teleoperation system with uncertain dynamics. Front. Neurorobot. 2022, 16, 928863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louca, J.; Eder, K.I.; Vrublevskis, J.; Tzemanaki, A. Impact of Haptic Feedback in High Latency Teleoperation for Space Applications. ACM Trans. Human-Robot Interact. 2024, 13, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Lin, Z.; Li, Y.; Yang, C. A Teleoperation Framework for Mobile Robots Based on Shared Control. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicaiza, F.A.; Slawiñski, E.; Salinas, L.R.; Mut, V.A. Evaluation of Path Planning with Force Feedback for Bilateral Teleoperation of Unmanned Rotorcraft Systems. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2022, 105, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebri, A.; Acharya, S.; Theofanidis, M.; Makedon, F. A Teleoperation Framework for Robots Utilizing Control Barrier Functions in Virtual Reality. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on PErvasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environments, Corfu, Greece, 5–7 July 2023; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X. Haptic teleoperation of a multirotor aerial robot using path planning with human intention estimation. Intell. Serv. Robot. 2021, 14, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanes, J.E.; Muñoz, A.; Gracia, L.; Tornero, J. Virtual Reality-Based Interface for Advanced Assisted Mobile Robot Teleoperation. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leica, P.; Balseca, J.; Cabascango, D.; Chávez, D.; Andaluz, G.; Andaluz, V.H. Controller Based on Null Space and Sliding Mode (NSB SMC) for Bidirectional Teleoperation of Mobile Robots Formation in an Environment with Obstacles. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Fourth Ecuador Technical Chapters Meeting (ETCM), Guayaquil, Ecuador, 11–15 November 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riera, J.; Daquilema, E.; Andaluz, G.M.; Leica, P. Teleoperation of the TurtleBot Mobile Robot using an SMC controller in environments with obstacles. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Eighth Ecuador Technical Chapters Meeting (ETCM), Cuenca, Ecuador, 15–18 October 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Su, T.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Zhao, Q.; Yuan, J.; Huang, C.; Zhao, L.; He, G. An Adaptive Time-Varying Impedance Controller for Manipulators. Front. Neurorobot. 2022, 16, 789842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carranza, D.A.; Andaluz, G.M.; Leica, P. Bilateral Teleoperation with Force Feedback and Obstacle Detection-Based Navigation for Mobile Robots in Congested Environments. Eng. Proc. 2025, 115, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025115022
Carranza DA, Andaluz GM, Leica P. Bilateral Teleoperation with Force Feedback and Obstacle Detection-Based Navigation for Mobile Robots in Congested Environments. Engineering Proceedings. 2025; 115(1):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025115022
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarranza, Diego Andrés, Gabriela M. Andaluz, and Paulo Leica. 2025. "Bilateral Teleoperation with Force Feedback and Obstacle Detection-Based Navigation for Mobile Robots in Congested Environments" Engineering Proceedings 115, no. 1: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025115022
APA StyleCarranza, D. A., Andaluz, G. M., & Leica, P. (2025). Bilateral Teleoperation with Force Feedback and Obstacle Detection-Based Navigation for Mobile Robots in Congested Environments. Engineering Proceedings, 115(1), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025115022





