Abstract
Pakistan’s solar boom, now contributing 25% of its utility electricity, the highest among major countries, presents a strategic opportunity to localize solar supply chains within Special Economic Zones (SEZs) under the China–Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC). This study investigates pathways for enabling solar localization, identifies key barriers to local manufacturing, and assesses the potential for domestic value chain development. Employing a mixed-methods approach, combining policy analysis, stakeholder consultations, and feasibility analysis, the study outlines an implementation strategy centered on leveraging SEZs and promoting technology transfer. Results indicate that if Pakistan succeeds in localizing even half of its solar imports, it could reduce import dependency and switching to solar energy could potentially save over $5 billion over two decades. This shift would not only enhance energy security but also enhance sustainable industrial development under CPEC 2.0.
1. Introduction
Globally, solar photovoltaic (PV) technology has experienced an exponential rise, driven by dramatic cost reductions; solar PV costs have fallen by approximately 90% in the last decade [1], making it the most cost-effective electricity source in many parts of the world.
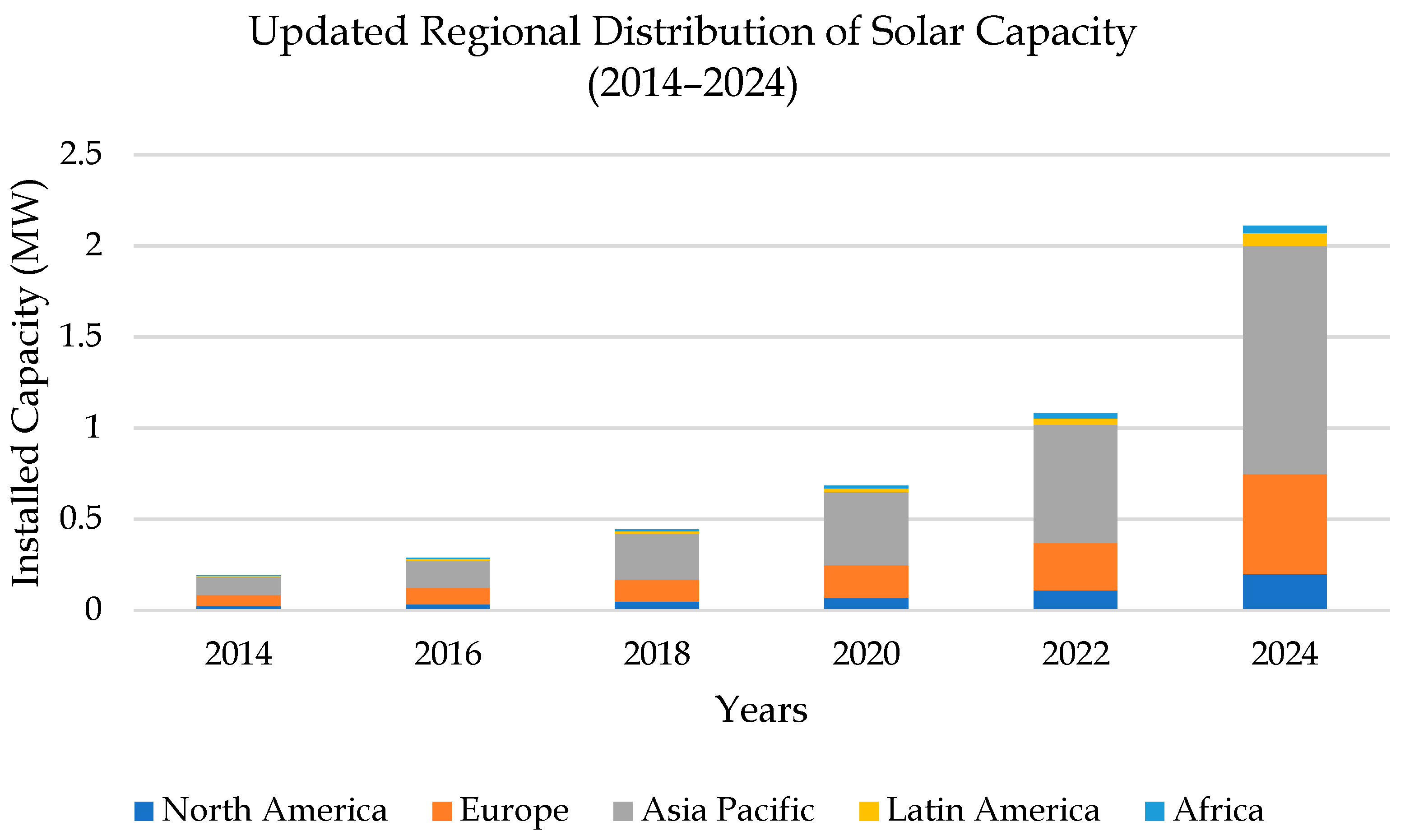
Countries like China, India, and the U.S. have emerged as global leaders in solar adoption, largely due to robust policy support, economies of scale in manufacturing, and investment in grid modernization. Figure 1 shows the increase in global solar capacity from 2014–2024 [2].
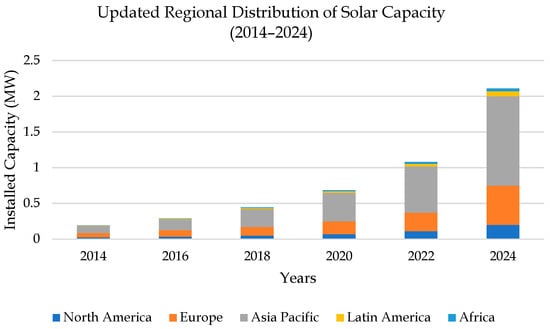
Figure 1.
Regional solar capacity growth (2014–2024), led by Asia–Pacific, with rising contributions from all regions (Adapted with permission from Ref. [2]. 2024, SolarInsure).
Since mid-2023, Pakistan has experienced a surge in solar photovoltaic (PV) adoption, with over 22 GW of solar panels imported in just 18 months [3]. This makes Pakistan the largest Chinese solar export market in Asia and the second largest globally after Europe [4]. This momentum, driven by rising electricity tariffs, grid unreliability, and falling solar costs, has transformed solar into Pakistan’s largest electricity source in 2025, up from the fifth largest just two years ago. Backing this transition, the government aims to increase the share of renewables in the power mix to 20–30% by 2030, with solar expected to play a central role [5].
Yet several obstacles persist, including intermittent grid reliability, lack of skilled labor, and insufficient local manufacturing. Since the past four years, Pakistan has spent over roughly $4.1 billion on imports of solar equipment [6], yet local manufacturing and value addition remain minimal. Sustaining this solar uptake requires developing domestic production capabilities across the PV value chain, including not just assembly, but also system integration and upstream manufacturing. This transition demands a deeper analysis of both the enabling role of China and how domestic capabilities support this momentum without disrupting the economics and market dynamics.
China’s Role in Energy and the Emerging Opportunity for Localization
China plays a central role in advancing solar energy development in Pakistan and remains Pakistan’s largest energy investor, committing nearly USD 68 billion between 2005 and 2024, 74% of which has been directed toward energy projects under the China–Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) [7]. While CPEC’s first phase prioritized infrastructure and power generation, CPEC 2.0 aims to develop industrialization and technology transfer through Special Economic Zones (SEZs) [8]. Drawing from its position as the global leader in solar PV manufacturing and its success in establishing Green Special Economic Zones (GSEZs), China offers a replicable model for Pakistan to localize solar technology production, enhance energy efficiency, and promote circular economy practices. Chinese investments and joint ventures in SEZs aim to facilitate the manufacturing of solar panels, inverters, and storage systems, supported by technology transfer and the development of local supply chains.
The SEZs under CPEC can be envisioned as critical platforms for solar PV localization. Among the nine formally designated CPEC SEZs, three, Rashakai, Allama Iqbal Industrial City, and Bostan, have received priority status. More recently, the Dhabeji SEZ in Sindh has attracted direct interest from Chinese solar firms; in 2024, leading Chinese firms visited Dhabeji SEZ, where proposals were also made to set up manufacturing units for solar panels, inverters, and batteries [9]. Since the past two years, multiple memorandums of understanding have been signed to establish state of the art solar PV manufacturing plants in Pakistan.
Building on the preceding discussion, this paper aims to (i) examine Pakistan’s readiness to localize its solar PV value chain leveraging its SEZ infrastructure under CPEC 2.0 in partnership with Chinese investors, (ii) analyze key enabling and constraining factors, including policy frameworks, market dynamics, and industrial capabilities, and (iii) outline strategic pathways to transition from import-led adoption to a localized solar manufacturing ecosystem.
2. Methodology
This study employs an exploratory sequential mixed-methods approach to analyze the localization potential of Pakistan’s solar PV industry under CPEC 2.0. The study integrates qualitative and quantitative data collection and analysis, using a sequential design where qualitative findings inform and complement quantitative assessment, to build a comprehensive understanding of the structural, market, and policy dimensions of solar PV localization [10]. The first phase involved primary qualitative data collection through key informant interviews, focus group discussions, and consultative dialogues with relevant stakeholders. A rigorous selection process was used to identify participants with direct expertise and involvement in solar energy, industrial development, and investment policy. These included SEZ authorities, including representatives from the Board of Investment (BOI), experts from leading Pakistan–China think tanks, such as those focused on renewable energy cooperation, Chinese energy governance experts, and representatives from Pakistan’s solar manufacturing association. The consultations explored key themes such as industrial development under CPEC, co-production potential in SEZs, tariff-related barriers, capacity gaps in solar manufacturing, and the broader policy environment for renewable energy investment.
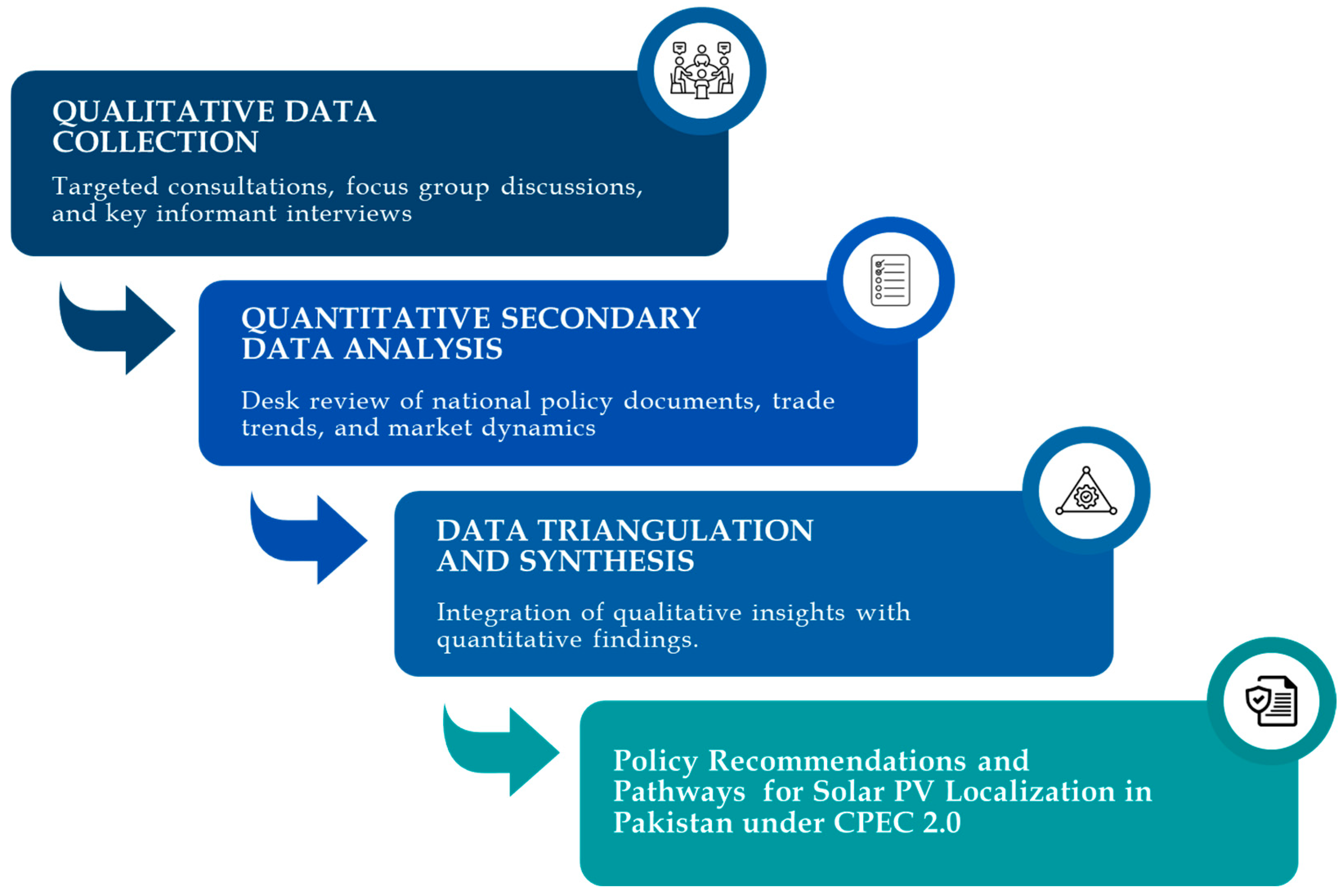
Building on the qualitative insights, the second phase involved secondary data analysis to contextualize and validate stakeholder inputs. This included a systematic desk review of solar import volumes and tariff data, regulatory frameworks related to renewable energy and industrial localization, China’s global green energy investment patterns, and national policy documents, including Pakistan’s updated climate commitments under its Nationally Determined Contributions. Findings were then triangulated allowing for cross-verification of qualitative narratives with quantitative evidence to ensure analytical validity and mitigate bias. This multi-source, stakeholder-informed methodology provides a strong basis for identifying opportunities, challenges, and policy pathways for advancing solar PV localization in Pakistan. The study’s methodological framework is outlined in Figure 2.
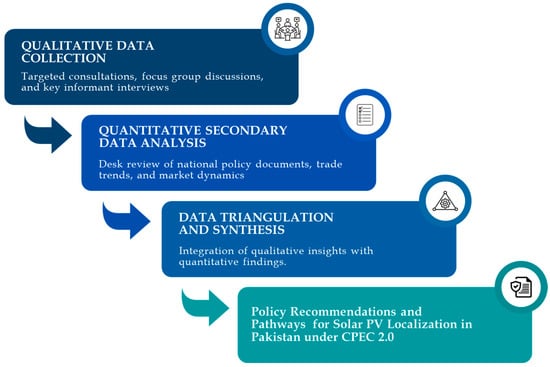
Figure 2.
Methodological approach for the study.
3. Key Findings & Discussion
3.1. China’s Green Governance and Localization Strategy
China’s green governance has positioned it as a global renewable energy leader, with the country accounting for approximately one-third of global renewable capacity. As of May 2025, China’s cumulative solar PV capacity surpassed 1 TW, reaching 1080 GW (~1.08 TW) [11]. This success stems from robust policy planning, regulatory enforcement, and over $100 billion invested by the Chinese government in renewables by 2024 [12], including solar and EV sectors. Under the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), China has shifted from financing overseas coal to promoting clean energy projects and GSEZs across Asia, Africa, and Latin America. These zones integrate solar energy, energy-efficient infrastructure, and circular economy models, such as solar PV recycling, critical as global PV waste is projected to reach 78 million tons by 2050 [13]. China’s global localization strategy is also driven by industrial overcapacity and rising domestic costs, prompting relocation of solar and EV manufacturing to countries like Pakistan, where the SEZs under CPEC are key recipients of this shift, with potential to localize solar supply chains, boost grid integration, and scale renewable technologies. Yet, in order to benefit fully, recipient countries must invest in domestic manufacturing, skilled labor, and policy coherence, ensuring that localization goes beyond assembly to genuine technology transfer and sustainable industrial growth.
3.2. Solar PV Localization and Implications for Pakistan
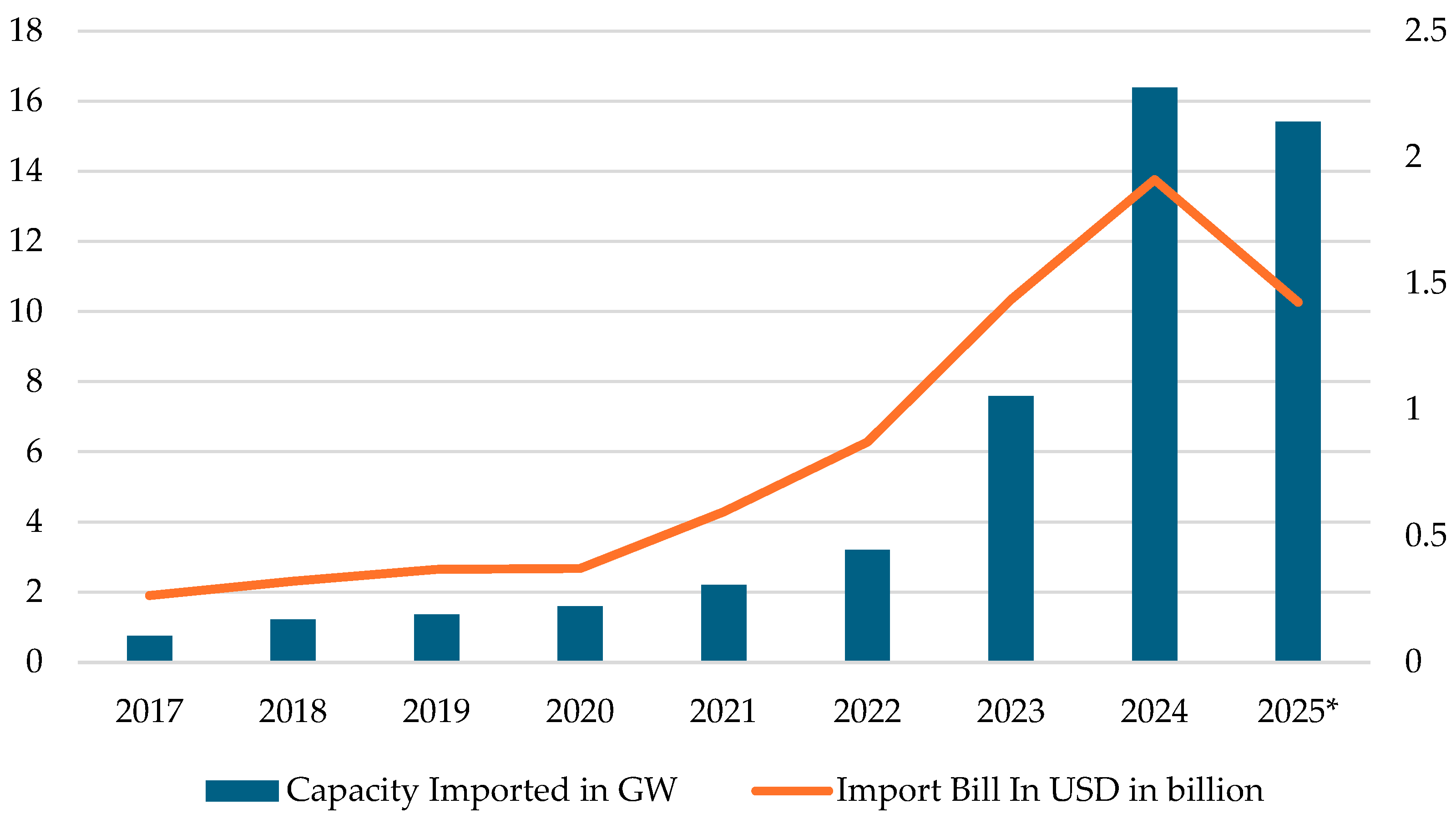
In this evolving landscape, Pakistan has a strategic opportunity to become a competitive hub for Chinese green manufacturing, as Chinese firms seek to diversify production and mitigate trade risks from rising tariffs imposed by the U.S., EU, and Canada [14]. Entering the second, more “people-centric” phase of the China–Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC 2.0), Pakistan is shifting focus toward green development, with energy and environment emerging as key pillars under the 5-E framework. Within this context, localizing the solar PV industry offers a particularly promising avenue for industrial growth. Global examples show that successful localization hinges on aligning industrial policy with long-term renewable energy goals and strengthening institutional capacity to turn investor interest into operational success. For Pakistan, CPEC 2.0 presents a timely opportunity to apply these lessons, by sequencing structural reforms, mitigating investment risks, and strengthening domestic capabilities in tandem with foreign technology integration, particularly by leveraging the country’s ongoing solar energy boom to accelerate renewable infrastructure, attract green investment, and localize clean energy value chains. Figure 3 shows this momentum, showing the rapid rise in China’s solar PV exports to Pakistan, both in terms of installed capacity and value, as per Ember data. In early 2025, Pakistan sourced 25% of its utility electricity from solar power, the highest share among major regions [15].
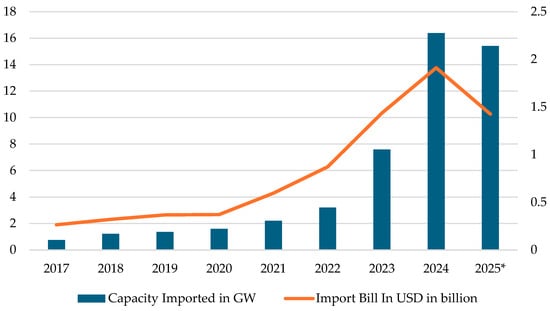
Figure 3.
China’s Solar PV Exports to Pakistan: Capacity and Export Value (2017–2025*). * 2025 depicts data from January through August.
Solar energy offers significant economic potential for Pakistan, with the ability to reduce reliance on expensive fossil fuel imports and generate savings of up to $5 billion in energy costs over the next two decades, according to a report by the World Bank [16]. Through its SEZs under CPEC, Pakistan has a significant opportunity to advance renewable energy manufacturing. With solar potential exceeding 2.9 million MW [17] and global renewable investments reaching $2.1 trillion in 2024 [18], SEZs offer a critical opportunity to attract foreign investment, modernize industry, and boost exports. While local solar assembly exists informally, the real opportunity lies in formalizing and localizing the entire supply chain, including balance-of-system components, inverters, and PV module assembly, to cut costs and reduce import dependence. SEZs also provide platforms for job creation in clean energy, recycling, and EV component manufacturing, sectors set to expand amid the global green transition. Alignment with China’s green Belt and Road strategy further enables technology transfer and green finance access, enhancing Pakistan’s climate resilience and export competitiveness. In 2024, solar accounted for 14.3% of Pakistan’s power generation, nearly double China’s 8.4% and India’s 7.4%. Pakistan tripled its solar share in three years, while China and India took seven [19].
Against this backdrop, the adverse impact of non-localization is twofold: a growing trade deficit and missed domestic industrial opportunity. With solar imports reaching $2.1 billion in 2024 alone, Pakistan forfeits billions that could otherwise be redirected into local manufacturing. If this demand were met domestically, it could stimulate growth in the local economy, leading to job creation, technological development, and upstream supply chain activity. Additionally, there is growing momentum for policy reform to enable this shift. ReneSola Pakistan, a joint venture (JV) with a Chinese solar panel manufacturer, has proposed a long-term solar panel manufacturing policy, calling for a streamlined and equitable tax and duty framework. According to their estimates, this approach could save Pakistan $300–500 million in foreign exchange by year five and generate $300 million annually in economic output [20]. However, realizing these gains will require addressing key structural bottlenecks outlined in Table 1.

Table 1.
Structural Challenges to Solar PV Localization in Pakistan.
Addressing these challenges will require an integrated localization strategy aligned with Pakistan’s broader industrial and energy goals. Table 2 outlines six key policy pathways for enabling PV manufacturing under CPEC 2.0, emphasizing financial incentives, such as tax and duty rationalization and machinery import exemptions, to boost investment, enhance competitiveness, and potentially save up to $500 million in foreign exchange while generating $300 million annually [20].

Table 2.
Implementation roadmap for Solar PV Localization in Pakistan.
4. Conclusions
Pakistan’s rapid solar uptake has opened a clear window to transition from import reliance to localized manufacturing. Sustaining this growth will require building industrial capacity, aligning policy frameworks, and partnering with China under CPEC 2.0 to absorb relocated production and technology. China’s green outbound strategy increasingly favors localized value chains, and Pakistan’s SEZs offer a timely platform to attract such investment. However, this opportunity can only be realized through coherent reforms that address policy gaps, tariff distortions, and skill deficits. If pursued strategically, solar PV localization can strengthen energy security, reduce import dependency, and position Pakistan within the global solar value chain.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: High-Level Conference on CPEC & Beyond: How China Enabled Pakistan’s Energy Transition (https://sdpi.org/high-level-conference-on-cpec--beyond-how-china-enabled-pakistans-energy-transition/event_detail) (accessed on 1 July 2025), Experts highlight green SEZs under CPEC for sustainable development (https://sdpi.org/8904/news_detail) (accessed on 1 July 2025), The Great Solar Rush in Pakistan [6] (accessed on 28 June 2025).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.N., A.I. and S.Z.; methodology, A.N. and A.I.; writing—original draft preparation, A.N. and A.I.; writing—review and editing, U.U.R.Z.; supervision, U.U.R.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article and Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the support received from the Pakistan–China Institute (PCI), the Private Power Infrastructure Board (PPIB), the Board of Investment (BOI), the Pakistan Solar Association (PSA), Renewables First (RF), and SDPI. Also, we really appreciate the valuable inputs from Erfa Iqbal, Muhammad Faisal Sharif, Haneea Isaad, Muhammad Mustafa Amjad, Khalid Waleed, and Hina Aslam.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ritchie, H. Solar Panel Prices Have Fallen by Around 20% Every Time Global Capacity Doubled. 2024. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/data-insights/solar-panel-prices-have-fallen-by-around-20-every-time-global-capacity-doubled (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- SolarInsure. How Much Solar Energy Does the World Generate? 2024. Available online: https://www.solarinsure.com/how-much-solar-energy-does-the-world-generate (accessed on 25 June 2025).
- APP. Pakistan’s Solar Revolution Rewriting Energy Landscape; 22 GW of Solar Panels Imported in 18 Months. 2025. Available online: https://www.app.com.pk/national/pakistans-solar-revolution-rewriting-energy-landscape-22-gw-of-solar-panels-imported-in-18-months/#:~:text=Balochi/Brahvi-,Pakistan’s%20solar%20revolution%20rewriting%20energy%20landscape;%2022%20GW%20of%20solar,because%20economics%20make%20perfect%20sense.%E2%80%9D (accessed on 29 June 2025).
- CPECInfo. Pakistan Becomes Second-Largest Market for Chinese Solar Exports in 2024. 2024. Available online: https://cpecinfo.com/pakistan-becomes-second-largest-market-for-chinese-solar-exports-in-2024/#:~:text=Pakistan%20has%20become%20a%20key,%2C%20households%2C%20hospitals%20and%20mosques (accessed on 25 June 2025).
- GoP. Updated Nationally Determined Contributions. 2021. Available online: https://unfccc.int/sites/default/files/NDC/2022-06/Pakistan%20Updated%20NDC%202021.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Amjad, M.M.; Malik, S.; Ahmad, A.; Ahmed, A.; Ali, H.; Naveed, H.; Ghauri, M.B.; Babar, R.; Ashfaq, Z. The Great Solar Rush in Pakistan. 2024. Available online: https://uploads.renewablesfirst.org/The_Great_Solar_Rush_in_Pakistan_38157451a3.pdf#:~:text=BloombergNEF%20reports%20that%20Pakistan%20imported%20solar%20panels,of%20panels%20from%20China%20in%20just%20the (accessed on 28 June 2025).
- Isaad, H.; Sayed, M.H. Pakistan Must Rebuild Chinese Investor Confidence in Its Energy Transition. 2025. Available online: https://dialogue.earth/en/energy/pakistan-must-rebuild-chinese-investor-confidence-in-its-energy-transition/#:~:text=What%20will%20CPEC%202.0%20look%20like?%20CPEC’s,industrialisation%2C%20agriculture%2C%20and%20technology%20transfer%20through%20SEZs (accessed on 2 July 2025).
- CPECInfo. Experts Say Pakistan Needs Stable Policies to Fully Utilize China’s Expertise in Clean Energy and Industrial Development. 2025. Available online: https://cpecinfo.com/experts-say-pakistan-needs-stable-policies-to-fully-utilize-chinas-expertise-in-clean-energy-and-industrial-development/ (accessed on 29 June 2025).
- Sindh, I.D. A Delegation of 12 Major Chinese Companies Visited Dhabeji Special Economic Zone Along with Special Assistant to the Chief Minister of Sindh Syed Qasim Naveed Qamar. 2024. Available online: https://sindhinvestment.gos.pk/node/475#:~:text=Karachi%2C%20December%2011%2C%202024,friendship%20between%20China%20and%20Pakistan (accessed on 2 July 2025).
- Fetters, M.D.; Curry, L.A.; Creswell, J.W. Achieving integration in mixed methods designs-principles and practices. Health Serv. Res. 2013, 48, 2134–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, V. China Hits 1 TW Solar Milestone. 2025. Available online: https://www.pv-magazine.com/2025/06/23/china-hits-1-tw-solar-milestone/ (accessed on 3 July 2025).
- Fleck, A. China Pulls Far Ahead in Green Energy Investment. 2025. Available online: https://www.statista.com/chart/34682/global-investment-in-renewable-power-and-fuels/#:~:text=China%20is%20the%20world%20leader,REN21%20Global%20Status%20Report%202025 (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- Chowdhury, M.S.; Rahman, K.S.; Chowdhury, T.; Nuthammachot, N.; Techato, K.; Akhtaruzzaman, M.; Tiong, S.K.; Sopian, K.; Amin, N. An overview of solar photovoltaic panels’ end-of-life material recycling. Energy Strategy Rev. 2020, 27, 100431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midfa, N.A. The U.S.-China Trade War: China’s Challenge in Navigating U.S. Tariffs and Global Trade Tensions. 2025. Available online: https://trendsresearch.org/insight/the-u-s-china-trade-war-chinas-challenge-in-navigating-u-s-tariffs-and-global-trade-tensions/#:~:text=Furthermore%2C%20China%20is%20focusing%20on,economic%20growth%20and%20export%20capabilities (accessed on 4 July 2025).
- Maguire, G. Pakistan’s Solar Surge Lifts It into Rarefied 25% Club. 2025. Available online: https://www.reuters.com/markets/commodities/pakistans-solar-surge-lifts-it-into-rarefied-25-club-2025-06-17/ (accessed on 15 June 2025).
- PVknowhow. Solar Energy in Pakistan Backed by Government: No Taxes. 2024. Available online: https://www.pvknowhow.com/news/solar-energy-in-pakistan-no-taxes/#:~:text=Economic%20Benefits%20of%20Solar%20Energy,costs%20and%20increased%20energy%20independence (accessed on 11 July 2025).
- Hussain, F.; Maeng, S.-J.; Cheema, M.J.M.; Anjum, M.N.; Afzal, A.; Azam, M.; Wu, R.-S.; Noor, R.S.; Umair, M.; Iqbal, T. Solar Irrigation Potential, Key Issues and Challenges in Pakistan. Water 2023, 15, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuters. Global Energy Transition Investment Exceeded $2 Trillion Last Year, Report Shows. 2025. Available online: https://www.reuters.com/business/energy/global-energy-transition-investment-exceeded-2-trln-last-year-report-shows-2025-01-30/ (accessed on 26 June 2025).
- Reuters. Pakistan’s Solar Revolution Leaves Its Middle Class Behind. 2025. Available online: https://www.reuters.com/business/energy/pakistans-solar-revolution-leaves-its-middle-class-behind-2025-04-29/ (accessed on 13 July 2025).
- News, A. Chinese Company Asks Govt to End Duties on Solar Panel Components. 2024. Available online: https://english.aaj.tv/news/330376268/chinese-company-asks-govt-to-end-duties-on-solar-panel-components (accessed on 9 July 2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).